Apportionment of Chemical Components and Sources of PM2.5 in Shihezi City of Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
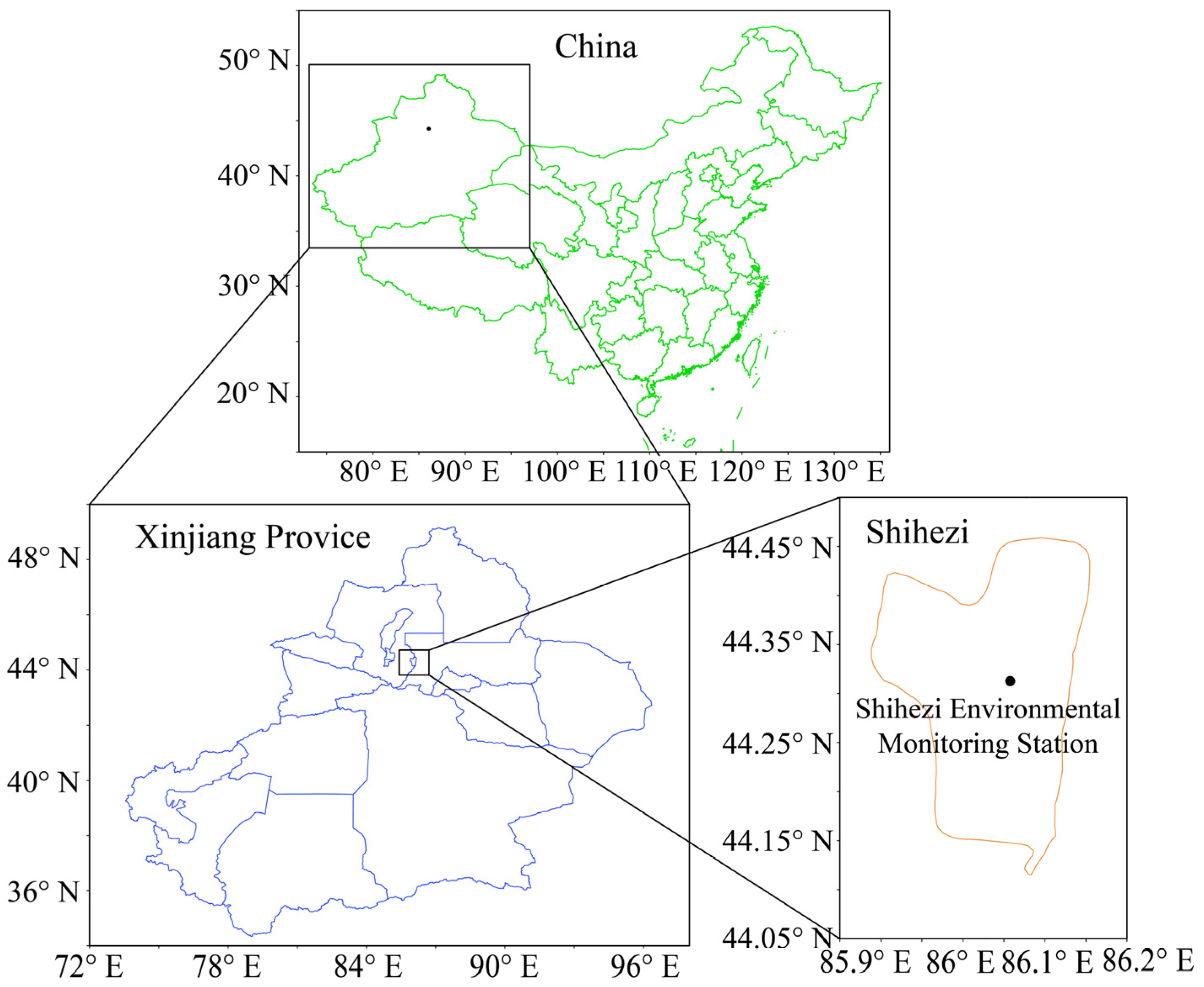
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis Methods
2.3. Source Apportionment Receptor Model
2.4. HYSPLIT Model
3. Results and Discussion
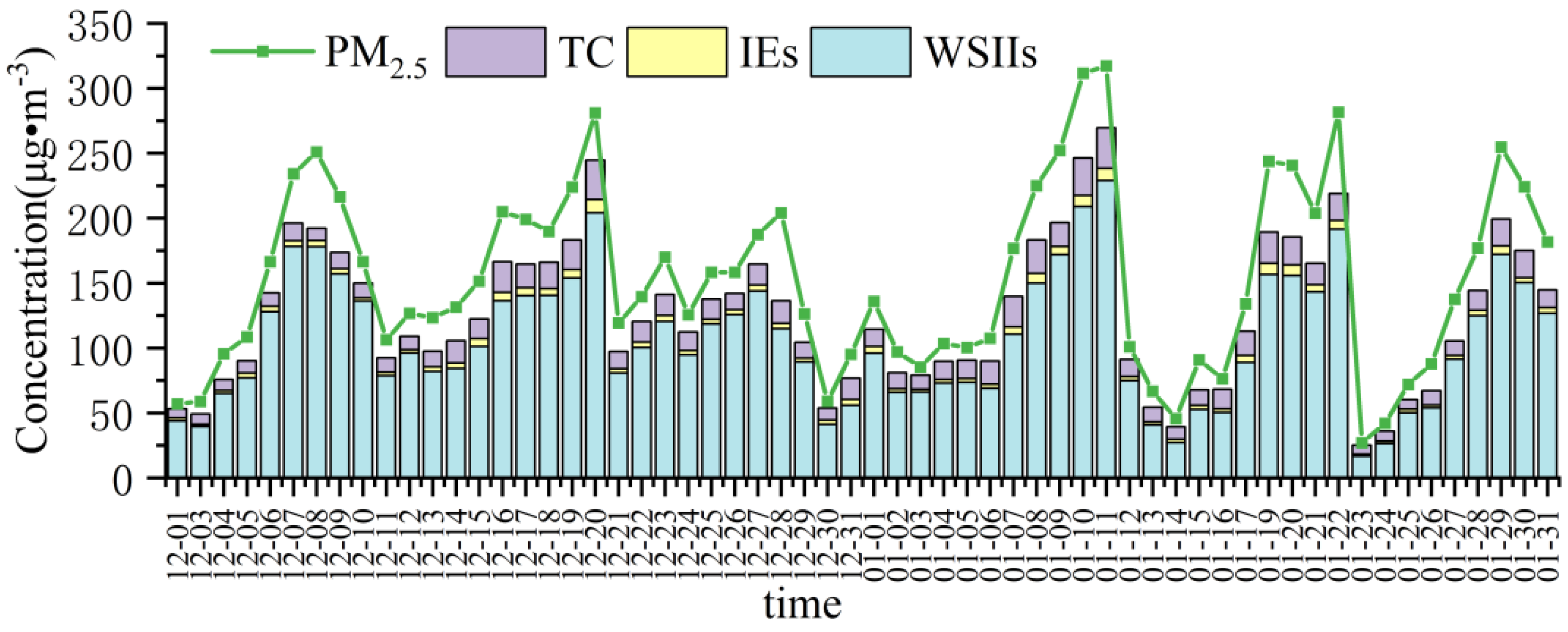
3.1. Characteristicsof PM2.5 Mass Concentration
3.2. Mass Concentration Characteristics of Chemical Components in PM2.5
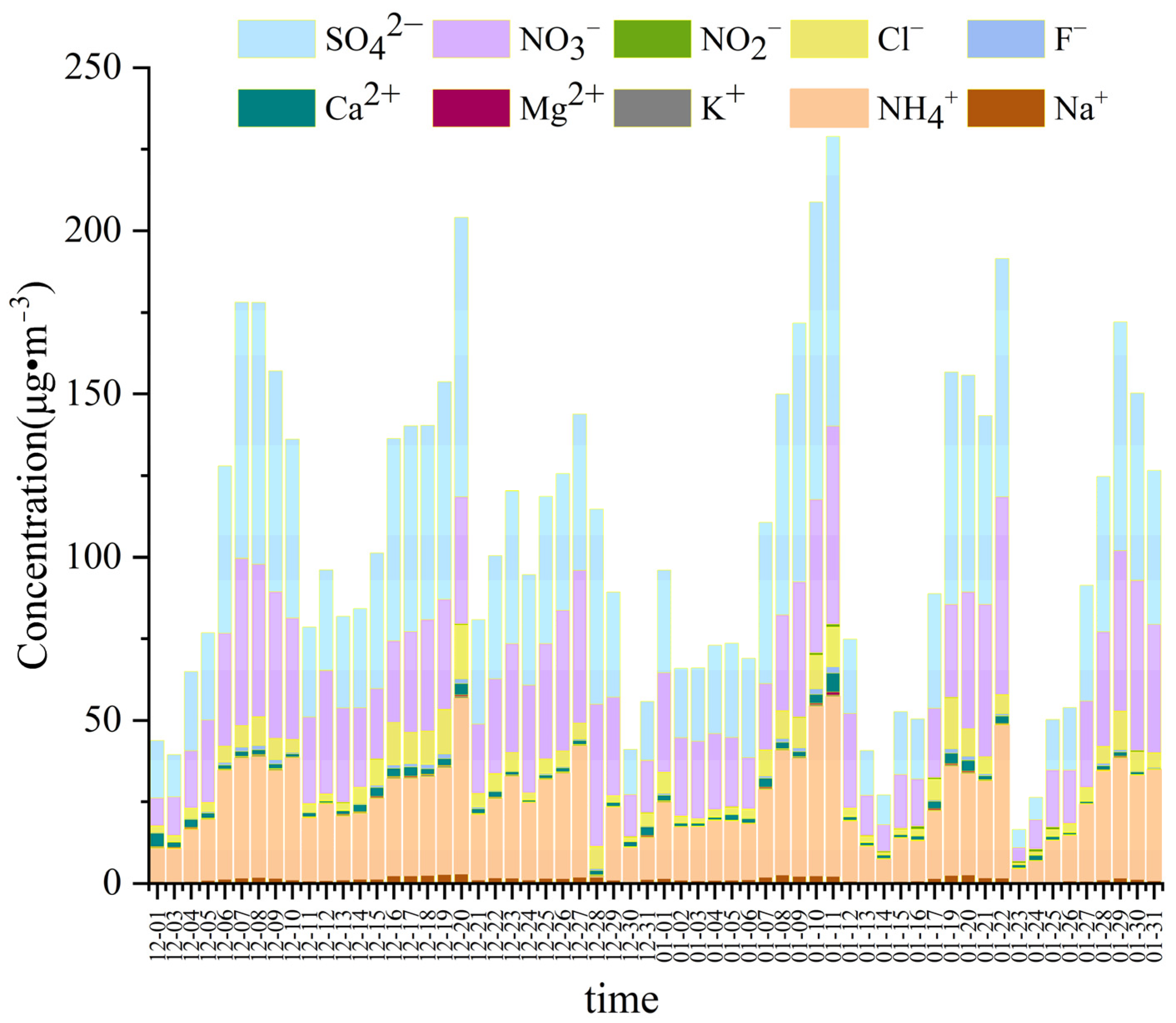
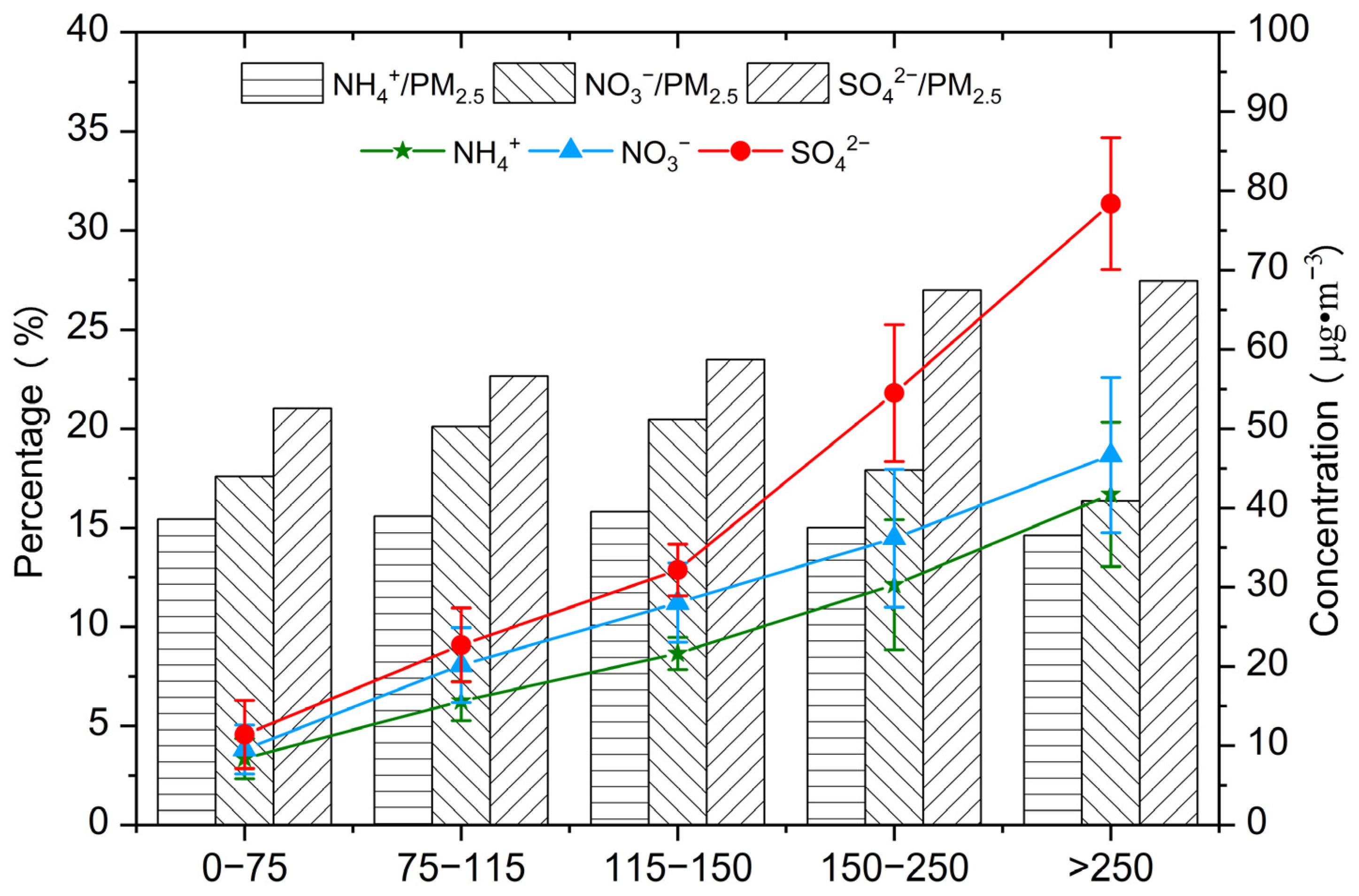
3.2.1. Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions
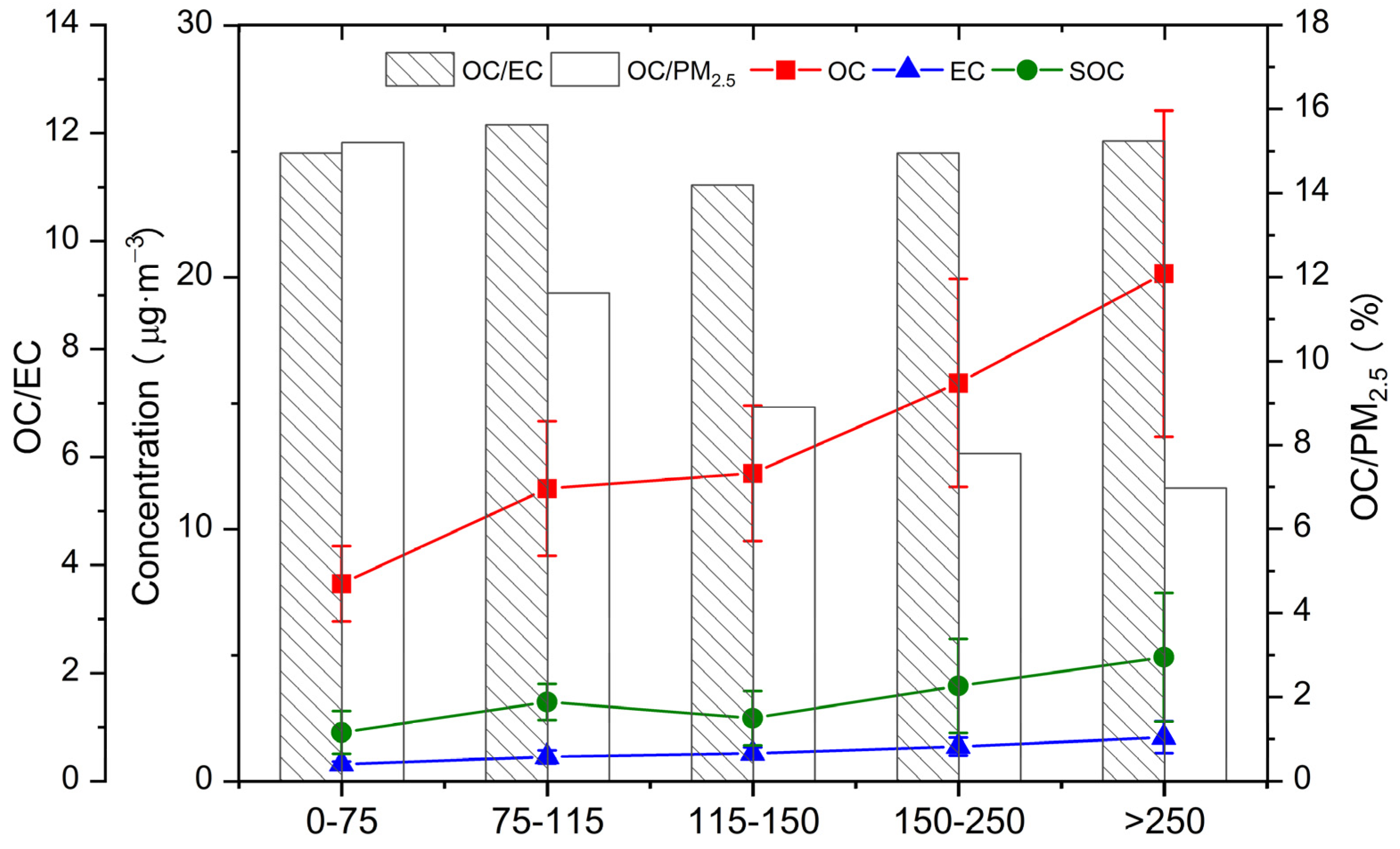
3.2.2. Organic Carbon and Elemental Carbon
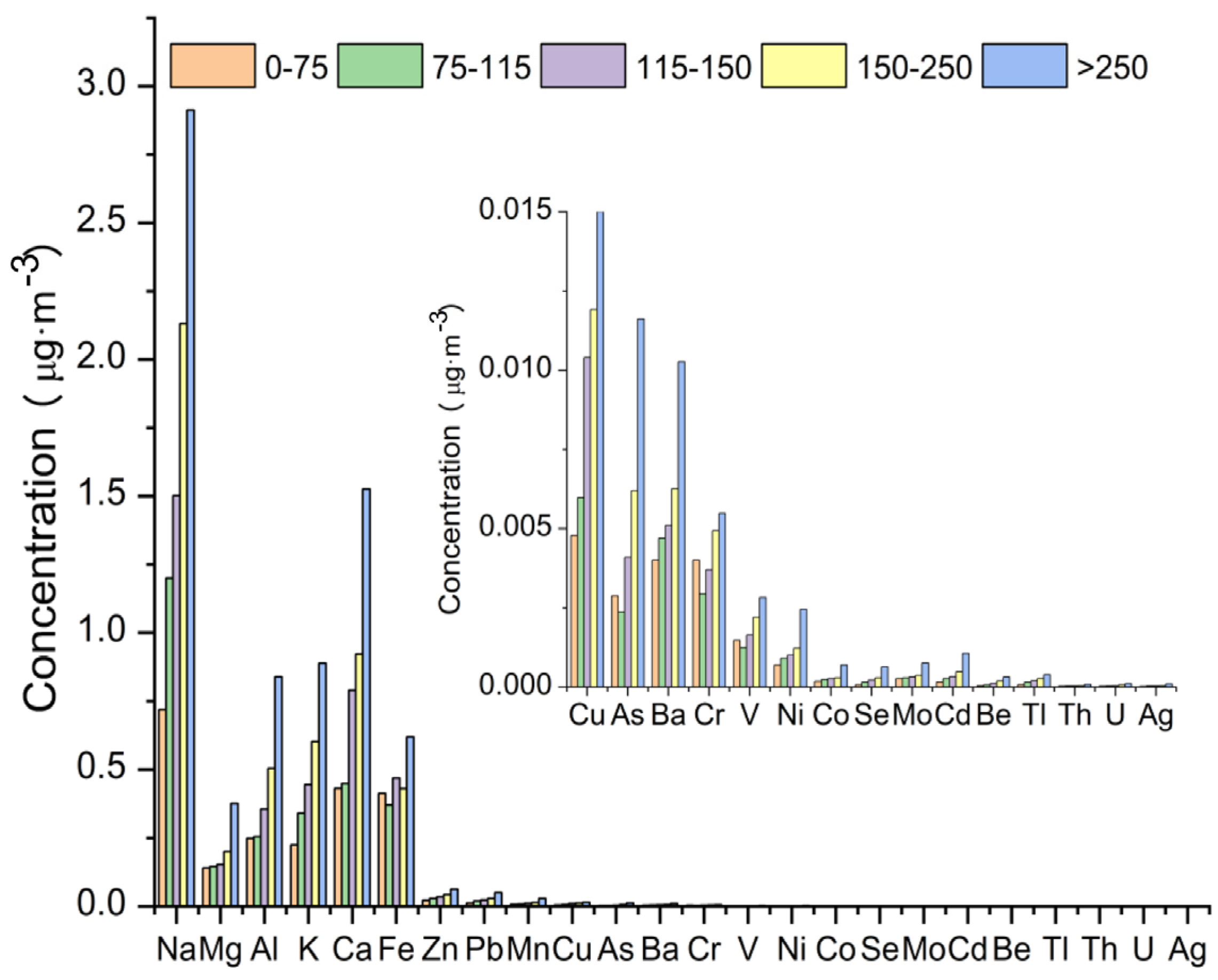
3.2.3. Inorganic Elements
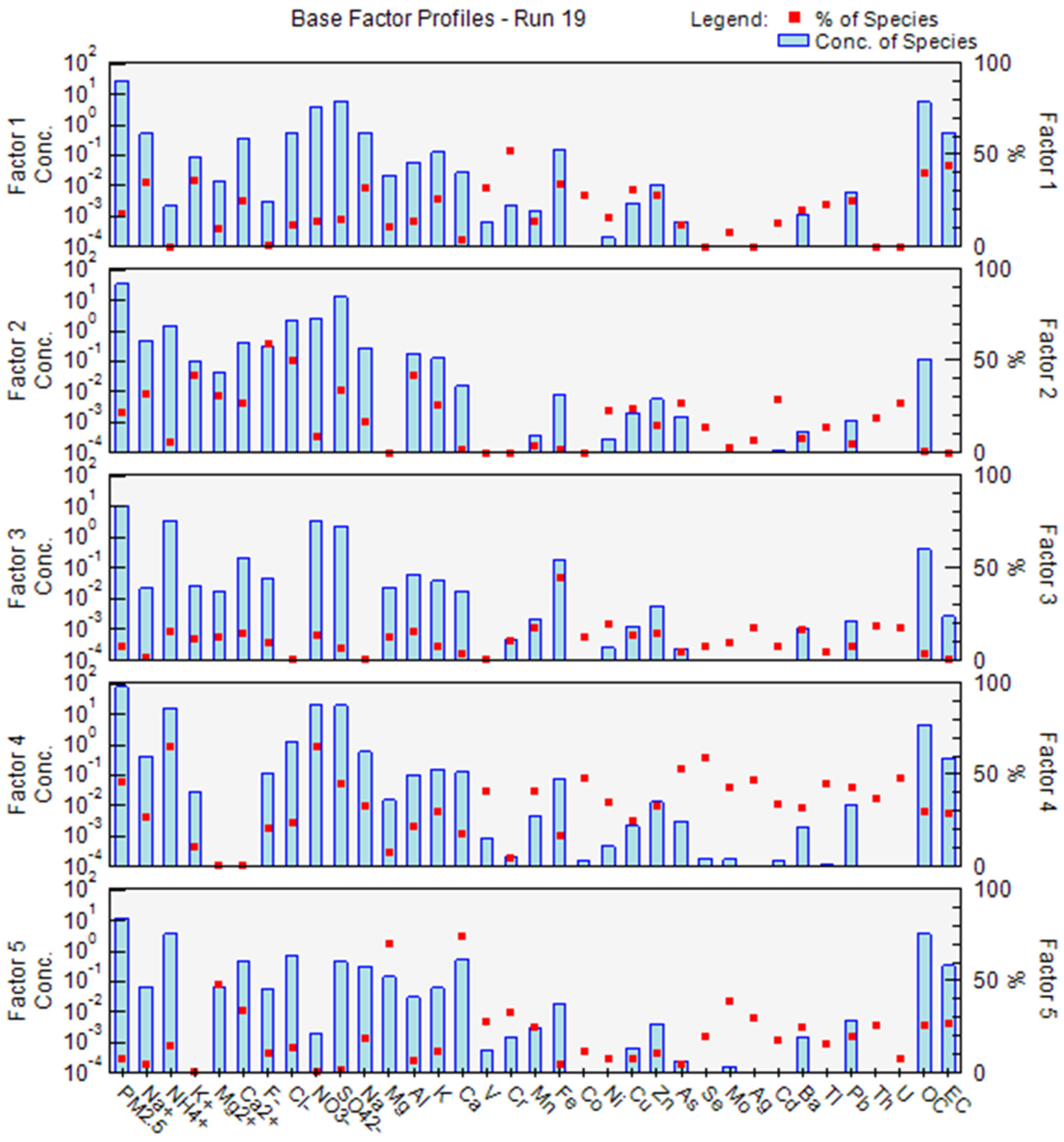
3.3. Source Apportionment by PMF
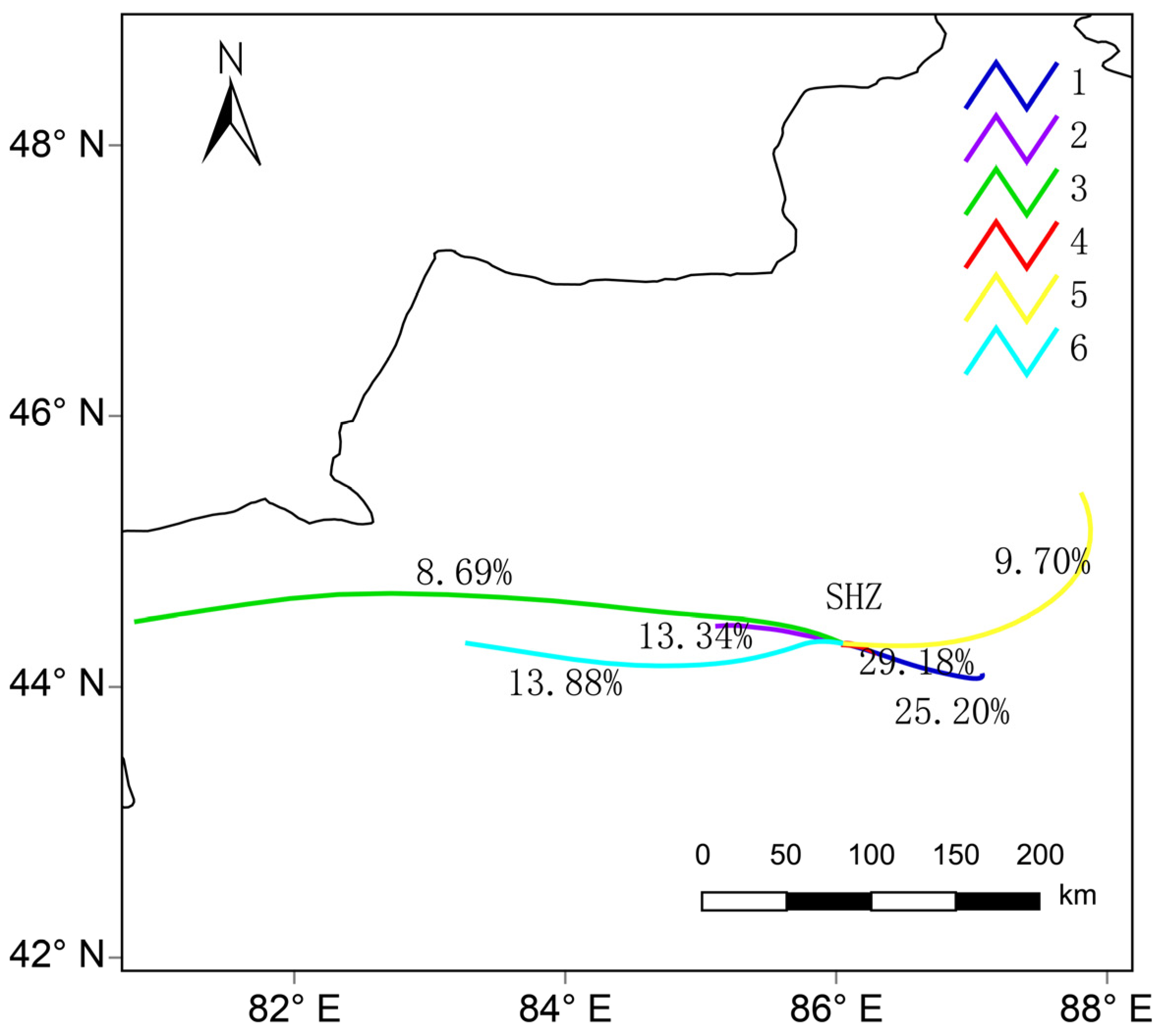
3.4. Backward Trajectory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, M. Atmospheric and Environmental Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 365–446. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Tan, Q.; Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Jiang, W. Effects of relative humidity and PM2.5 chemical compositions on visibility impairment in Chengdu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 86, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Tan, J.; Duan, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C.; Ji, S.; Qi, M.; Lu, X.H.; Wang, Y. Changes of chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 during 2013–2017 in urban handan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X. Characteristics, Source Apportionment and Influence on Visual Range of PM2.5 in Jinna. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Xing, J.; Morawska, L.; Ding, A.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kujansuu, J. Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwubinuer, R.; Yusan, T.; Dilnuer, T.; Wang, X.; Ding, X. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in urban area of hotan city, China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Shen, L.; Xu, H.; An, J.; Xue, G.; Cao, J. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in five sites in the Yangtze river delta, China: Size-fractionated, seasonal variations and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Duan, F.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, B. Characteristics of the secondary water-soluble ions in a typical autumn haze in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.P.; Zhang, J.K.; Huang, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.Q. Pollution characteristics of water-soluble inorganic ions in Chengdu in summer and winter. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 3012–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bao, J.M.; Bi, F.; Gao, R.; Peng, L.; Xu, Y.S.; Chai, F.H. Synergistic control of PM2.5 and ozone pollution: Challenges and responses. World Environ. 2020, 5, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.N.; Wen, T.X.; Hua, W.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Hu, B.; Xin, J. Characterization and size distribution of carbonaceous aerosols at Mountain Dinghu. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Chen, C.R.; Vu, T.V.; Liu, D.; Harrison, R.M. Source apportionment of fine organic carbon (OC) using receptor modelling at a rural site of Beijing: Insight into seasonal and diurnal variation of source contributions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, J.Y.; Duan, X.L.; Chen, H.; Yan, Y.L.; Peng, L. Characteristics and sources analysis of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 in winter in four cities of Shanxi Province. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.M.; Tang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.K.; Liu, Q.; Yan, G.X.; Chen, M.M.; Gao, W.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, S.Y. Characteristics of carbonaceous species in PM2.5 in southern Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Kang, S.C.; Tripathee, L.; Ram, K.; Li, C. Light absorption properties of elemental carbon (EC) and water-soluble brown carbon (WS-BrC) in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: A 5-year study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.R.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Sun, N.; Huang, Y.; Lei, W.K.; Liu, X.G. Chemical composition and source analysis of PM2.5 in Yuncheng, Shanxi Province in autumn and winter. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.Q.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, X.; Bi, S.Q.; Zhang, B.H.; Gao, Y.; Cao, H.B. Concentrations, sources, and health risks of PM2.5 carrier metals in the Beijing urban area and suburbs. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, Y.R.; Zhaxi, Y.; Ba, L.; Wang, W.; Li, X.W. Spatio-temporal variation trends of satellite-based aerosol optical depth in China during 1980–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6802–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D. Hazy weather research in China in the last decade: A review. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y. Build Tianshan mountain north slope economic development belt of Xinjiang China. China Soft Sci. Mag. 2002, 3, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.M.; Wang, L.; Qin, H.; Feng, Z.M. The air pollution characteristics and the impact of meteorological conditions in Urumqi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.T.; Li, X.; Mauren, A.; Zhong, Y.T.; Wang, H.Q. Characteristics of air pollution and its polluted weather types of urban agglomeration on the north slope of the middle Tianshan Mountains from 2017 to 2019. Arid. Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Kou, J.Z. The Causes of Heavy Atmospheric Pollution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region and Surrounding Areas Are Clearer. People’s Daily, 21 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Ning, J.; Lu, J. Characteristics and source apportionment of organic carbon and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Shihezi, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Analysis of different modes of factor analysis as least squares fit problems. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1993, 18, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 in a border city in southwest China. Atmosphere 2021, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemori, F.; Uranishi, K.; Asakawa, D.; Nakatsubo, R.; Sugata, S. Source apportionment in PM2.5 in central Japan using positive matrix factorization focusing on small-scale local biomass burning. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display System: READY. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yin, S.S.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Kang, P.R.; Zhang, R.Q.; Tang, X.Y. Characteristics of mass concentration, chemical composition, source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 and health risk assessment in the emerging megacity in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, A.B.; Liu, M. Comparative Study on Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 and Total Suspended Particulate in Qingdao Suburban Area. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2016, 29, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Li, X.; Fan, Z.A.; Ayitken, M.; Li, S.T.; Liu, X.C. Chemical Composition Characteristics and Source Contributions of Precipitation in Typical Cities on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountain in Xinjiang during 2010–2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shi, M.; Liu, W.; Mao, Y.; Hu, J.; Tian, Q.; Chen, Z.; Hu, T.; Xing, X.; Qi, S. Characteristics and source apportionment of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 during a wintertime haze event in huanggang, central China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Bi, L.; Shi, J.; Xiang, F.; Qian, L.; Ning, P. Characterization and source identification of PM2.5 in ambient air of Kunming in windy spring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Feng, Y.; Ren, L.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Han, X.; Ning, P. Mass concentration, chemical composition, and source characteristics of PM2.5 in a plateau slope city in southwest China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.; Wu, P.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, N. Composition and source analysis of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 during autumn in Guiyang. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.S.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yao, Q.; Liu, H.Y. Characteristics of concentrations and chemical compositions for PM2.5 in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.M.; Harrison, R.M.; Djt, S.; Pio, C.A. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, T.; He, M.; Wang, J. Pollution characteristics and sources of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 during winter in Chengdu. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y. Study on chemical composition and pollution source of atmospheric PM2.5 in Xi’an City. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, D.F.; Zhao, Q.B.; Cui, H.X.; Li, J.; Duan, Y.S.; Fu, Q.Y. Characteristics and sources of organic carbon and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Shanghai urban area. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wu, F.; Chow, J.C.; Lee, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.W.; An, Z.S.; Fung, K.K.; Watson, J.G.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.W.; Nie, S.S.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y.P.; Yao, B.; Cui, J.S. Seasonal variation and source apportionment of carbonaceous species in PM2.5 in Chengde. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5152–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Z.E.; Zhai, C.Z.; Bai, Z.G.; Chen, G.C.; Ji, Y.Q.; Ren, L.H.; Fang, W.K. Carbon source apportionment of PM2.5 in Chongqing based on local carbon profiles. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, G.; Bi, X.; Feng, Y.; Mai, B.; Fu, J. Emission factors for carbonaceous particles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from residential coal combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lu, Z.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Frazier, C.A.; Solomon, P.A.; Thuillier, R.H.; Magliano, K. Descriptive analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 at regionally representative locations during SJVAQS/AUSPEX. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2079–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Feng, X.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Yin, H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Pollution characteristics of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 in the Chengdu City. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Li, S.P.; Wang, M.M.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhen, M.; Zhang, L.X.; Li, Y.G.; Chen, Q.C. Source apportionment of environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) in PM2.5 over Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Environmental response to variation of the atmospheric maximum mixing depth in Urumqi. Arid. Zone Res. 2011, 28, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Zhen, Y.; Ayitken, M.; Li, S.; Wang, N. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of aerosol optical depth in Xinjiangfrom 2003 to 2019. Arid. Land. Geo. 2022, 45, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Shihezi | Baoshan [26] | Huanggang [33] | Kunming [34] | Wenshan [35] | Guiyang [36] | Beijing [37] | Tianjing [37] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2020–2021 | 2016 | 2018 | 2013 | 2016 | 2017 | 2009 | 2009 |
| Season | Winter | Wet and Dry Season | Winter | Spring | Spring and Autumn | Autumn | Four Seasons | Four Seasons |
| PM2.5 | 164.69 ± 76.48 | 23.17 ± 12.32 | 110.40 ± 45.9 | - | 44.85 ± 10.99 | 27.12 | 123.45 ± 71.59 | 141.47 ± 78.03 |
| Na+ | 1.54 ± 0.7 | 0.33 ± 0.25 | 1.10 ± 0.50 | - | - | 0.07 | 0.53 ± 0.45 | 0.63 ± 0.30 |
| NH4+ | 24.88 ± 12.1 | 0.95 ± 0.48 | 13.0 ± 6.90 | 0.52 | 2.81 ± 1.16 | 2.56 | 6.37 ± 3.91 | 7.64 ± 4.27 |
| K+ | 0.27 ± 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.28 | 0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.63 ± 0.24 | 0.37 | 1.68 ± 1.29 | 2.08 ± 1.36 |
| Mg2+ | 0.17 ± 0.14 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.30 | 0.3 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.18 ± 0.11 | 0.23 ± 0.13 |
| Ca2+ | 1.63 ± 0.99 | 1.17 ± 0.35 | 0.60 ± 0.30 | 2.83 | 1.04 ± 0.5 | 1.98 | 1.55 ± 1.38 | 1.79 ± 1.44 |
| F− | 0.59 ± 0.47 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.03 | - | - |
| Cl− | 5.27 ± 3.84 | 0.34 ± 0.23 | 2.70 ± 1.20 | 0.72 | 0.31 ± 0.109 | 0.16 | 2.92 ± 3.46 | 8.14 ± 6.10 |
| SO42− | 42.47 ± 22.96 | 1.42 ± 0.69 | 15.0 ± 7.30 | 9.72 | 5.98 ± 2.07 | 8.53 | 19.07 ± 16.36 | 24.97 ± 22.59 |
| NO3− | 29.85 ± 13.36 | 0.73 ± 0.31 | 30.8 ± 15.7 | 0.51 | 1.00 ± 0.40 | 2.21 | 20.47 ± 18.07 | 18.83 ± 15.77 |
| NO3−/SO42− | 0.70 | 0.51 | 2.05 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 1.07 | 0.75 |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trajectory proportion | 25.20% | 13.34% | 8.69% | 29.18% | 9.70% | 13.88% |
| PM2.5 mean concentration | 158.73 | 167.90 | 175.67 | 160.39 | 98.86 | 218.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Ayitken, M.; Liu, X. Apportionment of Chemical Components and Sources of PM2.5 in Shihezi City of Xinjiang, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040703
Zhong Y, He Y, Li X, Li S, Ayitken M, Liu X. Apportionment of Chemical Components and Sources of PM2.5 in Shihezi City of Xinjiang, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040703
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yuting, Youjiang He, Xia Li, Shuting Li, Maulen Ayitken, and Xinchun Liu. 2023. "Apportionment of Chemical Components and Sources of PM2.5 in Shihezi City of Xinjiang, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040703
APA StyleZhong, Y., He, Y., Li, X., Li, S., Ayitken, M., & Liu, X. (2023). Apportionment of Chemical Components and Sources of PM2.5 in Shihezi City of Xinjiang, China. Atmosphere, 14(4), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040703






