Prediction of the Concentration and Source Contributions of PM2.5 and Gas-Phase Pollutants in an Urban Area with the SmartAQ Forecasting System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description and Application
2.1. Particle and Gas-Phase Measurements
2.2. Evaluation
2.2.1. Evaluation Metrics
2.2.2. European Air Quality Index
3. Results
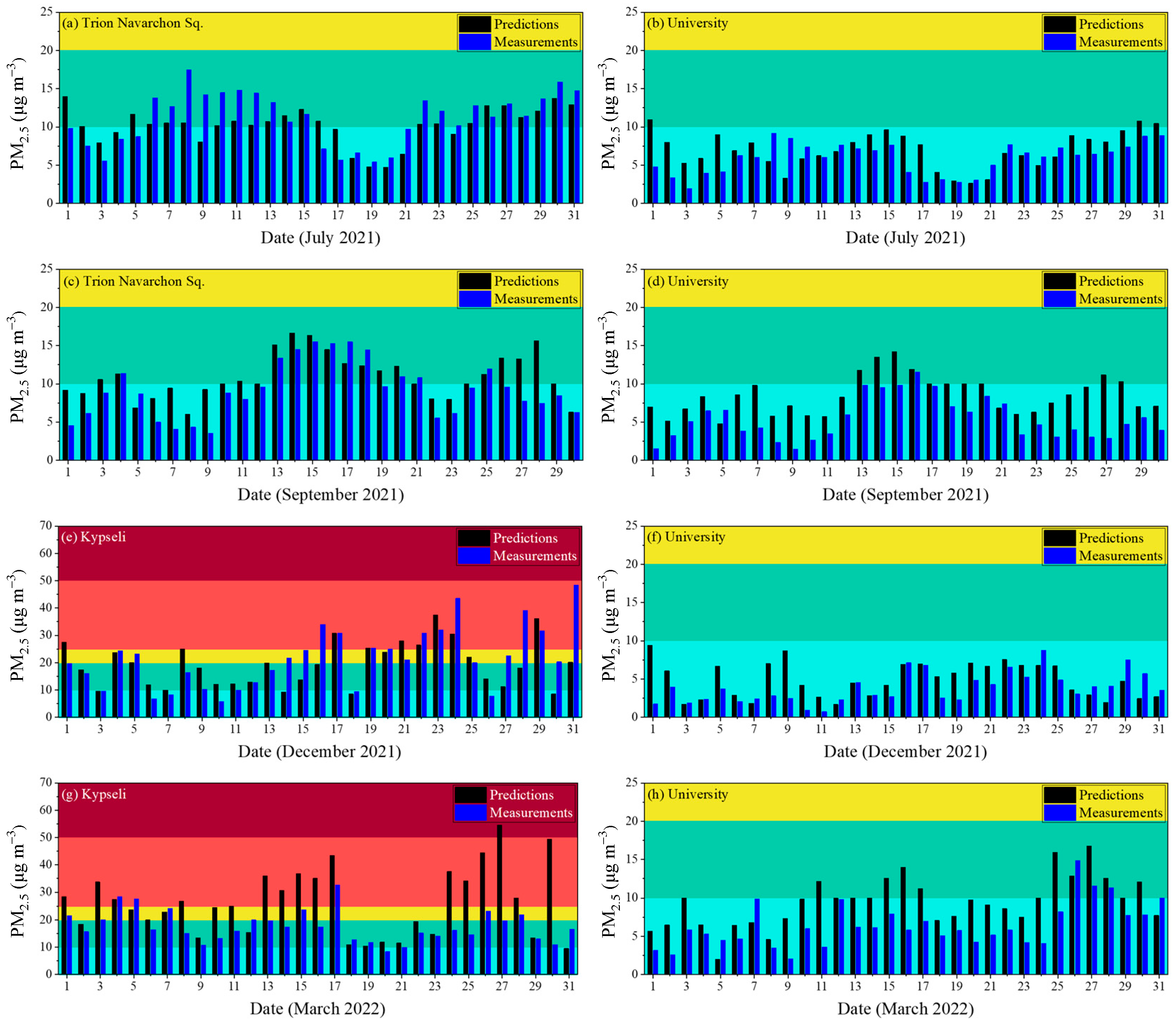
3.1. ΡΜ2.5 Predictions
3.1.1. Prediction of Air Quality Levels
3.1.2. Mean Measured and Predicted Concentrations
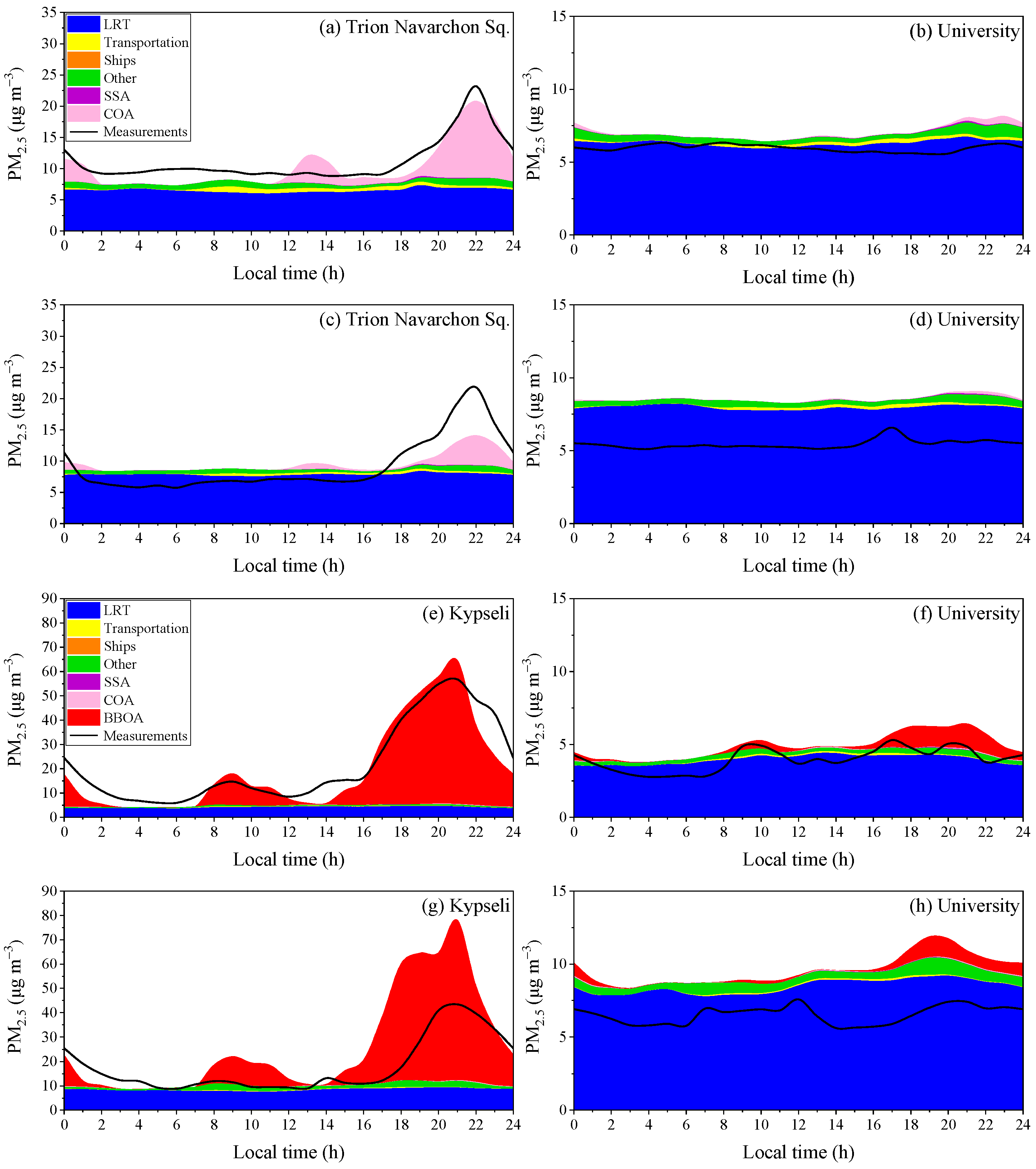
3.1.3. Average Diurnal Patterns
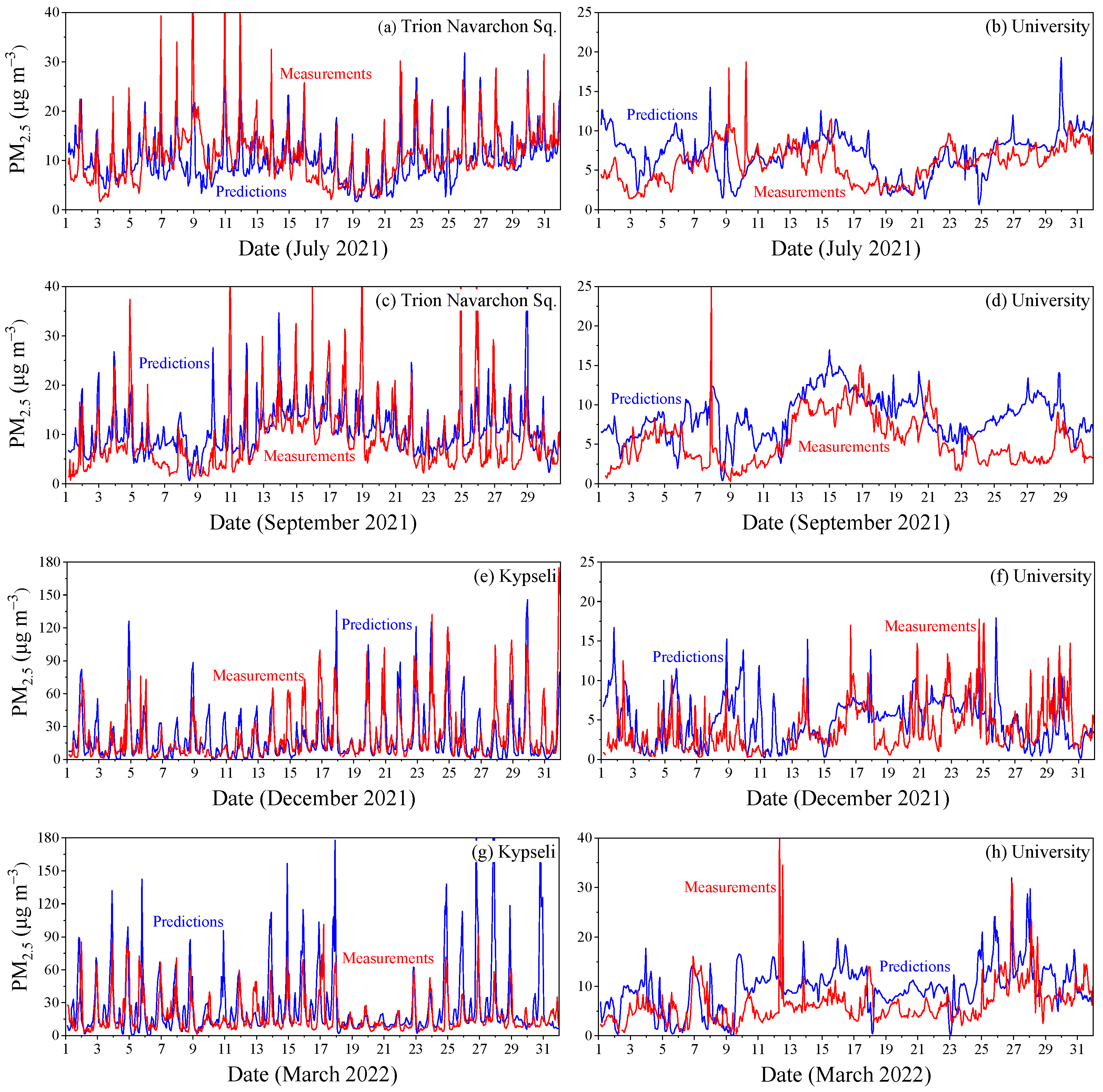
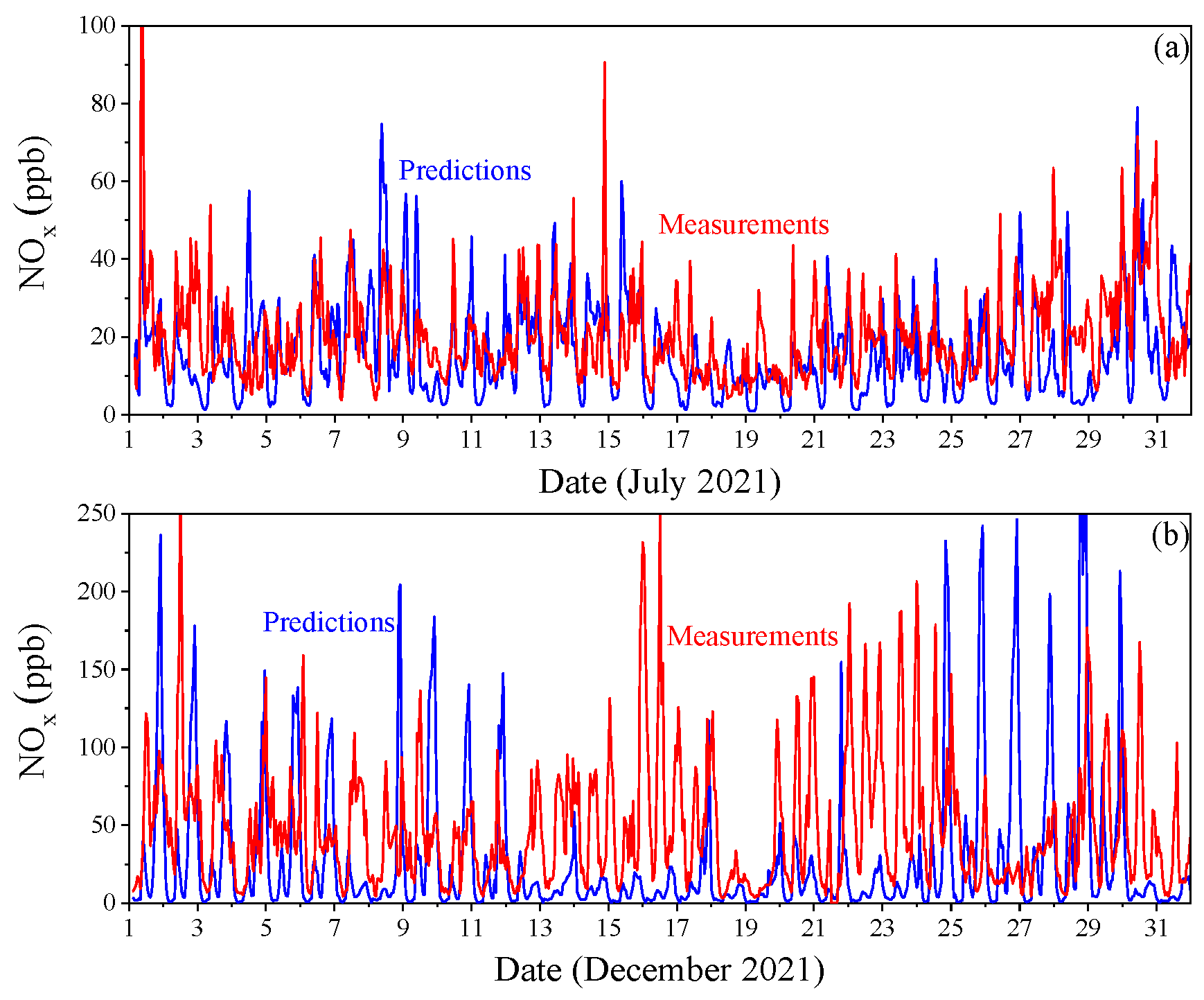
3.1.4. Detailed Temporal Variations
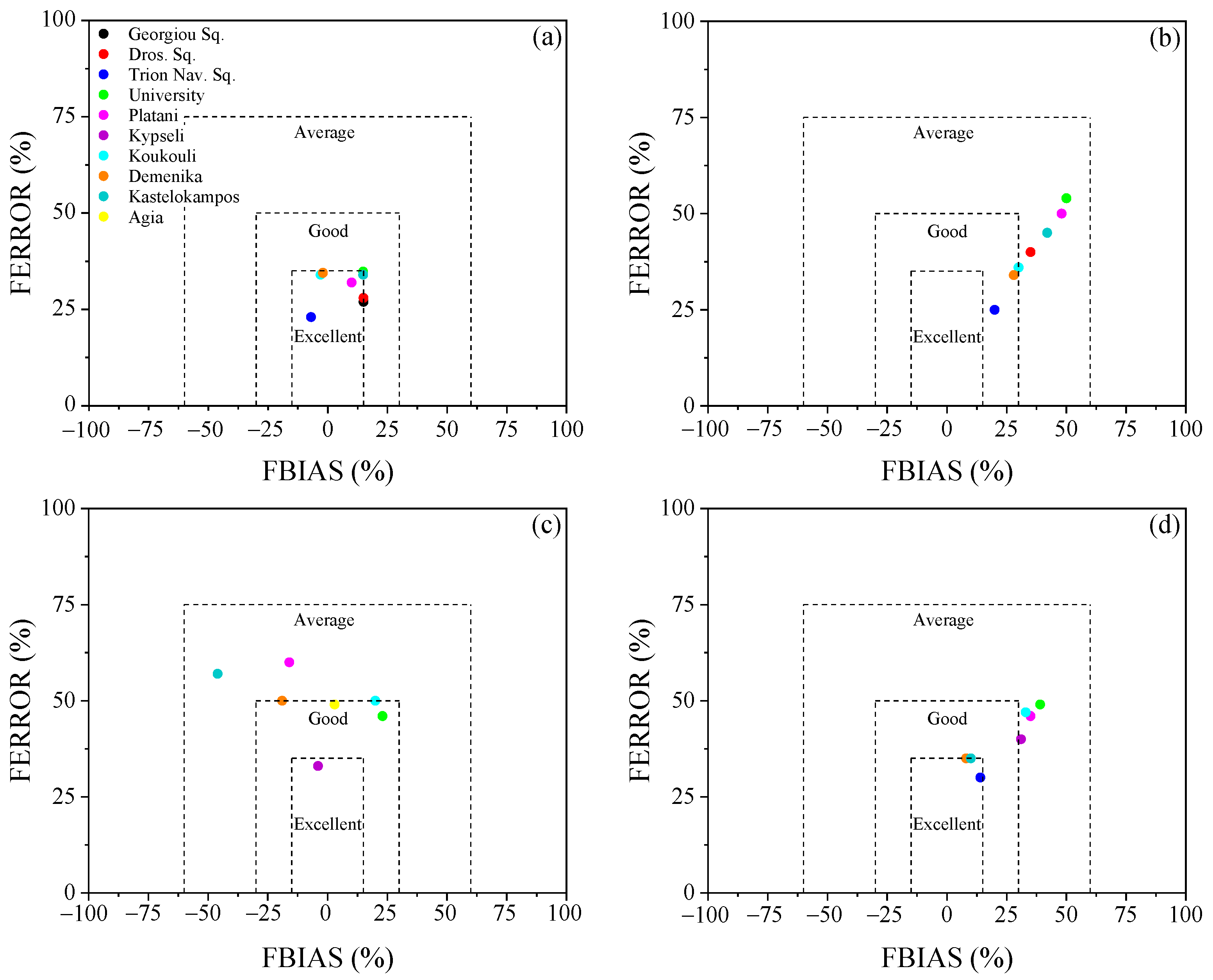
3.1.5. Model Performance
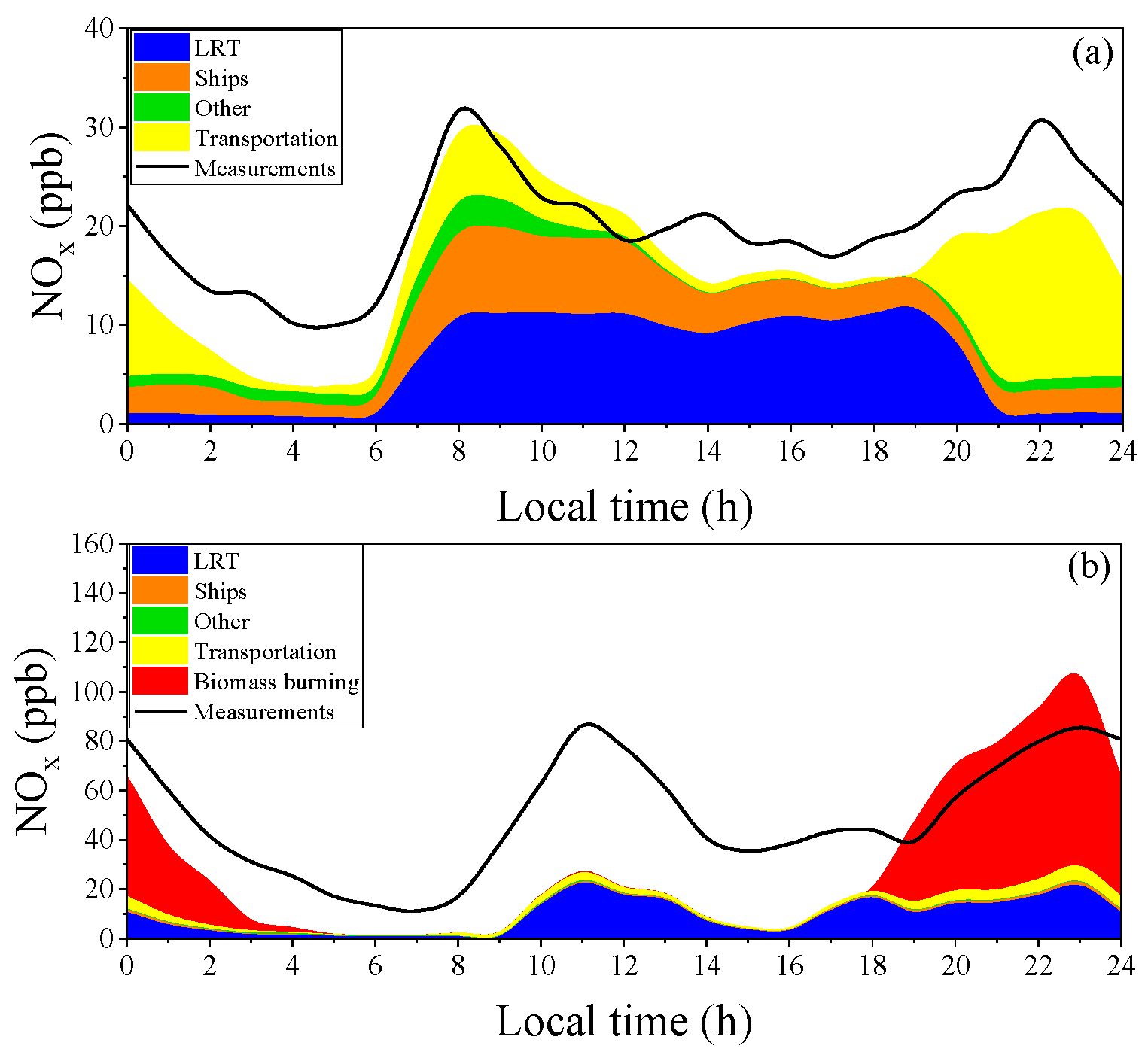
3.2. NOx Predictions
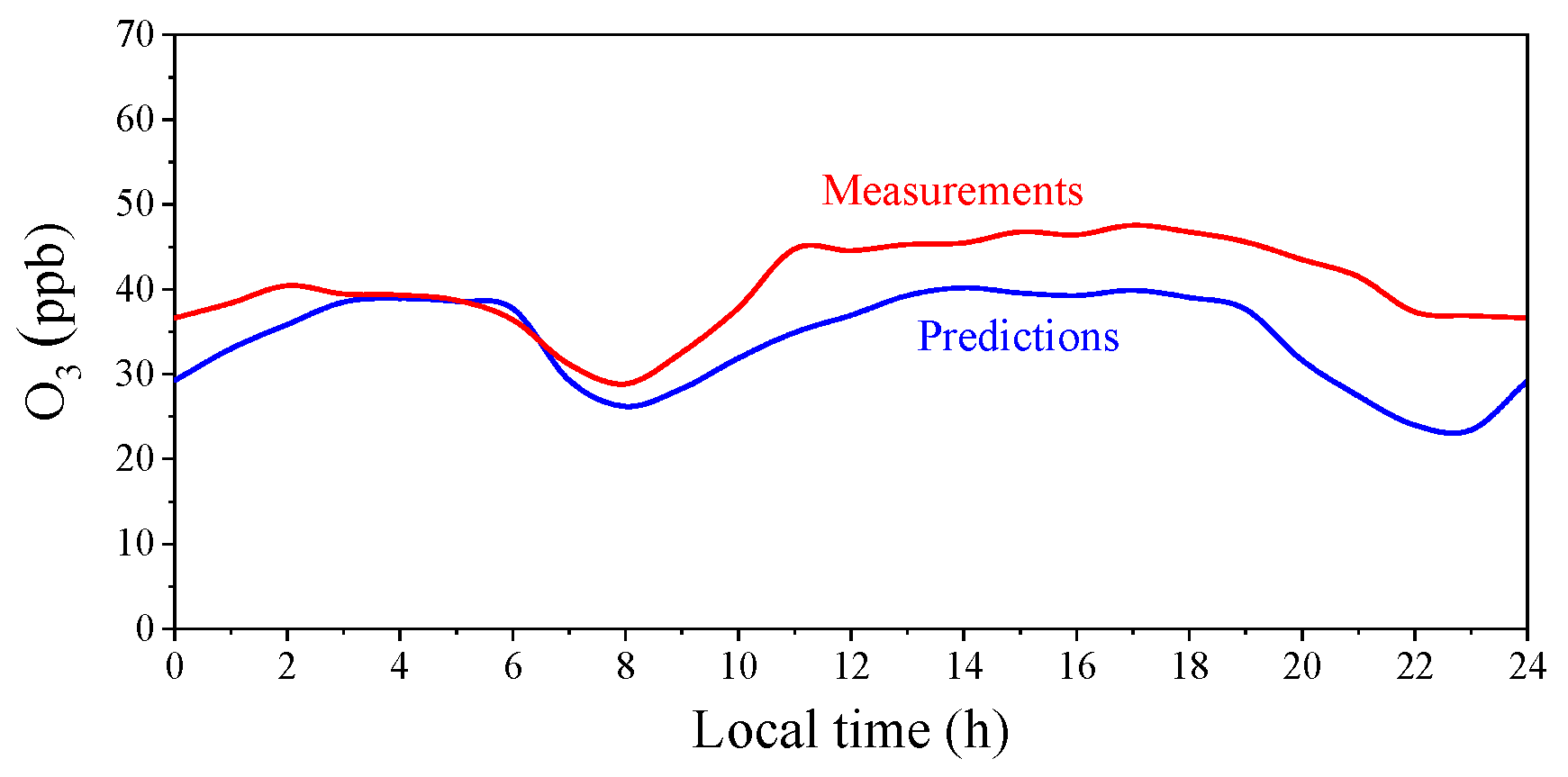
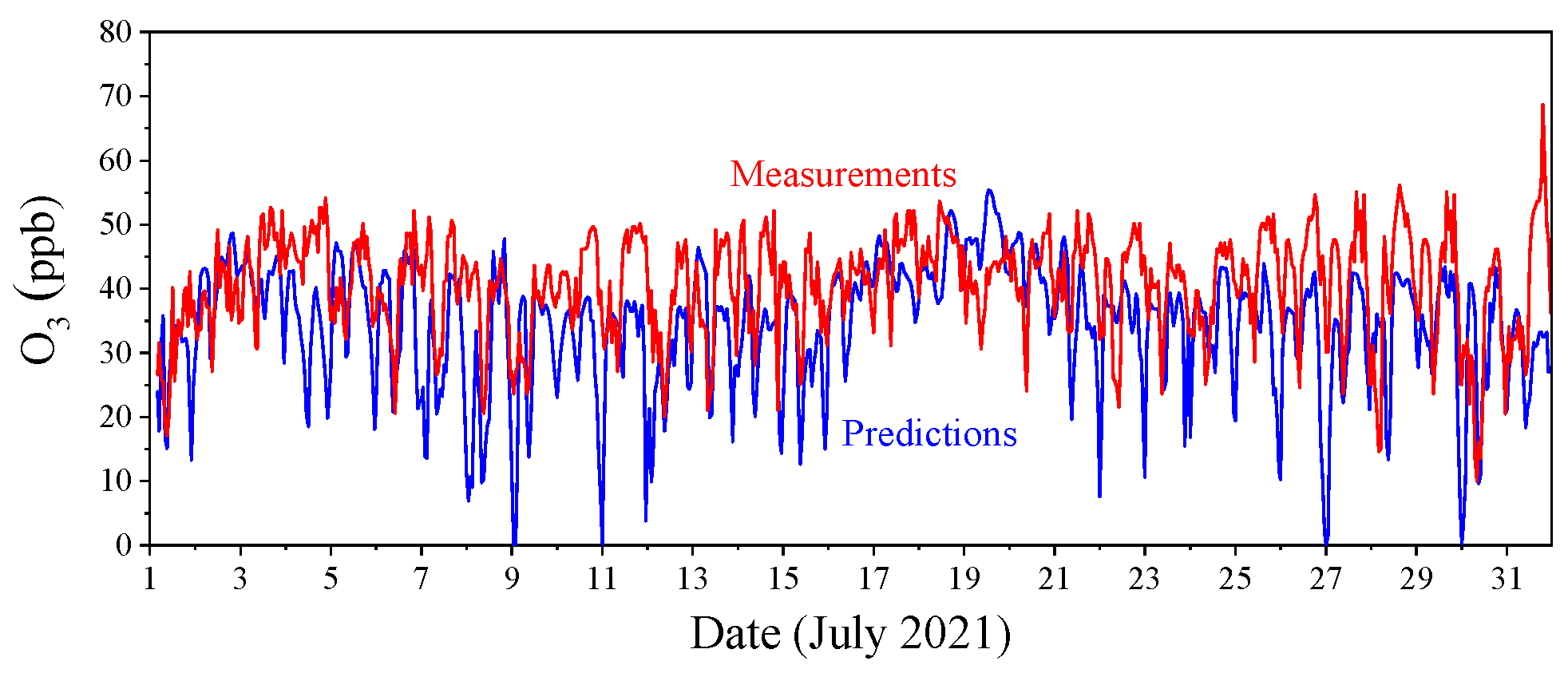
3.3. O3 Predictions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Fact Sheet: Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Health and Environmental Effects of Particulate Matter (PM). 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/health-and-environmental-effects-particulate-matter-pm (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Marécal, V.; Peuch, V.-H.; Andersson, C.; Andersson, S.; Arteta, J.; Beekmann, M.; Benedictow, A.; Bergström, R.; Bessagnet, B.; Cansado, A.; et al. A regional air quality forecasting system over Europe: The MACC-II daily ensemble production. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 2777–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honoré, C.; Rouil, L.; Vautard, R.; Beekmann, M.; Bessagnet, B.; Dufour, A.; Elichegaray, C.; Flaud, J.-M.; Malherbe, L.; Meleux, F.; et al. Predictability of European air quality: Assessment of 3 years of operational forecasts and analyses by the PREV’AIR system. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D04301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Xie, Y.; Petersen, A.K.; Bouarar, I.; Flemming, J.; Gauss, M.; Jiang, F.; Kouznetsov, R.; Kranenburg, R.; Mijling, B.; et al. Ensemble forecasts of air quality in eastern China–Part 1: Model description and implementation of the MarcoPolo-Panda prediction system, version 1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, P.; Tong, D.; Pan, L.; Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; McQueen, J.; Tsidulko, M.; Stajner, I. Evaluation of the United States National Air Quality Forecast Capability experimental real-time predictions in 2010 using Air Quality System ozone and NO2 measurements. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 6, 1831–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAMS. Regional Production, Updated Documentation Covering All Regional Operational Systems and the ENSEMBLE. ECMWF Copernicus Report. 2020. Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/sites/default/files/2020-09/CAMS50_2018SC2_D2.0.2-U2_Models_documentation_202003_v2.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2023).
- Katragkou, E.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Poupkou, A.; Lisaridis, I.; Markakis, K.; Karathanasis, S.; Melas, D.; Balis, D. An air quality study for Greece with the MM5/CAMx modelling system. In Proceedings of the Electronic ‘Envisat Symposium 2007’, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D.; Williams, P.I.; Morgan, W.T.; Martin, C.L.; Flynn, M.J.; Lee, J.; Nemitz, E.; Phillips, G.J.; Gallagher, M.W.; Coe, H. Contributions from transports solid fuel burning, and cooking to primary organic aerosols in two UK cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Slowik, J.G.; Richter, R.; Reche, C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Seco, R.; et al. Identification and quantification of organic aerosol from cooking and other sources in Barcelona using aerosol mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Slowik, J.G.; Mohr, C.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Poulain, L.; Freutel, F.; Sciare, J.; Cozic, J.; et al. Wintertime aerosol chemical composition and source apportionment of the organic fraction in the metropolitan area of Paris. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 961–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenidou, E.; Florou, K.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Tsiflikiotou, M.; Vratolis, E.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Pandis, S.N. Sources and chemical characterization of organic aerosol during the summer in the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11355–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florou, K.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Pikridas, M.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Louvaris, E.; Gkatzelis, G.I.; Patoulias, D.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Pandis, S.N. The contribution of wood burning and other pollution sources to wintertime organic aerosol levels in two Greek cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3145–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouti, E.; Skyllakou, K.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Patoulias, D.; Fouskas, G.; Pandis, S.N. Development and application of the SmartAQ high-resolution air quality and source apportionment forecasting system for European urban areas. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouti, E.; Skyllakou, K.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Ciarelli, G.; Pandis, S.N. Simulation of the cooking organic aerosol concentration variability in an urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 265, 118710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouti, E.; Kilafis, K.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Pandis, S.N. Simulation of the influence of residential biomass burning on air quality in an urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Model Version 4.1; (No. NCAR/TN-556+STR); National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenen, J.J.P.; Visschedijk, A.J.H.; Jozwicka, M.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C. TNO-MACC_II emission inventory; a multi-year (2003–2009) consistent high-resolution European emission inventory for air quality modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10963–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Jiang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Sakulyanontvittaya, T.; Duhl, T.; Emmons, L.K.; Wang, X. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): An extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Jiang, X.; Shah, T.; Huang, L.; Kemball-Cook, S.; Yarwood, G. Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosol from Nature Version 3 (MEGAN3) for estimating biogenic emissions. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XXVI; Mensink, C., Gong, W., Hakami, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; Langmann, B.; Varghese, S.; Scannell, C.; Ceburnis, D.; Facchini, M.C. A combined organic-inorganic sea-spray source function. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Spiel, D.E.; Davidson, K.L. A model of marine aerosol generation via whitecaps and wave disruption. In Oceanic Whitecaps; Monahan, E.C., Niocaill, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Fountoukis, C.; Koraj, D.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Charalampidis, P.E.; Pilinis, C.; Pandis, S.N. Impact of grid resolution on the predicted fine PM by a regional 3-D chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstrom, K.M.; Pandis, S.N.; Yarwood, G.; Wilson, G.M.; Morris, R.E. Development and application of a computationally efficient particulate matter apportionment algorithm in a three-dimensional chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5650–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, G.; Salamalikis, V.; Pandis, S.N.; Yannopoulos, P.; Bloutsos, A.A.; Kazantzidis, A. Low-cost sensors for measuring airborne particulate matter: Field evaluation and calibration at a South-Eastern European site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.E.; McNally, D.E.; Tesche, T.W.; Tonnesen, G.; Boylan, J.W.; Brewer, P. Preliminary Evaluation of the Community Multiscale Air Quality Model for 2002 over the Southeastern United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.E.; Koo, B.; Lau, S.; Tesche, T.W.; McNally, D.; Loomis, C.; Stella, G.; Tonnesen, G.; Wang, Z. VISTAS Emissions and Air Quality Modeling Phase I Task 4cd Report: Model Performance Evaluation and Model Sensitivity Tests for Three Phase I Episodes; Final report; Visibility Improvement State and Tribal Association of the Southeast (VISTAS): Swannanoa, NC, USA, 2004.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Health Risks of Air Pollution in Europe: HRAPIE Project: New Emerging Risks to Health from Air Pollution: Results from the Survey of Experts. 2013. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/WHO-EURO-2013-6696-46462-67326 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Guidance for Regulatory Application of the Urban Airshed Model (UAM); Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1991.
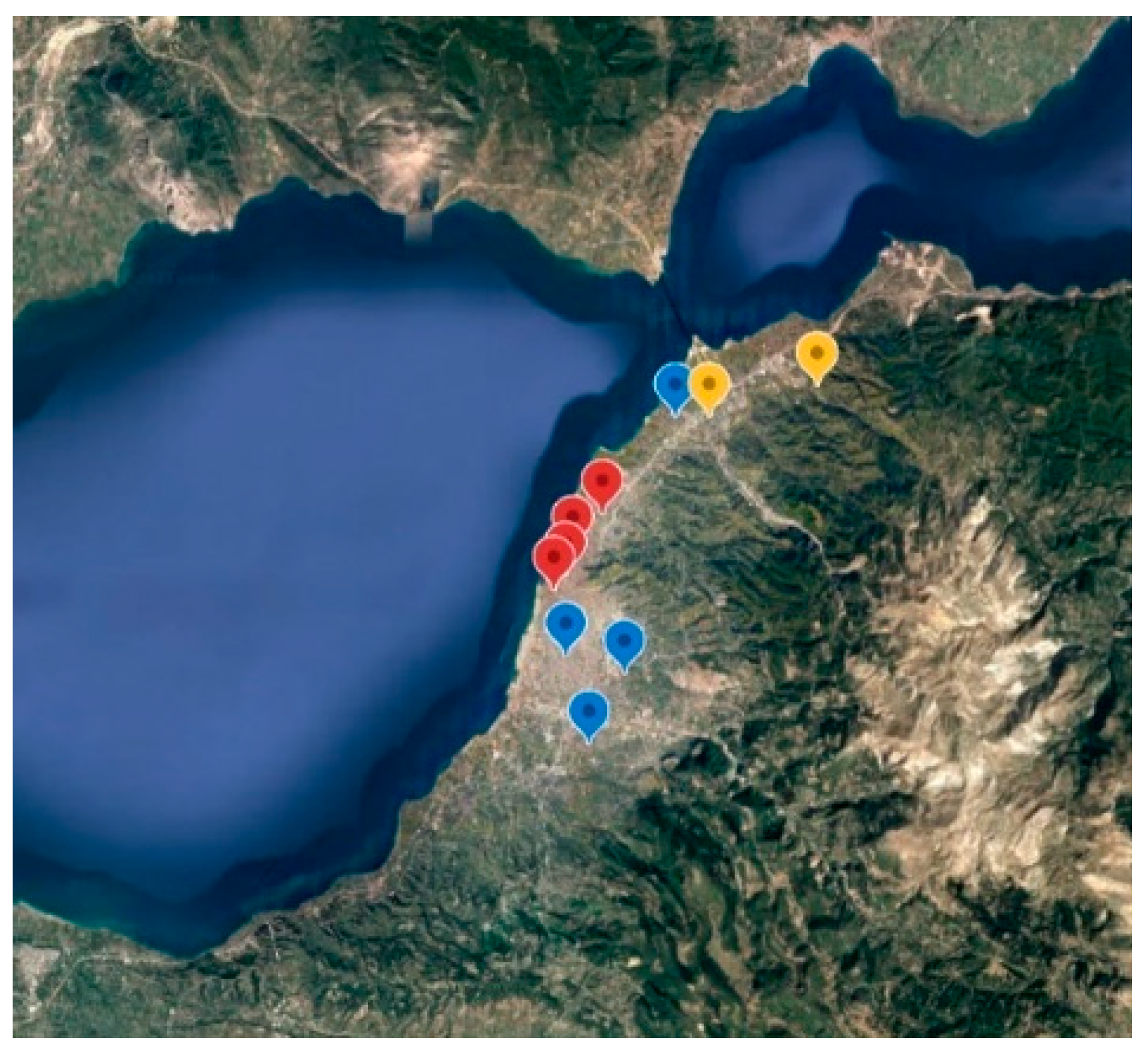
| Station | Type |
|---|---|
| Agia | Urban |
| Demenika | Suburban |
| Drosopoulou Square | Urban |
| Georgiou Square | Urban-city center |
| Kastelokampos | Suburban |
| Koukouli | Suburban |
| Kypseli | Suburban |
| Platani | Background |
| Trion Navarchon Square | Urban-city center |
| University of Patras | Background |
| Index Level | PM2.5 (μg m−3) |
|---|---|
| Good | 0–10 |
| Fair | 10–20 |
| Moderate | 20–25 |
| Poor | 25–50 |
| Very poor | 50–75 |
| Extremely poor | 75–800 |
| July 2021 | September 2021 | December 2021 | January 2022 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Observed (μg m−3) | Predicted (μg m−3) | Observed (μg m−3) | Predicted (μg m−3) | Observed (μg m−3) | Predicted (μg m−3) | Observed (μg m−3) | Predicted (μg m−3) |
| Agia | - | - | - | - | 7.8 | 8.1 | - | - |
| Demenika | 6.9 | 6.7 | 6.1 | 7.7 | 16 | 16.2 | 16.6 | 18.7 |
| Drosopoulou Sq. | 7.4 | 8.8 | 7 | 9.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Georgiou Sq. | 7.2 | 8.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kastelokampos | 6.2 | 7.2 | 6 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 5.5 | 9.1 | 9.9 |
| Koukouli | 7.4 | 7 | 6 | 7.9 | 11 | 13.8 | 12 | 18 |
| Kypseli | - | - | - | - | 21.5 | 19.5 | 17.7 | 26.2 |
| Platani | 5.8 | 6.5 | 5.3 | 8.2 | 5.3 | 4.5 | 6.3 | 9 |
| Trion Navarchon Sq. | 11.2 | 10.2 | 9.2 | 10.8 | - | - | 14.5 | 17.3 |
| U. of Patras | 6 | 7 | 5.4 | 8.5 | 3.7 | 4.8 | 6.5 | 9.5 |
| July 2021 | September 2021 | December 2021 | January 2022 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | MB (μg m−3) | ME (μg m−3) | MB (μg m−3) | ME (μg m−3) | MB (μg m−3) | ME (μg m−3) | MB (μg m−3) | ME (μg m−3) |
| Agia | - | - | - | - | 0.32 | 3.7 | - | - |
| Demenika | −0.3 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 2.1 | −0.35 | 8.5 | 2.1 | 6.5 |
| Drosopoulou Sq. | 1.4 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.9 | - | - | - | - |
| Georgiou Square | 1.5 | 2.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kastelokampos | 1 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.9 | −3.1 | 4 | 0.8 | 3.1 |
| Koukouli | −0.5 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 6 | 7.8 |
| Kypseli | - | - | - | - | −2 | 6.6 | 8.5 | 9.9 |
| Platani | 0.6 | 1.9 | 3 | 3.1 | −0.8 | 3 | 2.9 | 3.4 |
| Trion Navarchon Sq. | −0.9 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 2.3 | - | - | 2.8 | 5.2 |
| University of Patras | 1 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 3 | 3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siouti, E.; Skyllakou, K.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Patoulias, D.; Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Fouskas, G.; Pandis, S.N. Prediction of the Concentration and Source Contributions of PM2.5 and Gas-Phase Pollutants in an Urban Area with the SmartAQ Forecasting System. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010008
Siouti E, Skyllakou K, Kioutsioukis I, Patoulias D, Apostolopoulos ID, Fouskas G, Pandis SN. Prediction of the Concentration and Source Contributions of PM2.5 and Gas-Phase Pollutants in an Urban Area with the SmartAQ Forecasting System. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiouti, Evangelia, Ksakousti Skyllakou, Ioannis Kioutsioukis, David Patoulias, Ioannis D. Apostolopoulos, George Fouskas, and Spyros N. Pandis. 2024. "Prediction of the Concentration and Source Contributions of PM2.5 and Gas-Phase Pollutants in an Urban Area with the SmartAQ Forecasting System" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010008
APA StyleSiouti, E., Skyllakou, K., Kioutsioukis, I., Patoulias, D., Apostolopoulos, I. D., Fouskas, G., & Pandis, S. N. (2024). Prediction of the Concentration and Source Contributions of PM2.5 and Gas-Phase Pollutants in an Urban Area with the SmartAQ Forecasting System. Atmosphere, 15(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010008









