The Effects of Fog on the Atmospheric Electrical Field Close to the Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
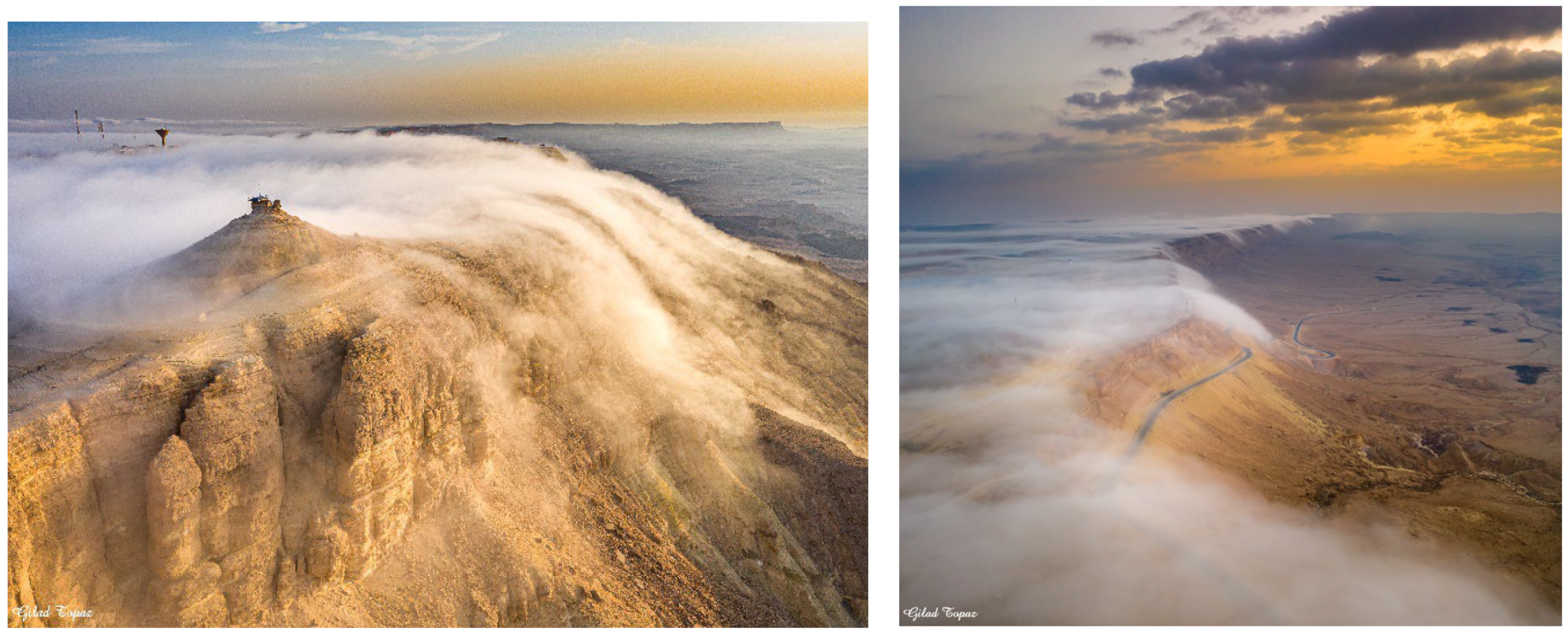
2. Meteorological Conditions for Fog in the Negev Desert
3. Instrumentation, Observation Site, and Data
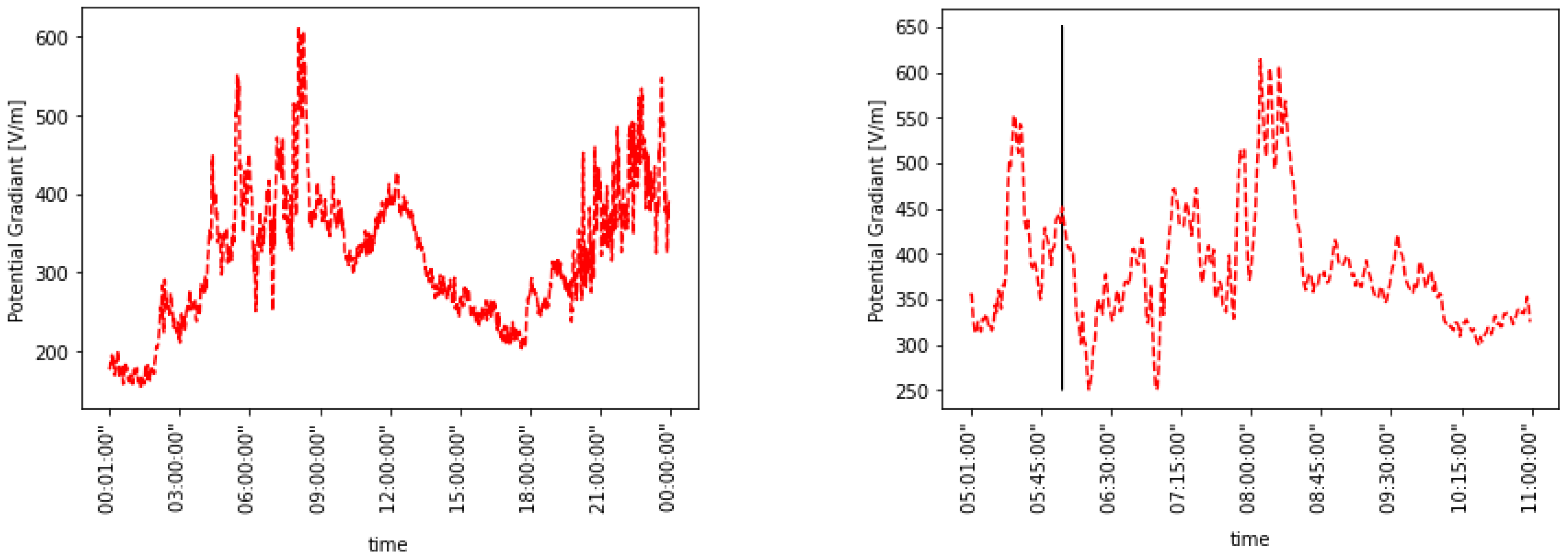
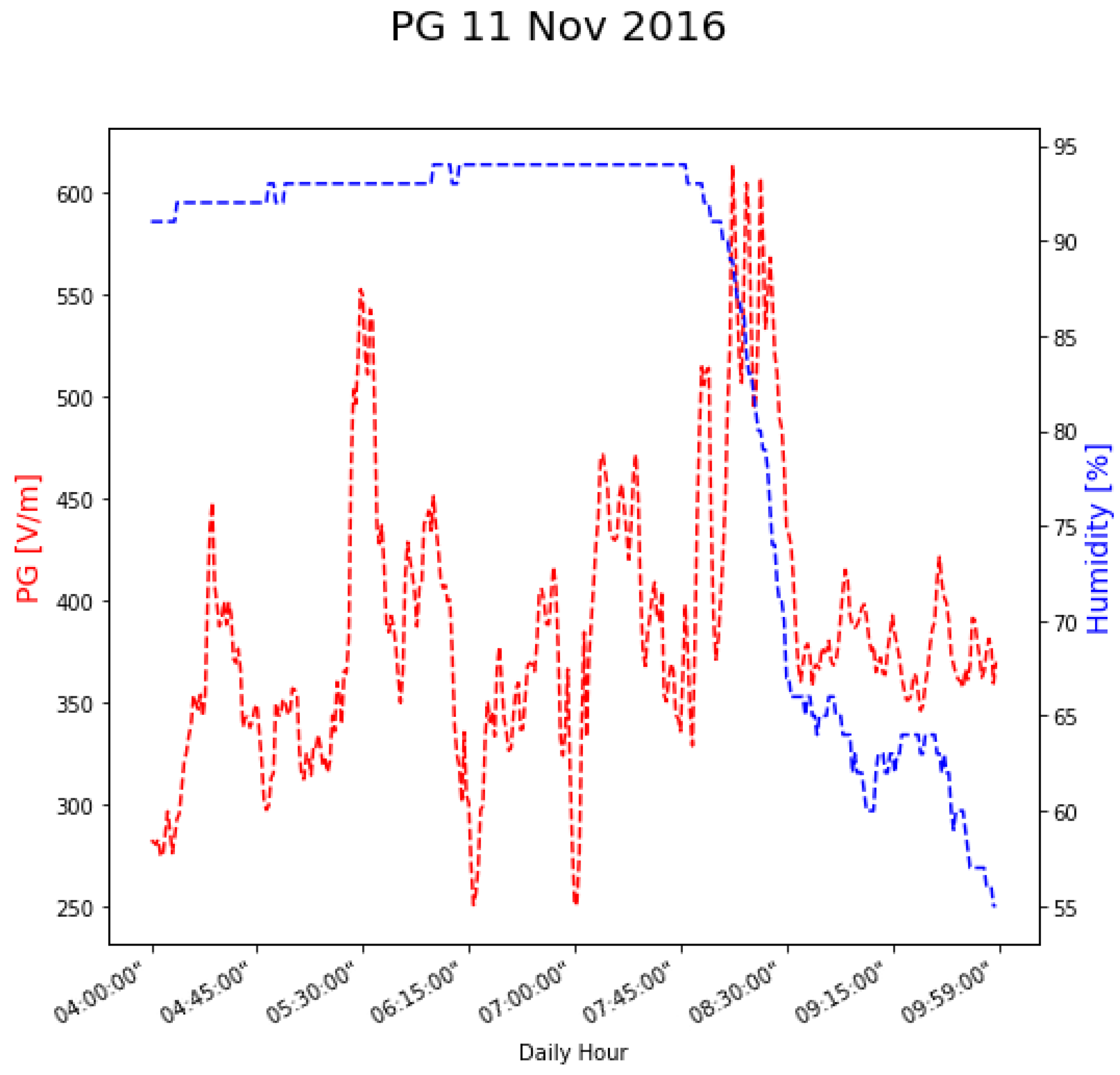
4. Results
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, R.G. The Carnegie Curve. Surv. Geophys. 2013, 34, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G.; Carslaw, K.S. Ion-aerosol-cloud processes in the lower atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G. Urban smoke concentrations at Kew, London, 1898-2004. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G. Fair weather atmospheric electricity. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 301, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycroft, M.J.; Harrison, R.G.; Nicoll, K.A.; Mareev, E.A. An overview of Earth’s global electric circuit and atmospheric conductivity. Sp. Sci. Rev. 2008, 137, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycroft, M.J.; Nicoll, K.A.; Aplin, K.L.; Harrison, R.G. Recent advances in global electric circuit coupling between the space environment and the troposphere. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2012, 90–91, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, K.L. Smoke emissions from industrial western Scotland in 1859 inferred from Lord Kelvin’s atmospheric electricity measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, D.M.; Blakeslee, R.; Bateman, M.G. Global electric circuit implications of combined aircraft storm electric current measurements and satellite-based diurnal lightning statistics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D05201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtidis, K.; André, K.S.; Karagioras, A.; Nita, I.A.; Sátori, G.; Bór, J.; Kastelis, N. The influence of circulation weather types on the exposure of the biosphere to atmospheric electric fields. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, R.; Yair, Y.; Price, C.; Katz, S. Local and global impacts on the fair-weather electric field in Israel. Atmos. Res. 2016, 172–173, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, R.; Yair, Y.; Price, C.; Mkrtchyan, H.; Lynn, B.; Reymers, A. Ground-based measurements of the vertical E-field in mountainous regions and the “Austausch” effect. Atmos. Res. 2017, 189, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, S.; Victor, N.J.; Nazir, S.; Siingh, D.; Bashir, G.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, S.J.; Singh, R.P. Fair-weather atmospheric electric field measurements at Gulmarg, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 131, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagioras, A.; Kourtidis, K. A Study of the Effects of Rain, Snow and Hail on the Atmospheric Electric Field near Ground. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronayne, T. XVIII. A letter from Thomas Ronayne, Esq; to Benjamin Franklin, LL. DFRS inclosing an account of some observations on atmospherical electricity; in regard of fogs, mists &c. with some remarks; communicated by Mr. William Henley. Phil. Tran. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1772, 62, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov, S.; Mareev, E.; Shikhova, N.; Sorokin, A.; Dmitriev, E. On the electro–dynamical characteristics of the fog. Atmos. Res. 2005, 76, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.; Harrison, R. Evidence for global circuit current flow through water droplet layers. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2009, 71, 1219–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.M.; Thayer, J.P.; Deierling, W. Statistical analysis of spatial and temporal variations in atmospheric electric fields from a regional array of field mills. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. Radiation Fog. Part I: Observations of Stability and Drop Size Distributions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 139, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldreich, Y. The Climate of Israel: Observation, Research and Application; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; 270p. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, W.M. Fog in Israel. Isr. J. Earth Sci. 1967, 16, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- David, N.; Rayitsfeld, A.; Gao, H.O. Analyzing 50 years of major fog events across the central coastal plain of Israel. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2009.05113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, A.; Tzadok, T.; Rostkier-Edelstein, D.; Agassi, E. Fog Measurements with IR Whole Sky Imager and Doppler Lidar, Combined with In Situ Instruments. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, G.J. Altitude dependent dew and fog in the Negev Desert, Israel. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, G.J. Analysis of dew precipitation in three habitats within a small arid drainage basin, Negev Highlands, Israel. Atmos. Res. 2000, 55, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, W.T.; Brown, R.; Caughey, S.J.; Garland, J.A.; Readings, C.J. The physics of radiation fog: I—A field study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1976, 102, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hůnová, I.; Brabec, M.; Malý, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; Geletič, J. Terrain and its effects on fog occurrence. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 768, 144359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.; Yair, Y.; Price, C.; Yaniv, R.; Silber, I.; Lynn, B.; Ziv, B. Electrical properties of the 8–12th September, 2015 massive dust outbreak over the Levant. Atmos. Res. 2018, 201, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, R.; Yair, Y. Electric Field Variations Caused by Low, Middle and High-Altitude Clouds over the Negev Desert, Israel. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, Y.; Katz, S.; Yaniv, R.; Ziv, B.; CPrice, C. An electrified dust storm over the Negev desert. Israel. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, K.; Harrison, R.; Barta, V.; Bor, J.; Brugge, R.; Chillingarian, A.; Chum, J.; Georgoulias, A.; Guha, A.; Kourtidis, K.; et al. A global atmospheric electricity monitoring network for climate and geophysical research. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 184, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G.; Usoskin, I. Solar modulation in surface atmospheric electricity. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2020, 72, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G.; Aplin, K. Mid-nineteenth century concentrations of smoke near London. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4037–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, J.; Bott, A.; Gera, M. Fog Prediction for Road Traffic Safety in a Coastal Desert Region. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2012, 145, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Rajagopal, E.N.; Boutle, I.A.; George, J.P.; Mohandas, S.; Webster, S.; Aditi, S. An operational fog prediction system for Delhi using the 330 m Unified Model. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2018, 19, e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithani, P.; Ghude, S.D.; Chennu, V.N.; Kulkarni, R.G.; Steeneveld, G.-J.; Sharma, A.; Prabhakaran, T.; Chate, D.M.; Gultepe, I.; Jenamani, R.K.; et al. WRF Model Prediction of a Dense Fog Event Occurred During the Winter Fog Experiment (WIFEX). Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, N.; Alpert, P.; Messer, H. Novel method for fog monitoring using cellular networks infrastructures. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2012, 5, 5725–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, N.; Sendik, O.; Messer, H.; Alpert, P. Cellular Network Infrastructure: The Future of Fog Monitoring? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domen, J.K.; Stringfellow, W.T.; Camarillo, M.K.; Gulati, S. Fog water as an alternative and sustainable water resource. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Design of water harvesting towers and projections for water collection from fog and condensation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaDochy, S.; Witiw, M. The Continued Reduction in Dense Fog in the Southern California Region: Possible Causes. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclea, R.-C.; Dughir, C.; Alexa, F.; Sandru, F.; Silea, I. Laser and LIDAR in A System for Visibility Distance Estimation in Fog Conditions. Sensors 2020, 20, 6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, E.M. Multi-spectral Remote Sensing of Sea Fog with Simultaneous Passive Infrared and Microwave Sensors. In Marine Fog: Challenges and Advancements in Observations, Modeling, and Forecasting; Koračin, D., Dorman, C., Eds.; Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jin, W.; Fu, R.; He, C. Daytime sea fog monitoring using multimodal self-supervised learning with band attention mechanism. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 21205–21222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, R. Analysis of the Influence of Foggy Weather Environment on the Detection Effect of Machine Vision Obstacles. Sensors 2020, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.-Y.; Park, S.; Ha, K.-J.; Shim, J.-S. Algorithm for sea fog monitoring with the use of information technologies. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

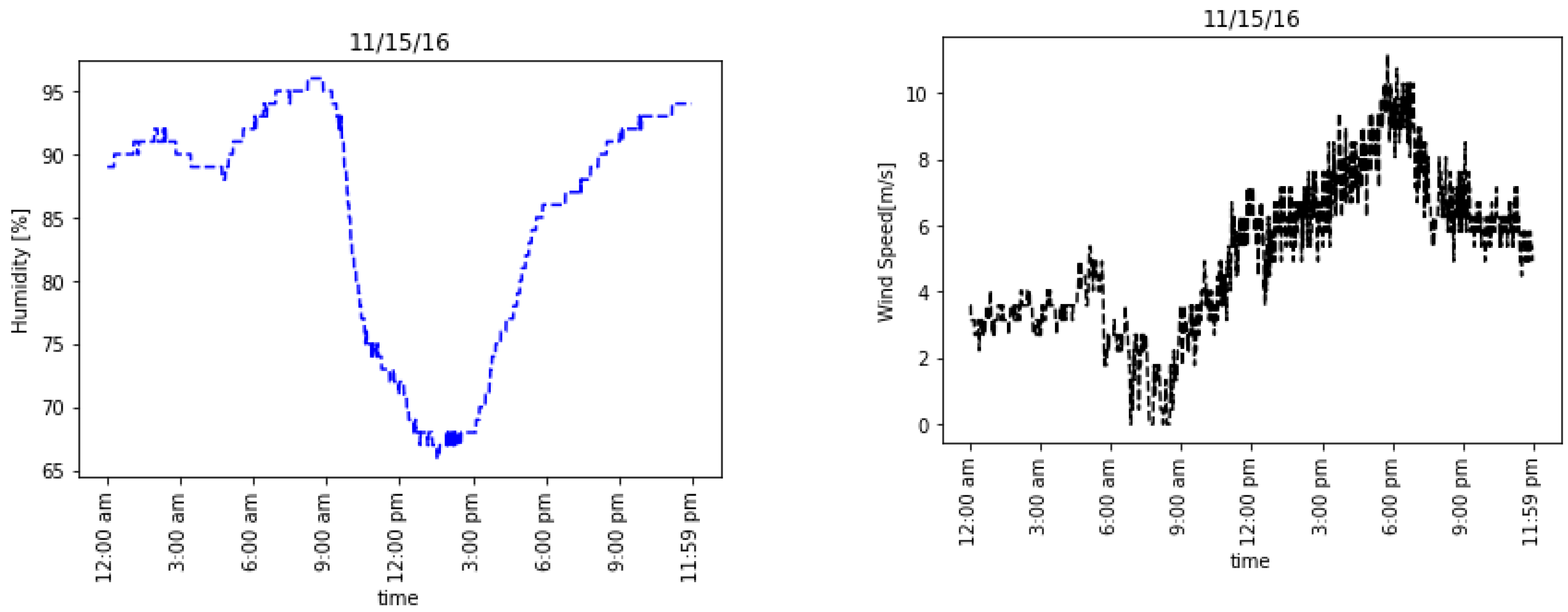
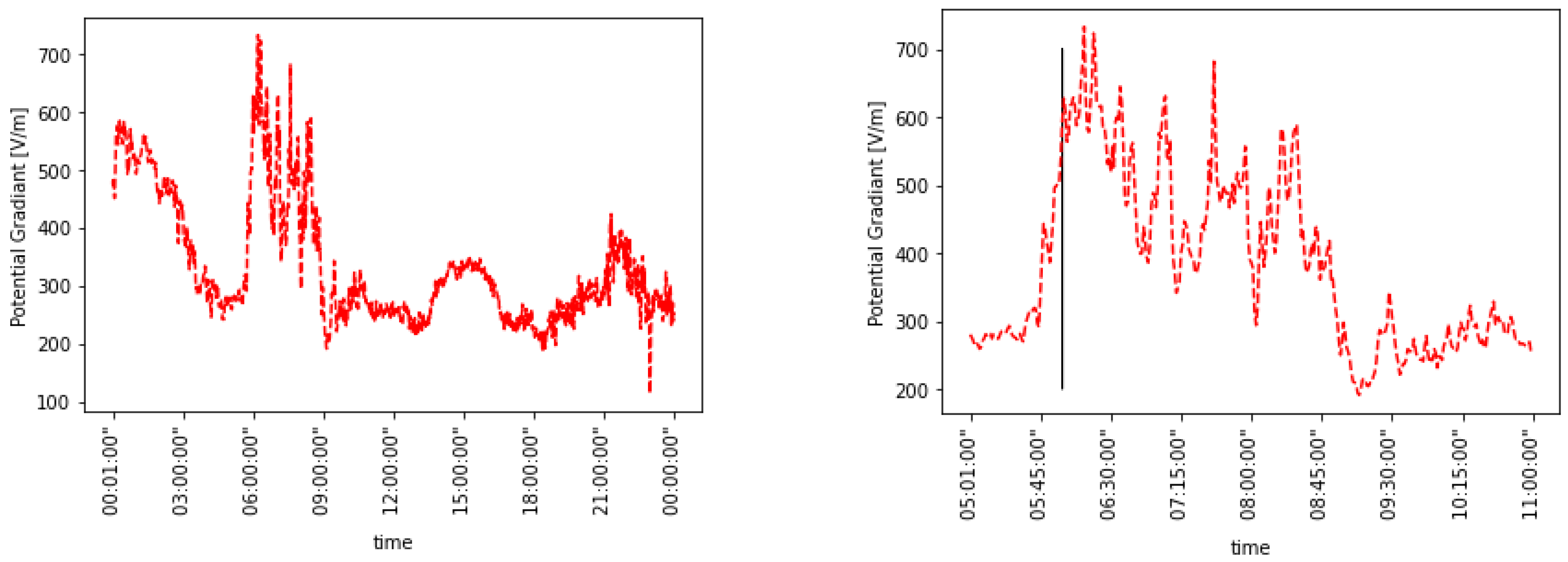

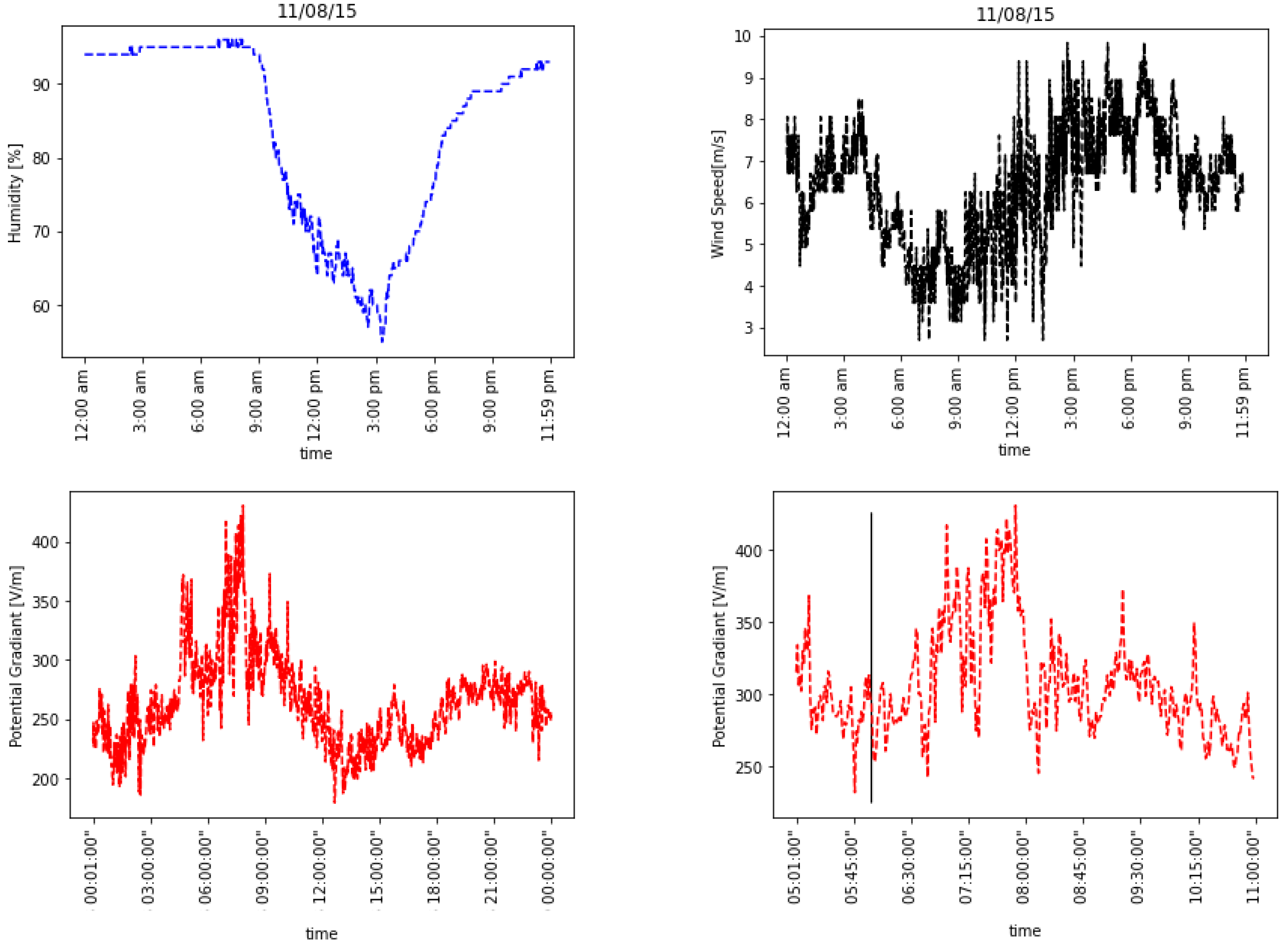
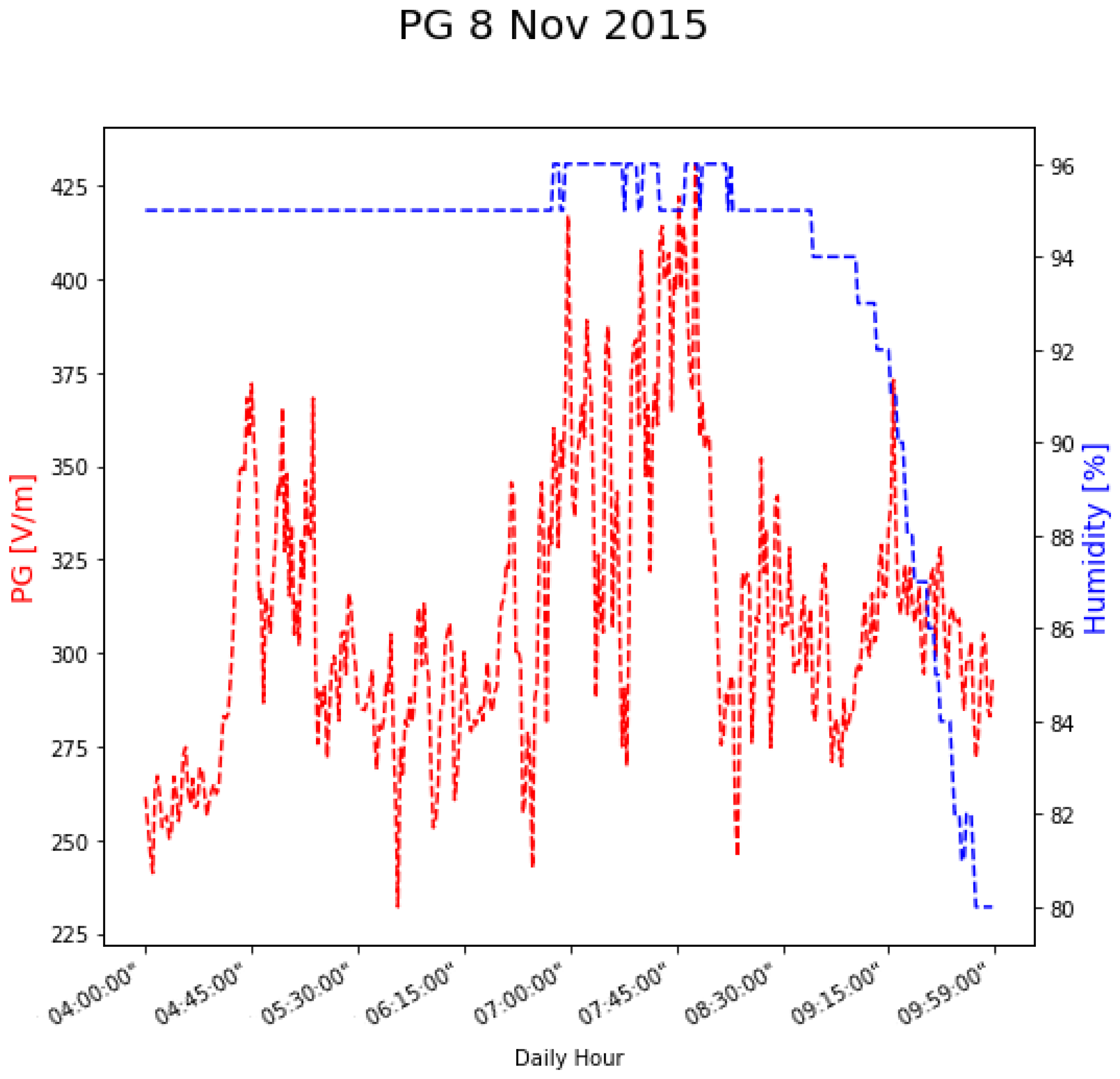

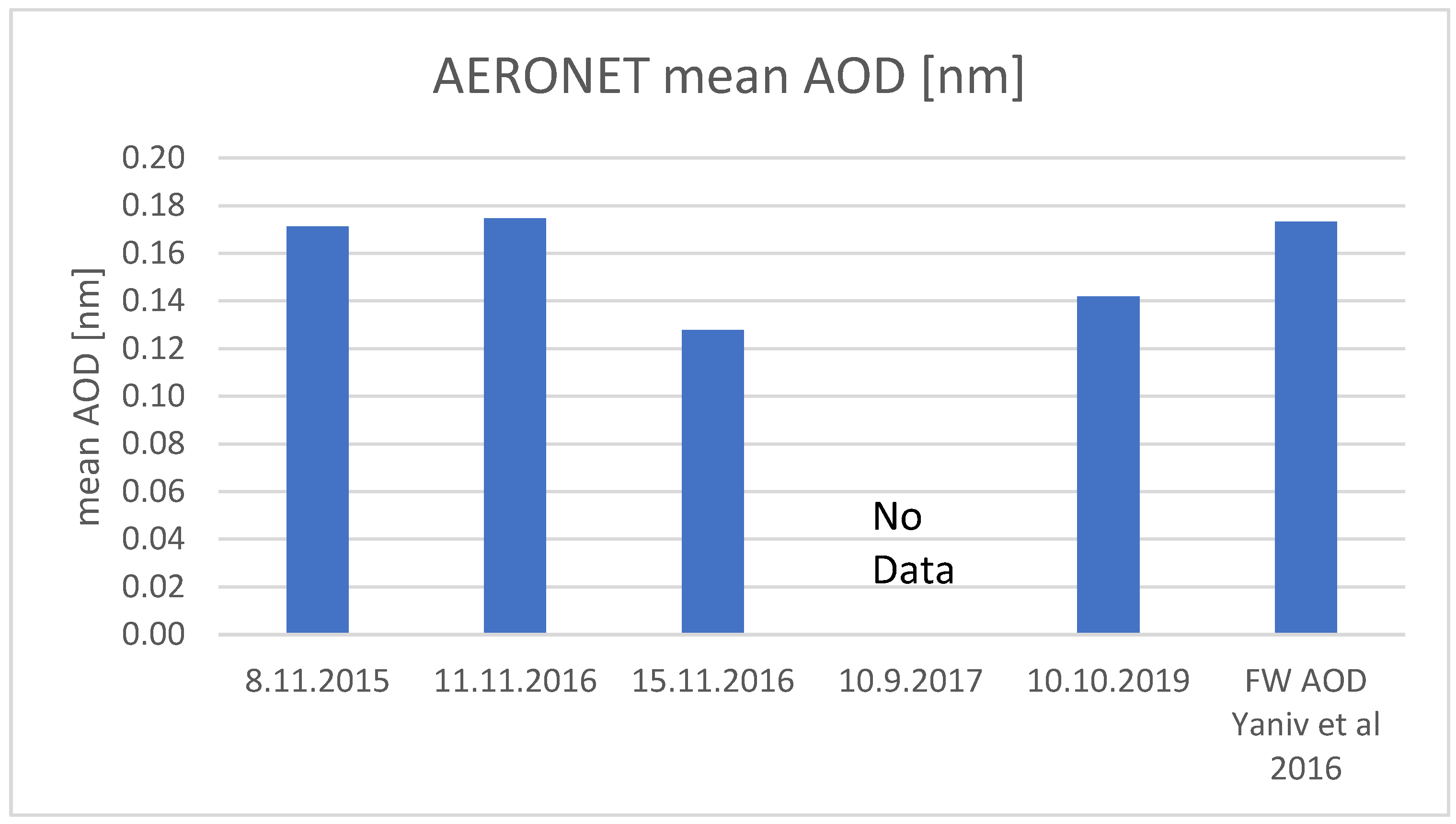
| Date | Max Humidity Value [%] | Wind Speed Range (m s−1) | Mean Monthly FW PG (V m−1) | Maximum Measured PG (V m−1) | ∆PG from FW Values to Diurnal Mean (V m−1) | Aeronet Value vs. FW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 November 2015 | 97 | 2–5 | 180 | 431 | 251 | FW |
| 2 | 11 November 2016 | 96 | 0.5–3.5 | 180 | 614 | 434 | FW |
| 3 | 15 November 2016 | 96 | 0–3 | 180 | 733 | 553 | FW |
| 4 | 10 September 2017 | 97 | 0–4 | 190 | 686 | 496 | N/A |
| 5 | 10 October 2019 | 95 | 4–6 | 185 | 320 | 135 | FW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yair, Y.; Yaniv, R. The Effects of Fog on the Atmospheric Electrical Field Close to the Surface. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030549
Yair Y, Yaniv R. The Effects of Fog on the Atmospheric Electrical Field Close to the Surface. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030549
Chicago/Turabian StyleYair, Yoav, and Roy Yaniv. 2023. "The Effects of Fog on the Atmospheric Electrical Field Close to the Surface" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030549
APA StyleYair, Y., & Yaniv, R. (2023). The Effects of Fog on the Atmospheric Electrical Field Close to the Surface. Atmosphere, 14(3), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030549







