Sub-Seasonal Prediction of Sea-Gale Processes in the Yangtze River Estuary of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
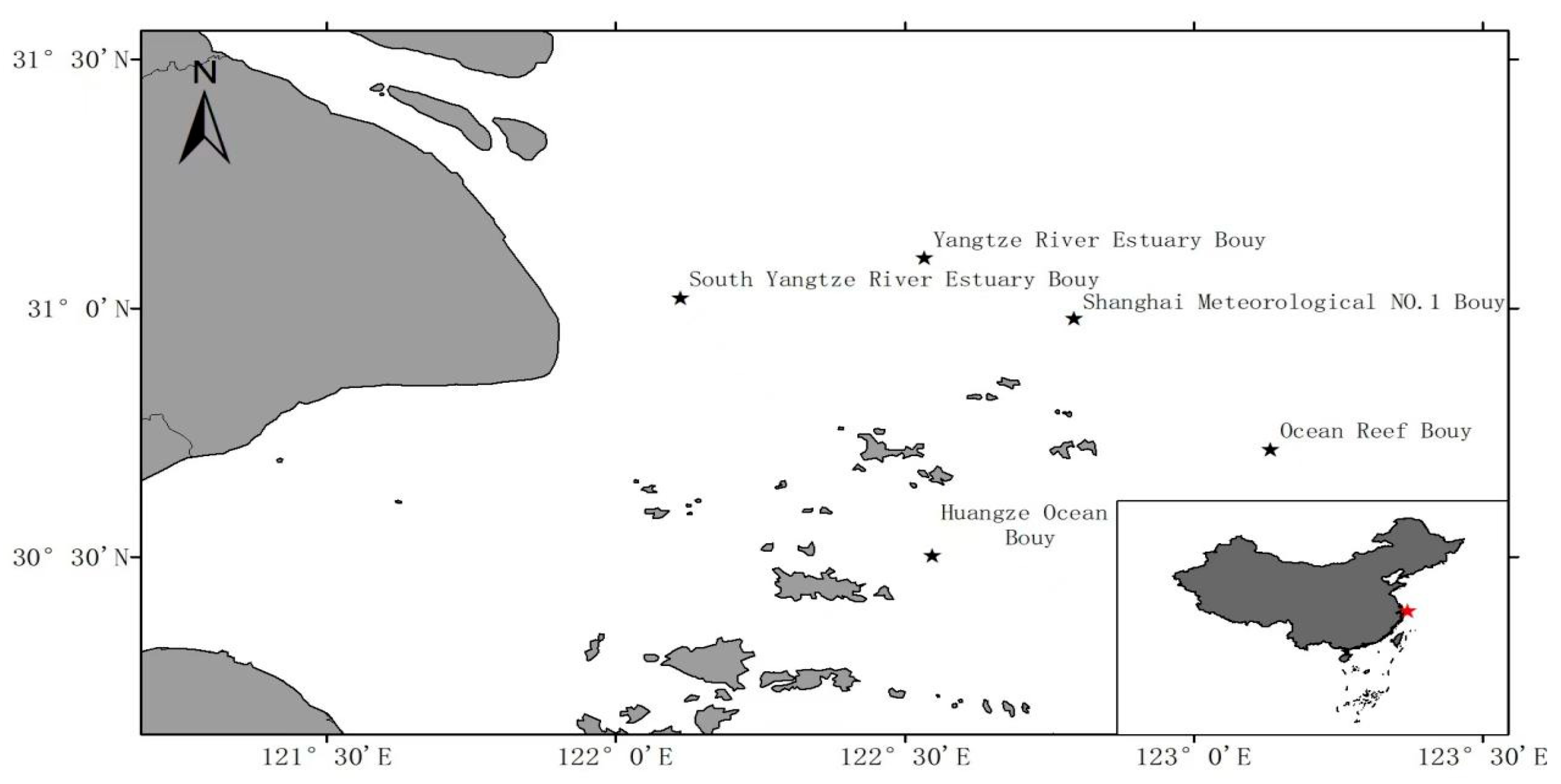
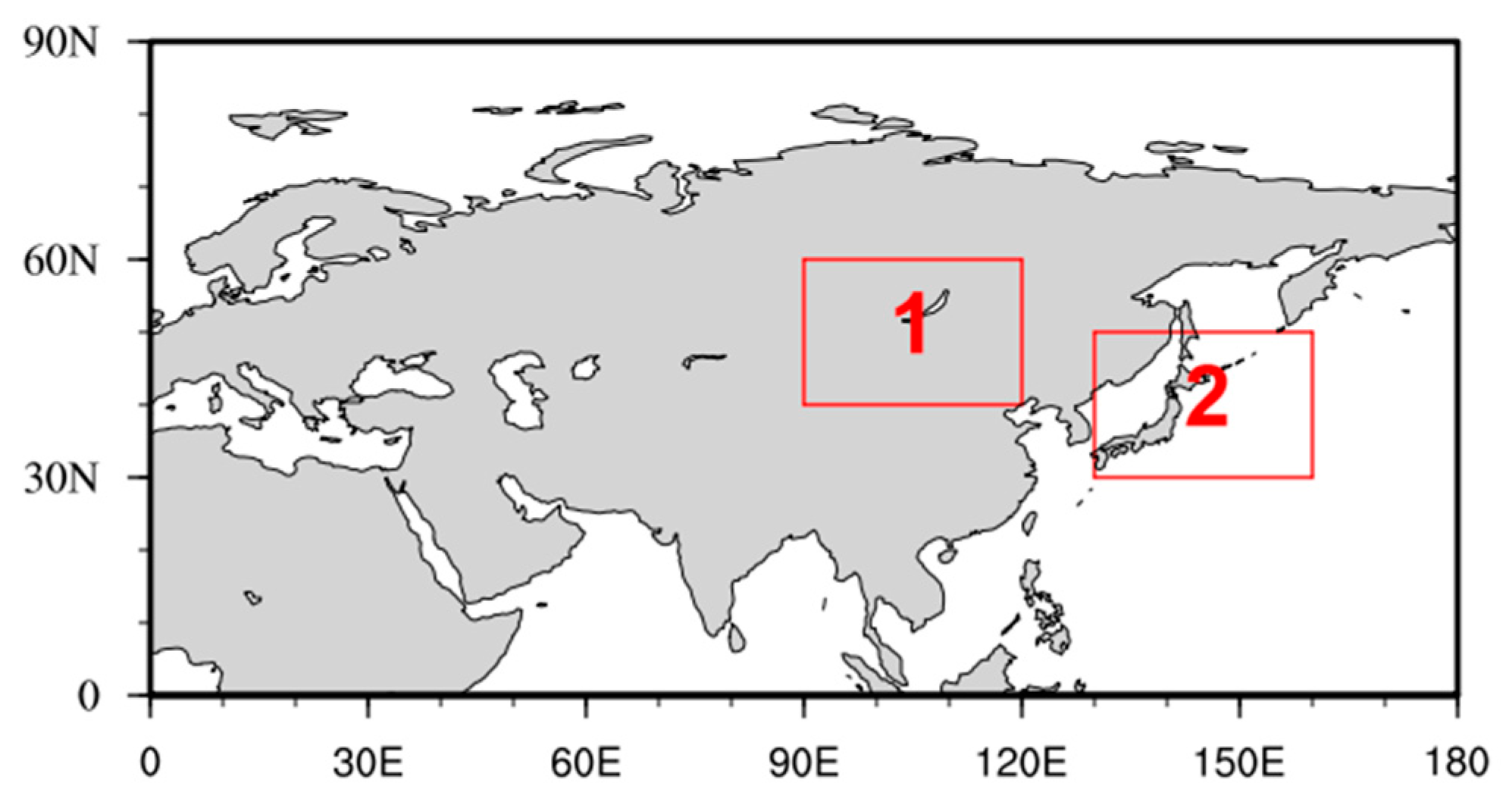
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
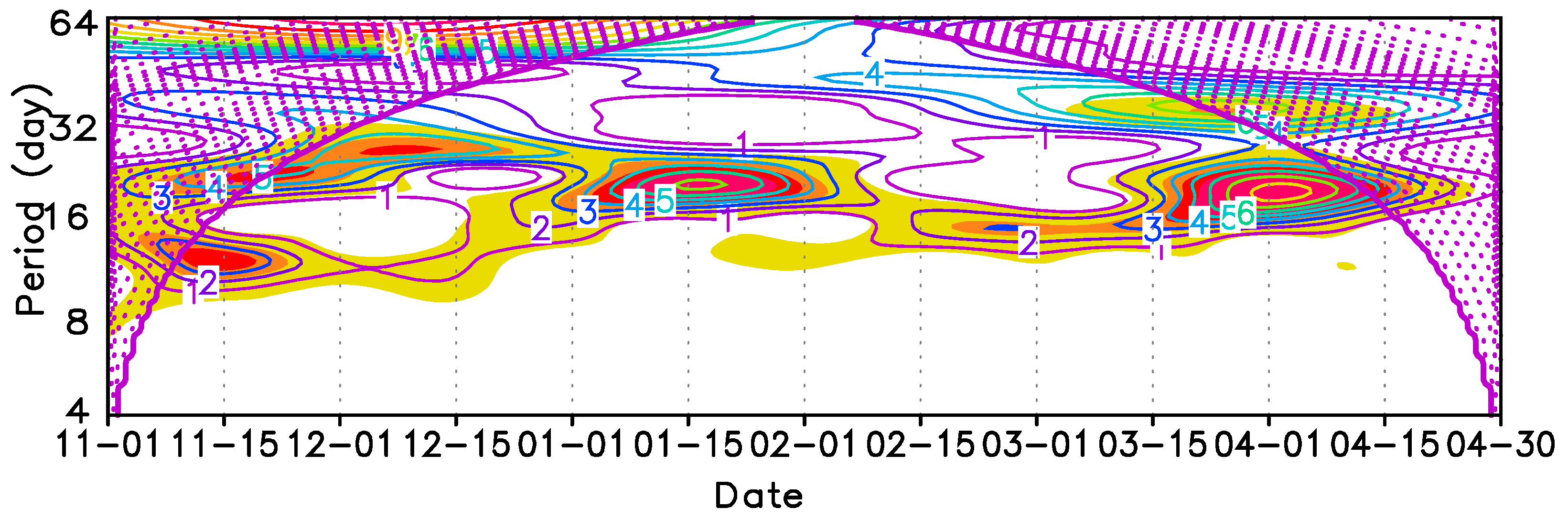
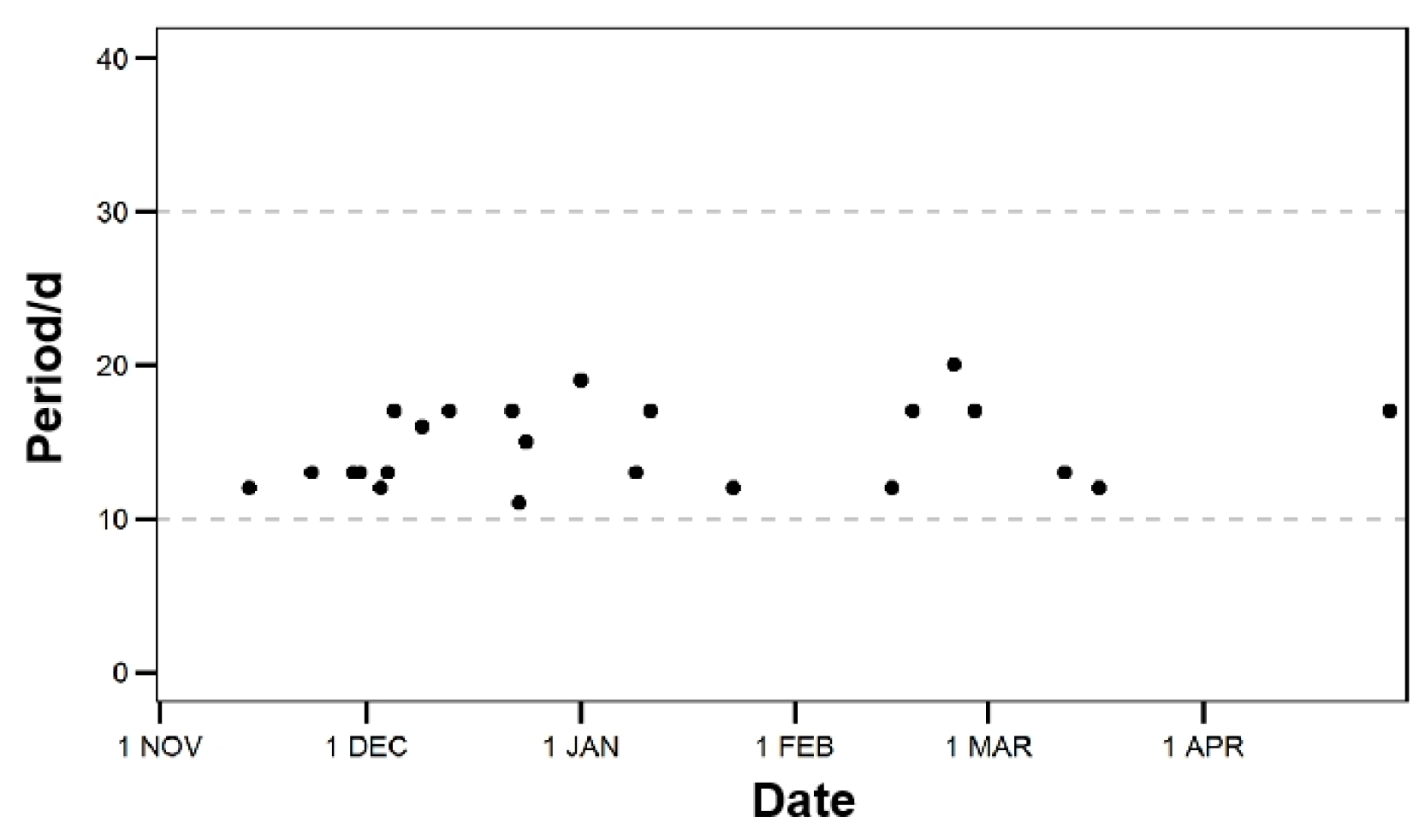
3.1. Characteristics of the Low-Frequency Oscillations of SGPs in Winter Half-Years
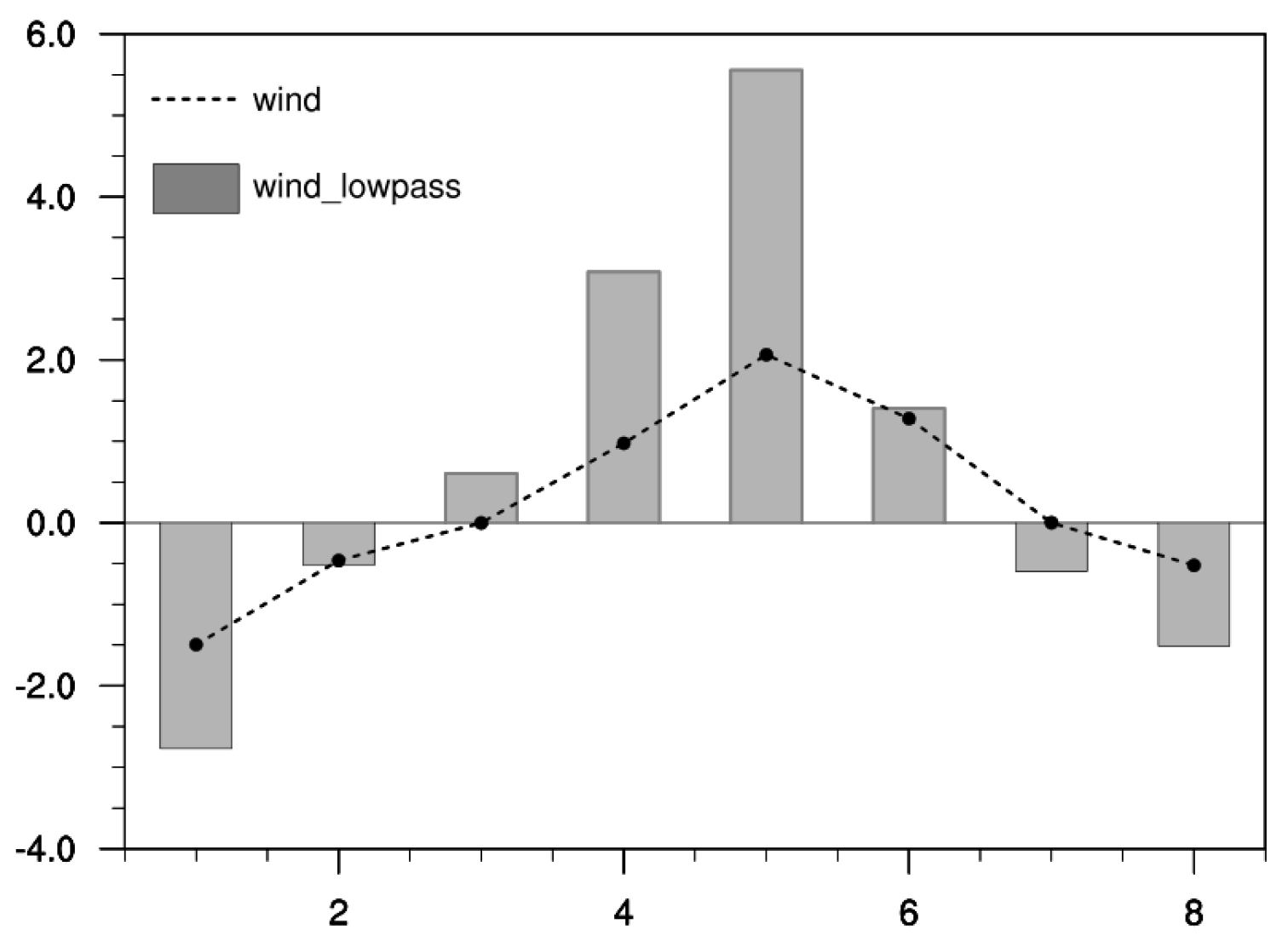
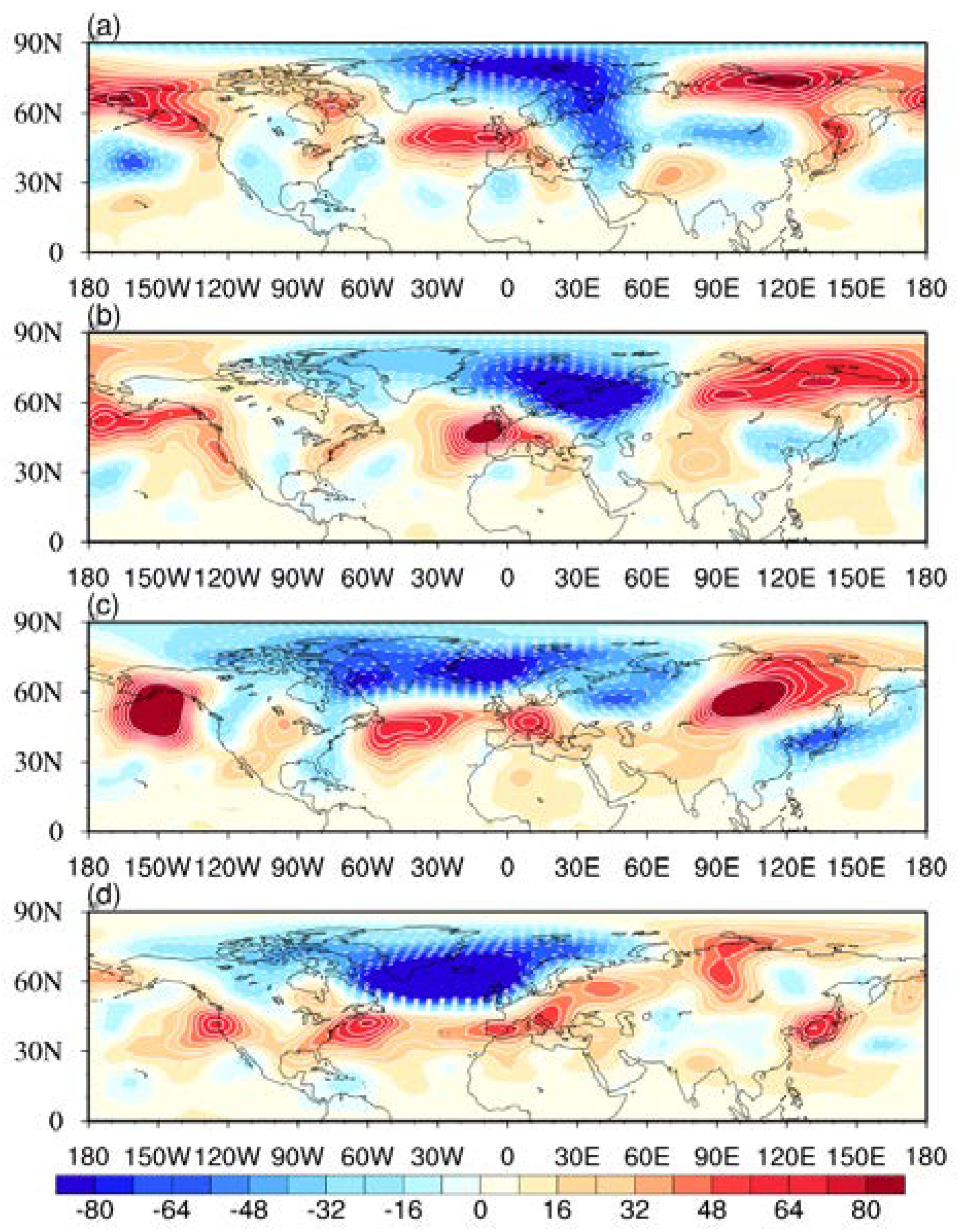
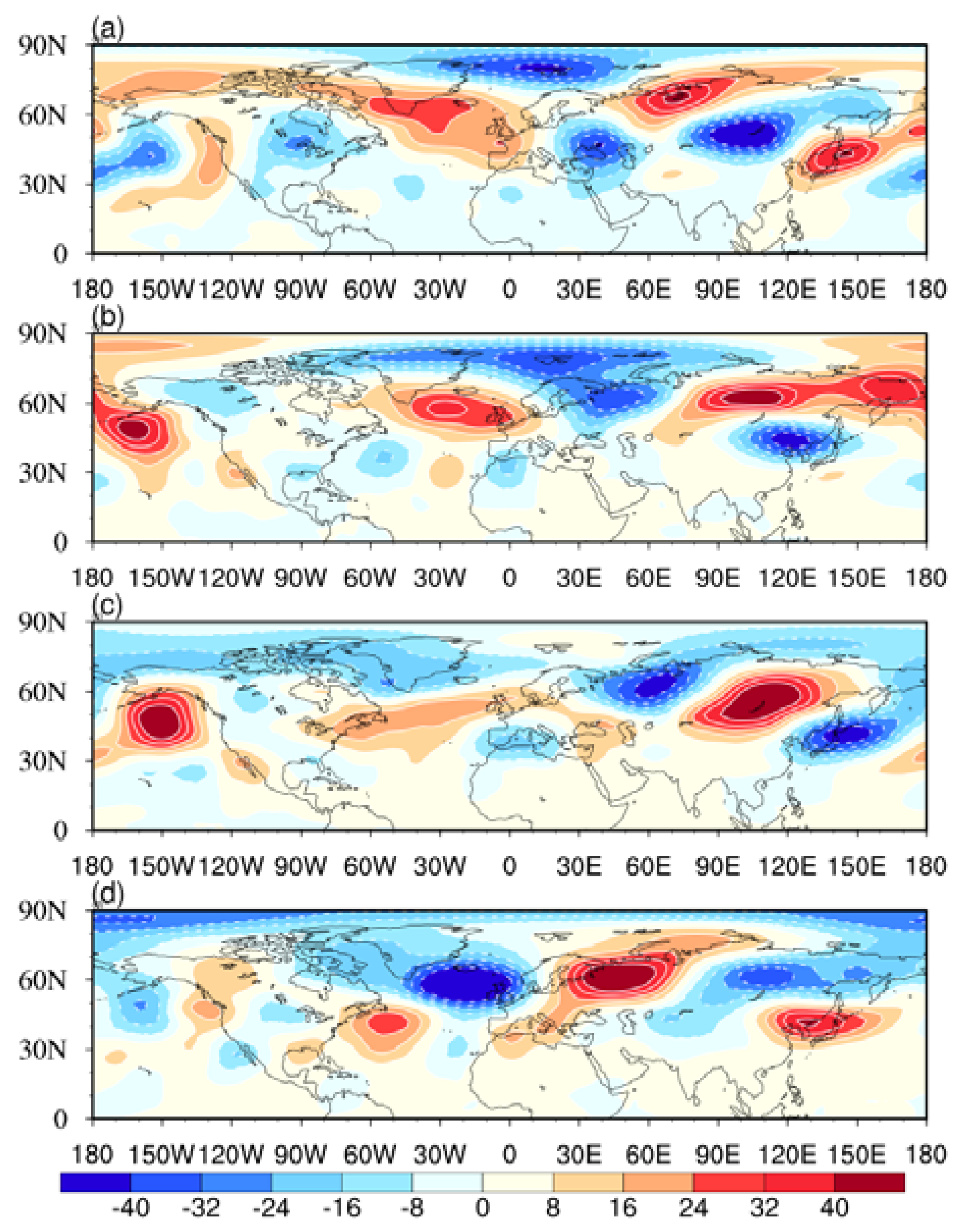
3.2. Characteristics of Circulation Background of SGPs
3.3. Evolution of the 10~30 Day Low-Frequency Circulation of SGPs
3.4. Sub-Seasonal Forecast Experiments of SGPs
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, G.; Kootval, H.K.; Kull, D.W.; Clements, J.; Consulting, S.; Fleming, G.; Éireann, M.; Frei, T.; Switzerland, Z.; Lazo, J.K.; et al. Valuing Weather and Climate: Economic Assessment of Meteorological and Hydrological Services. WMO 2015. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/711881495514241685/valuing-weather-and-climate-economic-assessment-of-meteorological-and-hydrological-services (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Alizadeh, O. Advances and challenges in climate modeling. Clim. Chang. 2022, 170, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Ardilouze, C.; Bonet, A.; Brookshaw, A.; Chen, M.; Codorean, C.; Déqué, M.; Ferranti, L.; Fucile, E.; Fuentes, M.; et al. The Subseasonal to Seasonal (S2S) prediction project database. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.J.; Carlsen, H.; Robertson, A.W.; Klein, R.J.; Lazo, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Vitart, F.; de Perez, C.; Ray, A.J.; Murray, V.; et al. Potential applications of subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) predictions. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.; Vitart, F. Sub-Seasonal to Seasonal Prediction: The Gap between Weather and Climate Forecasting; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Molteni, F. Simulation of the Madden-Julian oscillation and its teleconnections in the ECMWF forecast system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutham, N.; Plougonven, R.; Omrani, H.; Parey, S.; Tankov, P.; Tantet, A.; Hitchcock, P.; Drobinski, P. How skillful are the European. subseasonal predictions of wind speed and surface temperature? Mon. Weather Rev. 2022, 150, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, G.; Shapiro, M.; Hoskins, B.; Moncrieff, M.; Dole, R.; Kiladis, G.N.; Kirtman, B.; Lorenc, A.; Mills, B.; Morss, R.; et al. Collaboration of the weather and climate communities to advance sub seasonal-to-seasonal prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 5, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40–50 day period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E.; Jones, C.; Schemm, J.E.; Graham, N.E. A statistical extended-range tropical forecast model based on the slow evolution of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1918–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B. Predictability beyond the Deterministic Limit. World Meteorological Organization. 2012. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/bulletin/predictability-beyond-deterministic-limit (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Zhang, C. Madden–Julian oscillation: Bridging weather and climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1849–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lin, H. Sub-seasonal prediction over East Asia during boreal summer using the ECCC monthly forecasting system. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lin, H.; Ding, Y. Dominant modes of subseasonal variability of East Asian summertime surface air temperature and their predictions. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 2729–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, T.N. Summer monsoon experiment: A review. Mon. Weather Rev. 1985, 112, 1590–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y. Intraseasonal oscillation in atmosphere. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 14, 32–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kwon, W.T. Influence of the Madden-Julian oscillation on wintertime surface air temperature and cold surges in East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Lin, H.; Wu, Z.W. Another look at influences of the Madden-Julian oscillation on the wintertime East Asian weather. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D03109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lin, H.; Wu, Q. Subseasonal variability of precipitation in China during boreal winter. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6548–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Hu, Z.Z.; Ding, Y.H.; Qian, Q.W. The extreme Mei-yu season in 2020: Role of the Madden-Julian oscillation and the cooperative influence of the Pacific and Indian oceans. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 2040–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Z.Z.; Chen, Q. The 2022 extreme heatwave in Shanghai, the lower reach of the Yangtze river valley: Combined influences of multi-scale variabilities. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Vitart, F. Evolution of ECMWF sub-seasonal forecast skill scores. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2014, 140, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizza, R.; Leutbecher, M. The forecast skill horizon. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 141, 3366–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, O. Dynamical downscaling of CSIRO-Mk3.6 seasonal forecasts over Iran with the regional climate model version 4. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 39, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, G.; Riwal, P.; Hiba, O.; Alexis, T.; Sylvie, P.; Peter, T.; Peter, H.; Philippe, D. Statistical Downscaling to Improve the Subseasonal Predictions of Energy-Relevant Surface Variables. Mon. Weather Rev. 2023, 151, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.J.; Brayshaw, D.J.; Charlton-Perez, A. Verification of European subseasonal wind speed forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, A.; Torralba, V.; Cortesi, N.; Christel, I.; Palma, L.; Manrique-Suñén, A.; Lledó, L.; González-Reviriego, N.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. Sub-seasonal to seasonal climate predictions for wind energy forecasting. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1222, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Waliser, D.E.; Lau, K.M.; Stern, W. Global occurrences of extreme precipitation and the Madden–Julian oscillation: Observations and predictability. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4575–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Waliser, D.E.; Lau, K.M.; Stern, W. The Madden–Julian oscillation and its impact on Northern Hemisphere weather predictability. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lledo, L.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. Predicting daily mean wind speed in Europe. weeks ahead from MJO status. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 3413–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo-Besteiro, S.; García-Rodríguez, M.; Labandeira, X.; Añel, J.A. Seasonal and subseasonal wind power characterization and forecasting for the Iberian Peninsula and the Canary Islands: A systematic review. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Li, T.; You, L.J.; Gao, J.Y.; Hong, L.R. A spatial-temporal projection model for 10–30 day rainfall forecast in South China. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1227–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Li, T. Empirical prediction of the onset dates of South China Sea summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Li, T. The statistical extended-range (10-30-day) forecast of summer rainfall anomalies over the entire China. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Li, T. Statistical extended-range forecast of winter surface air temperature and extremely cold days over China. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Xue, Y.B.; Shi, L.; Wang, J.F. An analysis on relationship between the shipwreck of combination vessels and the gale accident in the Bohai Straits. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2006, 22, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woollen, J. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, D.C.; Gong, X.C. The method and application of automatic quality control for real time data from automatic weather stations. Meteorol. Mon. 2007, 33, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.L.; Wang, S.W. Application of Gamma percentile to rainfall change. J. Trop. Meteorol. 1997, 13, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Liu, C.M. Applications of wavelet analysis to hydrology: Status and prospects. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth, S. On the Theory of Filter Amplifiers. Wirel. Eng. 1930, 7, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Takaya, K.; Nakamura, H. A formulation of a phase-independent wave-activity flux for stationary and migratory quasi-geostrophic eddies on a zonally varying basic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, L.; Palmer, T.N.; Molteni, F. Tropical-extratropical interaction associated with the 30-60 day oscillation and its impact on medium and extended range prediction. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 2177–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiladis, G.N.; Weickmann, K.M. Circulation anomalies associated with tropical convection during northern winter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1900–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Phillips, T.J. Coherent fluctuations of extratropical geopotential height and tropical convection in intraseasonal time scales. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 1164–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, H.J.; Baek, M.K.; Ho, C.H. Systematic variation in wintertime precipitation in East Asia by MJO-induced extratropical vertical motion. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 788–801. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.M.; Lim, G.H.; Kim, K.Y. A new look at the midlatitude MJO teleconnection in the northern hemisphere winter. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Liang, P.; Qian, Q. Sub-Seasonal Prediction of Sea-Gale Processes in the Yangtze River Estuary of China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040682
Xie X, Liang P, Qian Q. Sub-Seasonal Prediction of Sea-Gale Processes in the Yangtze River Estuary of China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040682
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xiao, Ping Liang, and Qiwen Qian. 2023. "Sub-Seasonal Prediction of Sea-Gale Processes in the Yangtze River Estuary of China" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040682
APA StyleXie, X., Liang, P., & Qian, Q. (2023). Sub-Seasonal Prediction of Sea-Gale Processes in the Yangtze River Estuary of China. Atmosphere, 14(4), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040682




