Abstract
There is a need for monitoring air pollution associated with black carbon (BC) using a passive monitor is required in remote areas where the measurements are absent. In this pilot study, we developed a quantitative method to determine dry deposition submicron BC using dual-wavelength ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. Furthermore, we measured the levels of dry deposition BC on plant leaves from 30 plant species located in urban Nanjing using the established method. The oxidative potential of BC on plant leaves as passive bio-monitoring samplers was assessed. The concentrations of black carbon (BC) on tree leaves varied from 0.01 to 1.6 mg m−2. Significant differences in levels of BC across leaves from different tree types were observed. The values of oxidative potential in deposited particles of leaf samples were observed to be in the range of 33–46 nmol min−1 mg−1 using the dithiothreitol (DTT) assay and 18–32 nmol min−1 mg−1 using the ascorbic acid (AA) assay, respectively. In comparison, the oxidative potential of BC-dominated mass in water extracts of leaf samples was in the range of 5–35 nmol min−1 mg−1 measured using the DTT assay and 2 to 12 nmol min−1 mg−1 using the AA assay, respectively. We found variations in the levels of OP across the leaves of different tree types were not large, while the levels of OP in terms of BC-dominated mass varied greatly. These results indicate that the established method with dual-wavelength ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy could provide a simple tool to determine submicron BC in plant leaves of the passive monitor.
1. Introduction
The United Nations proposed Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of target 3.9, which target significantly reducing the amounts of diseases and premature death due to exposure to air, water, and soil pollution [1]. Black carbon (BC) is released from the incomplete combustion of fuels such as coal, wood, and fossil fuels [2,3], which could absorb visible light in the atmosphere and thus exert potentially negative effects on climate, which has been regarded as an important contributor to global warming [2,4,5]. Furthermore, BC can be transferred into the cardiovascular system of human beings and lead to many respiratory diseases due to the presence of harmful reactive oxygen species on the surface [6,7,8].
Globally, BC emissions from anthropogenic sources were estimated to be 4400 Gg in 2000 [9]. China contributed to the largest emissions around the world, which accounted for about 30% of global emissions [10]. The largest source contribution to BC in China was residential combustion (~55%), followed by industrial emissions (~30%), transportation (~10%) and power production (~2%) [10]. Over half of the population lives in cities in China, and this number is expected to increase over the next several decades [10]. Thus, cities are often hotspots of air pollution [11,12]. Urban forest parks in cities provide physical activity spaces, as well as reduce air pollution and noise from anthropogenic sources substantially [13,14]
Terrestrial plants can alleviate air pollution by acting as sinks of particulate matter (PM) [15,16]. Novak et al. [17] illustrated that trees in urban areas across the United States can absorb 711,000 metric tons of air pollutants every year (O3, PM10, NO2, SO2, and CO). Cai et al. [18] documented that the average deposition of PM on leaves was estimated to be 1.71 ± 0.05 g m−2 wk−1 after summarizing 150 studies conducted in 15 countries from 1960 to 2016. Terrestrial trees can considered an effective low-cost, low-energy strategy for removing BC from the atmosphere [19,20]. Some large-scale experiments, including the European Cooperative Air Quality Assessment Network using Bio-indicator Plants and the European Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition Survey, have been conducted in European countries to measure the metal and particulate matter deposited on leaves in the air [21,22]. A study showed that oak trees in Denton, Texas, can accumulate BC ranging from 160 to 299 mg m−2 canopy per year [20]. Previous research has shown that submicron soot particles emitted from traffic emissions and fuel combustions can be captured by the leaves of Platanus acerifolia trees [19]. Furthermore, the adsorption mechanism between carbon black serving as a model compound of soot particles and straight chain alkanes (C36H74) as a leaf wax model was studied [23]. Our prior study found the hydrogen bonding between hexatriacontane wax and soot resulted in the adsorption of BC on the leaf surface, and then soot particles could be captured and penetrate the mechanical barrier of the stomata of the sycamore leaves and ultimately migrate to the mesophyll system [23].
In the ambient environment, the current method for measuring submicron BC includes a multi-wavelength aethalometer and soot-particle aerosol mass spectrometer [24,25]. These two methods have been widely used to measure real-time submicron BC in the ambient air worldwide [26]. On the other hand, the leaves of trees are commonly adopted to bio-monitor air pollution in areas where measurement sites are scarce [19,27]. However, a method for measuring the BC on tree leaves of bio-monitoring samplers is absent. The water-soluble brown carbon in particulate matter contributes to the ultraviolet–visible absorption varying from 200 to 550 nm [28]. Therefore, the measurement of BC on filter samples is normally performed using thermo–optical methods to avoid interference from water-soluble brown carbon [29]. Thermo–optical methods are incapable of determining the BC on the leaves of plants [30]. These interferences may result in a large bias in the measurements of BC collected using bio-monitoring tools. Ambient water-soluble brown carbon mainly includes humic-like fluorescence substances and a mixture of airborne amino acids [8,31]. Some prior studies have shown that leaves can uptake water-soluble brown carbon and different amino acids via stomata within 30 min serving as nutrients to maintain growth [32,33,34,35]. Our prior study also examined the interaction process between the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) at high concentrations and tree leaves using whole-transcriptome analysis [36]. Based on the analysis of the significant differentially expressed genes, seven main pathways play roles in absorbing high concentrations of PAHs on the surface of plant leaves [36]. Consequently, the tree leaves could retain the BC on their wax layers [23]. Due to the characteristic of selective adsorption on water-soluble brown carbon by leaves, ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy may serve as an option to measure the BC in tree leaves [37]. During the periods of leaf development and expansion, leaves could emit methanol in the range from 10.0 to 26.8 μg g−1 [38]. Zhang et al. [39] also found that the leaves of four plants could emit a great amount of nanoparticles with sizes ranging from 50 to 300 nm, which are composed of sulfate, phosphate, and metals. In contrast, few studies illustrated that inorganic carbon (e.g., BC) could be emitted from the leaves of plants to date. Thus, it is supposed that the leaves of trees could retain BC in the environment and not emit BC due to the physiological functions of leaves.
The health risks associated with reactive oxygen species on the surface of BC can be assessed using oxidative potential (OP) assays [40]. Two common assays (i.e., the DTT assay and AA assay) are widely used to characterize the OP of carbonaceous particles and are linked to various health effects [6,41]. Previous studies have shown that the OP of aged soot particles increases by 2 to 7 times compared with fresh particles [42]. Soot particles originate from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass, which are composed of spherical carbon particles, including internal carbon nuclei and externally bound organic matter [42]. The enhancement of aging particle OP can be attributed to the structural changes in nanoscale soot particles after visible light irradiation, which is linked with the formation of single-bond oxygen groups on aging particles [42]. Considerable studies have investigated the OP levels of ambient particles across the world [40]. Limited studies have been conducted to illustrate the OP levels of dry-deposited BC on leaves. Since it is not documented that BC is emitted from the leaves of trees due to physiological functions, the measurements of OP levels in this study refer to the OP levels associated with dry-deposited BC from the environment.
This study aims to measure the submicron BC collected from the leaves of bio-monitoring trees. We used dual-wavelength ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy to determine the submicron BC in water extracts of leaves. Then, the OP of water extracts was measured using DTT and AA assays. The OP levels in water extracts of leaves were compared with OP levels of submicron BC, which can identify the contribution of submicron BC to the OP levels of deposited PM on leaves. This pilot study could provide a robust method to bio-monitor BC from the atmosphere to reduce the air pollution associated with BC for achieving the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collections
The leaf samples were collected in the urban area of Nanjing from June to July (Summer) 2023, respectively. The collection of leaf samples was conducted based on previous studies and under the National Atmospheric Deposition Programme (NADP) monitoring initiative protocol [19,20]. Briefly, the leaf samples were taken from 30 species of plants, which are Eucommia ulmoides, Koelreuteria paniculata, Osmanthus fragrans, Buddleja Davidii, Platanus acerifolia, Fatsia japonica, Hedera Helix, Eriobotrya japonica, Cerasus yedoensis, Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn., Hydrangea macrophylla (Thunb.) Ser., Euonymusalatus (Thunb.) Sieb., Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait., Photinia serrulata Lindl, Aucuba japonica, Cercis glabra, Iris tectorum Maxim, Aucuba japonica Variegata, Canna indica, Liriodendron tulipifera, Ligustrum lucidum, Cinnamomum camphora,, Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu, Yulania denudate, White Mulberry, Hederanepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, Pseudasasa japonica, Hosta ventricosa., Trachycarpus fortune, and Viburnum awabuki K. Koch. A respective sample was created from a mixture of four parallel leaves in one tree throughout the growing season. For each species, we sampled three respective trees separately. The duplicate tree is 3–5 m in height and 30–50 cm in trunk diameter and lives in environmental conditions with similar conditions of water, soil, and wind. Leaves were sampled from the south-facing side of each tree between 135 and 225 degrees, where dominant emission sources (mobile source) of BC are located. The sampling periods exclude rainy days because rain could wash off the deposited BC on leaves and add new materials contained in raindrops [20]. The collection of mature leaf samples with similar leaf ages starts three days after the rain. All the sampled trees were situated in the same location for three years or longer [19]. We harvested the leaves from different types of trees using the same selection criterion. We collected approximately 20 g of leaves for analysis in each leaf sample. A total of 90 samples were collected from each species for analysis.
2.2. Water Extracts
Before extraction, the area of the leaf was measured using a leaf-area meter (Yaxin, Beijing). Additionally, the leaf samples were extracted with mixtures of 50 mL de-ionized water and 0.1 g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (NH4)2H2PO4. The extraction was carried out three times using a centrifuge table with 200 rpm. Each time lasts for 15-min. The water extracts were stored at 4 °C for 24 h. Then, the micrometer-size particles in the extracts were removed from water extracts using a 0.22 μm PTFE syringe filter before the analysis [20]. In addition, we prepared an environmentally relevant water-soluble brown carbon solution (5 μg mL−1) using humic acids and a mixture of amino acids (i.e., glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, aspartate, glutamate, serine, and threonine) at a mass ratio of 1:1. The humic acid solution was dissolved in 100 mL of sodium hydroxide with the use of 0.005 g of humic acid. Then, the solution was adjusted to pH 7.0 using 10 mM hydrochloric acid.
2.3. Measurements of Submicron Soot and BC
The extraction solution was then aliquoted into two equal portions. The levels of submicron soot in water extracts were determined using a Multi N/C3000 analyzer (Analytik Jena, Jena City, Germany). The details of the method are illustrated in a prior study [19]. In brief, the submicron soot in water extracts was pumped into a Multi N/C3000 analyzer and then converted to CO2 at 150 °C with a mixture of 10% H3PO4. The CO2 was then quantitatively measured using a non-dispersive infrared detector in a Multi-N/C 3000 analyzer. The detection limits for soot samples were found to be 0.05 μg mL−1, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) was 3.2 ± 0.4%. A quality control experiment was carried out with the spiked experiments. The average recoveries of soot on leaves ranged from 90–95%, and the relative standard deviation was lower than 4%.
The determination of submicron BC in water extracts was performed using the Chinese national standard method (GB34323-2017) [37]. First, the standard solutions were prepared using 0.5–200 μg mL−1 of nanoscale carbon black. The nanoscale carbon black in a diameter ranging from 3 nm to 5 nm at N234 grade is commercially produced by Alfa Aesar Chemical., (Haverhill, MA, USA), which is used as an additive to rubber tires [43]. We used the nanoscale carbon black at N234 grade as a proxy for the BC to prepare the standard solution in this study because carbon black at N234 grade pertains to BC [44,45]. Then, we recorded the ultraviolet–visible light absorbance of submicron BC at an interval of 0.1 nm from 400 nm to 410 nm using a Perkin-Elmer Lambda950 spectrophotometer (Waltham, MA, USA). We adopted a dual-wavelength ultraviolet–visible method to eliminate the background interferences [46]. The differences in the ultraviolet–visible absorption spectra at 405 nm and 410 nm versus the levels of submicron BC in the extraction solution were plotted (Figure 1). Under optimal conditions, the coefficients of BC determination were found to be higher than 0.99 with the linear range from 0.5 to 200 μg mL−1. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) measured varied from 1.8 to 5.0%, and the limit of detection was 0.1 μg mL−1. We carried out the spiked experiments for the quality control of the established method. The average recoveries of BC on leaves varied from 87% to 97%, and the relative standard deviation was lower than 5%.
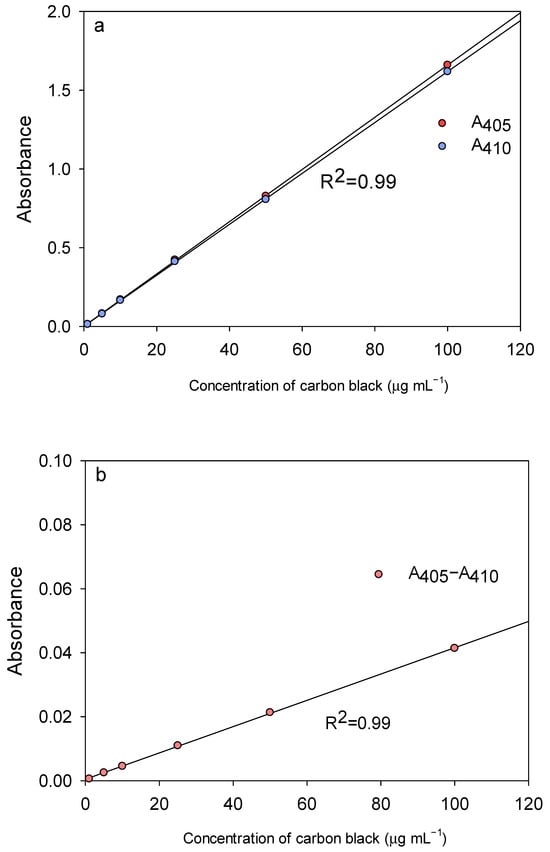
Figure 1.
(a) The absorption of BC recorded at 405 nm and 410 nm are plotted versus the levels of BC. (b) The difference between 405 nm and 410 nm is plotted versus the levels of BC.
2.4. OP Assay
The DTT depletion rate was investigated using water extracts of leaf samples using 10 mM DTT. The 10 mM DTT was prepared in a phosphate buffer (100 mM) at a pH of 7.4, which was stored in a water bath at 37°C. The depletion rate of DTT was measured within 30 min. After that, 100 μL of DTT mixed with water extracts of leaf samples was added to 25 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid for quenching the reaction. Then, we added 5,5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB) at 0.24 mM and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acetic acid (EDTA) at 20 mM to 100 mL of 0.4 M Tris-HCl solution. The pH was maintained at 8.9 to react with the massive DTT [6]. The concentration of products between DTNB and massive DTT was determined at 412 nm. The mean depletion rate of DTT over a 30 min course was calculated using Equation (1).
where DTTm is the average consumption rate (nmol min−1 m−3); Co is the beginning concentration of DTT; Ct is the concentration of DTT after the 30 min reaction; m refers to sample mass added in the reaction system. We used naphthoquinone at 0.2 µg mL−1 as a positive control to verify the DTT depletion experiment [6]. The average levels of positive controls (n = 7) were found to be 0.02 ± 0.01 nmol min−1 mg−1. In addition, 0.1 µg mL−1 of nanoscale BC was measured for OP using a DTT assay. The final DTTm in the water extracts of leaf samples was calculated with the differences between the levels measured by the DTTm of the sample and the blank samples.
We determined the depletion rate of AA with the water extracts of leaf samples. The loss rate of the experiment was performed with 10 mM AA and 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH = 7) at 37 °C [41]. The depletion rate of AA was measured at 265 nm within 30 min. The mean depletion rate of AA in 30 min was estimated using Equation (2).
where AAm refers to the mean consumption rate (nmol min−1 m−3); Co refers to the beginning concentration of AA; Ct refers to the concentration of AA after a 30 min reaction; m is the sample mass added in the reaction system. We chose 0.2 µg mL−1 of naphthoquinone as a positive control to verify the AA depletion experiment. The average levels of the positive controls (n = 7) were found to be 0.05 ± 0.01 nmol min−1 mg−1. We also determined OP levels of 0.1 µg mL−1 of nanoscale BC for comparisons.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The measured levels are shown as the mean and standard deviation with three independent experiments. We used the ANOVA test to compare these differences in mean concentrations across different groups [47]. We expressed the significant differences at an adjusted p-value of <0.05. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS V26.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of BC onLeaves
Figure 1 presents the linear equation between BC ranging from 0.5–200 μg mL−1 and absorbance of ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. As shown in Figure 1a, the concentrations of BC were linear with the absorbance of ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy at 405 nm and 410 nm (R2 = 0.99), respectively. Notably, the ultraviolet–visible absorption of water-soluble brown carbon ranged from 200 to 550 nm [28]. We adopted a wavelength range of 400–410 nm to determine the levels of BC on leaves because tree leaves serve as the specific samplers for absorbing water-soluble brown carbon (i.e., humic acids, glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, aspartate, glutamate, serine, and threonine) and retaining the ambient BC (Figure S1). To minimize the matrix effects, we adopted the dual-wavelength ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy method to quantify the BC on leaves (Figure 1b) [46]. The differences between 405 nm and 410 nm were associated with the levels of BC in the range of 0.5 to 200 μg mL−1 in water extracts. The coefficient of determination was found to be higher than 0.99, and the limit of detection was 0.1 μgmL−1.
3.2. Concentration of BC onLeaves across Species
Using the established method, we measured the BC and soot in water extracts of leaves from 30 types of plants. The concentration of BC was observed to vary from 0.01 to 1.6 mg m−2, while the levels of soot were found to range from 0.02 to 1.8 mg m−2 (Figure 2). The levels of soot in water extracts of leaves using a Multi N/C3000 analyzer were greater than the levels of BC in water extracts of leaves using an ultraviolet–visible light analyzer because the method to determine soot using a Multi N/C3000 analyzer could not avoid the interference from the organic layer on the surface of BC. Therefore, the values derived from a Multi N/C3000 analyzer were comparably higher than those derived from an ultraviolet–visible light analyzer. The average level of BC on leaves of Platanus acerifolia was 0.5 mg m−2, which was comparable with our measured results of dry deposited BC on leaves of Platanus acerifolia [19]. Rindy et al. determined the concentration of elemental carbon in leaves of Oak species in Texas, United States, with the use of a thermal optical carbon analyzer [20]. The findings from our study are incapable of comparing with the level of elemental carbon in leaves conducted by Rindy et al. [20] because the methods for quantifying the levels of soot particles are different. We observed the significant differences between BC and soot on leaves across types of plants. The average levels of BC and soot on leaves of some types of plants, including Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait., Cercis glabra, Canna indica and Liriodendron tulipifera were found to be lower than 0.02 mg m−2, while the average levels of BC and soot on leaves of some types of plants, including Eucommia ulmoides, Hedera Helix, Cerasus yedoensis, Euonymus alatus (Thunb.) Sieb., Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu, and Viburnum awabuki K. Koch. were observed to be greater than 1.4 mg m−2. The large variations in BC and soot on leaves across species may be ascribed to the differences in the accumulation of wax layers in leaves across species [23]. This finding indicated that some types of trees with relatively greater amounts of dry-deposited BC and soot may be properly used as bio-monitors of BC and soot relative to other types of trees with a small amount of dry-deposited BC and soot.
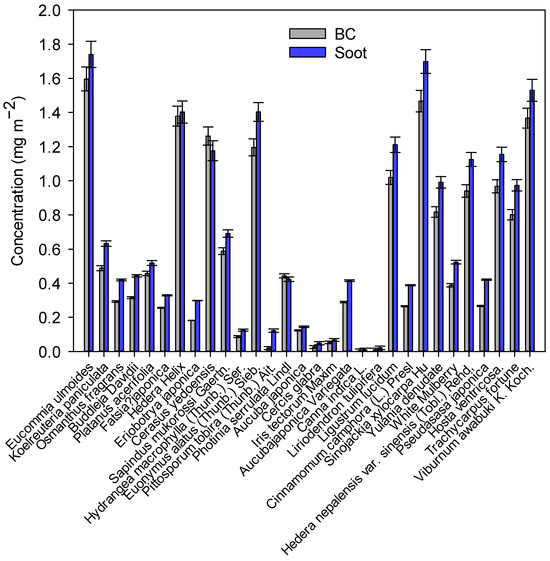
Figure 2.
The average concentration of deposited BC and soot on the leaves of 30 species of plants.
The levels of BC on tree leaves in this study are unable to quantitatively assess the BC emission near the studied sites because concentration data regarding ambient BC in the air is absent. The associations between the levels of BC on tree leaves and the ambient level of BC could provide an insightful understanding of the transfer amounts of BC from the ambient environment to the tree leaves [48,49,50]. In addition, the transfer amounts of BC from the ambient environment to tree leaves will also be influenced by multiple environmental and meteorological factors (rain, wind speed, and direction), as well as the physiological condition of plants [48,50,51]. The limitation of this study is that it is incapable of elucidating the influences of multiple environmental and meteorological factors, as well as the physiological condition of plants on the transfer amounts of BC from the ambient environment to the tree leaves [48,50,51]. Our study strives to compare the levels of BC on leaves across the species under relatively same conditions. The findings showed that some types of plants (Eucommia ulmoides, Hedera Helix, Cerasus yedoensis, Euonymus alatus (Thunb.) Sieb., Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu, and Viburnumawabuki K. Koch.) could be used as the bio-monitoring tree for assessing the concentration of dry deposition of BC.
3.3. Oxidative Potential
As shown in Figure 3, we measured the OP of water extracts of leaves. The levels of OP in the extract solution determined using the DTT assay were observed to be from 33 to 46 nmol min−1 mg−1. The levels of OP measured using the AA assay varied from 18 to 32 nmol min−1 mg−1. The studies about the OP of deposited particles on leaves are scarce. Therefore, our study is unable to compare the OP results with other prior studies. While some studies have documented the OP of ambient fine particles, our results were comparable with the results in cities of China (~20–100 nmol min−1 mg−1) and other regions (~1–80 nmol min−1 mg−1) around the world [52,53,54]. For example, Daellenbach et al. [55] found that OP levels of PM10 determined using the DTT assay ranged from 1 to 5 nmol min−1 m−3 over Europe. Xu et al. [56] show that OP levels of PM2.5 measured using the DTT assay varied from 10 to 150 pmol min−1 m−3, and OP levels of PM2.5 determined using the AA assay in the range from 5 to 20 pmol min−1 m−3 over Canada.
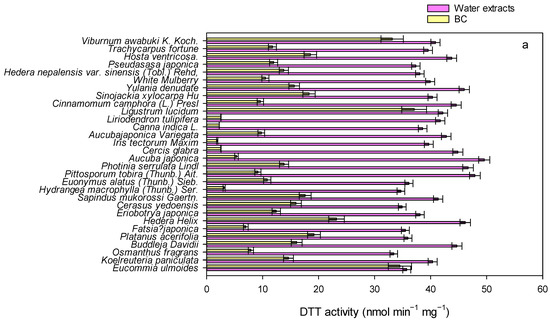
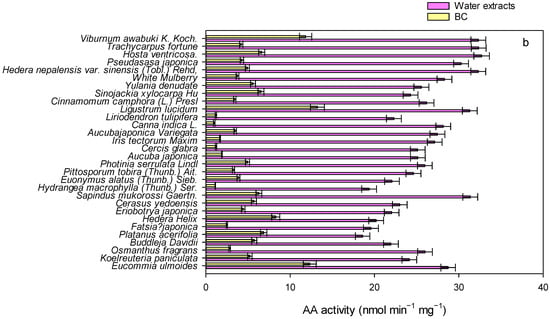
Figure 3.
The oxidative potential of water extracts of leaves and BC-dominated mass measured using the DTT (a) and AA (b) assay.
To estimate the oxidative potential of BC-dominated mass in the water extracts, we measured the OP of BC using the DTT and AA assays, respectively. The OP associated with BC was 70 ± 4 nmol min−1 mg−1 and 25 ± 3 nmol min−1 mg−1 with the DTT and AA assays, respectively. Using the measured values of BC, we calculated the OP associated with BC mass in the extract solution across species. For the DTT assay, the levels of BC-dominated mass ranged from 3 to 37 nmol min−1 mg−1, which accounted for 5–95% of the OP of water extracts. The levels of OP in terms of BC mass determined using the AA assay were in the range of 1–12 nmol min−1 mg−1, which contributed to approximately 7–42% of the OP of water extracts. The acellular assays, including the DTT assay and AA assay, target different reactive oxygen species and diverse sensitivities to specific chemical compounds [57]. It is reported that the DTT assay is sensitive to carbonaceous compounds and some soluble transition metals, while the AA assay mainly responds to transition metals [57]. We adopted two acellular assays to assess the OP of deposited particles on leaves because it could provide more comprehensive information to understand the health risks of deposited particles on leaves [57]. The levels of OP in terms of BC mass using the AA assay were found to be lower than those determined using the DTT assay because the DTT assay is more sensitive to carbonaceous compounds than the AA assay [57]. Since the OP was influenced by the mixtures of chemical compounds, including carbonaceous compounds, water-soluble ions, metals, and carbonaceous aerosols in ambient particles [40,54], the large differences in the levels of OP in terms of BC mass between the AA assay and DTT assay demonstrated large variations in the chemical compositions of deposited BC particles on leaves across tree species. Since the heterogeneity of sources obtained with the different OP assays for a given ambient PM exposure, the combination of OP methods characterized by different chemical mechanisms must be rationally evaluated as part of the health risk assessment strategy [57].
4. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this study is the first to determine the dry deposition of BC on leaves using a low-cost method and measure the associated oxidative potential using two in vitro assays. Our findings indicate that large differences in the levels of BC were found on leaves across tree species, indicating different dry-deposited characteristics of leaves across species. Some types of plants (Eucommia ulmoides, Hedera Helix, Cerasus yedoensis, Euonymus alatus (Thunb.) Sieb., Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu, and Viburnum awabuki K. Koch.) could be used to monitor the dry deposition of BC as bio-monitor. The oxidative potential in terms of the dry deposited mass of leaves measured using the DTT and AA assays was comparable across tree types in this study. This result may indicate that similar public health risks exposed to dry deposited particles existed. In contrast, the large differences in oxidative potential based on BC-dominated mass on leaves were observed across tree types, demonstrating that different leaves of trees exhibited specific characteristics in adsorbing the chemical components of ambient particles. The findings of this study could be used as passive bio-tools of BC in areas where routine measurements of BC are lacking.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos15010127/s1, Figure S1: The concentration of humic acids and a mixture of amino acids (i.e., glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, aspartate, glutamate, serine, and threonine) at 5 μg mL−1 against time in leaves of three trees.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.L.; methodology, Y.X.; validation, Y.X.; formal analysis, Q.L.; investigation, Y.X.; resources, Y.X. and Q.L.; data curation, Y.X. and Q.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X. and Q.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.L.; visualization, Y.X. and Q.L.; supervision, Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the main text and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgiç, E.; Tuna Tuygun, G.; Gündüz, O. Development of an emission estimation method with satellite observations for significant forest fires and comparison with global fire emission inventories: Application to catastrophic fires of summer 2021 over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 308, 119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, T.; Olson, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Schauer, J.J. Temporal variations of black carbon during haze and non-haze days in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.; Bisht, G.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Huang, H.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R. A cleaner snow future mitigates Northern Hemisphere snowpack loss from warming. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, N.; Ding, A. Weakened Haze Mitigation Induced by Enhanced Aging of Black Carbon in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7629–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Oxidative Potential and Inflammatory Impacts of Source Apportioned Ambient Air Pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12920–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Schauer, J.J. Source apportionment of Beijing air pollution during a severe winter haze event and associated pro-inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, K.; Iwata, A.; Kiriya, M.; Yoshino, A.; Takami, A.; Matsuki, A.; Nishita-Hara, C.; Hara, K.; Hayashi, M.; Kaneyasu, N.; et al. Lung deposited surface area of atmospheric aerosol particles at three observatories in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bhardwaj, E.; Dong, R.; Jogani, R.; Jung, S.; Roden, C.; Streets, D.G.; Nina, M. Historicalemissionsofblackandorganiccarbonaerosolfromenergy-relatedcombustion, 1850–2000. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21, GB2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black Carbon Emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. New urban models for more sustainable, liveable and healthier cities post covid19; reducing air pollution, noise and heat island effects and increasing green space and physical activity. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of MERRA-2 Black Carbon Characteristics and Potential Sources over China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Sun, T.; Cao, T. Study on landscape quality assessment of urban forest parks: Take Nanjing Zijinshan National forest Park as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, A.N.; Sebastiani, A.; Gaglio, M.; Fano, E.A.; Manes, F. Assessment of air pollutants removal by green infrastructure and urban and peri-urban forests management for a greening plan in the Municipality of Ferrara (Po river plain, Italy). Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Das, S.; Roy, A.; Rakwal, R.; Jones, O.A.H.; Popek, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Sarkar, A. Interactive relations between plants, the phyllosphere microbial community, and particulate matter pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Bing, H.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L. Impacts of atmospheric particulate matter pollution on environmental biogeochemistry of trace metals in soil-plant system: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Xin, Z.; Yu, X. Spatio-temporal variations in PM leaf deposition: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Liu, Q.; Schauer, J.J. Direct measurement of the deposition of submicron soot particles on leaves of Platanus acerifolia tree. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindy, J.E.; Ponette-González, A.G.; Barrett, T.E.; Sheesley, R.J.; Weathers, K.C. Urban Trees Are Sinks for Soot: Elemental Carbon Accumulation by Two Widespread Oak Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10092–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, A.; Ansel, W.; Klumpp, G.; Belluzzo, N.; Calatayud, V.; Chaplin, N.; Garrec, J.P.; Gutsche, H.J.; Hayes, M.; Hentze, H.W.; et al. EuroBionet: A Pan-European Biomonitoring Network for Urban Air Quality Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2002, 9, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, W.; Nickel, S.; Schönrock, S.; Meyer, M.; Wosniok, W.; Harmens, H.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, J.; Barandovski, L.; et al. Spatially valid data of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and nitrogen derived by moss surveys for pollution risk assessments of ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10457–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tian, S.; Schauer, J.J. Penetration of submicron amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots in plant stomata, implication for the depollution of atmospheric soot particles. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Cho, C.; Rupakheti, M. Estimating contributions of black and brown carbon to solar absorption from aethalometer and AERONET measurements in the highly polluted Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Shen, Y.; Ge, S.; Chen, M. Characteristics and sources of ambient refractory black carbon aerosols: Insights from soot particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 185, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkens, T.A.; Boies, A.; Corbin, J.C.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Olfert, J.; Rogak, S.N. Overview of methods to characterize the mass, size, and morphology of soot. J. Aerosol Sci. 2023, 173, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.; Guidolotti, G.; Baldacchini, C.; Pallozzi, E.; Grote, R.; Nowak, D.J.; Calfapietra, C. Comparing i-Tree Eco Estimates of Particulate Matter Deposition with Leaf and Canopy Measurements in an Urban Mediterranean Holm Oak Forest. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6613–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; He, C.; Brown, Z.E.; Miljevic, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z. Light absorption properties of black and brown carbon during the prescribed burning season at an urban background site in Brisbane, Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 313, 120072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintér, M.; Ajtai, T.; Kiss-Albert, G.; Kiss, D.; Utry, N.; Janovszky, P.; Palásti, D.; Smausz, T.; Kohut, A.; Hopp, B.; et al. Thermo-optical properties of residential coals and combustion aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 178, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Patton, A.P.; Durant, J.L.; Frey, H.C. A review of factors impacting exposure to PM2.5, ultrafine particles and black carbon in Asian transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fu, P.; Ram, K.; Song, J.; Chen, Q.; Kawamura, K.; Wan, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, X.; Laskin, A.; et al. Fluorescence characteristics of water-soluble organic carbon in atmospheric aerosol. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Li, X.; Lian, F.; Wang, C.; White, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Nanoscale iron trioxide catalyzes the synthesis of auxins analogs in artificial humic acids to enhance rice growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasani, H.; Rajabzadeh, F.; Mozafari, H.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Water deficit stress impairment of morphophysiological and phytochemical traits of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) buffered by humic acid application. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 154, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaetxea, M.; De Hita, D.; Garcia, C.A.; Fuentes, M.; Baigorri, R.; Mora, V.; Garnica, M.; Urrutia, O.; Erro, J.; Zamarreño, A.M.; et al. Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot- growth. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, A.; Tas, T. Foliar application of humic acid at heading improves physiological and agronomic characteristics of durum wheat (Triticum durum L.). J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liu, Q.; Qu, J.; Yang, M.; Ma, Q.; Liu, J.; Shao, P.; Liu, Y. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis on the Leaves of Rosa chinensis Jacq. under Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Toxics 2023, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 34323-2017; Chinese National Standard Method, CarbonBlack—Determination of Light Transmittance of Water Dispersion-Specrophotometer Method. China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Nemecek-Marshall, M.; MacDonald, R.C.; Franzen, J.J.; Wojciechowski, C.L.; Fall, R. Methanol Emission from Leaves (Enzymatic Detection of Gas-Phase Methanol and Relation of Methanol Fluxes to Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Development). Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Luo, X.; Qiu, J.; Qi, Y. Plants emit sulfate-, phosphate- and metal-containing nanoparticles. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chan, C.K. The oxidative potential of fresh and aged elemental carbon-containing airborne particles: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.J.; Utinger, B.; Barth, A.; Paulson, S.E.; Kalberer, M. Iron and Copper Alter the Oxidative Potential of Secondary Organic Aerosol: Insights from Online Measurements and Model Development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13546–13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhu, T. Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Inside-to-Outside Oxidation of Soot Particles Triggered by Visible-Light Irradiation: Physicochemical Property Changes and Oxidative Potential Enhancement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8558–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yu, J.; He, W.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.; Li, G. Replacing commercial carbon black by pyrolytic residue from waste tire for tire processing: Technically feasible and economically reasonable. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, E.; Moon, H.; Son, H.; Hong, J.; Wi, E.; Kwon, J.-T.; Seo, D.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y. Estimation of the concentration of nano-carbon black in tire-wear particles using emission factors of PM10, PM2.5, and black carbon. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gong, H.; Peng, N.; Zhang, J.Z. Molecular Adsorption Mechanism of Elemental Carbon Particles on Leaf Surface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5182–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, X.D.; Che, L. Determination of ultra-low milk fat content using dual-wavelength ultraviolet spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9652–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, A.F.; Wagner, M.R. Chapter 15—ANOVA: Testing for Differences Among Many Samples and Much More. In Practical Business Statistics (Eighth Edition); Siegel, A.F., Wagner, M.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 485–510. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, P.L.; Zaidan, M.A.; Timonen, H.; Niemi, J.V.; Kousa, A.; Kuula, J.; Luoma, K.; Tarkoma, S.; Petäjä, T.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Evaluation of white-box versus black-box machine learning models in estimating ambient black carbon concentration. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2021, 152, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybysz, A.; Popek, R.; Stankiewicz-Kosyl, M.; Zhu, C.Y.; Małecka-Przybysz, M.; Maulidyawati, T.; Mikowska, K.; Deluga, D.; Griżuk, K.; Sokalski-Wieczorek, J.; et al. Where trees cannot grow – Particulate matter accumulation by urban meadows. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponette-González, A.G.; Chen, D.; Elderbrock, E.; Rindy, J.E.; Barrett, T.E.; Luce, B.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Ko, Y.; Weathers, K.C. Urban edge trees: Urban form and meteorology drive elemental carbon deposition to canopies and soils. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldacchini, C.; Castanheiro, A.; Maghakyan, N.; Sgrigna, G.; Verhelst, J.; Alonso, R.; Amorim, J.H.; Bellan, P.; Bojović, D.Đ.; Breuste, J.; et al. How Does the Amount and Composition of PM Deposited on Platanus acerifolia Leaves Change Across Different Cities in Europe? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J. Oxidative potential of ambient PM2.5 in Wuhan and its comparisons with eight areas of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tao, S. Oxidative potential of ambient PM2.5 in the coastal cities of the Bohai Sea, northern China: Seasonal variation and source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.T.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J.; Tolbert, P.E.; Abrams, J.Y.; Sarnat, S.E.; Klein, M.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Review of Acellular Assays of Ambient Particulate Matter Oxidative Potential: Methods and Relationships with Composition, Sources, and Health Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daellenbach, K.R.; Uzu, G.; Jiang, J.; Cassagnes, L.-E.; Leni, Z.; Vlachou, A.; Stefenelli, G.; Canonaco, F.; Weber, S.; Segers, A.; et al. Sources of particulate-matter air pollution and its oxidative potential in Europe. Nature 2020, 587, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Martin, R.V.; Evans, G.J.; Umbrio, D.; Traub, A.; Meng, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; You, H.; Kulka, R.; Burnett, R.T.; et al. Predicting Spatial Variations in Multiple Measures of Oxidative Burden for Outdoor Fine Particulate Air Pollution across Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9750–9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominutti, P.A.; Borlaza, L.J.S.; Sauvain, J.-J.; Ngoc Thuy, V.D.; Houdier, S.; Suarez, G.; Jaffrezo, J.-L.; Tobin, S.; Trébuchon, C.; Socquet, S.; et al. Source apportionment of oxidative potential depends on the choice of the assay: Insights into 5 protocols comparison and implications for mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2023, 3, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).