Ural Blocking and the Amplitude of Wintertime Cold Surges over North China Detected by a Cooling Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. A Method for Estimating the Cooling Amplitude for a Blocking Event
- 1.
- For each spatial grid point, the surface temperature anomaly for each calendar day is estimated by removing the long-term average of the surface temperature on that calendar date during 1958–2022 (for JRA55). The area-averaged land surface temperature anomalies (LSTA) over North China (90–150Ŷ E and 30–50Ŷ N) are estimated for each calendar day during 1958–2022 (for JRA55);
- 2.
- For each blocking event, the start and end dates for the analysis period are determined based on the start and end dates of that blocking event and the start date of the next blocking event (Figure 1a). The start date for the analysis period is the start date of the particular blocking event. When another blocking event occurs within ten days of the end date of a particular blocking event, the end of the analysis period of the event is the end date of the blocking event under analysis, otherwise the analysis period ends five days after the end date of the event;
- 3.
- All local maximum and minimum values of the LSTA time series within the analysis period of a blocking event are identified (Figure 1b). Note that, in this step, the LSTA on the start (end) date of the analysis period cannot be considered a minimum (maximum). This exclusion is to ensure that all identified extrema can be partitioned into chronologically ordered pairs, beginning with local maximum and followed by local minimum. The end dates of each pair of extrema can be viewed as the dates remarking cooling events;
- 4.
- The cooling amplitude for each cooling event is defined as the difference between the LSTA extremum (Figure 1c);
- 5.
- Two neighboring cooling events are merged together when the increase in LSTA is less than 2 K (Figure 1d). As a result of this step, several major cooling events are recognized;
- 6.
- The cooling amplitude of each major event is calculated as the difference between the maximum and minimum LSTA during the corresponding analysis period (Figure 1d). The dates for the corresponding maximum and minimum are recorded;
- 7.
- The major event with maximum cooling amplitude of all the major events is viewed as the cooling event associated with a specific blocking event (Figure 1d). The start and end dates of the associated cooling event are the dates for the corresponding major cooling events saved during the sixth step. Note that when the LSTA monotonically increases with time over the analysis period, the cooling amplitude is assigned to 0 K.
3. Results and Discussion
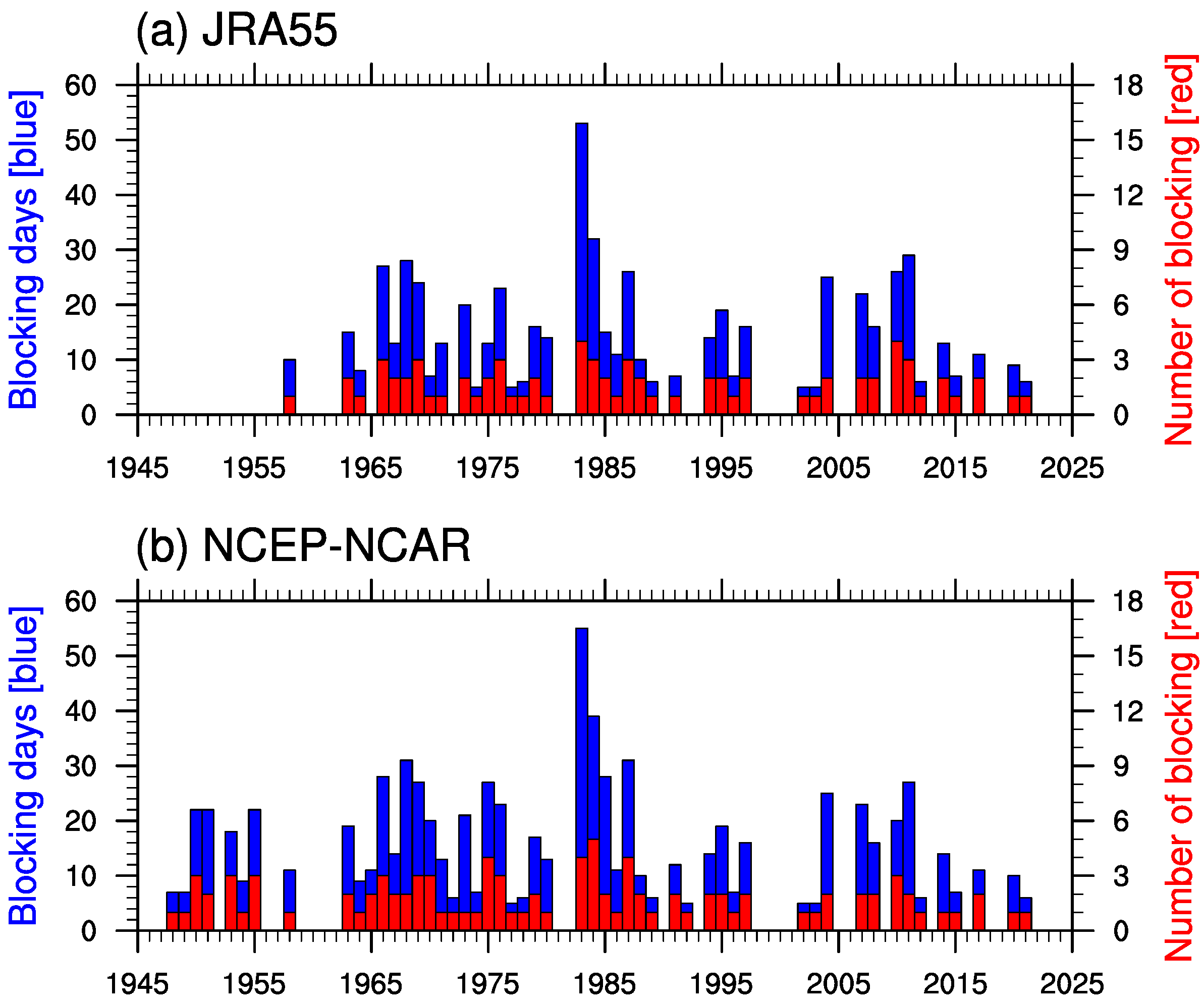
3.1. Distributions of Cooling Amplitude Associated with Blocking Events
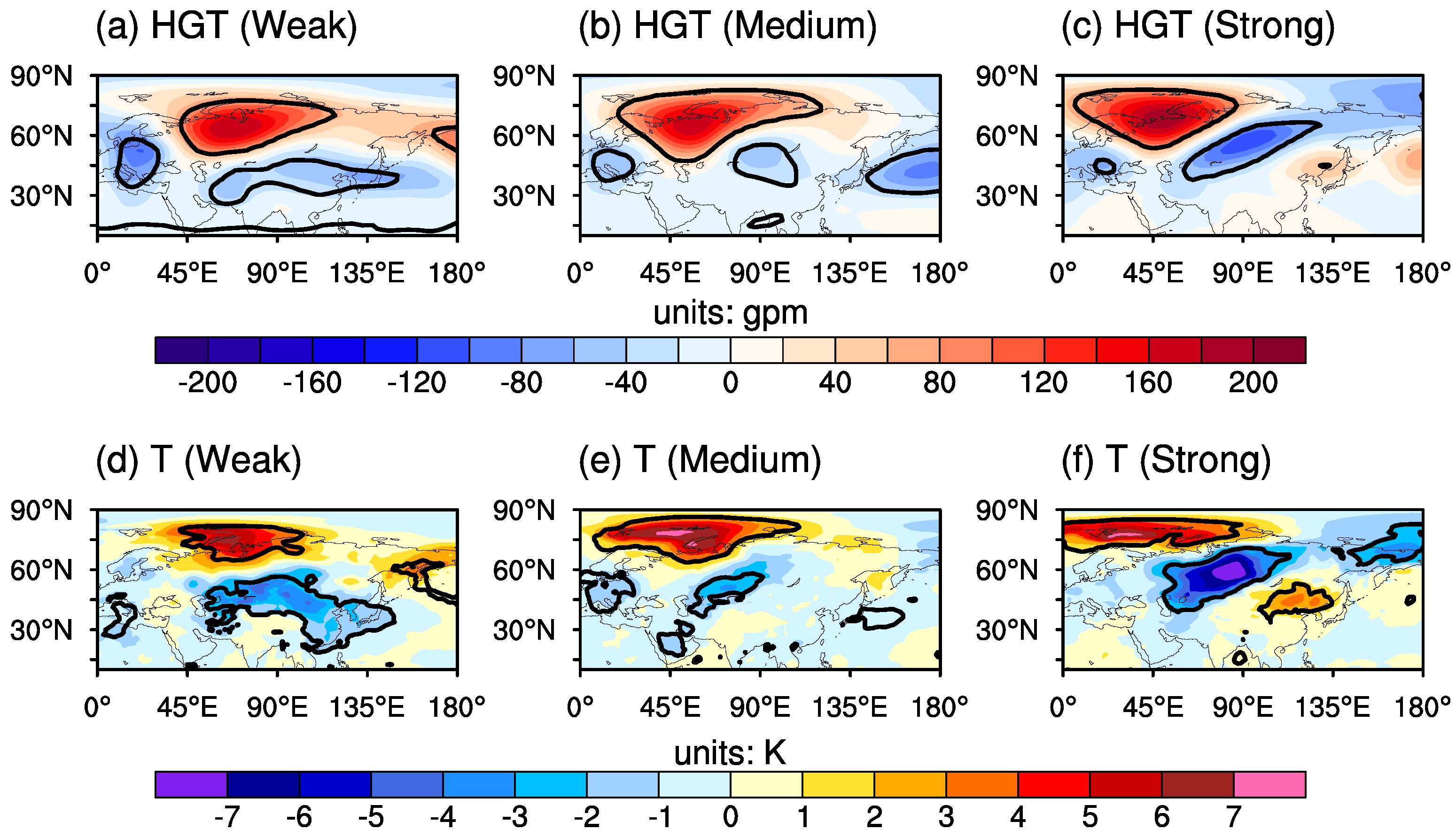
3.2. Early Signals for Blocking Events with Different Cooling Amplitude
3.3. Relation of Snowfall to the Amplitude of Cooling Events
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Krishnamurti, T.N. Heat Budget of the Siberian High and the Winter Monsoon. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1987, 115, 2428–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Huang, W.R.; Yoon, J.H. Interannual Variation of the East Asian Cold Surge Activity. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ho, C.H. Changes in occurrence of cold surges over east Asia in association with Arctic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.W.; Ho, C.H.; Yang, S. Relationship between the Arctic Oscillation and Cold Surges over East Asia. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, B.; Wright, J.S. A potential vorticity-based index for the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9382–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, B.; Wright, J.S.; Chen, R. On the Non-Stationary Relationship between the Siberian High and Arctic Oscillation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, Z.; He, X.; Qiu, T.; Wang, B.; Wright, J.S. Impacts of Wintertime Extratropical Cyclones on Temperature and Precipitation Over Northeastern China During 1979–2016. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1514–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.W.; Hong, J.G.; Park, D.S.R. Intra-seasonal characteristics of wintertime extreme cold events over South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 2639–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, C.H.; Hitchman, M.H. On the Role of Successive Downstream Development in East Asian Polar Air Outbreaks. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1982, 110, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, D. A New Blocking Index and Its Application: Blocking Action in the Northern Hemisphere. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4819–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.N.; Zhou, W.; Mok, H.Y.; Wu, M.C. Relationship between Ural–Siberian Blocking and the East Asian Winter Monsoon in Relation to the Arctic Oscillation and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4242–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W. The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid-2000s. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.W.; Ho, C.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Heo, J.W.; Deng, Y. A new dynamical index for classification of cold surge types over East Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Xiao, Y.; Diao, Y.; Dai, A.; Franzke, C.L.E.; Simmonds, I. Impact of Ural Blocking on Winter Warm Arctic–Cold Eurasian Anomalies. Part II: The Link to the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3949–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, B.; Wright, J.S.; Yang, Z.; Ma, W. Potential vorticity regimes over East Asia during winter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1524–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, D.; Zhong, L.; Pei, L. Seasonal Cumulative Effect of Ural Blocking Episodes on the Frequent Cold events in China during the Early Winter of 2020/21. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Gong, Z.; Luo, B.; Luo, D.; Zheng, F.; Zhong, L.; Huang, F.; Ma, S.; Zhu, C.; et al. Extreme Cold Events in North America and Eurasia in November-December 2022: A Potential Vorticity Gradient Perspective. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, K.; Nakamura, H. Geographical Dependence of Upper-Level Blocking Formation Associated with Intraseasonal Amplification of the Siberian High. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Chang, C.P. Unusual Late-Season Cold Surges during the 2005 Asian Winter Monsoon: Roles of Atlantic Blocking and the Central Asian Anticyclone. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5205–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.W.; Ho, C.H.; Deng, Y. A synoptic and dynamical characterization of wave-train and blocking cold surge over East Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, L.; Ren, Y.; Ni, W.; Liu, L. The Frequency of Extreme Cold Events in North China and Their Relationship with Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; et al. The JRA-55 reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebita, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Moriya, M.; Kumabe, R.; Onogi, K.; Harada, Y.; Yasui, S.; Miyaoka, K.; Takahashi, K.; et al. The Japanese 55-year Reanalysis “JRA-55”: An Interim Report. SOLA 2011, 7, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriopedro, D.; García-Herrera, R.; Lupo, A.R.; Hernández, E. A Climatology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1042–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Curry, J.A.; Wang, H.; Song, M.; Horton, R.M. Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4074–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Francis, J.A. Cold winter extremes in northern continents linked to Arctic sea ice loss. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sperber, K.R.; Boyle, J.S. Climatology and Interannual Variation of the East Asian Winter Monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1997, 125, 2605–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Graf, H.F.; Huang, R. The interannual variability of East Asian Winter Monsoon and its relation to the summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 17, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lau, K.M.; Kim, K.M. Variations of the East Asian Jet Stream and Asian–Pacific–American Winter Climate Anomalies. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Watanabe, M.; Shiogama, H.; Inoue, J.; Kimoto, M. Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Dai, A.; Simmonds, I.; Franzke, C.L.E. Impact of Ural Blocking on Winter Warm Arctic–Cold Eurasian Anomalies. Part I: Blocking-Induced Amplification. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3925–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, D.; Dai, A.; Simmonds, I. Increased Quasi Stationarity and Persistence of Winter Ural Blocking and Eurasian Extreme Cold Events in Response to Arctic Warming. Part I: Insights from Observational Analyses. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3549–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrlis, E.; Bader, J.; Manzini, E.; Ukita, J.; Nakamura, H.; Matei, D. On the role of Ural Blocking in driving the Warm Arctic–Cold Siberia pattern. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 2138–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Deng, J. Recent Eurasian winter cooling partly caused by internal multidecadal variability amplified by Arctic sea ice-air interactions. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 3261–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, B. Arctic Warming and Eurasian Cooling: Weakening and Reemergence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Rind, D. The Effect of Snow Cover on the Climate. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Entekhabi, D. Eurasian snow cover variability and northern hemisphere climate predictability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterstrasser, S.; Zängl, G. Cooling by melting precipitation in Alpine valleys: An idealized numerical modelling study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 1489–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoshikane, T.; Hatsushika, H.; Kawase, H.; Suzuki, C.; Uno, F.; Kimura, F. Cooling by the Melting of Snowfall on the Toyama Plain during the Winter Monsoon. SOLA 2014, 10, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, G.J. Climate change and the regulation of the surface moisture and energy budgets. Clim. Dyn. 1993, 8, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; van Meijgaard, E. Increase in hourly precipitation extremes beyond expectations from temperature changes. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Lin, D.; Wang, B.; Ma, W. Ural Blocking and the Amplitude of Wintertime Cold Surges over North China Detected by a Cooling Algorithm. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060623
Yang Z, Huang W, Chen R, Lin D, Wang B, Ma W. Ural Blocking and the Amplitude of Wintertime Cold Surges over North China Detected by a Cooling Algorithm. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(6):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060623
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zifan, Wenyu Huang, Ruyan Chen, Daiyu Lin, Bin Wang, and Wenqian Ma. 2024. "Ural Blocking and the Amplitude of Wintertime Cold Surges over North China Detected by a Cooling Algorithm" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060623
APA StyleYang, Z., Huang, W., Chen, R., Lin, D., Wang, B., & Ma, W. (2024). Ural Blocking and the Amplitude of Wintertime Cold Surges over North China Detected by a Cooling Algorithm. Atmosphere, 15(6), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060623







