Dry Deposition of Hydrophilic Black Carbon Aerosols in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
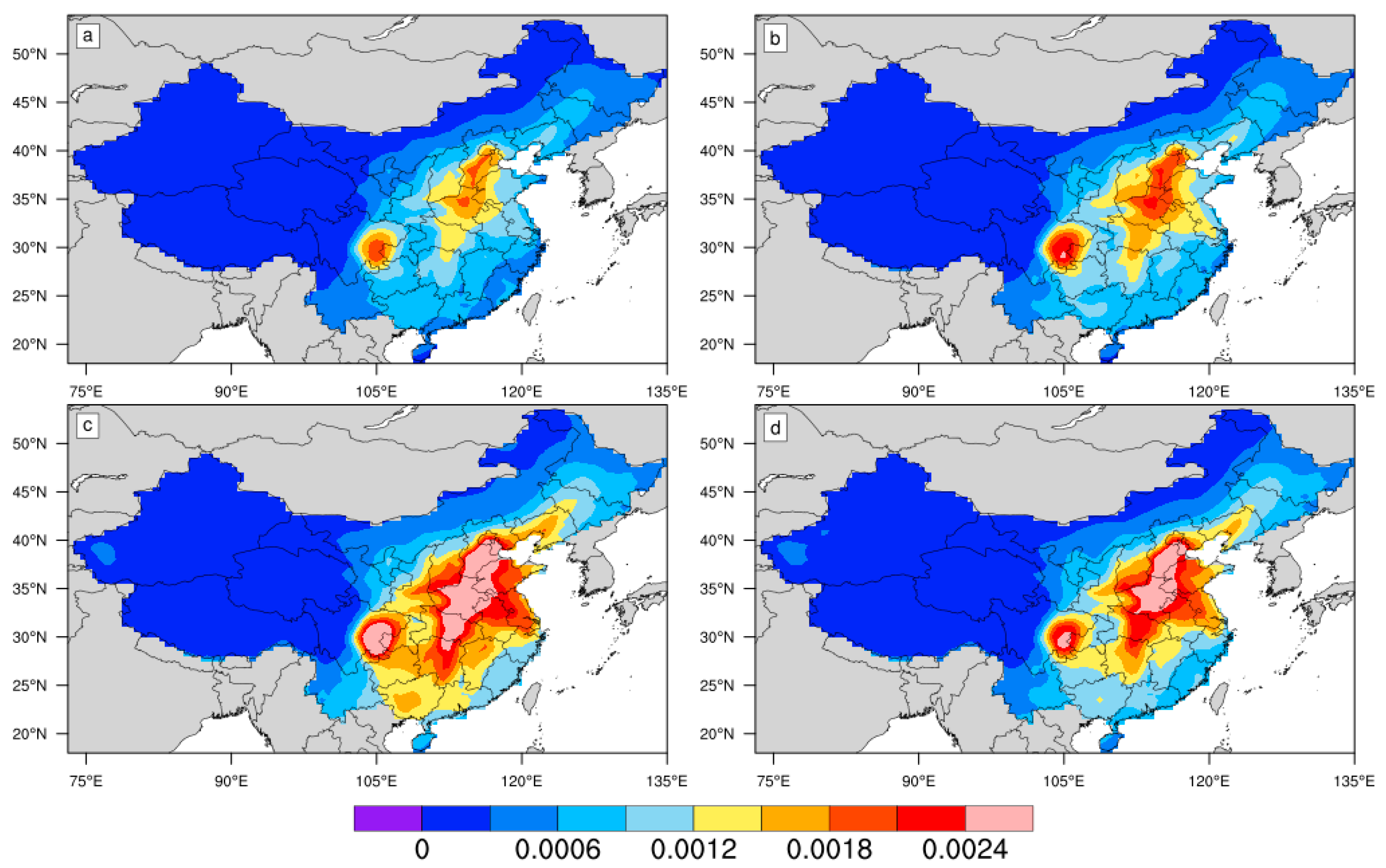
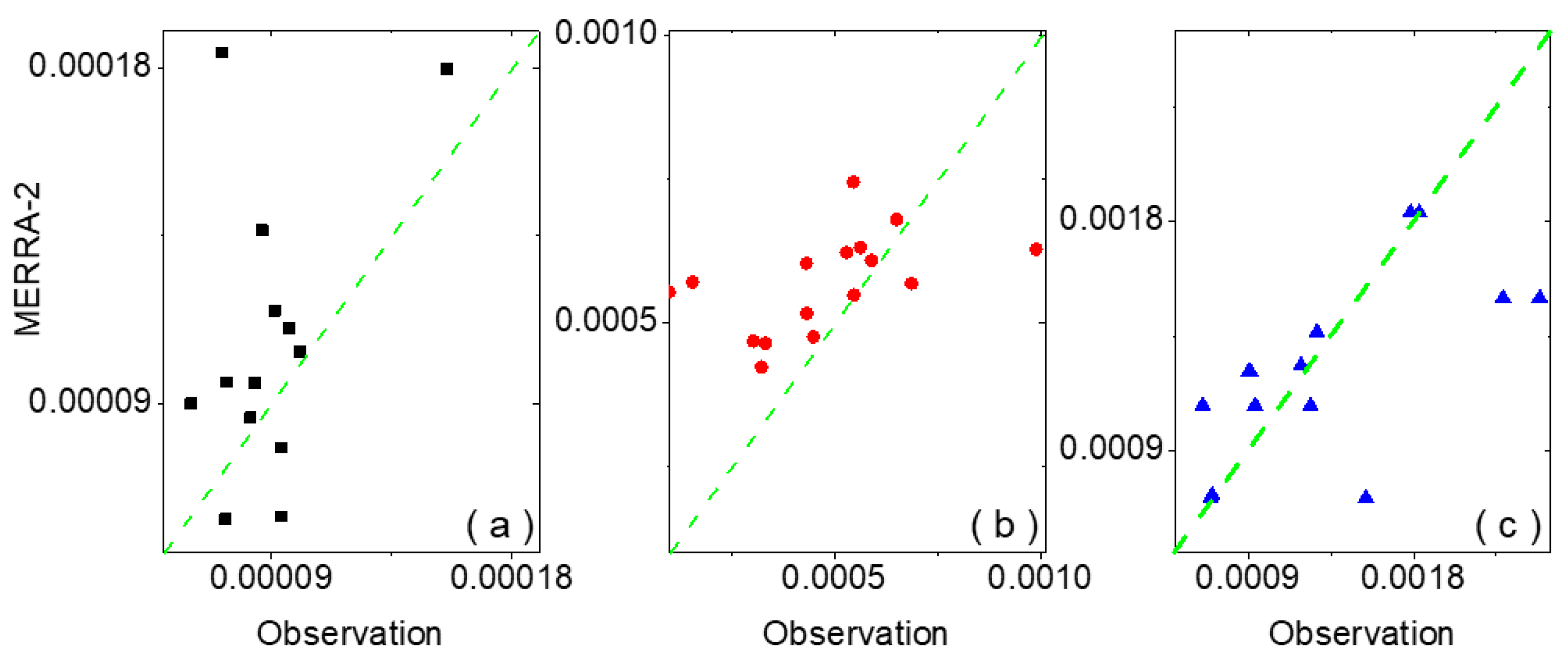
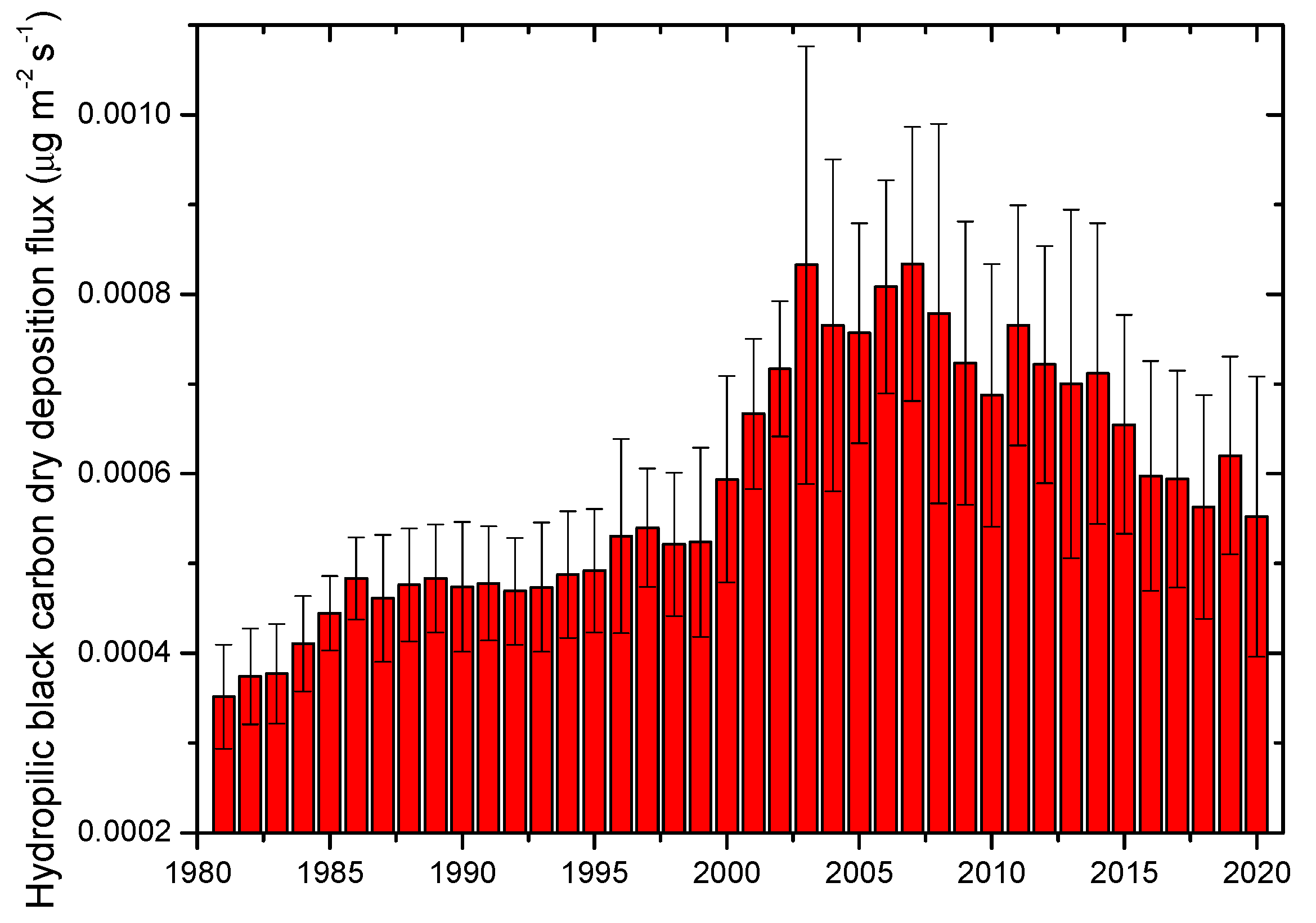
3.1. Dry Deposition Fluxes of Hydrophilic Black Carbon over China
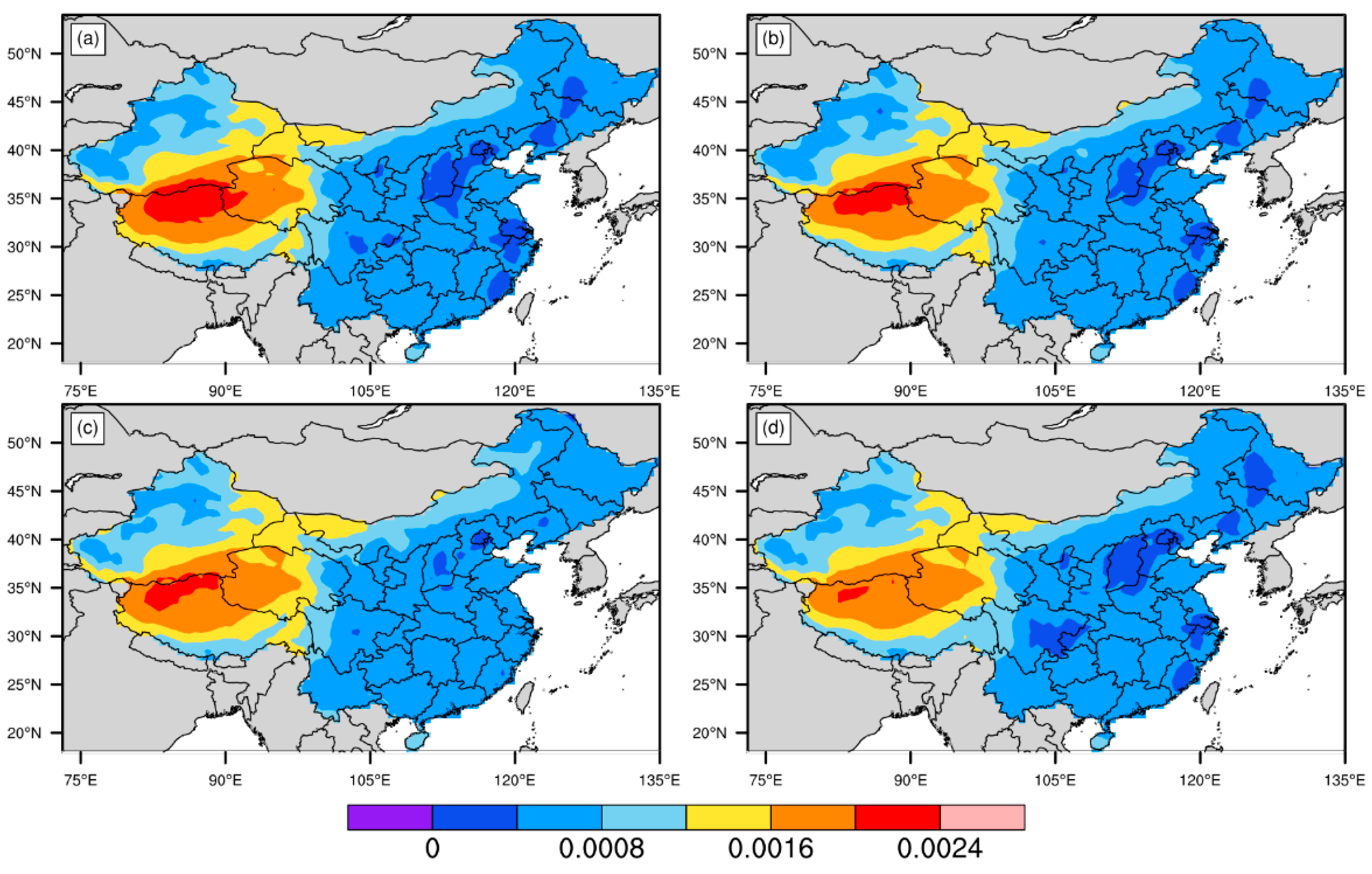
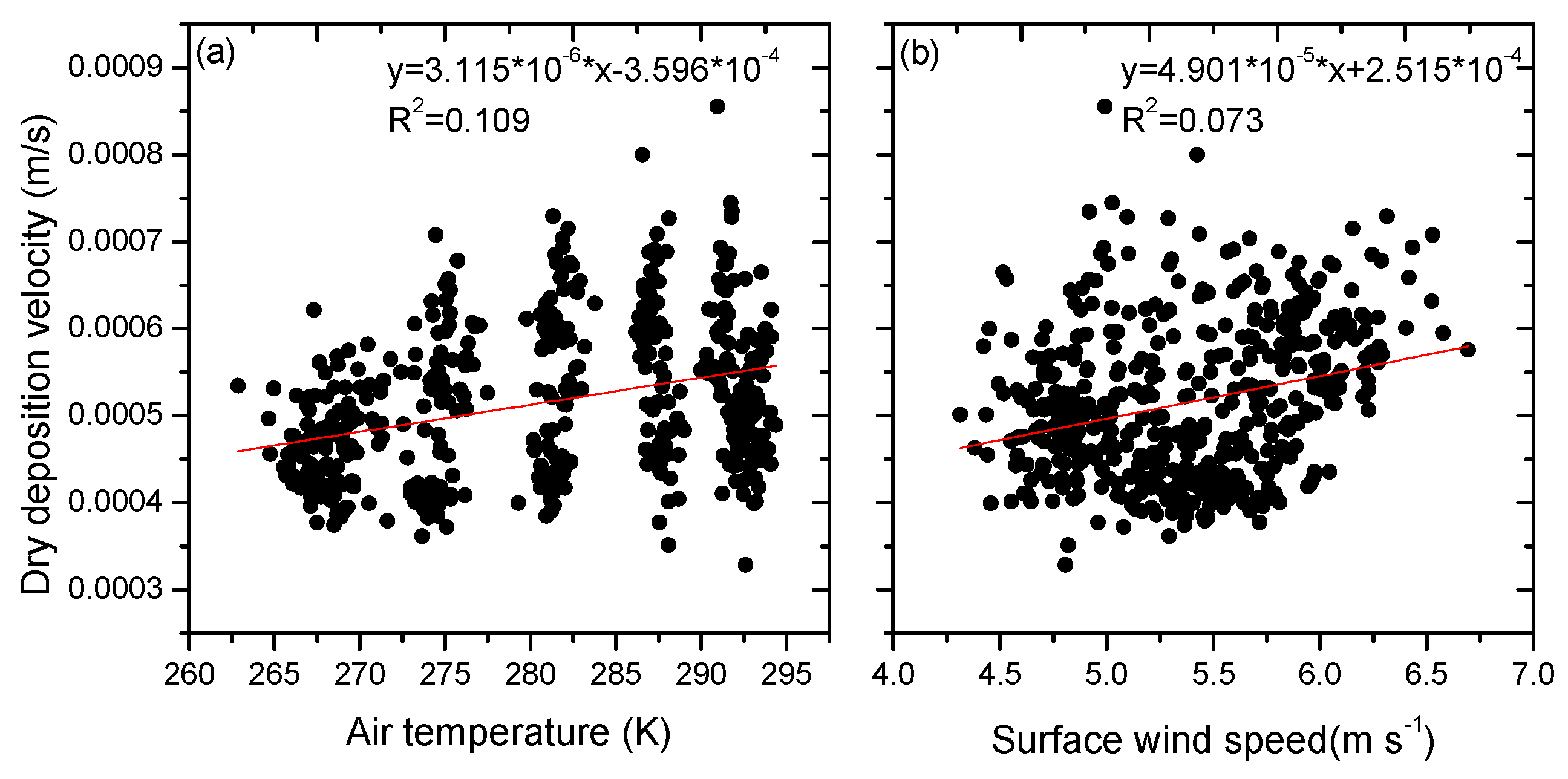
3.2. Dry Deposition Velocity of Hydrophilic Black Carbon over China
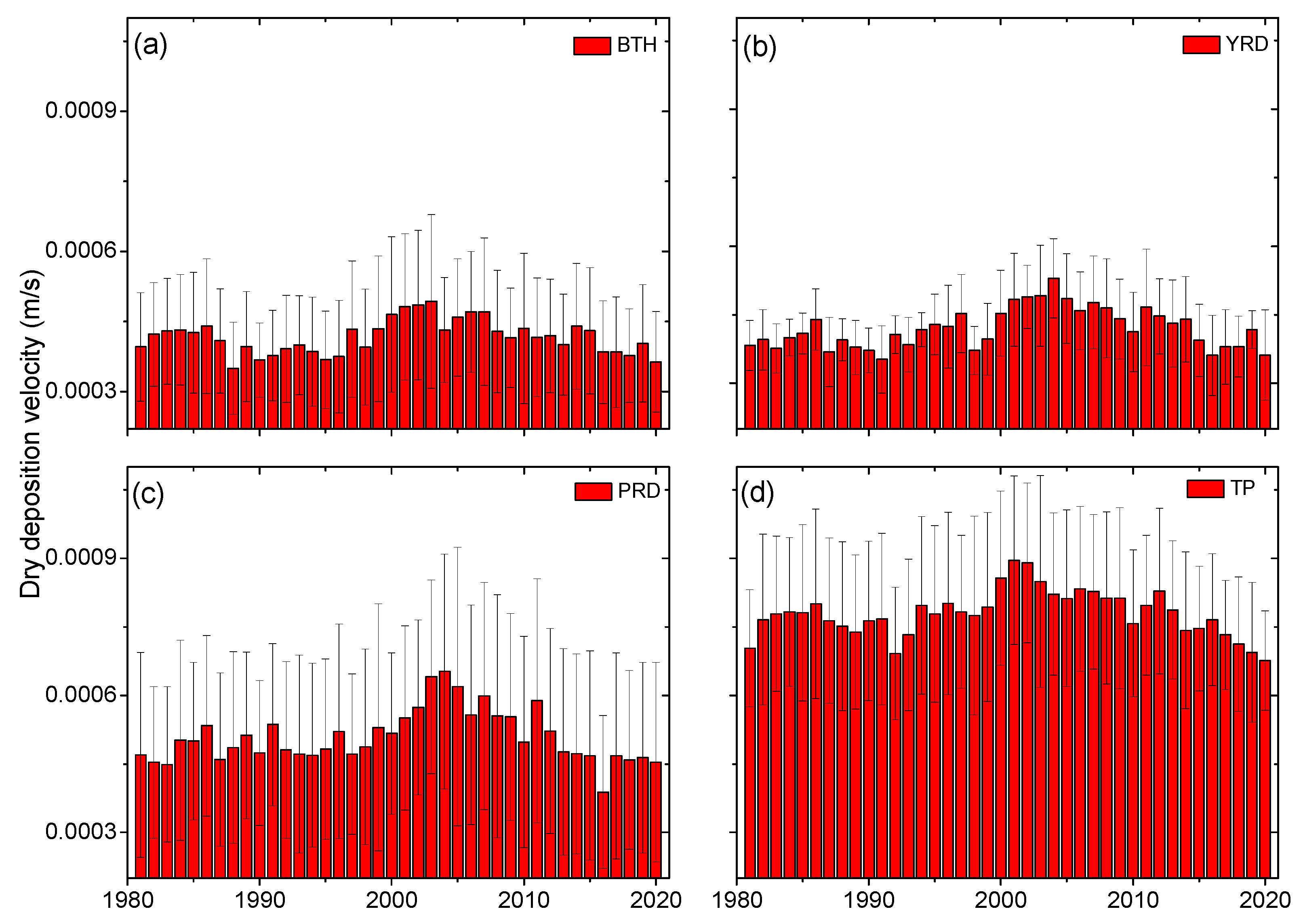
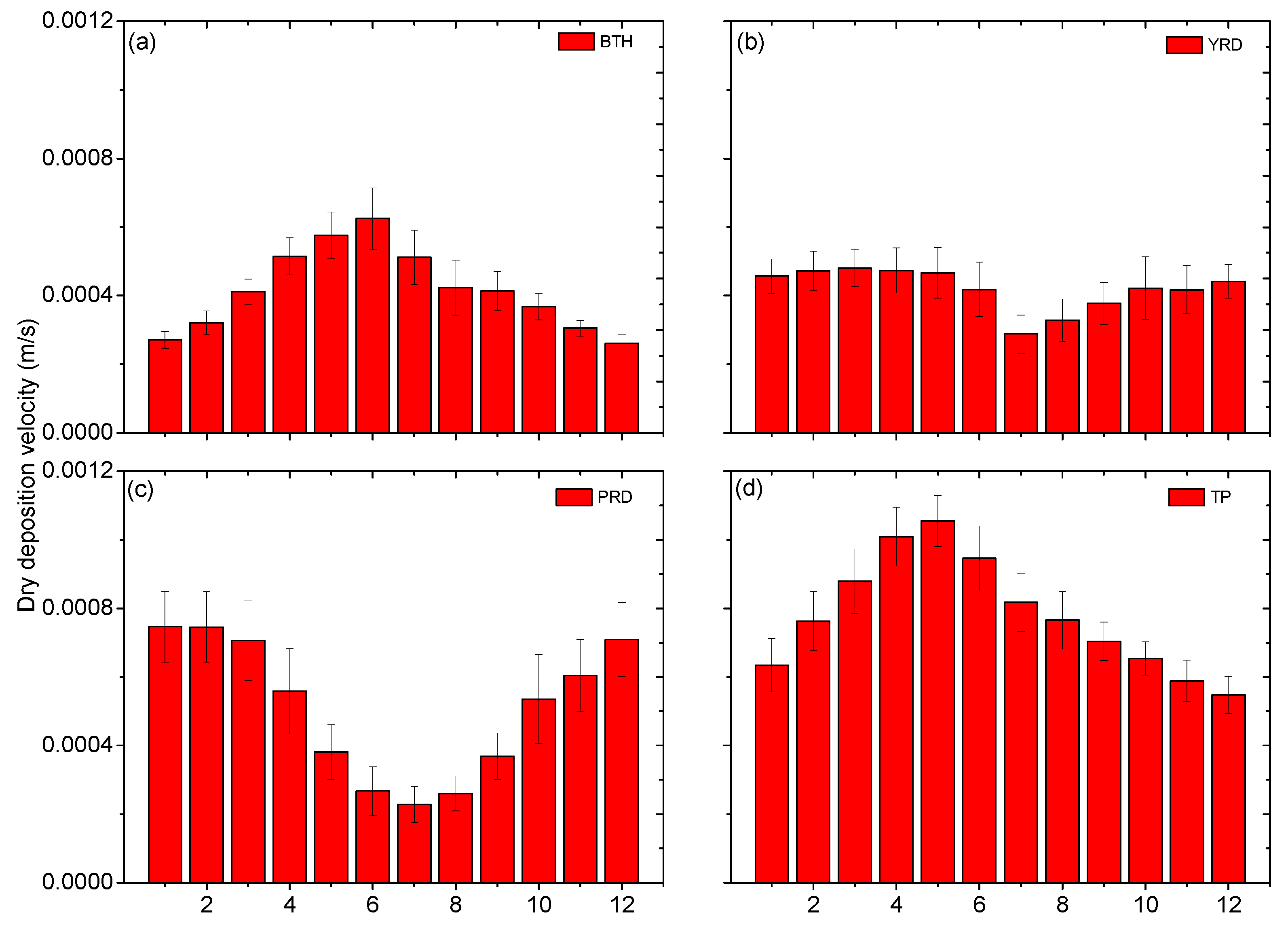
3.3. Dry Deposition Velocity of Hydrophilic Black Carbon over Typical Regions of China
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pleim, J.E.; Ran, L.; Saylor, R.D.; Willison, J.; Binkowski, F.S. A new aerosol dry deposition model for air quality and climate modeling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2022MS003050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, M.; Chen, H.; Tang, S. The Angstrom exponents of black carbon aerosols with non-absorptive coating: A numerical investigation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 257, 107362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Aerosol direct radiative forcing over China: A 40-year MERRA-2-based evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 299, 119659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z. Significant underestimation in the optically based estimation of the aerosol first indirect effect induced by the aerosol swelling effect. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5690–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.H.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, D.; Del Genio, A.D. Black carbon semi-direct effects on cloud cover: Review and synthesis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7685–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kaercher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, E.W.; Katich, J.M.; Schwarz, J.P.; McMeeking, G.R.; Farmer, D.K. Direct measurements of dry and wet deposition of black carbon over a grassland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12277–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, A.; Gao, C.; He, S.; Mao, M. Scavenging of Black Carbon Aerosols by Radiation Fog in Urban Central China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, E.W.; Hodshire, A.L.; DeBolt, H.M.; Bilsback, K.R.; Pierce, J.R.; McMeeking, G.R.; Farmer, D.K. Revisiting particle dry deposition and its role in radiative effect estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26076–26082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwede, D.B.; Lear, G.G. A novel hybrid approach for estimating total deposition in the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, D.; Schulz, M.; Kinne, S.; McNaughton, C.; Spackman, J.R.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.; Berntsen, T.; Bond, T.C.; Boucher, O.; et al. Evaluation of black carbon estimations in global aerosol models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9001–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Makar, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Milbrandt, J.; Gravel, S.; Hayden, K.L.; Macdonald, A.M.; Leaitch, W.R. Modelling aerosol-cloud-meteorology interaction: A case study with a fully coupled air quality model (GEM-MACH). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 695–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; McQueen, J.; Stajner, I.; Huang, J.P.; Pan, L.; Tong, D.; Kim, H.; Tang, Y.H.; Kondragunta, S.; Ruminski, M.; et al. NAQFC developmental forecast guidance for fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.A.; Pringle, K.J.; Reddington, C.L.; Mann, G.W.; Stier, P.; Spracklen, D.V.; Pierce, J.R.; Carslaw, K.S. The magnitude and causes of uncertainty in global model simulations of cloud condensation nuclei. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8879–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Vecchi, R.; Viana, M. Carbonaceous Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L. Research progress in multimedia cycle processes and simulation of POPs in urban surface system. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Jurado, E.; Dachs, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Simo, R. Atmospheric deposition of organic and black carbon to the global oceans. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7931–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Feng, T.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Rose, N.L. Sources and dry deposition of carbonaceous aerosols over the coastal East China Sea: Implications for anthropogenic pollutant pathways and deposition. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.; Lewandowska, A.; Falkowska, L.M. Parallel measurements of organic and elemental carbon dry (PM1, PM2.5) and wet (rain, snow, mixed) deposition into the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; He, C.; Kang, S.; Chen, P.; Hu, Z.; Han, X.; Gautam, S.; Yan, C.; Zheng, M.; Sillanpaa, M.; et al. Deposition of organic and black carbon: Direct measurements at three remote stations in the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 16, 9702–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, G.L.; Xu, Z.F. Black carbon in the atmospheric dust of Beijing City and its north area. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Vong, R.J.; Vong, I.J.; Vickers, D.; Covert, D.S. Size-dependent aerosol deposition velocities during BEARPEX’07. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5749–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlm, L.; Krejci, R.; Nilsson, E.D.; Martensson, E.M.; Vogt, M.; Artaxo, P. Emission and dry deposition of accumulation mode particles in the Amazon Basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10237–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönholm, T.; Aalto, P.P.; Hiltunen, V.J.; Rannik, U.; Rinne, J.; Laakso, L.; HyvoNen, S.; Vesala, T.; Kulmala, M. Measurements of aerosol particle dry deposition velocity using the relaxed eddy accumulation technique. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2007, 59, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, D.K.; Boedicker, E.K.; DeBolt, H.M. Dry Deposition of Atmospheric Aerosols: Approaches, Observations, and Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2021, 72, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesely, M.L.; Hicks, B.B. A review of the current status of knowledge on dry deposition. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2261–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Gong, S.L.; Padro, J.; Barrie, L. A size-segregated particle dry deposition scheme for an atmospheric aerosol module. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Suarez, M.; Bacmeister, J. Development of the GEOS-5 atmospheric general circulation model: Evolution from MERRA to MERRA2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleist, D.T.; Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C.; Treadon, R.; Wu, W.-S.; Lord, S. Introduction of the GSI into the NCEP Global Data Assimilation System. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, W.; Lin, S.-J. Finite-volume transport on various cubed sphere grids. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 227, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.R.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Ziemba, L.D.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part II: Evaluation and case studies. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colarco, P.; da Silva, A.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T. Online simulations of global aerosol distributions in the NASA GEOS-4 model and comparisons to satellite and ground-based aerosol optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Ginoux, P.; Kinne, S.; Torres, O.; Holben, B.N.; Duncan, B.N.; Martin, R.V.; Logan, J.A.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Tropospheric aerosol optical thickness from the GOCART model and comparisons with satellite and Sun photometer measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeeking, G.R.; Morgan, W.T.; Flynn, M.; Highwood, E.J.; Turnbull, K.; Haywood, J.; Coe, H. Black carbon aerosol mixing state, organic aerosols and aerosol optical properties over the United Kingdom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9037–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Chin, M.; Martin, R.V. Sources of carbonaceous aerosols over the United States and implications for natural visibility. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.T.; Lu, C.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, S.P.; Tsai, F.; Chou, C.K. Investigation of long-range transported PM2.5 events over Northern Taiwan during 2005–2015 winter seasons. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 217, 116920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Liao, H. Radiative forcing and health impact of aerosols and ozone in China as the consequence of clean air actions over 2012–2017. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 12511–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Z.; Xie, Z. Model analysis of long-term trends of aerosol concentrations and direct radiative forcings over East Asia. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 20410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Gallet, J.C.; Pedersen, C.A.; Zhang, X.S.; Strom, J.; Ci, Z.J. Elemental carbon in snow at Changbai Mountain, northeastern China: Concentrations, scavenging ratios, and dry deposition velocities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 14221–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, W.; Liu, M.; Xu, H. Atmospheric elemental carbon deposition from urban and suburban sites of Shanghai: Characteristics, sources and comparison with aerosols and soils. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Matsui, H. Aerosol radiative forcings induced by substantial changes in anthropogenic emissions in China from 2008 to 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5965–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Donateo, A.; Belosi, F.; Grasso, F.M.; Santachiara, G.; Prodi, F. Deposition velocity of ultrafine particles measured with the Eddy-Correlation Method over the Nansen Ice Sheet (Antarctica). J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Tan, Q.; Lau, K.M.; Bonasoni, P.; Marinoni, A.; Laj, P.; Menegoz, M.; Takemura, T.; Chin, M. Estimated range of black carbon dry deposition and the related snow albedo reduction over Himalayan glaciers during dry pre-monsoon periods. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Mohammed, A.H.A.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, M. Dry Deposition of Hydrophilic Black Carbon Aerosols in China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071114
Zhang X, Mohammed AHA, Zhou Y, Mao M. Dry Deposition of Hydrophilic Black Carbon Aerosols in China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071114
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaolin, Awad Hussien Ahmed Mohammed, Yu Zhou, and Mao Mao. 2023. "Dry Deposition of Hydrophilic Black Carbon Aerosols in China" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071114
APA StyleZhang, X., Mohammed, A. H. A., Zhou, Y., & Mao, M. (2023). Dry Deposition of Hydrophilic Black Carbon Aerosols in China. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071114







