Development and Field Testing of an Online Monitoring System for Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section for System Setup
2.1. Primary Materials and Reagent Preparation
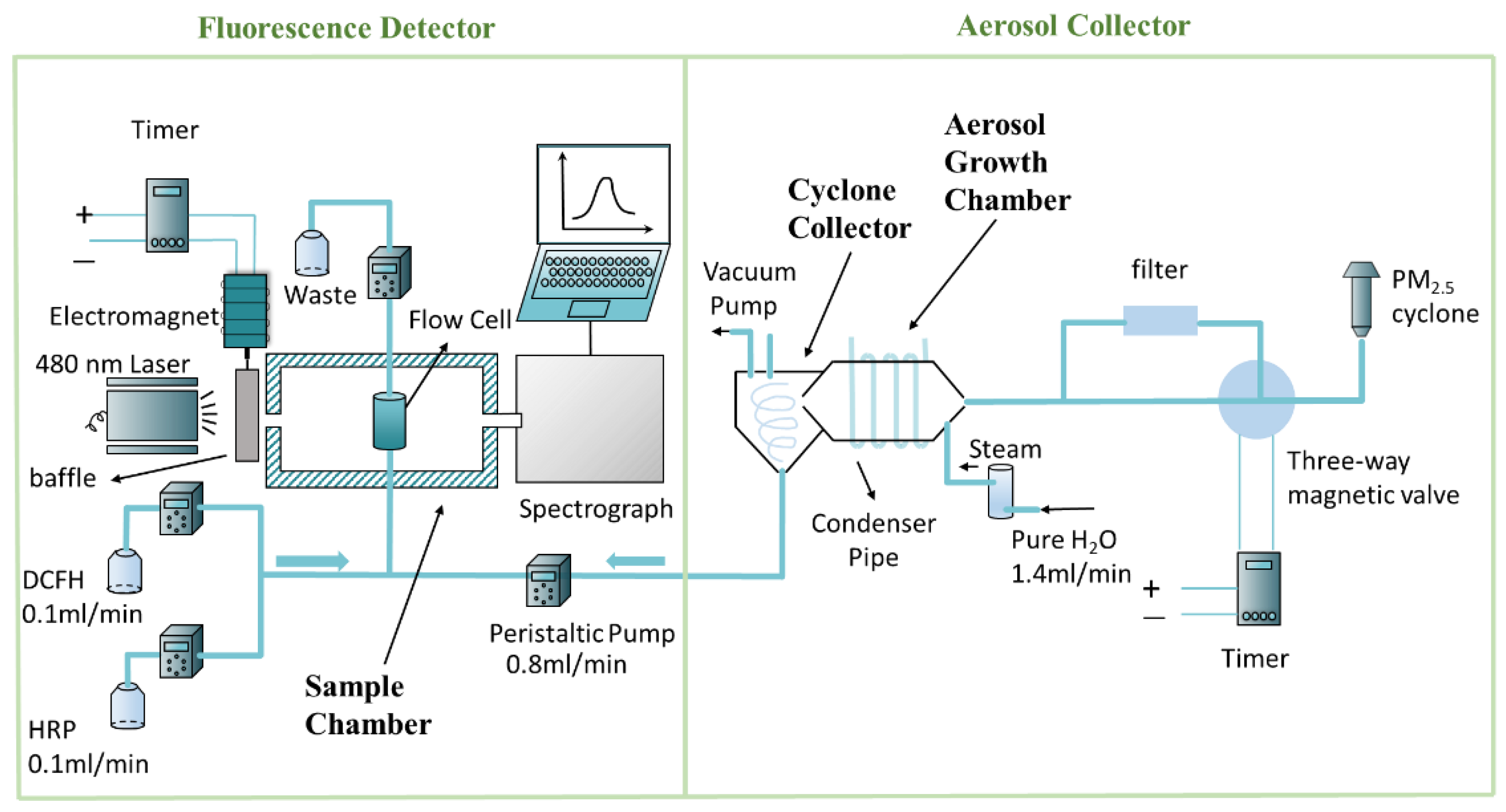
2.2. Online System Development
2.2.1. Aerosol Collector
2.2.2. Fluorescence Detector
2.2.3. Calculation of Particle-Bound ROS Concentration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Collection Efficiency
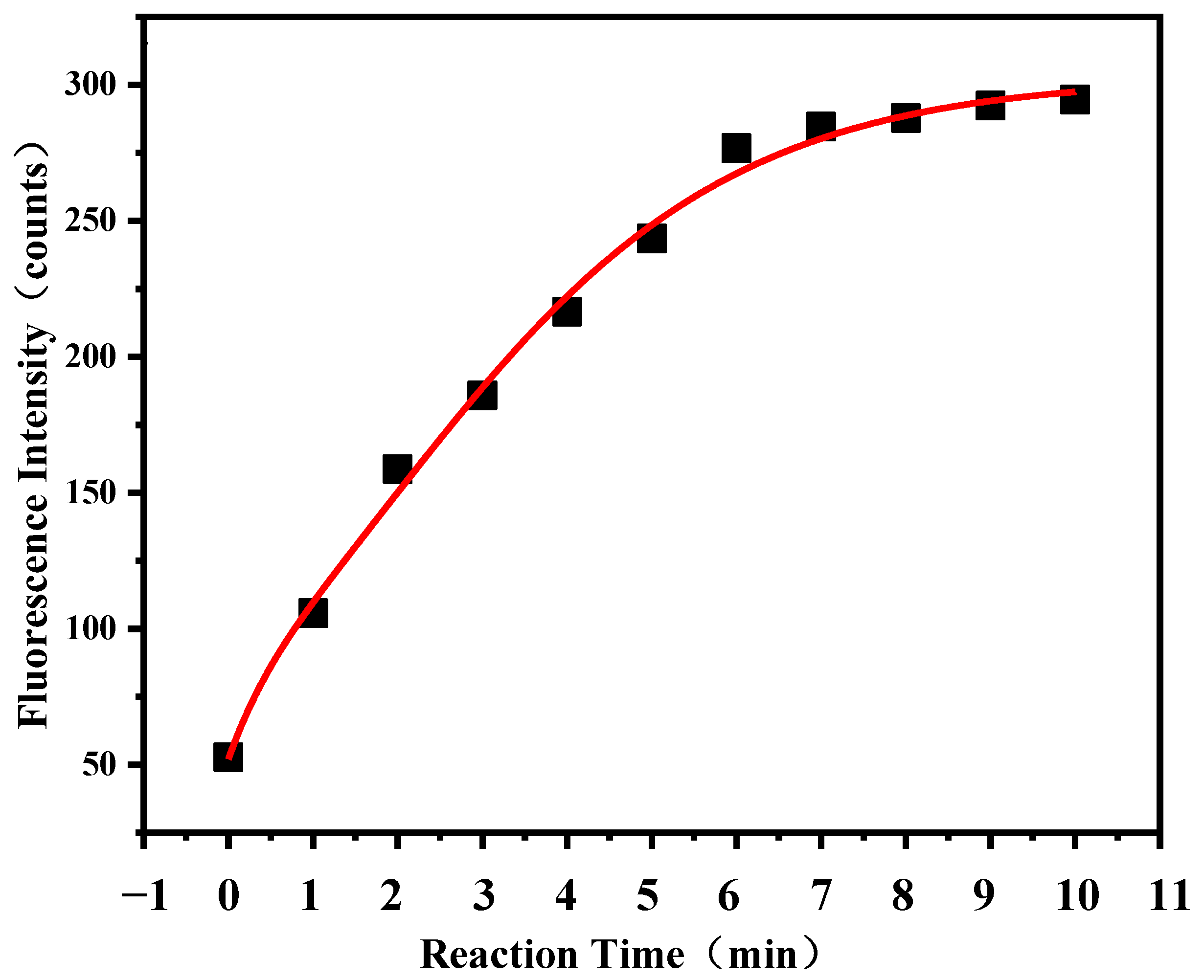
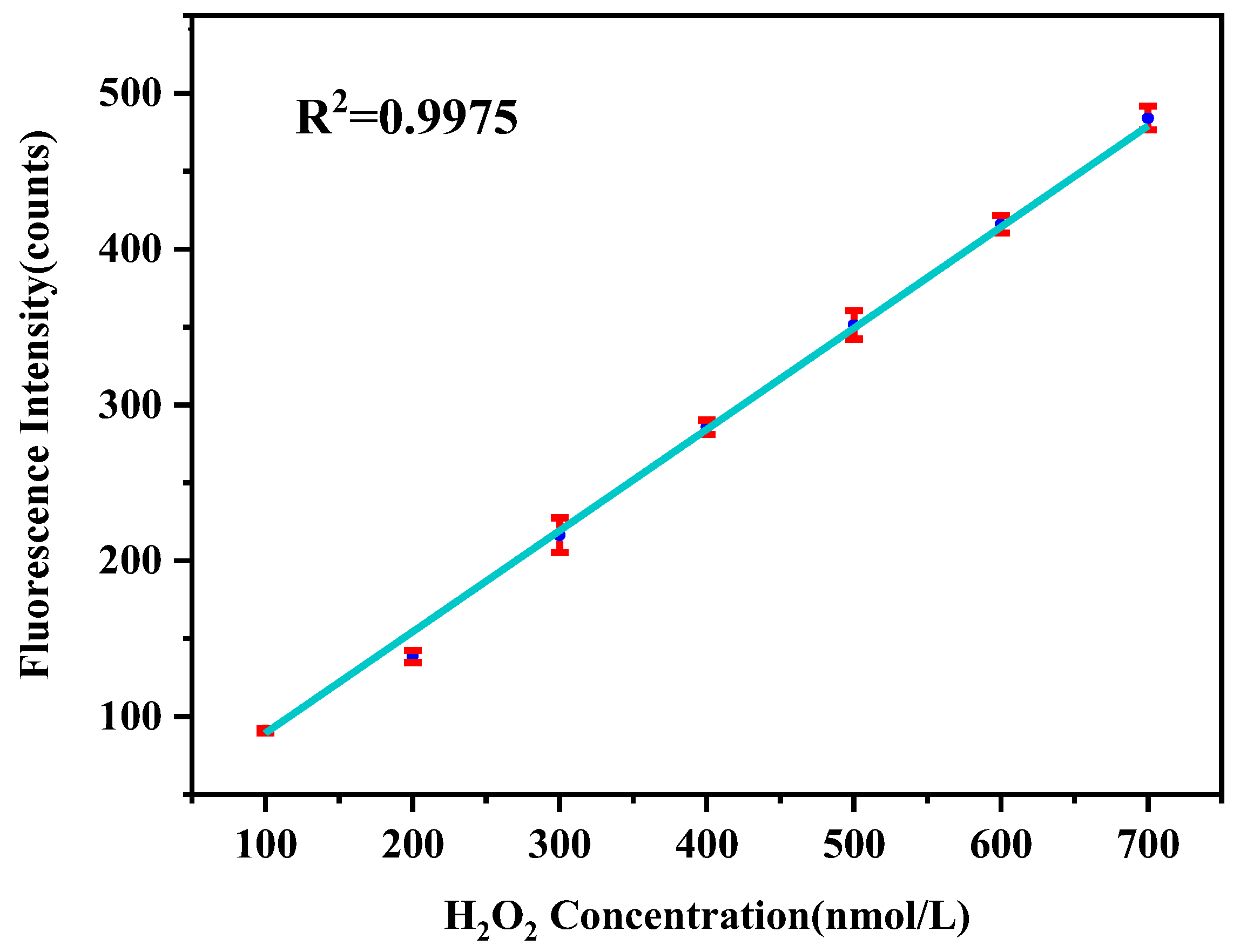
3.2. Calibration of the Detection System
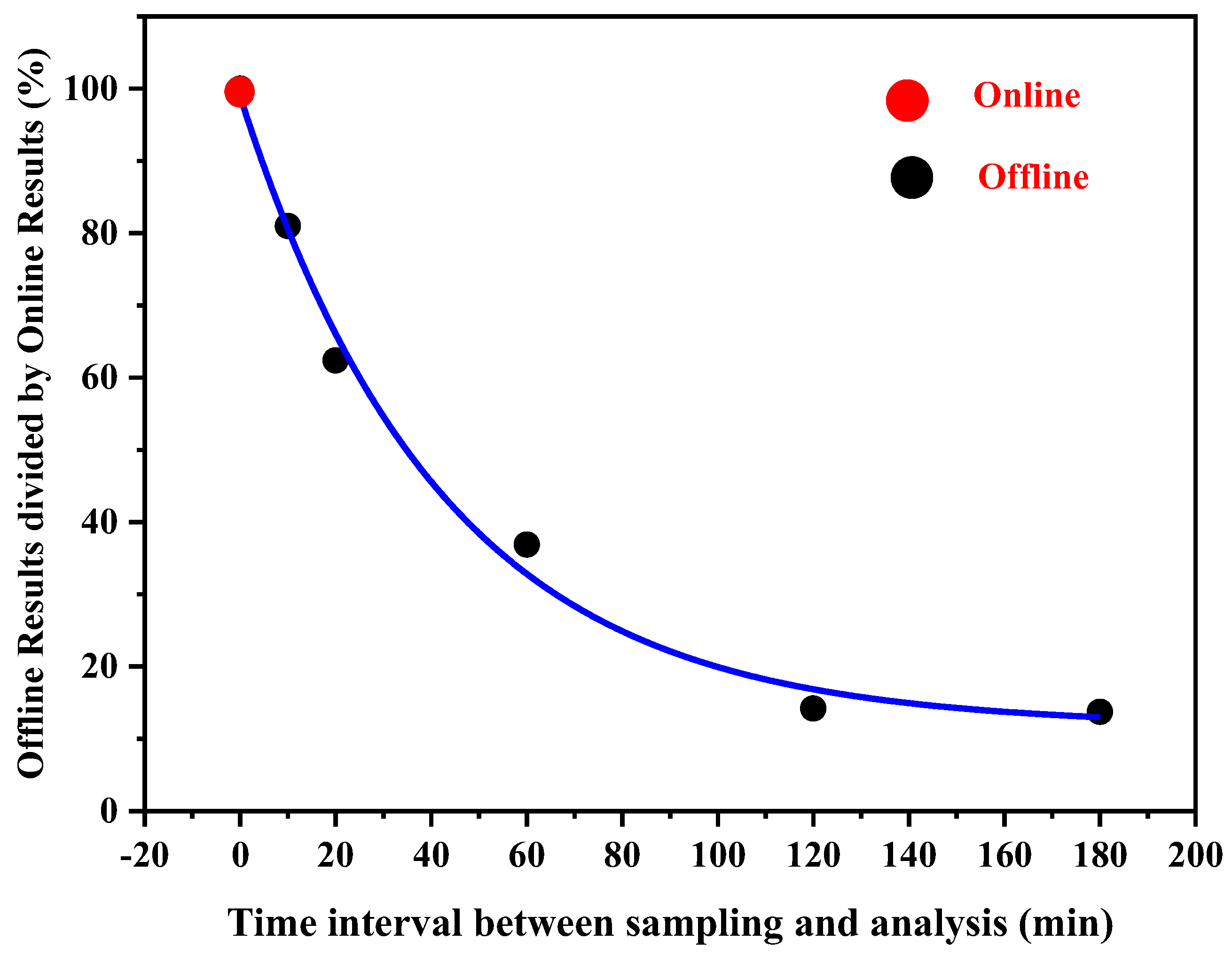
3.3. Comparison with Offline Method
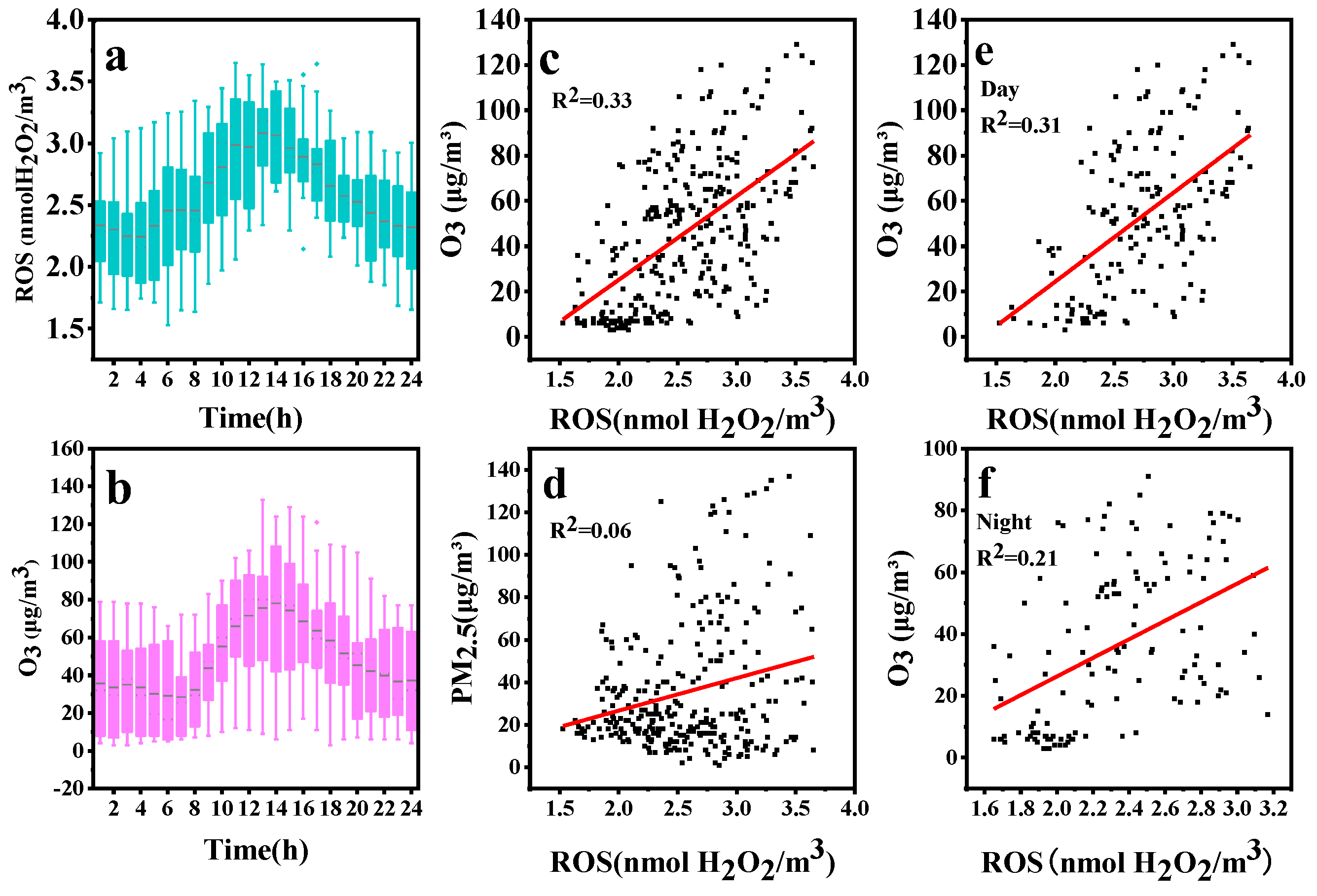
3.4. Results of Field Observation
| Study Location | Date | Method Type | Concentration (nmol H2O2/m3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flushing, NY | January–February 2004 | offline | 0.87 ± 0.18 | [55] |
| Taipei | July–December 2000 | offline | 0.54 ± 0.40 | [56] |
| Rubidoux, CA | July 2003 | offline | 5.90 ± 1.70 | [57] |
| Singapore(ambient) | December 2005 | offline | 5.71 ± 2.30 | [43] |
| Singapore (traffic) | December 2005 | offline | 15.10 ± 0.10 | [43] |
| Austin, homes(outdoor) | January–August 2012 | offline | 1.41 ± 1.0 | [44] |
| Austin, institutional building(outdoor) | January–August 2012 | offline | 1.68 ± 1.3 | [44] |
| Austin, retail stores(outdoor) | January–August 2012 | offline | 1.12 ± 1.1 | [44] |
| Rochester, NY | August 2009 | online | 8.30 ± 2.19 | [58] |
| Atlanta, GA | May, July 2012 | online | 0.25 ± 0.01 | [29] |
| Atlanta, GA | July 2012 | offline | 0.15 ± 0.019 | [29] |
| St Louis Mo, USA (gas phase) | August 2018 | online | 2.67 ± 1.11 | [8] |
| St Louis Mo, USA (particle phase) | August 2018 | online | 2.47 ± 0.33 | [8] |
| Beijing (gas phase) | December 2014 | online | 12.95 ± 3.91 | [10] |
| Beijing (particle phase) | December 2014 | online | 13.29 ± 5.09 | [10] |
| Shanghai | January 2023 | online | 2.56 ± 0.49 | This study |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, L.; Krewski, D.; Shortreed, J.; Samet, J. Special Issue: Strategies for Clean Air and Health. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A-Curr. Issues 2007, 70, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, M.; Masieroz, G.; Steinbach, S. The impact of ambient air pollution on hospital admissions. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2019, 20, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.T.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J.; Tolbert, P.E.; Abrams, J.Y.; Sarnat, S.E.; Klein, M.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Review of Acellular Assays of Ambient Particulate Matter Oxidative Potential: Methods and Relationships with Composition, Sources, and Health Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, L. Oxidative stress and oxidative damage-induced cell death. In Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), Nanoparticles, and Endoplasmic Reticulum (er) Stress-Induced Cell Death Mechanisms; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, S.; Finelli, R.; Agarwal, A.; Henkel, R. Reactive oxygen species in male reproduction: A boon or a bane? Andrologia 2021, 53, e13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulig, A.; Garlatti, M.; Bonvallot, V.; Marchand, A.; Barouki, R.; Marano, F.; Baeza-Squiban, A. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in the metabolic pathways triggered by diesel exhaust particles in human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L671–L679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A.; Fortenberry, C.F.; Williams, B.J.; Walker, M.J.; Dang, A.; Pfaff, A.; Ercal, N.; Morrison, G.C. Continuous measurement of reactive oxygen species inside and outside of a residential house during summer. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Roychoudhury, S. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Reproductive System: Sources and Physiological Roles. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1358, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Dong, H.; Huo, P.; Fang, D.; Schauer, J.J. Development of an automated sampling-analysis system for simultaneous measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in gas and particle phases: GAC-ROS. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 134, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Miguel, A.H.; Kumagai, Y.; Froines, J.R. Redox activity of airborne particulate matter (PM) at different sites in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Xu, L.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.G.; Ng, N.L.; Weber, R.J. Organic Aerosols Associated with the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Water-Soluble PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Cao, G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Yu, J.; Hu, D. Sources and oxidative potential of water-soluble humic-like substances (HULISWS) in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5607–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Ren, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, B.; Zheng, M.; Xu, Z. Production of hydroxyl radicals from Fe-containing fine particles in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.H.; Yang, A.; Strak, M.; Steenhof, M.; Hellack, B.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Kelly, F.; Harrison, R.M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Oxidative potential of particulate matter collected at sites with different source characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitani, Y.; Furuyama, A.; Tanabe, K.; Hirano, S. Comparison of Oxidative Abilities of PM2.5 Collected at Traffic and Residential Sites in Japan. Contribution of Transition Metals and Primary and Secondary Aerosols. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhinney, R.D.; Badali, K.; Liggio, J.; Li, S.-M.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Filterable Redox Cycling Activity: A Comparison between Diesel Exhaust Particles and Secondary Organic Aerosol Constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Uzu, G.; Calas, A.; Chevrier, F.; Besombes, J.-L.; Charron, A.; Salameh, D.; Jezek, I.; Mocnik, G.; Jaffrezo, J.-L. An apportionment method for the oxidative potential of atmospheric particulate matter sources: Application to a one-year study in Chamonix, France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9617–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calas, A.; Uzu, G.; Kelly, F.J.; Houdier, S.; Martins, J.M.F.; Thomas, F.; Molton, F.; Charron, A.; Dunster, C.; Oliete, A.; et al. Comparison between five acellular oxidative potential measurement assays performed with detailed chemistry on PM10 samples from the city of Chamonix (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7863–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Bates, J.T.; Abrams, J.; Klein, M.; Strickland, M.J.; Sarnat, S.E.; Chang, H.H.; Mulholland, J.A.; Tolbert, P.E.; et al. Oxidative potential of ambient water-soluble PM2.5 in the southeastern United States: Contrasts in sources and health associations between ascorbic acid (AA) and dithiothreitol (DTT) assays. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3865–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. Characterization of springtime airborne particulate matter-bound reactive oxygen species in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9325–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Guo, H.; King, L.; Bates, J.T.; Peltier, R.E.; Edgerton, E.; Russell, A.G.; Weber, R.J. Reactive oxygen species associated with water-soluble PM2.5 in the southeastern United States: Spatiotemporal trends and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12915–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Oxidative Potential and Inflammatory Impacts of Source Apportioned Ambient Air Pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12920–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secrest, M.H.; Schauer, J.J.; Carter, E.M.; Lai, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Shan, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Baumgartner, J. The oxidative potential of PM2.5 exposures from indoor and outdoor sources in rural China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirizzi, D.; Cesari, D.; Guascito, M.R.; Dinoi, A.; Giotta, L.; Donateo, A.; Contini, D. Influence of Saharan dust outbreaks and carbon content on oxidative potential of water-soluble fractions of PM2.5 and PM10. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugica, V.; Ortiz, E.; Molina, L.; De Vizcaya-Ruiz, A.; Nebot, A.; Quintana, R.; Aguilar, J.; Alcantara, E. PM composition and source reconciliation in Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5068–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, J.I. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: From air pollution to climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1998, 40, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, M.-C.; Wang, C.-S. Reactive oxygen species in incense smoke. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2002, 2, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.E.; Weber, R.J. Development and testing of an online method to measure ambient fine particulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) based on the 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin (DCFH) assay. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K. New directions: Reactive particles as a source of human health effects. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3192–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, A.C.; Wyzga, R.E. Attributing health effects to individual particulate matter constituents. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, D.; Falasca, G.; Canepari, S.; Massimi, L. Potential of PM-selected components to induce oxidative stress and root system alteration in a plant model organism. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Yu, J.Z. Dithiothreitol (DTT) concentration effect and its implications on the applicability of DTT assay to evaluate the oxidative potential of atmospheric aerosol samples. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ahmed, C.M.S.; Canchola, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Use of Dithiothreitol Assay to Evaluate the Oxidative Potential of Atmospheric Aerosols. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sisler, J.D.; Shaffer, J.; Leonard, S.S.; Morris, A.M.; Qian, Y.; Bello, D.; Demokritou, P. Assessment of reactive oxygen species generated by electronic cigarettes using acellular and cellular approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, C.P.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Bondy, S.C. Evaluation of the probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1992, 5, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.T. The scopoletin assay for hydrogen peroxide A review and a better method. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1989, 18, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y. Determination of the antioxidant capacity of different food natural products with a new developed flow injection spectrofluorimetry detecting hydroxyl radicals. Talanta 2005, 65, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.J.; Wragg, F.P.H.; Nutter, J.; Kalberer, M. Comparison of on-line and off-line methods to quantify reactive oxygen species (ROS) in atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Pakbin, P.; Cheung, K.L.; Cho, A.K.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Kleinman, M.T.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and oxidative characteristics of semi-volatile components of quasi-ultrafine particles in an urban atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godri, K.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Evans, T.; Baker, T.; Dunster, C.; Mudway, I.S.; Kelly, F.J. Increased Oxidative Burden Associated with Traffic Component of Ambient Particulate Matter at Roadside and Urban Background Schools Sites in London. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wragg, F.P.H.; Fuller, S.J.; Freshwater, R.; Green, D.C.; Kelly, F.J.; Kalberer, M. An automated online instrument to quantify aerosol-bound reactive oxygen species (ROS) for ambient measurement and health-relevant aerosol studies. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4891–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, S.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Balasubramanian, R. Contrasting reactive oxygen species and transition metal concentrations in combustion aerosols. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.S.; Siegel, J.A.; Kinney, K.A. Indoor particulate reactive oxygen species concentrations. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.S.; Siegel, J.A.; Kinney, K.A. Particulate reactive oxygen species on total suspended particles—Measurements in residences in Austin, Texas. Indoor Air 2016, 26, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bruns, E.A.; Zotter, P.; Stefenelli, G.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; El-Haddad, I.; Dommen, J. Development, characterization and first deployment of an improved online reactive oxygen species analyzer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlino, A.; Romano, M.P.; Lionetto, M.G.; Contini, D.; Guascito, M.R. An Overview of the Automated and On-Line Systems to Assess the Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachari, P.; Hopke, P.K. Development and laboratory testing of an automated monitor for the measurement of atmospheric particle-bound reactive oxygen species (ROS). Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, K.A.; Shapiro, J.; Sameenoi, Y.; Henry, C.; Volckens, J. Laboratory Evaluation of a Microfluidic Electrochemical Sensor for Aerosol Oxidative Load. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.A.; Stevanovic, S.; Bottle, S.; Ristovski, Z.D. An instrument for the rapid quantification of PM-bound ROS: The Particle Into Nitroxide Quencher (PINQ). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, D.A.; Rhoads, K.; McElhoney, K.; Schick, E.; Koehler, D.; Hogrefe, O. A water cyclone to preserve insoluble aerosols in liquid flow—An interface to flow cytometry to detect airborne nucleic acid. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Blough, N.V. Photoproduction of one-electron reducing intermediates by chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM): Relation to O2–and H2O2 photoproduction and CDOM photooxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11008–11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Orsini, D.; Daun, Y.; Lee, Y.N.; Klotz, P.J.; Brechtel, F. A particle-into-liquid collector for rapid measurement of aerosol bulk chemical composition. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpless, C.M.; Blough, N.V. The importance of charge-transfer interactions in determining chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) optical and photochemical properties. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachari, P.; Hopke, P.K.; Brune, W.H.; Ren, X.R.; Lesher, R.; Mao, J.Q.; Mitchel, M. Characterization of wintertime reactive oxygen species concentrations in Flushing, New York. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.F.; Wang, C.S. Experimental determination of reactive oxygen species in Taipei aerosols. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2001, 32, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachari, P.; Hopke, P.K.; Grover, B.D.; Eatough, D.J. Measurement of Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species in Rubidoux Aerosols. J. Atmos. Chem. 2005, 52, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yungang, W.; Hopke, P.K.; Liping, S.; Chalupa, D.C.; Utell, M.J. Laboratory and Field Testing of an Automated Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species Sampling-Analysis System. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 419476. [Google Scholar]
- Zikova, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Hopke, P.K. On the source contribution to Beijing PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 134, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, F.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y. Development, characterization, and application of an improved online reactive oxygen species analyzer based on the Monitor for AeRosols and Gases in ambient Air (MARGA). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Concentration of (NH4)2SO4 Solution (mmol/L) | Collection Efficiency |
|---|---|
| 0.40 | 96.5% |
| 0.50 | 93.9% |
| 0.60 | 95.6% |
| 0.70 | 95.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, J. Development and Field Testing of an Online Monitoring System for Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060924
Liu Y, Tang X, Zhang Z, Li L, Chen J. Development and Field Testing of an Online Monitoring System for Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060924
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuan, Xiancheng Tang, Zhiwei Zhang, Ling Li, and Jianmin Chen. 2023. "Development and Field Testing of an Online Monitoring System for Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060924
APA StyleLiu, Y., Tang, X., Zhang, Z., Li, L., & Chen, J. (2023). Development and Field Testing of an Online Monitoring System for Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Atmosphere, 14(6), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060924






