Influences of the Mid-Level Vortex on the Formation of Tropical Cyclone Toraji (2013)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Piecewise Potential Vorticity Inversion (PPVI)
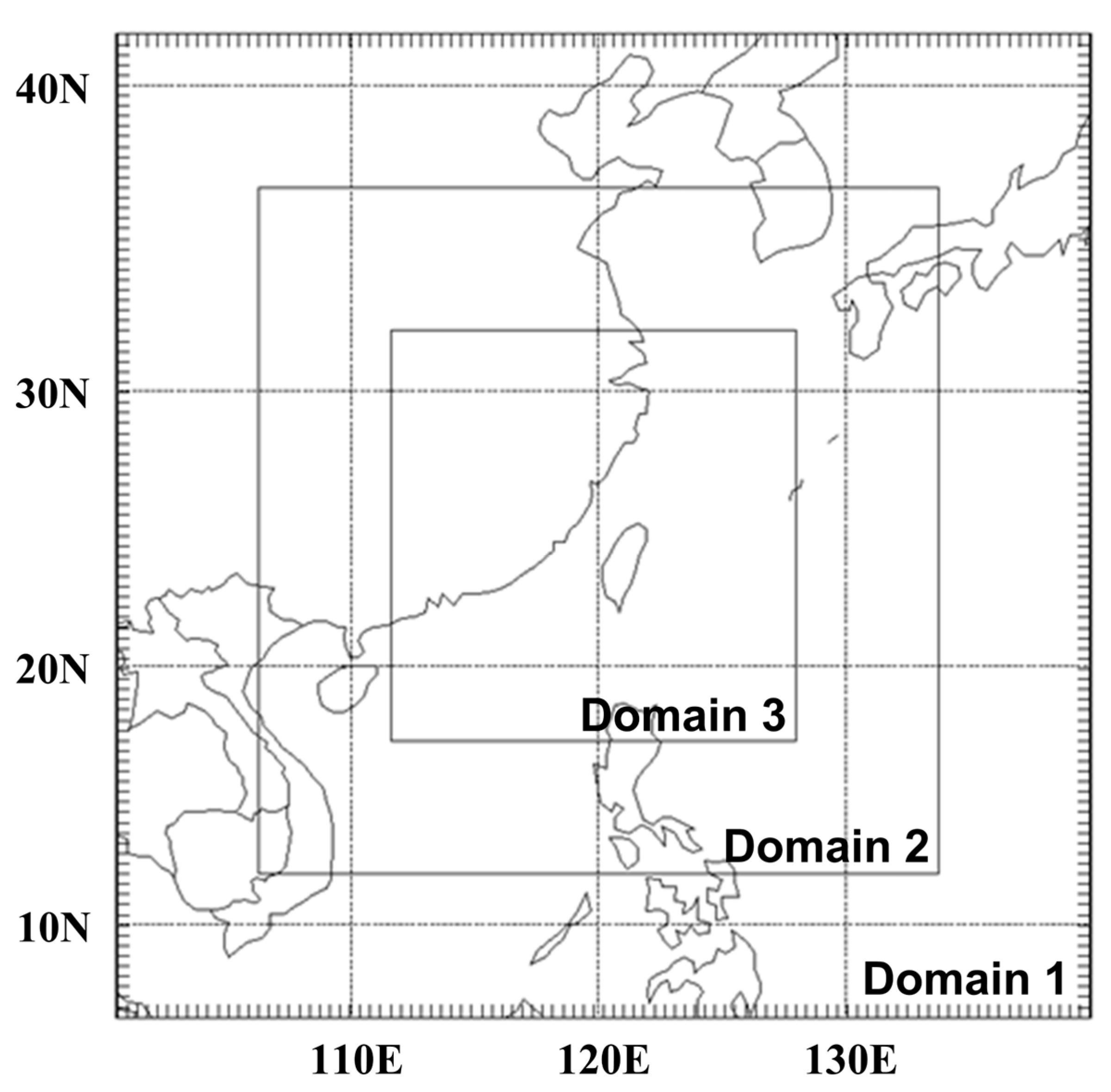
2.3. Experiment Design
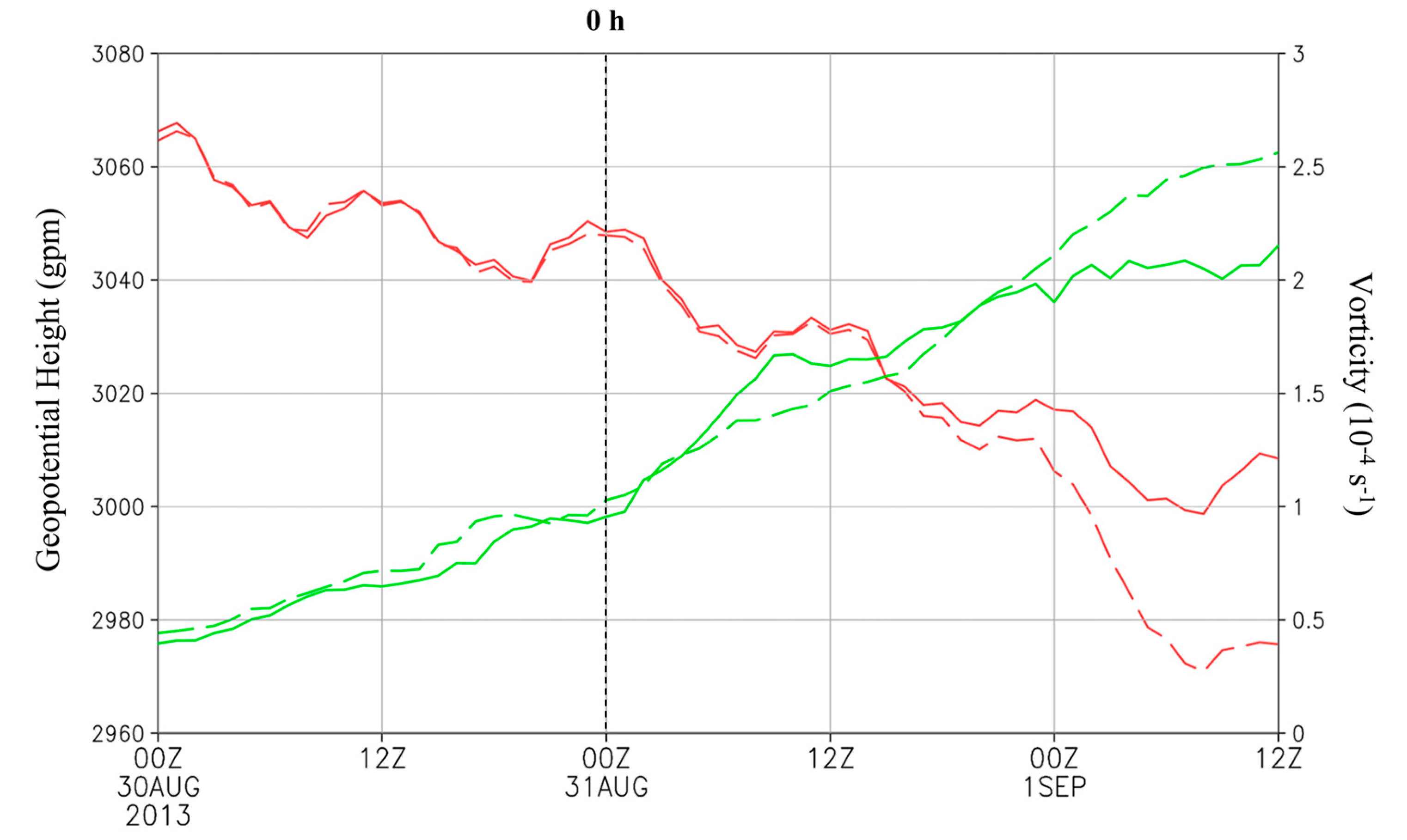
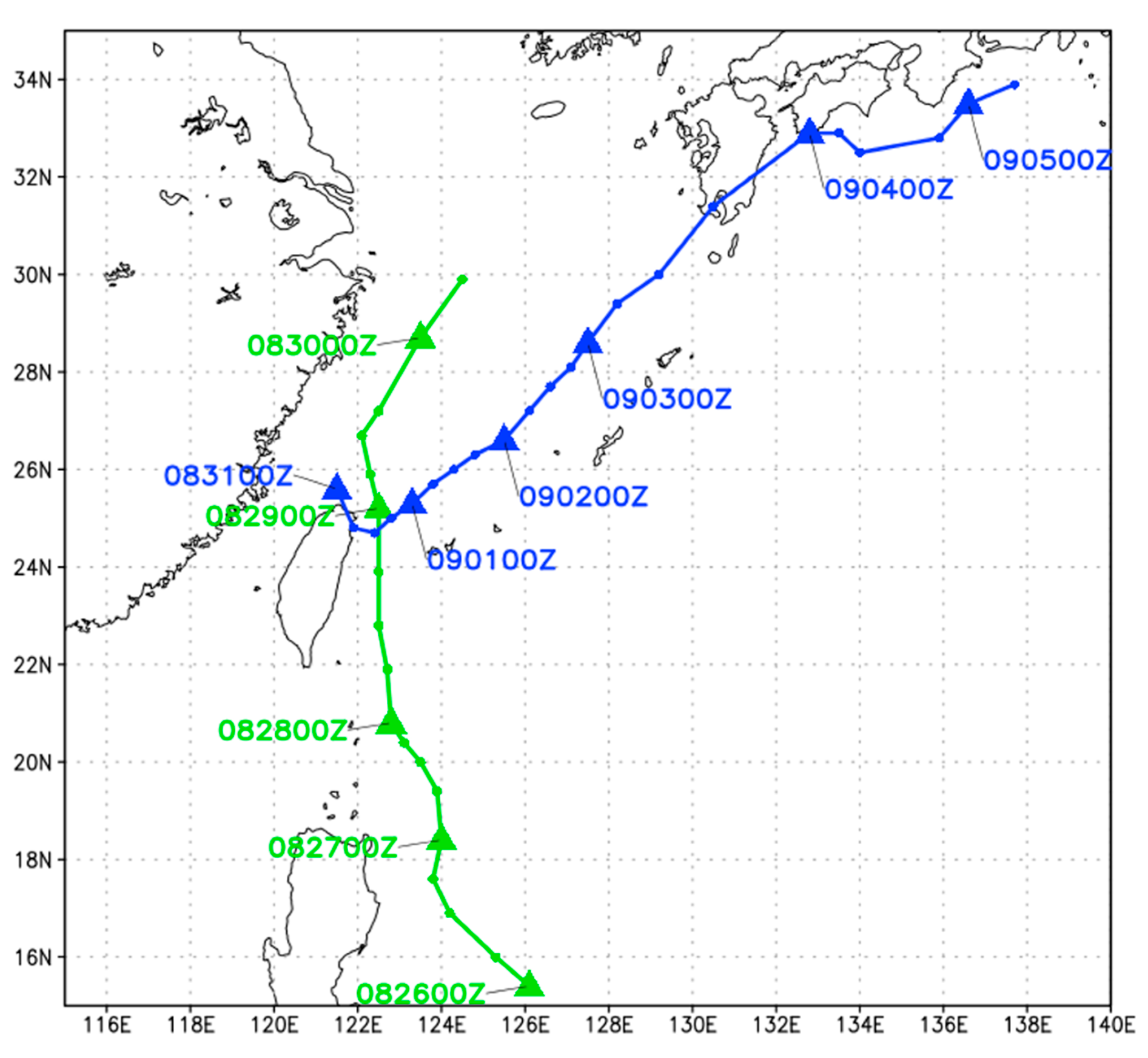
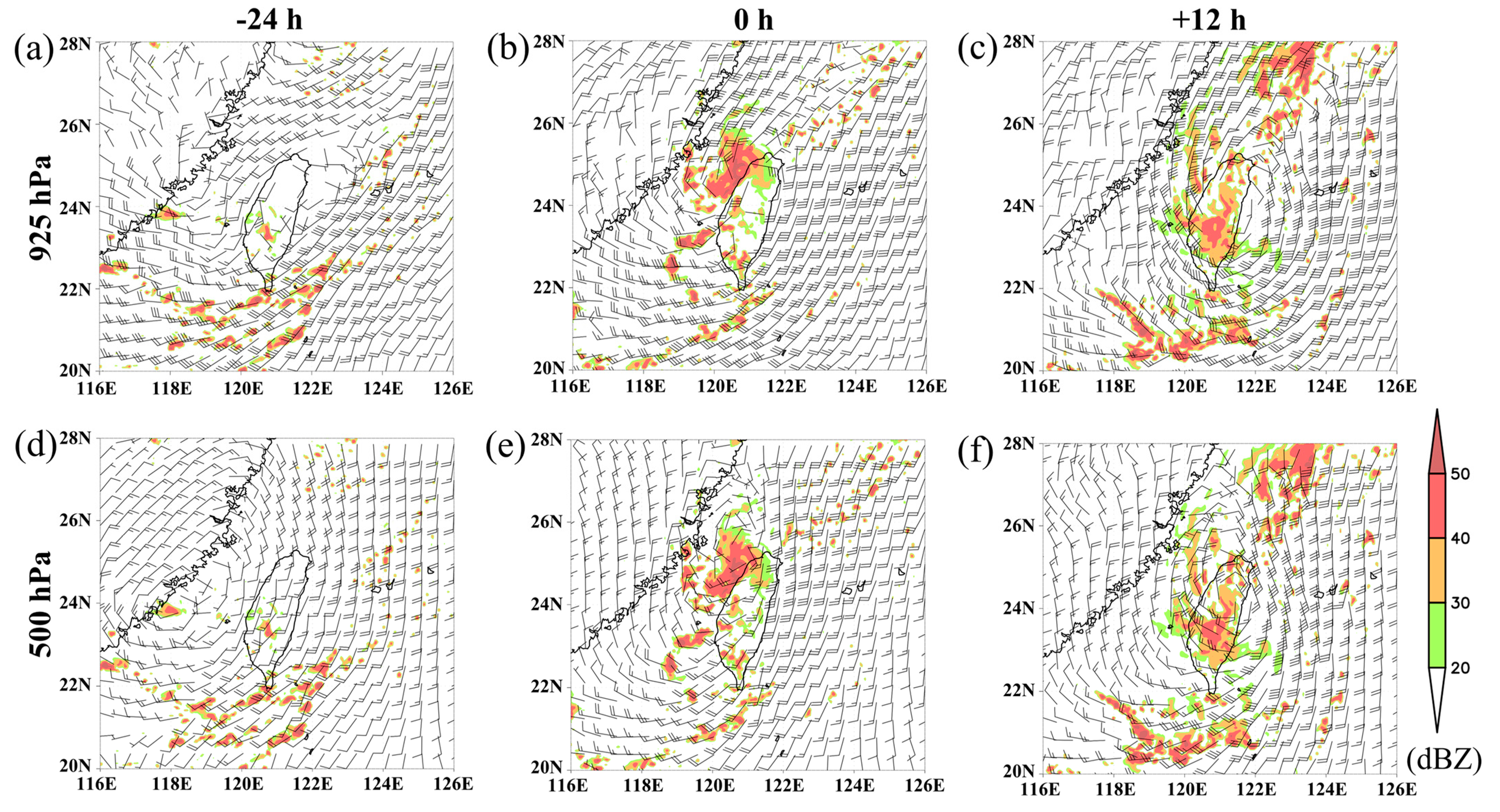
3. Observation and Analysis
3.1. The Synoptic and Mesoscale Environment during the Period of Toraji Formation
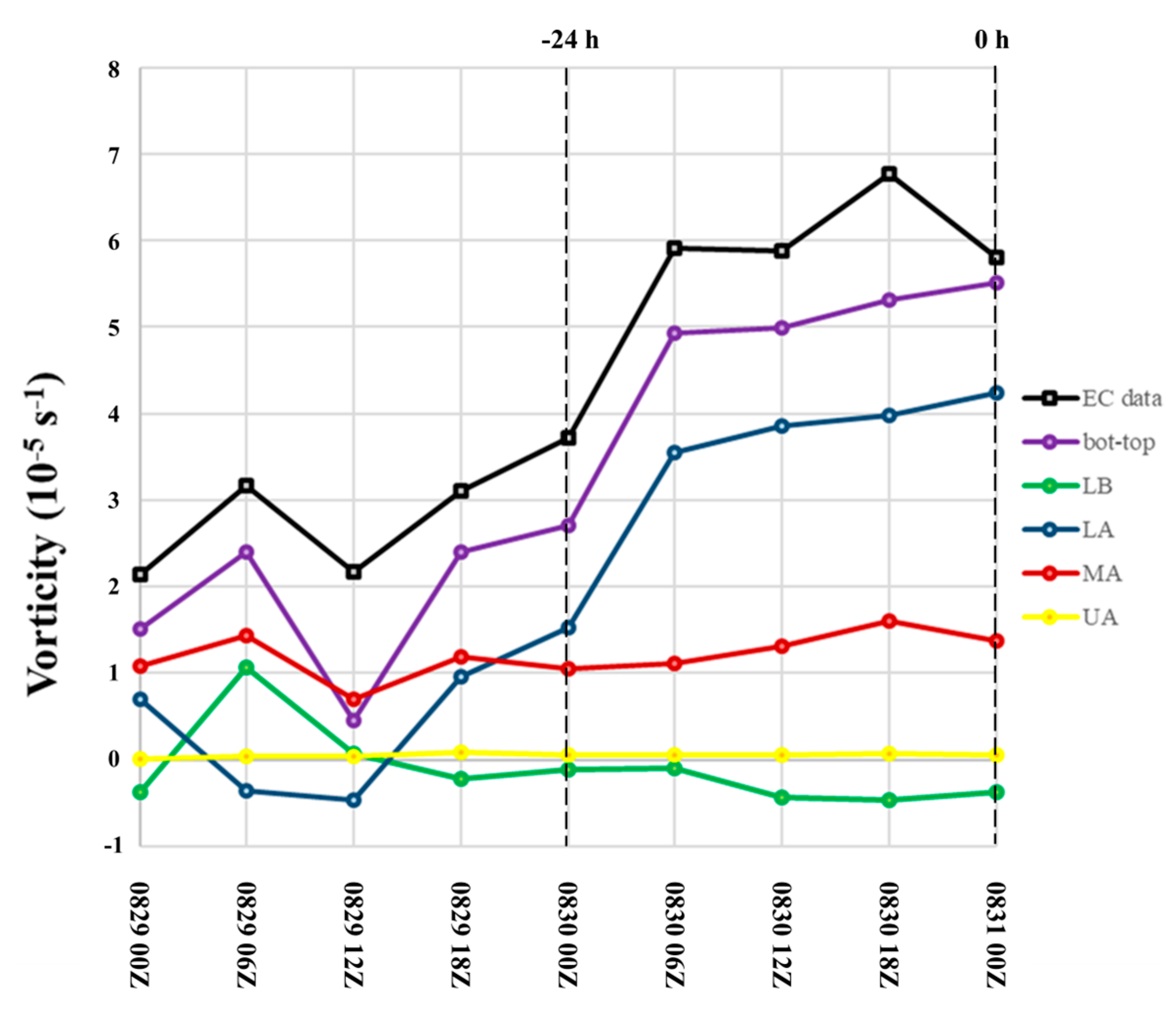
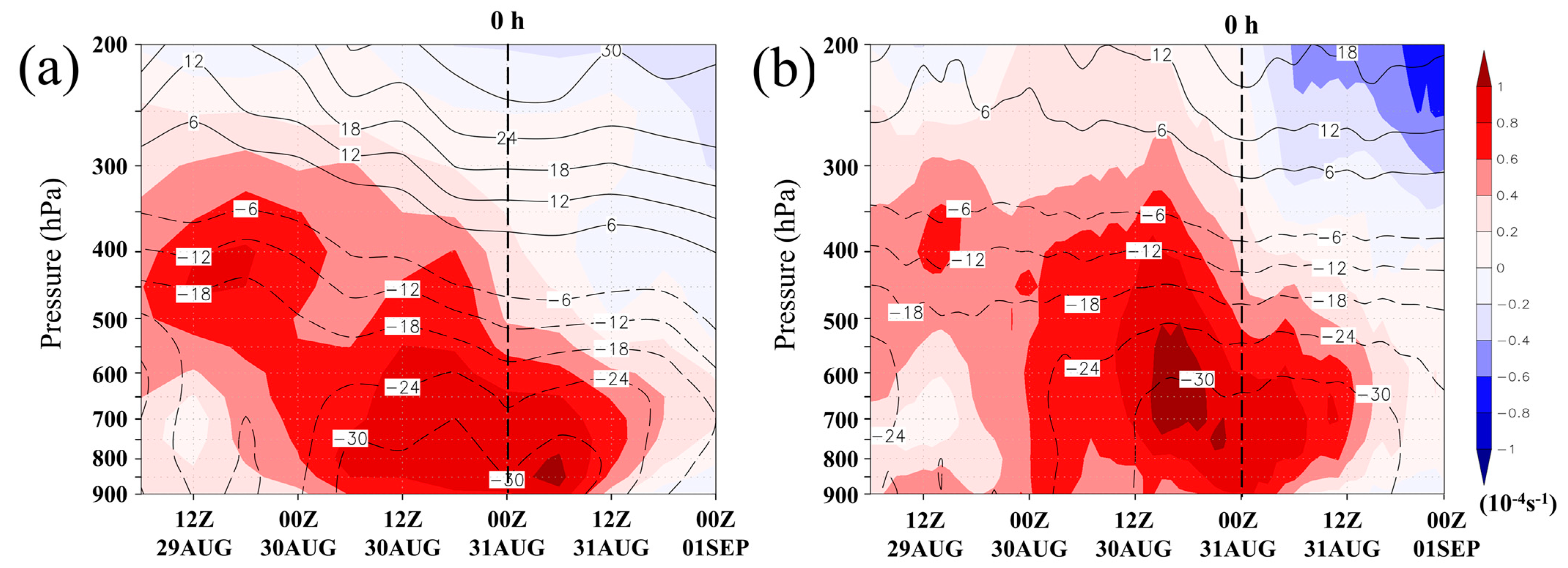
3.2. The Contribution of the Mid-Level Vortex
3.3. Verification of CTRL
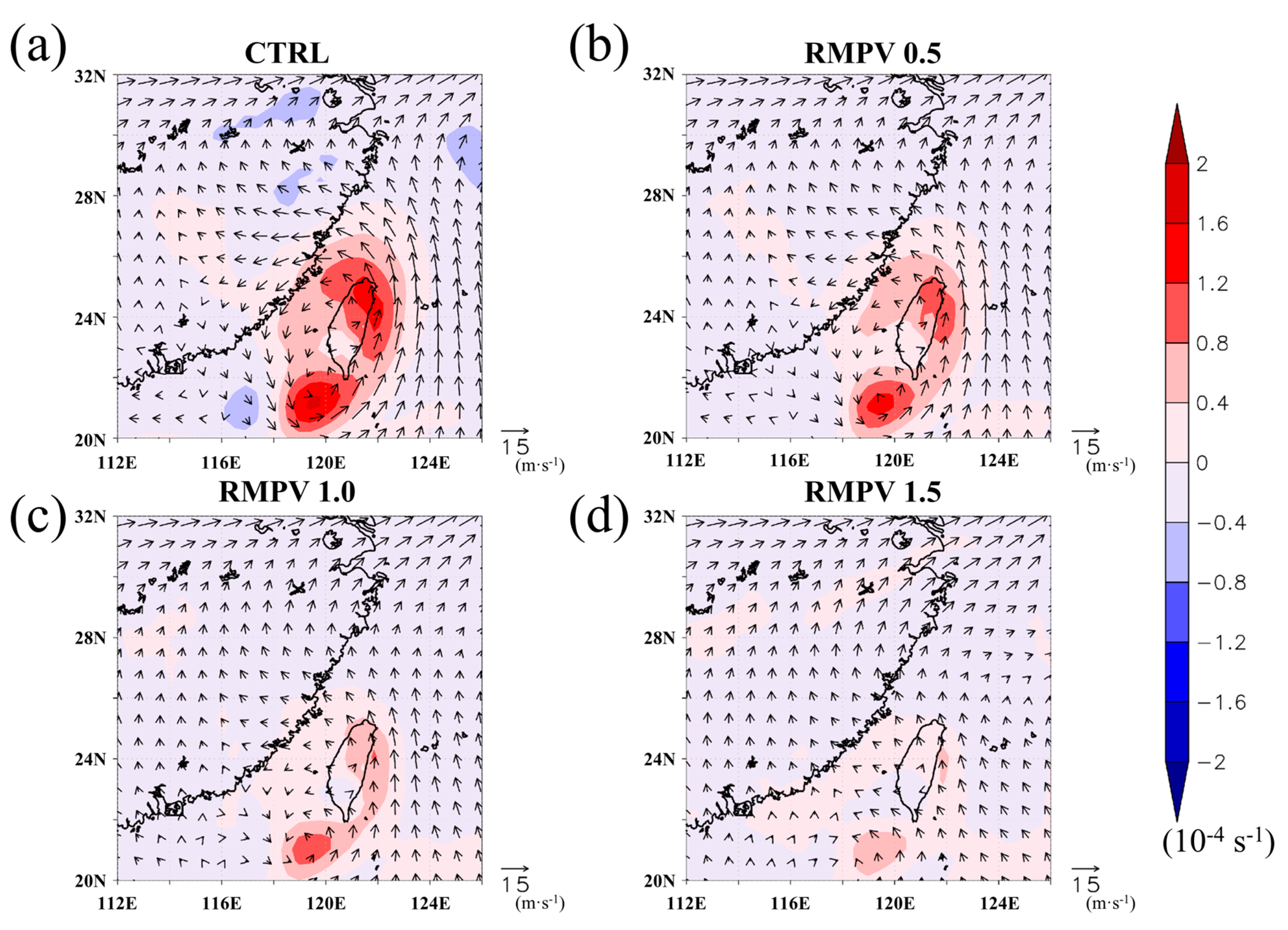
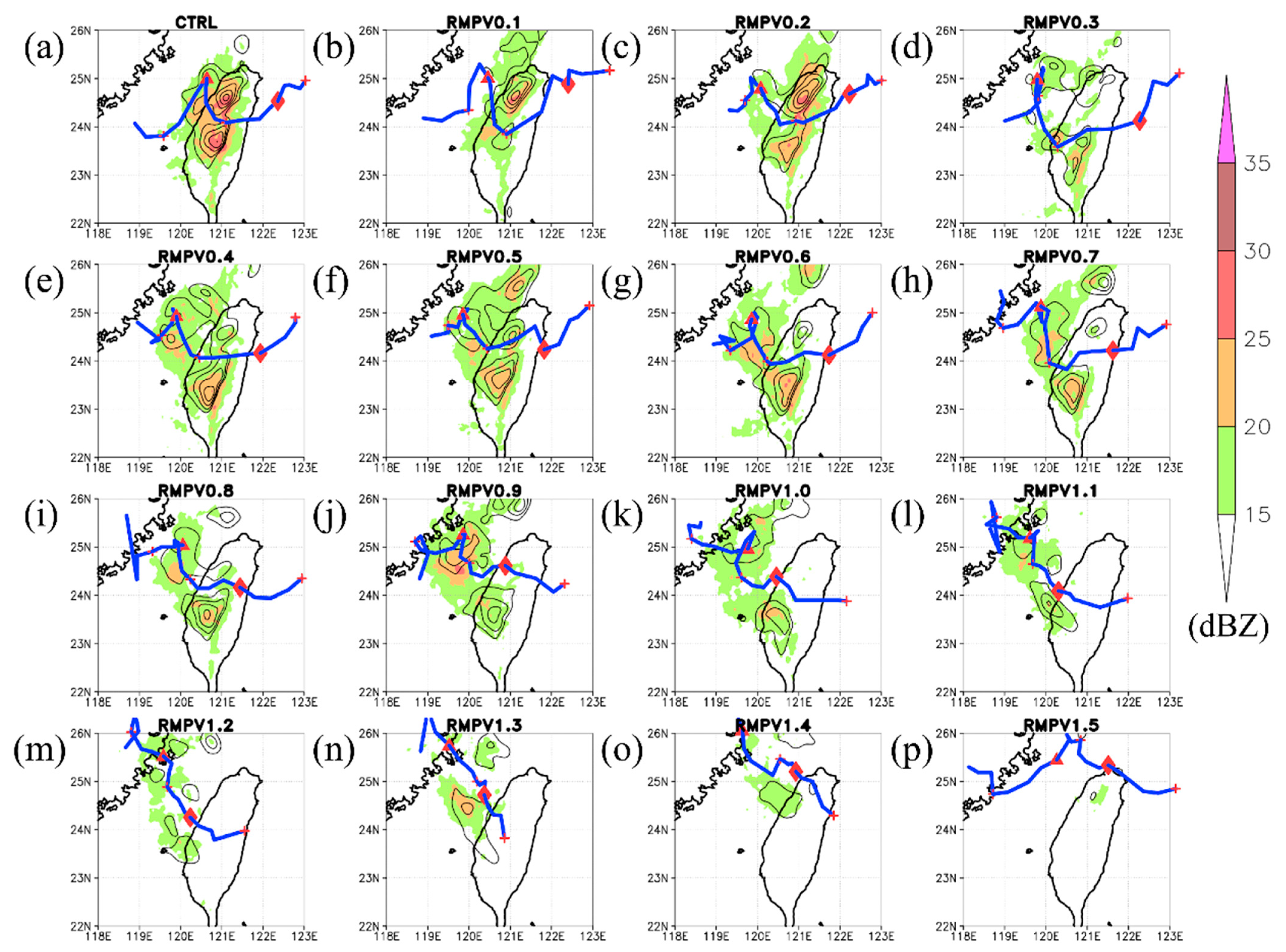
4. RMPVs Experiments
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Lee, C.S. Observational analysis of tropical cyclogenesis in the western North Pacific. Part I: Structural Evolution of Cloud Clusters. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 2580–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S. Observational analysis of tropical cyclogenesis in the western North Pacific. Part II: Budget analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 2599–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Cheung, K.K.W.; Hui, J.S.N.; Elsberry, R.L. Mesoscale features associated with tropical cyclone formations in the western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 2006–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. The formation of tropical cyclones. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 67, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Lee, C.S.; Hsu, H.H. Influence of ENSO on Formation of Tropical Cloud Clusters and their Development into Tropical Cyclones in the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 9120–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Lee, C.S.; Hsu, H.H.; Done, J.M.; Holland, G.J. Tropical Cloud Cluster Environments and Their Importance for Tropical Cyclone Formation. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4069–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.A.; Holland, G.J. Large-scale patterns associated with tropical cyclogenesis in the western Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2027–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Lin, Y.L.; Cheung, K.K.W. Tropical cyclone formations in the South China Sea associated with the mei-yu front. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2670–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerton, T.J.; Montgomery, M.T.; Wang, Z. Tropical cyclogenesis in a tropical wave critical layer: Easterly waves. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5587–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.Y.; Cheung, K.K.; Lee, C.S. The Role of Trade Wind Surges in Tropical Cyclone Formations in the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 4120–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Ishikawa, H. Environmental Factors Contributing to Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Eito, H.; Muroi, C.; Nishimura, S.; Bessho, K.; Oikawa, Y.; Koide, N. Development Conditions for Tropical Storms over the Western North Pacific Stratified by Large-Scale Flow Patterns. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 2020, 98, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Peng, M.S.; Li, T.; Stevens, D.E. Developing versus nondeveloping disturbances for tropical cyclone formation. Part II: Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.S.; Fu, B.; Li, T.; Stevens, D.E. Developing versus Nondeveloping Disturbances for Tropical Cyclone Formation. Part I: North Atlantic. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1047–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Fudeyasu, H. How Significant are Low-Level Flow Patterns in Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the Western North Pacific? Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Done, J.M. Importance of Midlevel Moisture for Tropical Cyclone Formation in Easterly and Monsoon Environments over the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 2449–2469. [Google Scholar]
- Zehr, R.M. Tropical Cyclogenesis in the Western North Pacific; NOAA Technical Report NESDIS 61; 1992; p. 181. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/13116/noaa_13116_DS1.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2012).
- Hendricks, E.A.; Montgomery, M.T.; Davis, C.A. The role of “vortical” hot towers in the formation of tropical cyclone Diana (1984). J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1209–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M.T.; Nicholls, M.E.; Cram, T.A.; Saunders, A.B. A Vortical Hot Tower Route to Tropical Cyclogenesis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 355–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A., Jr.; Lee, W.; Mell, M.M. Convective contribution to the genesis of Hurricane Ophelia (2005). Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 2778–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.L.; Zehr, R. Observational Analysis of Tropical Cyclone Formation. Part II: Comparison of Non-Developing versus Developing Systems. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 1132–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.A.; Holland, G.J. Scale interactions during the formation of Typhoon Irving. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J.; López Carrillo, C. The vorticity budget of developing typhoon Nuri (2008). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A. The Formation of Moist Vortices and Tropical Cyclones in Idealized Simulations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 3499–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Ritchie, E.; Holland, G.J.; Halverson, J.; Stewart, S. Mesoscale interactions in tropical cyclone genesis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 2643–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bister, M.; Emanuel, K.A. The genesis of Hurricane Guillermo: TEXMEX analyses and a modeling study. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 2662–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A., Jr. Stratiform precipitation in regions of convection: A meteorological paradox? Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1997, 78, 2179–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Montgomery, M.T.; Dunkerton, T.J. Genesis of Pre–Hurricane Felix (2007). Part I: The Role of the Easterly Wave Critical Layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1711–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Montgomery, M.T.; Dunkerton, T.J. Genesis of Pre–Hurricane Felix (2007). Part II: Warm Core Formation, Precipitation Evolution, and Predictability. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1730–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Thermodynamic aspects of tropical cyclone formation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 2433–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Lee, C.S.; Sui, C.H. A Study on the Influences of Low-Frequency Vorticity on Tropical Cyclone Formation in the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 4151–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Lee, C.S.; Teng, H.F. The Characteristics of Tropical Cyclone Formation in an Environment with Large Low-Level Low-Frequency (more than 10 days) Vorticity in the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 4101–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Done, J.M.; Lee, C.S.; Hsu, H.H.; Kuo, Y.H. Large-Scale Environmental Influences on Tropical Cyclone Formation Processes and Development Time. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9763–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W. A Case Study of Tropical Cyclone Formation near Taiwan: Toraji (2013). Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.; Jao, H.C.; Hsieh, Y.H. A Study on the Heavy Rainfall Event Occurred in the Southwestern Taiwan when Typhoon Kong-Rey (2013) was Affecting Taiwan. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 46, 149–171, In Chinese with English Abstract. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, M.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Tsuboki, K. On the separation of upper and low-level centres of tropical storm Kong-Rey (2013) near Taiwan in association with asymmetric latent heating. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Hirose, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Kumazawa, R.; Yamasaki, S. A Global View of the Landfall Characteristics of Tropical Cyclones. Trop. Cyclone Res. Rev. 2014, 3, 178–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Yoshida, R. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Characteristics Stratified by Genesis Environment. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Done, J.M.; Kuo, Y.H. Landfalling tropical cyclone characteristics and their multi-timescale variability connected to monsoon and easterly formation environments over the western North Pacific. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 2953–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsberry, R.L.; Tsai, H.-C.; Capalbo, C.; Chin, W.-C.; Marchok, T.P. Critical Pre-Formation Decision Flowchart to Apply Tropical Cyclone Lifecycle Predictions in Eastern North Pacific. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennon, C.C.; Hobgood, J.S. Forecasting Tropical Cyclogenesis over the Atlantic Basin Using Large-Scale Data. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 2927–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, D.; Nakano, M.; Sugiyama, D.; Uchida, S. Deep learning approach for detecting tropical cyclones and their precursors in the simulation by a cloud-resolving global nonhydrostatic atmospheric model. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemendaal, N.; Moel, H.D.; Jantsje, M.M.; Bosma, P.R.M.; Polen, A.N.; Collins, J.M. Adequately reflecting the severity of tropical cyclones using the new Tropical Cyclone Severity Scale. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Guo, C.; Han, Y.; Qing, R. Impact of Tropical Cyclone Avoidance on Fishing Vessel Activity over Coastal China Based on Automatic Identification System Data during 2013–2018. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2022, 13, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, H.; Qiu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mao, J.; Fan, W.; Huang, M. Typhoon-Induced Fragility Analysis of Transmission Tower in Ningbo Area Considering the Effect of Long-Term Corrosion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.L.; Lin, P.F.; Jou, B.J.D.; Zhang, J. An Application of Reflectivity Climatology in Constructing Radar Hybrid Scans over Complex Terrain. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A.; Emanuel, K.A. Potential vorticity diagnostics of cyclogenesis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1991, 119, 1929–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A. Piecewise potential vorticity inversion. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 1397–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A. A potential-vorticity diagnosis of the importance of initial structure and condensational heating in observed extratropical cyclogenesis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 2409–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Emanuel, K.A. Potential vorticity diagnostics of hurricane movement. Part I: A case study of Hurricane Bob (1991). Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Emanuel, K.A. Potential vorticity diagnostics of hurricane movement. Part II: Tropical Storm Ana (1991) and Hurricane Andrew (1992). Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charney, J.G. The use of primitive equations of motion in numerical prediction. Tellus 1955, 7, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.J. The motion of Hurricane Gloria: A potential vorticity diagnosis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1996, 124, 1497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Huang, T.S.; Chou, K.H. Potential vorticity diagnosis of the key factors affecting the motion of Typhoon Sinlaku (2002). Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J. Nonlinear Balance and Potential-Vorticity Thinking at Large Rossby Number. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 118, 987–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Weisman, M.L. The Impact of Positive-Definite Moisture Transport on NWP Precipitation Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Fritsch, J.M. Convective parameterization for mesoscale models: The Kain-Fritsch scheme. Represent. Cumulus Convect. Numer. Model. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, E. On the Distribution and Continuity of Water Substance in Atmospheric Circulations; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1969; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tory, K.J.; Montgomery, M.T. Internal Influences on Tropical Cyclone Formation. Proc. Sixth Int. Workshop on Tropical Cyclones, San Jose, Costa Rica, WMO, Topic 2.2. 2006. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA594102.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2015).
- Leppert, K.D.; Cecil, D.J.; Petersen, W.A. Relation between tropical easterly waves, convection, and tropical cyclogenesis: A Lagrangian perspective. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2649–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawislak, J.; Zipser, E.J. A multisatellite investigation of the convective properties of developing and nondeveloping tropical disturbances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 4624–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. What is the Key Feature of Convection Leading up to Tropical Cyclone Formation? J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 1609–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, W.H.; Hack, J.J. Inertial stability and tropical cyclone development. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, J.J.; Schubert, W.H. Nonlinear response of atmospheric vortices to heating by organized cumulus convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


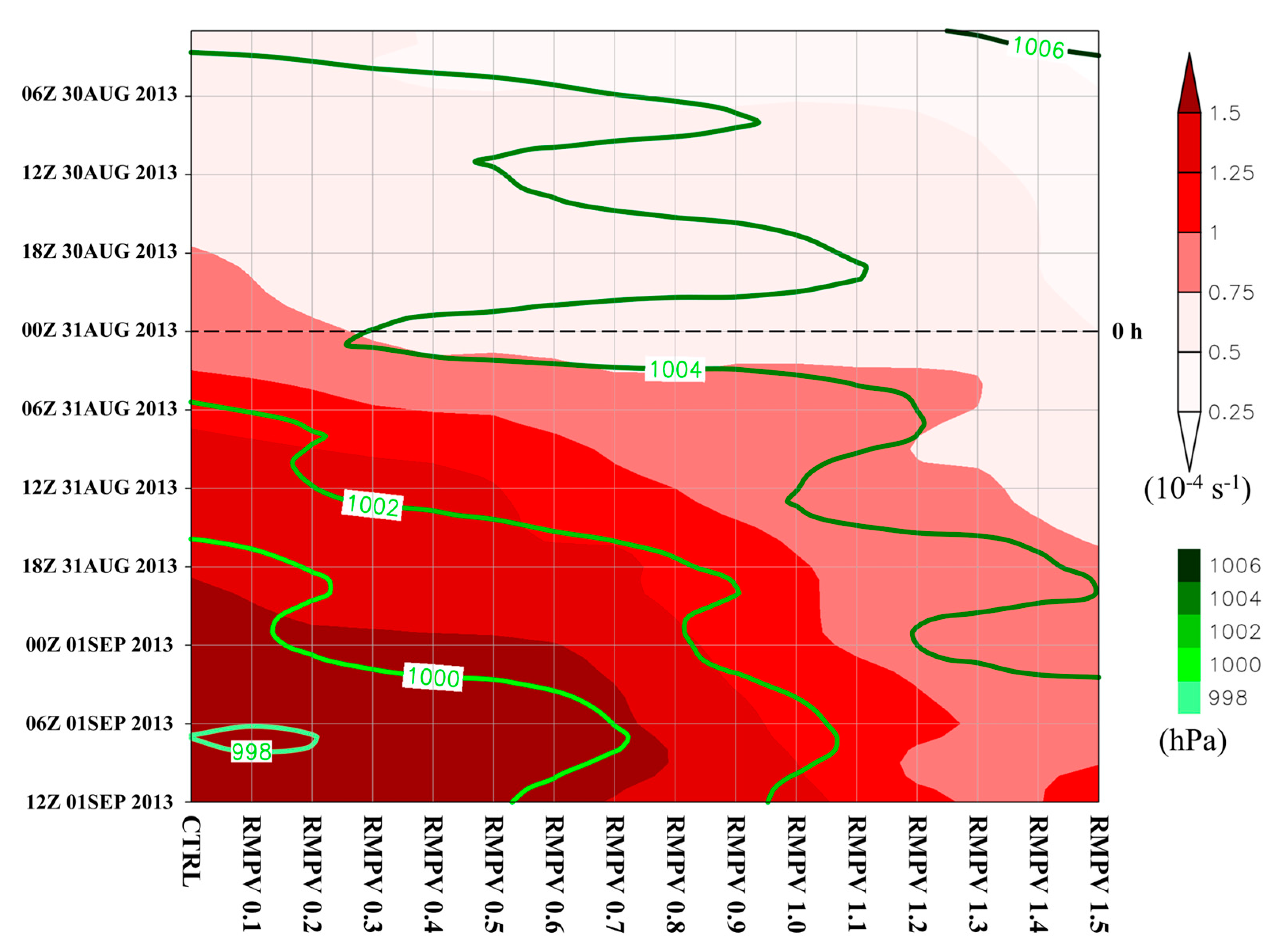
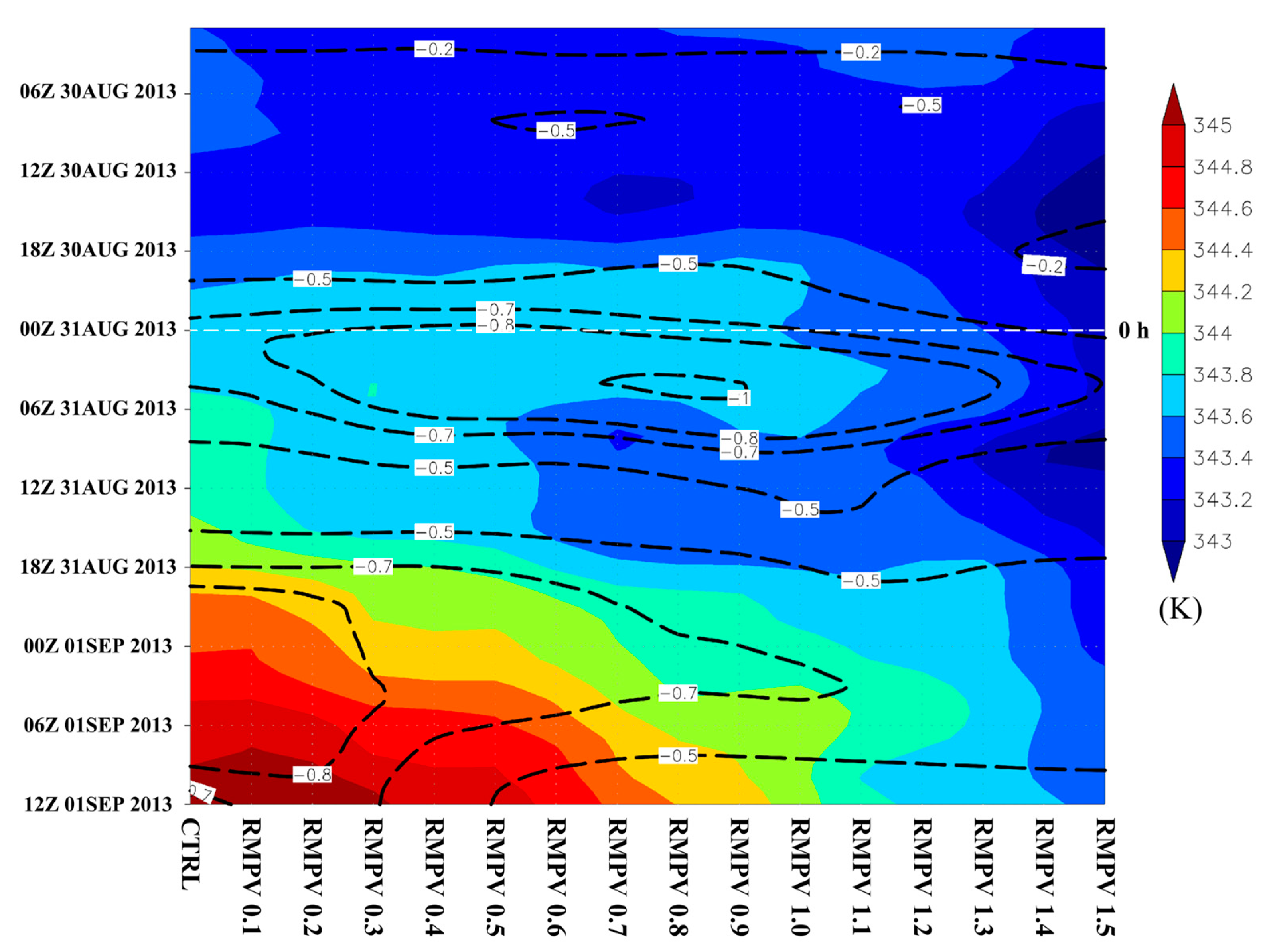
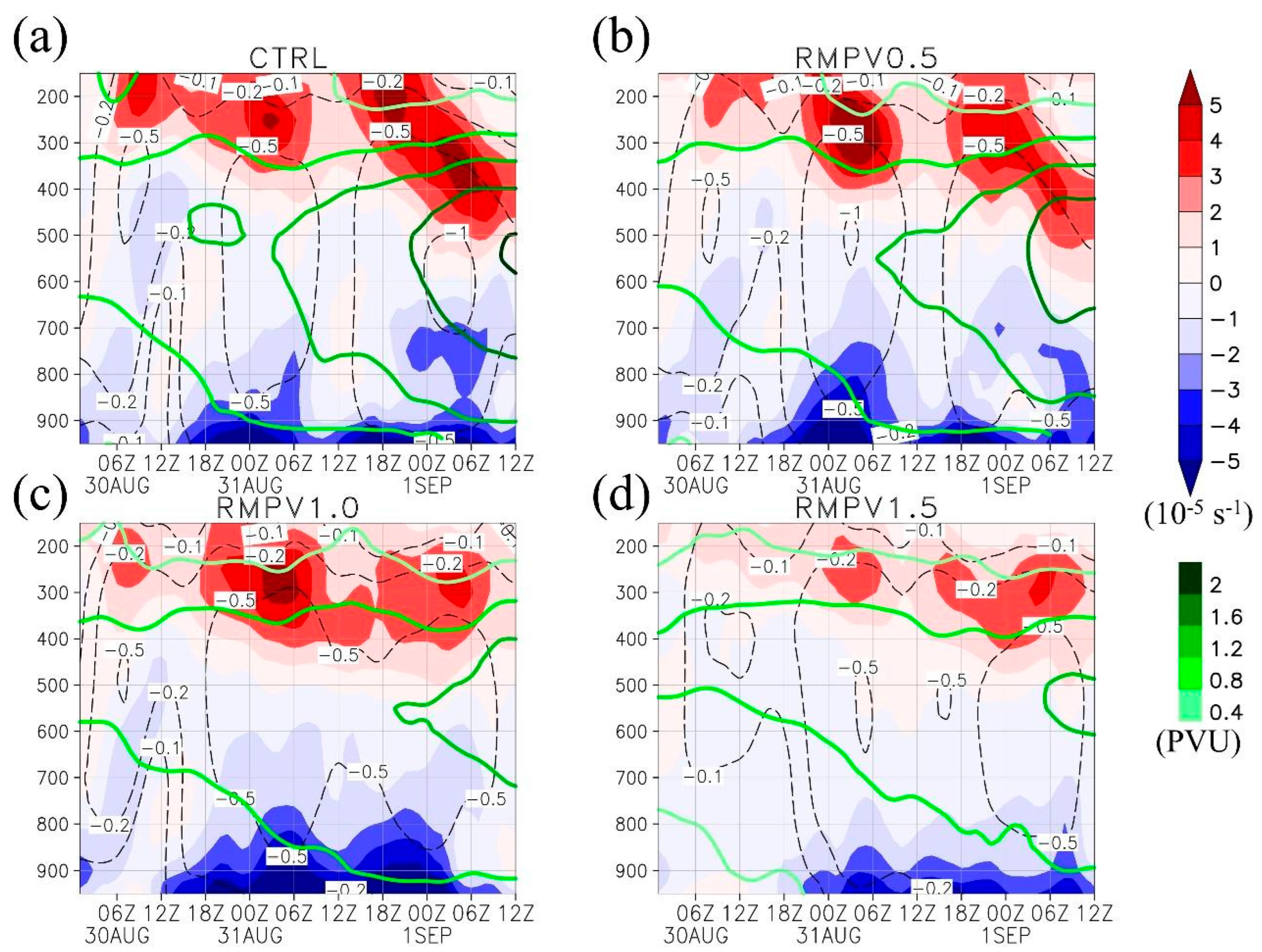
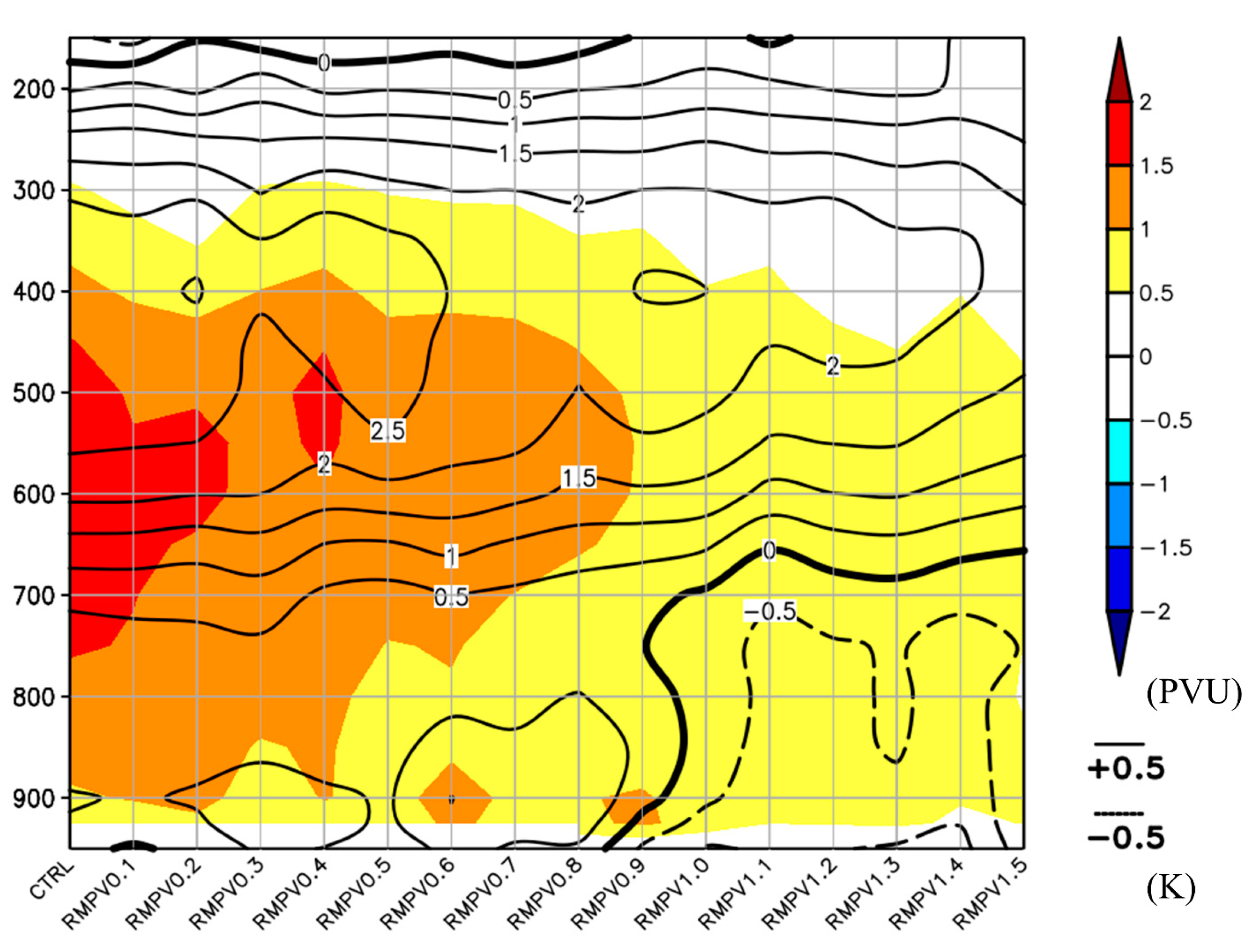
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, C.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Liu, P.-Y.; Teng, H.-F.; Lee, C.-S. Influences of the Mid-Level Vortex on the Formation of Tropical Cyclone Toraji (2013). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040709
Chuang C-H, Hsieh Y-H, Liu P-Y, Teng H-F, Lee C-S. Influences of the Mid-Level Vortex on the Formation of Tropical Cyclone Toraji (2013). Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040709
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Chen-Hao, Yi-Huan Hsieh, Pin-Yen Liu, Hsu-Feng Teng, and Cheng-Shang Lee. 2023. "Influences of the Mid-Level Vortex on the Formation of Tropical Cyclone Toraji (2013)" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040709
APA StyleChuang, C.-H., Hsieh, Y.-H., Liu, P.-Y., Teng, H.-F., & Lee, C.-S. (2023). Influences of the Mid-Level Vortex on the Formation of Tropical Cyclone Toraji (2013). Atmosphere, 14(4), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040709






