Revisiting the Influence of ENSO on the Arctic Stratosphere in CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
3. Results
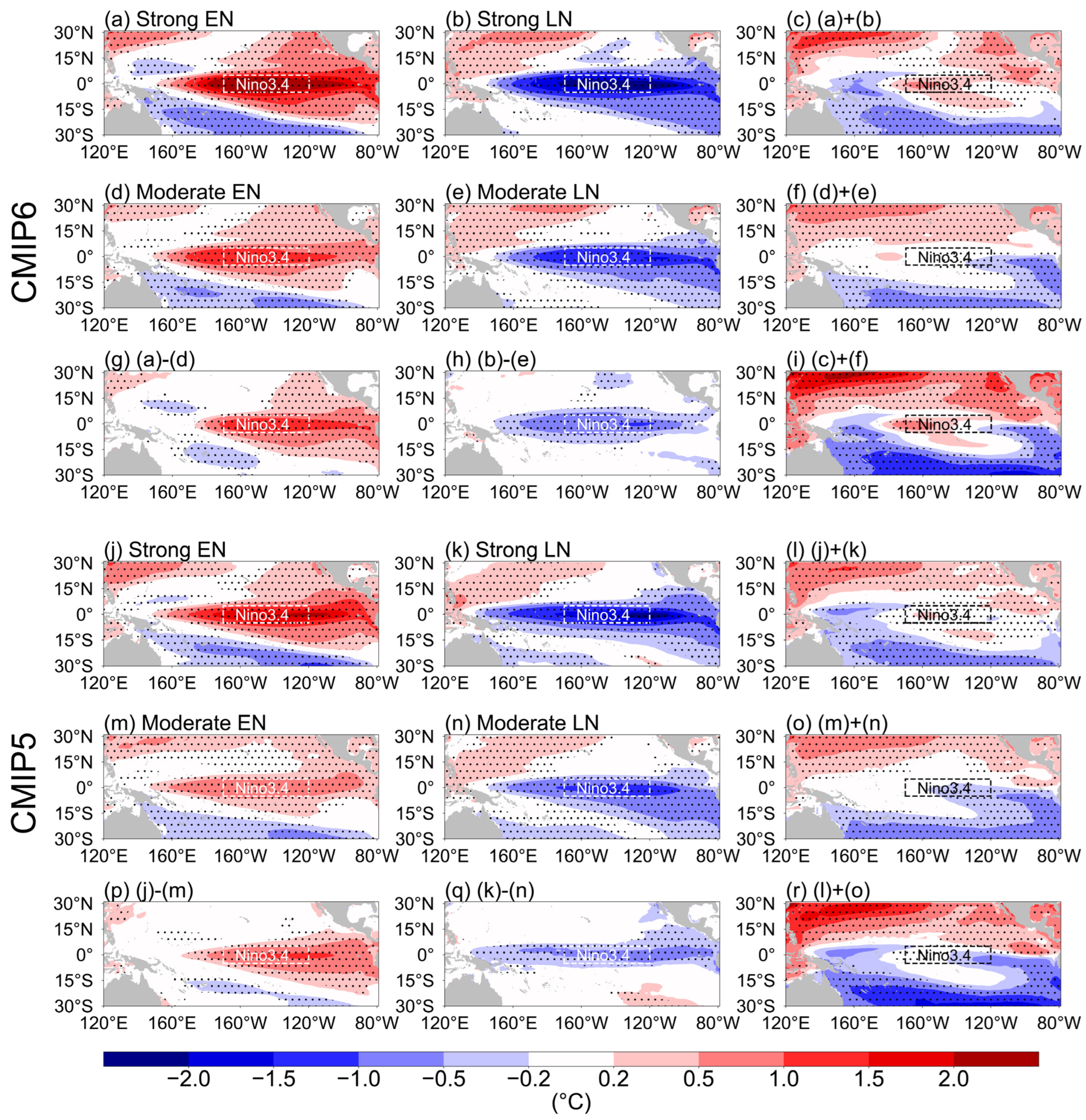
3.1. SST Anomalies and Arctic Stratospheric Response Associated with ENSO Events
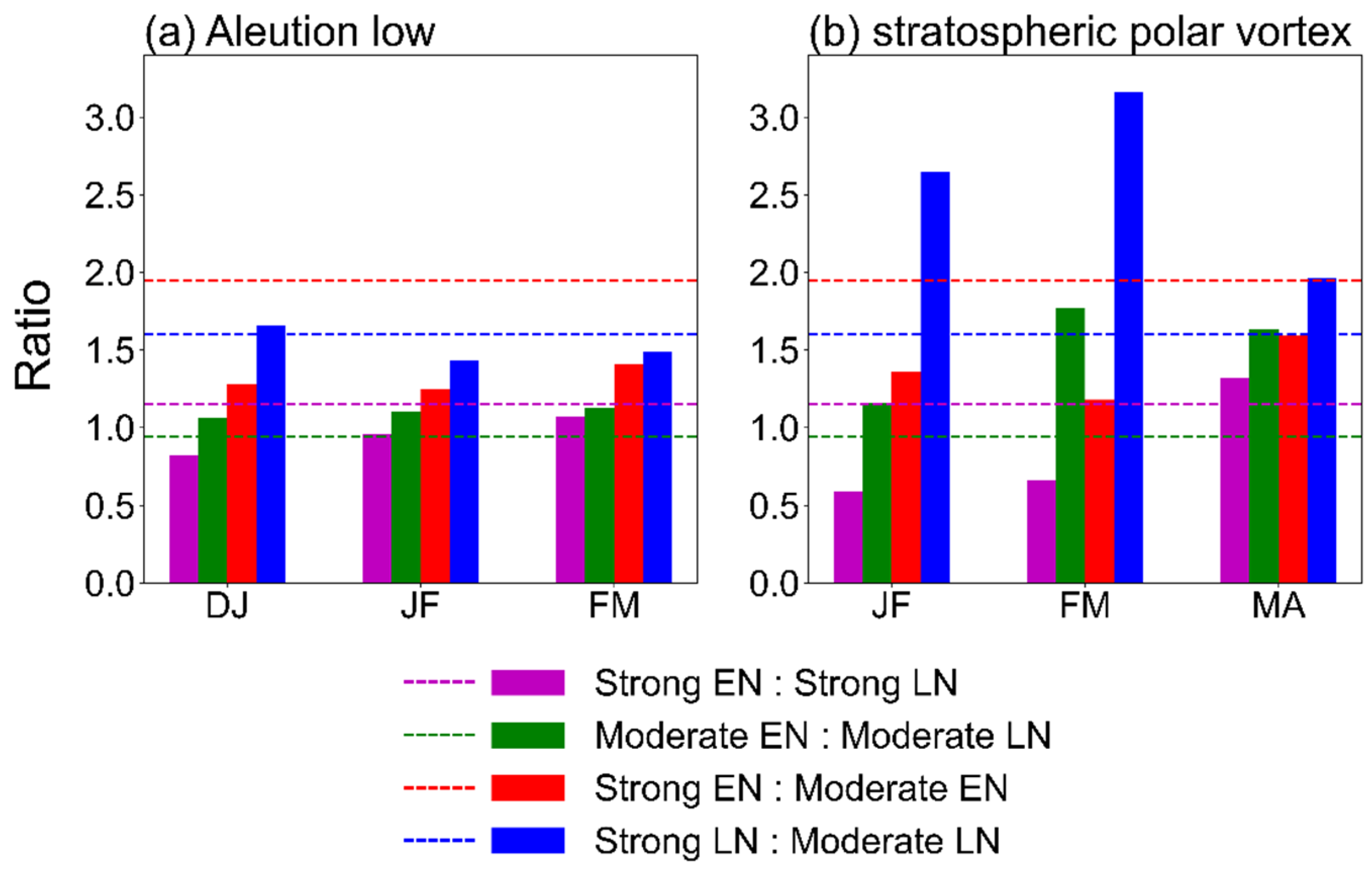
3.2. ENSO-SSW Relationship
3.3. Tropospheric Teleconnection and Planetary Wave Activities
3.4. Asymmetry and Nonlinearity
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sassi, F.; Kinnison, D.; Boville, B.A.; Garcia, R.R.; Roble, R. Effect of El Niño–Southern Oscillation on the dynamical, thermal, and chemical structure of the middle atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, E.; Giorgetta, M.A.; Esch, M.; Kornblueh, L.; Roeckner, E. The influence of sea surface temperatures on the Northern winter stratosphere: Ensemble simulations with the MAECHAM5 model. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, C.D.; Tung, K.K. Stratospheric polar warming by ENSO in winter: A statistical study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L04809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, M.; Seidel, D.J. Observed El Niño-Southern Oscillation temperature signal in the stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D23108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Hartmann, D.L. Effects of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation on polar temperatures in the stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D19112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Hartmann, D.L. Different ENSO teleconnections and their effects on the stratospheric polar vortex. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Hartmann, D.L.; Sassi, F. Tropospheric precursors of anomalous Northern Hemisphere stratospheric polar vortices. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 3282–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Waugh, D.W.; Butler, A.H. Are the teleconnections of Central Pacific and Eastern Pacific El Niño distinct in boreal wintertime? Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 1835–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ren, R. Asymmetry and nonlinearity of the influence of ENSO on the northern winter stratosphere: 1. Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9000–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ren, R. Asymmetry and nonlinearity of the influence of ENSO on the northern winter stratosphere: 2. Model study with WACCM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9017–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Li, J.; Tian, W.; Feng, J.; Huo, Y. Signals of El Niño Modoki in the tropical tropopause layer and stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5259–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Li, J.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. The relative impacts of El Niño Modoki, canonical El Niño, and QBO on tropical ozone changes since the 1980s. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 064020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Feng, J.; Ma, X. The key role of background sea surface temperature over the cold tongue in asymmetric responses of the Arctic stratosphere to El Niño–Southern Oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 114007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Yang, S. Lessened response of boreal winter stratospheric polar vortex to El Niño in recent decades. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, T.; Hu, J.; Shen, X. Decadal variation of the impact of La Niña on the winter Arctic stratosphere. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeisen, D.I.V.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Butler, A.H. The teleconnection of El Niño Southern Oscillation to the stratosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 5–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzina, B.; Palmeiro, F.M.; García-Serrano, J.; Bladé, I.; Batté, L.; Benassi, M. Multi-model assessment of the late-winter stratospheric response to El Niño and La Niña. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 58, 1987–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineson, S.; Scaife, A.A. The role of the stratosphere in the European climate response to El Niño. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, M.; Hartmann, D.L. Increased occurrence of stratospheric sudden warmings during El Niño as simulated by WACCM. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iza, M.; Calvo, N.; Manzini, E. The stratospheric pathway of La Niña. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 8899–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, M.M.; Calvo, N.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Butler, A.H.; Ineson, S.; Cagnazzo, C.; Manzini, E.; Pena-Ortiz, C. Extra-tropical atmospheric response to ENSO in the CMIP5 models. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, S.C.; Dunstone, N.J.; Scaife, A.A.; Smith, D.M.; Ineson, S.; Lim, J.; Fereday, D. The impact of strong El Niño and La Niña events on the North Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2874–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, I.; Garfinkel, C.I.; White, I.P.; Oman, L.D. The salience of nonlinearities in the boreal winter response to ENSO: Arctic stratosphere and Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4591–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, Q.; Ding, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Does extreme El Niño have a different effect on the stratosphere in boreal winter than its moderate counterpart? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3071–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trascasa-Castro, P.; Maycock, A.C.; Yiu, Y.Y.S.; Fletcher, J.K. On the linearity of the stratospheric and Euro-Atlantic sector response to ENSO. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 6607–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.H.; Deser, C.; Sun, L. Effects of stratospheric variability on El Niño teleconnections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, N.; Iza, M.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Manzini, E.; Pena-Ortiz, C.; Butler, A.H.; Cagnazzo, C.; Ineson, S.; Garfinkel, C.I. Northern Hemisphere stratospheric pathway of different El Niño flavors in stratosphere-resolving CMIP5 Models. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 4351–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.H.; Polvani, L.M. El Niño, La Niña, and stratospheric sudden warmings: A reevaluation in light of the observational record. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.H.; Polvani, L.M.; Deser, C. Separating the stratospheric and tropospheric pathways of El Niño-Southern Oscillation teleconnections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 024014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Son, S.-W. Revisiting the ENSO–SSW relationship. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Weinberger, I.; White, I.P.; Oman, L.D.; Aquila, V.; Lim, Y.-K. The salience of nonlinearities in the boreal winter response to ENSO: North Pacific and North America. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 52, 4429–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Polvani, L.M. A new look at stratospheric sudden warmings. Part I: Climatology and modeling benchmarks. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.G.; Holton, J.R.; Leovy, C.B. Middle Atmosphere Dynamics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.M.; Gutzler, D.S. Teleconnections in the geopotential height field during the Northern Hemisphere Winter. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1981, 109, 784–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Yu, J.-Y. The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton-Perez, A.J.; Baldwin, M.P.; Birner, T.; Black, R.X.; Butler, A.H.; Calvo, N.; Davis, N.A.; Gerber, E.P.; Gillett, N.; Hardiman, S.; et al. On the lack of stratospheric dynamical variability in low-top versions of the CMIP5 models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2494–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L.J.; Charlton-Perez, A.J. Final warming of the Southern Hemisphere polar vortex in high- and low-top CMIP5 models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2535–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Garfinkel, C.I. CMIP5/6 models project little change in the statistical characteristics of sudden stratospheric warmings in the 21st century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Wu, T.; Lu, Y.; Chu, M. Mean state of the Northern Hemisphere stratospheric polar vortex in three generations of CMIP models. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 4603–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Ren, R.; Jin, D. On the spring stratospheric final warming in CMIP5 and CMIP6 models. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | CMIP5 Models | Resolution for Atmospheric Variables (Lon × Lat) | Resolution for SST (Lon × Lat) | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACCESS1-0 | 192 × 144 | 360 × 300 | 1950–2005 |
| 2 | ACCESS1-3 | 192 × 144 | 360 × 300 | 1950–2005 |
| 3 | CanESM2 | 128 × 64 | 256 × 192 | 1950–2005 |
| 4 | CMCC-CESM | 96 × 48 | 182 × 149 | 1950–2005 |
| 5 | CMCC-CMS | 192 × 96 | 182 × 149 | 1950–2005 |
| 6 | CNRM-CM5 | 256 × 128 | 362 × 292 | 1950–2005 |
| 7 | FGOALS-s2 | 128 × 108 | 360 × 196 | 1950–2005 |
| 8 | GFDL-CM3 | 144 × 90 | 360 × 200 | 1860–2005 |
| 9 | GFDL-ESM2G | 144 × 90 | 360 × 210 | 1861–2005 |
| 10 | IPSL-CM5A-LR | 96 × 96 | 182 × 149 | 1850–2005 |
| 11 | IPSL-CM5A-MR | 144 × 143 | 182 × 149 | 1850–2005 |
| 12 | IPSL-CM5B-LR | 96 × 96 | 182 × 149 | 1850–2005 |
| 13 | MIROC5 | 256 × 128 | 256 × 224 | 1850–2005 |
| 14 | MIROC-ESM | 128 × 64 | 256 × 192 | 1950–2005 |
| 15 | MIROC-ESM-CHEM | 128 × 64 | 256 × 192 | 1950–2005 |
| 16 | MPI-ESM-LR | 192 × 96 | 256 × 220 | 1950–2005 |
| 17 | MPI-ESM-MR | 192 × 96 | 802 × 404 | 1950–2005 |
| 18 | MPI-ESM-P | 192 × 96 | 256 × 220 | 1950–2005 |
| 19 | MRI-CGCM3 | 320 × 160 | 360 × 368 | 1950–2005 |
| 20 | MRI-ESM1 | 320 × 160 | 360 × 368 | 1950–2005 |
| 21 | NorESM1-M | 144 × 96 | 320 × 384 | 1950–2005 |
| No. | CMIP6 Models | Resolution for Atmospheric Variables (Lon × Lat) | Model Top | Resolution for SST (Lon × Lat) | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | 192 × 144 | 85 km (High-top) | 360 × 300 | 1950–2014 |
| 2 | BCC-ESM1 | 128 × 64 | 2.19 hPa (Low-top) | 360 × 232 | 1950–2014 |
| 3 | CanESM5 | 128 × 64 | 1 hPa (High-top) | 361 × 290 | 1850–2014 |
| 4 | CESM2 | 288 × 192 | 2.25 hPa (Low-top) | 320 × 384 | 1850–2014 |
| 5 | CESM2-FV2 | 144 × 96 | 2.25 hPa (Low-top) | 320 × 384 | 1850–2014 |
| 6 | CESM2-WACCM | 288 × 192 | 4.5 × 10–6 hPa (High-top) | 320 × 384 | 1850–2014 |
| 7 | EC-Earth3 | 512 × 256 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 362 × 292 | 1850–2014 |
| 8 | GFDL-CM4 | 360 × 180 | 10 hPa (Low-top) | 1440 × 1080 | 1850–2014 |
| 9 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | 144 × 143 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 362 × 332 | 1850–2014 |
| 10 | MPI-ESM-1-2-HAM | 192 × 96 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 256 × 220 | 1850–2014 |
| 11 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR | 384 × 192 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 802 × 404 | 1850–2014 |
| 12 | MPI-ESM1-2-LR | 192 × 96 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 256 × 220 | 1850–2014 |
| 13 | MRI-ESM2-0 | 320 × 160 | 0.01 hPa (High-top) | 360 × 364 | 1950–2014 |
| 14 | NorESM2-LM | 144 × 96 | 3 hPa (Low-top) | 360 × 384 | 1950–2014 |
| 15 | NorESM2-MM | 288 × 192 | 3 hPa (Low-top) | 360 × 384 | 1950–2014 |
| Models | ENSO Magnitude | Winter SST Anomalies in Niño3.4 Region | Winter Numbers | SSW Numbers | SSW Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIP6 | Strong El Niño | 2.32 | 158 | 97 | 0.61 |
| Moderate El Niño | 1.19 | 299 | 179 | 0.60 | |
| Strong La Niña | –2.01 | 108 | 61 | 0.56 | |
| Moderate La Niña | –1.26 | 356 | 187 | 0.53 | |
| Neutral | — | 1039 | 618 | 0.59 | |
| All | — | 1960 | 1142 | 0.58 | |
| CMIP5 | Strong El Niño | 1.61 | 155 | 52 | 0.34 |
| Moderate El Niño | 0.80 | 273 | 94 | 0.34 | |
| Strong La Niña | –1.54 | 74 | 25 | 0.34 | |
| Moderate La Niña | –1.01 | 271 | 80 | 0.30 | |
| Neutral | — | 961 | 256 | 0.27 | |
| All | — | 1734 | 507 | 0.29 |
| Models | ENSO Magnitude | Winter Numbers | SSW Numbers | SSW Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-top | Strong El Niño | 101 | 69 | 0.68 |
| Moderate El Niño | 188 | 137 | 0.73 | |
| Strong La Niña | 66 | 42 | 0.64 | |
| Moderate La Niña | 234 | 144 | 0.62 | |
| Neutral | 687 | 457 | 0.67 | |
| All | 1276 | 849 | 0.67 | |
| Low-top | Strong El Niño | 57 | 28 | 0.49 |
| Moderate El Niño | 111 | 42 | 0.38 | |
| Strong La Niña | 42 | 19 | 0.45 | |
| Moderate La Niña | 122 | 43 | 0.35 | |
| Neutral | 352 | 161 | 0.46 | |
| All | 684 | 293 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Deng, J.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, A. Revisiting the Influence of ENSO on the Arctic Stratosphere in CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050785
Hu J, Shen Y, Deng J, Jia Y, Wang Z, Li A. Revisiting the Influence of ENSO on the Arctic Stratosphere in CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050785
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jinggao, Yifan Shen, Jiechun Deng, Yanpei Jia, Zixu Wang, and Anqi Li. 2023. "Revisiting the Influence of ENSO on the Arctic Stratosphere in CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050785
APA StyleHu, J., Shen, Y., Deng, J., Jia, Y., Wang, Z., & Li, A. (2023). Revisiting the Influence of ENSO on the Arctic Stratosphere in CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere, 14(5), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050785





