The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
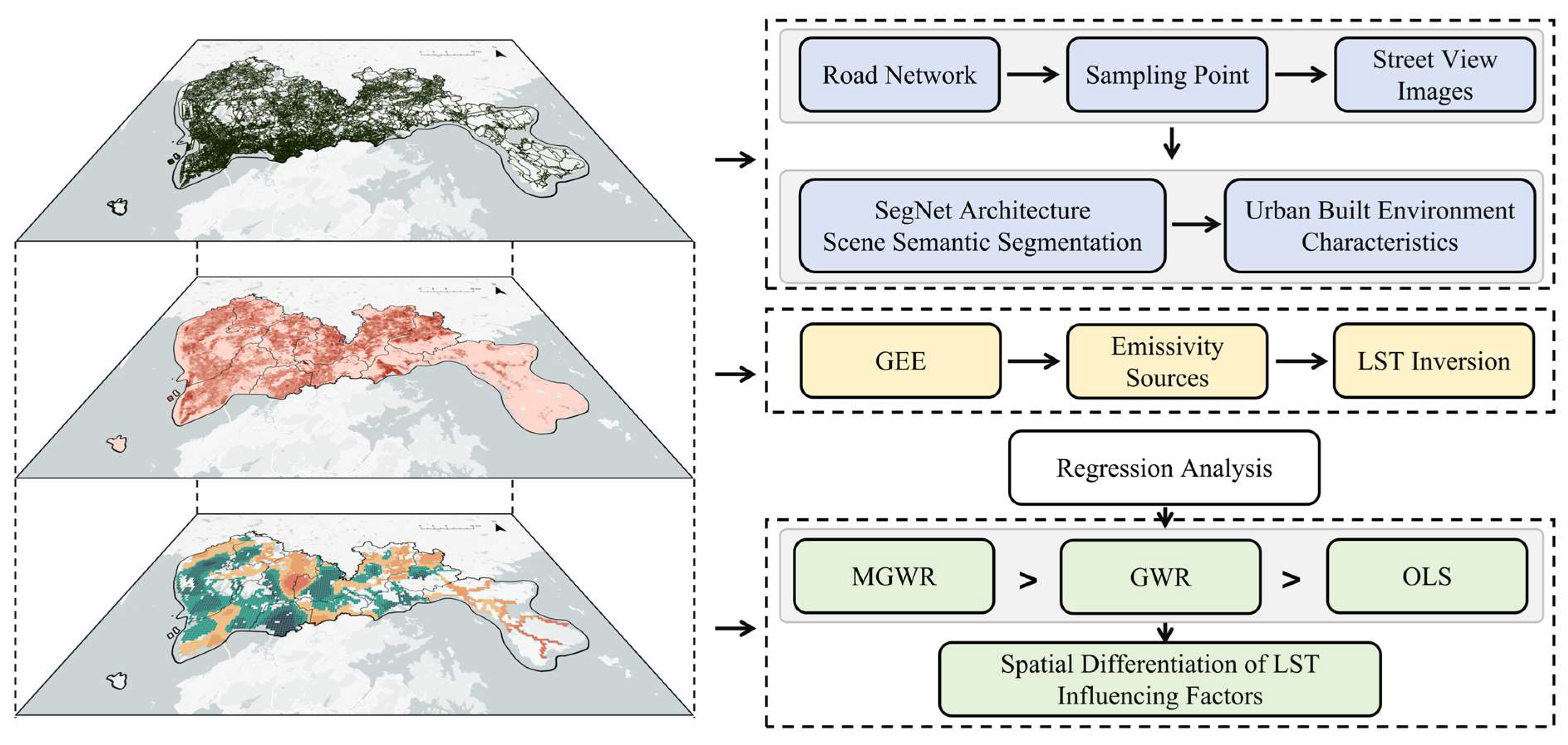
2.1. Research Framework
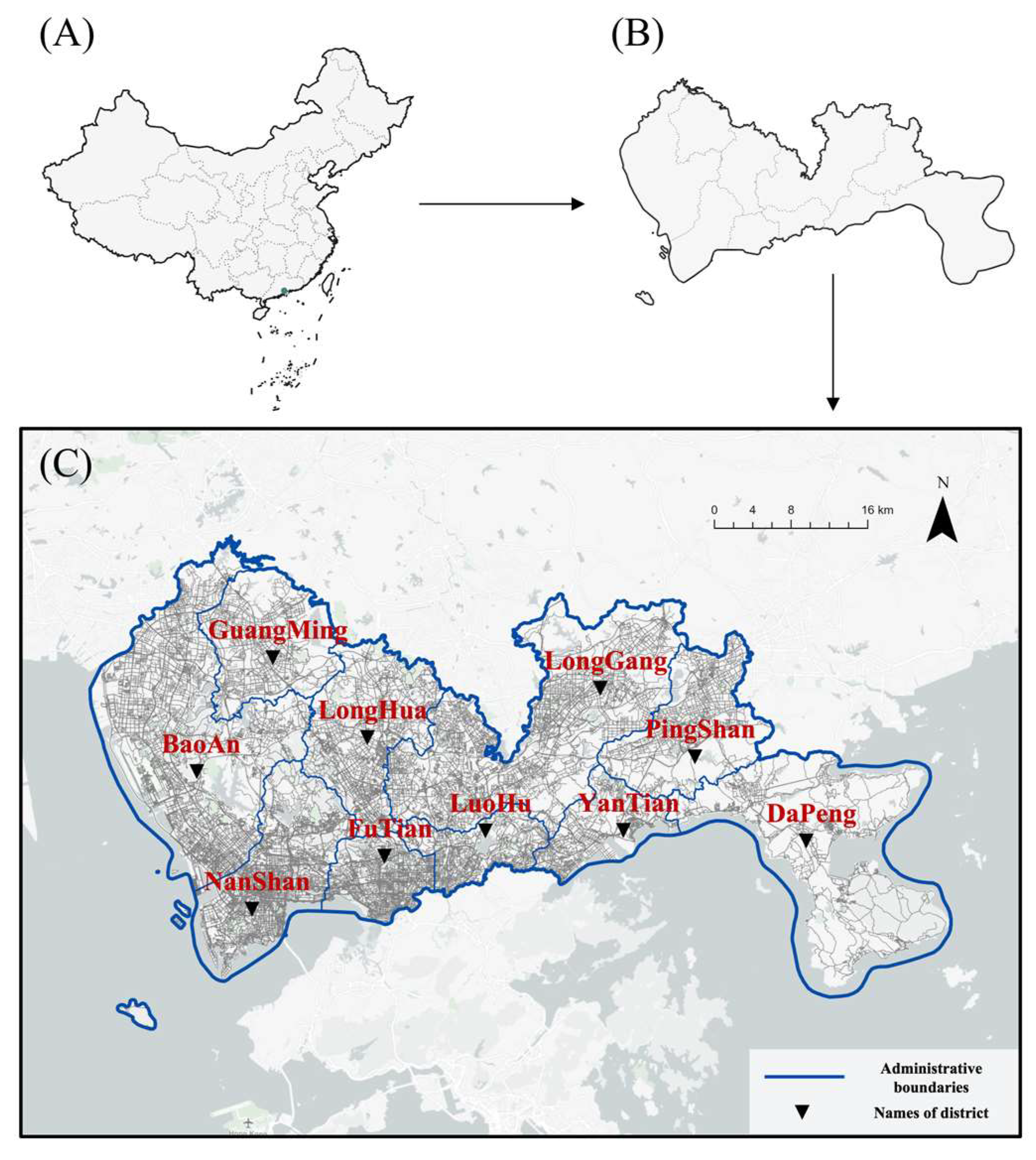
2.2. Study Area
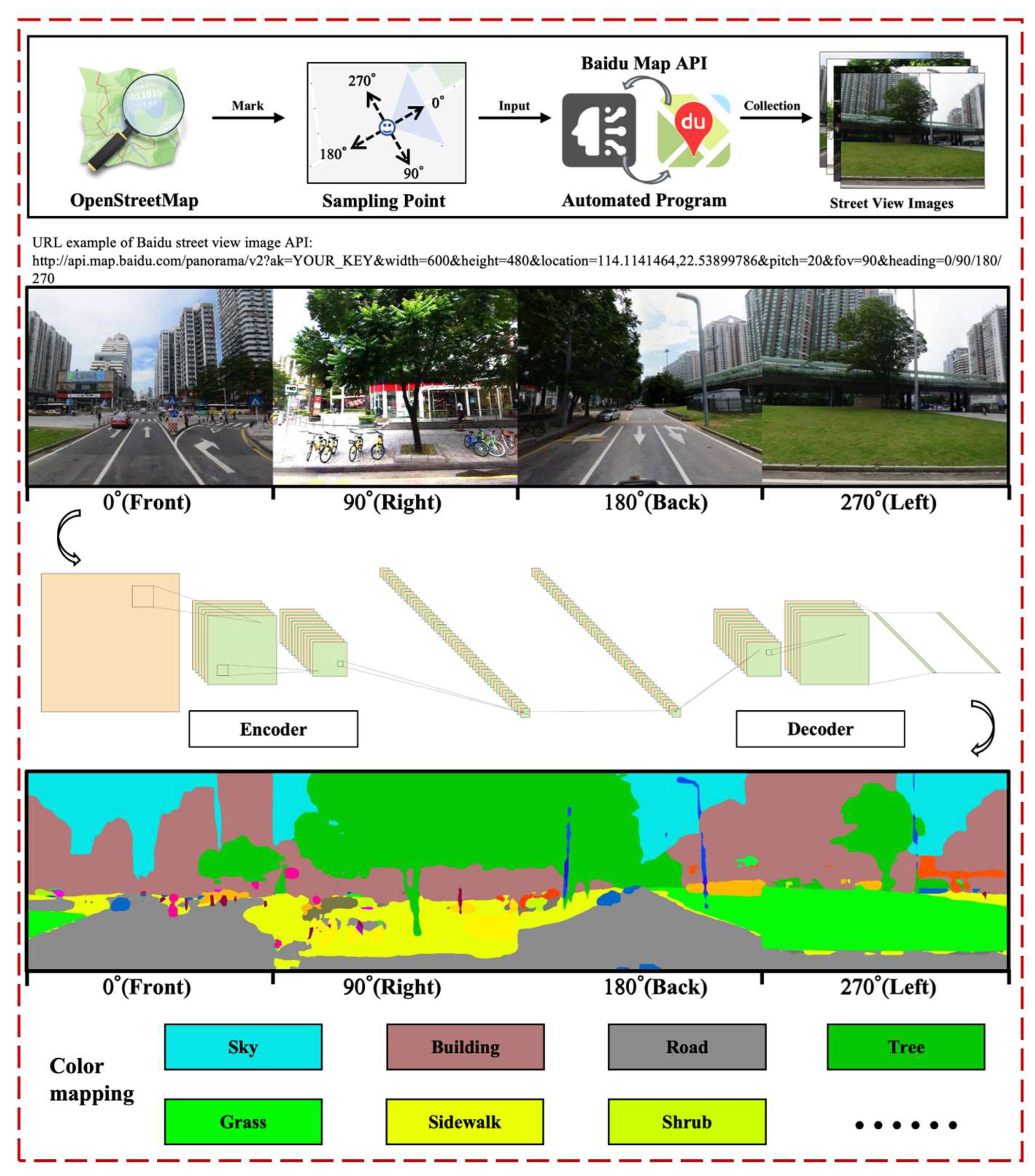
2.3. Street View Data Collection
2.4. Microscale-Built Environment Features Measurement Based on Image Segmentation
2.5. Urban LST Inversion Based on GEE
2.6. Explaining the Relationship between the Microscale Urban-Built Environment and LST
3. Results
3.1. Microscale-Built Environment Features
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Urban LST
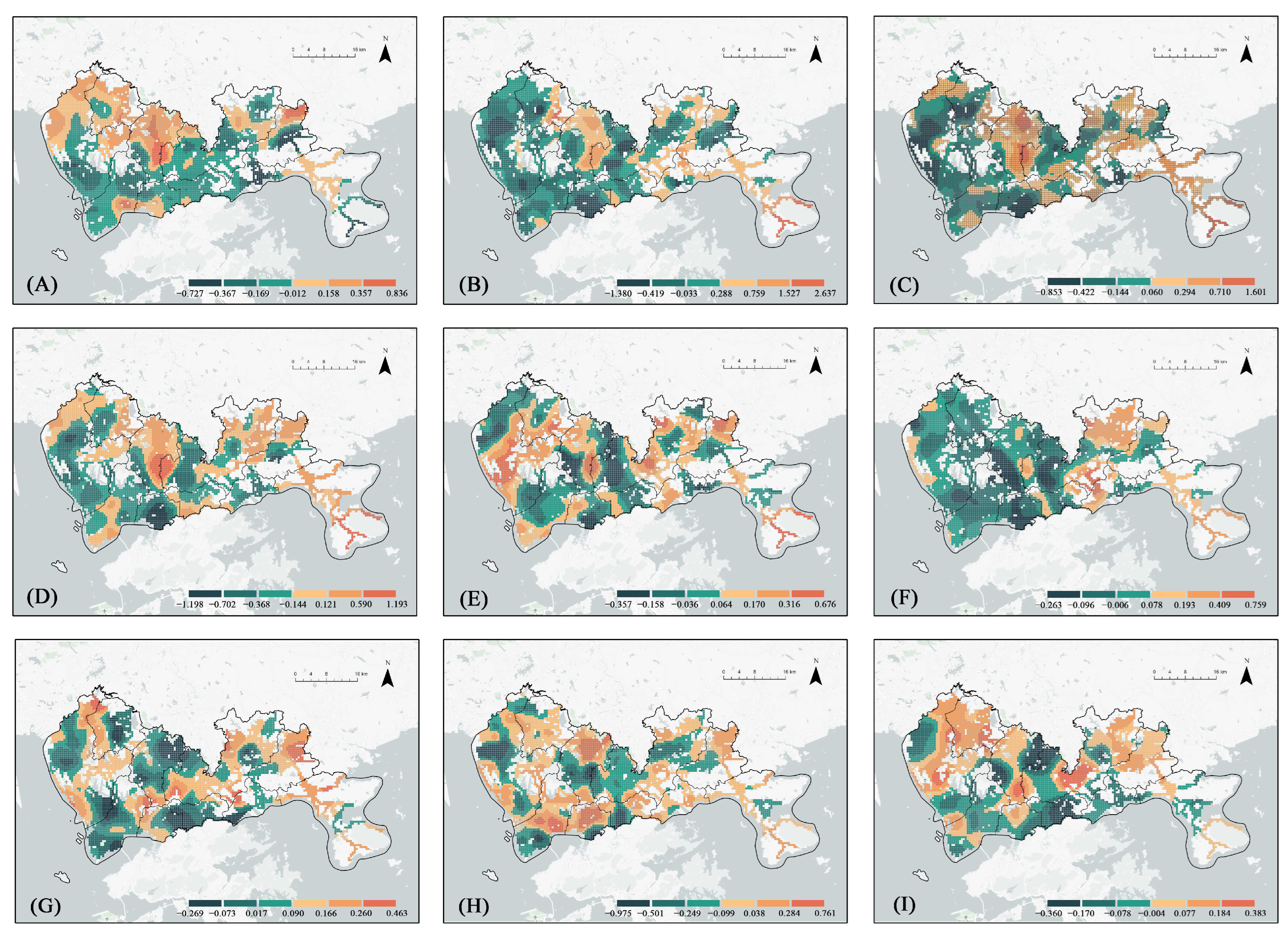
3.3. Regression Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Exploring the Effects of Microscale Built Environment on LST
4.2. Policy Implications
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full term |
| LST | Land surface temperatures |
| UHI | Urban heat island |
| GEE | Google earth engine |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
| GWR | Geographically weighted regression |
| MGWR | Multiscale geographically weighted regression |
| GIS | Geographic information systems |
| OSM | Open street map |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion corrected |
References
- Samson, J.; Berteaux, D.; McGill, B.J.; Humphries, M.M. Geographic Disparities and Moral Hazards in the Predicted Impacts of Climate Change on Human Populations: Spatially Explicit Impacts of Climate Change on Human Populations. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.-C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity Redistribution under Climate Change: Impacts on Ecosystems and Human Well-Being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, C. Health and Urban Living. Science 2008, 319, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xue, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Y. The Relationship between Urbanization and Depression in China: The Mediating Role of Neighborhood Social Capital. Int. J. Equity Health 2018, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeman, R. Impacts of Population Change on Vulnerability and the Capacity to Adapt to Climate Change and Variability: A Typology Based on Lessons from “a Hard Country”. Popul. Environ. 2010, 31, 286–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamnett, C. Is Chinese Urbanisation Unique? Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y. Redefining Chinese City System with Emerging New Data. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 75, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Chang, C.; Paulsen, K. The Changing Spatial Form of Cities in Western China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 135, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbich, M. Toward Dynamic Urban Environmental Exposure Assessments in Mental Health Research. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of Urbanization and Land-Use Change on Climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zeng, Y.; Koga, M.; Vejre, H. Variations in Land Surface Temperature and Cooling Efficiency of Green Space in Rapid Urbanization: The Case of Fuzhou City, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.; Tan, P.Y. Multi-Year Comparison of the Effects of Spatial Pattern of Urban Green Spaces on Urban Land Surface Temperature. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 184, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Addas, A.; Crull, D.; Maghrabi, A.; Levin, G.G.; Rubinyi, S. Remotely Sensed Derived Land Surface Temperature (LST) as a Proxy for Air Temperature and Thermal Comfort at a Small Geographical Scale. Land 2021, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.; Watson, J.E.M.; Salazar, A.; Thatcher, M.; McAlpine, C.A. The Impact of Urbanization and Climate Change on Urban Temperatures: A Systematic Review. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, Morbidity, and Risk Factors in China and Its Provinces, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoh, S.; Sato, K.; Okazaki, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Hirasawa, A.; Morimoto, K.; Shibasaki, M. Blood Flow Distribution during Heat Stress: Cerebral and Systemic Blood Flow. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Luo, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. The Impact of Building Operations on Urban Heat/Cool Islands under Urban Densification: A Comparison between Naturally-Ventilated and Air-Conditioned Buildings. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Oltra-Carrió, R.; Sòria, G.; Bianchi, R.; Paganini, M. Impact of Spatial Resolution and Satellite Overpass Time on Evaluation of the Surface Urban Heat Island Effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayet, N.; Pathak, K.; Chakrabarty, A.; Sahoo, S. Urban Heat Island Explored by Co-Relationship between Land Surface Temperature vs Multiple Vegetation Indices. Spat. Inf. Res. 2016, 24, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Baldinelli, G.; Verducci, P. Sustainable Strategies for Smart Cities: Analysis of the Town Development Effect on Surface Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing Methodologies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngie, A.; Abutaleb, K.; Ahmed, F.; Darwish, A.; Ahmed, M. Assessment of Urban Heat Island Using Satellite Remotely Sensed Imagery: A Review. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2014, 96, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, B.; Yu, X. Study on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Urban Heat Islands and Influencing Factors. Build. Environ. 2022, 208, 108604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streutker, D.R. A Remote Sensing Study of the Urban Heat Island of Houston, Texas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2595–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Sharifi, E. Daily Variation of Urban Heat Island Effect and Its Correlations to Urban Greenery: A Case Study of Adelaide. Front. Archit. Res. 2017, 6, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, H. Impact of Urbanization-Related Land Use Land Cover Changes and Urban Morphology Changes on the Urban Heat Island Phenomenon. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tsou, J.; Li, Y. Surface Urban Heat Island Analysis of Shanghai (China) Based on the Change of Land Use and Land Cover. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, Q.; Lang, K.; Wu, J. Linking Potential Heat Source and Sink to Urban Heat Island: Heterogeneous Effects of Landscape Pattern on Land Surface Temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Paul, S.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Kuttippurath, J. Anthropogenic Forcing Exacerbating the Urban Heat Islands in India. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.C.T.; Mahoney, R.; Privette, J.L.; Tucker, C.J. Development of a Daily Long Term Record of NOAA-14 AVHRR Land Surface Temperature over Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Zhang, P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Remote Sensing of the Urban Heat Island Effect across Biomes in the Continental USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Norouzi, H. Land Surface Temperature Variability across India: A Remote Sensing Satellite Perspective. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Ren, C.; Hang, J.; Li, Y. Urban Heat Island Circulations over the Beijing-Tianjin Region under Calm and Fair Conditions. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounoua, L.; Zhang, P.; Mostovoy, G.; Thome, K.; Masek, J.; Imhoff, M.; Shepherd, M.; Quattrochi, D.; Santanello, J.; Silva, J.; et al. Impact of Urbanization on US Surface Climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Richards, D.; Lu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhong, T. Measuring Daily Accessed Street Greenery: A Human-Scale Approach for Informing Better Urban Planning Practices. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ito, K. Street View Imagery in Urban Analytics and GIS: A Review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 215, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; He, J.; Jung, T. Measuring Residents’ Perceptions of City Streets to Inform Better Street Planning through Deep Learning and Space Syntax. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y. A Review of Urban Physical Environment Sensing Using Street View Imagery in Public Health Studies. Ann. GIS 2020, 26, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Garcia, L.M.T.; Goodman, A.; Johnson, R.; Aldred, R.; Murugesan, M.; Brage, S.; Bhalla, K.; Woodcock, J. Estimating City-Level Travel Patterns Using Street Imagery: A Case Study of Using Google Street View in Britain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Hou, Y. Sensitivity of Measuring the Urban Form and Greenery Using Street-Level Imagery: A Comparative Study of Approaches and Visual Perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, S.; Peng, W.; Ratti, C. Human Settlement Value Assessment from a Place Perspective: Considering Human Dynamics and Perceptions in House Price Modeling. Cities 2021, 118, 103333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. “Perception Bias”: Deciphering a Mismatch between Urban Crime and Perception of Safety. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 207, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Middel, A.; Turner, B.L. Evaluating the Effect of 3D Urban Form on Neighborhood Land Surface Temperature Using Google Street View and Geographically Weighted Regression. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Liu, L. How Green Are the Streets? An Analysis for Central Areas of Chinese Cities Using Tencent Street View. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.-Y.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Ng, E.; Norford, L.K. Mapping Sky, Tree, and Building View Factors of Street Canyons in a High-Density Urban Environment. Build. Environ. 2018, 134, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xing, H.; Cao, D.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. Exploring the Effects of Roadside Vegetation on the Urban Thermal Environment Using Street View Images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, D. Pattern Dynamics of Thermal-Environment Effect during Urbanization: A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Jung, T. Restorative Perception of Urban Streets: Interpretation Using Deep Learning and MGWR Models. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1141630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, L.; Seo, S.H.; He, J.; Jung, T. Measuring Perceived Psychological Stress in Urban Built Environments Using Google Street View and Deep Learning. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 891736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, C.; Xi, Y.; Yang, R.; Peng, N.; Zhang, C.; Ren, F. Measuring Human Perceptions of Streetscapes to Better Inform Urban Renewal: A Perspective of Scene Semantic Parsing. Cities 2021, 110, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Xiao, T.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Semantic Understanding of Scenes Through the ADE20K Dataset. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1511.00561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fung, H.H.; Lin, H.; Ratti, C. Measuring Human Perceptions of a Large-Scale Urban Region Using Machine Learning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 180, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, W. A Comparative Analysis of Retrieval Algorithms of Land Surface Temperature from Landsat-8 Data: A Case Study of Shanghai, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastatidis, D.; Mitraka, Z.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Abrams, M. Online Global Land Surface Temperature Estimation from Landsat. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, L. Examining the Association between the Built Environment and Pedestrian Volume Using Street View Images. Cities 2022, 127, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, A.O. Comparing Spatially-varying Coefficients Models for Analysis of Ecological Data with Non-stationary and Anisotropic Residual Dependence. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.M.; Dennis, L.Y.C.; Liu, C. A Review on the Generation, Determination and Mitigation of Urban Heat Island. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Berardi, U.; Akbari, H. Comparing the Effects of Urban Heat Island Mitigation Strategies for Toronto, Canada. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Bakaric, J.; Jeffrey-Bailey, T. The Urban Heat Island Effect, Its Causes, and Mitigation, with Reference to the Thermal Properties of Asphalt Concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Moser, A.; Rötzer, T.; Pauleit, S. Comparing the Transpirational and Shading Effects of Two Contrasting Urban Tree Species. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winbourne, J.B.; Jones, T.S.; Garvey, S.M.; Harrison, J.L.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Templer, P.H.; Hutyra, L.R. Tree Transpiration and Urban Temperatures: Current Understanding, Implications, and Future Research Directions. BioScience 2020, 70, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanda-Jansen, A. Evolution of The Metropolitan Area of Shenzhen, Analysis: From Theory to Selected Examples. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number | Elements | Mean | Max. | Min. | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sky | 0.239 | 0.571 | 0.000 | 0.095 |
| 2 | Road | 0.208 | 0.397 | 0.000 | 0.056 |
| 3 | Tree | 0.194 | 0.666 | 0.000 | 0.109 |
| 4 | Building | 0.141 | 0.600 | 0.000 | 0.110 |
| 5 | Sidewalk | 0.038 | 0.257 | 0.000 | 0.027 |
| 6 | Shrub | 0.035 | 0.357 | 0.000 | 0.032 |
| 7 | Wall | 0.023 | 0.547 | 0.000 | 0.041 |
| 8 | Earth | 0.017 | 0.404 | 0.000 | 0.028 |
| 9 | Grass | 0.013 | 0.260 | 0.000 | 0.019 |
| 10 | Water | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.000 | 0.002 |
| —— | OLS Coefficients | GWR Coefficients | MGWR Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean | Mean | Min., Max. | Mean | Min., Max. |
| Sky | 12.971 *** | 0.031 | (−1.698, 2.436) | 0.021 | (−0.853, 1.601) |
| Road | 17.361 *** | 0.083 | (−1.017, 1.117) | 0.062 | (−0.357, 0.676) |
| Tree | 3.230 * | −0.126 | (−1.902, 2.173) | −0.116 | (−1.198, 1.194) |
| Building | 17.684 *** | 0.128 | (−1.889, 2.655) | 0.106 | (−1.380, 2.637) |
| Sidewalk | 30.933 *** | 0.088 | (−0.770, 0.735) | 0.073 | (−0.268, 0.078) |
| Shrub | 5.946 ** | 0.021 | (−0.805, 0.864) | 0.004 | (−0.360. 0.383) |
| Wall | 6.440 * | −0.009 | (−1.676, 1.305) | −0.009 | (−1.468, 0.836) |
| Earth | 5.287 * | −0.077 | (−2.005, 3.106) | −0.075 | (−0.975, 0.761) |
| Grass | 8.709 ** | 0.036 | (−0.818, 1.933) | 0.032 | (−0.263, 0.759) |
| Water | −5.889 | −0.001 | (−2.438, 4.998) | 0.011 | (−1.895, 1.648) |
| R2 | 0.263 | 0.747 9992.3 | 0.830 8878.2 | ||
| AICc | 26,999.8 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050549
Zhang T, Lin Z, Wang L, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Hu Y. The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(5):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050549
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tianlin, Zhao Lin, Lei Wang, Wenzheng Zhang, Yazhuo Zhang, and Yike Hu. 2024. "The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images" Atmosphere 15, no. 5: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050549
APA StyleZhang, T., Lin, Z., Wang, L., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., & Hu, Y. (2024). The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images. Atmosphere, 15(5), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050549








