Experimental Investigation on the Influence of Swirl Ratio on Tornado-like Flow Fields by Varying Updraft Radius and Inflow Angle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulator and Experiment Setup
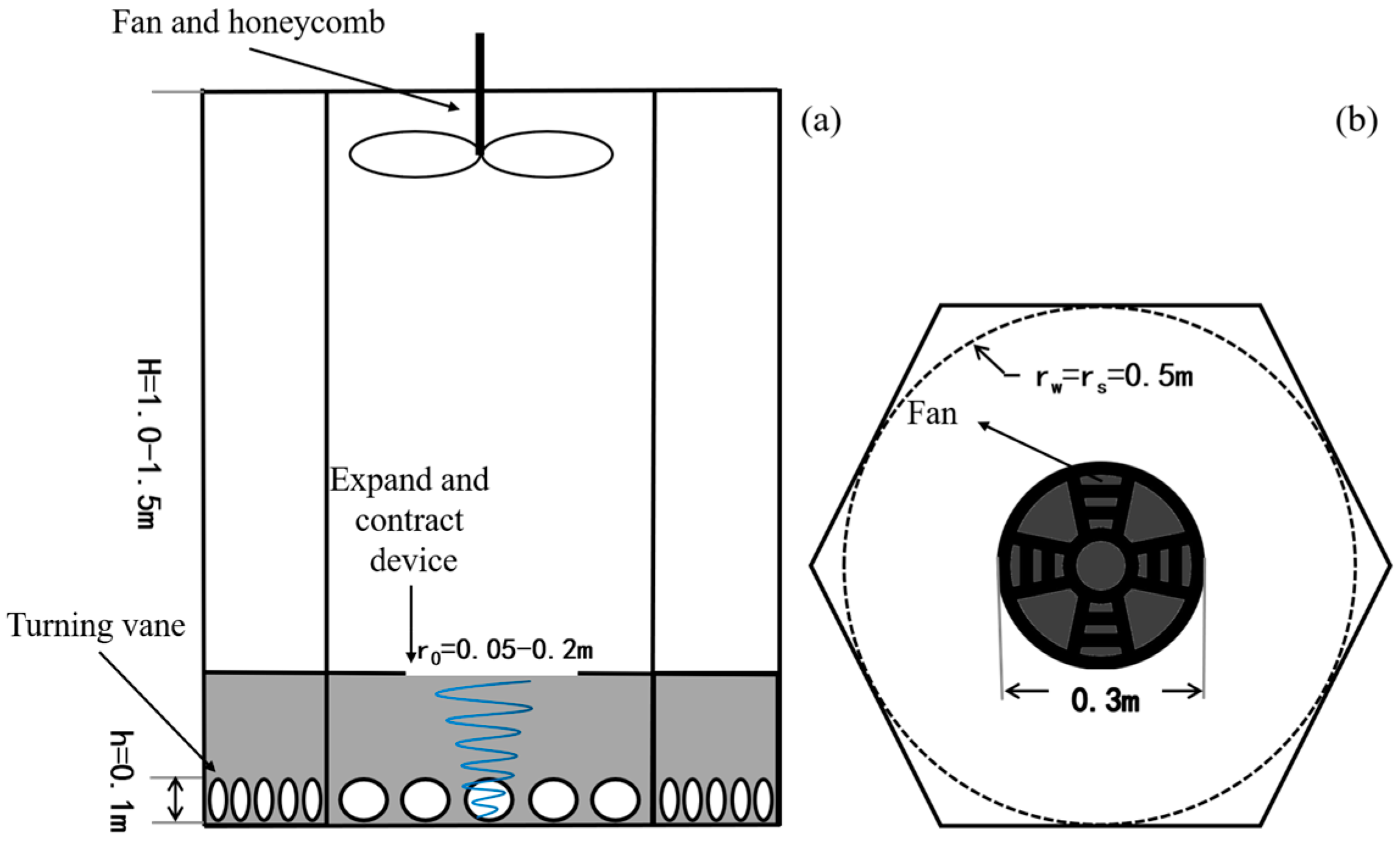
2.1. Simulator Design
2.2. Experiment Setup
3. Controlling Parameters and Validation
3.1. Controlling Parameters
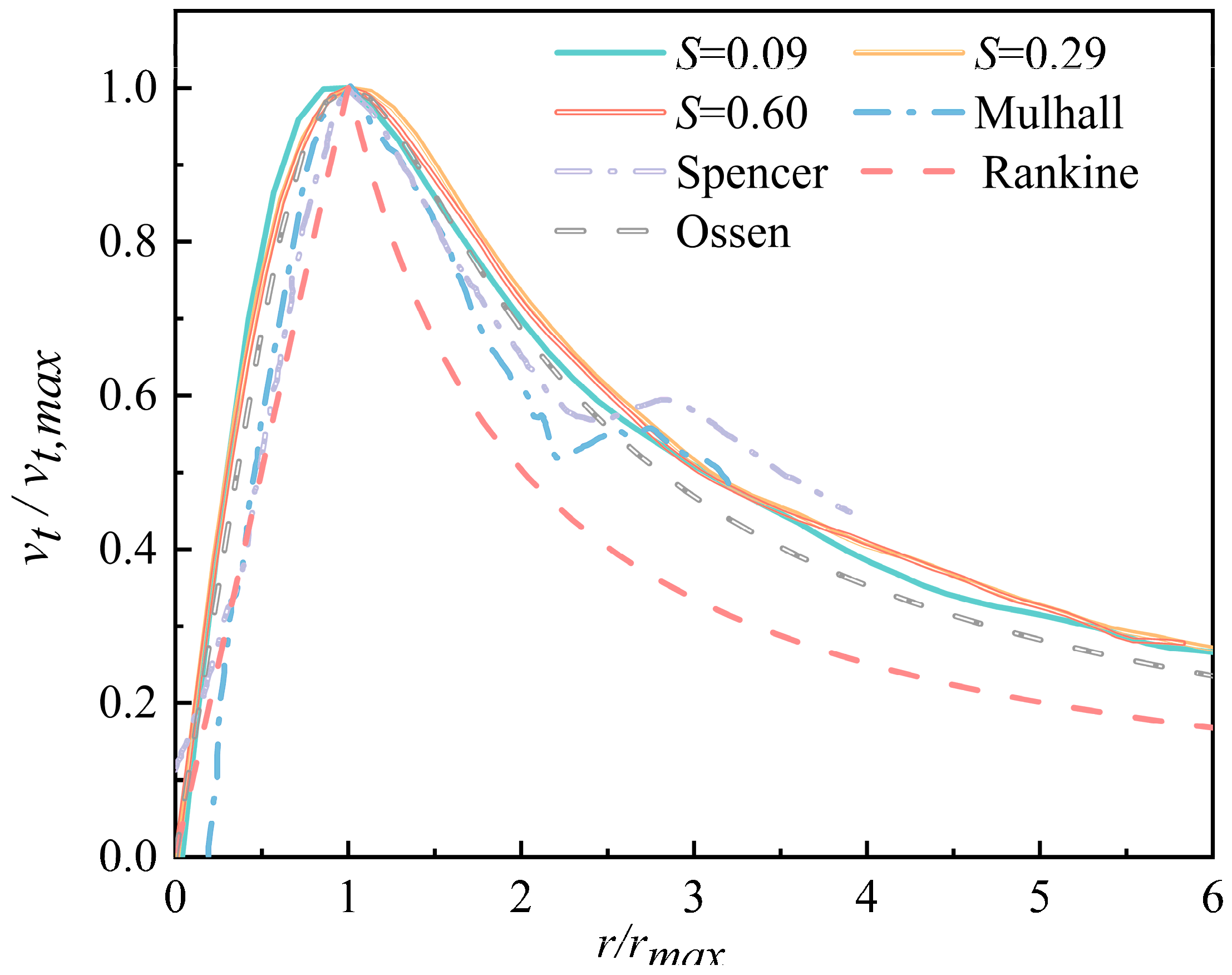
3.2. Validation Objectives
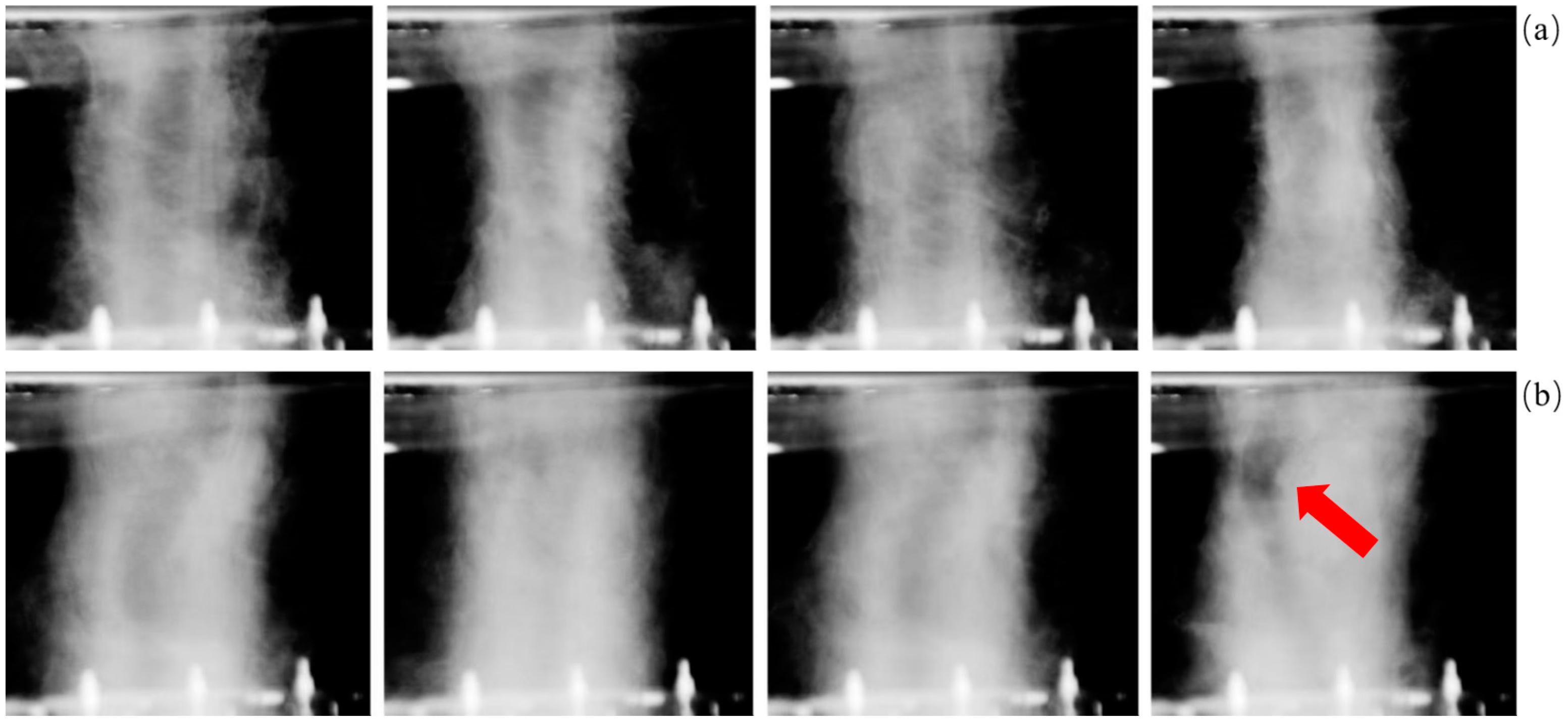
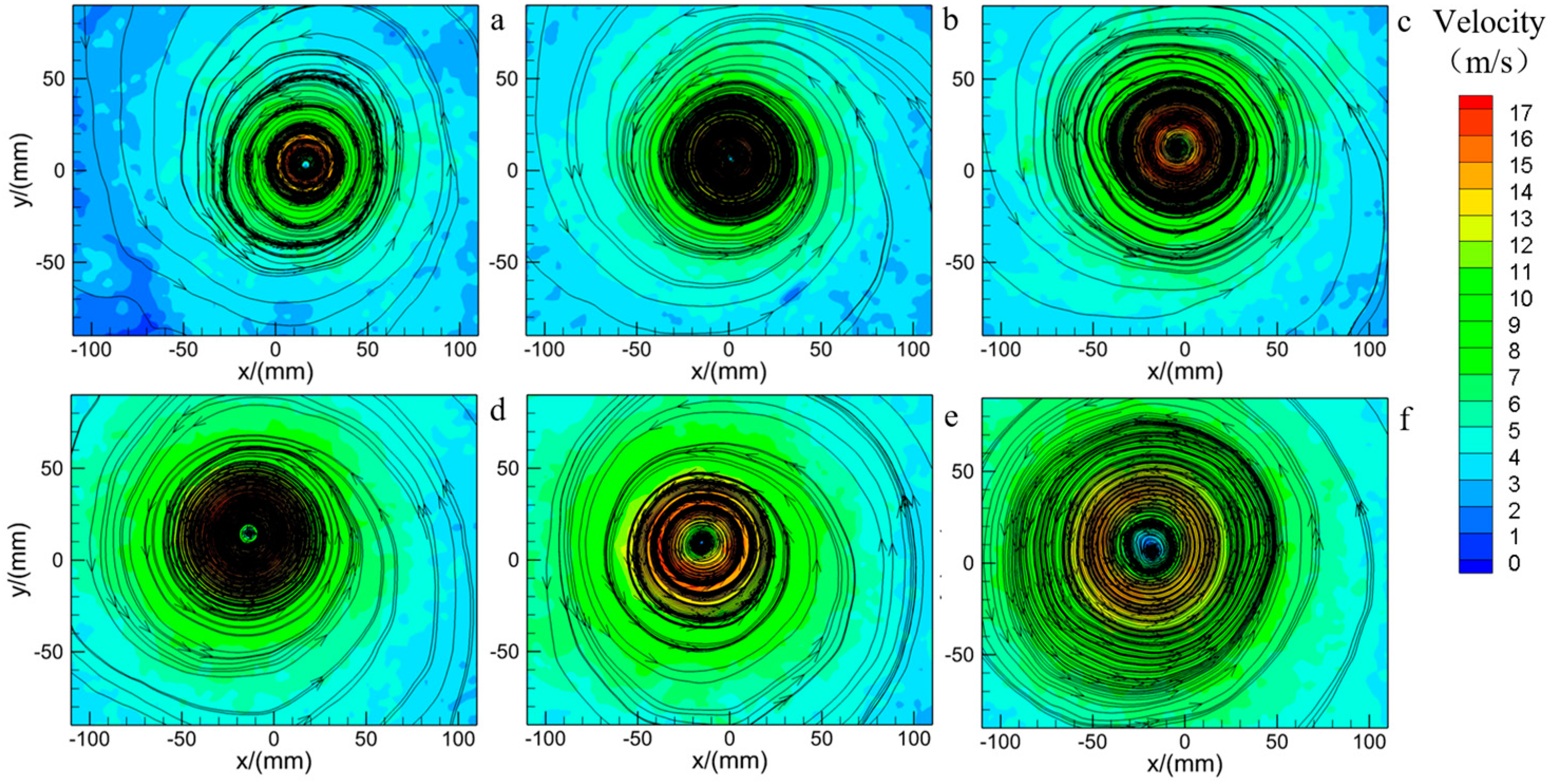
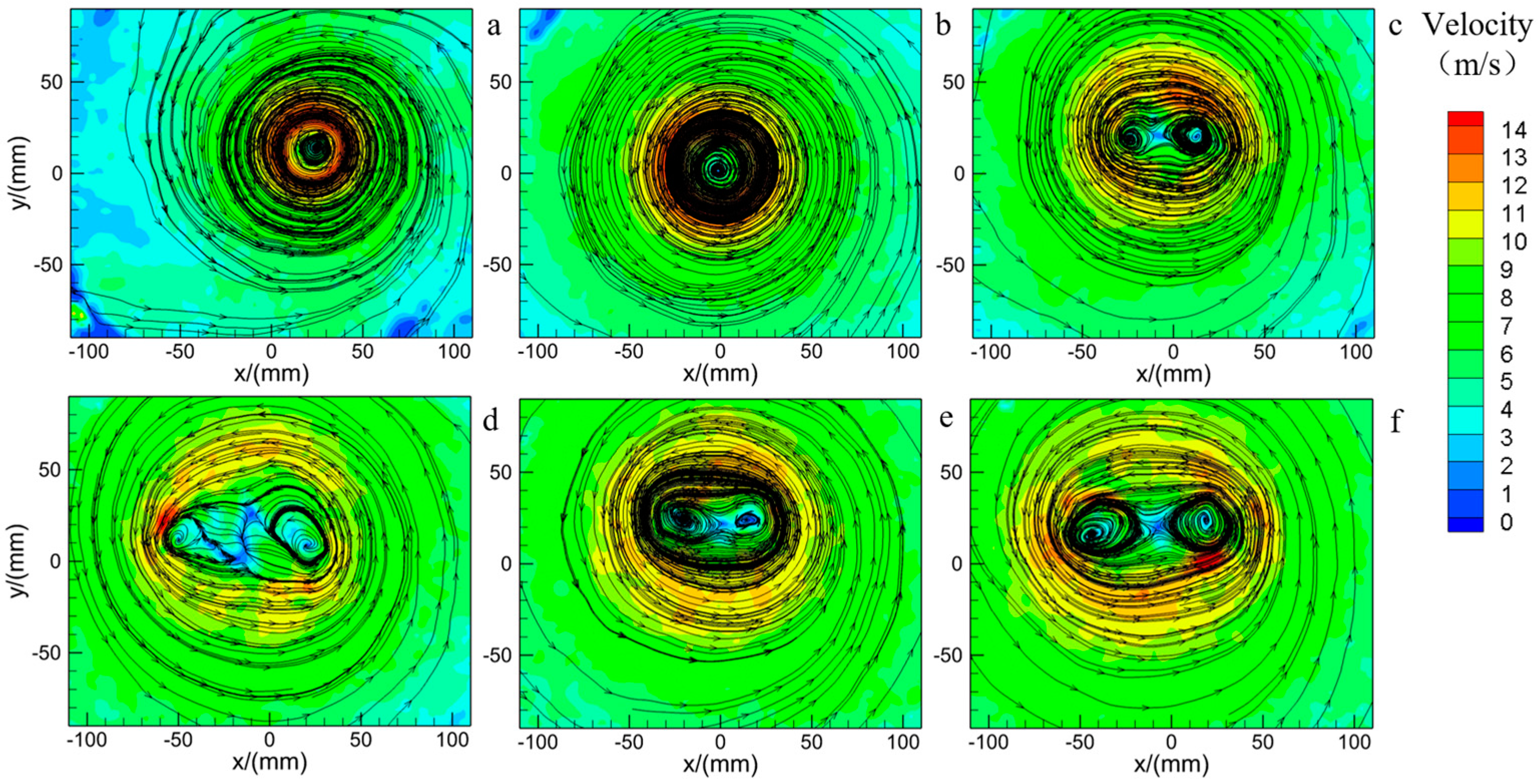
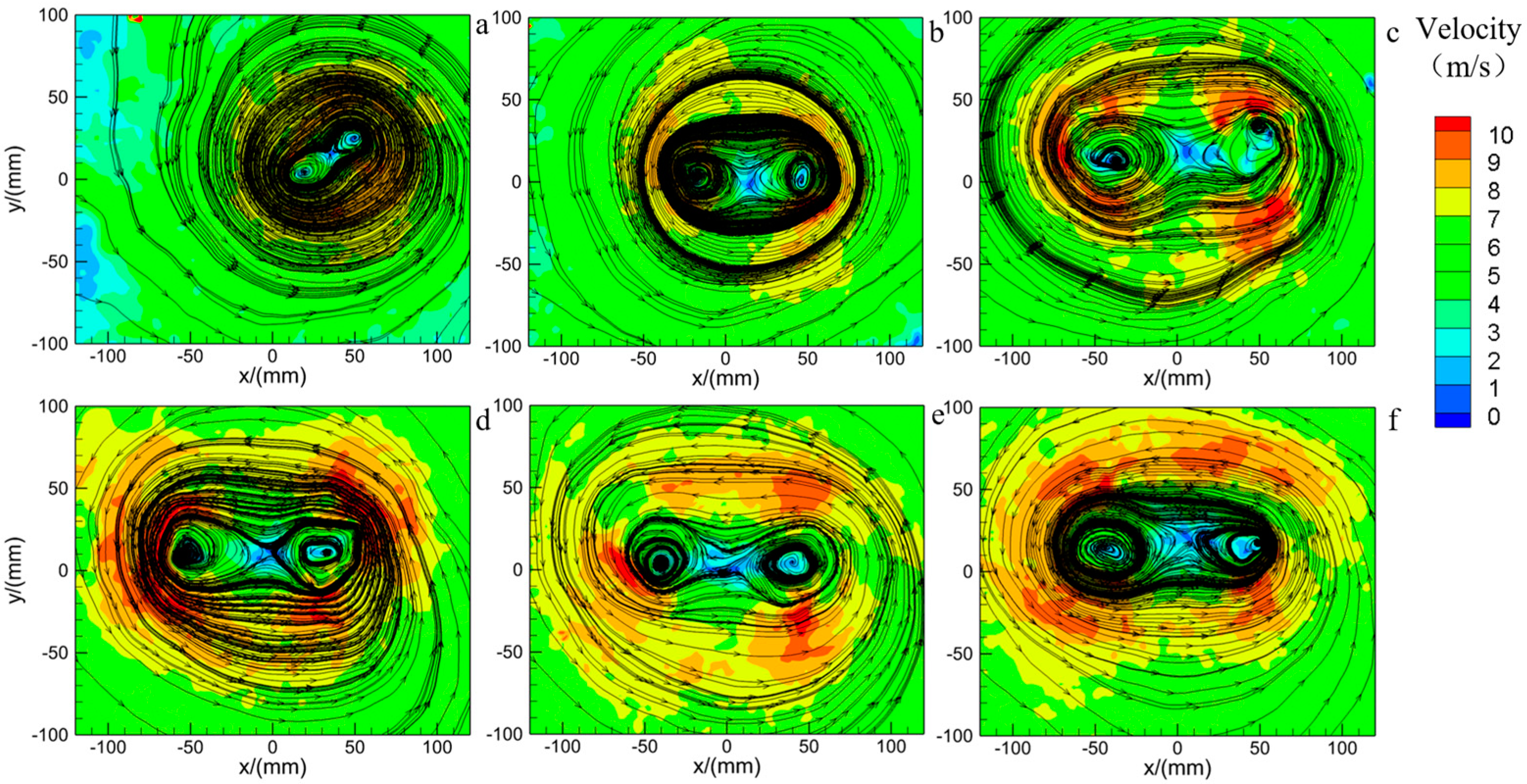
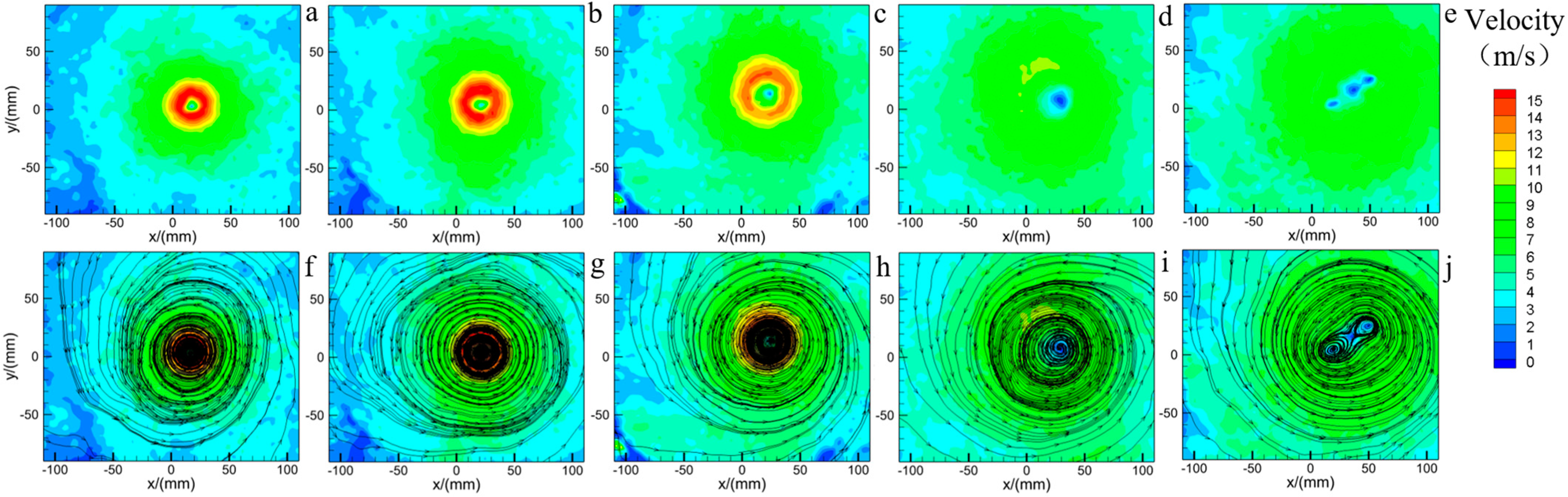
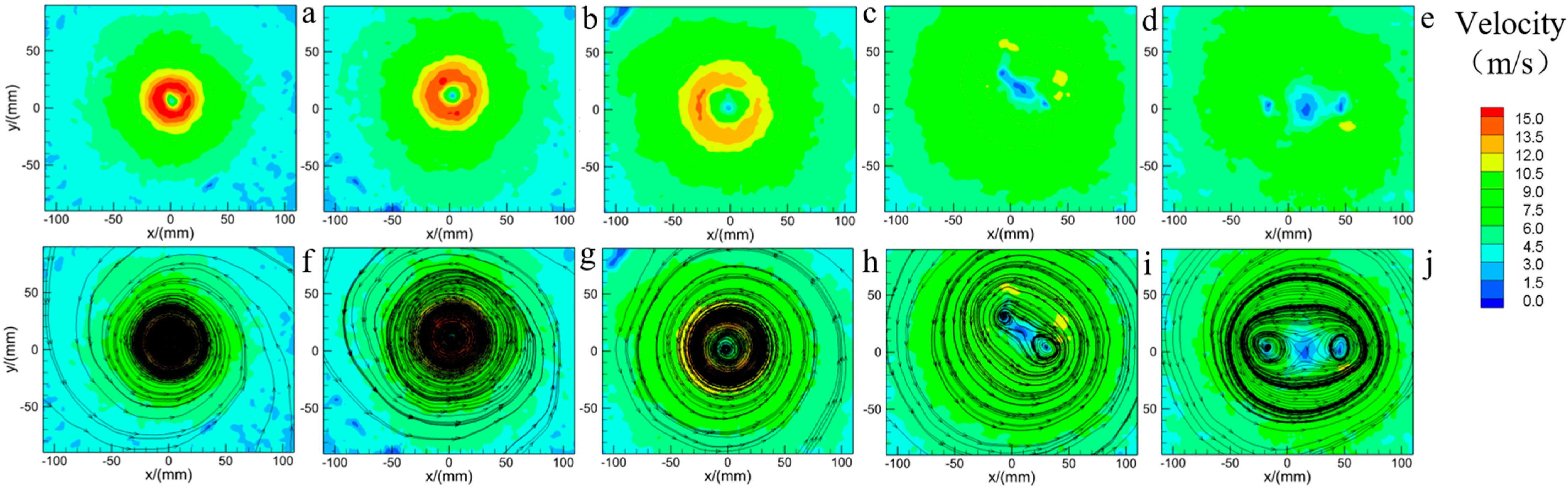
4. Different Swirl Ratios Caused by the Angle of the Turning Vanes
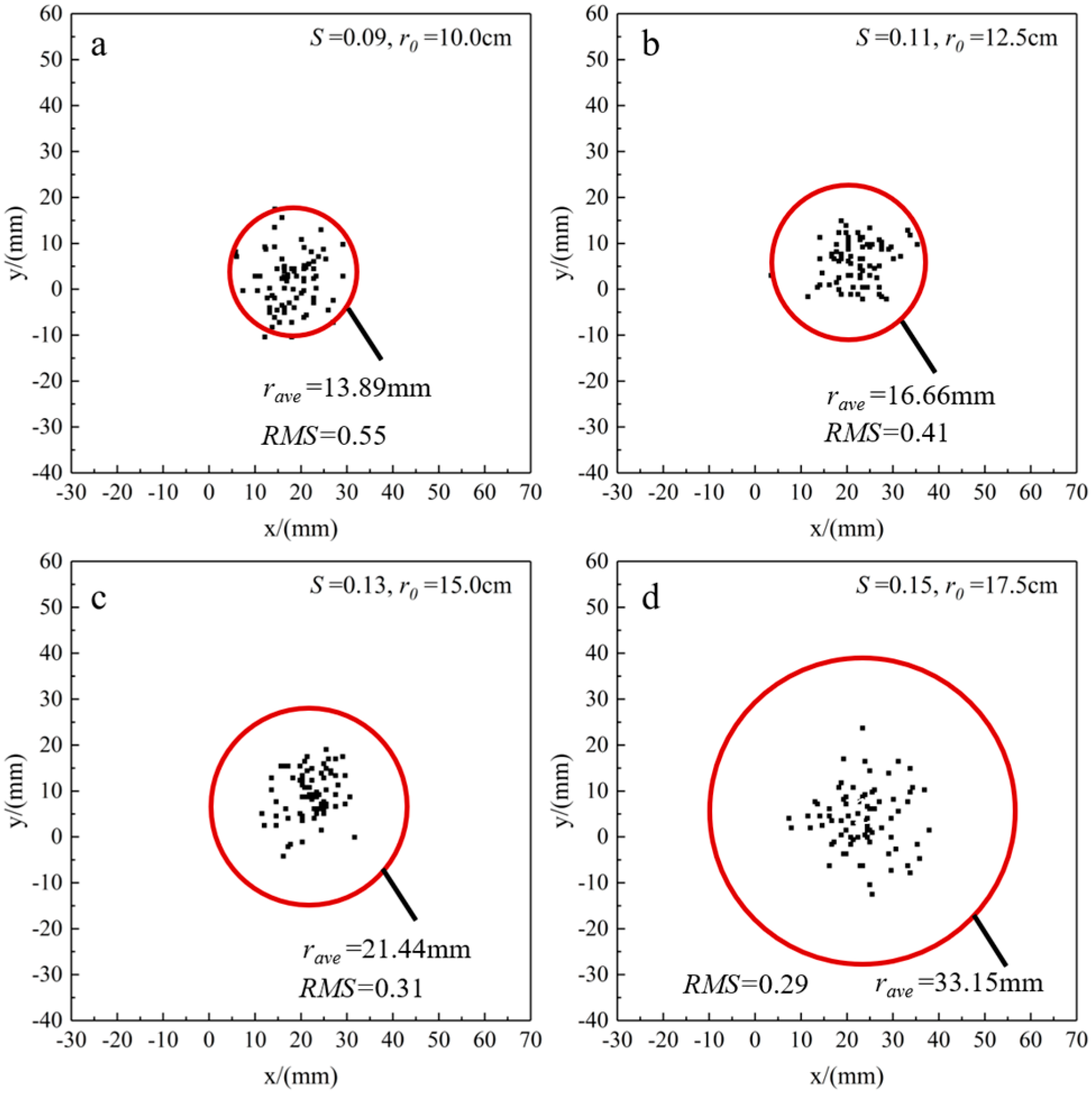
5. Different Swirl Ratios Caused by the Updraft Radius
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karstens, C.D.; Samaras, T.M.; Lee, B.D.; Gallus, W.A.; Finley, C.A. Near-ground pressure and wind measurements in tornadoes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 2570–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.T.; Roueche, D.B.; Prevatt, D.O. Comparison of two methods of near-surface wind speed estimation in the 22 May, 2011 Joplin, Missouri Tornado. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 138, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.W. On the temporal and spatial characteristics of tornado days in the United States. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, J. Statistical summary and case studies of strong wind damage in China. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Hangan, H.; Carassale, L.; Peerhossaini, H. Coherent structures in tornado-like vortices. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 085118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiba, K.A.; Wurman, J. The three-dimensional structure and evolution of a tornado boundary layer. Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refan, M.; Hangan, H.; Wurman, J. Reproducing tornadoes in laboratory using proper scaling. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 135, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, H.B.; Ladue, J.G.; Stein, H.; Speheger, D.; Unruh, W.F. Doppler radar wind spectra of supercell tornadoes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2200–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, H.B.; Pazmany, A.L.; Galloway, J.C.; Mcintosh, R.E. Studies of the substructure of severe convective storms using a mobile 3-mm-wavelength Doppler radar. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 2155–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.R.; Wurman, J. The 30 May 1998 Spencer, South Dakota, storm. Part I: The structural evolution and environment of the tornadoes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 72–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurman, J.; Alexander, C.R. The 30 May 1998 Spencer, South Dakota, storm. Part II: Comparison of observed damage and radar-derived winds in the tornadoes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoecker, W.H., Jr. Wind speed and air flow patterns in the Dallas tornado of April 2, 1957. AMS J. 1960, 88, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-K. Dynamic Tornadic Wind Loads on Tall Buildings. J. Struct. Div. 1975, 101, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, R. A study in tornado-like vortex dynamics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1979, 36, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellen, W.S.; Lewellen, D.C.; Sykes, R.I. Large-Eddy Simulation of a Tornado’s Interaction with the Surface. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 581–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangan, H.; Kim, J. Swirl ratio effects on tornado vortices in relation to the Fujita scale. Wind Struct. 2008, 11, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yan, G.; Honerkamp, R.; Isaac, K.M.; Zhao, M.; Mao, X. Numerical simulation of laboratory tornado simulator that can produce translating tornado-like wind flow. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2019, 190, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Selvam, R.P. CFD model validation with experimental tornado wind field & comparison of wind field in different tornado chambers. Wind Struct. 2021, 33, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, G.; Feng, R.; Kang, H.; Duan, Z. Influence of swirl ratio and radial Reynolds number on wind characteristics of multi-vortex tornadoes. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2023, 26, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.J.; Chang, C.C. Exploratory Model Study of Tornado-Like Vortex Dynamics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1970, 27, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.B. The Exploration of Certain Features of Tornado Dynamics Using a Laboratory Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, C.R.; Snow, J.T.; Agee, E.M. Tornado Vortex Simulation at Purdue University. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 58, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, F.L.; Sarkar, P.P.; Gallus, W.A. Design, construction and performance of a large tornado simulator for wind engineering applications. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 1146–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, P.M.; Richardson, Y.P. Tornadogenesis: Our current understanding, forecasting considerations, and questions to guide future research. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refan, M.; Hangan, H. Characterization of tornado-like flow fields in a new model scale wind testing chamber. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2016, 151, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuta, Y.; Monji, N. Development of a laboratory simulator for small scale atmospheric vortices. Nat. Disaster Sci. 1984, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, L.; Zuo, D.; James, D.L. Characteristics of tornado-like vortices simulated in a large-scale ward-type simulator. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 166, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, S.; Cao, J. Numerical study on applicability of various swirl ratio definitions to characterization of tornado-like vortex flow field. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2022, 220, 104841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amots, N. Dynamics and thermodynamics of a tornado: Rotation effects. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Jones, R. A review of supercell and tornado dynamics. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Jones, R. The dependence of core radius on swirl ratio in a tornado simulator. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, C.R.; Snow, J.T.; Baker, G.L.; Agee, E.M. Characteristics of Tornado-Like Vortices as a Function of Swirl Ratio: A Laboratory Investigation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1979, 36, 1755–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M. The structure of concentrated vortex cores. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1966, 7, 53–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.; Refan, M.; Iungo, G.V.; Hangan, H. Wandering corrections from PIV measurements of tornado-like vortices. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2019, 189, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, M.N.; Selvam, R.P. The variation in the maximum loading of a circular cylinder impacted by a 2D vortex with time of impact. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 58, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, M.N.; Yousef, M.A.; Selvam, R.P. Defining the vortex loading period and application to assess dynamic amplification of tornado-like wind loading. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 63, 188–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sarkar, P.P. Near-ground tornado-like vortex structure resolved by particle image velocimetry (PIV). Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refan, M.; Hangan, H. Near surface experimental exploration of tornado vortices. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 175, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungo, G.V.; Skinner, P.; Buresti, G. Correction of wandering smoothing effects on static measurements of a wing-tip vortex. Exp. Fluids 2009, 46, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, W.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, G. Numerical study of flow characteristics of tornado-like vortices considering both swirl ratio and aspect ratio. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2023, 240, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Expermental Tornado Simulator | Author and Institution | Characteristics | Variable Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISU simulator [23] | Iowa State University, Haan et al. |
|
|
| VorTECH simulator [27] | Texas Tech University, Tang et al. |
|
|
| Wind Engineering Energy and Environment (WindEEE) Dome [25] | Western University Refan et al. |
|
|
| Group | Updraft Radius (cm) | Angle of the Turning Vanes θ (°) | Swirl Ratio S |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 | 0.09, 0.18, 0.29, 0.42, 0.60, 0.87 |
| 2 | 15 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 | 0.13, 0.27, 0.43, 0.63, 0.89, 1.30 |
| 3 | 20 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 | 0.18, 0.36, 0.58, 0.84, 1.19, 1.73 |
| Group | Angle of the Turning Vanes θ (°) | Updraft Radius (cm) | Swirl Ratio S |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 10 | 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, 20 | 0.09, 0.11, 0.13, 0.15, 0.18 |
| 5 | 20 | 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, 20 | 0.18, 0.23, 0.27, 0.32, 0.36 |
| 6 | 30 | 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, 20 | 0.28, 0.36, 0.43, 0.51, 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Experimental Investigation on the Influence of Swirl Ratio on Tornado-like Flow Fields by Varying Updraft Radius and Inflow Angle. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091425
Lv P, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang B. Experimental Investigation on the Influence of Swirl Ratio on Tornado-like Flow Fields by Varying Updraft Radius and Inflow Angle. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(9):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091425
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Pengfei, Yumeng Zhang, Yanlei Wang, and Bo Wang. 2023. "Experimental Investigation on the Influence of Swirl Ratio on Tornado-like Flow Fields by Varying Updraft Radius and Inflow Angle" Atmosphere 14, no. 9: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091425
APA StyleLv, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, B. (2023). Experimental Investigation on the Influence of Swirl Ratio on Tornado-like Flow Fields by Varying Updraft Radius and Inflow Angle. Atmosphere, 14(9), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091425






