Investigation and Prediction of the Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Changes for Mashhad City in Iran during 1990–2030
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
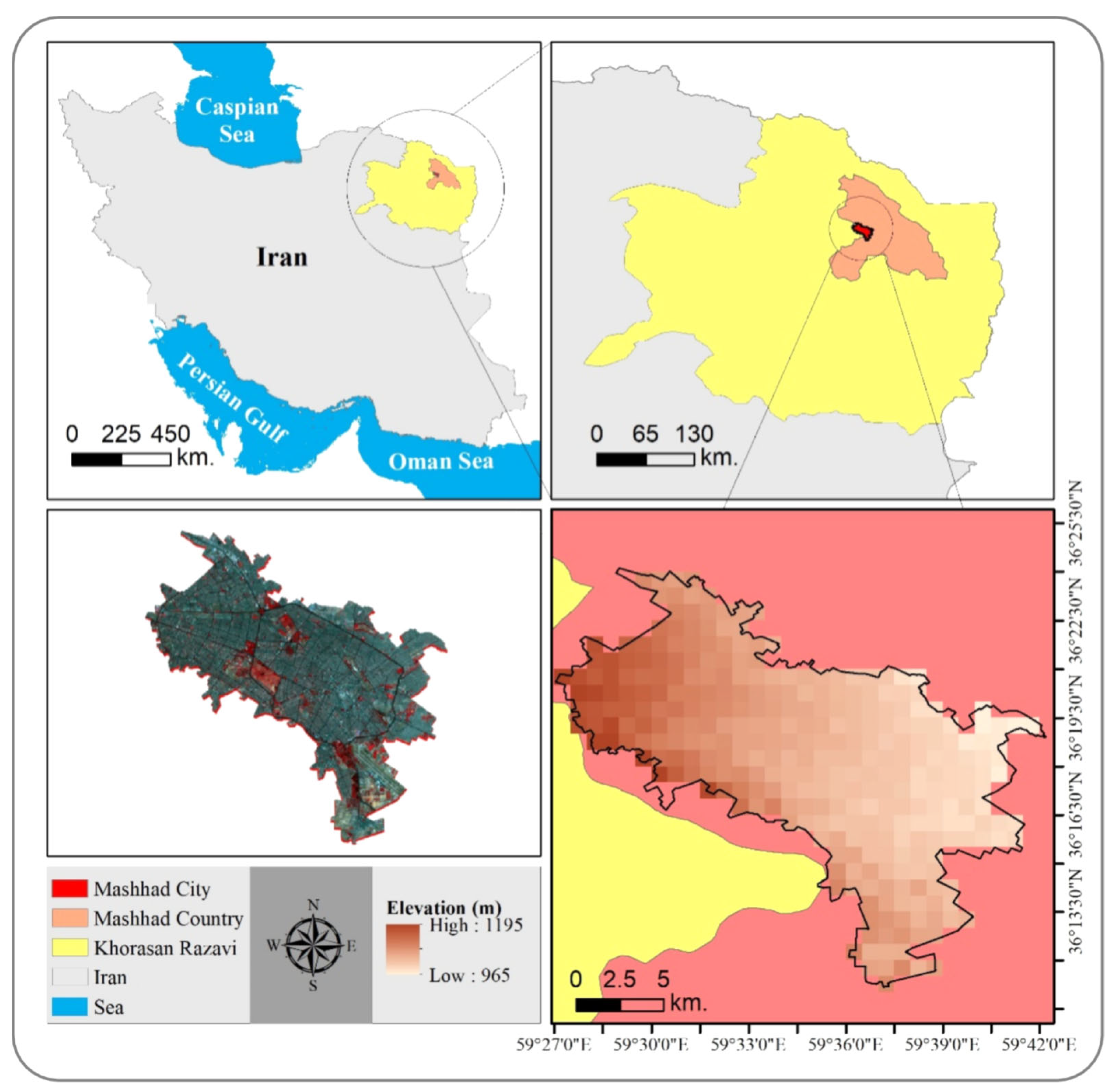
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methods
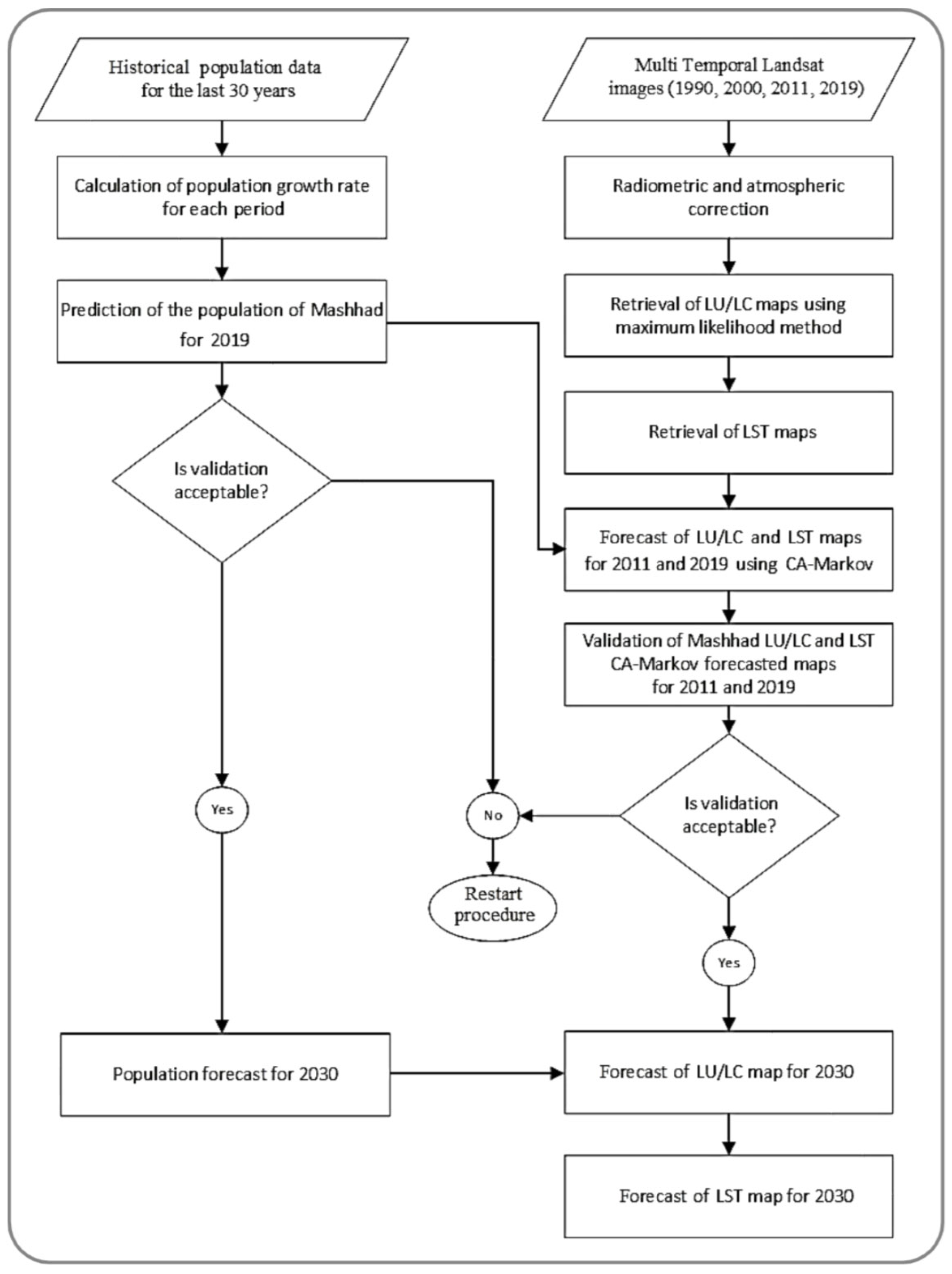
3.1. Flowchart of the Data Processing
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Calculation of Population Growth Rate
Historical Population Growth Rates
Prediction of Population
3.2.2. LU/LC Classification
Maximum Likelihood Method
LU/LC Classification Accuracy Assessment
3.2.3. Calculation of LST
3.2.4. Calculation of NDVI
3.2.5. LU/LC and LST Prediction
Markov Model for Forecasting of LU/LC and LST Changes
Markov Model Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
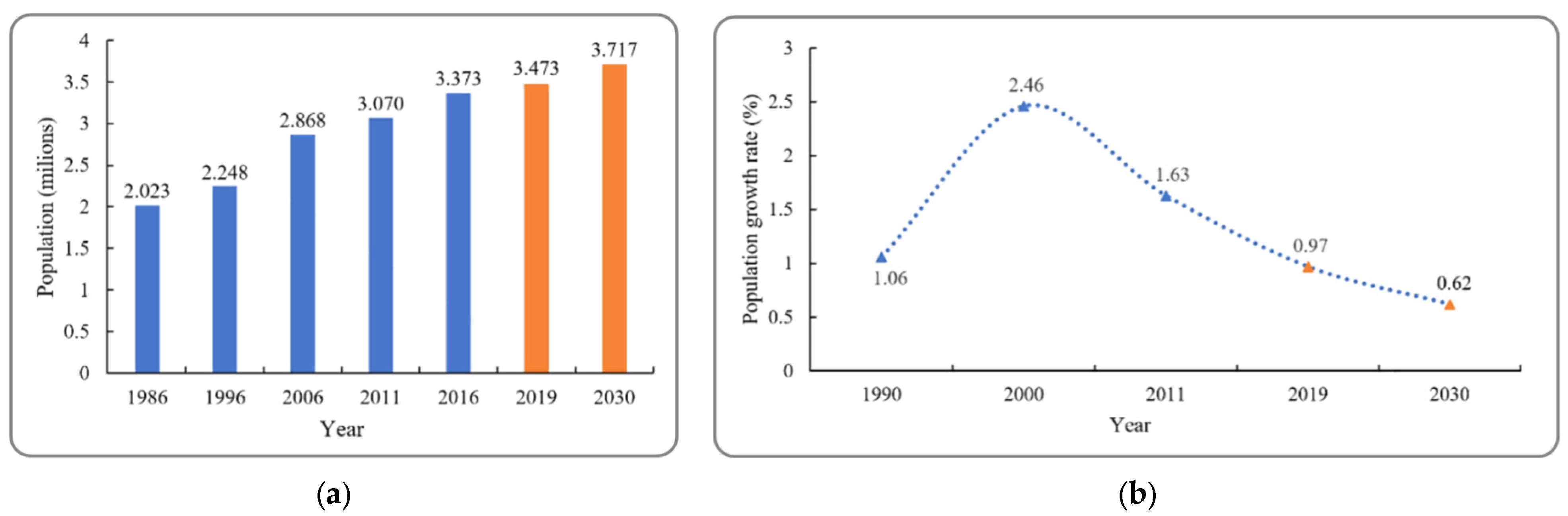
4.1. Population Changes
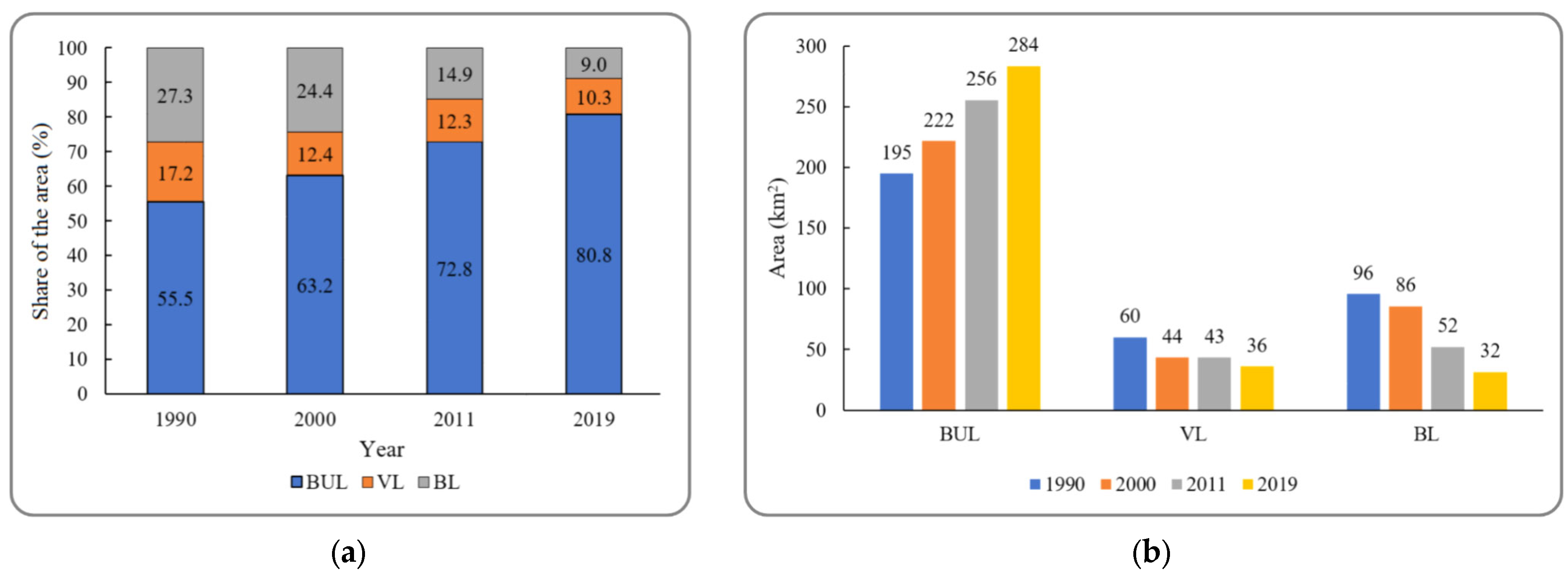
4.2. LU/LC Classification
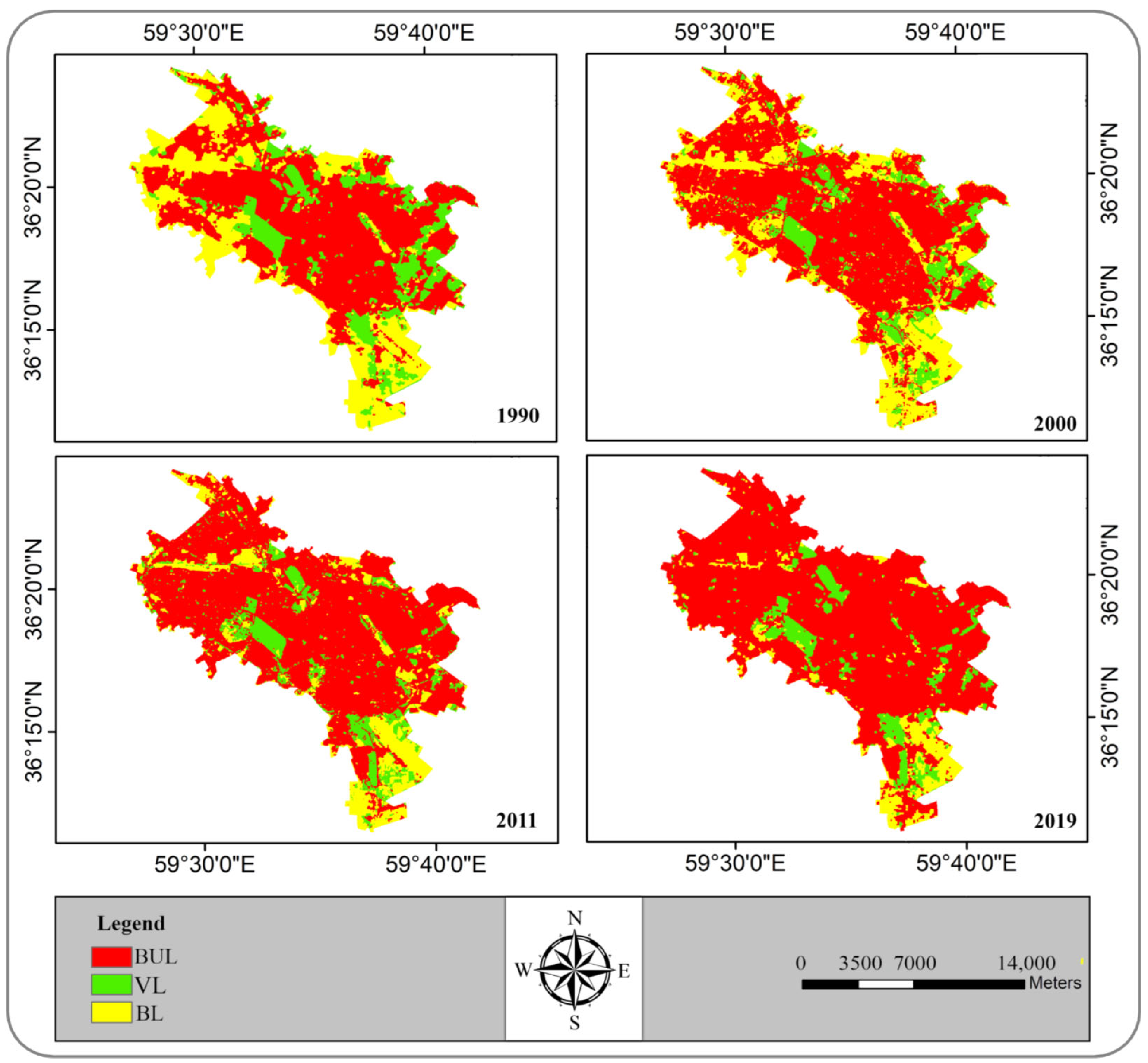
4.2.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern of LU/LC
4.2.2. LU/LC Classification Accuracy Assessment
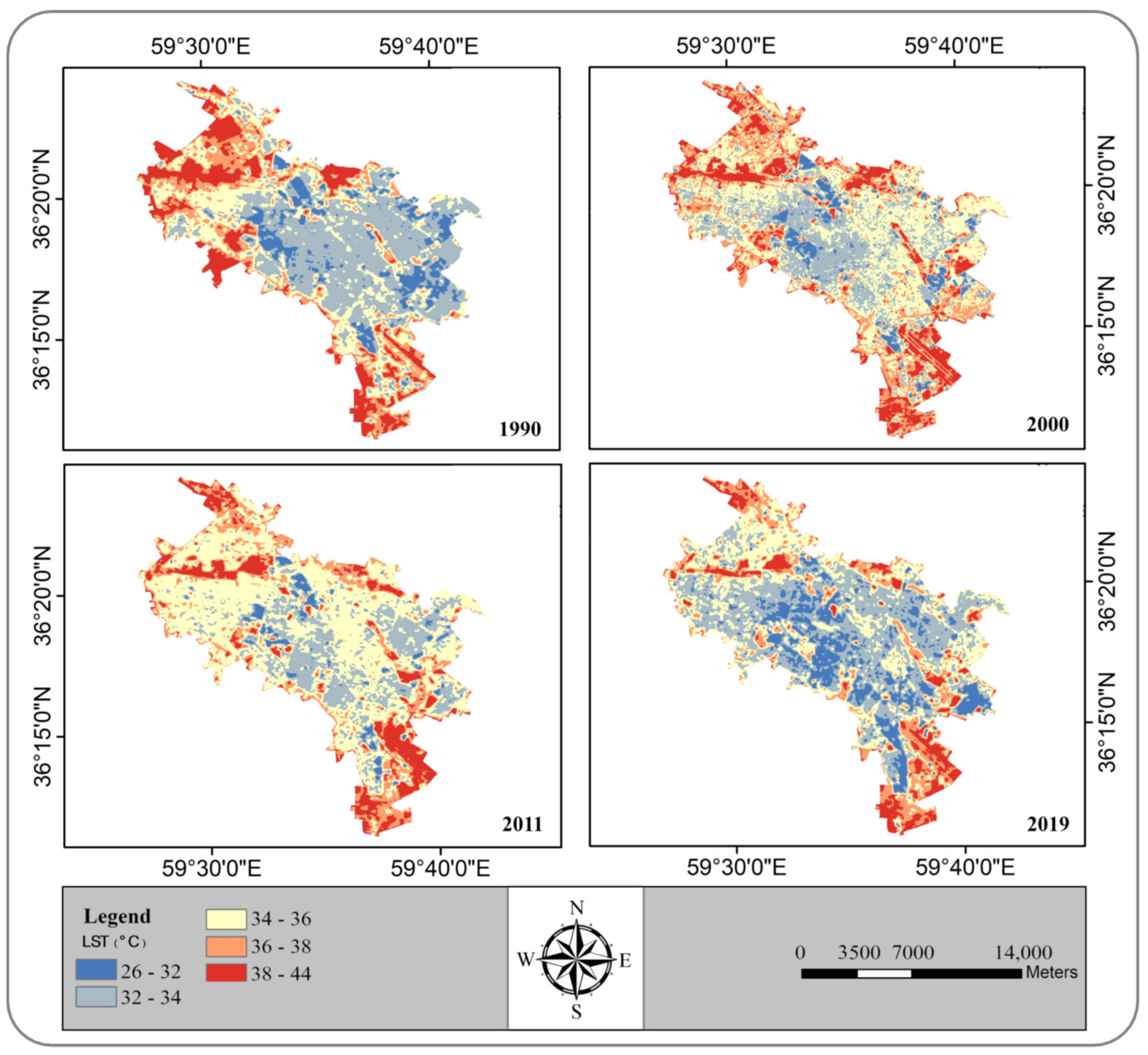
4.3. Spatiotemporal Pattern of LST
4.4. Prediction of LU/LC and LST
4.4.1. Assessment of the Accuracy of the Markov Model for LU/LC and LST Prediction
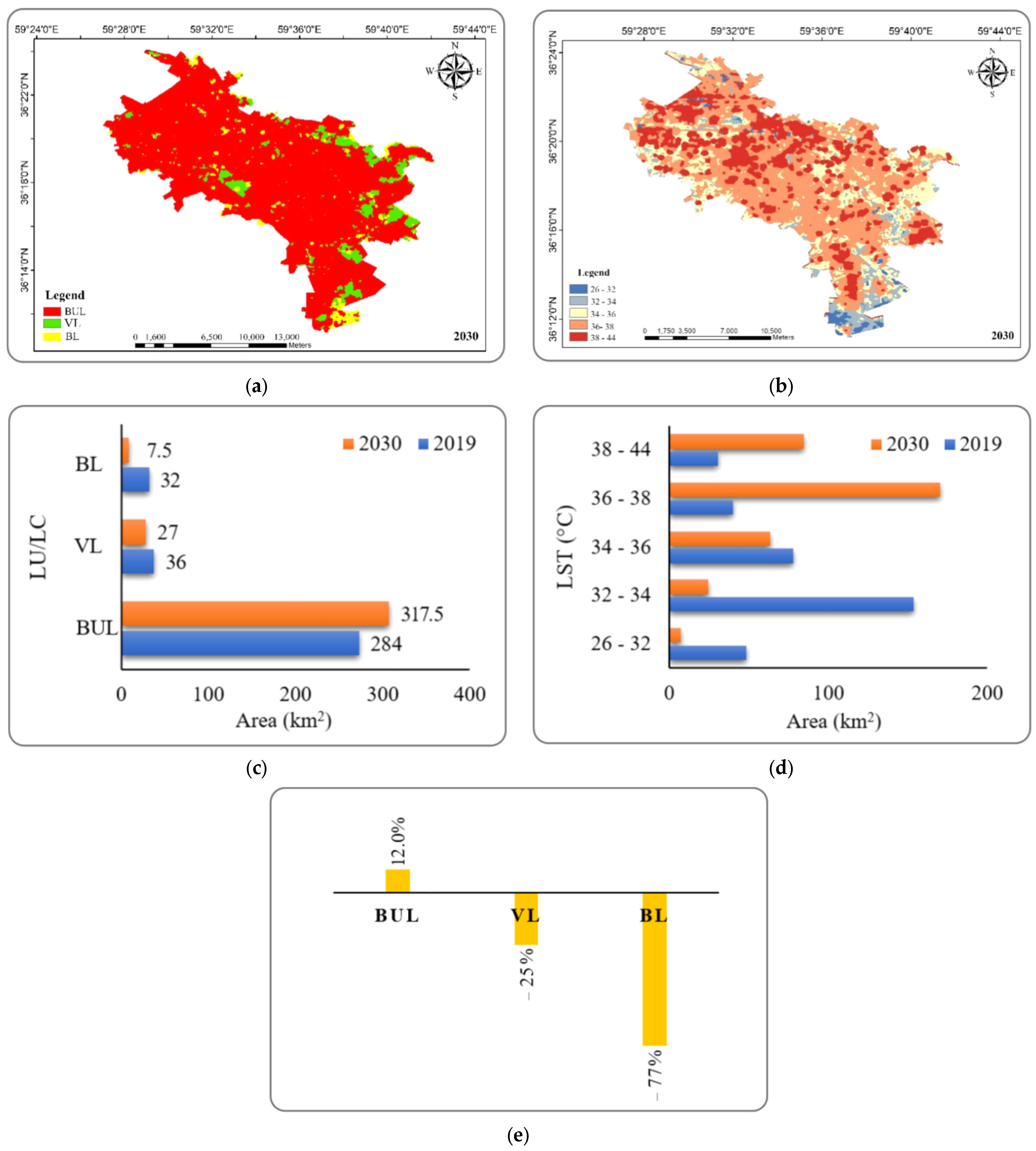
4.4.2. Markov Model Forecast of the Changes in the LU/LC and LST for 2030
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shayegan, M.; Alimohammadi, A.; Mansourian, A. Multi-objective optimization of land use allocation using NSGA-II algorithm. Iran. Remote Sens. GIS 2013, 10, 163–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, L.; Rasuli, A.A.; Hejazi, M.; Roastamzade, H. Land Cover/Use Changes Detection by Object-Oriented Processing Satellite Image Dates (Case Study: Tabriz County). J. Geogr. Plan. 2013, 17, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Omidvar, K.; Narangifard, M.; Abbasi, H. Detection of land use and vegetation changes in Yasuj city using remote sensing. Geogr. Reg. Urban Plan. 2013, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Remote sensing and geostatistics in urban water-resource monitoring: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Song, L.; Peng, Z.; Yang, J.; Luan, G.; Chu, C.; Ding, J.; Feng, S.; Jing, Y.; Xie, Z. Night-time light remote sensing mapping: Construction and analysis of ethnic minority development index. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi Lomer, A.R.; Rezaeian, M.; Rezaei, H.; Lorestani, A.; Mijani, N.; Mahdad, M.; Raeisi, A.; Arsanjani, J.J. Optimizing Emergency Shelter Selection in Earthquakes Using a Risk-Driven Large Group Decision-Making Support System. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Ghafarian Malamiri, H.R.; Arabi Aliabad, F.; Fallah Tafti, M.; Haghani, M.; Shojaei, S. The Separation of the Unpaved Roads and Prioritization of Paving These Roads Using UAV Images. Air Soil Water Res. 2022, 15, 11786221221086285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Ghafarian Malamiri, H. Evaluation of the classification accuracy of NDVI index in the preparation of land cover map. Desert 2022, 27, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Ghaffarian, H.; Mokhtari, M.H. Evaluating the capability of spatial and spectral fusion in land-cover mapping enhancement. Earth Obs. Geomat. Eng. 2022, 6, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hande, A.; Rousta, I.; Olafsson, H.; Mondal, K.K. Estimation of particulate matter (PM 2.5, PM 10) concentration and its variation over urban sites in Bangladesh. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Rezaei, H.; Majidi, M.Z. A Pricing Model for Freeway Tolls Based on the Share of Mode Shift, Route Shift, Travel Time Change and Users’ Willingness to Pay (Case study: Tehran_Saveh Freeway). J. Transp. Res. 2022, 19, 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Mohamadzadeh, N.; Sadeghnejad, M.; Ingram, B.; Ostovari, Y. Fractal Features of Soil Particles as an Index of Land Degradation under Different Land-Use Patterns and Slope-Aspects. Land 2023, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Sarif, M.O.; Gupta, R.D.; Olafsson, H.; Ranagalage, M.; Murayama, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mushore, T.D. Spatiotemporal analysis of land use/land cover and its effects on surface urban heat island using Landsat data: A case study of Metropolitan City Tehran (1988–2018). Sustainability 2018, 10, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Derdouri, A.; Murayama, Y. Spatiotemporal simulation of future land use/cover change scenarios in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdoohi, A.R.; Rezaei, H.; Irannezhad, E.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Abbasi, M. Hour-and Period-based congestion pricing, case of Tehran mode choice. Q. J. Transp. Eng. 2022, 14, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Ghafarian Malamiri, H.R.; Rousta, I.; Olafsson, H.; Zhang, H. Assessment of Palm Jumeirah Island’s Construction Effects on the Surrounding Water Quality and Surface Temperatures during 2001–2020. Water 2022, 14, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, B. Temporal march of the Chicago heat island. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1985, 24, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloustian, N.; Diab, Y. Effects of urbanization on the urban heat island in Beirut. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coseo, P.; Larsen, L. How factors of land use/land cover, building configuration, and adjacent heat sources and sinks explain Urban Heat Islands in Chicago. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Thakur, P.K.; Kumar, P.; Ashraful Alam, M.; Garg, V.; Rousta, I.; Olafsson, H. Decadal Urban Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Its Impact on Surface Runoff Potential for the Dhaka City and Surroundings Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.-X.; Gou, Z.-H.; Qi, J.-D.; Wang, J. Co-benefits approach: Opportunities for implementing sponge city and urban heat island mitigation. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-J. Towards the next generation of green building for urban heat island mitigation: Zero UHI impact building. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z. The impact of urban renewal on land surface temperature changes: A case study in the main city of Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavipanah, S.K.; Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Gomeh, Z.; Galehban, E.; Hamzeh, S. The reciprocal effect of global warming and climatic change (new perspective): A review. Desert 2022, 27, 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, S.M. Landsat-based vegetation abundance and surface temperature for surface urban heat island studies: The tale of Greater Amman Municipality. Ann. GIS 2018, 24, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, V.; Mackres, E.; Shickman, K. Cool policies for Cool Cities: Best Practices for Mitigating Urban Heat Islands in North American Cities; ACEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ruijsink, S. Integrating Climate Change into City Development Strategies (CDS): Climate Change and Strategic Planning; UN-HABITAT: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, R.; Weng, Q.; Alimohammadi, A.; Alavipanah, S.K. Spatial–temporal dynamics of land surface temperature in relation to fractional vegetation cover and land use/cover in the Tabriz urban area, Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2606–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-W.; Hong, J. Changes in the Seoul metropolitan area urban heat environment with residential redevelopment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Gu, J. Urban renewal simulation with spatial, economic and policy dynamics: The rent-gap theory-based model and the case study of Chongqing. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, A.; Sadeghnejad, M.; Sodhi, H.S.; Samia, J. The Search for Path-Dependency Mechanisms Using Physically-Based Soil-Landscape Modelling of Landslides. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Deakin, M.; Allwinkle, S. Urban regeneration and sustainable communities: The role of networks, innovation, and creativity in building successful partnerships. J. Urban Technol. 2007, 14, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Jian-ming, C. The evolution and reconstruction of peri-urban rural habitat in China. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Ding, F.; Li, Q. Remote sensing analysis of changes of urban thermal environment of Fuzhou city in China in the past 20 years. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 385–395. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Ming, T.; Tao, Y.; Peng, Z. Numerical analysis on the thermal environment of an old city district during urban renewal. Energy Build. 2015, 89, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B. Characterizing urban redevelopment process by quantifying thermal dynamic and landscape analysis. Habitat Int. 2019, 86, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Mao, D.; Li, J.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, Y. Resolution Enhancement for Large-Scale Real Beam Mapping Based on Adaptive Low-Rank Approximation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piringer, M.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Joffre, S.M.; Mestayer, P.; Middleton, D.; Rotach, M.; Baklanov, A.; De Ridder, K.; Ferreira, J.; Guilloteau, E. Investigating the surface energy balance in urban areas–recent advances and future needs. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2002, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmond, C. Progress in measuring and observing the urban atmosphere. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, T. Temperature-and pressure-dependent pore microstructures using static and dynamic moduli and their correlation. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 4073–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Weng, Q. The impact of land use and land cover changes on land surface temperature in a karst area of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature–vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Ma, M. Geospatial monitoring of land surface temperature effects on vegetation dynamics in the Southeastern Region of Bangladesh from 2001 to 2016. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Liang, S.; Zhou, T.; Huang, K.; Tang, B.; Zhao, W. Time-lag effects of global vegetation responses to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3520–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, S.; Govil, H. An assessment on the relationship between land surface temperature and normalized difference vegetation index. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 1944–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Olafsson, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ardö, J.; Zhang, H.; Mushore, T.D.; Shahin, S.; Azim, S. The 2000–2017 drought risk assessment of the western and southwestern basins in Iran. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1201–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, G. Analysis of the impact of land use/land cover change on land surface temperature with remote sensing. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Arthur, S.T. The impact of land use—Land cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: A satellite perspective. Glob. Planet. Change 2000, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, P.-X.; Yin, Z.-Y. Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use/cover changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, P.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. The mediation effect of land surface temperature in the relationship between land use-cover change and energy consumption under seasonal variations. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Chapter 1: Urban Heat Island Basics. In Heat Island Compendium; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.; Quattrochi, D.A. Land-use and land-cover change, urban heat island phenomenon, and health implications. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Han, P.; Yu, L.; Sun, F. Empirical estimation of near-surface air temperature in China from MODIS LST data by considering physiographic features. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.E. High-resolution surface temperature patterns related to urban morphology in a tropical city: A satellite-based study. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Naghipur, N.; Rousta, I.; Ghaffarian, H.R. Temporal and spatial monitoring and forecasting of suspended dust using google earth engine and remote sensing data (Case Study: Qazvin Province). Desert Manag. 2022, 10, 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Borana, S.; Yadav, S. Prediction of land cover changes of Jodhpur city using cellular automata Markov modelling techniques. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 17, 15402–15406. [Google Scholar]
- Bokaie, M.; Zarkesh, M.K.; Arasteh, P.D.; Hosseini, A. Assessment of urban heat island based on the relationship between land surface temperature and land use/land cover in Tehran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Zamani, M.; Mokhtari, M.H.; Karimi Firozjaei, M.; Alavipanah, S.K. Study and prediction of land surface temperature changes of Yazd city: Assessing the proximity and changes of land cover. J. RS GIS Nat. Resour. 2021, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Imhoff, M.; Li, X. The surface urban heat island response to urban expansion: A panel analysis for the conterminous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Satyanarayana, A. Urban heat island intensity during winter over metropolitan cities of India using remote-sensing techniques: Impact of urbanization. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 6692–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranagalage, M.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. An urban heat island study of the Colombo metropolitan area, Sri Lanka, based on Landsat data (1997–2007). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranagalage, M.; Estoque, R.C.; Zhang, X.; Murayama, Y. Spatial changes of urban heat island formation in the Colombo District, Sri Lanka: Implications for sustainability planning. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Water bodies’ cooling effects on urban land daytime surface temperature: Ecosystem service reducing heat island effect. Sustainability 2019, 11, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Zamani, M.; Olafsson, H. Investigating and predicting Land Surface Temperature (LST) based on remotely sensed data during 1987–2030 (A case study of Reykjavik city, Iceland). Urban Ecosyst. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.; Gould, P.; Keary, B.S. Global urbanization and impact on health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2003, 206, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmond, S.U. Urbanization and global environmental change: Local effects of urban warming. Geogr. J. 2007, 173, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurucu, Y.; Chiristina, N.K. Monitoring the impacts of urbanization and industrialization on the agricultural land and environment of the Torbali, Izmir region, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lyu, Y.; Sha, H.; Xiu, L. Seismic performance assessment of unsaturated soil slope in different groundwater levels. Landslides 2021, 18, 2813–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lan, W.; Ren, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J. Modeling of coupled transfer of water, heat and solute in saline loess considering sodium sulfate crystallization. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 189, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserikia, M.; Asadi Shamsabadi, E.; Rafieian, M.; Leal Filho, W. The urban heat island in an urban context: A case study of Mashhad, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavipanah, S.K.; Darrehbadami, S.H.; Kazemzadeh, A. Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Urban Heat-Island of Mashhad City due to Land Use/Cover Change and Expansion. Geogr. Urban Plan. Res. 2015, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- United States Geological Survey Earth Explorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X. Uncertain population model. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exelis Visual Information Solutions. ENVI, Version 5.3.1; Exelis Visual Information Solutions: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010.
- Karakuş, C.B. The impact of land use/land cover (LULC) changes on land surface temperature in Sivas City Center and its surroundings and assessment of Urban Heat Island. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 55, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Keeratikasikorn, C. Land surface temperature and urban density: Multiyear modeling and relationship analysis using MODIS and Landsat data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, K.; Sajjad, R.U.; Abbasi, A.M.; Nazeer, A.; Tahir, A.A. Analysis and simulation of land cover changes and their impacts on land surface temperature in a lower Himalayan region. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, J.D.; Schowengerdt, R.A. A detailed comparison of backpropagation neural network and maximum-likelihood classifiers for urban land use classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaul, S.; Pal, S. Image based surface temperature extraction and trend detection in an urban area of West Bengal, India. J. Environ. Geogr. 2016, 9, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.O.; Urban, D.L.; Donohue, M.J.; Song, C. Long-term land cover dynamics by multi-temporal classification across the Landsat-5 record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Shrestha, M.; Chhetri, N. Rapid urban growth in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: Monitoring land use land cover dynamics of a himalayan city with landsat imageries. Environments 2017, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.D.; Walter, S.D. A reappraisal of the kappa coefficient. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdan, U.; Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for automated mapping of land surface temperature using LANDSAT 8 satellite data. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1480307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LANDSAT 8 Data Users Handbook; Department of the Interior US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Pal, S.; Ziaul, S. Detection of land use and land cover change and land surface temperature in English Bazar urban centre. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 20, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Olafsson, H.; Krzyszczak, J.; Baranowski, P.; Zhang, H.; Tkaczyk, P. Analysis of the recent trends in vegetation dynamics and its relationship with climatological factors using remote sensing data for Caspian Sea watersheds in Iran. Int. Agrophys 2022, 36, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Mathew, S. Land use change modelling using a Markov model and remote sensing. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2014, 5, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, M.G.; Bell, E.J.; Westerlund, F.V. Probability mapping of land use change: A GIS interface for visualizing transition probabilities. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1996, 20, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.R.; Middleton, J. A Markov model of land-use change dynamics in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Landsc. Ecol. 1994, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D.; Gao, W.; Watari, K.; Fukahori, H. Land use change of Kitakyushu based on landscape ecology and Markov model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, P.N.; Hanaoka, S. Remote sensing, GIS and Markov’s method for land use change detection and prediction of Jaipur district. J. Geomat. 2010, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, C.; Ma, S.; Yuan, H.; Gao, L.; Fan, W. Using Markov chains to analyze changes in wetland trends in arid Yinchuan Plain, China. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianping, L.; Bai, Z.; Feng, G. RS-and-GIS-supported forecast of grassland degradation in southwest Songnen plain by Markov model. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2005, 8, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Duan, W.; Chen, W.; Ye, W.; Mao, F.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Q. Infrared radiation coatings fabricated by plasma spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J. An emissivity modulation method for spatial enhancement of thermal satellite images in urban heat island analysis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikon, N.; Singh, P.; Singh, S.K.; Vyas, A. Assessment of urban heat islands (UHI) of Noida City, India using multi-temporal satellite data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 22, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Zamani, M.S.; Mokhtari, M.H.; Karimi Firozjaei, M.; Alavipanah, S.K. Investigating And Modeling the Effect of The Composition and Arrangement of The Landscapes of Yazd City on The Land Surface Temperature Using Machine Learning and Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Data. Iran. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2022, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanifard, H.; Aliabadi, K. Impact of urban spatial configuration on land surface temperature and urban heat islands: A case study of Mashhad, Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 2889–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, B.; Jahani, A.; Sattari rad, A.; Shoghi, N. Predicting Land Use Change for 2030 Using Remote Sensing and Landsat Multi-Time Images (Case Study: Mashhad). J. Land Manag. 2018, 10, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, F. Who makes the (new) metropolis? Cross-border coalition and urban development in Paris. Environ. Plan. A 2012, 44, 1875–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, C. From barricades to back gardens: Cross-border urban expansion from the City of Derry into Co. Donegal. In Renewing Urban Communities; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 114–131. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnama, M.R. Forecasting land-use changes in Mashhad Metropolitan area using Cellular Automata and Markov chain model for 2016–2030. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 64, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sensor | Scene ID | AQ. Date | AQ. Time (GMT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-5 TM | LT05_L1TP_159035_19900930_20171207_01_T1 | 30 September 1990 | 05:56:51 |
| Landsat-7 ETM+ | LE07_L1TP_159035_20000917_20170210_01_T1 | 17 September 2000 | 06:27:44 |
| Landsat-5 TM | LT05_L1TP_159035_20110807_20161009_01_T1 | 7 August 2011 | 06:26:06 |
| Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS | LC08_L1TP_159035_20190914_20190917_01_T1 | 14 September 2019 | 07:07:15 |
| Year | 1986 | 1996 | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 2,022,966 | 2,247,996 | 2,868,350 | 3,069,941 | 3,372,660 |
| Sensor | Band | K1 [W/(m2·sr·µm)] | K2 [K] |
|---|---|---|---|
| TM | 6 | 607.76 | 1260.56 |
| ETM+ | 6 | 666.09 | 1282.71 |
| TIRS | 10 | 774.8 | 1321.0 |
| Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LU/LC Class | 1990 | 2000 | 2011 | 2019 | |
| User accuracy | BUL | 95.1 | 96.7 | 90.4 | 99.5 |
| VL | 83.3 | 82.1 | 97.3 | 95.9 | |
| BL | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.2 | |
| Producer accuracy | BUL | 97.4 | 97.8 | 98.6 | 99.7 |
| VL | 99.4 | 98.8 | 99.3 | 99.9 | |
| BL | 97.3 | 97.4 | 97.1 | 99.4 | |
| Overall accuracy | 97.4 | 99.5 | 97.5 | 97.6 | |
| Kappa coefficient | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.95 | |
| 2011 | 2019 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BUL | VL | BL | |
| BUL | 13.6 | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| VL | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
| BL | 1.1 | 0.008 | 0.05 |
| LU/LC Class | Simulated Value (E) 2011 (km2) | Actual Value (O) 2011 (km2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUL | 280.41 | 283.43 | −3.02 | 9.13 | 0.03 |
| VL | 38.65 | 36.09 | 2.56 | 6.56 | 0.17 |
| BL | 31.94 | 31.48 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
| LST Class | Simulated Value (E) 2019 (km2) | Actual Value (O) 2019 (km2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26–32 | 47.41 | 44.95 | 2.46 | 6.06 | 0.13 |
| 32–34 | 127.86 | 127.42 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| 34–36 | 95.33 | 95.43 | −0.09 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 36–38 | 51.95 | 53.37 | −1.42 | 2.01 | 0.04 |
| 38–44 | 28.43 | 29.83 | −1.40 | 1.96 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansourmoghaddam, M.; Rousta, I.; Cabral, P.; Ali, A.A.; Olafsson, H.; Zhang, H.; Krzyszczak, J. Investigation and Prediction of the Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Changes for Mashhad City in Iran during 1990–2030. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040741
Mansourmoghaddam M, Rousta I, Cabral P, Ali AA, Olafsson H, Zhang H, Krzyszczak J. Investigation and Prediction of the Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Changes for Mashhad City in Iran during 1990–2030. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040741
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansourmoghaddam, Mohammad, Iman Rousta, Pedro Cabral, Ashehad A. Ali, Haraldur Olafsson, Hao Zhang, and Jaromir Krzyszczak. 2023. "Investigation and Prediction of the Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Changes for Mashhad City in Iran during 1990–2030" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040741
APA StyleMansourmoghaddam, M., Rousta, I., Cabral, P., Ali, A. A., Olafsson, H., Zhang, H., & Krzyszczak, J. (2023). Investigation and Prediction of the Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Changes for Mashhad City in Iran during 1990–2030. Atmosphere, 14(4), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040741












