Influence of Various Urban Morphological Parameters on Urban Canopy Ventilation: A Parametric Numerical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. RANS Canopy Model with Drag Force Approach
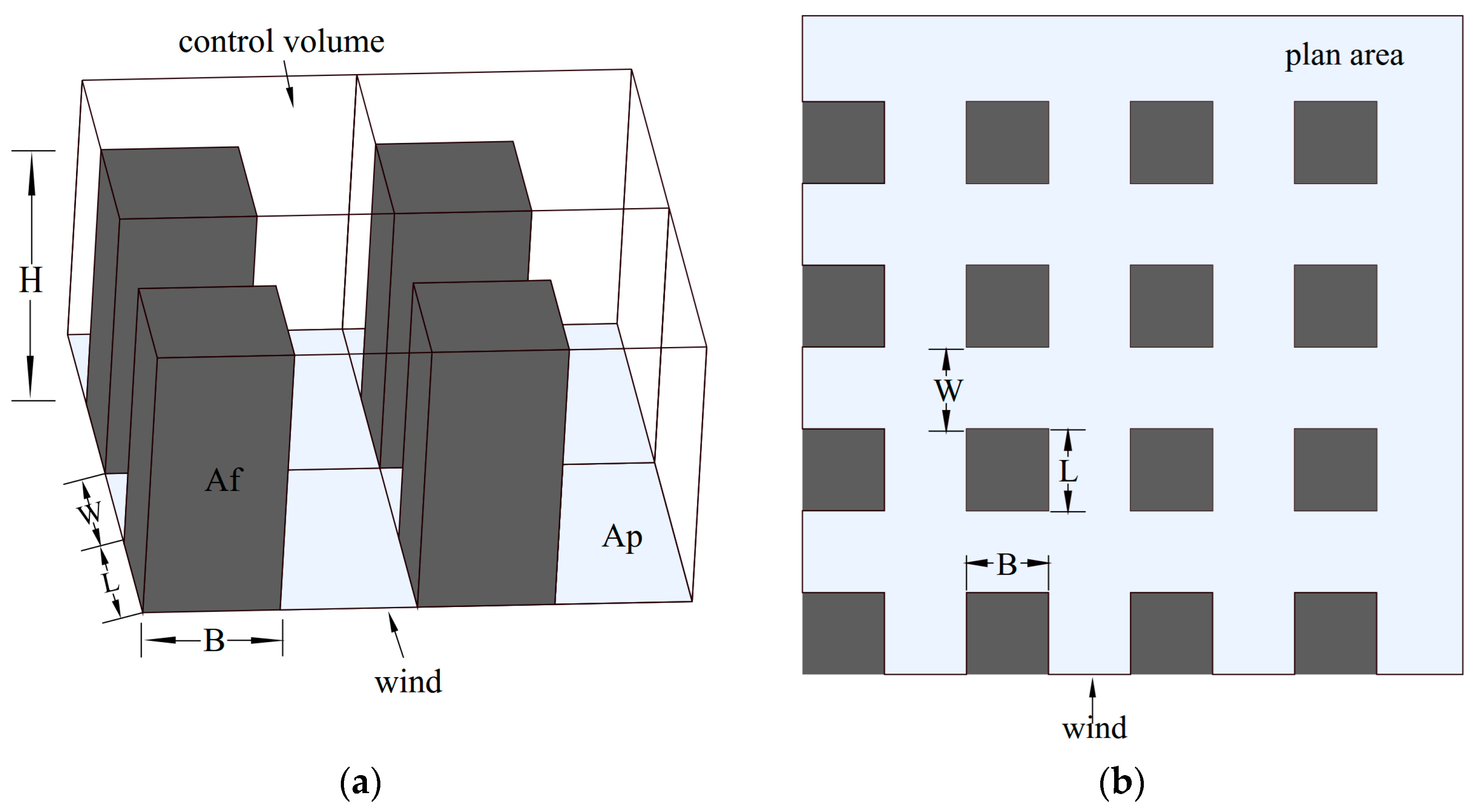
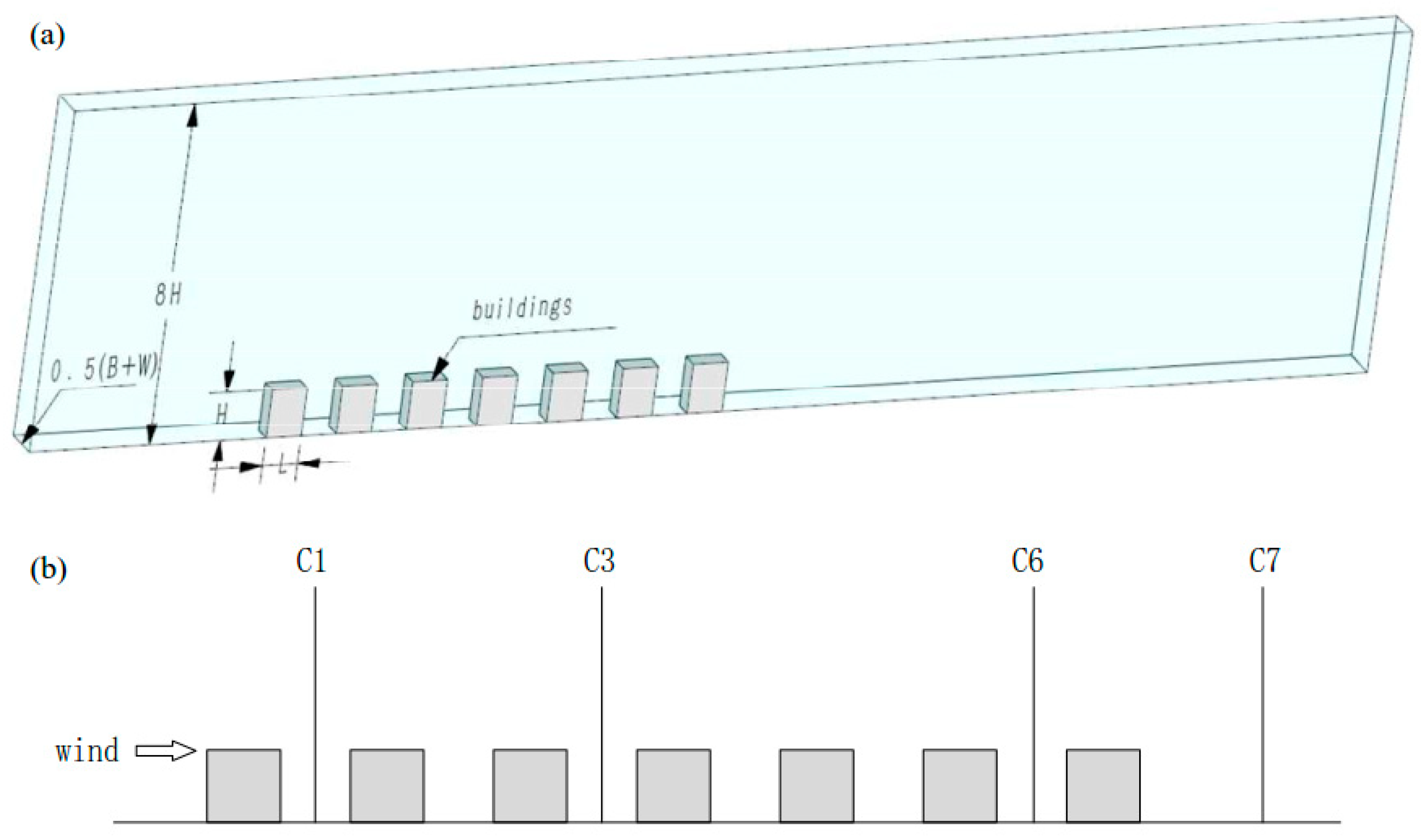
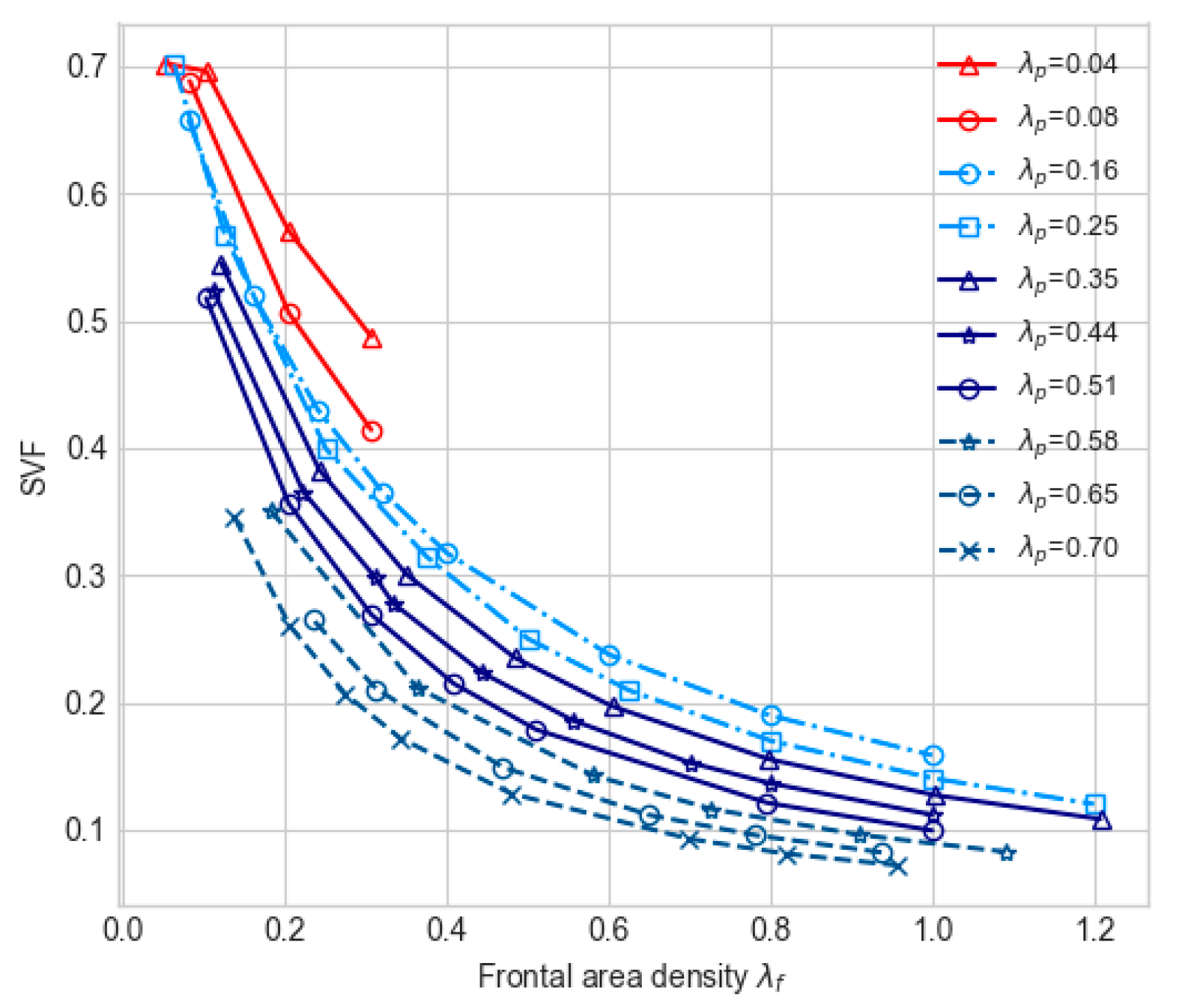
2.2. Idealized Building Array Configurations
2.3. Numerical Settings
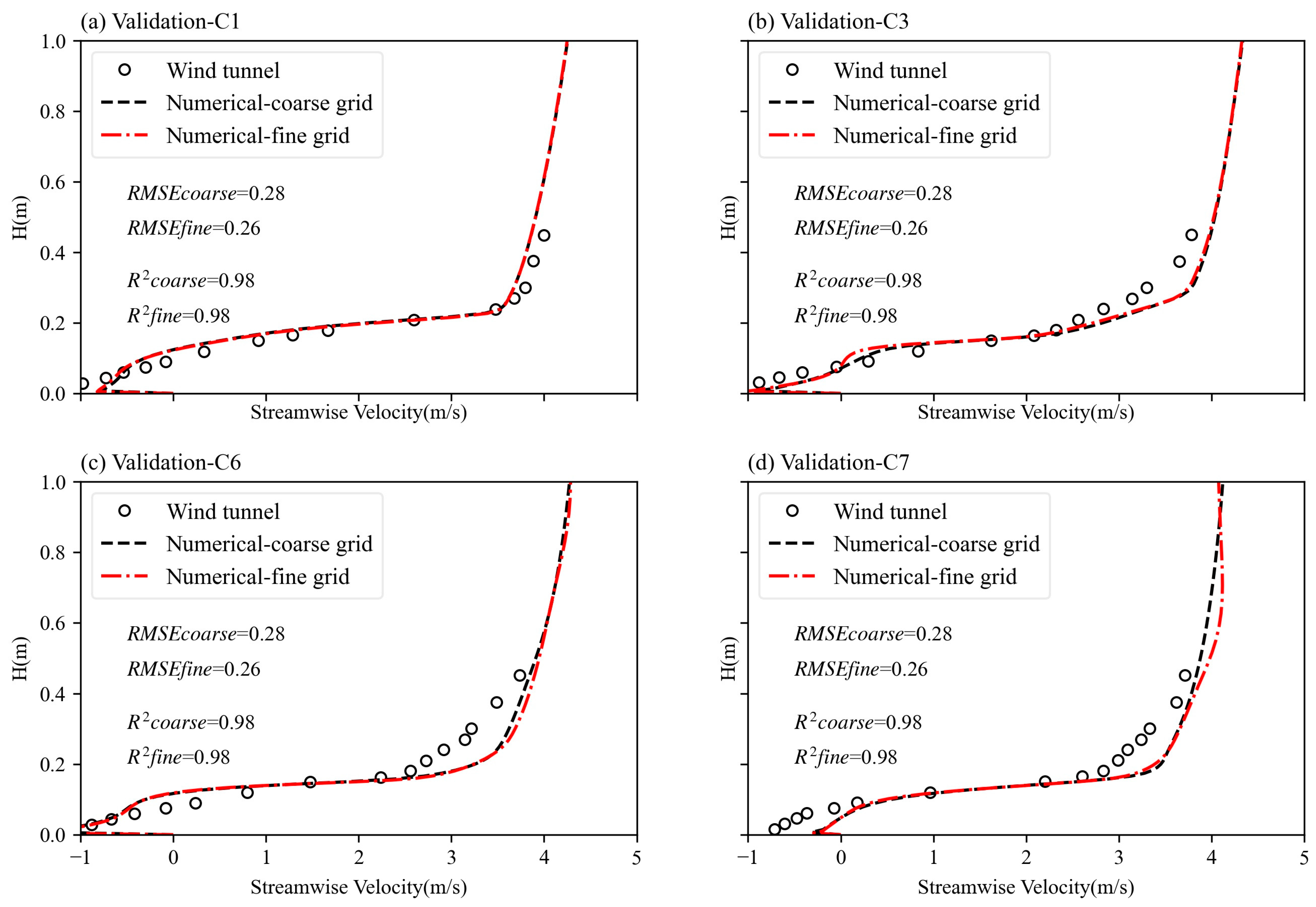
2.4. Validation Study
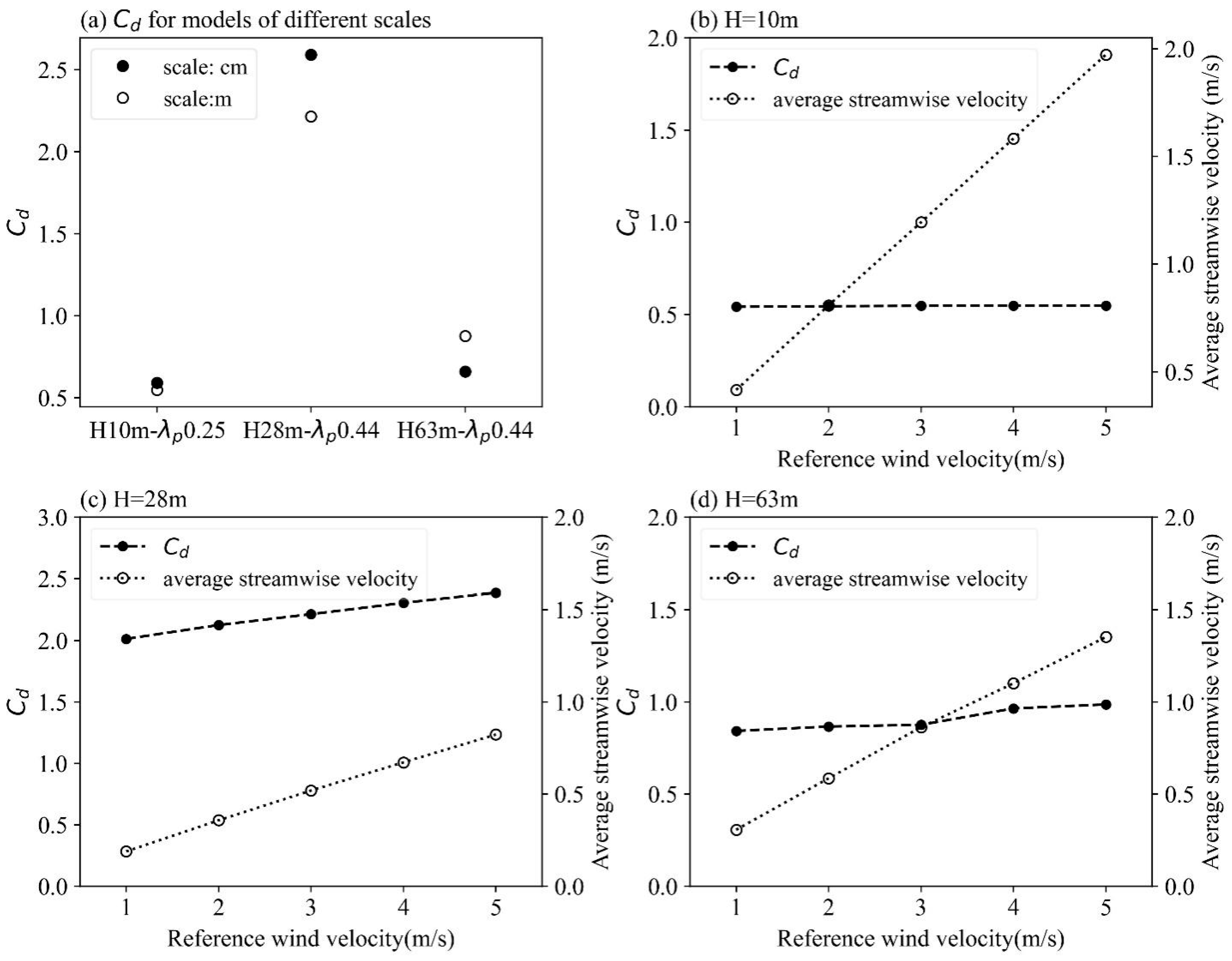
2.5. Effect of Model Scale and Background Wind Condition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Urban Morphology on Urban Ventilation in Rectangular Building Blocks
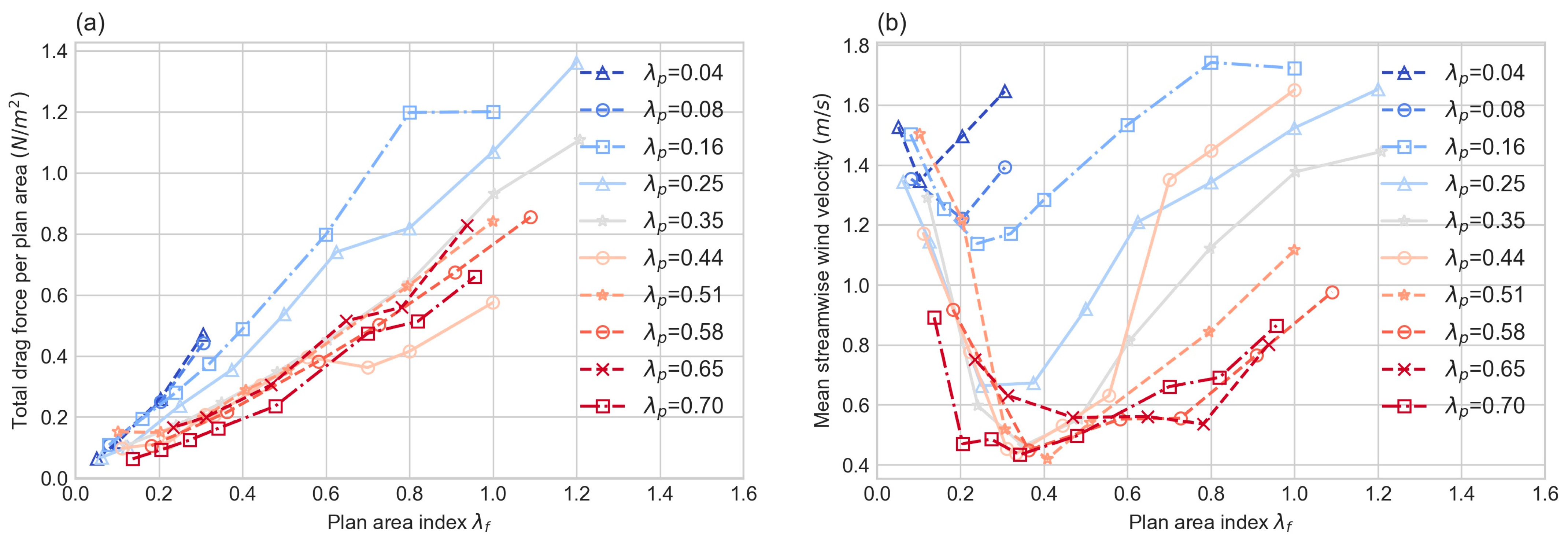
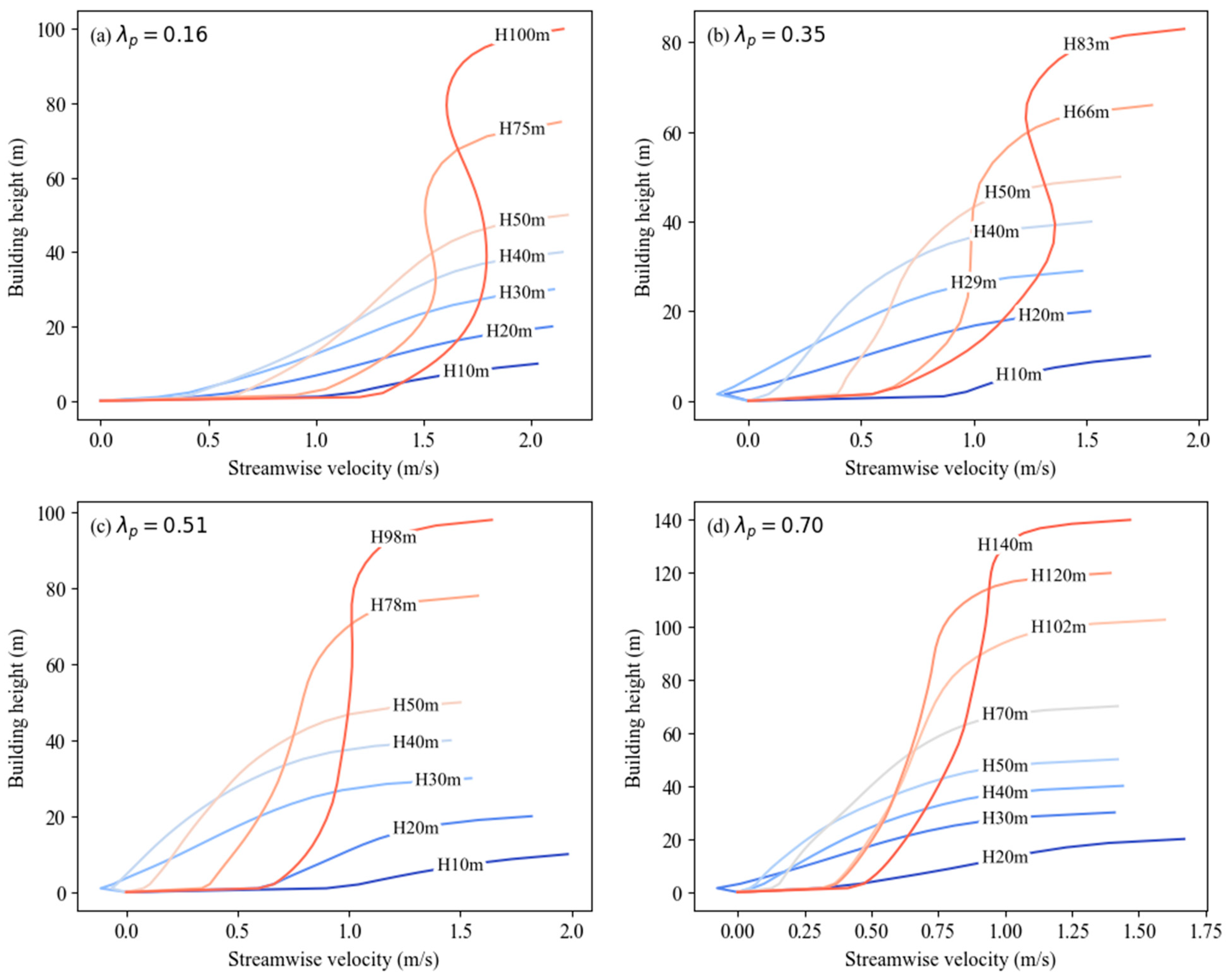
3.1.1. Influence of Urban Morphology on Surface Drag Force and Streamwise Velocity
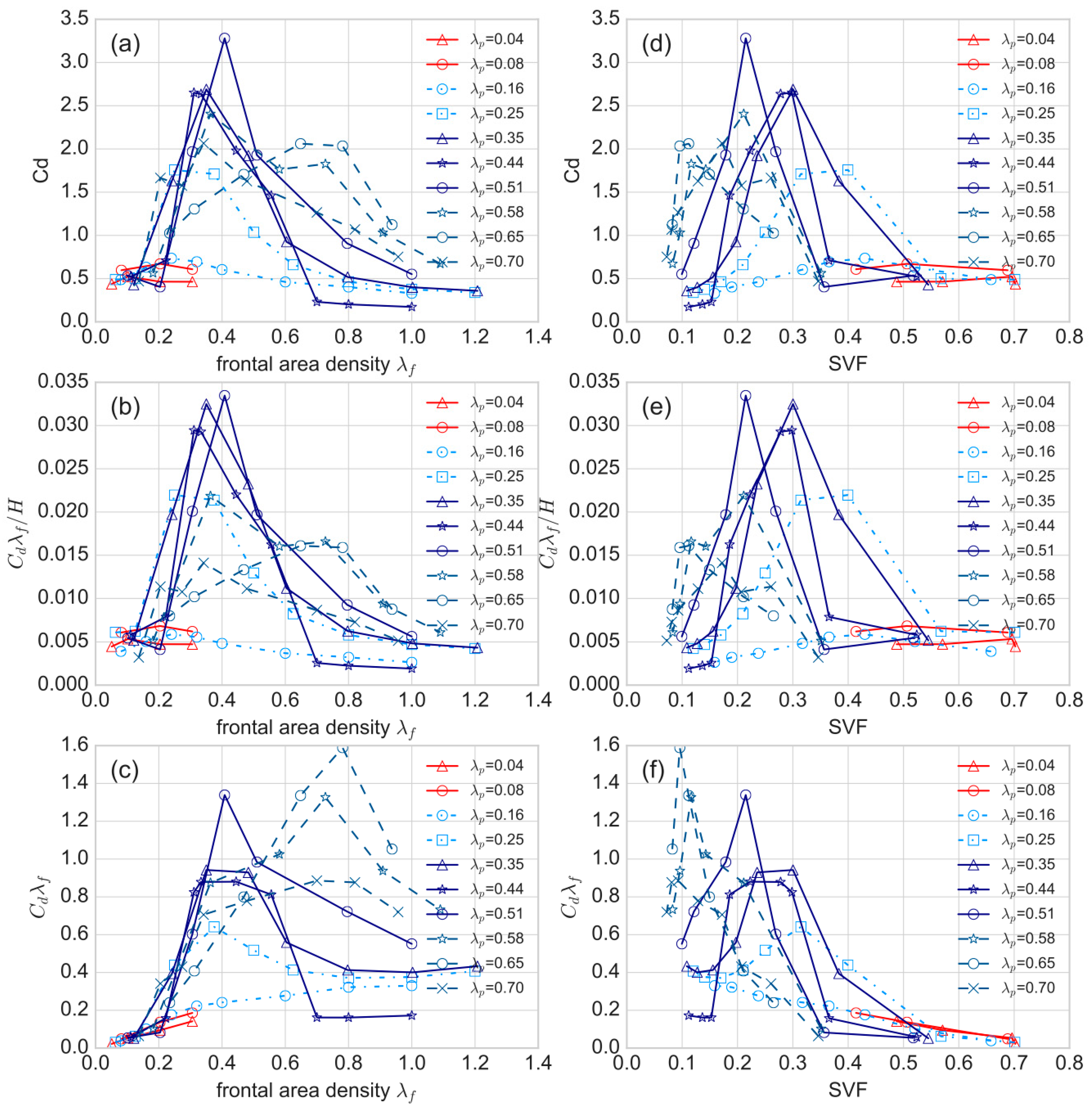
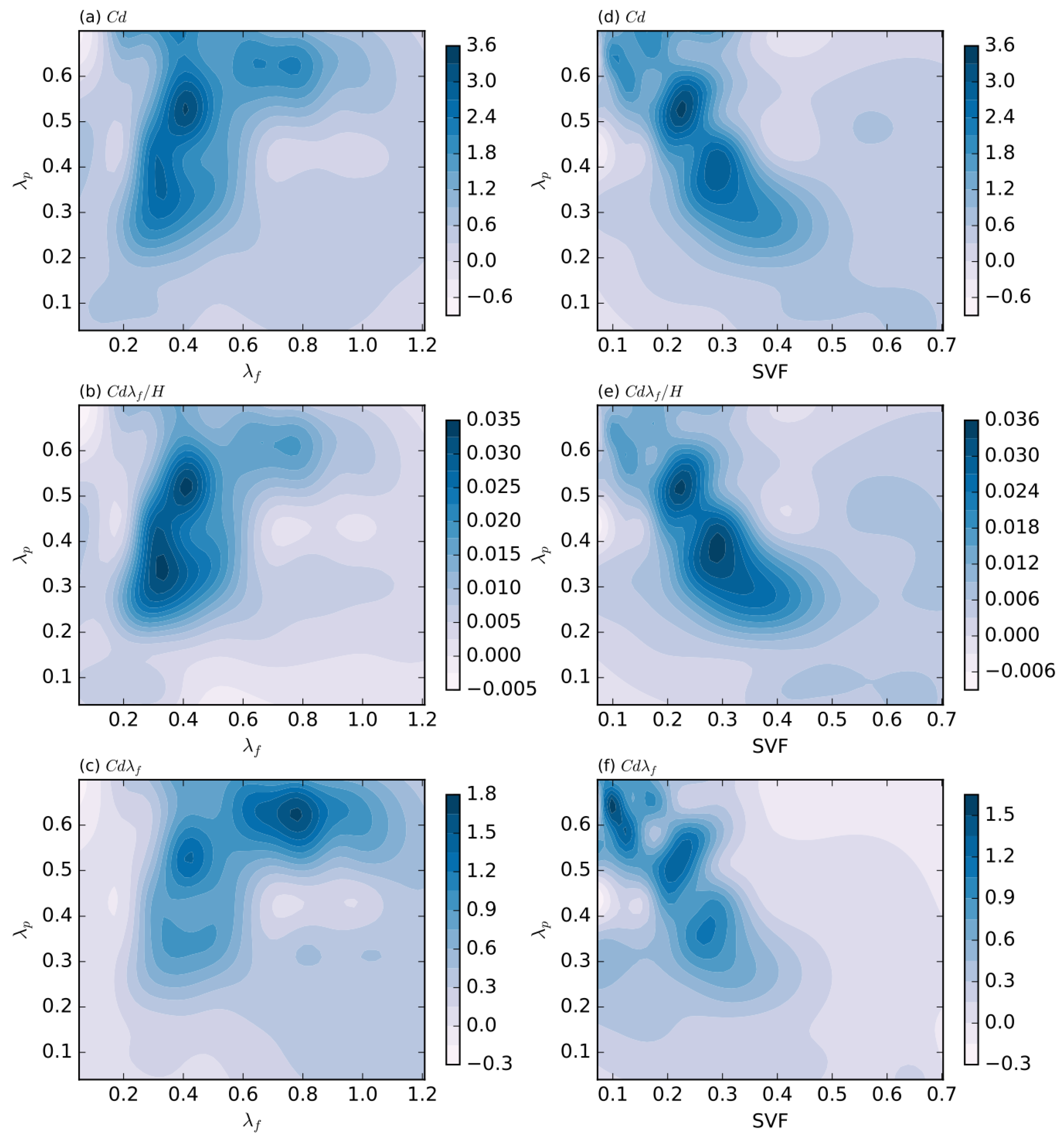
3.1.2. Influence of Urban Morphology on Drag Force Coefficient Cd
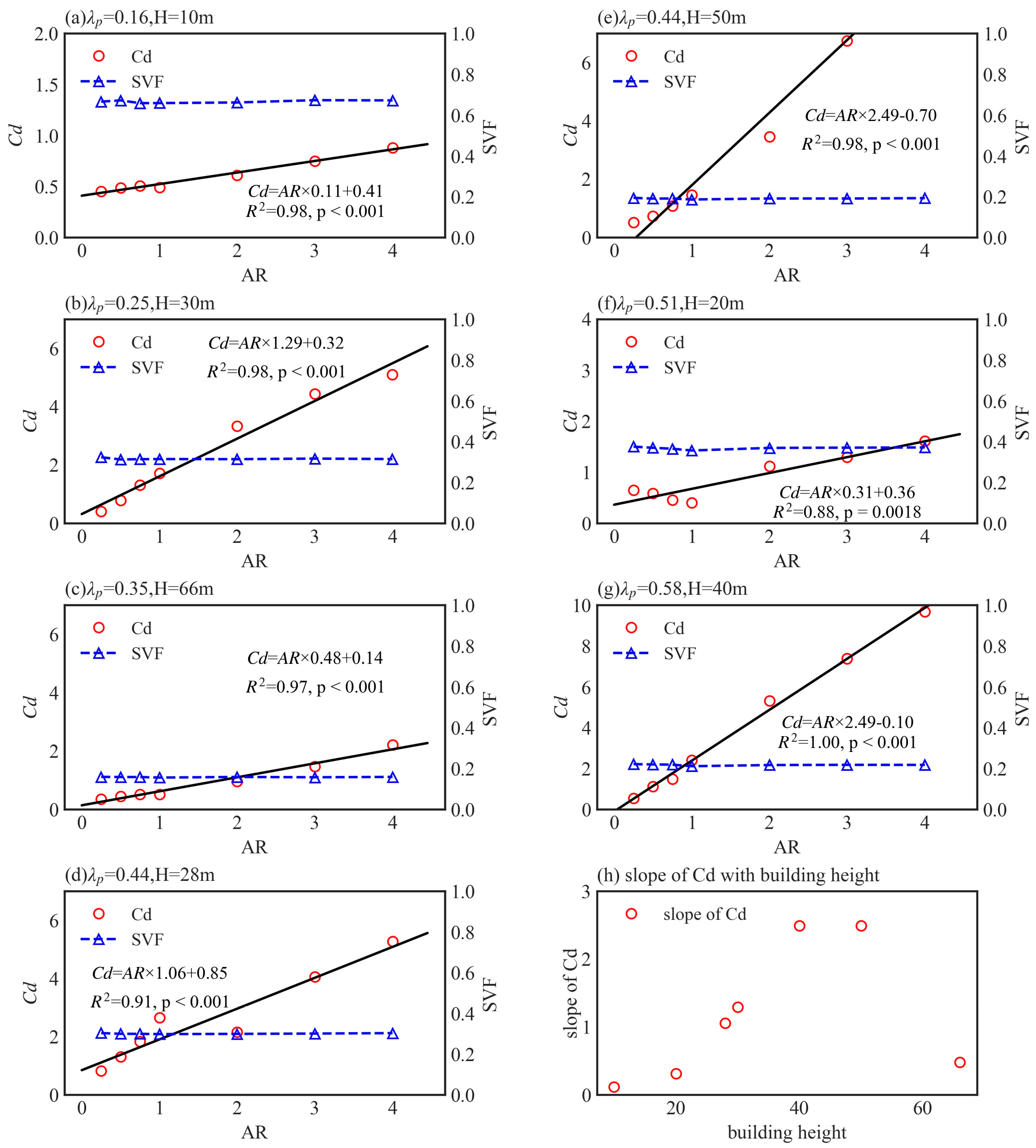
3.2. Effect of Building Floor AR (Aspect Ratio) on Drag Force Coefficient Cd
3.3. Limitations and Future Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richmond-Bryant, J.; Reff, A. Air pollution retention within a complex of urban street canyons: A two-city comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B.; Carmeliet, J. Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings: Literature Review and Practical Examples. J. Build. Phys. 2004, 28, 107–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Sui, X.; Yao, L.; Zheng, L.; Wen, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, W. Indoor PM2.5 and its chemical composition during a heavy haze-fog episode at Jinan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over northern China in January 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. 50 years of Computational Wind Engineering: Past, present and future. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 129, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.F. Progress in observing and modelling the urban boundary layer. Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 216–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hayden, P.; Robins, A.G.; Castro, I.P. Flow over cube arrays of different packing densities. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 715–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusci, O.; Monti, P.; Cecere, C.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B. Impact of morphological parameters on urban ventilation in compact cities: The case of the Tuscolano-Don Bosco district in Rome. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovsky, J.; Simonsen, A.; Gaitani, N. Validation of a CFD model for the evaluation of urban microclimate at high latitudes: A case study in Trondheim, Norway. Build. Environ. 2021, 205, 108175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.S.; Shimada, T.; Hoshi, H. Modeling and simulation of the Tokyo urban heat island. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Sandberg, M.; Li, Y. Age of air and air exchange efficiency in idealized city models. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coceal, O.; Belcher, S.E. A canopy model of mean winds through urban areas. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 130, 1349–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coceal, O.; Belcher, S.E. Mean winds through an inhomogeneous urban canopy. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2005, 115, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A.; Novak, M.D. E-epsilon modelling of turbulent air flow downwind of a model forest edge. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1996, 77, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, F.S.; Yee, E.; Cheng, Y. Simulation of mean flow and turbulence over a 2D building array using high-resolution CFD and a distributed drag force approach. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2004, 92, 117–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antohe, B.V.; Lage, J.L. A general two-equation macroscopic turbulence model for incompressible flow in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 40, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Yuan, C.; Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Fung, J.C.H. Improving the wind environment in high-density cities by understanding urban morphology and surface roughness: A study in Hong Kong. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.A.; Nichol, J.E.A.; Ng, E.Y.Y.B.; Guilbert, E.A.; Kwok, K.H.A.; To, P.H.A.; Wang, J.Z.A. GIS techniques for mapping urban ventilation, using frontal area index and least cost path analysis. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. 2010, 38, 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.S.; Nichol, J.E.; To, P.H.; Wang, J. A simple method for designation of urban ventilation corridors and its application to urban heat island analysis. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.W. Modelling the Mean Velocity Profile in the Urban Canopy Layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 97, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebric, J.; Heidarinejad, M.; Liu, J. Building neighborhood emerging properties and their impacts on multi-scale modeling of building energy and airflows. Build. Environ. 2015, 91, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Li, Y. Macroscopic simulations of turbulent flows through high-rise building arrays using a porous turbulence model. Build. Environ. 2012, 49, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hang, J.; Sandberg, M.; Claesson, L.; Di Sabatino, S.; Wigo, H. The impacts of building height variations and building packing densities on flow adjustment and city breathability in idealized urban models. Build. Environ. 2017, 118, 344–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, J.; Li, M. Wind tunnel study on the morphological parameterization of building non-uniformity. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 121, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M. Large-eddy simulations on the effects of surface geometry of building arrays on turbulent organized structures. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2006, 118, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagishima, A.; Tanimoto, J.; Nagayama, K.; Meno, S. Aerodynamic parameters of regular arrays of rectangular blocks with various geometries. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2009, 132, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.A.; Hagishima, A.; Tanimoto, J.; Ikegaya, N. Aerodynamic Parameters of Urban Building Arrays with Random Geometries. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 138, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.L.; Martilli, A. A Dynamic Urban Canopy Parameterization for Mesoscale Models Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes Microscale Simulations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 137, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Martilli, A.; Santiago, J.L.; González, J.E. A Mechanical Drag Coefficient Formulation and Urban Canopy Parameter Assimilation Technique for Complex Urban Environments. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 157, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. Computational Fluid Dynamics for urban physics: Importance, scales, possibilities, limitations and ten tips and tricks towards accurate and reliable simulations. Build. Environ. 2015, 91, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.L.; Bresson, R.; Qu, Y.F.; Milliez, M.; de Munck, C.; Carissimo, B. High resolution unsteady RANS simulation of wind, thermal effects and pollution dispersion for studying urban renewal scenarios in a neighborhood of Toulouse. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Britter, R.E.; Norford, L.K. Transport processes in and above two-dimensional urban street canyons under different stratification conditions: Results from numerical simulation. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ng, E. Air ventilation assessment under unstable atmospheric stratification—A comparative study for Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2018, 130, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. LES over RANS in building simulation for outdoor and indoor applications: A foregone conclusion? Build. Simul. 2018, 11, 821–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroney, R.N. Ten questions concerning hybrid computational/physical model simulation of wind flow in the built environment. Build. Environ. 2016, 96, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Cai, X.-M.; Bloss, W.J. Modelling the dispersion and transport of reactive pollutants in a deep urban street canyon: Using large-eddy simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashie, Y.; Kono, T. Urban-scale CFD analysis in support of a climate-sensitive design for the Tokyo Bay area. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Sandberg, M.; Zhu, W.; Buccolieri, R.; Di Sabatino, S. City breathability in medium density urban-like geometries evaluated through the pollutant transport rate and the net escape velocity. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, G.W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, B.M.; Hang, J. Integrated impacts of turbulent mixing and NOx-O3 photochemistry on reactive pollutant dispersion and intake fraction in shallow and deep street canyons. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 712, 135553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Ling, H.; Luo, Z.; Hang, J. Numerical Investigations of Urban Pollutant Dispersion and Building Intake Fraction with Various 3D Building Configurations and Tree Plantings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhra, A. Estimating the Sensitivity of Urban Surface Drag to Building Morphology; University of Reading: Reading, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.R. Modelling turbulent air flow in a stand of widely-spaced trees. Phoenics J. 1992, 5, 294–312. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, J.C.P.L. Atmospheric Flow over Forested and Non-Forested Complex Terrain. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2007; pp. 1–159. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, J.L.; Coceal, O.; Martilli, A.; Belcher, S.E. Variation of the sectional drag coefficient of a group of buildings with packing density. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2008, 128, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martilli, A.; Santiago, J.L. CFD simulation of airflow over a regular array of cubes. Part II: Analysis of spatial average properties. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 122, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, F.S.; Yee, E. Numerical modelling of the turbulent flow developing within and over a 3-D building array, part I: A high-resolution Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes approach. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2004, 112, 427–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, J.; Yang, X.I.A.; Meneveau, C.; Mittal, R. Aerodynamic Properties of Rough Surfaces with High Aspect-Ratio Roughness Elements: Effect of Aspect Ratio and Arrangements. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 163, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. Street Design and Urban Canopy Layer Cliamte. Energy Build. 1988, 11, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ga, T.; Unger, J.Ã. Detection of ventilation paths using high-resolution roughness parameter mapping in a large urban area. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Lam, C.K.C.; Hang, J.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, Y.L.; Ling, H. Integrated impacts of tree planting and aspect ratios on thermal environment in street canyons by scaled outdoor experiments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 764, 142920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, J.; Chen, G.W. Experimental study of urban microclimate on scaled street canyons with various aspect ratios. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Wang, D.Y.; Zeng, L.Y.; Ren, L.H.; Shi, Y.R.; Zhang, X.L. Scaled outdoor experimental investigation of thermal environment and surface energy balance in deep and shallow street canyons under various sky conditions. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.R.; Zeng, L.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Hang, J.; Hua, J.J.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, W.W. Quantifying cooling benefits of cool roofs and walls applied in building clusters by scaled outdoor experiments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 97, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Set | λp | B = L (m) | W (m) | H (m) | λf | SVF | Set | λp | B = L (m) | W (m) | H (m) | λf | SVF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.04 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 6 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 28 | 0.31 | 0.30 |
| 0.04 | 5 | 20 | 10 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 30 | 0.33 | 0.28 | ||
| 0.04 | 5 | 20 | 20 | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 0.44 | 0.22 | ||
| 0.04 | 5 | 20 | 30 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 50 | 0.56 | 0.19 | ||
| 2 | 0.08 | 8 | 20 | 8 | 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 63 | 0.70 | 0.15 | |
| 0.08 | 8 | 20 | 20 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 72 | 0.80 | 0.14 | ||
| 0.08 | 8 | 20 | 30 | 0.31 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 90 | 1.00 | 0.11 | ||
| 3 | 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 10 | 0.08 | 0.66 | 7 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 10 | 0.10 | 0.52 |
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 0.16 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 20 | 0.20 | 0.36 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 0.24 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 30 | 0.31 | 0.27 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 40 | 0.41 | 0.21 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 50 | 0.51 | 0.18 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 75 | 0.60 | 0.24 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 78 | 0.80 | 0.12 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 100 | 0.80 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 50 | 20 | 98 | 1.00 | 0.10 | ||
| 0.16 | 20 | 30 | 125 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 8 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 20 | 0.18 | 0.35 | |
| 4 | 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 5 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 40 | 0.36 | 0.21 | |
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 0.13 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 64 | 0.58 | 0.14 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 80 | 0.73 | 0.12 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 100 | 0.91 | 0.10 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 63.8 | 20 | 120 | 1.09 | 0.08 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 50 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 9 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 120 | 0.94 | 0.08 | |
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 64 | 0.80 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 100 | 0.78 | 0.10 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 80 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 83 | 0.65 | 0.11 | ||
| 0.25 | 20 | 20 | 96 | 1.20 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 60 | 0.47 | 0.15 | ||
| 5 | 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 10 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 40 | 0.31 | 0.21 | |
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 20 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.65 | 83.2 | 20 | 30 | 0.23 | 0.27 | ||
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 29 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 10 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 20 | 0.14 | 0.35 | |
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 40 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 30 | 0.21 | 0.26 | ||
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 50 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 40 | 0.27 | 0.21 | ||
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 66 | 0.80 | 0.16 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 50 | 0.34 | 0.17 | ||
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 83 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 70 | 0.48 | 0.13 | ||
| 0.35 | 29 | 20 | 100 | 1.21 | 0.11 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 102.4 | 0.70 | 0.09 | ||
| 6 | 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 10 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 120 | 0.82 | 0.08 | |
| 0.44 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.7 | 102.4 | 20 | 140 | 0.96 | 0.07 |
| Set | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λp | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.58 |
| W (m) | 30 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| H (m) | 10 | 30 | 66 | 28 | 50 | 20 | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Hang, J.; Hua, J.; Zhao, B.; Ling, H. Influence of Various Urban Morphological Parameters on Urban Canopy Ventilation: A Parametric Numerical Study. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030352
Zeng L, Zhang X, Lu J, Li Y, Hang J, Hua J, Zhao B, Ling H. Influence of Various Urban Morphological Parameters on Urban Canopy Ventilation: A Parametric Numerical Study. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Liyue, Xuelin Zhang, Jun Lu, Yongcai Li, Jian Hang, Jiajia Hua, Bo Zhao, and Hong Ling. 2024. "Influence of Various Urban Morphological Parameters on Urban Canopy Ventilation: A Parametric Numerical Study" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030352
APA StyleZeng, L., Zhang, X., Lu, J., Li, Y., Hang, J., Hua, J., Zhao, B., & Ling, H. (2024). Influence of Various Urban Morphological Parameters on Urban Canopy Ventilation: A Parametric Numerical Study. Atmosphere, 15(3), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030352










