Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 1: Zoning of Areas with Heat Conditions Favorable for Apple Growing under Observed Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- The FB date was calculated: starting from the beginning of the year, the first appearance of the six consecutive days above the determined threshold value (base temperature—Tb) was calculated, the sixth day was chosen as the FB date;
- The accumulation of temperatures above the threshold value starts from the calculated FB date, and the date when the accumulated value reaches the determined threshold (predefined by the sum of active temperatures) was chosen as the harvest date (assuming it is close to biological ripening);
- If these heat criteria were possible to reach in each year of the chosen period, the areas that belong to that grid point are considered to be the areas with favorable heat conditions for apple growing.
- Minimum heat requirements for apple growing: if there are favorable heat conditions in the grid point for at least for one variety, the area which belongs to that grid point is designated as having favorable heat conditions for apple growing;
- Heat requirements for the growing of any apple variety (including more heat-demanding varieties): if there are favorable heat conditions for all varieties in the grid point the area which belongs to that grid point is designated as having favorable heat conditions for growing of any apple variety.
3. Results
3.1. Base Temperature for Apple Varieties
3.2. Heat Required for Fruit Development
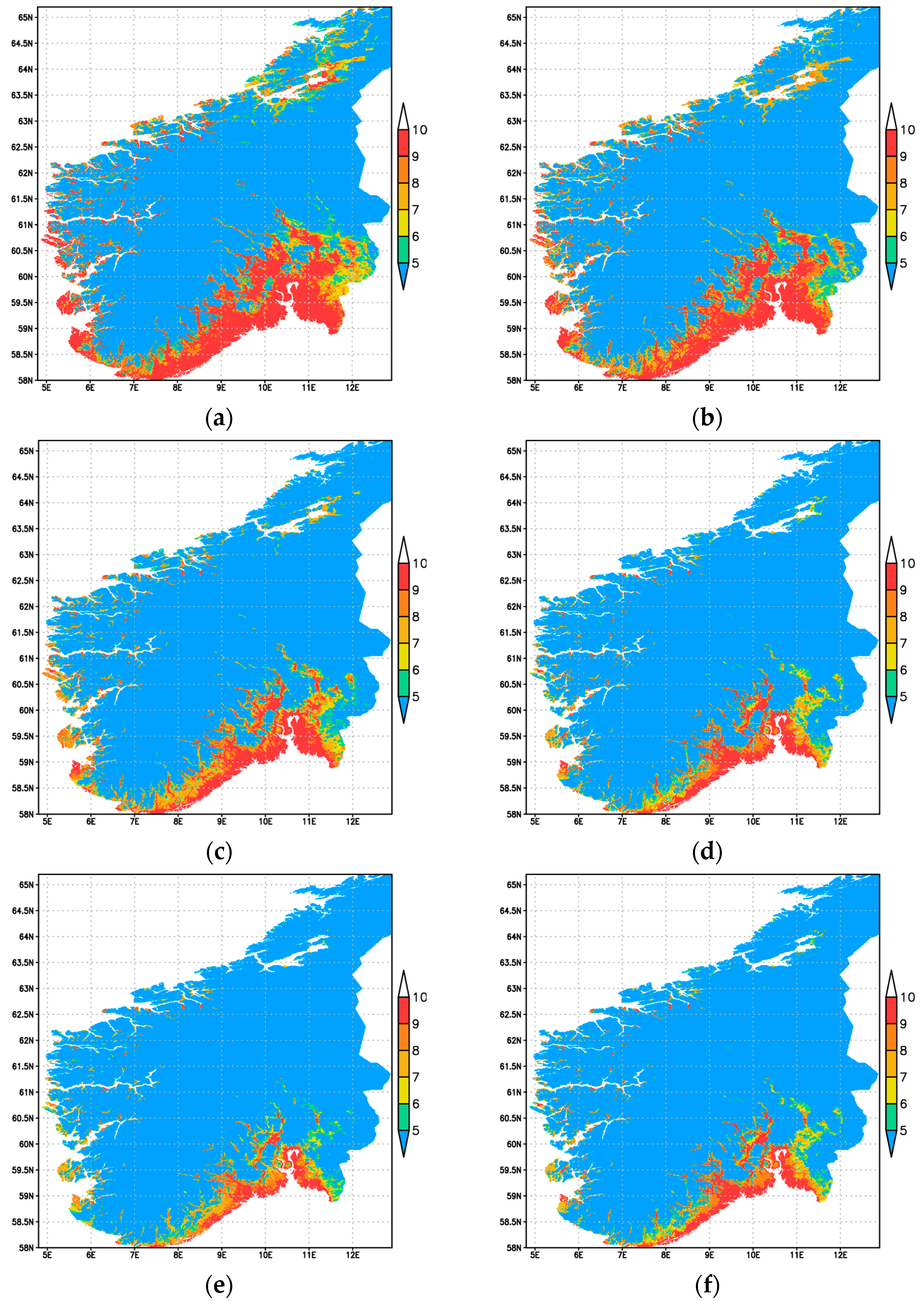
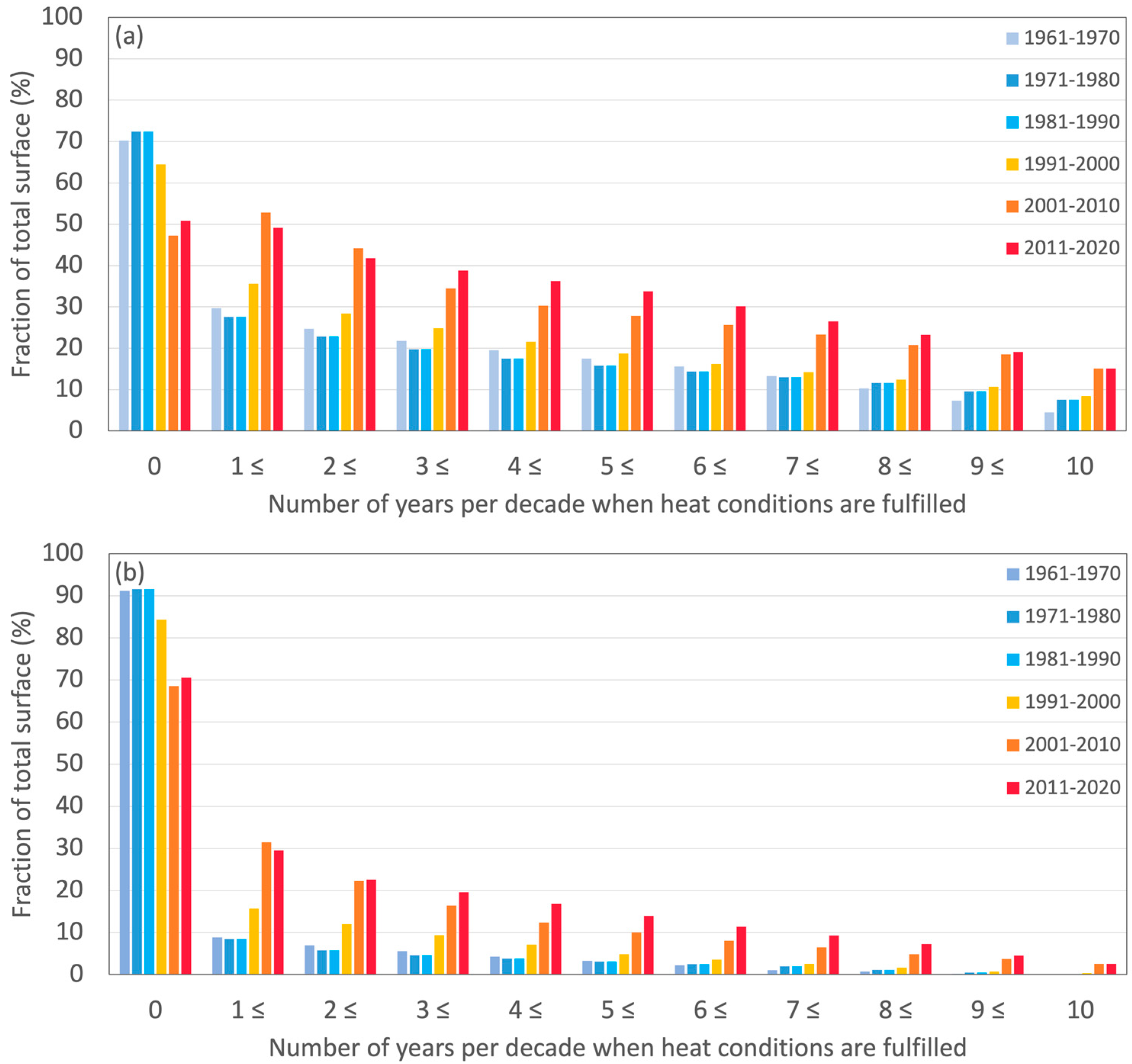
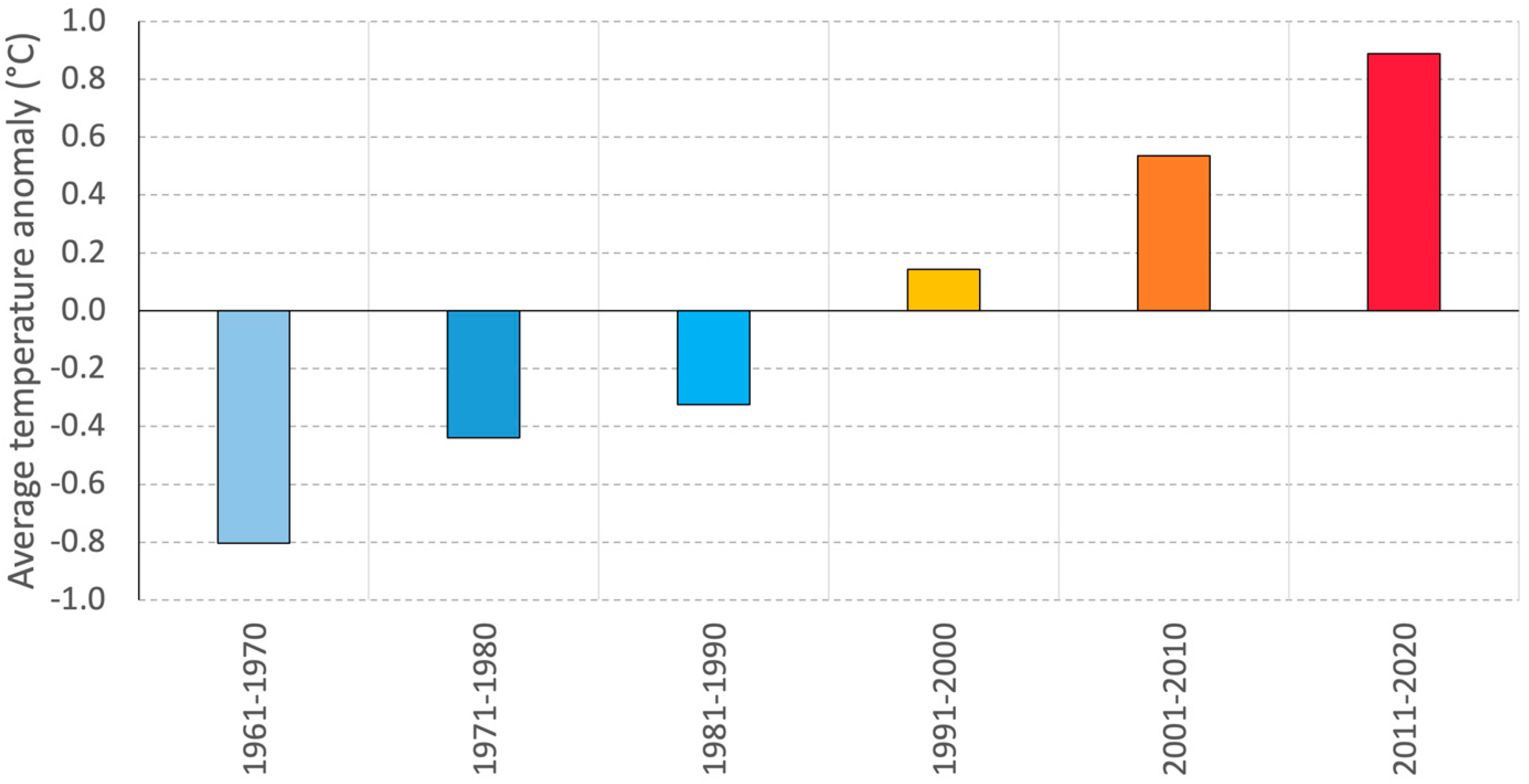
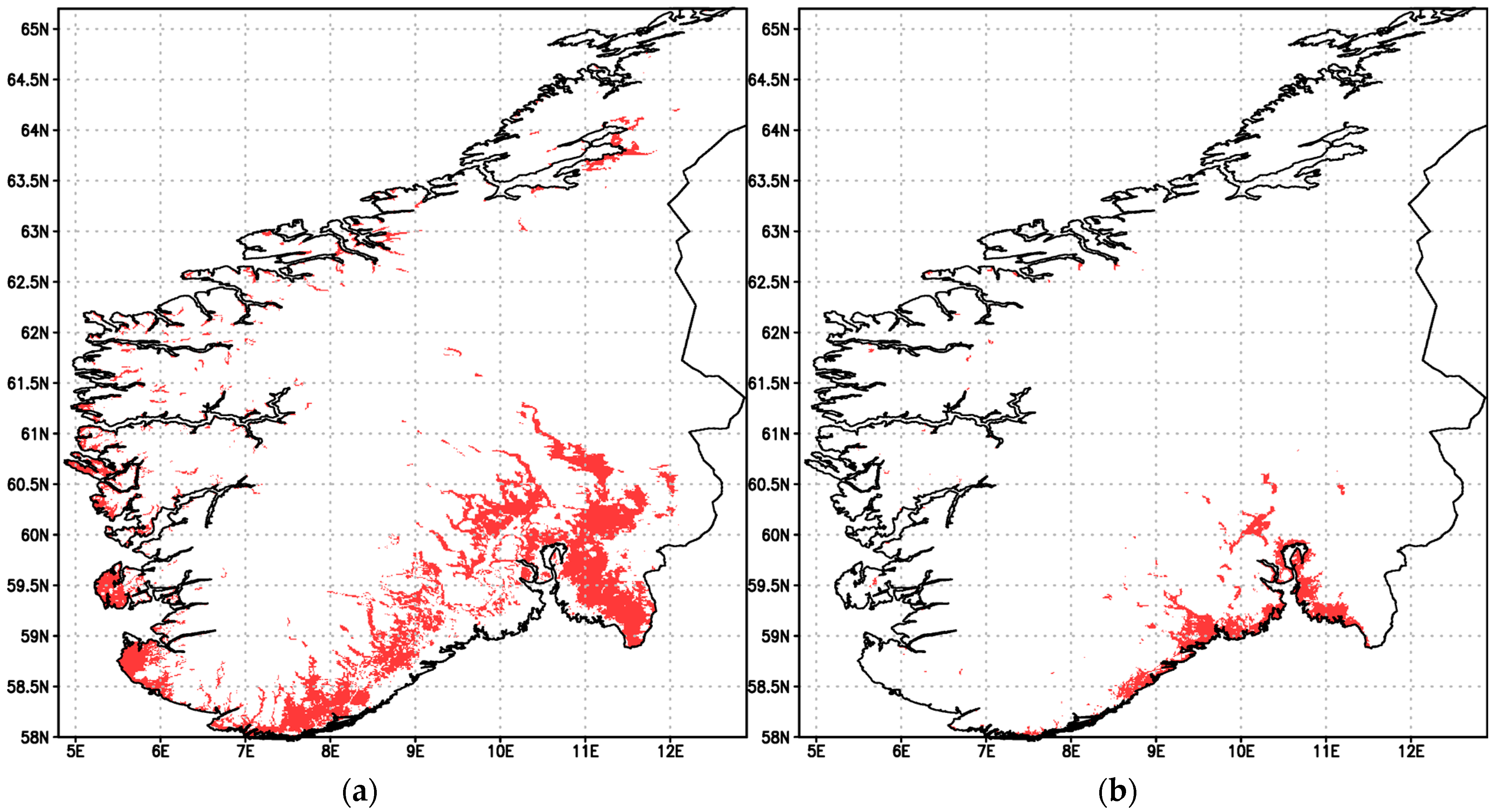
3.3. Zoning of Areas with Heat Favorable Conditions for Apple Growing and Their Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
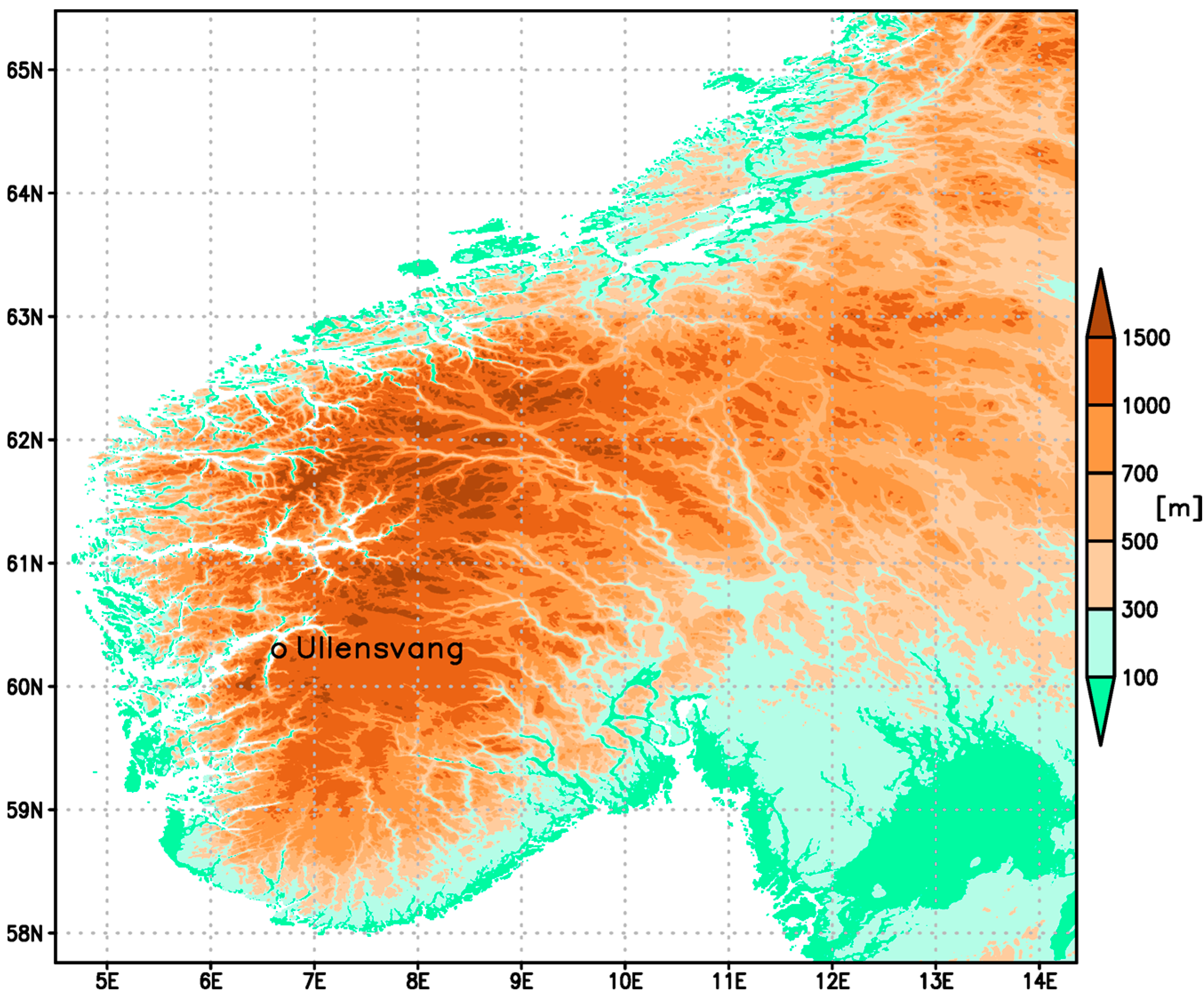
Appendix A. Supplement to the Analysis Implemented Using Data from Ullensvang




Appendix B. Supplement to the Assessment of the Heat Requirements for Apple Growing

Appendix C. Interpolated Temperature Data

Appendix D. Supplement to Zoning of Areas with Heat Favorable Conditions for Apple Growing
References
- FaoStat. 2023. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Lazarević, K.; Šegan, S.; Natić, M.; Tosti, T.; Ćirić, I.; Meland, M. Assessing the Fatty Acid, Carotenoid, and Tocopherol Compositions of Seeds from Apple Cultivars (Malus domestica Borkh.) Grown in Norway. Foods 2021, 10, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.E. Biology of Apples and Pears; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; 488p. [Google Scholar]
- Benmoussa, H.; Ghrab, M.; Ben Mimoun, M.; Luedeling, E. Chilling and heat requirements for local and foreign almond (Prunus dulcis Mill.) cultivars in a warm mediterranean location based on 30 years of phenology records. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 239, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.A.; Costa, R.; Fraga, H. New insights into thermal growing conditions of Portuguese grapevine varieties under changing climates. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 135, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.B.; Munoz, A.R.; Curetti, M.; Raffo, M.D. Impact of seasonal climate variability on the phenology of pear (Pyrus communis L.) cv. Williams from Rio Negro-Argentina. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2020, 36, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.G.; Kumar, S.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.H.; Durso, C.S.; Martin, P.H. Apple phenology occurs earlier across South Korea with higher temperatures and increased precipitation. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Qu, Z.; Su, B.; et al. Evaluating late spring frost risks of apple in the Loess Plateau of China under future climate change with phenological modeling approach. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 308, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.I.; Wani, A.W.; Dar, S.Q.; Younus Wani, M.; Sofi, J.A.; Baba, T.R.; Parray, E.; Rasool, A. Physiology of Fruit Set and Development in Apple under Temperate conditions: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2020, 9, 618–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, O.M.; Rivero, R.; Sønsteby, A. Temperature control of shoot growth and floral initiation in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakso, A.N.; Piccioni, R.M.; Denning, S.S.; Sottile, F.; Costa Tura, J. Validating an apple dry matter production model with whole canopy gas exchange measurements in the field. Acta Hortic. 1999, 499, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hanssen-Bauer, I.; Førland, E.J.; Haddeland, I.; Hisdal, H.; Mayer, S.; Nesje, A.; Nilsen, J.E.Ø.; Sandven, S.; Sandø, A.B.; Sorteberg, A.; et al. Klima i Norge 2100; Kunnskapsgrunnlag for klimatilpasning oppdatert i 2015; Bakgrunnsmateriale til NOU Klimatilpassing., Norsk Klimasenter: Oslo, Norway, 2015; ISSN 2387-3027. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Tignor, M., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, N. Apple Tree Phenology in Relation to Temperature in Sauherad (Norway). Int. J. Nat. Resour. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 7, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedeling, E.; Brown, P.H. A global analysis of the comparability of winter chill models for fruit and nut trees. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2011, 55, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadon, E.; Herrera, S.; Guerrero, B.I.; Guerra, M.E.; Rodrigo, J. Chilling and Heat Requirements of Temperature Fruit Trees (Prunus sp.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Campoy, J.A.; Egea, J. Chilling and heat requirements of apricot cultivars for flowering. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaman, K.; Koudahe, K.; Darapuneni, M.; Irmak, S. Chilling and Heat Accumulation of Fruit and Nut Trees and Flower Bud Vulnerability to Early Spring Low Temperatures in New Mexico: Meteorological Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruml, M.; Vuković, A.; Milatović, D. Evaluation of different methods for determining growing degree-day thresholds in apricot cultivars. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruml, M.; Milatović, D.; Vulić, T.; Vuković, A. Predicting apricot phenology using meteorological data. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2011, 55, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuković Vimić, A.; Djurdjević, V.; Ranković-Vasić, Z.; Nikolić, D.; Ćosić, M.; Lipovac, A.; Cvetković, B.; Sotonica, D.; Vojvodić, D.; Vujadinović Mandić, M. Enhancing Capacity for Short-Term Climate Change Adaptations in Agriculture in Serbia: Development of Integrated Agrometeorological Prediction System. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łysiak, G. The Sum of Active Temperatures as a Method of Determining the Optimum Harvest Date of ‘Šampion’ and ‘Ligol’ Apple Cultivars. Acta Sci. Pol. Hort. Cultus 2012, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Łysiak, G.P. Degree Days as a Method to Estimate the Optimal Harvest Date of ‘Conference’ Pears. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Nešović, M.; Ćirić, I.; Tešić, Ž.; Pezo, L.; Tosti, T.; Gašić, U.; Dojčinović, B.; Lončar, B.; Meland, M. Polyphenolics and Chemical Profiles of Domestic Norwegian Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) Cultivars. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 941487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Dabić Zagorac, D.; Gašić, U.; Tosti, T.; Natić, M.; Meland, M. Analysis of Apple Fruit (Malus × domestica Borkh.) Quality Attributes Obtained from Organic and Integrated Production Systems. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, F.M.; Fotirić Akšić, M.; Meland, M. Response of ’Rubinstep’ apple to flower and fruitlet thinning in a northern climate. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1295, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicklund, T.; Guyot, S.; Le Quere, J.-M. Chemical Composition of Apples Cultivated in Norway. Crops 2021, 1, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Guidlines on Analysis of Extremes in a Chaniging Climate in Support of Informed Decisions for Adaptation; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hack, H.; Bleiholder, H.; Buhr, L.; Meier, U.; SchnockFricke, U.; Weber, E.; Witzenberger, A. Einheitliche Codierung der phanologischen Entwicklungsstadien mono- und dikotyler Pfl anzen-Erweiterte BBCH-Skala, Allgemein. Nachrichtenbl. Deut. Pflanzenschutzd 1992, 44, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono-and Dicotyledonous Plants-BBCH Monograph; Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Available online: https://www.politicheagricole.it/flex/AppData/WebLive/Agrometeo/MIEPFY800/BBCHengl2001.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Laaksonen, O.; Kuldjärv, R.; Paalme, T.; Virkki, M.; Yang, B. Impact of apple cultivar, ripening stage, fermentation type and yeast strain on phenolic composition of apple ciders. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornes, R.C.; van der Schrier, G.; van den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Jones, P.D. An Ensemble Version of the E-OBS Temperature and Precipitation Datasets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressman, G.P. An operational objective analysis system. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1959, 87, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, D.; Jaksic, D.; Korac, N. Atlas of Viticulture; In Serbian; Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia: Belgrade, Serbia, 2015; p. 413. ISBN 978-86-6161-138-4. [Google Scholar]
- Djurović, D.; Vulić, T.; Veličković, M.; Oparnica, Č.; Djordjević, A.; Milatović, D.; Nikolić, D.; Zec, G.; Fortirić-Akšić, M.; Djordjević, B.; et al. Zoning of Fruit Production in Belgrade, South and East Serbia; In Serbian; Project Report; University of Belgrade-Faculty of Agriculture: Belgrade, Serbia, 2020; p. 306. [Google Scholar]
- Vujadinović Mandić, M.; Vuković Vimić, A.; Ranković-Vasić, Z.; Đurović, D.; Ćosić, M.; Sotonica, D.; Nikolić, D.; Đurđević, V. Observed Changes in Climate Conditions and Weather-Related Risks in Fruit and Grape Production in Serbia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, A.; Vujadinovic, M.; Djurdjevic, V.; Cvetkovic, B.; Rankovic-Vasic, Z.; Przic, Z.; Ruml, M.; Krzic, A. Fine scale Climate Change Analysis: From Global Models to Local Impact Studies in Serbia. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2015), Kavala, Greece, 17–20 September 2015; Volume 1498, pp. 892–901, ISSN 1613-0073. [Google Scholar]
- EC. EU Strategy on Adaptation to Climate Change; EC: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=COM:2021:82:FIN (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation, Disaster Risk Reduction and the Fight against Hunger; Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Oslo, Norway, 2023; Available online: https://www.regjeringen.no/contentassets/1d1d0105047e42f28f33008fcc90eef7/klimatilpasningstrategi_2023_en.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Ministry of Climate and Environment, 2022 Norway’s First Adaptation Communication. 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/Adaptation%20Communication%20Norway.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Moinina, A.; Lahlali, R.; Boulif, M. Important pests, diseases and weather conditions affecting apple production: Current state and perspectives. Rev. Mar. Sci. Agron. Vét. 2019, 7, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, D.; Gao, L.; Thapa, R.; Olmstead, D.; Khan, A. Field apple scab susceptibility of a diverse Malus germplasm collection identifies potential sources of resistance for apple breeding. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestras, R.E.; Sestras, A.F. Quantitative Traits of Interest in Apple Breeding and Their Implications for Selection. Plants 2023, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujadinović Mandić, M.; Vuković Vimić, A.; Fotirić Akšić, M.; Meland, M. Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 2: Assessment of Suitability of Heat Conditions under Future Climate Change. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
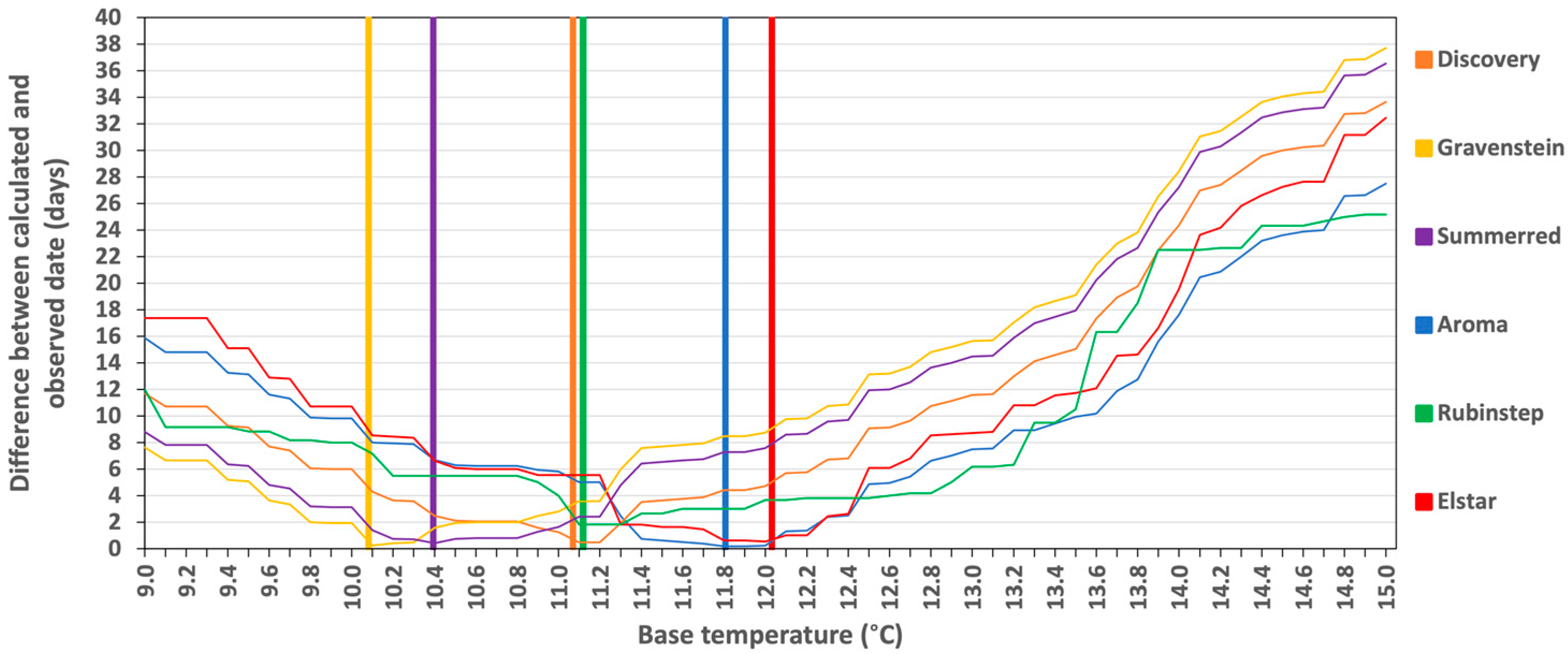
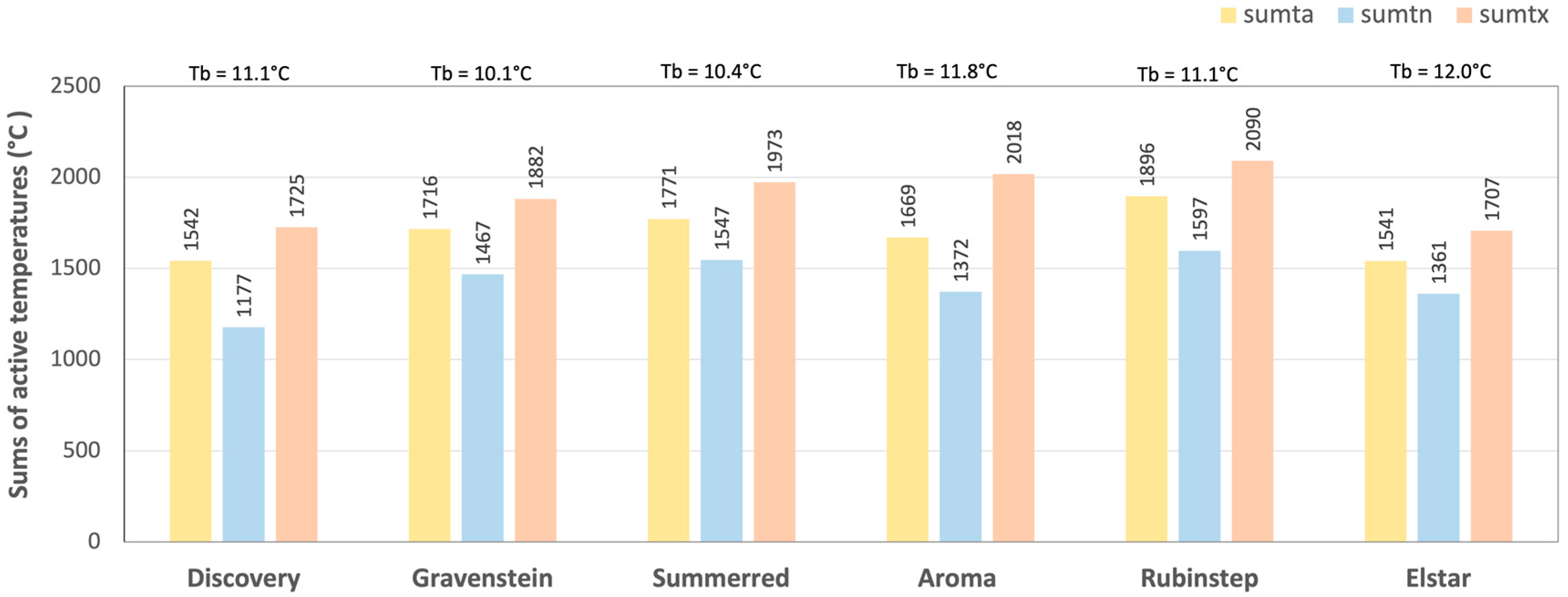

| Variety | Number of Years with Observed FB | Average Observed Date (Day of Year (Date)) | Selected Base Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravenstein | 17 | 139 (18.5.) | 10.1 |
| Summerred | 17 | 140 (19.5.) | 10.4 |
| Discovery | 17 | 143 (22.5.) | 11.1 |
| Rubinstep | 6 | 144 (23.5.) | 11.1 |
| Aroma | 16 | 147 (26.5.) | 11.8 |
| Elstar | 11 | 148 (27.5.) | 12.0 |
| Variety | Number of Years FB&HAR (HAR) | Earliest HAR | Average HAR | Difference between latest and earliest HAR Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery | 15 (16) | 235 (23.8.) | 249 (6.9.) | 25 |
| Gravenstein | 4 (5) | 243 (31.8.) | 257 (14.9.) | 24 |
| Summerred | 13 (14) | 242 (30.8.) | 259 (16.9.) | 32 |
| Aroma | 16 (18) | 253 (10.10.) | 273 (30.9.) | 36 |
| Rubinstep | 3 (13) | 259 (16.9.) | 279 (6.10.) | 31 |
| Elstar | 4 (11) | 258 (15.9.) | 280 (7.10.) | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuković Vimić, A.; Vujadinović Mandić, M.; Fotirić Akšić, M.; Vukićević, K.; Meland, M. Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 1: Zoning of Areas with Heat Conditions Favorable for Apple Growing under Observed Climate Change. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060993
Vuković Vimić A, Vujadinović Mandić M, Fotirić Akšić M, Vukićević K, Meland M. Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 1: Zoning of Areas with Heat Conditions Favorable for Apple Growing under Observed Climate Change. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060993
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuković Vimić, Ana, Mirjam Vujadinović Mandić, Milica Fotirić Akšić, Ksenija Vukićević, and Mekjell Meland. 2023. "Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 1: Zoning of Areas with Heat Conditions Favorable for Apple Growing under Observed Climate Change" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060993
APA StyleVuković Vimić, A., Vujadinović Mandić, M., Fotirić Akšić, M., Vukićević, K., & Meland, M. (2023). Climate Potential for Apple Growing in Norway—Part 1: Zoning of Areas with Heat Conditions Favorable for Apple Growing under Observed Climate Change. Atmosphere, 14(6), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060993








