Comparative Analysis of Different Heavy Rainstorm Periods Lasting for Two Consecutive Days in the Qinba Region under the Influence of the Southwest Vortex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.3. Study Area
3. Results
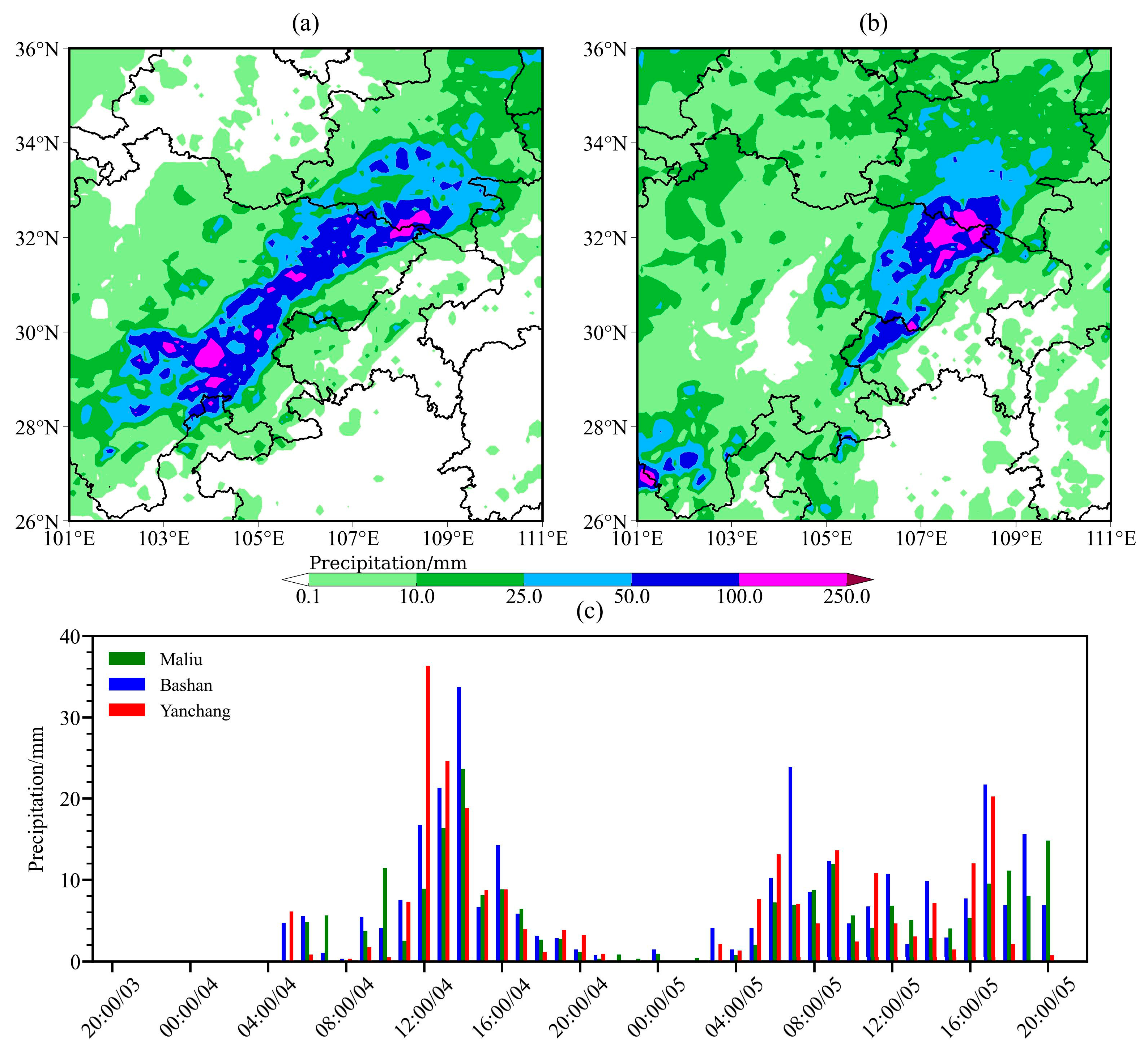
3.1. Precipitation Events and Mesoscale Convective System Characteristics
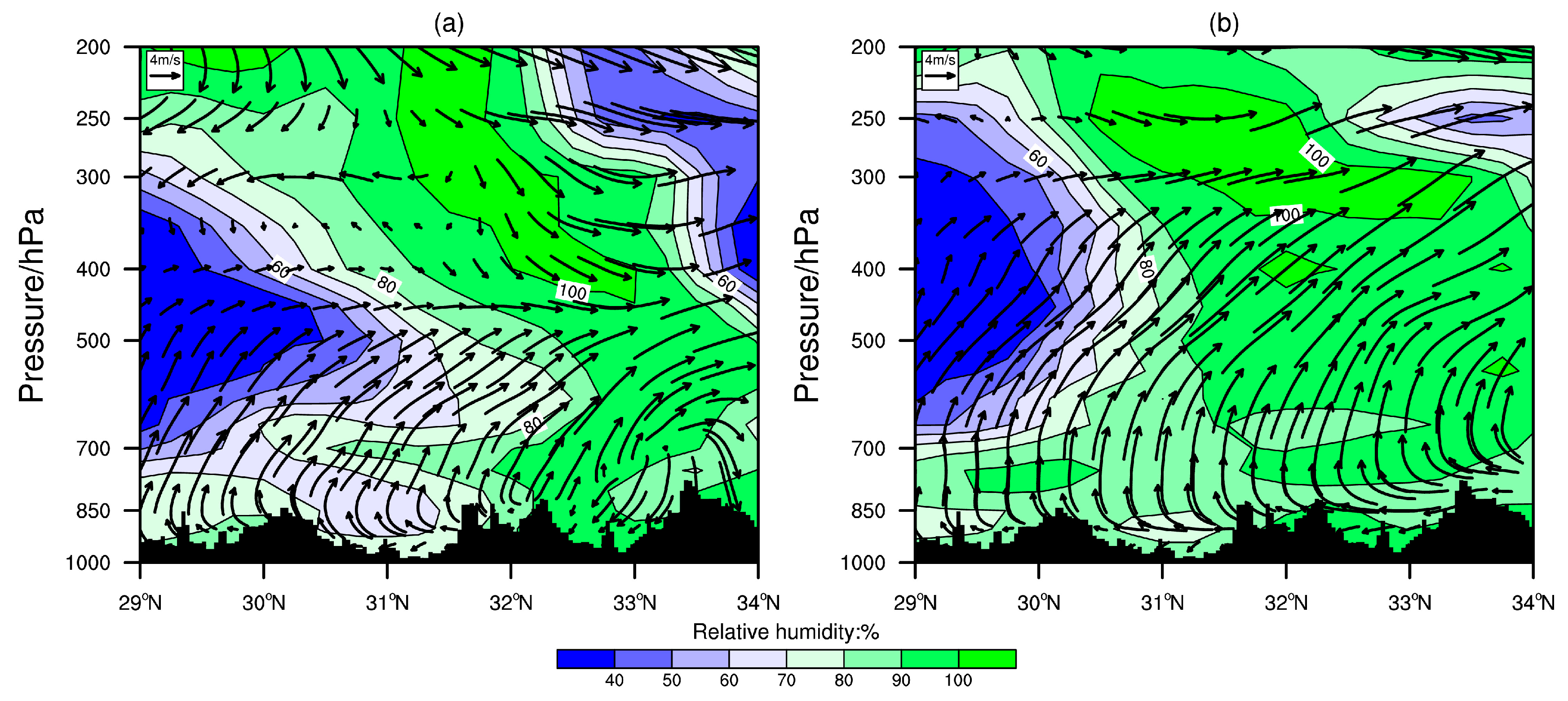
3.2. Synoptic Weather Conditions and Physical Conditions
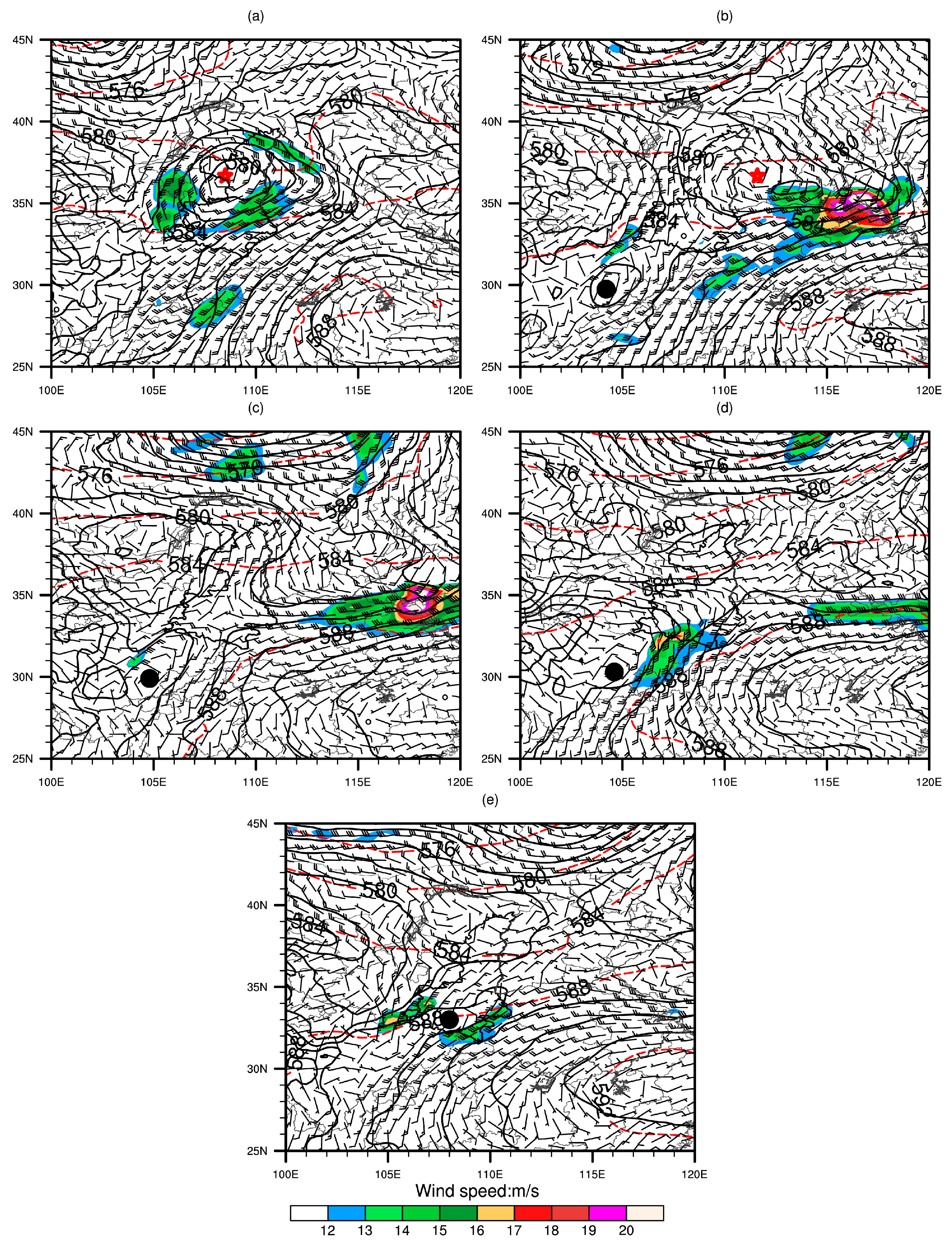
3.2.1. Synoptic Weather and Circulation Conditions
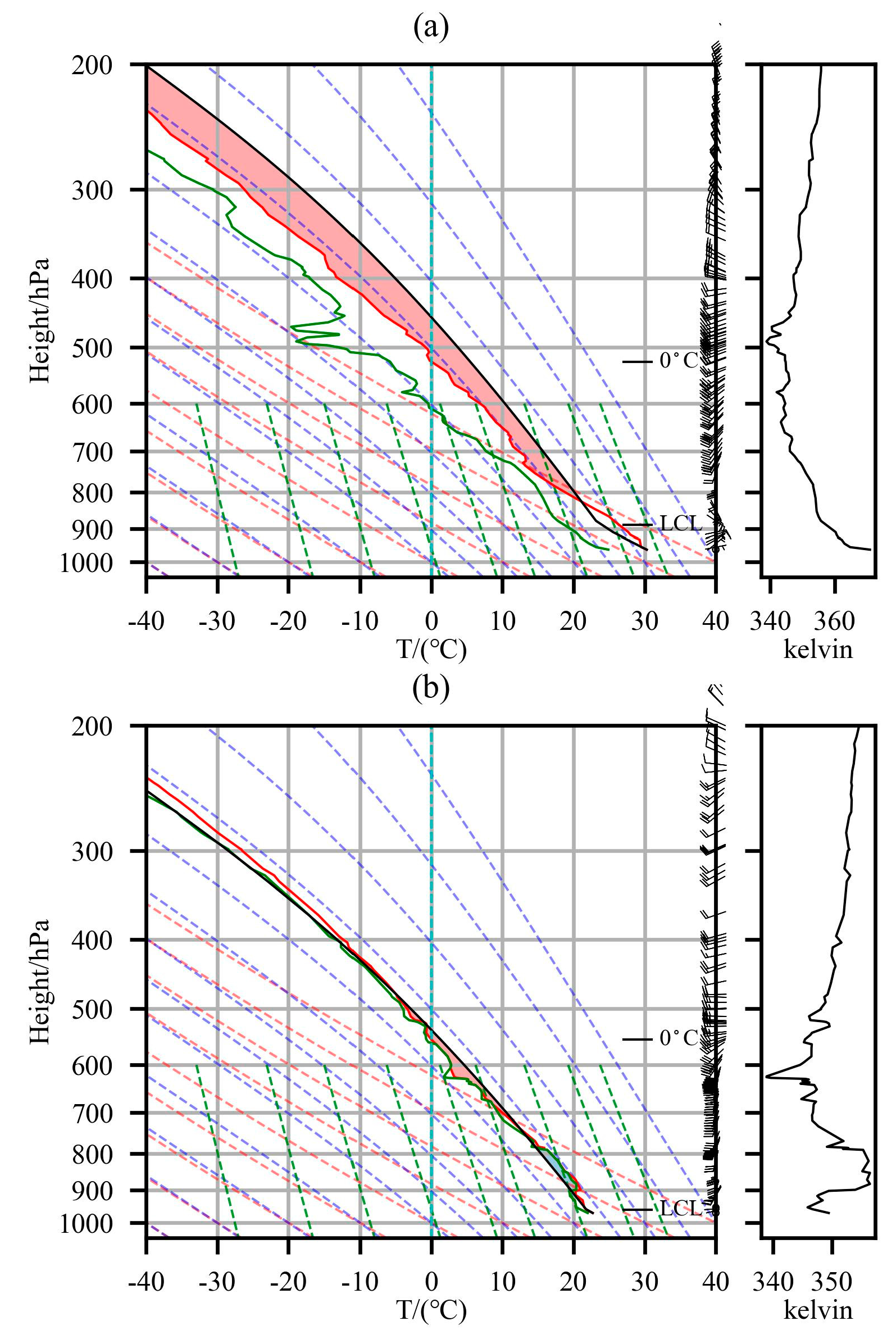
3.2.2. Thermal Convective Conditions
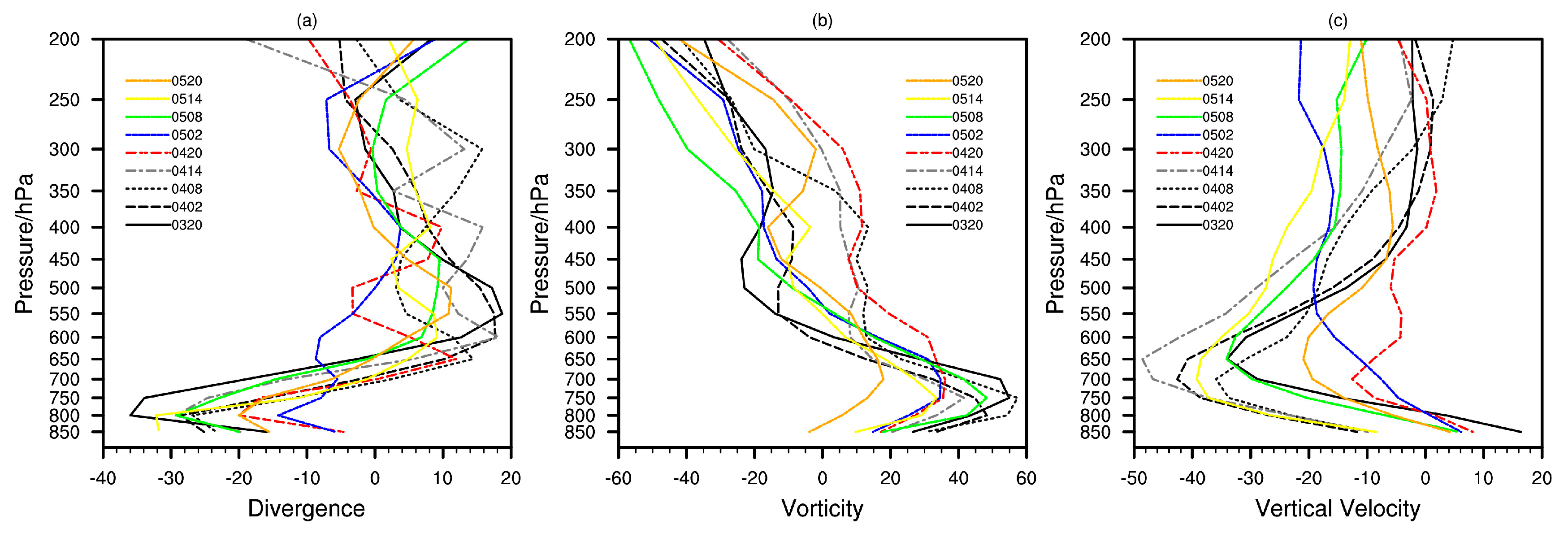
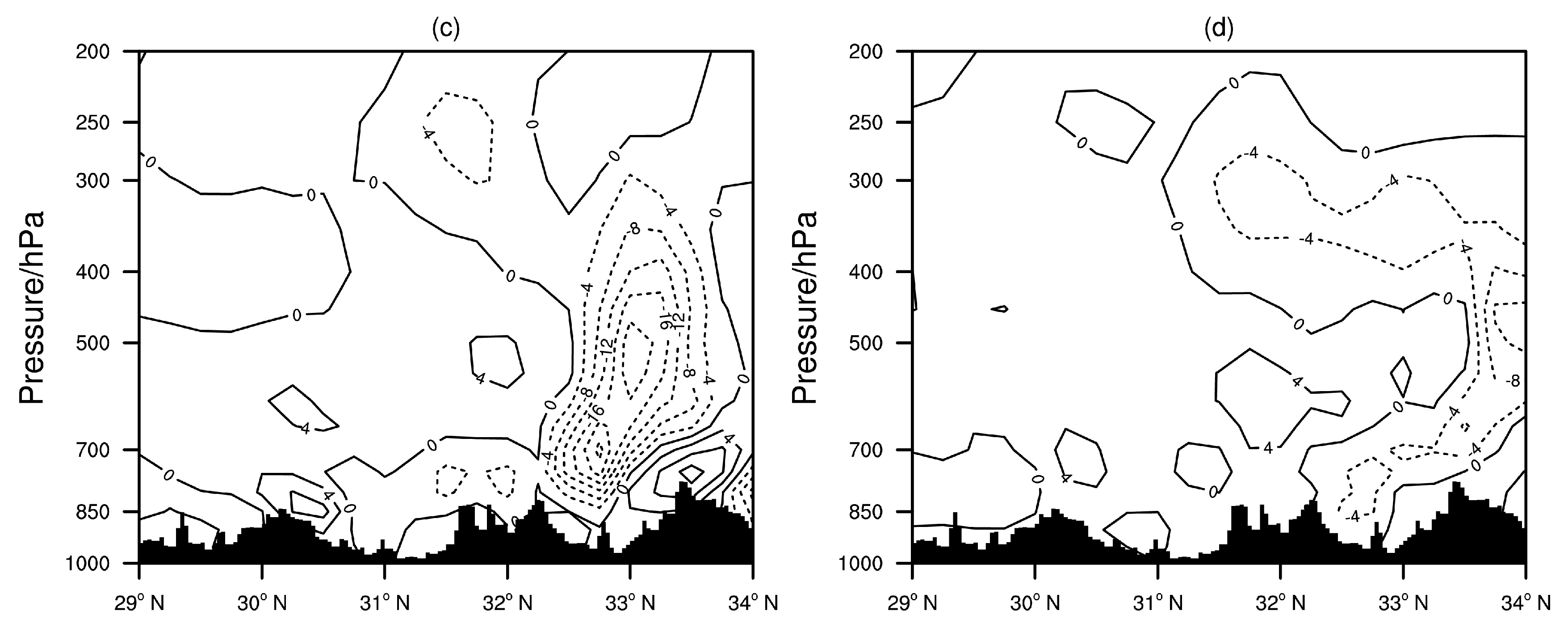
3.2.3. Dynamic Conditions
3.2.4. Vertical Structure
3.3. Characteristics of the SWV
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.; Liu, C.; Fan, G.; Liu, X.; Feng, C. Climatology and Structures of Southwest Vortices in the NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7675–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, M. Physical Formation Mechanisms of the Southwest China Vortex. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S. The Heavy Rainfalls in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X. A Review of the Research and Observing Experiment on Southwest China Vortex. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 134–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y. A Numerical Experiment Study on a Southwest Vortex Rainstorm: Scientific Experiment, Operational Experiment and Weather Dynamics of Rainstorm Research on Academic Theory; Beijing Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Advances in Tibetan Plateau Vortex and Southwest Vortex Research and Related Scientific Problems. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2013, 7, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Sun, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, W. The impact of the eastward propagation of convective systems over the Tibetan Plateau on southwest vortex formation in summer. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2010, 3, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J. Statistical of moving-out southwest vortex and correlation between vortex and precipitation in central and eastern China. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2019, 39, 818–826. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Feng, X. Climate Characteristic of Moving-out and Non-moving-out Southwest Vortices. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 41, 59–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Gao, W.; Hou, J.; Xiao, D. Analysis on a Heavy Rainstorm from Southwest Vortex Moving Toward Northeast Direction in Sichuan and Shaanxi Provinces. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 133–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, G. Numerical experiments of the impact of Qin-Ba mountainous terrain on a rainstorm caused by southwest vortex. J. Yunnan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2016, 38, 418–429. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Bai, A. Precipitation Characteristics of Southwest Vortex in Sichuan Basin from May to October in 2004–2017. Plateau Meteorol. 2019, 38, 552–562. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, J. Analysis on Strong Convective Weather Triggered by Southwest Vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 525–534. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Gu, Q.; He, G. Diagnostic Analysis of Vorticity in a Heavy Rain Event under Interaction of Plateau Vortex and Southwest Vortex. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 538–544. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Sun, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Li, B. A study of the impacts of the eastward propagation of convective cloud systems over the Tibetan Plateau on the rainfall of the Yangtze-Huai River basin. Acta Meteor. Sin. 2011, 69, 581–600. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Gao, W. The Causing Storm Rain in Southwest Sichuan Basin Characteristic Analysis of Tibetan Plateau Vortex. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 35, 9–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, G.; Hao, L. Diagnostic Analysis of Potential Vorticity on a Heavy Rain in Sichuan Basin under Interaction between Plateau Vortex and Southwest Vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 1556–1565. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Gao, W. Analysis of Environmental Background and Potential Vorticity of Different Accompanied Moving Cases of Tibetan Plateau Vortex and Southwest China Vortex. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 41, 831–856. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Yu, S. The Case Study in Causes and Environmental Fields Analysis of Departure Plateau Vortex Accompanying with Induced Southwest Vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2018, 37, 54–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Comparative Study Based on TRMM Data of the Heavy Rainfall Caused by the Tibetan Plateau Vortex and the Southwest Vortex. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 249–259. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Gao, W.; Xiao, D.; Peng, J. Observational facts regarding the joint activities of the southwest vortex and plateau vortex after its departure from the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. The Developmental Characteristics of the Structure of a Stationery Cold Southwest Vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2018, 37, 1628–1642. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Wu, T.; Xie, Z. Comparative Analysis of Two Rainstorm Processes in Sichuan Province Affected by the Tibetan Plateau Vortex and Southwest Vortex. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 43, 813–830. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, R.S.; Rasmussen, K.L. The formation, character and changing nature of mesoscale convective systems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.M.; Schumacher, R.S. Mechanisms for organization and echo training in a flash-flood-producing mesoscale convective system. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 1058–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, R.A. Mesoscale convective complexes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 61, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, S.; Zhou, K.; Shen, D.; Jiao, B.; Li, N. Observational analysis of the dynamic, thermal, and water vapor characteristics of the “7.20” extreme rainstorm event in Henan province, 2021. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 1366–1383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, B. Impact of double low-level jets on the extreme rainstorm in Henan province in July 2021. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 47, 1611–1625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Lou, P.; Li, M.; Wang, J. Analysis on a heavy rainstorm in Qinba region caused by southwest vortex and northwest vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2023, 42, 98–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Zhu, Y. Discussion and analysis on the geo-ecological boundary in Qinling range. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 2774–2784. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, C.; Zhujie, S. Characteristics of dry-wet climate change in China during the past 60 years and its trends projection. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Study on influence of the mechanical forcing of mesoscale topography on the extremely heavy rainfall in southern Shaanxi on 8~9 June 2002. Plateau Meteorol. 2006, 25, 485–494. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, N.; Wu, Z. Terrain effects on regional precipitation in a warm season over Qinling-Daba mountains in central China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Dai, C. Diagnostic study of topographic effect of a rainstorm in Qinba Mountain in summer in 2012. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 45, 139–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X. A numerical study on a heavy rainfall caused by an abnormal-path coupling vortex with the assimilation of southwest China vortex scientific experiment data. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 343–360. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Heng, Z. Research and Numerical Simulation of a Torrential Rain Caused by the Southwest China Vortex during Flood Period. Plateau Meteorol. 2019, 38, 359–367. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Bai, A.; Mao, X. Analysis of the Process of Heavy Rain and Cloud System Characteristics Caused by the Interaction of the Plateau Vortex and the Southwest Vortex. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 89–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Bai, A. Analysis of formation mechanism of MCC heavy rain caused by interaction between plateau vortex and southwest vortex. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2021, 41, 27–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- China News Network. 98 Towns and Offices in Ankang, Shaanxi Have Experienced Floods, Resulting in 56,748 People Affected. Available online: https://www.chinanews.com.cn/sh/2021/09-06/9558935.shtml (accessed on 6 September 2021). (In Chinese).
- Lu, F.; Zhang, X.H.; Chen, B.Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, R.H. FY-4 geostationary meteorological satellite imaging characteristics and its application prospects. J. Shandong Meteorol. 2017, 37, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. Review and prospects of research on low vortex on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Lanzhou Univ. Nat. Sci. 2012, 48, 53–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Min, W.; Miu, Q.; He, G. A Case Study on Coupling Interaction between Plateau and Southwest Vortexes. Plateau Meteorol. 2004, 23, 75–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y. A Case Study on Plateau Vortex Inducing SouthwestVortex and Producing Extremely Heavy Rain. Plateau Meteorol. 2010, 29, 819–831. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Analysis of the echo structure and its evolution as shown in a severe precipitation event caused by the plateau vortex and the southwest vortex. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 554–569. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Lou, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, S. Analysis on the cause and predictability of a γ-mesoscale short-time extremely rainstorm. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 13–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| CAPE/J·kg−1 | CIN/J·kg−1 | q850/g·kg−1 | q700/g·kg−1 | K/°C | SI/°C | WCD/m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20:00 on 3rd | 3100.1 | 71.2 | 14.0 | 9.4 | 36.4 | 0.9 | 4394 |
| 08:00 on 4th | 924.5 | 107.1 | 13.6 | 10.9 | 40.8 | −1.73 | 4365 |
| 20:00 on 4th | 9.6 | 0 | 14.0 | 10.2 | 37.2 | −0.1 | 4378 |
| 08:00 on 5th | 67.4 | 0.1 | 16.4 | 10.6 | 41 | −2.29 | 4678 |
| 20:00 on 5th | 611.6 | 0 | 15.3 | 11.0 | 41.3 | −1.88 | 4602 |
| CAPE/J·kg−1 | CIN/J·kg−1 | q850/g·kg−1 | q700/g·kg−1 | K/°C | SI/°C | WCD/m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20:00 on 3rd | 5 | 0 | 14.5 | 8.9 | 35.4 | −0.35 | 4132 |
| 08:00 on 4th | 83.7 | 1.1 | 15.0 | 11.1 | 37.9 | 0.09 | 4827 |
| 20:00 on 4th | 0 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 9.3 | 33.1 | 1.25 | 4814 |
| 08:00 on 5th | 73.7 | 0.7 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 32.4 | 3.7 | 4612 |
| 20:00 on 5th | 2.4 | 13.6 | 12.3 | 10.6 | 29.7 | 6.66 | 4859 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lou, P.; Gao, M. Comparative Analysis of Different Heavy Rainstorm Periods Lasting for Two Consecutive Days in the Qinba Region under the Influence of the Southwest Vortex. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030260
Xiao Y, Liu R, Ma Y, Zhang X, Lou P, Gao M. Comparative Analysis of Different Heavy Rainstorm Periods Lasting for Two Consecutive Days in the Qinba Region under the Influence of the Southwest Vortex. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030260
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yiqing, Ruifang Liu, Yongyong Ma, Xidi Zhang, Panxing Lou, and Meng Gao. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Different Heavy Rainstorm Periods Lasting for Two Consecutive Days in the Qinba Region under the Influence of the Southwest Vortex" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030260
APA StyleXiao, Y., Liu, R., Ma, Y., Zhang, X., Lou, P., & Gao, M. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Different Heavy Rainstorm Periods Lasting for Two Consecutive Days in the Qinba Region under the Influence of the Southwest Vortex. Atmosphere, 15(3), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030260





