Pollution Levels in Indoor School Environment—Case Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
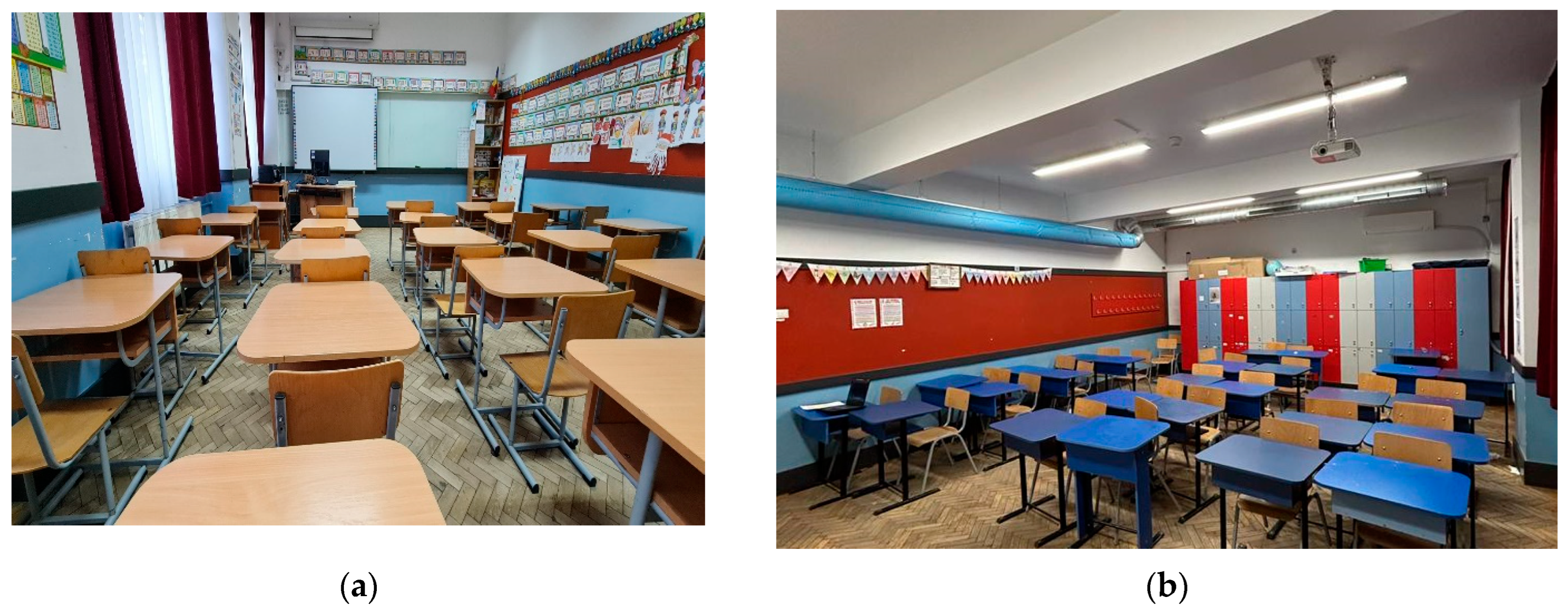
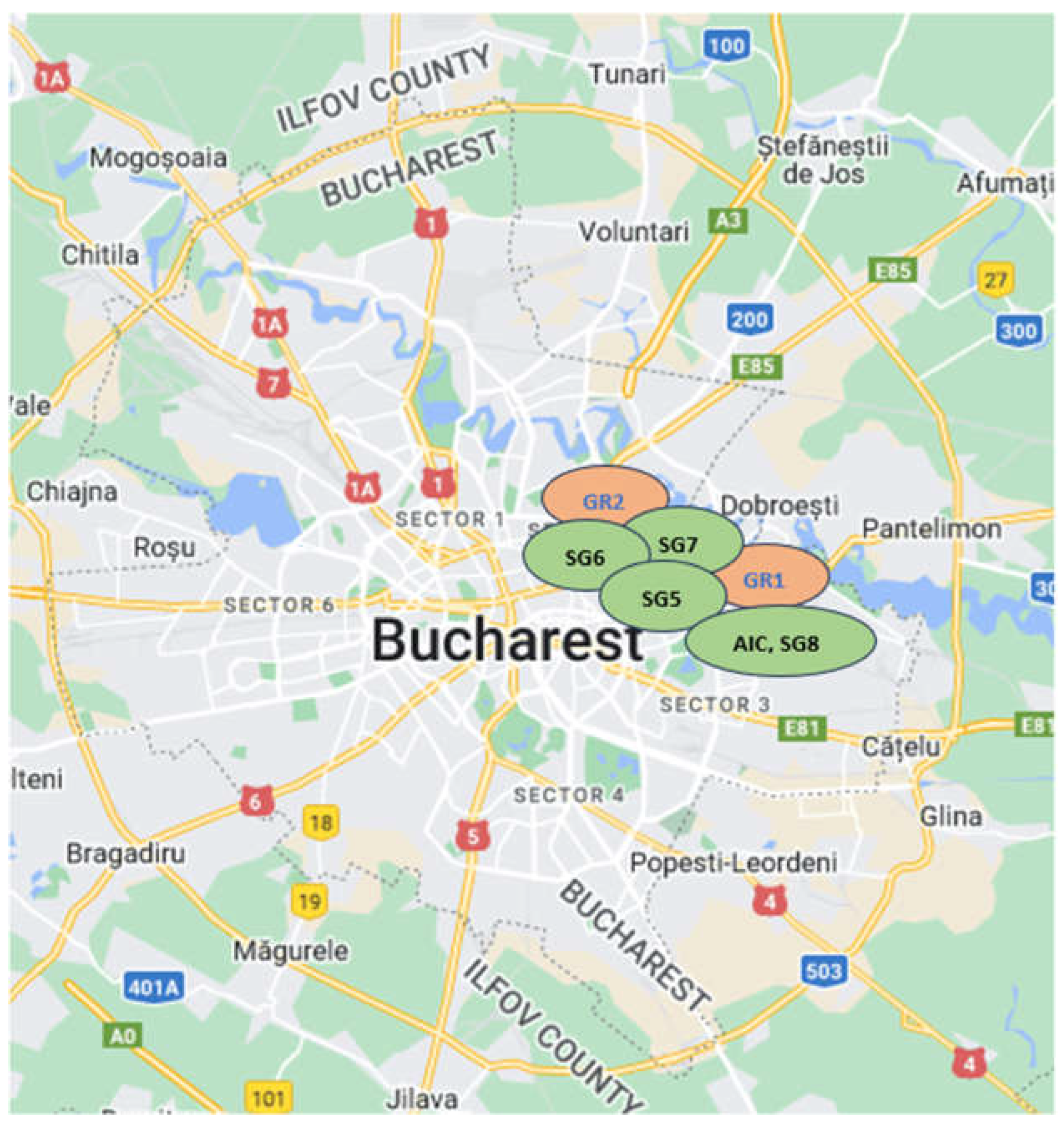
2.1. Monitored Space Description
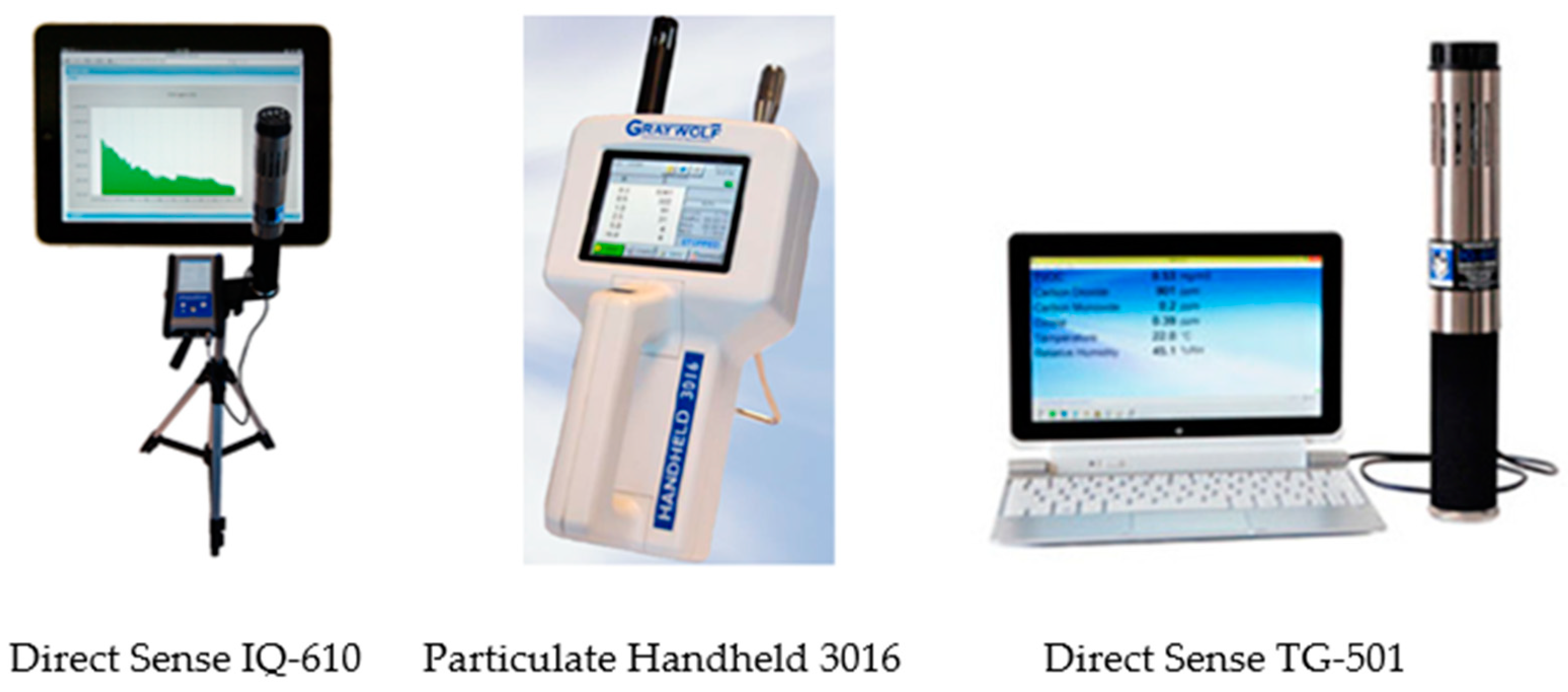
2.2. Equipment
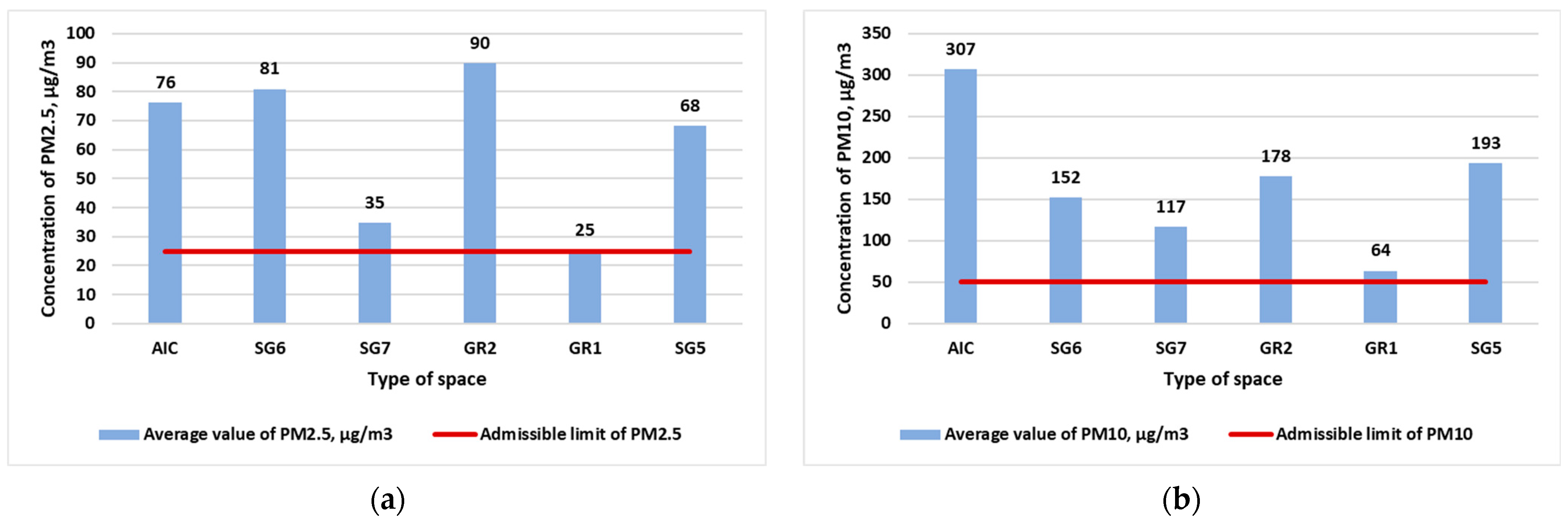
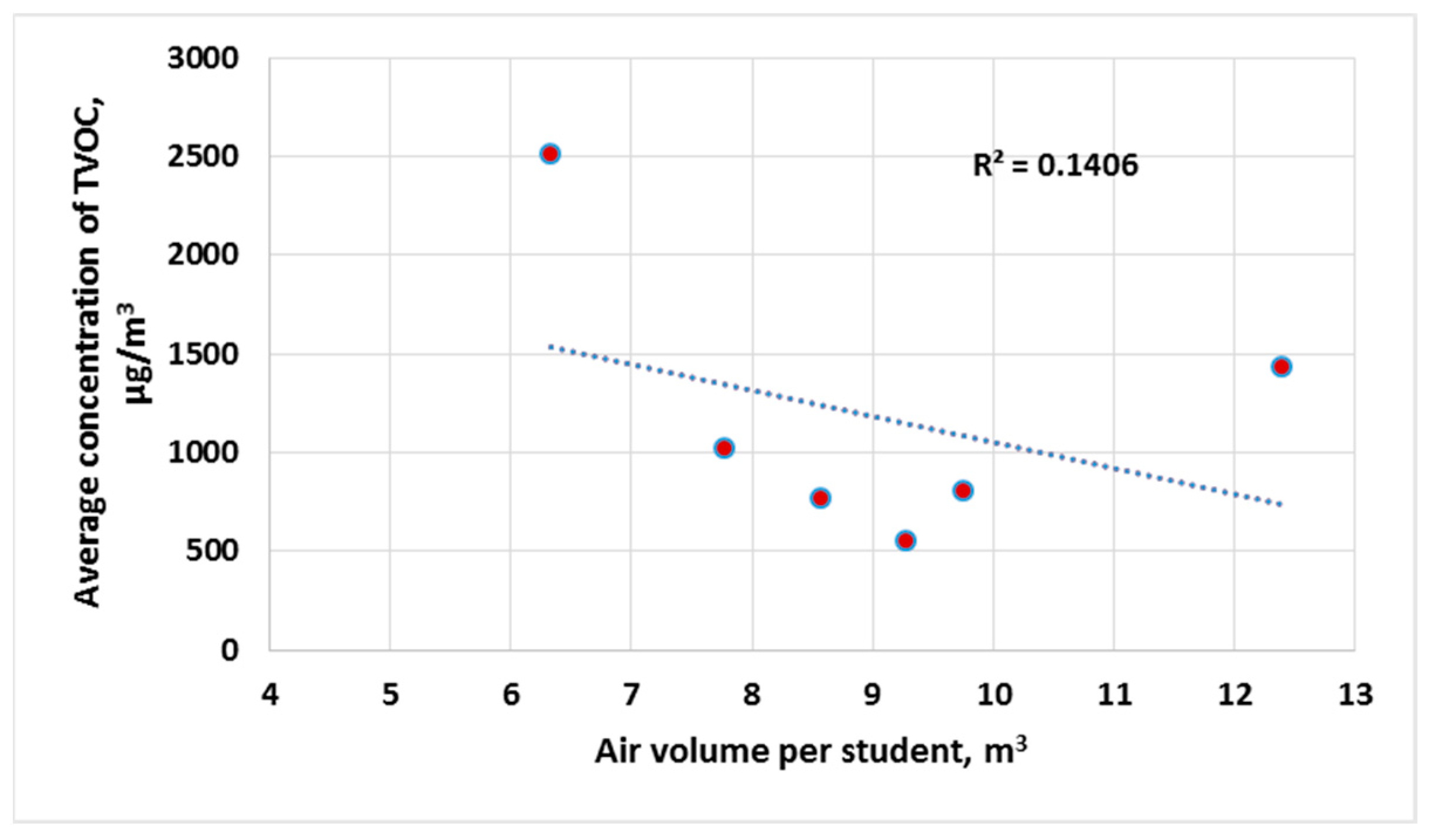
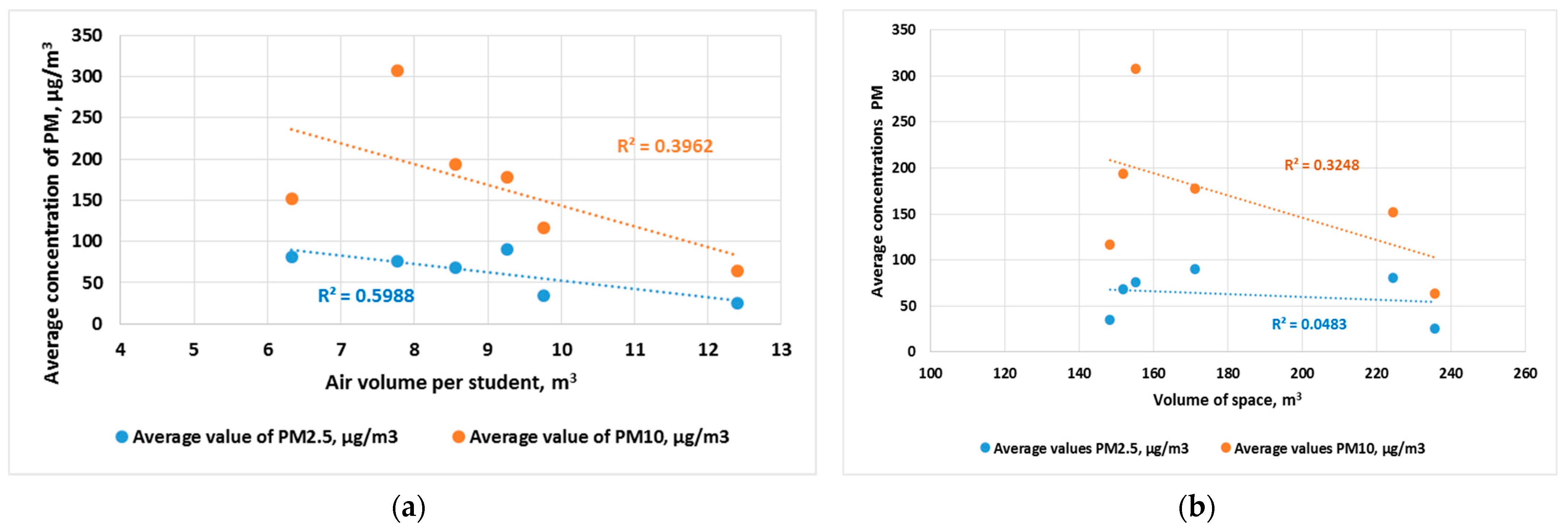
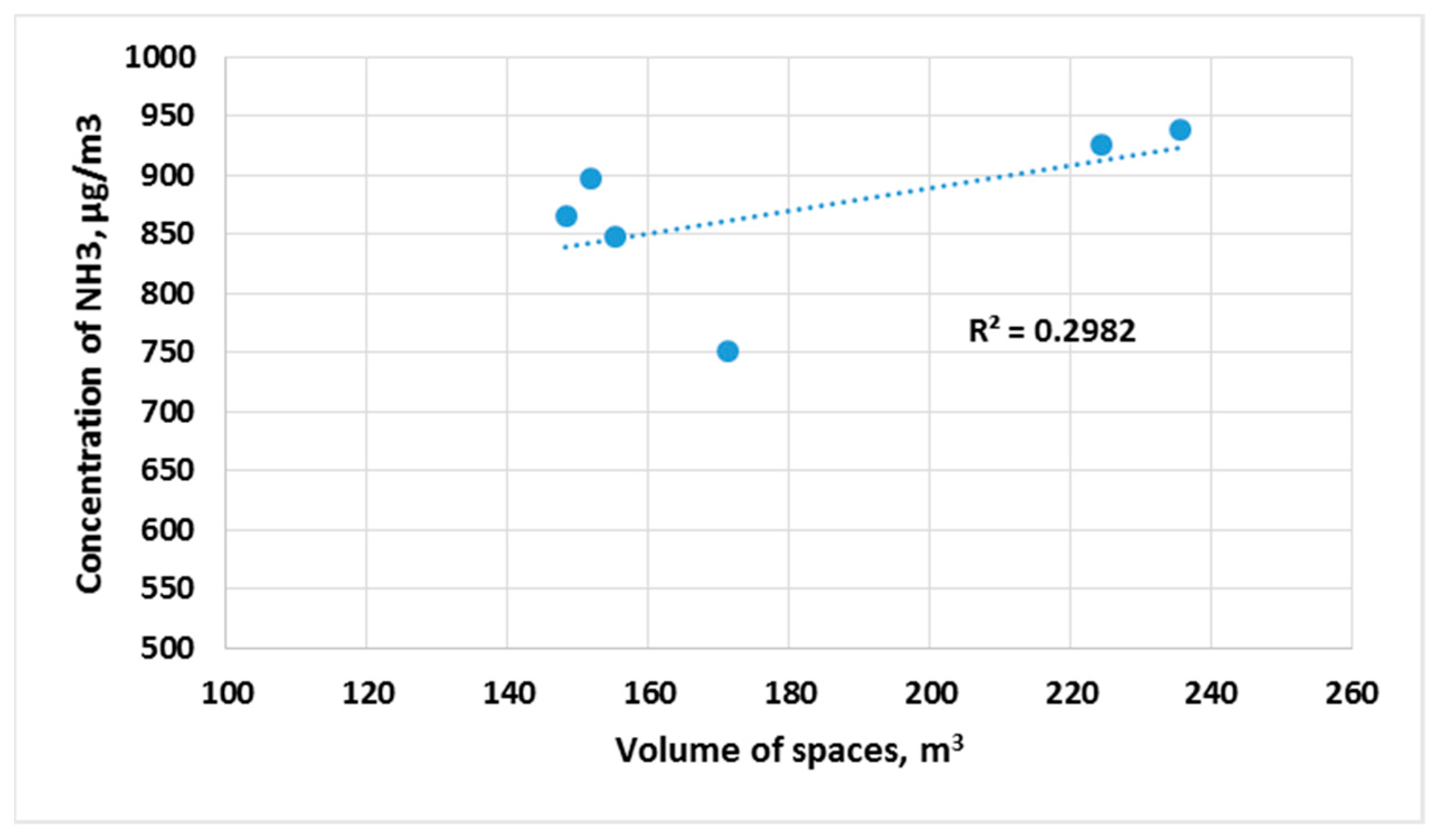
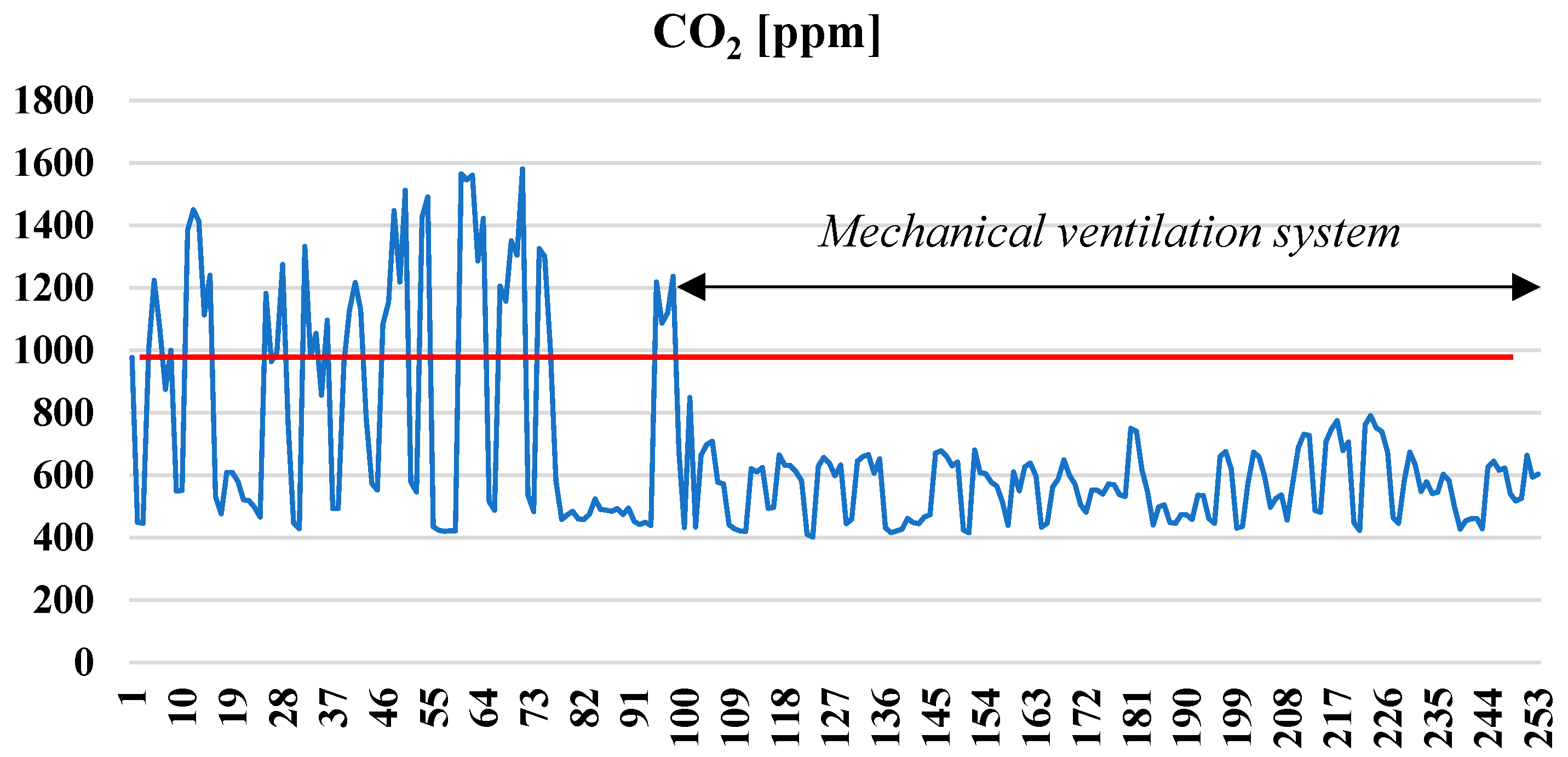
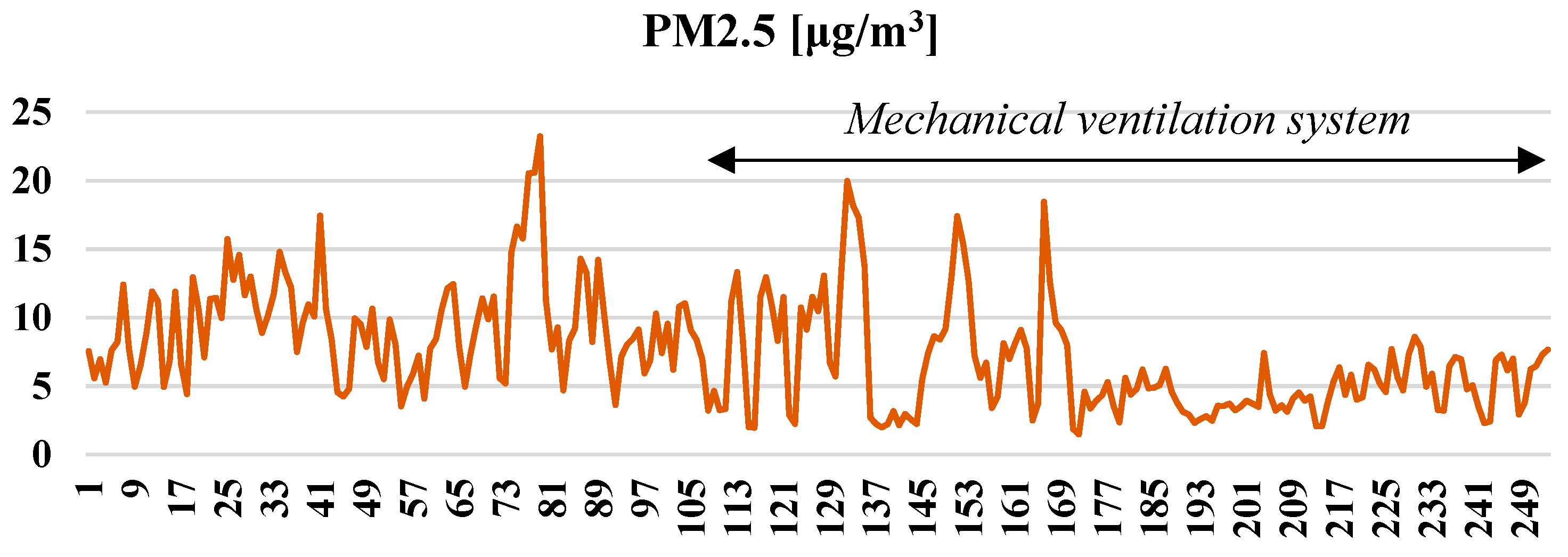
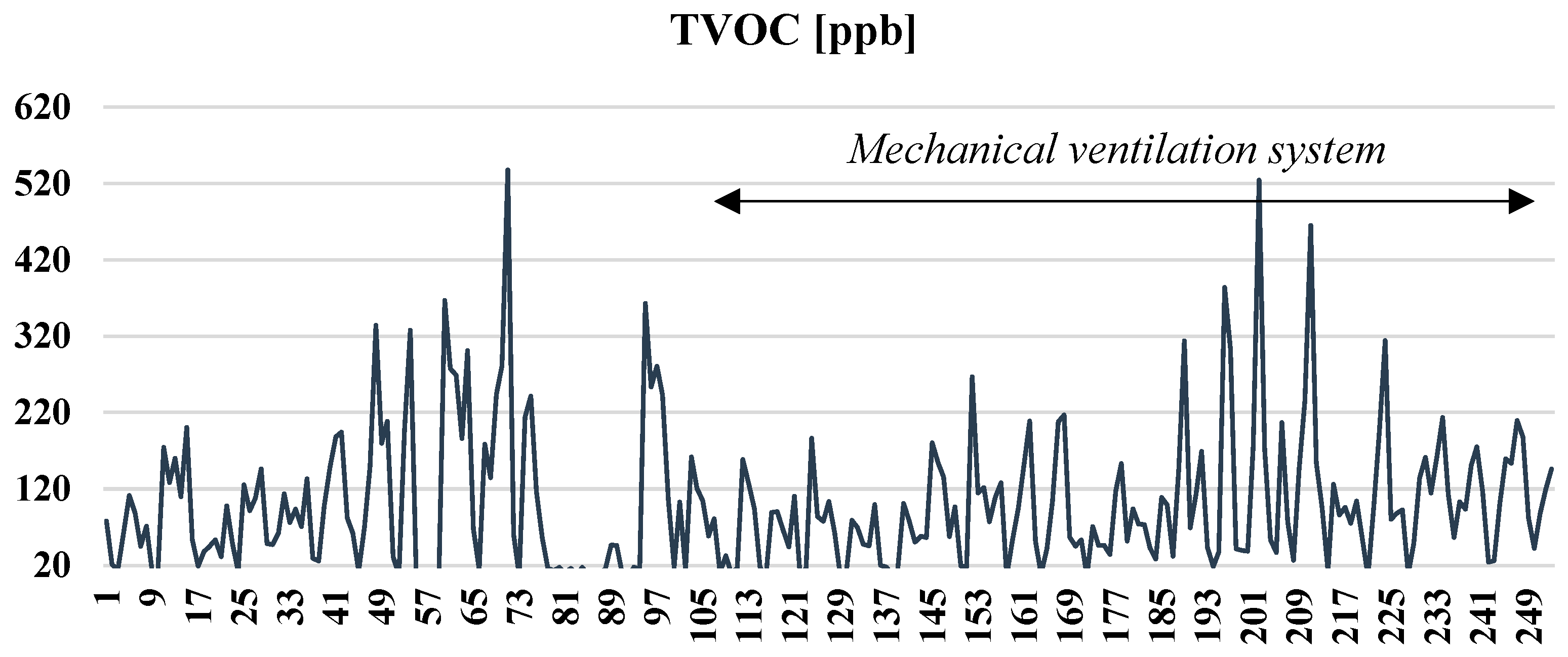
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.; Verma, V.; Thakur, M.; Singh, G.; Bhargava, B. A systematic review on mitigation of common indoor air pollutants using plant-based methods: A phytoremediation approach. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, R.; Su, C.; Huang, C. The new model for evaluating indoor air quality based on childhood allergic and respiratory diseases in Shanghai. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petigny, N.; Zhang, J.; Horner, E.; Steady, S.; Chenal, M.; Mialon, G.; Goletto, V. Indoor air depolluting material: Combining sorption testing and modeling to predict product’s service life in real conditions. Build. Environ. 2021, 202, 107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Suzuki, N.; Takaguchi, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Shimatani, K. Is indoor environment a risk factor of building-related symptoms? PLoS ONE 2023, 18, 0279757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.N.; Anand, P.; George, A.; Mondal, N. A review of strategies and their effectiveness in reducing indoor airborne, transmission and improving indoor air quality. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arar, M.; Jung, C.; Qassimi, N.A. Investigating the Influence of the Building Material on the Indoor Air Quality in Apartment in Dubai. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 7, 804216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martín, J.; Kraakman, N.J.R.; Perez, C.; Lebrero, R.; Munoz, R. A state-of-the-art review on indoor air pollution and strategies for indoor air pollution control. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karr, G.; Nicolas, M.; Maupetit, F.; Ramel, M. Cleaning product emissions and indoor built environments: Exposure and health risk assessments from experiments under realistic indoor conditions. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.; Gandolfo, A.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Strekowski, R.; Brochard, G.; Bergé, V.; Gligorovski, S.; Wortham, H. Application of a mineral binder to reduce VOC emissions from indoor photocatalytic paints. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.; Redon, N.; Thevenet, F.; Hanoune, B.; Coddeville, P. Performances and limitations of electronic gas sensors to investigate an indoor air quality event. Build. Environ. 2016, 107, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, P.; Sivachandiran, L.; Gaudion, V.; Thevenet, F.; Locoge, N. The 40 m3 Innovative experimental Room for INdoor Air studies (IRINA): Development and validations. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destaillats, H.; Sleiman, M.; Sullivan, D.P.; Jacquiod, C.; Sablayrolles, J.; Molins, L. Key parameters influencing the performance of photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) air purification under realistic indoor conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 128, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentese, S.; Mirici, N.A.; Elbir, T.; Tuygun, G.T.; Bakar, C.; Otkun, M.T.; Oymak, S. A comprehensive assessment of ambient air quality in Çanakkale city: Emission inventory, air quality monitoring, source apportionment, and respiratory health indicators. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalina, T.; Damian, A.; Vartires, A.; Niță, M.; Racovițeanu, V. Long-term analysis of indoor air quality and thermal comfort in a public school. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1185, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wei, T.; Zhenxia, D.; Lei, N.; Xiaoshuan, A.; Wenwen, L.; Xuechun, S.; Zhengchao, S.; Aijun, S. Source profiles and emission factors of VOCs from solvent-based architectural coatings and their contributions to ozone and secondary organic aerosol formation in China. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Liu, W.; Hailin, W.; Xia, S.; Aijun, S.; Xiaoshuan, A.; Guohao, L.; Lei, N. Emission factors and characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from adhesive application in indoor decoration in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 145169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, F.; Guichard, R.; Robert, L.; Verriele, M.; Thevenet, F. Behaviour of individual VOCs in indoor environments: How ventilation affects emission from materials. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 243, 117713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalina, T.; Lungu, C. Influence of A Descentralized Ventilation System on the Indoor Air Quality of A Primary School Classroom. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 664, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allab, Y.; Pellegrino, M.; Xiaofeng, G.; Nefzaoui, E.; Kindinis, A. Energy and comfort assessment in educational building: Case study in a French university campus. Energy Build. 2017, 143, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, V.; Petran, H.; Dima, A.; Petcu, C. Indoor Air Quality—A Key Element of the Energy Performance of the Buildings. Energy Procedia 2016, 96, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Z. Adsorption, membrane separation for removal, recovery of volatile organic compounds. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Yanru, W.; Liyuan, Z.; Zhe, M.; Weiping, Z. Estimates of emission strengths of 43 VOCs in wintertime residential indoor environments, Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurán, S.; Grace, J.; Urban, O. Temporal Changes in Ozone Concentrations and Their Impact on Vegetation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, A.; Lall, A.S.; Taneja, A.; Singhvi, R. Exposure levels and health risk assessment of ambient BTX at urban and rural environments of a terai region of northern India. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, V.T.D.; Lin, C.; Thanh, V.C.; Oanh NT, K.; Thanh, B.X.; Weng, C.E.; Yuan, C.-S.; Rene, E.R. An overview of the development of vertical sampling technologies for ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teiri, H.; Hajizadeh, Y.; Azhdarpoor, A. A review of different phytoremediation methods, critical factors for purification of common indoor air pollutants: An approach with sensitive analysis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Kagi, N.; Yanagi, U.; Osawa, H. Effects of low-level inhalation exposure to carbon dioxide in indoor environments: A short review on human health and psychomotor performance. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Zou, Z.; Huang, C. Indoor ammonia concentrations in college dormitories and the health effects. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108556. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2352710224001244 (accessed on 29 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng Lee, S.; Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.; Cao, N.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Y. Effect of ammonia on ozone-initiated formation of indoor secondary products with emissions from cleaning products. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 224–231. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1352231012004347 (accessed on 5 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Turunen, A.; Toyinbo, O.; Putus, T.; Nevalainen, A.; Shaughnessy, R.; Haverinen-Shaughnessy, U. Indoor environmental quality in school buildings, and the health and wellbeing of students. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Leccese, F. Measurement of CO2 concentration for occupancy estimation in educational buildings with energy efficiency purposes. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.; Byrne, M.; Armstrong, S.; Sheahan, J.; Coggins, A.M. A pre and post evaluation of indoor air quality, ventilation, and thermal comfort in retrofitted co-operative social housing. Build. Environ. 2017, 122, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Lynch, R.A.; Floyd, E.L.; Wang, J.; Bartels, J.N. Indoor air quality in classrooms: Environmental measures and effective ventilation rate modeling in urban elementary schools. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, E.; McCormack, M.; Davis, M.; Curriero, F.; Berman, J.; Connolly, F.; Leaf, F.; Rule, A.; Green, T.; Clemons-Erby, D.; et al. Indoor air quality in inner-city schools and its associations with building characteristics and environmental factors. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LEED Reference Guide for Green Building Design and Construction (v4.1 Edition). Available online: https://www.usgbc.org/guide/bdc (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Regulation for the Design, Execution and Operation of Ventilation and Air Conditioning Installations (in Romanian—Normativ Pentru Proiectarea, Executarea și Exploatarea Instalațiilor de Ventilare și Climatizare, Indicativ I5-2022). Available online: https://drimand.ro/download/43%20NORMATIV%20I%205%20-%202022.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/RO/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32008L0050 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Regulations Regarding the Hygiene of Air Composition in Spaces with Various Destinations, Depending on the Activities Carried out, in Winter-Summer Regime, Reference Number NP 008-97 (in Romanian, Normativ Privind igiena Compoziției Aerului în Spații cu Diverse Destinații, în Funcție de Activitățile Desfășurate, in Regim de Iarnă-Vară, Indicativ NP 008-97). Available online: https://www.mdlpa.ro/userfiles/reglementari/Domeniul_XXIV/24_7_NP_008_1997.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Ayame, T.; Ryoichi, K.; Hyuntae, K. Effects of Outdoor Air Pollutants on Indoor Environment Due to Natural Ventilation. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Catalina, T.; Damian, A.; Vartires, A. Study of the Impact of Indoor Environmental Quality in Romanian Schools through an Extensive Experimental Campaign. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalina, T.; Ghita, S.A.; Popescu, L.L.; Popescu, R. Survey and Measurements of Indoor Environmental Quality in Urban/Rural Schools Located in Romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalina, T.; Istrate, M.A.; Damian, A.; Vartires, A.; Dicu, T.; Cuco¸s, A. Indoor Air Quality Assessment in a Classroom Using a Heat Recovery Ventilation Unit. Rom. J. Phys. 2019, 64, 9–10. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Measuring Principle | Domain/Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| TVOCs | Photoionization detector (PID) | 20 ÷ 20,000 ppb/1 ppb |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) | 0 ÷ 10,000 ppm/±50 ppm |
| Ammonia (NH3) | Electrochemical | 0 ÷ 100 ppm/<1 ppm |
| Particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) | Optical | 0.3 ÷ 10.0 µm/100% for particle > 0.45 µm |
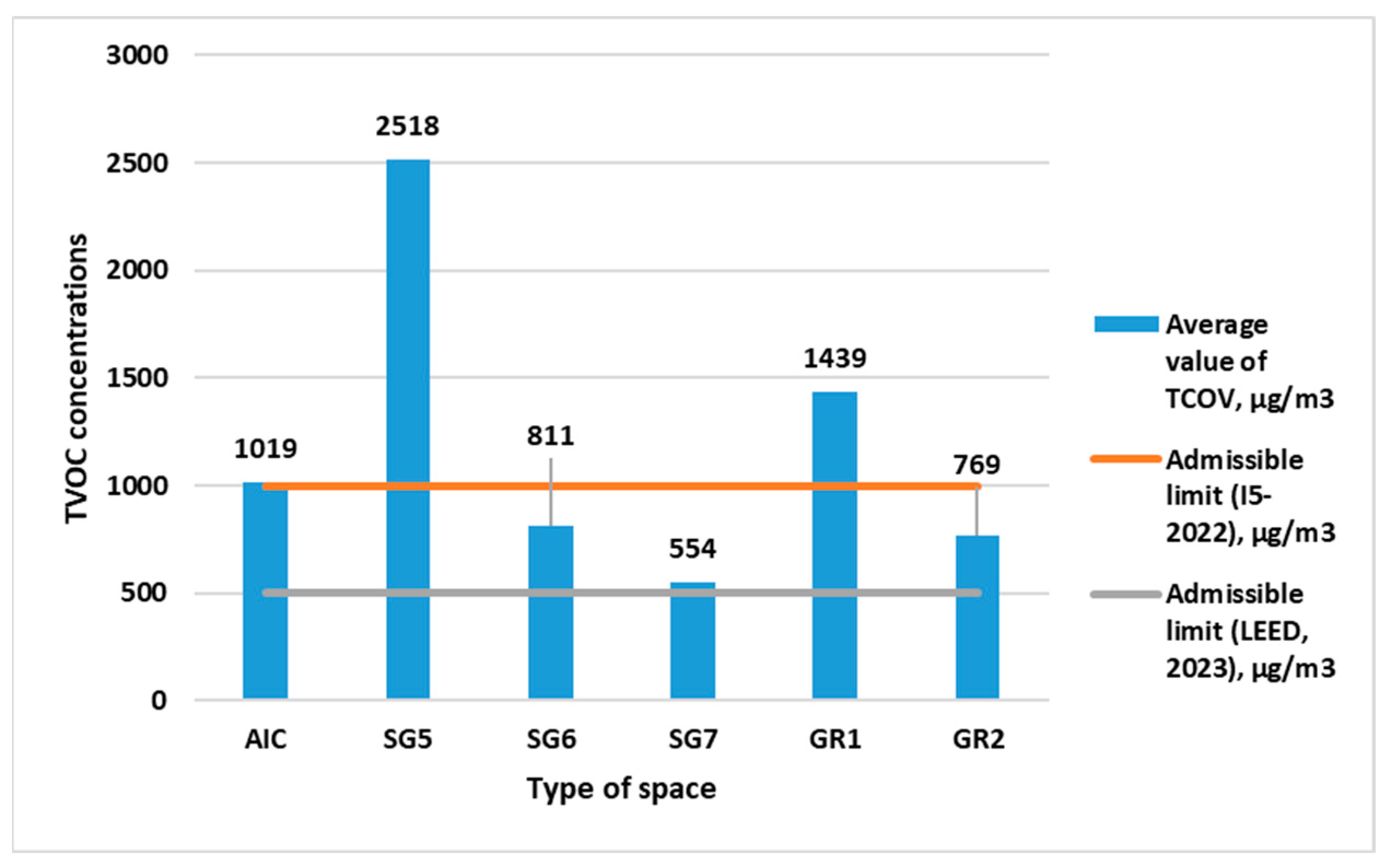
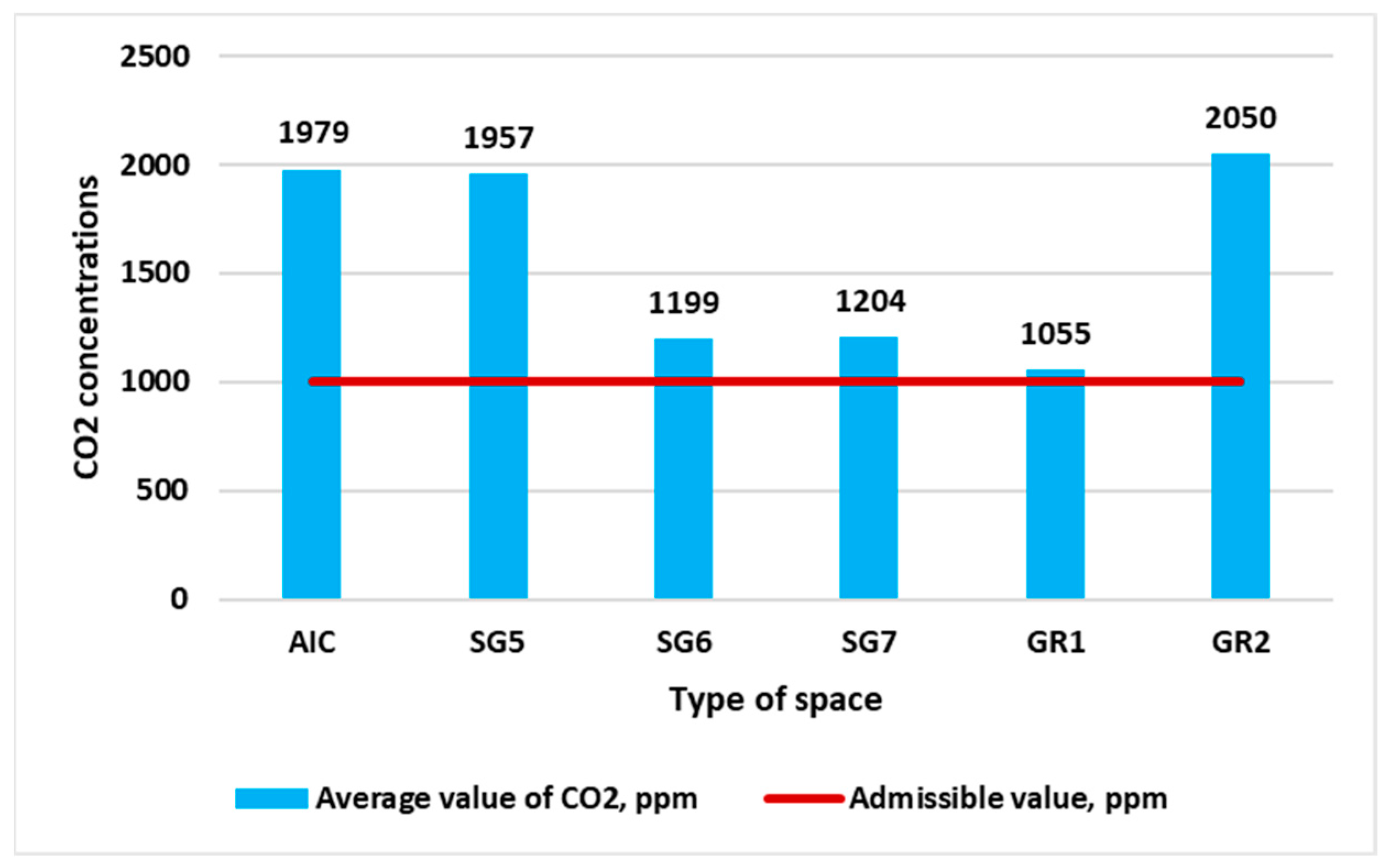
| Type of Space | Volume of Space, m3 | Number of Students | Air Volume per Student, m3 | TVOC, (min/max) µg/m3 | CO2, (min/max) ppm | PM2.5, (min/max) µg/m3 | PM10, (min/max) µg/m3 | NH3, (min/max) µg/m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIC | 155.3 | 20 | 7.8 | 727/1921 | 1485/2462 | 57.3/109.5 | 190.8/412.0 | 739.6/985.4 |
| SG5 | 151.9 | 24 | 6.3 | 1054/4917 | 1442/2269 | 58.3/78.0 | 144.4/228.4 | 768.4/1403.4 |
| SG6 | 224.4 | 23 | 9.8 | 584/1154 | 899/1487 | 61.8/102.0 | 116.5/209.8 | 740.1/1126.2 |
| SG7 | 148.3 | 16 | 9.3 | 469/695 | 1023/1489 | 33.2/36.0 | 86.7/141.9 | 543.5/843.2 |
| GR1 | 235.6 | 19 | 12.4 | 957/1991 | 957/1165 | 23.4/27.1 | 50.8/84.4 | 780.7/1231.7 |
| GR2 | 171.3 | 20 | 8.6 | 706/840 | 1495/2783 | 75.9/114.9 | 143.3/226.2 | 670.5/1020.3 |
| Admissible limit | 500/1000 | 1000 | 25 | 50 | 3001/1001 | |||
| References | [35,36] | [31,36] | [36,37] | [36,37] | [38] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasile, V.; Catalina, T.; Dima, A.; Ion, M. Pollution Levels in Indoor School Environment—Case Studies. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040399
Vasile V, Catalina T, Dima A, Ion M. Pollution Levels in Indoor School Environment—Case Studies. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040399
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasile, Vasilica, Tiberiu Catalina, Alina Dima, and Mihaela Ion. 2024. "Pollution Levels in Indoor School Environment—Case Studies" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040399
APA StyleVasile, V., Catalina, T., Dima, A., & Ion, M. (2024). Pollution Levels in Indoor School Environment—Case Studies. Atmosphere, 15(4), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040399






