Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observation of Trace Gases from 2019 to 2021 in Huaibei, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
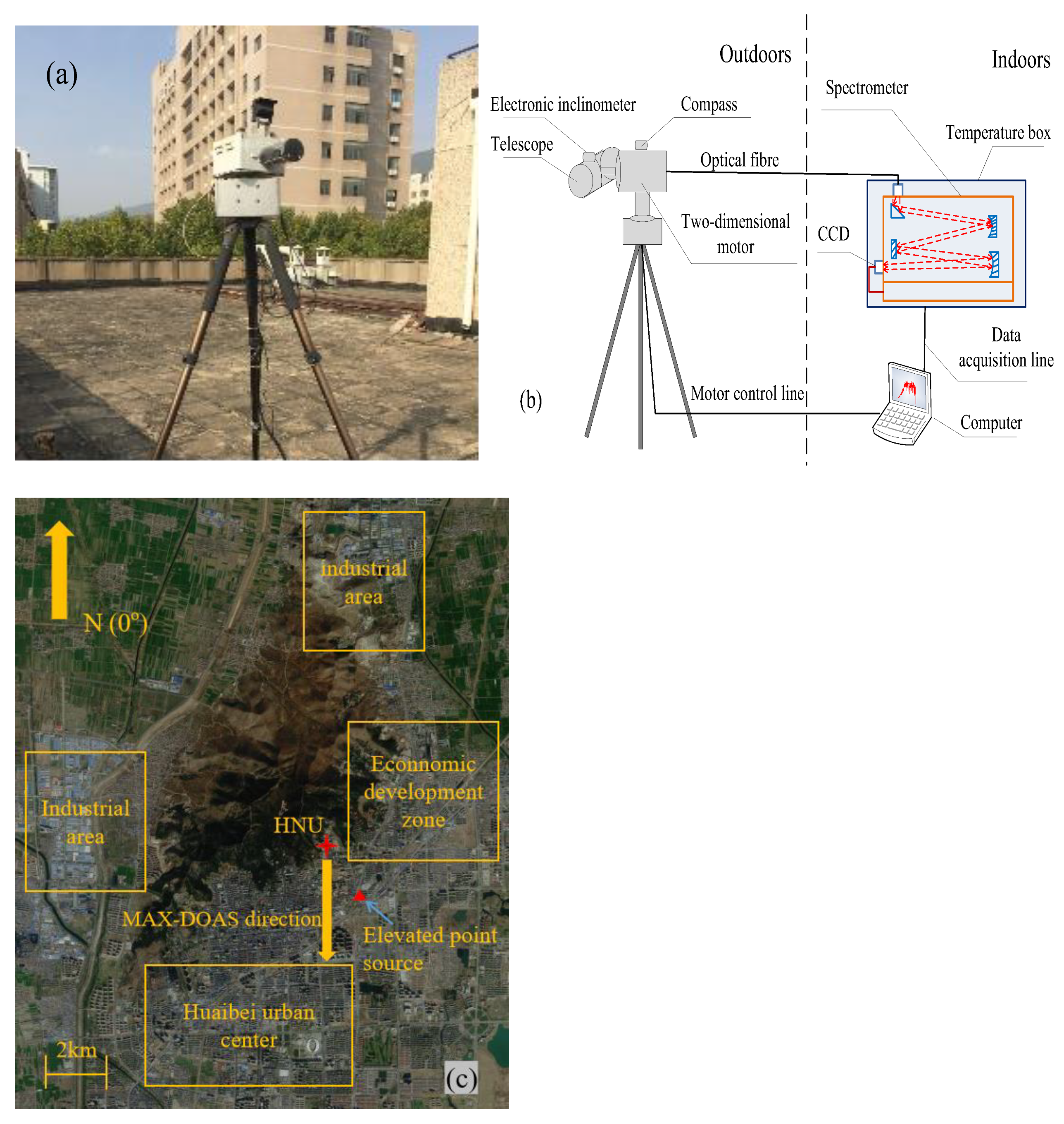
2.1. Instruments and Observation Positions
2.2. Spectral Inversion and Tropospheric Column Density Measurement
2.3. Ancillary Data
3. Results
3.1. MAX-DOAS Observation Results
3.2. Weekly Circles and Diurnal Variations
3.3. Wind Dependence of the Pollutants
3.4. In Situ Measurements
3.5. HCHO/NO2 and Source of HCHO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlemmix, T.; Hendrick, F.; Pinardi, G.; De Smedt, I.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Piters, A.; Wang, P.; Levelt, P.; Van Roozendael, M. MAX-DOAS observations of aerosols, formaldehyde and nitrogen dioxide in the Beijing area: Comparison of two profile retrieval approaches. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 941–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Hu, Z. Long-term observations of tropospheric NO2, SO2 and HCHO by MAX-DOAS in Yangtze River Delta area, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Puķīte, J.; Wagner, T.; Donner, S.; Beirle, S.; Hilboll, A.; Vrekoussis, M.; Richter, A.; Apituley, A.; Piters, A.; et al. Vertical Profiles of Tropospheric Ozone From MAX-DOAS Measurements During the CINDI-2 Campaign: Part 1—Development of a New Retrieval Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 10–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.H.; Wang, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y. Understanding primary and secondary sources of ambient carbonyl compounds in Beijing using the PMF model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Mou, F.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Q. Research of NO2 vertical profiles with look-up table method based on MAX-DOAS. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 014212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Gong, S.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Ke, H.; An, X. Quantification of SO2 Emission Variations and the Corresponding Prediction Improvements Made by Assimilating Ground-Based Observations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, D.C.Y. Spatial and socio-classifification of traffic pollutant emissions and associated mortality rates in high-density Hong Kong via improved data analytic approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Gupta, P.; Cribb, M. Ground-level gaseous pollutants (NO2, SO2, and CO) in China: Daily seamless mapping and spatiotemporal variations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 1511–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Hartl, A.; Lam, Y.F.; Xie, P.H.; Liu, W.Q.; Cheung, H.M.; Lampel, J.; Pöhler, D.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; et al. Observations of tropospheric NO2 using ground based MAX-DOAS and OMI measurements during the Shanghai World Expo 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric formaldehyde VCDs and comparisons with the CAMS model at a rural site near Beijing during APEC. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 19, 3375–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.-Z.; Luo, K.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, F.; Huang, C.; Fan, J.-R.; Fu, J.S.; Chen, C.-H. Spatial–temporal variations and process analysis of O3 pollution in Hangzhou during the G20 summit. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5963–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Tanvir, A.; Rehman, A.; Ji, X.; Xing, C.; Shakoor, A.; Liu, C. Investigating the Impacts of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Trace Gases Using Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, A.; Javed, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Xue, R.; Wang, S.; Bin, Z. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations of Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO During COVID-19 Lockdown and Spring Festival Over Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M. COVID-19 pandemic and environmental pollution: A blessing in disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, M.; Anshika; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Kota, S.H. Effect of restricted emissions during COVID-19 on air quality in India. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 728, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roșu, A.; Constantin, D.-E.; Voiculescu, M.; Arseni, M.; Roșu, B.; Merlaud, A.; Van Roozendael, M.; Georgescu, P.L. Assessment of NO2 Pollution Level during the COVID-19 Lockdown in a Romanian City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kanaya, Y.; Takashima, H.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Chong, J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.-S. Changes in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide vertical column densities over Japan and Korea during the COVID-19 using Pandora and MAX-DOAS. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 23, 220145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Li, Z.; Elnashar, A.; Allam, M.; De Leeuw, G. The Impact of the Control Measures during the COVID-19 Outbreak on Air Pollution in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Effect of lockdown amid COVID-19 pandemic on air quality of the megacity Delhi, India. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 730, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, F.; Luo, J.; Li, S.; Shan, W.; Hu, L. Vertical profile of aerosol extinction based on the measurement of O4 of multi-elevation angles with MAX-DOAS. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 084212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mou, F.; Li, S.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Quantifying emission fluxes of atmospheric pollutants from mobile differential optical absorption spectroscopic (DOAS) observations. Spectrochim. Acta A 2023, 286, 121959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Xia, M.; Lin, H.; Xing, C.; Ji, X.; Su, W.; Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q. Observations by Ground-Based MAX-DOAS of the Vertical Characters of Winter Pollution and the Influencing Factors of HONO Generation in Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Laughner, J.L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Zhu, Q.; Cohen, R.C. Improved Satellite Retrieval of Tropospheric NO2 Column Density via Updating of Air Mass Factor (AMF): Case Study of Southern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Ullah, K.; Tan, W.; Xing, C.; Liu, H. Investigating the Effect of Different Meteorological Conditions on MAX-DOAS Observations of NO2 and CHOCHO in Hefei, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Khokhar, M.F.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Subhani, M.A.; Rehman, A.; Tanvir, A. Investigating the impact of Glyoxal retrieval from MAX-DOAS observations during haze and non-haze conditions in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckaert, T.; Van Roozendael, M.; Letocart, V.; Merlaud, A.; Pinardi, G. QDOAS Software User Manual; Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy—Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vandaele, A.C.; Hermans, C.; Simon, P.C.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R.; Fally, S.; Mérienne, M.F.; Jenouvrier, A.; Coquart, B. Measurements of the NO2 absorption cross-section from 42,000 cm−1 to 10,000 cm−1 (238–1000 nm) at 220 K and 294 K. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 59, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdyuchenko, A.; Gorshelev, V.; Weber, M.; Chehade, W.; Burrows, J.P. High spectral resolution ozone absorption cross-sections—Part 2: Temperature dependence. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalman, R.; Volkamer, R. Temperature dependent absorption cross-sections of O2–O2 collision pairs between 340 and 630 nm and at atmospherically relevant pressure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15371–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meller, R.; Moortgat, G.K. Temperature dependence of the absorption cross sections of formaldehyde between 223 and 323 K in the wavelength range 225-375 nm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 7089–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, O.C.; Hartmann, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Orphal, J. New ultraviolet absorption cross-sections of BrO at atmospheric temperatures measured by time-windowing Fourier transform spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 168, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mou, F.; Wei, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Vertical profiles of aerosol and NO2 based on mobile multi-axis differential absorption spectroscopy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 2023, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Xie, P.H.; Chen, H.; Mou, F.S.; Xu, J.; Wu, F.-C.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.-G.; Liu, W.-Q. Measuring tropospheric vertical distribution and vertical column density of NO2 by multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 16, 200705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

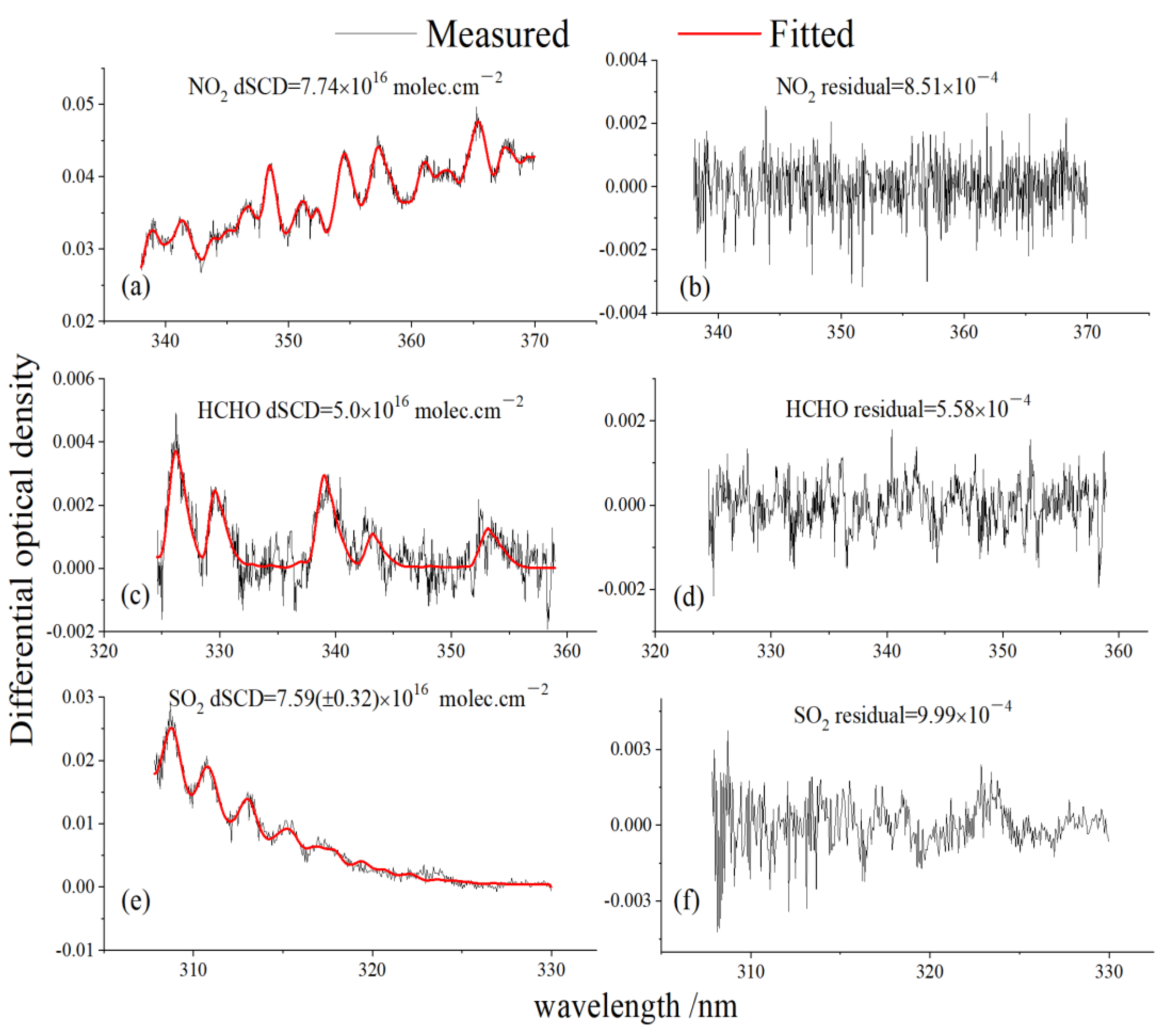

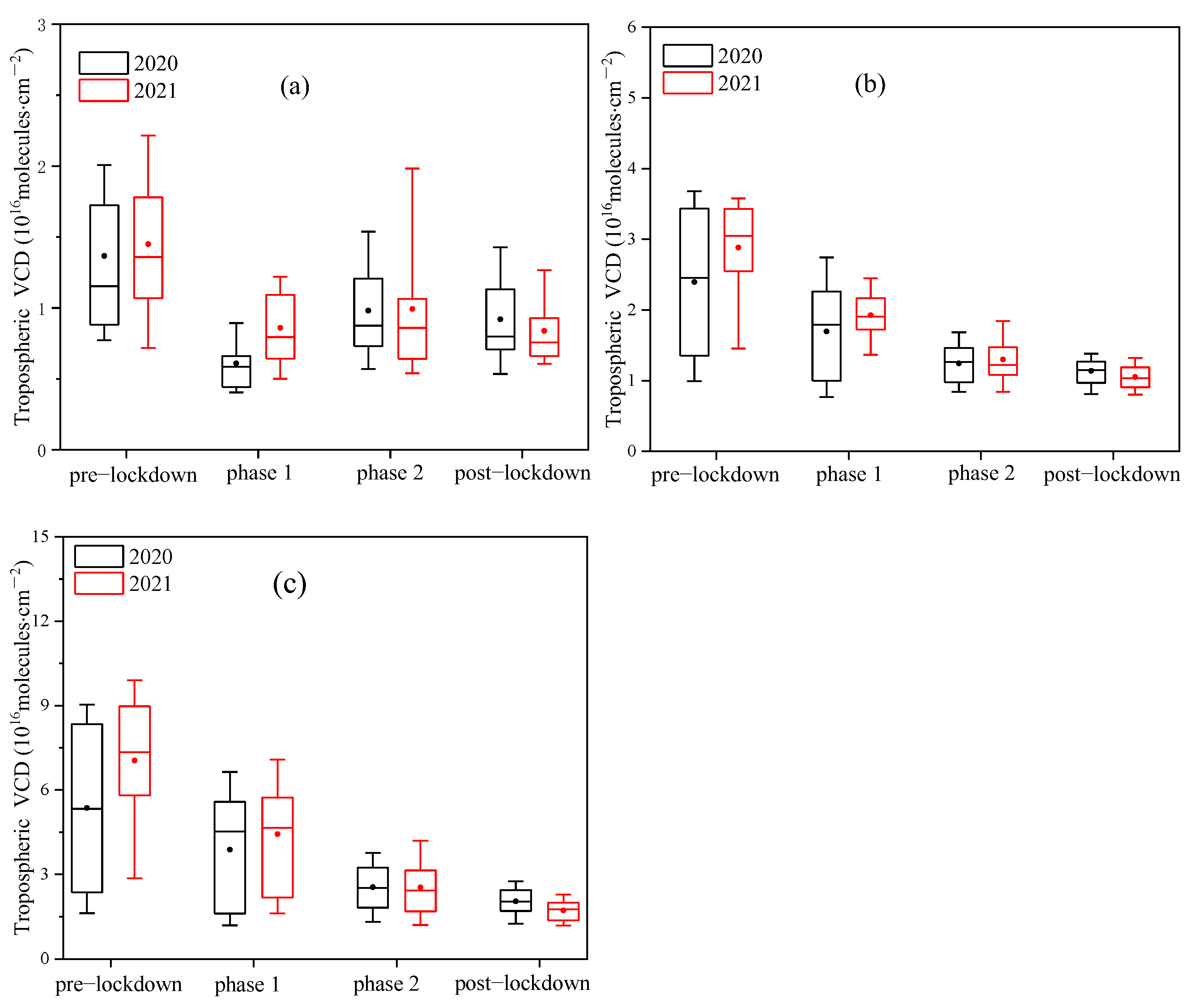






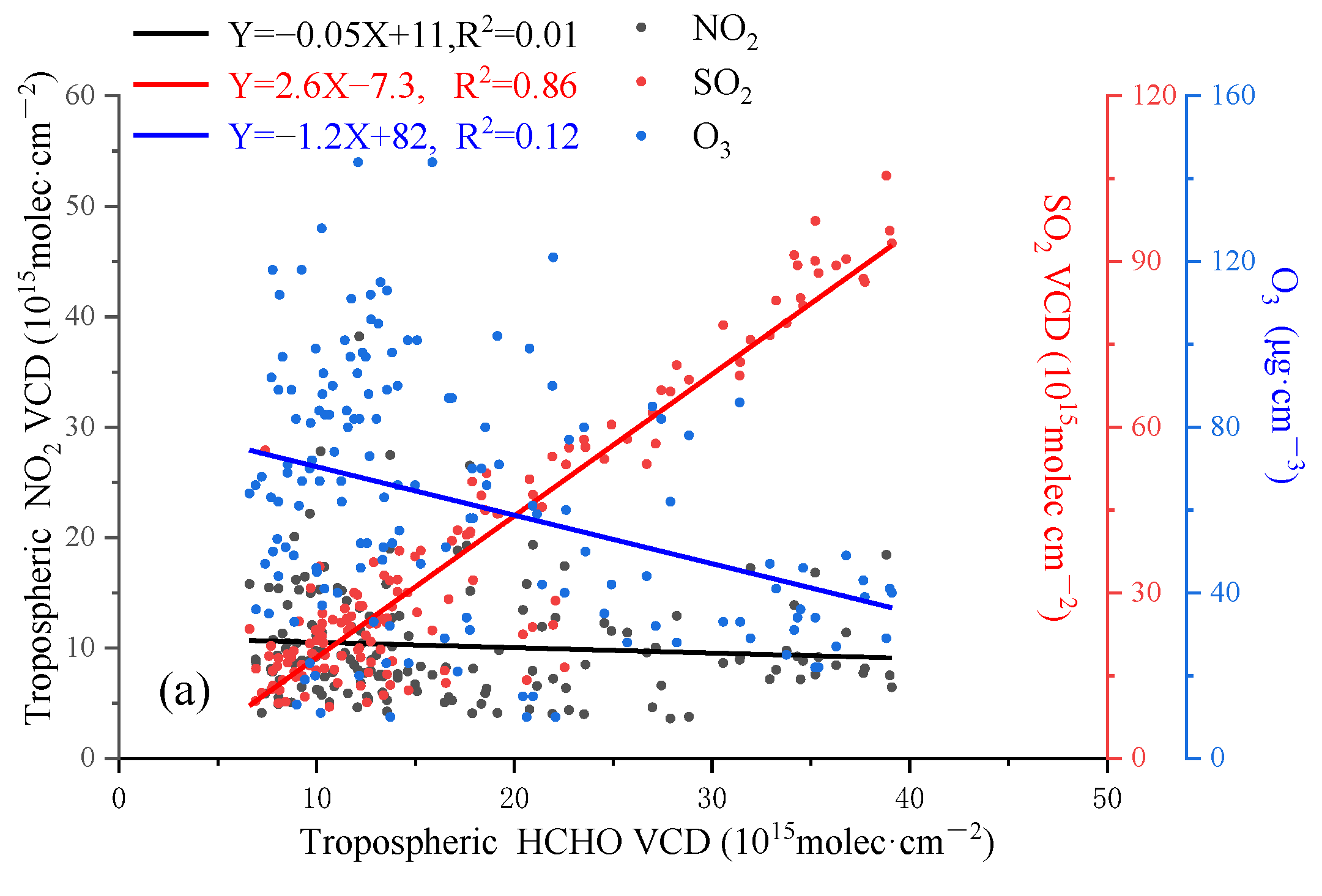


| Parameters | Sources | Species | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 | HCHO | SO2 | ||
| Fitting interval | 338–370 | 324.6–359 | 307.5–330 | |
| NO2 | 294 K, [28] | x | x | x |
| O3 | 223 K, [29] | x | x | x |
| O3 | 243 K, [29] | x | x | x |
| O4 | 293 K, [30] | x | x | |
| SO2 | 293 K, [31] | x | ||
| HCHO | 293 K, [31] | x | x | x |
| BrO | 223 K, [32] | x | x | |
| Ring | Calculated with QDOAS | x | x | x |
| Polynomial degree | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Intensity offset | constant | constant | constant | |
| Winter | Spring | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mon. 12 | Mon. 1 | Mon. 2 | Mon. 3 | Mon. 4 | ||
| NO2 | 2019.12.1–2020.5.10 | 1.32 | 1.23 | 0.62 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| HCHO | 2.79 | 1.85 | 1.67 | 1.24 | 1.10 | |
| SO2 | 6.56 | 3.85 | 3.64 | 2.65 | 2.15 | |
| NO2 | 2020.12.1–2021.5.10 | 1.57 | 1.29 | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.91 |
| HCHO | 2.82 | 2.69 | 1.98 | 1.24 | 1.02 | |
| SO2 | 6.69 | 6.54 | 4.65 | 2.40 | 1.64 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mou, F.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Ye, F.; Li, S.; Sun, Y. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observation of Trace Gases from 2019 to 2021 in Huaibei, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040739
Mou F, Luo J, Zhang Q, Zhou C, Wang S, Ye F, Li S, Sun Y. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observation of Trace Gases from 2019 to 2021 in Huaibei, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040739
Chicago/Turabian StyleMou, Fusheng, Jing Luo, Qijin Zhang, Chuang Zhou, Song Wang, Fan Ye, Suwen Li, and Youwen Sun. 2023. "Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observation of Trace Gases from 2019 to 2021 in Huaibei, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040739
APA StyleMou, F., Luo, J., Zhang, Q., Zhou, C., Wang, S., Ye, F., Li, S., & Sun, Y. (2023). Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observation of Trace Gases from 2019 to 2021 in Huaibei, China. Atmosphere, 14(4), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040739







