The Impact of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Changes in the CMAQ Model on PM2.5 Concentration Variations in Northeast Asia: Focusing on the Seoul Metropolitan Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Model Configuration
2.2. Experimental Design
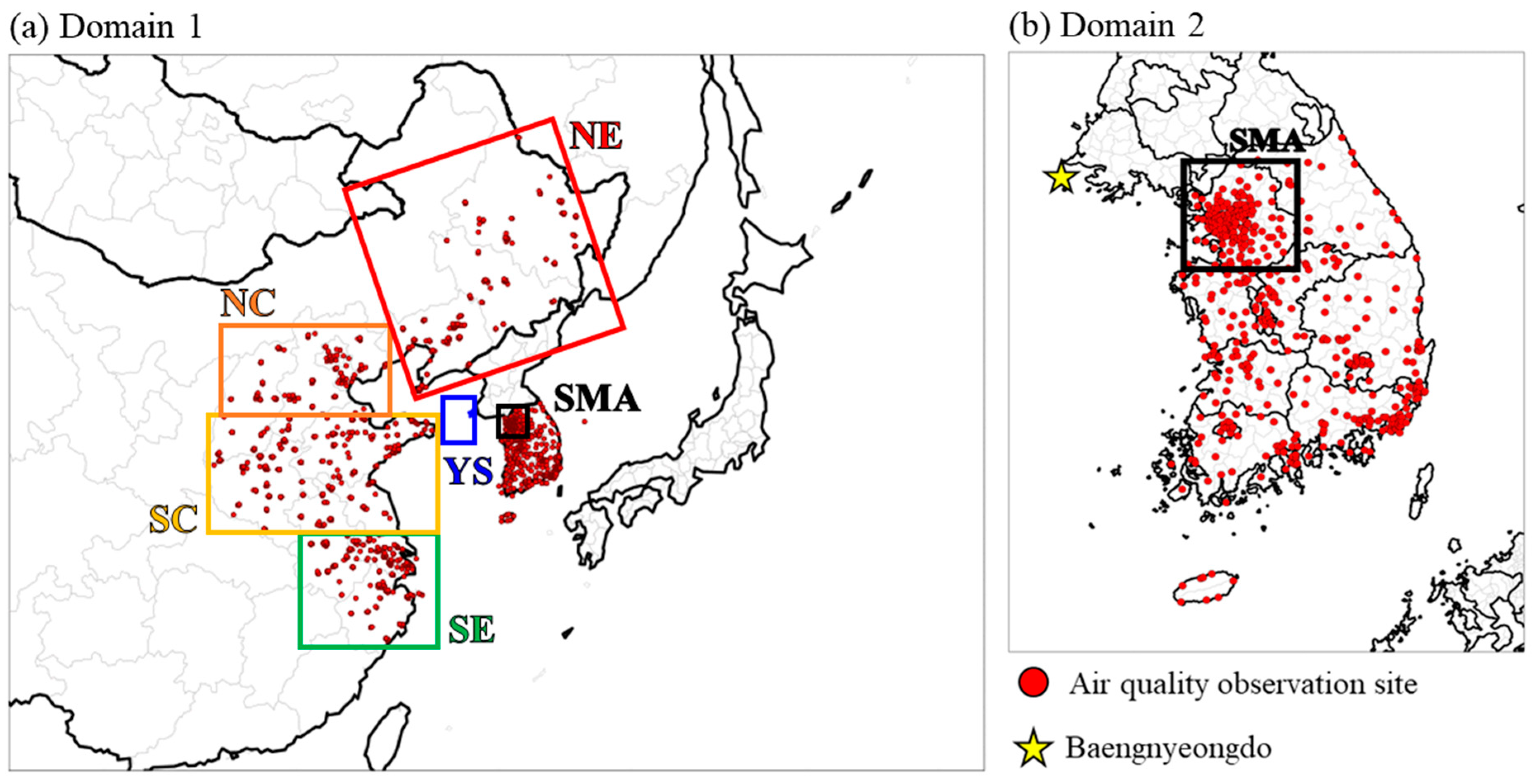
2.3. Target Cases and Regions
2.4. Analysis Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
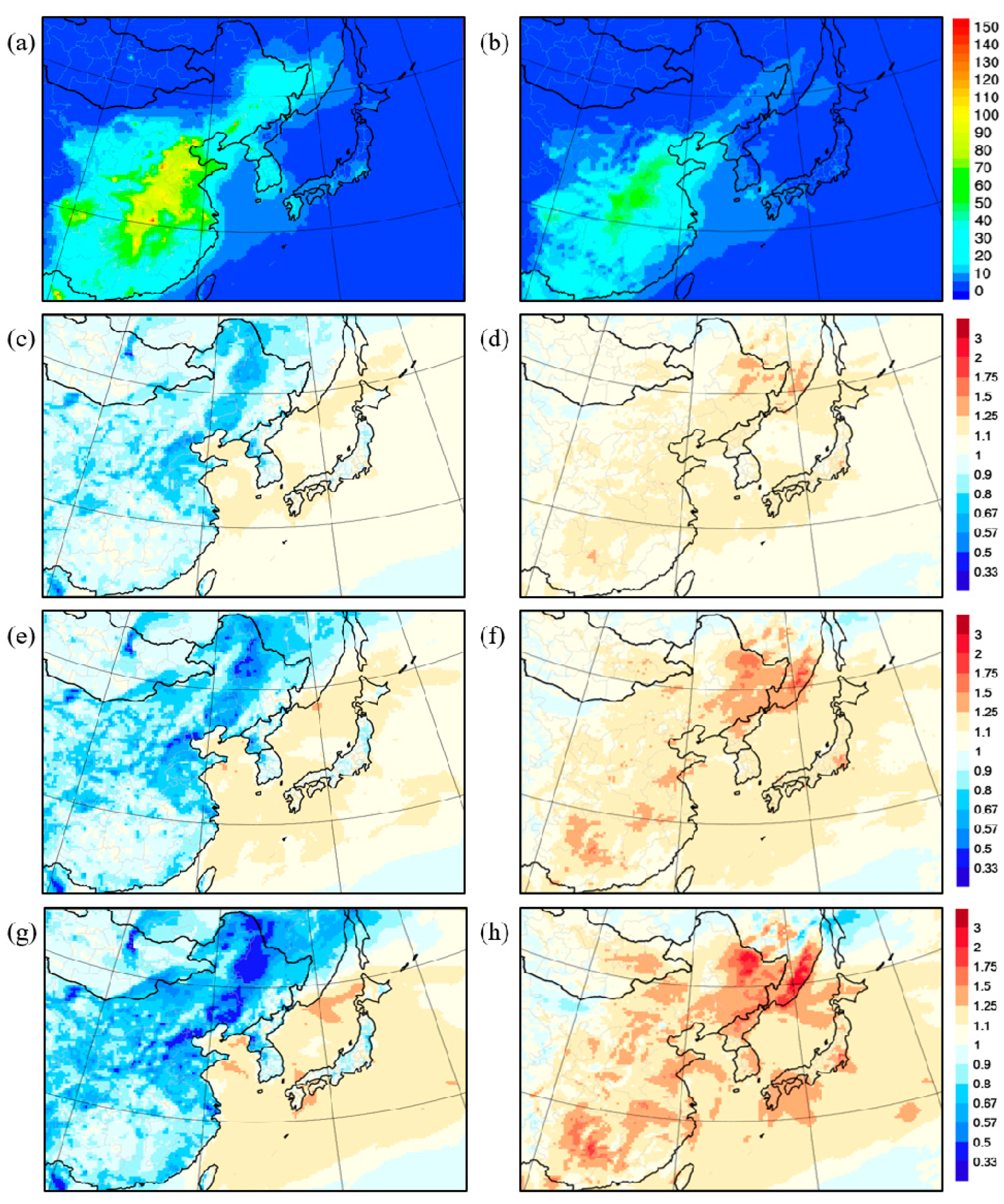
3.1. Case Analysis
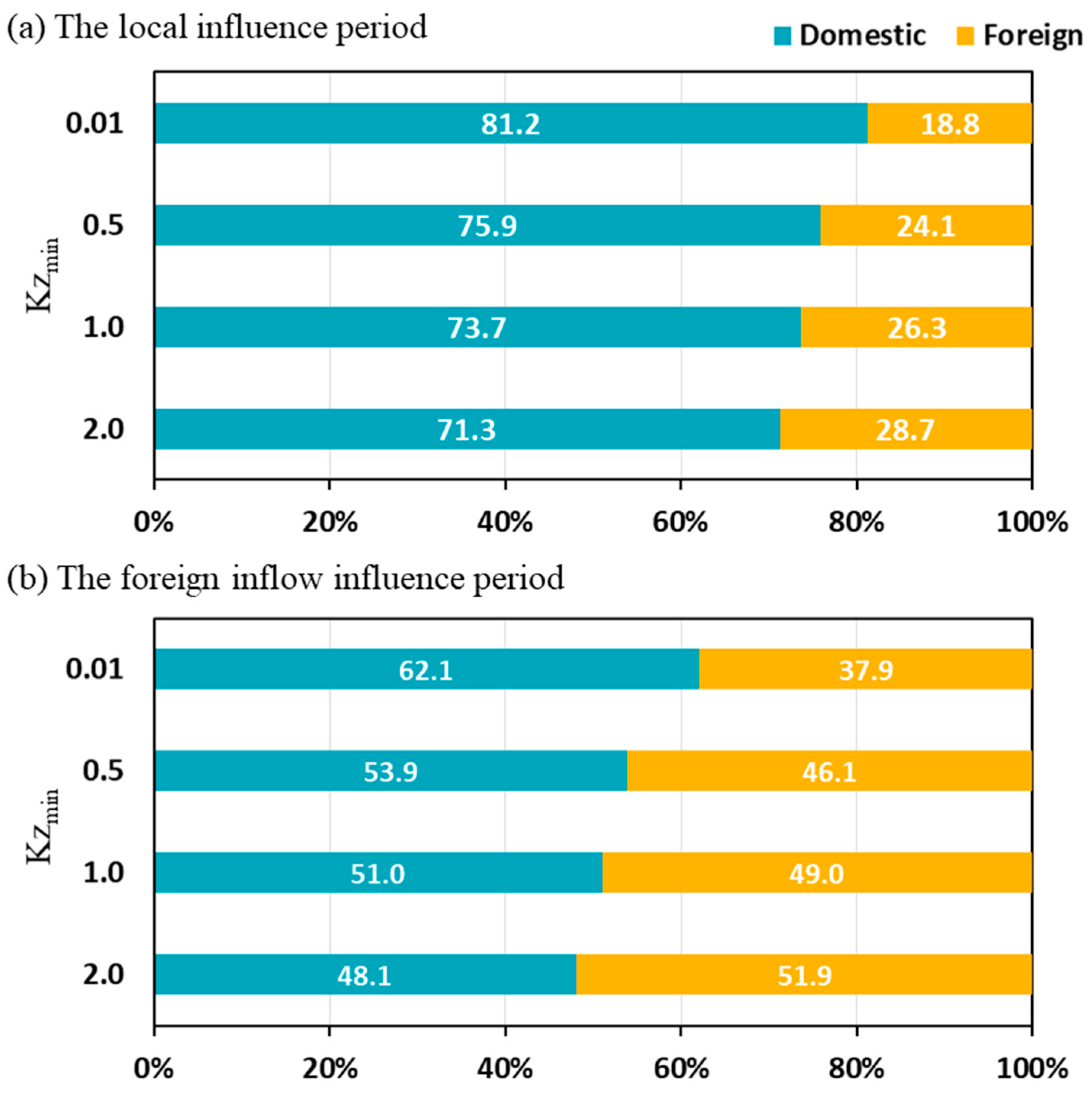
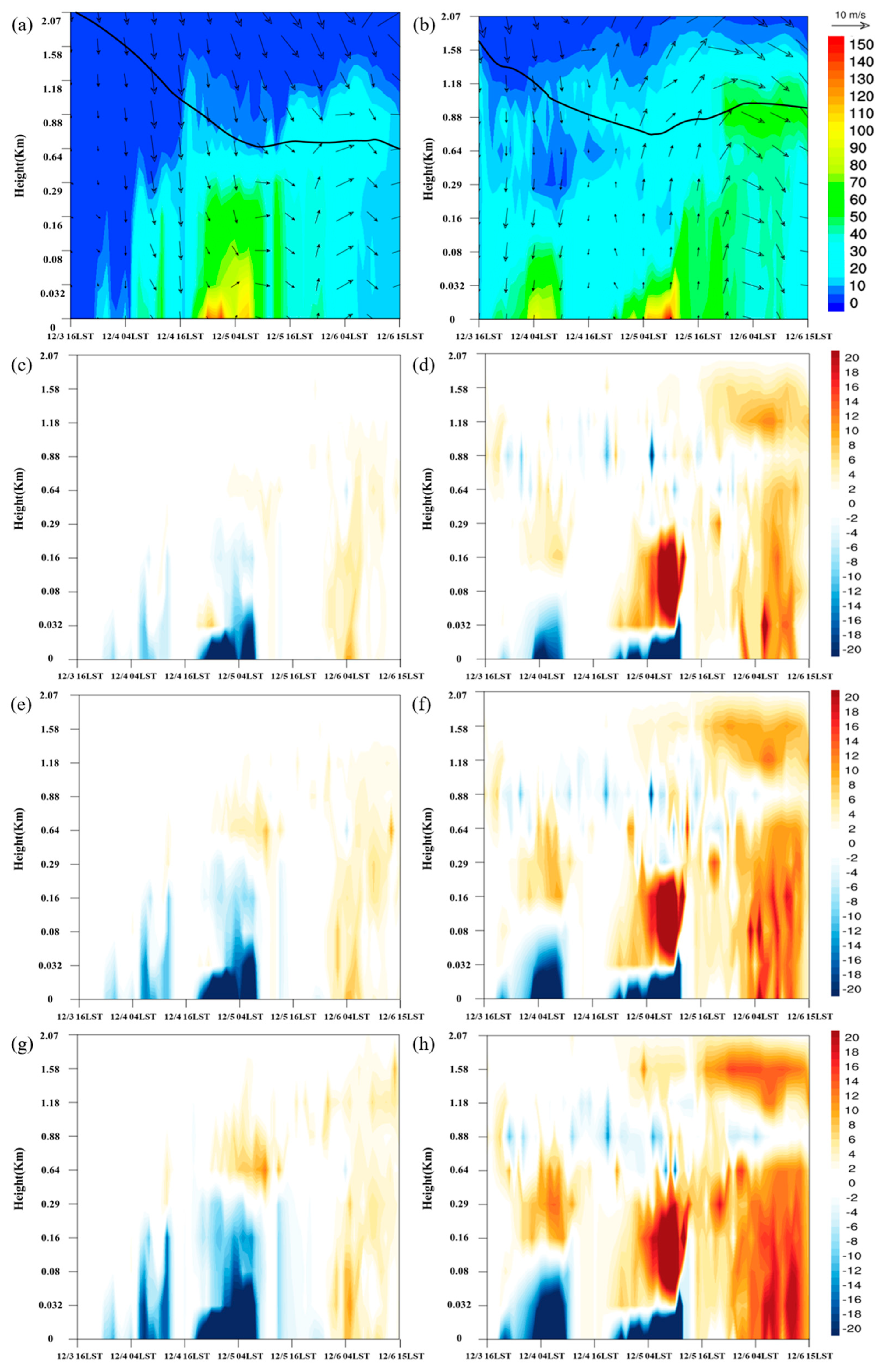
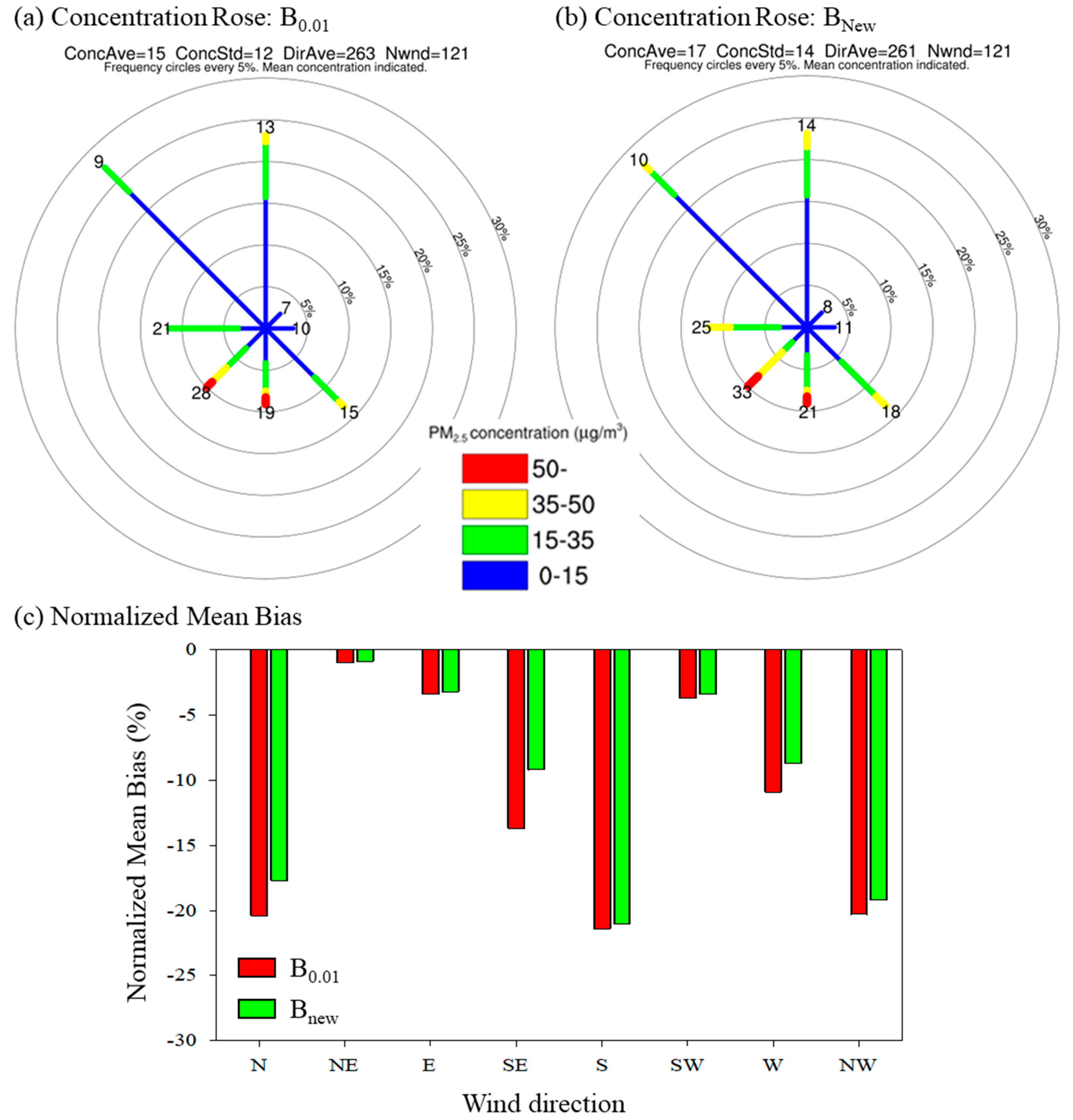
3.1.1. Local Influence Period
3.1.2. Long-Range Transport Influence Period
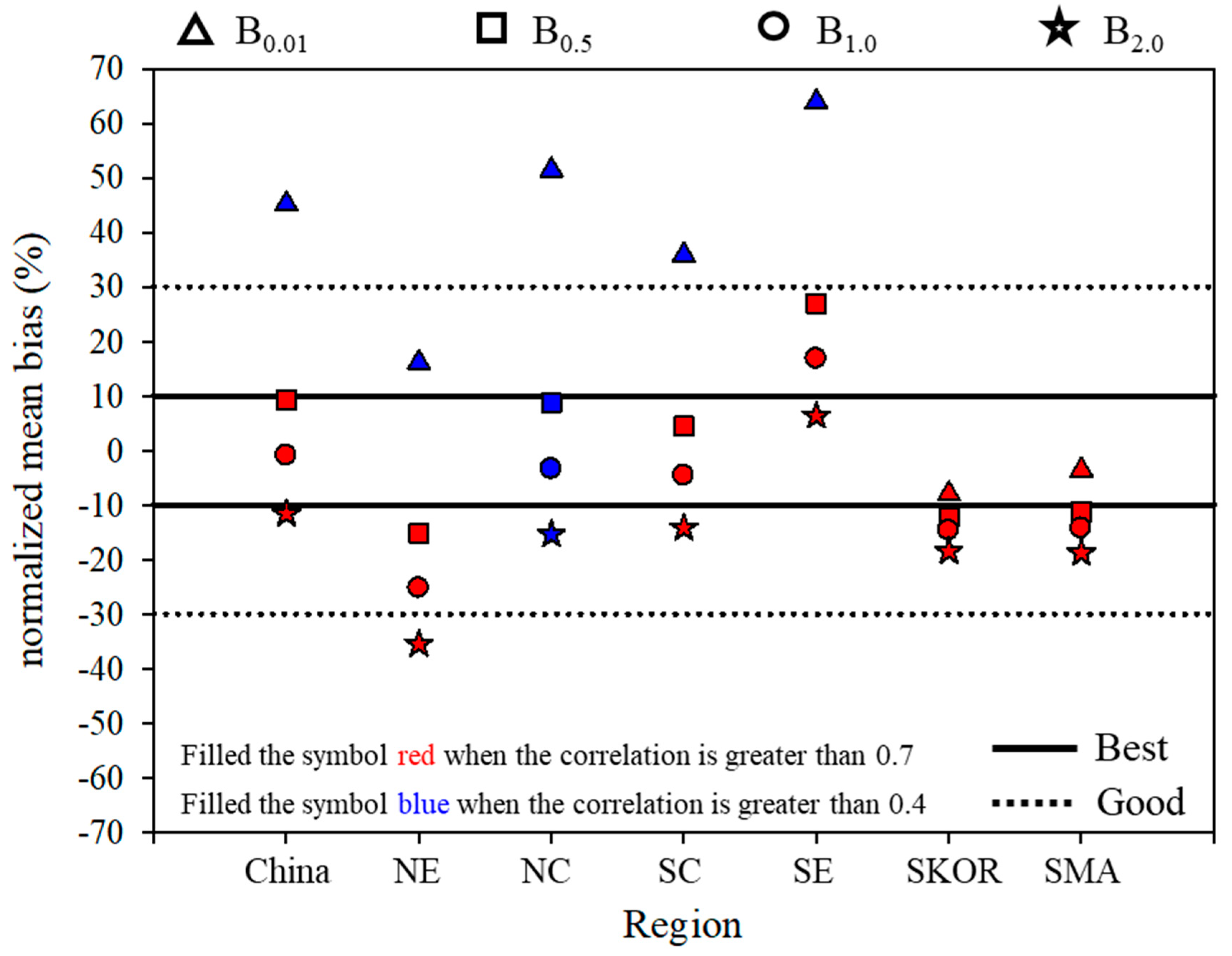
3.2. Long-Term Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.; Creswick, J.; Linn, L.; Muchnik, A. New WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines Aim to Save Millions of Lives from Air Pollution; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kloong, I.; Ridgway, B.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Shwartz, J.D. Long-and short term exposure to PM2.5 and morality: Using novel exposure models. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sram, R.J.; Binkova, B.; Rossner, P.; Rubes, J.; Topinka, J.; Dejmek, J. Adverse reproductive outcomes from exposure to environmental mutagens. Mutat. Res. 1999, 428, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Kousha, T.; Castner, J. Air pollution and emergency department visits for conjunctivitis: A case-crossover study. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2016, 29, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Lazar, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J. Impact of ambient PM2.5 on adverse birth outcome and potential molecular mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trnka, D. Policies, Regulatory Framework and Enforcement for Air Quality Management: The Case of Korea. In OECD Environment Working Papers; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Mohamed Tahrin, N. Impact of Gaseous Pollutants Reduction on Fine Particulate Matter and Its Secondary Inorganic Aerosols in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.M.; Kladakis, A.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. Inventory of Commerical Cooking Activities and Emissions in a Typical Urban Area in Greece. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillman, S.; Logan, J.A.; Wofsy, S.C. Aregional scale model for ozone in the United States with subgrid representation of urban and power plant plumes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 5731–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Meng, H.; Yao, X.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, H. Does Ambient Secondary Conversion or the Prolonged Fast Conversion in Combustion Plumes Cause Severe Pm2.5 Air Pollution in China? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, G.; Zeng, H. Multi-objective optimal dispatch strategy for power systems with Spatio-temporal distribution of air pollutants. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, B.U.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. Role of vertical advection and diffusion in long-range PM2.5 transport in Northeast Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 120997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, N.L. Meteorological modeling for air-quality assessments. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2231–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, T.; Tang, G.; Bai, Y.; Kong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Tan, C.; Shu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Vertical changes of PM2.5 driven by meteorology in the atmospheric boundary layer during a heavy air pollution event in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszar, P.; Karlicky, J.; Doubalova, J.; Sindelarova, K.; Novakova, T.; Belda, M.; Halenka, T.; Žák, M.; Pisoft, P. Urban canopy meteorological forcing and its impact on ozone and PM2.5: Role of vertical turbulent transpot. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1977–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rappenglueck, B. A study of model nighttime ozone bias in air quality modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, P.; Marufu, L.T.; Doddridge, B.G.; Taubman, B.F.; Schwab, J.J.; Hains, J.C.; Ehrman, S.H.; Dickerson, R.R. Ozone, oxides of nitrogen, and carbon monoxide during pollution events over the eastern United States: An evaluation of emissions and vertical mixing. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Brown, N.J.; Harley, R.A.; Bao, J.-W.; Michelson, S.A.; Wilczak, J.M. Seasonal versus episodic performance evaluation for an Eulerian photochemical air quality model. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.W.; Kim, S.-T.; Kim, S.-B. Evaluation of air quality models for the simulation of high ozone episode in the Houston metropolitan area. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, P.A.; Nissen, R.; Teakles, A.; Zhang, J.; Moran, M.D.; Yau, H.; diCenzo, C. Turbulent transport, emissions and the role of compensating errors in chemical transport models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1001–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morikawa, T.; Morino, Y.; Mori, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Nakatsuka, S.; Ohara, T. Urban Air Quality Model Inter-Comparison Study (UMICS) for Improvement of PM2.5 Simulation in Greater Tokyo Area of Japan. Asian J. Atmspheric. Environ. 2018, 12, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Pun, B.; Seigneur, C. A comprehensive performance evaluation of MM5-CMAQ for the summer 1999 southern oxidants study episode, Part III: Diagnostic and mechanistic evaluations. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4856–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Tang, Y.; Kang, D.; McQueen, J.; Tsidulko, M.; Huang, H.; Lu, S.; Hart, M.; Lin, H.-M.; Yu, S.; et al. Impact of consistent boundary layer mixing approaches between NAM and CMAQ. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2009, 9, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.U.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. Effects of vertical turbulent diffusivity on regional PM2.5 and O3 source contributions. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 118026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, S.; Jo, D.S.; Jeong, J.I.; Daven, K.H.; Woo, J.-H.; Ban, S.-J.; Lee, M.-D.; et al. Impacts of local vs. trans-boundary emissions from different sectors on PM2.5 exposure in South Korea during the KORUS-AQ campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, E.; Bae, C.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, S. Regional contributions to particulate matter concentration in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: Seasonal variation and sensitivity to meteorology and emissions inventory. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10315–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, M.; Jang, Y.; Kim, J.; Bu, C.; Lee, Y.; Park, R.; Oak, Y.; et al. KORUS emissions: A comprehensive Asian emissions information in support of the NASA/NIER KORUS-AQ mission. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.W.; Ki, T.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, H.C.; Han, J.; Lee, K.B.; Lim, E.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; Jin, H.-A.; Cho, E.; et al. Analysis of the National Air Pollutant Emission Inventory (CAPSS 2016) and the Major Cause of Change in Republic of Korea. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. (AJAE) 2020, 14, 422–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.W.; Dennis, R. Design artifacts in Eulerian air quality models: Evaluation of the effects of layer thickness and vertical profile correction on surface ozone concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ho, C.-H.; Choi, Y.-S. High-PM10 concentration episodes in Seoul, Korea: Background sources and related meteorological conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7240–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, H.C.; Yoo, C.; Kim, S. Long-range transport influence on key chemical components of PM2.5 in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea, during the years 2012–2016. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Hong, H.; Song, C.K. Determination of the inter-annual and spatial characteristics of the contribution of long-range transport to SO2 levels in Seoul between 2001 and 2010 based on conditional potential source contribution function (CPSCF). Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, W.; Mun, J.; Park, J.; Kim, C.-H.; Yoo, J.-W. Quantitative analysis of sulfate formation from crop burning in Northeast China: Unveiling the primary processes and transboundary transport to South Korea. Atmos. Res. 2024, 302, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Source-receptor relationship of transboundary particulate matter pollution between China, South Korea and Japan: Approaches, current understanding and limitations. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 3896–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.; Liu, Z.; Russell, A.G.; Odman, M.T.; Yarwood, G.; Kumar, N. Recommendations on statistics and benchmarks to assess photochemical model performance. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.J.; Blockley, A.; Rayner, K. Verification of a prognostic meteorological and air pollution model for year-long predictions in the Kwinana industrial region of Western Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Ackleson, S.G.; Davis, R.E.; Feddema, J.J.; Klink, K.M.; Legates, D.R.; O’Donnell, J.; Rowe, C.M. Statistics for the evaluation and comparison of models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1985, 90, 8995–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| D1 | D2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| WRF | Horizontal grid | 180 × 142 | 78 × 93 |
| Horizontal resolution | 27 km | 9 km | |
| Geogrid resolution | USGS 30s | ||
| Land use/Land cover | USGS 24 | ||
| Vertical layers | 30 layers | ||
| Microphysics | WRF Single-Moment 3-class simple ice | ||
| Radiation (long/short wave) | RRTM/Goddard | ||
| Land surface | Noah | ||
| Cumulus | Kain-Fritsch | ||
| Boundary layer | YSU | ||
| CMAQ | Horizontal grid | 174 × 128 | 67 × 82 |
| Horizontal resolution | 27 km | 9 km | |
| Vertical layers | 15 layers | ||
| Chemical mechanism | SAPRC99 | ||
| Aerosol module | AERO5 | ||
| Horizontal/Vertical advection | YAMO/YAMO | ||
| Horizontal/Vertical diffusion | Multiscale/ACM2 | ||
| Obs | Average | NMB | R | IOA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0.01 | BNew | B0.01 | BNew | B0.01 | BNew | B0.01 | BNew | ||
| SKOR | 24.1 | 22.2 | 23.2 | −8.0 | −4.0 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.87 |
| SMA | 28.0 | 27.0 | 28.2 | −3.6 | 0.7 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| YS | 26.5 | 14.7 | 16.8 | −43.8 | −35.9 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.69 |
| China | 54.0 | 79.6 | 56.0 | 45.2 | 2.1 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.88 |
| NE | 44.3 | 53.1 | 35.2 | 16.1 | −22.3 | 0.63 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| NC | 60.7 | 94.7 | 61.8 | 51.4 | −0.6 | 0.44 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.80 |
| SC | 66.6 | 92.3 | 67.6 | 35.8 | −14.2 | 0.62 | 0.79 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| SE | 46.3 | 75.3 | 55.2 | 63.9 | 19.6 | 0.59 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-b.; Kim, R.-H.; Son, J.-S.; Lee, D. The Impact of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Changes in the CMAQ Model on PM2.5 Concentration Variations in Northeast Asia: Focusing on the Seoul Metropolitan Area. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030376
Kim D-J, Kim T-H, Choi J-Y, Lee J-b, Kim R-H, Son J-S, Lee D. The Impact of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Changes in the CMAQ Model on PM2.5 Concentration Variations in Northeast Asia: Focusing on the Seoul Metropolitan Area. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030376
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong-Ju, Tae-Hee Kim, Jin-Young Choi, Jae-bum Lee, Rhok-Ho Kim, Jung-Seok Son, and Daegyun Lee. 2024. "The Impact of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Changes in the CMAQ Model on PM2.5 Concentration Variations in Northeast Asia: Focusing on the Seoul Metropolitan Area" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030376
APA StyleKim, D.-J., Kim, T.-H., Choi, J.-Y., Lee, J.-b., Kim, R.-H., Son, J.-S., & Lee, D. (2024). The Impact of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Changes in the CMAQ Model on PM2.5 Concentration Variations in Northeast Asia: Focusing on the Seoul Metropolitan Area. Atmosphere, 15(3), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030376





