Enhanced Wind-Field Detection Using an Adaptive Noise-Reduction Peak-Retrieval (ANRPR) Algorithm for Coherent Doppler Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
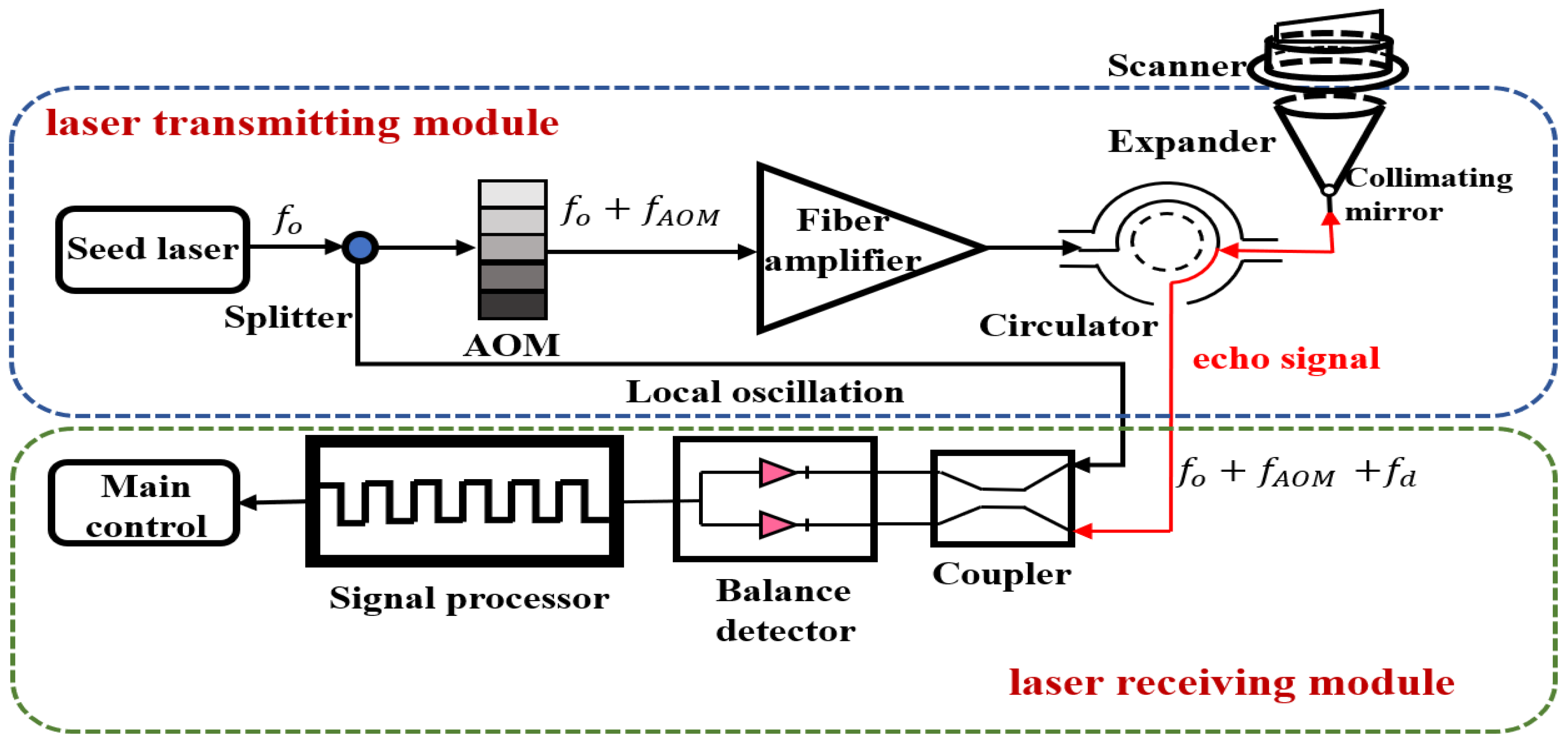
2. System and Principle
2.1. CDL System
2.2. Principle
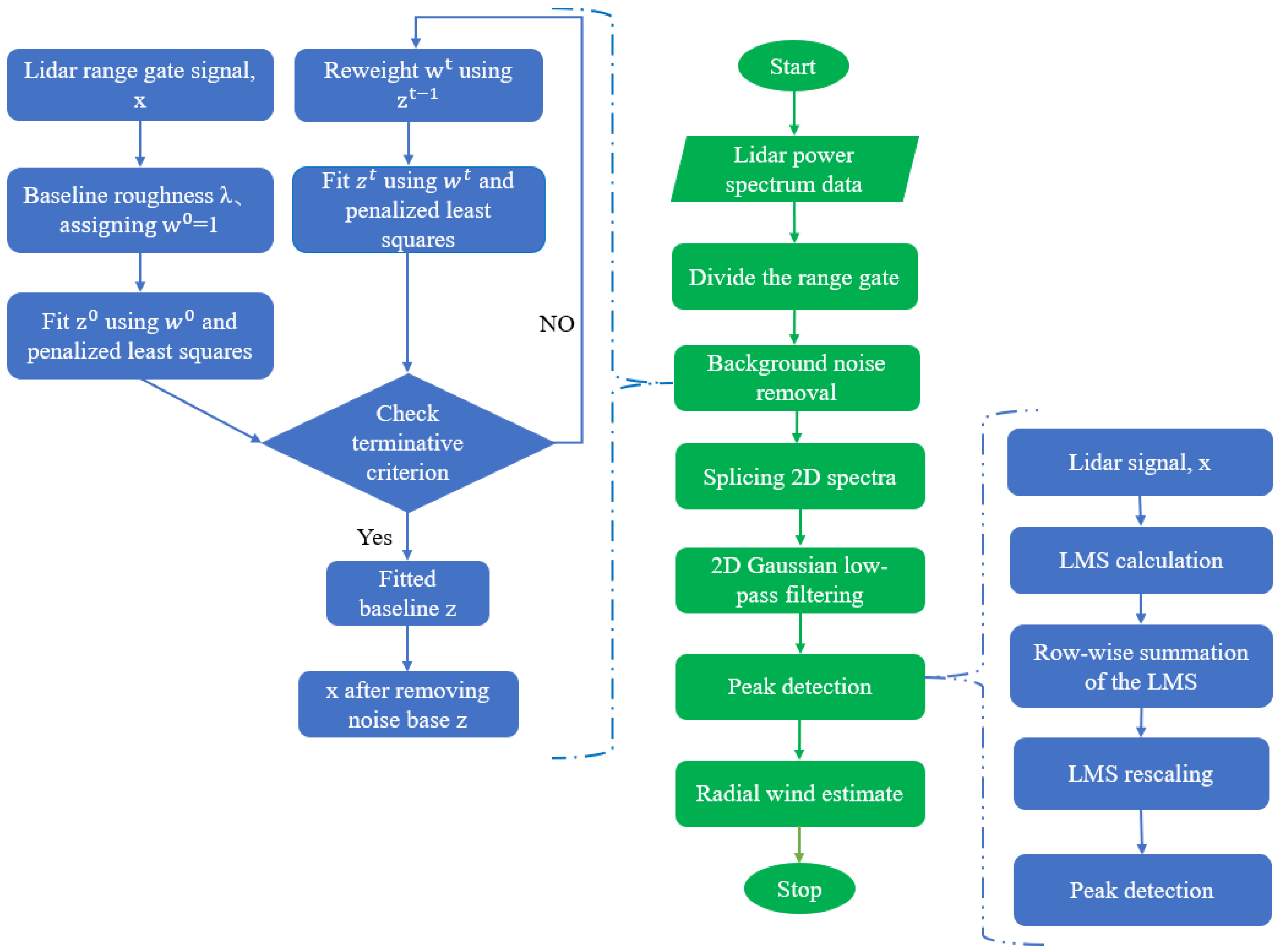
3. ANRPR Method
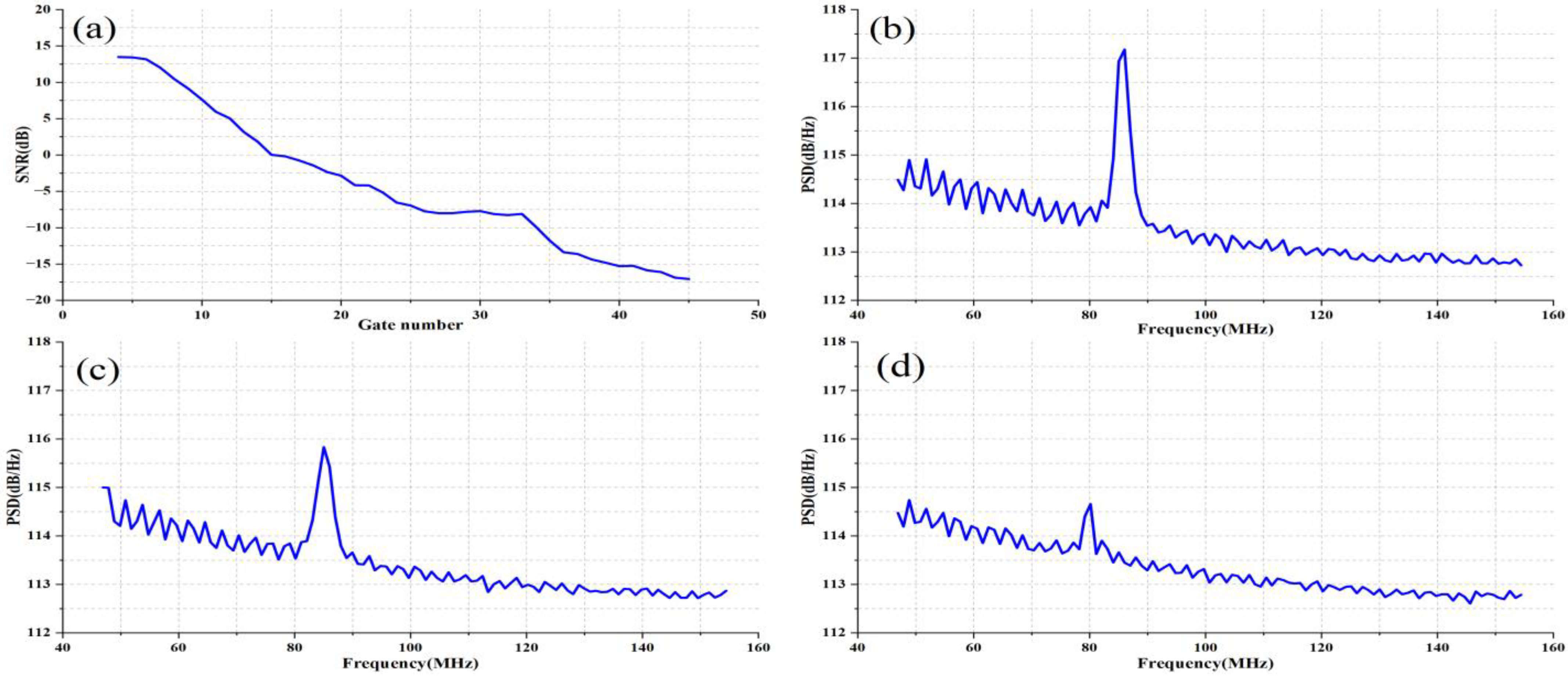
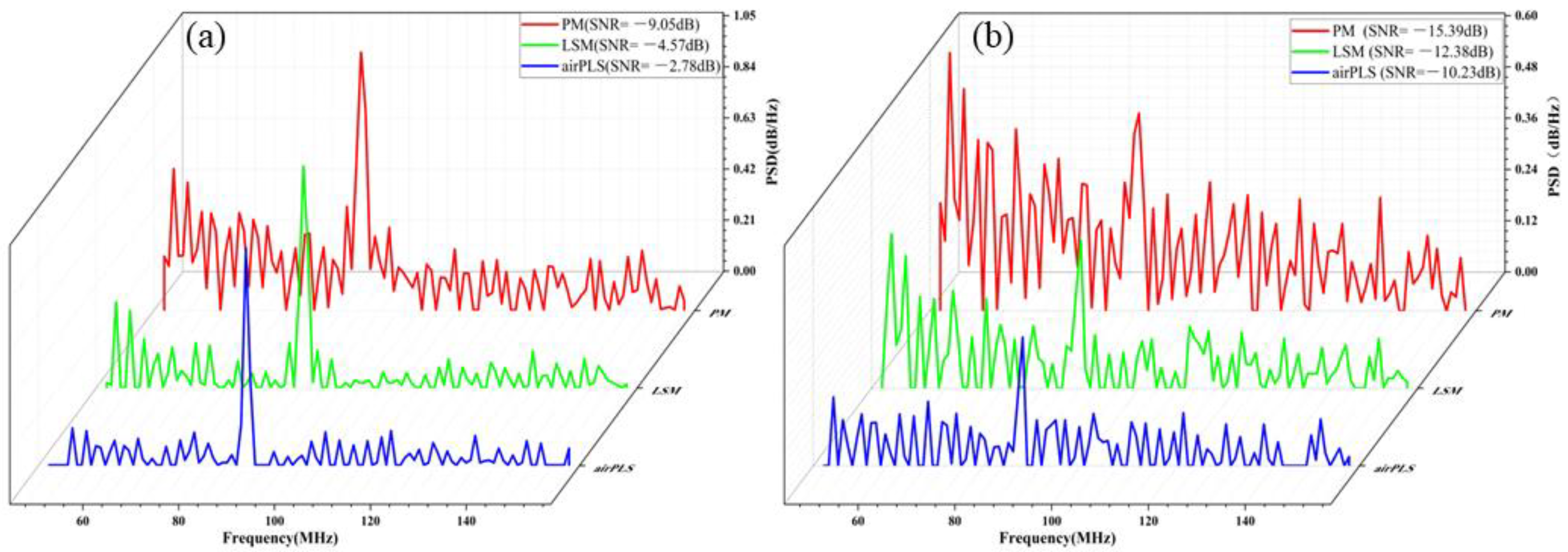
3.1. Existing Method Limitations in Low-SNR Environments
3.2. Division Range Gate
3.3. Range-Gate Noise Removal
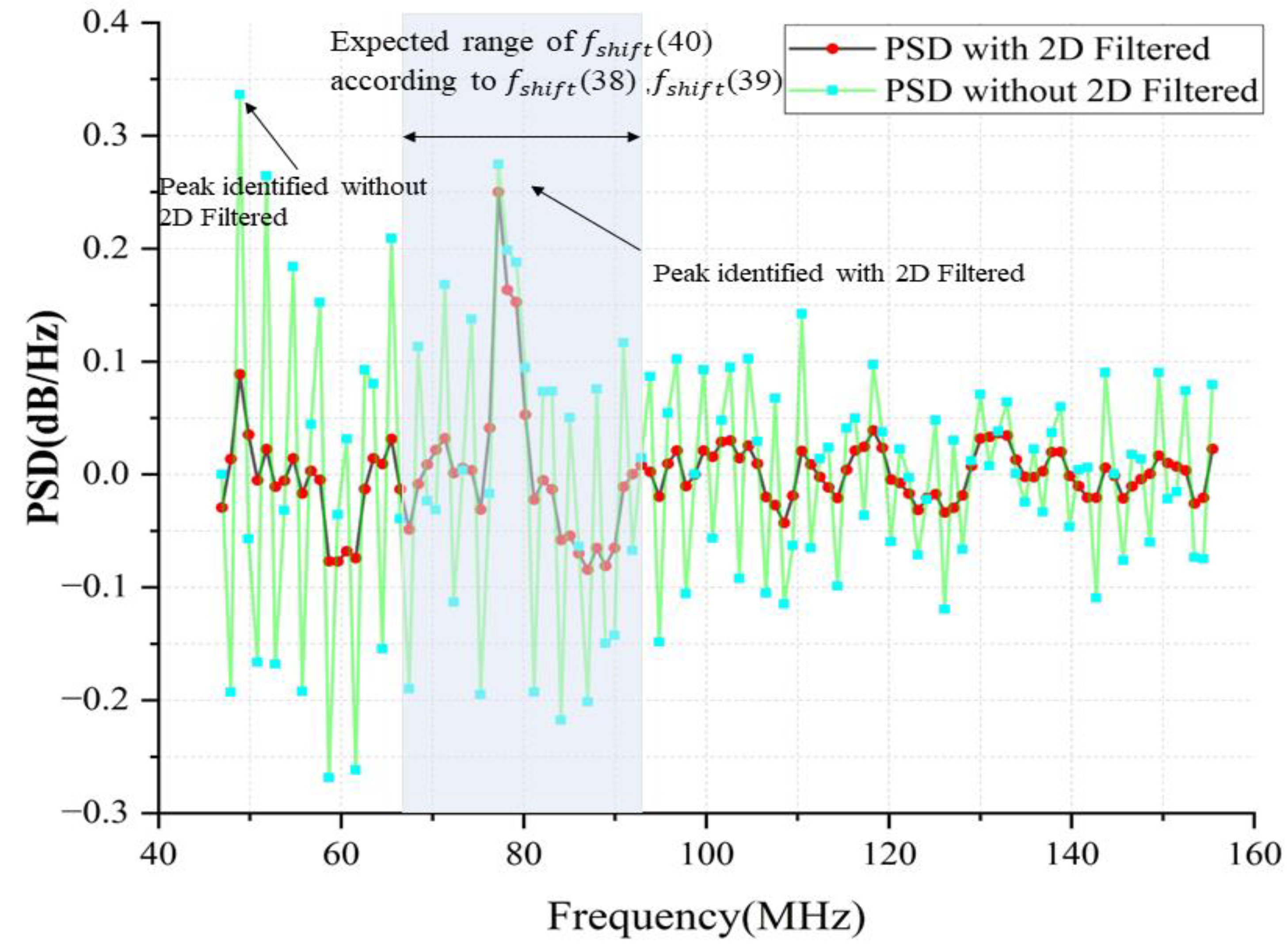
3.4. 2D Gaussian Filter
3.5. Adaptive Peak-Retrieval Algorithm
3.6. Design Procedure for ANRPR
- Substrate noise removal: The raw data for each range gate are subjected to adaptive iterative weighted penalized least-squares fitting, and the corresponding noise-substrate removal is performed for each range gate to obtain the power spectral data after the removal of background noise.
- Spectrum signal splicing: The power spectrum data with background noise removed are arranged radially by a range gate to form a 2D matrix spectrum.
- 2D Gaussian low-pass filtering: The 2D spectral matrix is subjected to 2D Gaussian low-pass filtering to improve the correlation of the range gates.
- Peak search: The filtered 2D spectral matrix is expanded by range gates to obtain the noise-reduced 1D power spectral data, and the peaks of each range gate are extracted using a peak-retrieval algorithm.
- Estimation of radial wind speed: For each distance gate retrieved peak, its corresponding frequency and the radial wind speed are found by the Doppler shift formula.
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
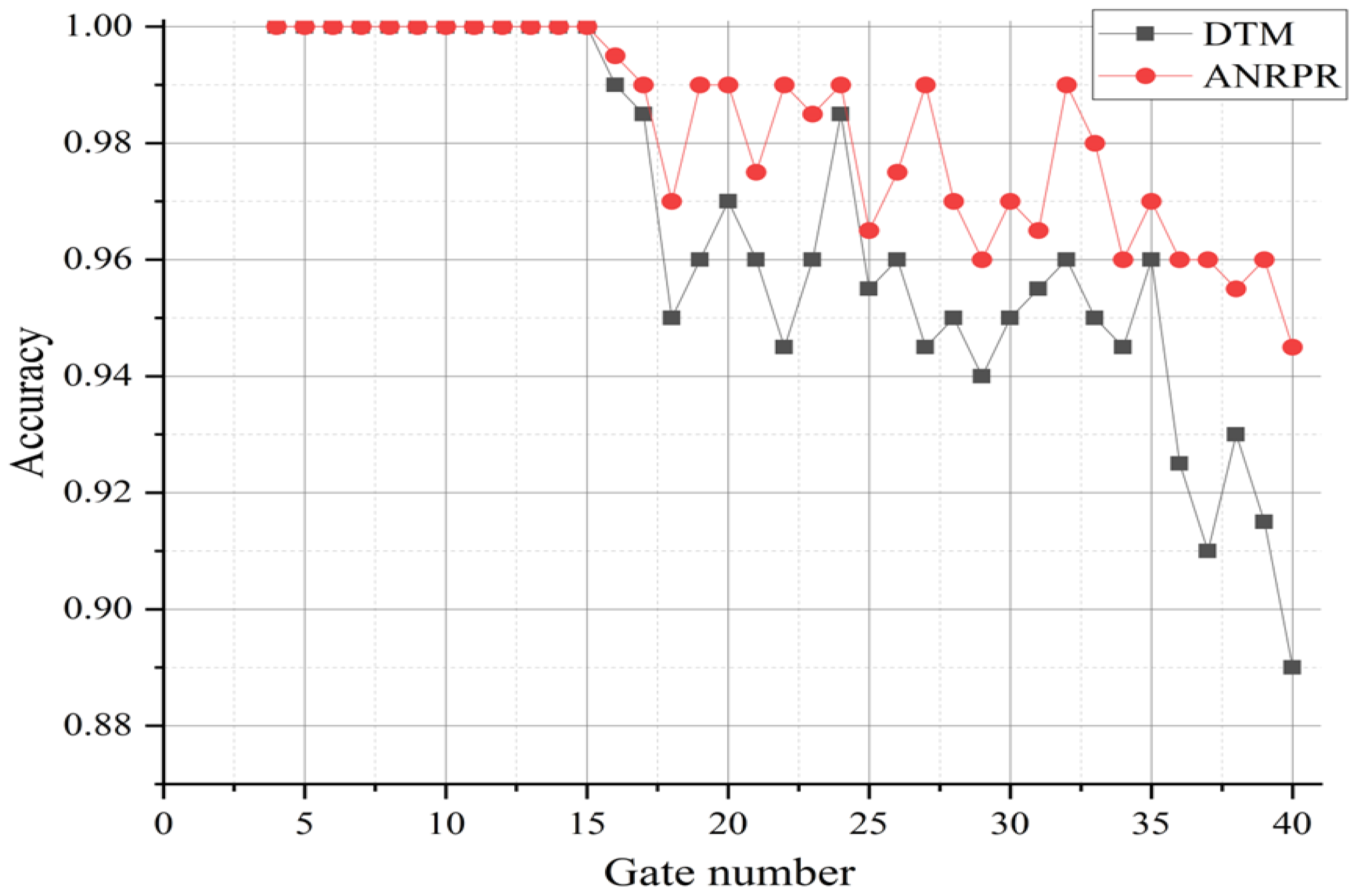
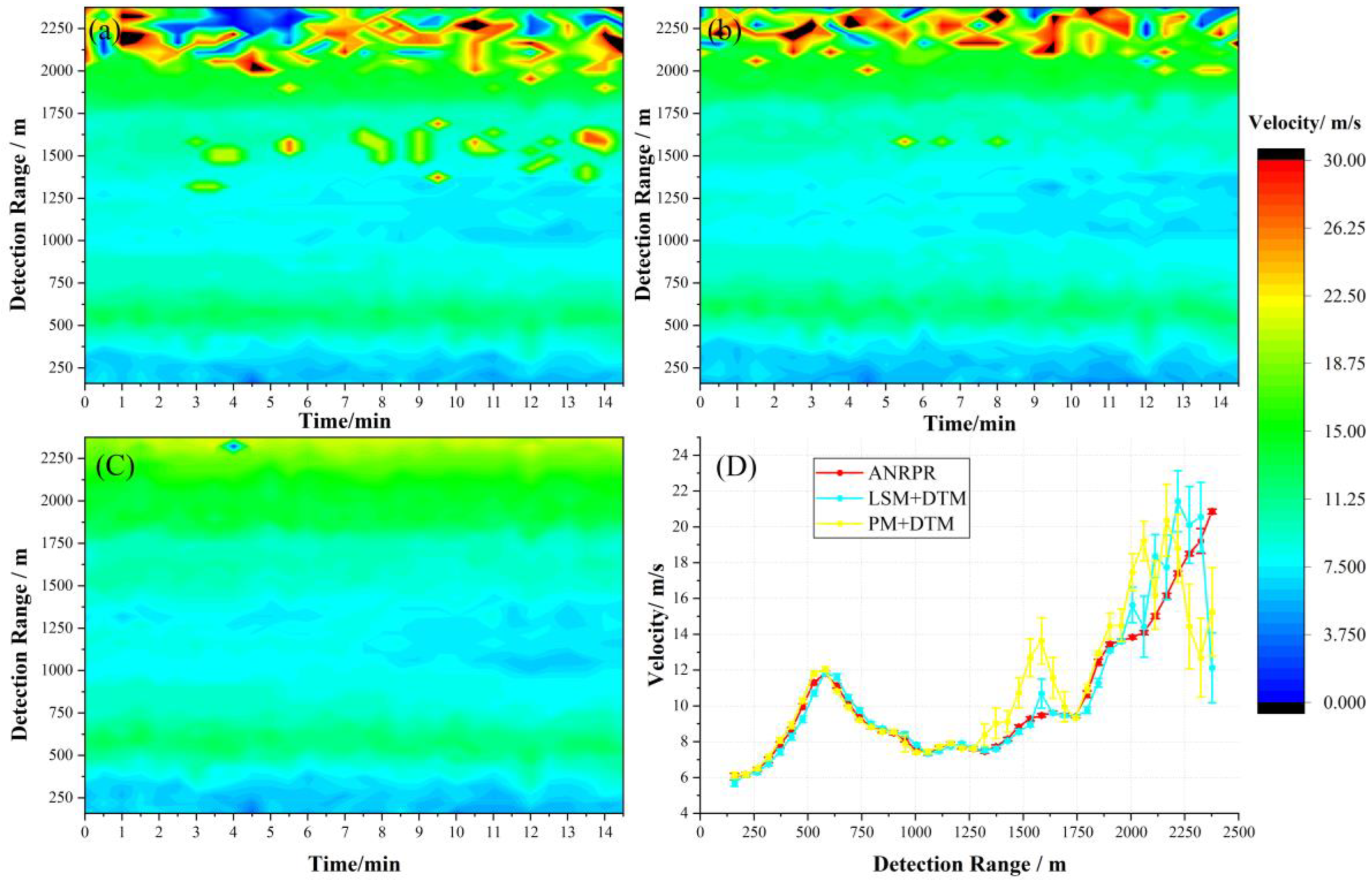
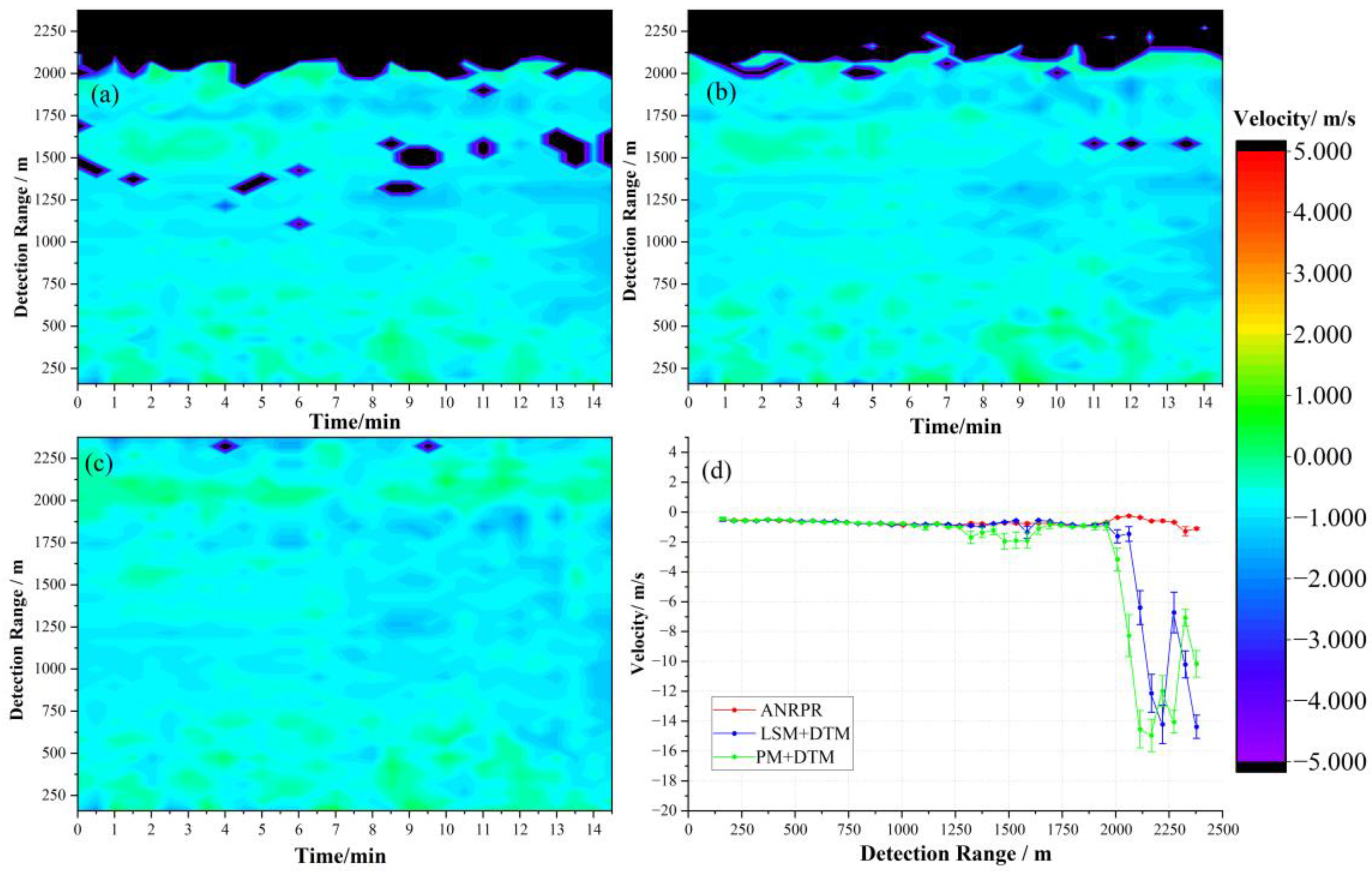
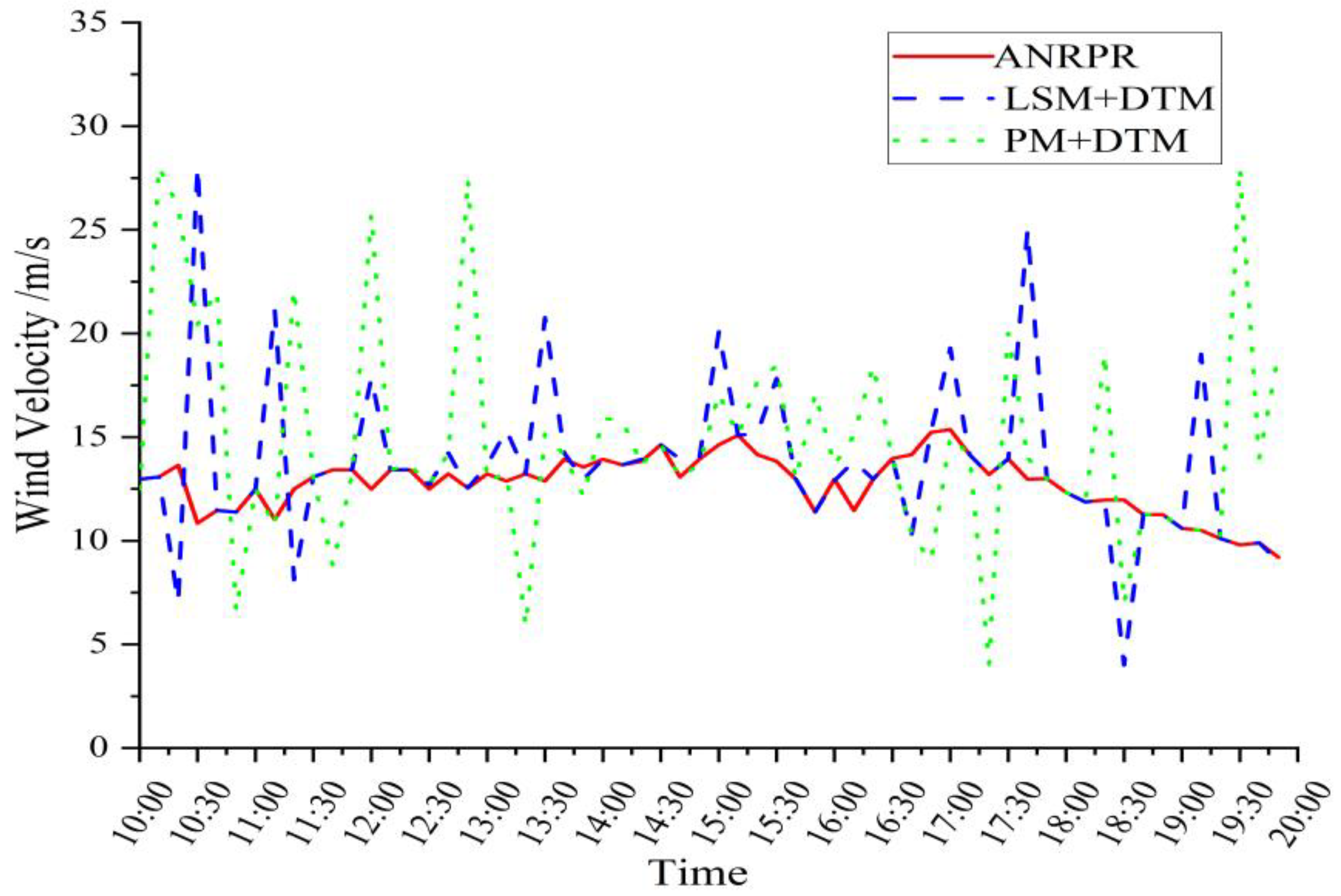
4.1. ANRPR Algorithm Analysis
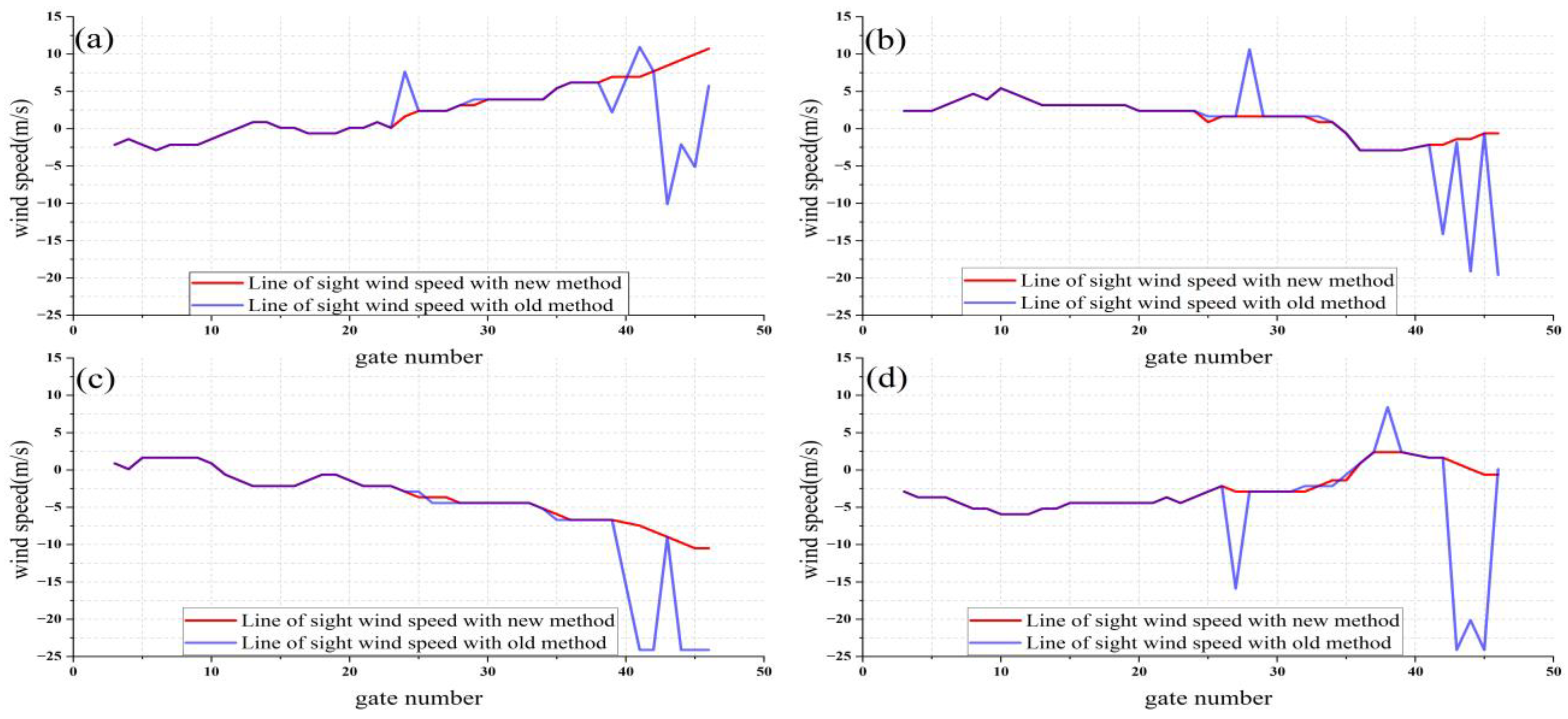
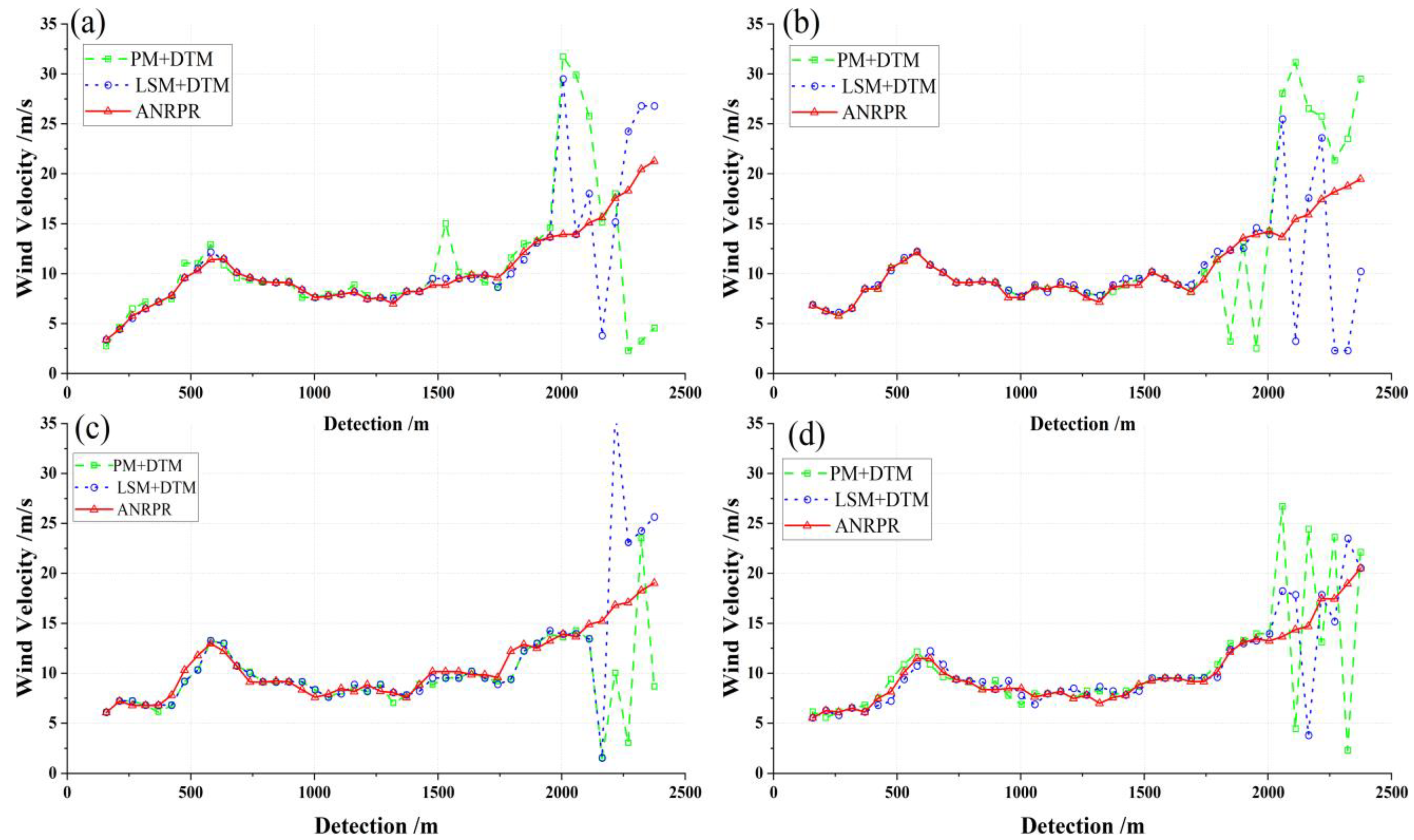
4.2. Wind-Field Inversion Based on ANRPR Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotake, N.; Sakamaki, H.; Imaki, M.; Miwa, Y.; Ando, T.; Yabugaki, Y.; Enjo, M.; Kameyama, S. Intelligent and compact coherent Doppler lidar with fiber-based configuration for robust wind sensing in various atmospheric and environmental conditions. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 20038–20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, M.; Xia, H.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Shentu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Dou, X.; Pan, J.W. All-fiber upconversion high spectral resolution wind lidar using a Fabry-Perot interferometer. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 19322–19336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Shentu, G.; Shangguan, M.; Xia, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Pelc, J.S.; Fejer, M.M.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Long-range micro-pulse aerosol lidar at 1.5 mum with an upconversion single-photon detector. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhme, G.S.; Fadigas, E.A.; Martinez, J.R.; Tassinari, C.E.M. Analysis of the Use of Remote Sensing Measurements for Developing Wind Power Projects. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2019, 141, 41005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Yim, S.H.L.; Haywood, J.; Osborne, M.; Chan, J.C.S.; Zeng, Z.L.; Cheng, J.C.H. Characteristics of Heavy Particulate Matter Pollution Events Over Hong Kong and Their Relationships With Vertical Wind Profiles Using High-Time-Resolution Doppler Lidar Measurements. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 9609–9623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dai, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Yin, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, S.; Wang, X. Coherent high-spectral-resolution lidar for the measurement of the atmospheric Mie-Rayleigh-Brillouin backscatter spectrum. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 38060–38076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Bi, D.C.; Chen, W.B. All fiber pulsed coherent lidar development for wind profiles measurements in boundary layers. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2014, 12, 72801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, J.; Gribben, B.; Stein, D.; Würth, I. Floating lidar as an advanced offshore wind speed measurement technique: Current technology status and gap analysis in regard to full maturity. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Energy Environ. 2017, 6, e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumchean, S.; Sharma, A.; Seed, A. Radar rainfall error variance and its impact on radar rainfall calibration. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, C.J.; Olsson, F.; Letalick, D.; Harris, M. All-fiber multifunction continuous-wave coherent laser radar at 1.55 μm for range, speed, vibration, and wind measurements. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.N.; Roberts, P.J.; Eacock, J.R.; Harris, M. Analysis of the performance of a coherent pulsed fiber lidar for aerosol backscatter applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 6442–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyon, J.Y.; Koch, G.J. Novel nonlinear adaptive Doppler-shift estimation technique for the coherent Doppler validation lidar. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Guo, P.; Li, L.; Chen, H. Noise modeling by the trend of each range gate for coherent Doppler LIDAR. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 63109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y. Wind profiling for a coherent wind Doppler lidar by an auto-adaptive background subtraction approach. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarman, K.H.; Daly, D.S.; Anderson, K.K.; Wahl, K.L. A new approach to automated peak detection. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 69, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.H.; Huang, R.; Qi, R.J.; Duan, C.A. Extraction of Structural and Chemical Information from High Angle Annular Dark-Field Image by an Improved Peaks Finding Method. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, H.; Mahjoob, M.; Farahabadi, E.; Farahabadi, A. R peak detection in electrocardiogram signal based on an optimal combination of wavelet transform, Hilbert transform, and adaptive thresholding. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2011, 1, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, F.; Su, J.S.; Wei, X.W.; Qin, R.S. Comparisons on Kalman-Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation Algorithms of Power Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 51035–51043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Smoothed accumulated spectra based wDSWF method for real-time wind vector estimation of pulsed coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhai, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; et al. Wind turbine wake visualization and characteristics analysis by Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A762–A780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, S.; Ando, T.; Asaka, K.; Hirano, Y.; Wadaka, S. Performance of Discrete-Fourier-Transform-Based Velocity Estimators for a Wind-Sensing Coherent Doppler Lidar System in the Kolmogorov Turbulence Regime. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3560–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, M.; Wang, C.; Xia, H.; Shentu, G.; Dou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.-W. Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry for fast detection of dynamic strain incorporating double-edge technique. Opt. Commun. 2017, 398, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Su, R.; Fang, J. Data Processing and Analysis of Eight-Beam Wind Profile Coherent Wind Measurement Lidar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xia, H.; Wei, T.; Wang, L.; Yue, B.; Wu, Y. Identifying cloud, precipitation, windshear, and turbulence by deep analysis of the power spectrum of coherent Doppler wind lidar. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 37406–37418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banakh, V.A.; Brewer, A.; Pichugina, E.L.; Smalikho, I.N. Measurements of wind velocity and direction with coherent Doppler lidar in conditions of a weak echo signal. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2010, 23, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Sarma, T.V.C.; Regeena, M.L. Estimation of Doppler Profile Using Multiparameter Cost Function Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Y. Field Verification of Vehicle-Mounted All-Fiber Coherent Wind Measurement Lidar Based on Four-Beam Vertical Azimuth Display Scanning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Boss, J.; Wolf, M. An Efficient Algorithm for Automatic Peak Detection in Noisy Periodic and Quasi-Periodic Signals. Algorithms 2012, 5, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
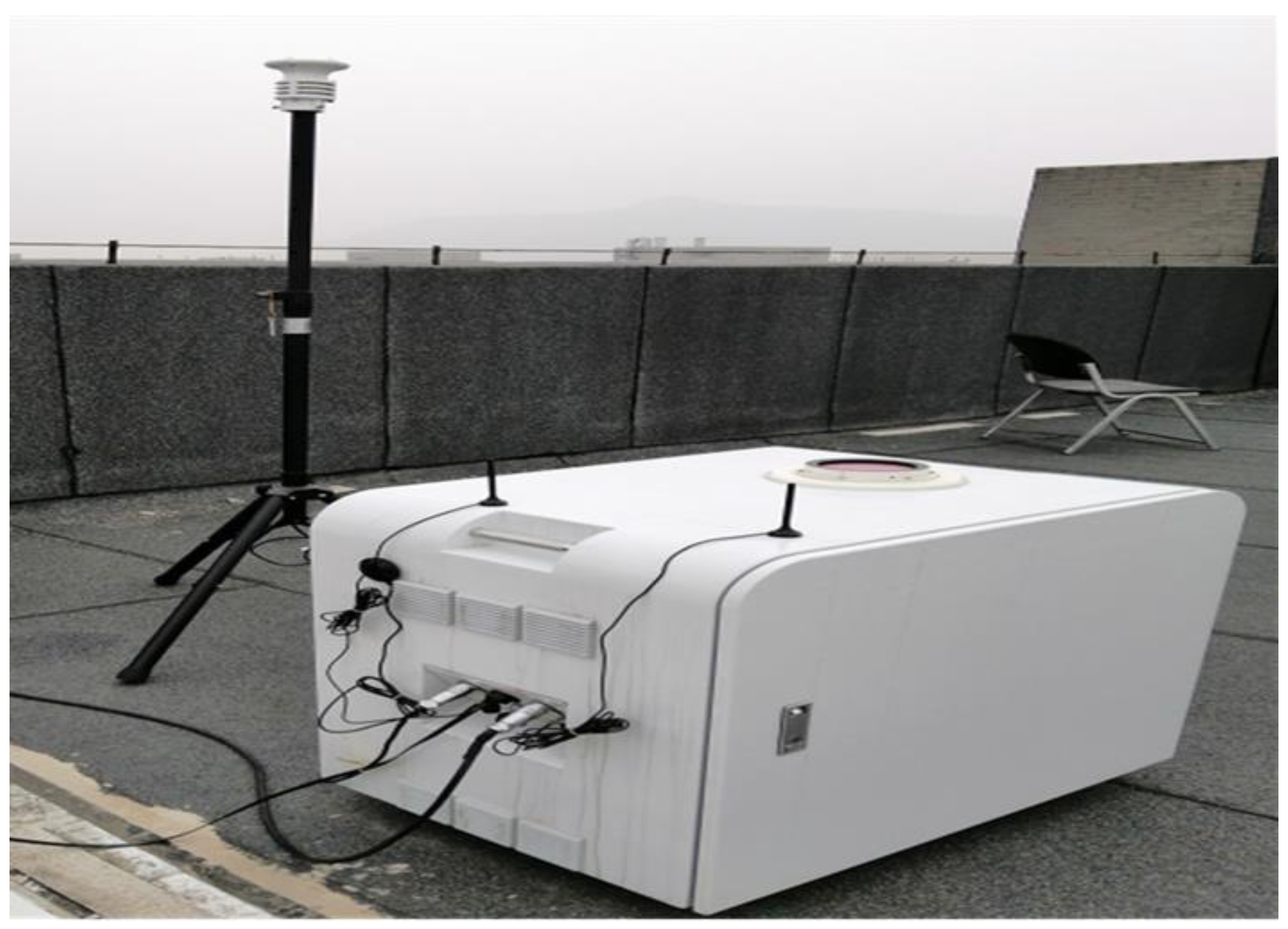

| Component | Qualification | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitter | Wavelength | 1550 nm |
| Pulse energy | 145 μJ | |
| Pulse repetition | 10 kHz | |
| Pulse width | 400 ns | |
| Transceiver | Laser mode | Pulse |
| Scan mode | Conical | |
| Elevation angle | 60° | |
| Start angle | 0° | |
| Step angle | 90° | |
| Data Acquisition | Sampling frequency | 1 GHz |
| Sampling points | 400 | |
| Range resolution | 60 m | |
| Blind range | 60 m | |
| Gate number | 128 |
| Method | Application Of Lidar Data | Noise Reduction | Peak Retrieval |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM [12] | |||
| LSM [13] | |||
| DTM [16] | |||
| DCM [15] | |||
| ANRPR |
| Height(m) | Horizontal Wind Velocity Correlation Based on ANRPR | Horizontal Wind Velocity Correlation Based on LSM+DTM | Horizontal Wind Velocity Correlation Based on PM+DTM | Horizontal Wind Direction Correlation Based on ANRPR | Horizontal Wind Direction Correlation Based on LSM+DTM | Horizontal Wind Direction Correlation Based on PM+DTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 0.9556 | 0.9442 | 0.9202 | 0.9514 | 0.9410 | 0.9257 |
| 200 | 0.9458 | 0.9332 | 0.9174 | 0.9421 | 0.9356 | 0.9210 |
| 250 | 0.9302 | 0.9101 | 0.8921 | 0.9287 | 0.9241 | 0.9142 |
| 300 | 0.9278 | 0.9076 | 0.8842 | 0.9217 | 0.9102 | 0.8987 |
| 350 | 0.9203 | 0.8962 | 0.8729 | 0.9129 | 0.8981 | 0.8845 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Luo, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced Wind-Field Detection Using an Adaptive Noise-Reduction Peak-Retrieval (ANRPR) Algorithm for Coherent Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010007
Li Q, Zhang X, Feng Z, Chen J, Zhou X, Luo J, Sun J, Zhao Y. Enhanced Wind-Field Detection Using an Adaptive Noise-Reduction Peak-Retrieval (ANRPR) Algorithm for Coherent Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingsong, Xiaojie Zhang, Zhihao Feng, Jiahong Chen, Xue Zhou, Jiankang Luo, Jingqi Sun, and Yuefeng Zhao. 2024. "Enhanced Wind-Field Detection Using an Adaptive Noise-Reduction Peak-Retrieval (ANRPR) Algorithm for Coherent Doppler Lidar" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010007
APA StyleLi, Q., Zhang, X., Feng, Z., Chen, J., Zhou, X., Luo, J., Sun, J., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Enhanced Wind-Field Detection Using an Adaptive Noise-Reduction Peak-Retrieval (ANRPR) Algorithm for Coherent Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere, 15(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010007





