Study on Lowering the Group 1 Protease Allergens from House Dust Mites by Exposing to Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. House Dust Sampling
2.2. Extraction of House Dust Mite Allergens
2.3. Evaluation of Allergen Content Using ELISA Assay
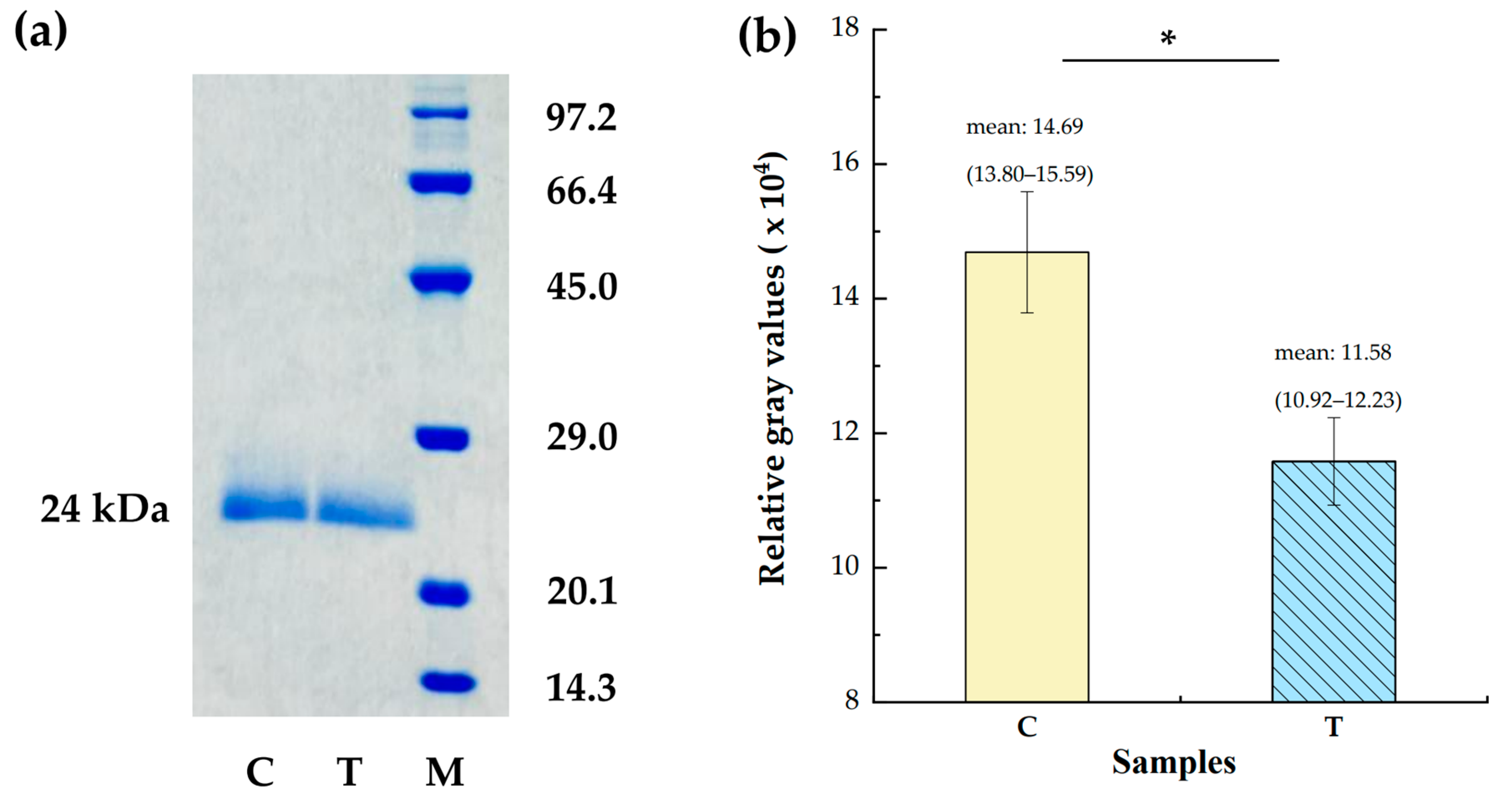
2.4. Determination of Allergen Level Employing SDS-PAGE
2.5. Assessment of Allergens and Ingredients-of-Todomatsu Oil Interactions Utilizing Molecular Docking Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
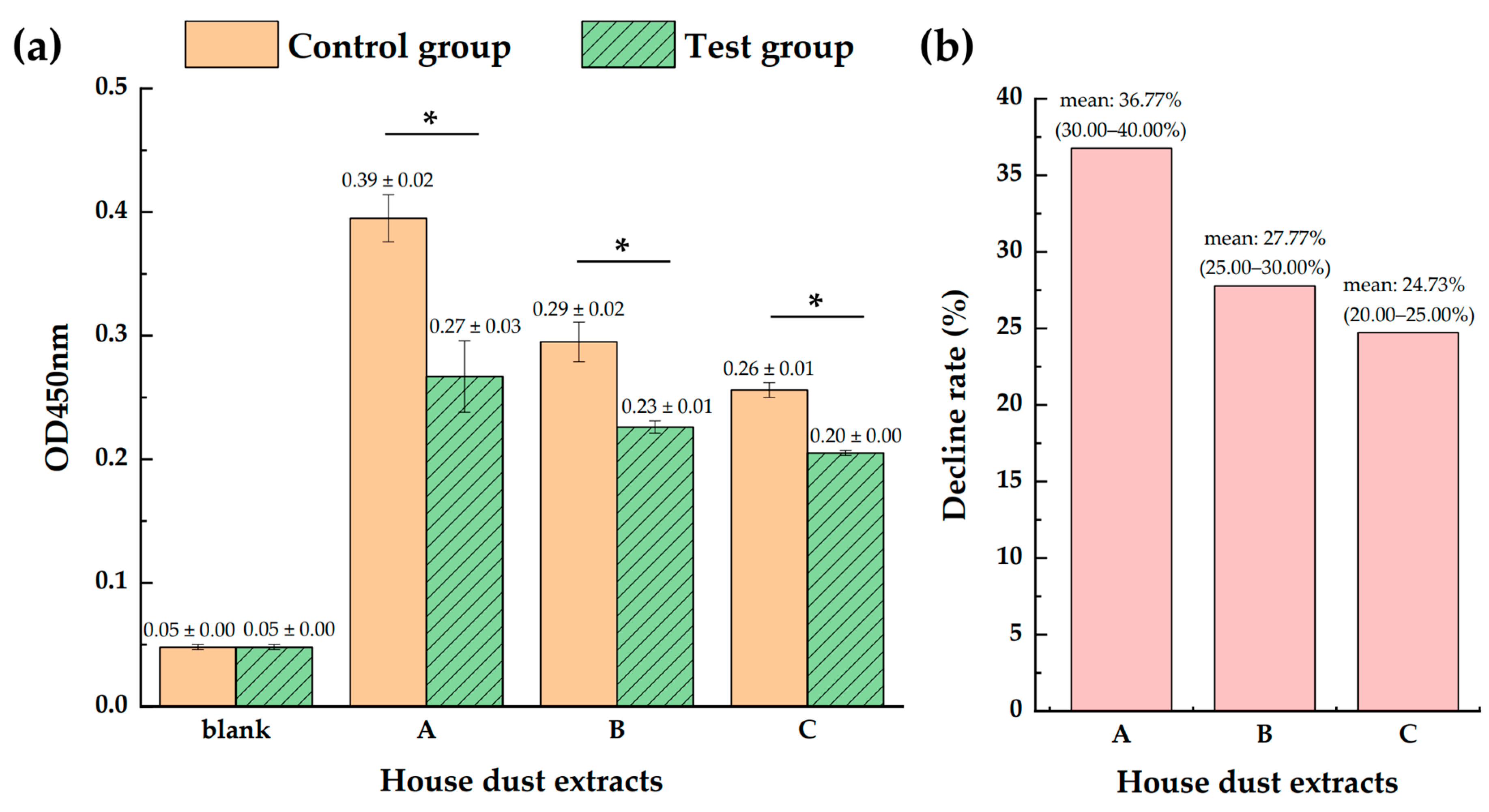
3.1. Significantly Lowered Levels of Allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1 in the Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere
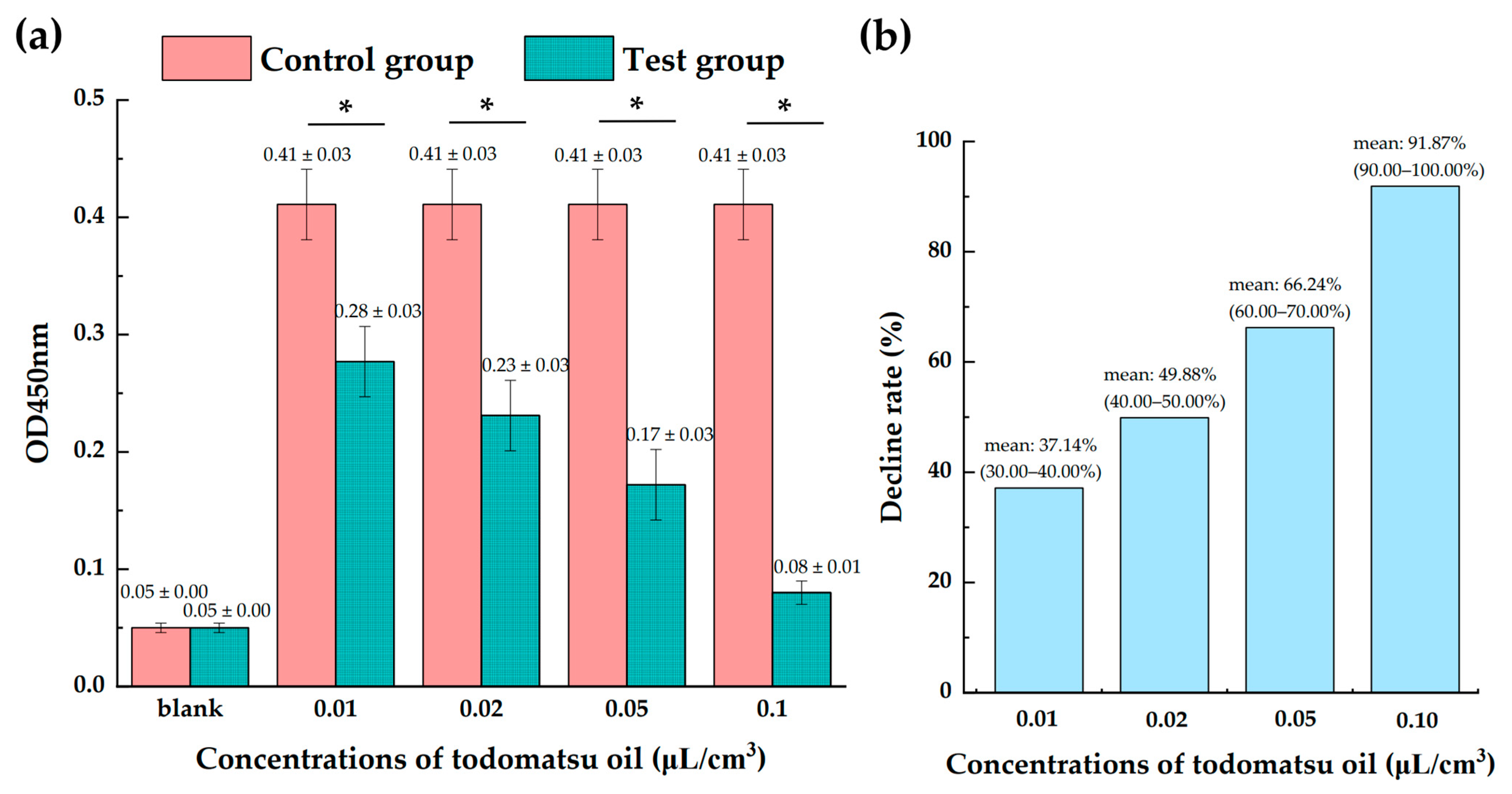
3.2. Higher Decline Rate with the Increasing Todomatsu Oil Concentration
3.3. Interactions among Ingredients-of-Todomatsu Oil and Allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1
3.4. Functional Sites on Allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1 Bound by Todomatsu Oil
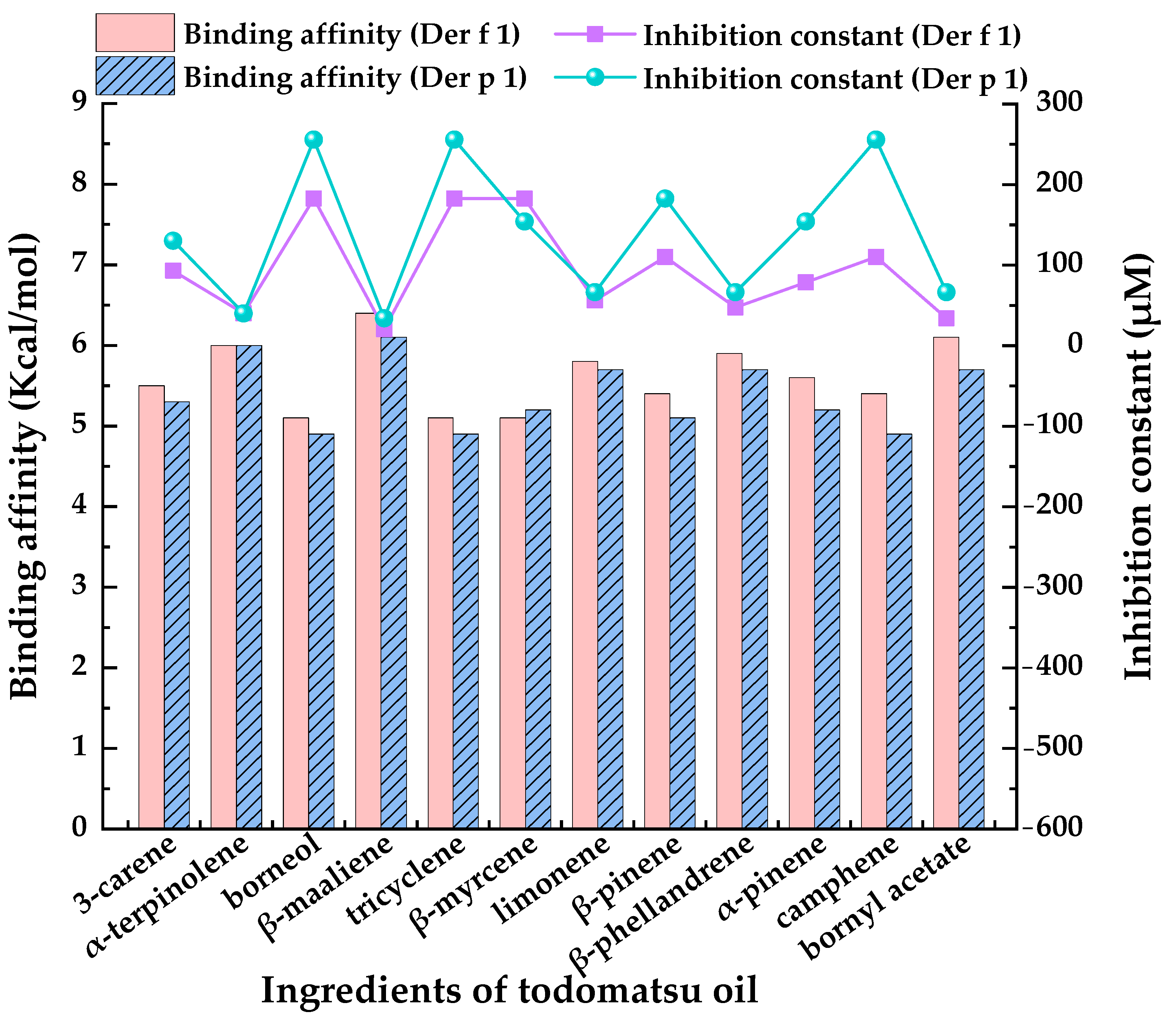
3.5. Inhibition Effectiveness of Each Ingredients-of-Todomatsu Oil on Allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil | 3D Complex Representation | 2D Complex Representation | Docking Amino Acid Residues | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | |
| 3-carene | 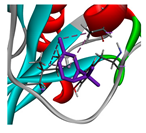 |  | 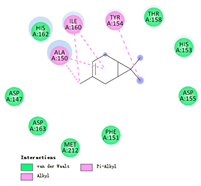 |  | AHI: AlA150 TYR154 ILE160 | AHI: ILE158 TYR185 TYR203 |
| borneol | 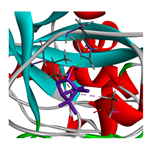 | 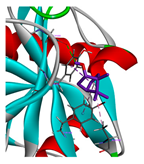 | 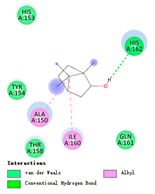 | 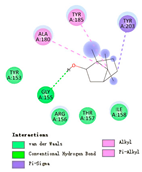 | AHI: ALA150 ILE160 HB: HIS162 | AHI: ALA180 TYR185 HB: GLY155 PS: TYR203 |
| tricyclene |  |  | 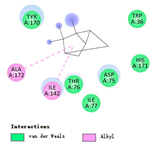 | 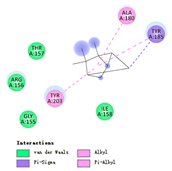 | AHI: ILE142 ALA172 | AHI: ALA180 TYR185 TYR203 PS: TYR185 |
| β-myrcene | 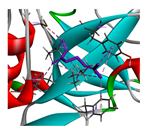 | 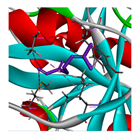 |  | 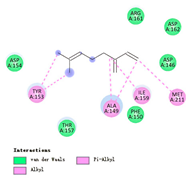 | AHI: CYS35 ILE77 ILE142 TYR170 ALA172 TYR217 PS: TYR170 | AHI: ALA149 TYR153 ILE159 MET211 |
| β-pinene | 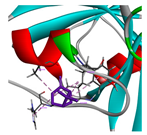 |  |  | 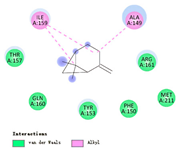 | AHI: ALA150 TYR154 ILE160 HIS162 | AHI: ALA149 ILE159 |
| α-pinene | 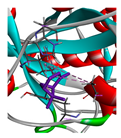 | 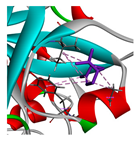 | 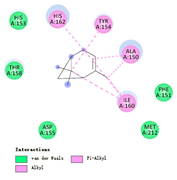 | 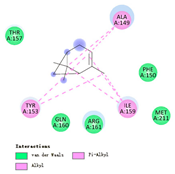 | AHI: ALA150 TYR154 ILE160 HIS162 | AHI: ALA149 TYR153 ILE159 |
| camphene | 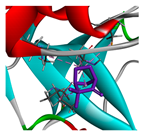 | 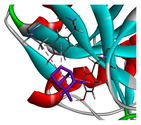 | 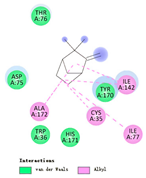 |  | AHI: CYS35 ILE77 ILE142 ALA172 | AHI: ALA180 TYR185 TYR203 |
| Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil | Docking Energy (ΔG, Kcal/mol) | Inhibition Constant (Ki, μM) | Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil | Docking Energy (ΔG, Kcal/mol) | Inhibition Constant (Ki, μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | ||
| 3-carene | −5.5 | −5.3 | 92.91 | 130.22 | limonene | −5.8 | −5.7 | 55.99 | 66.29 |
| α-terpinolene | −6.0 | −6.0 | 39.95 | 39.95 | β-pinene | −5.4 | −5.1 | 109.99 | 182.51 |
| borneol | −5.1 | −4.9 | 182.51 | 255.80 | β-phellandrene | −5.9 | −5.7 | 47.30 | 66.29 |
| β-maaliene | −6.4 | −6.1 | 20.34 | 33.74 | α-pinene | −5.6 | −5.2 | 78.48 | 154.16 |
| tricyclene | −5.1 | −4.9 | 182.51 | 255.80 | camphene | −5.4 | −4.9 | 109.99 | 255.80 |
| β-myrcene | −5.1 | −5.2 | 182.51 | 154.16 | bornyl acetate | −6.1 | −5.7 | 33.74 | 66.29 |
References
- Aggarwal, P.; Senthilkumaran, S. Dust Mite Allergy. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, Y.; Nagano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells and the House Dust Mite-Induced Asthma Mouse Model. Cells 2020, 9, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, M.A.; Linneberg, A.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; De Blay, F.; De Rojas, D.H.F.; Virchow, J.C.; Demoly, P. Respiratory Allergy Caused by House Dust Mites: What Do We Really Know? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloff, M.J. Dust Mites; Springer, CSIRO Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Available online: http://www.publish.csiro.au/pid/6022.htm (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Taylan-Özkan, A. Preventive Measures to Avoid Contact with House Dust Mites and Their Allergens. Acarol. Stud. 2020, 2, 1–6. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/acarolstud/issue/52206/659923 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Pomés, A.; Davies, J.M.; Gadermaier, G.; Hilger, C.; Holzhauser, T.; Lidholm, J.; Lopata, A.L.; Mueller, G.A.; Nandy, A.; Radauer, C.; et al. WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature: Providing a Common Language. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudharson, S.; Kalic, T.; Hafner, C.; Breiteneder, H. Newly Defined Allergens in the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Database during 01/2019–03/2021. Allergy 2021, 76, 3359–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruszcz, M.; Chapman, M.D.; Vailes, L.D.; Stura, E.A.; Saint-Remy, J.M.; Minor, W.; Pomés, A. Crystal Structures of Mite Allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1 Reveal Differences in Surface-Exposed Residues that May Influence Antibody Binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, P.W.; Chapman, M.D.; Aalberse, R.C.; Fox, J.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Antigenic and Structural Analysis of Group II Allergens (Der f II and Der p II) from House Dust Mites (Dermatophagoides Spp.). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1989, 83, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.D.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Purication and characterization of the major allergen from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus-antigen P1. J. Immunol. 1980, 125, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chruszcz, M.; Pomés, A.; Glesner, J.; Vailes, L.D.; Osinski, T.; Porebski, P.J.; Majorek, K.A.; Heymann, P.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Minor, W.; et al. Molecular Determinants for Antibody Binding on Group 1 House Dust Mite Allergens. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7388–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, A.; Robinson, C. Proteolytic, Lipidergic and Polysaccharide Molecular Recognition Shape Innate Responses to House Dust Mite Allergens. Allergy 2020, 75, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A. Characterization of Innate Immune Responses to House Dust Mite Allergens: Pitfalls and Limitations. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 662378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijink, I.H.; Kuchibhotla, V.N.S.; Roffel, M.P.; Maes, T.; Knight, D.A.; Sayers, I.; Nawijn, M.C. Epithelial Cell Dysfunction, a Major Driver of Asthma Development. Allergy 2020, 75, 1898–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Winton, H.L.; Soeller, C.; Tovey, E.R.; Gruenert, D.C.; Thompson, P.J.; Stewart, G.A.; Taylor, G.W.; Garrod, D.R.; Cannell, M.B.; et al. Der p 1 Facilitates Transepithelial Allergen Delivery by Disruption of Tight Junctions. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derewenda, U.; Li, J.; Derewenda, Z.; Dauter, Z.; Mueller, G.A.; Rule, G.S.; Benjamin, D.C. The crystal structure of a major dust mite allergen Der p 2, and its biological implications. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 318, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompette, A.; Divanovic, S.; Visintin, A.; Blanchard, C.; Hegde, R.S.; Madan, R.; Thorne, P.S.; Wills-Karp, M.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.P.; et al. Allergenicity Resulting from Functional Mimicry of a Toll-Like Receptor Complex Protein. Nature 2009, 457, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Robinson, C. Cellular and Molecular Events in the Airway Epithelium Defining the Interaction between House Dust Mite Group 1 Allergens and Innate Defences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillott, L.; Medjane, S.; Le-Barillec, K.; Balloy, V.; Danel, C.; Chignard, M.; Si-Tahar, M. Response of Human Pulmonary Epithelial Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Involves Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)-Dependent Signaling Pathways: Evidence for an Intracellular Compartmentalization of TLR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2712–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.P.; Kline, J.N.; Penisten, A.; Apicella, M.A.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.; McCray, P.B. Endotoxin Responsiveness of Human Airway Epithelia Is Limited by Low Expression of MD-2. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Soong, G.; Sokol, S.; Reddy, B.; Gomez, M.I.; Van Heeckeren, A.; Prince, A. Toll-Like Receptors in Normal and Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zuo, J.; Newton, G.K.; Stewart, M.R.; Perrior, T.R.; Garrod, D.R.; Robinson, C. Allergen Delivery Inhibitors: Characterisation of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Der p 1 and Their Attenuation of Airway Responses to House Dust Mite Allergens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Allen-Philbey, K.; Baruhupolage, C.P.; Tachie-Menson, T.; Mangat, S.C.; Garrod, D.R.; Robinson, C. Innate Generation of Thrombin and Intracellular Oxidants in Airway Epithelium by Allergen Der p 1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Tachie-Menson, T.; Shukla, N.; Garrod, D.R.; Robinson, C. Allergen-Dependent Oxidant Formation Requires Purinoceptor Activation of ADAM 10 and Prothrombin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 2023–2026.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J. Insecticidal Effect against House Dust Mite Using Ethanol Extract of Theobroma Cacao L. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 786–791. Available online: https://www.annalsofrscb.ro/index.php/journal/article/view/171 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Abidin, S.Z.; Ming, H.T. Effect of a Commercial Air Ionizer on Dust Mites Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides Farinae (Acari: Pyroglyphidae) in the Laboratory. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.S.; Foden, P.; Sumner, H.; Shepley, E.; Custovic, A.; Simpson, A. Preventing Severe Asthma Exacerbations in Children a Randomized Trial of Mite-Impermeable Bedcovers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halken, S.; Høst, A.; Niklassen, U.; Hansen, L.G.; Nielsen, F.; Pedersen, S.; Østerballe, O.; Veggerby, C.; Poulsen, L.K. Effect of Mattress and Pillow Encasings on Children with Asthma and House Dust Mite Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terreehorst, I.; Hak, E.; Oosting, A.J.; Tempels-Pavlica, Z.; de Monchy, J.G.R.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Aalberse, R.C.; van Wijk, R.G. Evaluation of Impermeable Covers for Bedding in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurikisawa, N.; Saito, A.; Oshikata, C.; Nakazawa, T.; Yasueda, H.; Akiyama, K. Encasing Bedding in Covers Made of Microfine Fibers Reduces Exposure to House Mite Allergens and Improves Disease Management in Adult Atopic Asthmatics. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijssenbeek-Nouwens, L.H.M.; Oosting, A.J.; De Bruin-Weller, M.S.; Bregman, I.; De Monchy, J.G.R.; Postma, D.S. Clinical Evaluation of the Effect of Anti-Allergic Mattress Covers in Patients with Moderate to Severe Asthma and House Dust Mite Allergy: A Randomised Double Blind Placebo Controlled Study. Thorax 2002, 57, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, R.B.; Durrell, B.; Bishop, S.; Curbishley, L.; Woodcock, A.; Custovic, A. High-Efficiency Vacuum Cleaners Increase Personal Mite Allergen Exposure, but Only Slightly. Allergy 2006, 61, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, J.; Sicherer, S.H. Results of a Home-Based Environmental Intervention among Urban Children with Asthma. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonicelli, L.; Bilò, M.B.; Pucci, S.; Schou, C.; Bonifazi, F. Efficacy of an Air-Cleaning Device Equipped with a High Efficiency Particulate Air Filter in House Dust Mite Respiratory Allergy. Allergy 1991, 46, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisman, R.E.; Mauriello, P.M.; Davis, G.B.; Georgitis, J.W.; DeMasi, J.M. A Double-Blind Study of the Effectiveness of a High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filter in the Treatment of Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 85, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlian, L.G.; Neal, J.S.; Vyszenski-Moher, D.A.L. Reducing Relative Humidity to Control the House Dust Mite Dermatophagoides Farinae. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.L.; Rose, G.; Diduch, K.B.; Domson, P.; Chapman, M.D.; Heymann, P.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Benzyl Benzoate Moist Powder: Investigation of Acarical Activity in Cultures and Reduction of Dust Mite Allergens in Carpets. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1992, 89, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Park, J. Insecticidal Effect of Dermatoohagoides Pteronyssinus Using Ginkgo Biloba Leaves Extracts. KSBB J. 2007, 22, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zeytun, E.; Doğan, S.; Özçiçek, F.; Ünver, E. Sensitivity to House Dust Mites Allergens in Patients with Allergic Asthma in Erzincan Province, Turkey. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2017, 41, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Lai, X.X.; Zhao, D.Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Q.Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, E.M.; Norback, D.; et al. Indoor Allergen Levels and Household Distributions in Nine Cities across China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Vervloet, D.; Thomas, W.R.; Aalberse, R.C.; Chapman, M.D. Indoor Allergens and Asthma: Report of the Third International Workshop. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, S2–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; De Weck, A. Dust Mite Allergens and Asthma—A Worldwide Problem. Bull. WHO 1989, 66, 769–780. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Miller, J.D.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Wheeler, A.J.; Héroux, M.E.; Goldberg, M.S.; Mallach, G. Household Determinants of Biocontaminant Exposures in Canadian Homes. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bemt, L.; Van Knapen, L.; De Vries, M.P.; Jansen, M.; Cloosterman, S.; Van Schayck, C.P. Clinical Effectiveness of a Mite Allergen-Impermeable Bed-Covering System in Asthmatic Mite-Sensitive Patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custovic, A.; Taggart, S.C.O.; Woodcock, A. House Dust Mite and Cat Allergen in Different Indoor Environments. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1994, 24, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insung, A.; Pumnuan, J.; Mahakittikun, V.; Wangapai, T. Effectiveness of Essential Oils of Medicinal Plants at Reducing the Amounts of Allergen Produced by the European House Dust Mite, Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus (Trouessart). J. Acarol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 25, S179–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Enyoh, C.E.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, K.; Zhou, S.; Kaneko, T.; Seguchi, A.; Wang, W.; et al. Novel Approaches for Inhibiting the Indoor Allergen Der f 2 Excreted from House Dust Mites by Todomatsu Oil Produced from Woodland Residues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.D.; Heymann, P.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Epitope Mapping of Two Major Inhalant Allergens, Der p I and Der f I, from Mites of the Genus Dermatophagoides. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Halleux, S.; Stura, E.; VanderElst, L.; Carlier, V.; Jacquemin, M.; Saint-Remy, J.M. Three-Dimensional Structure and IgE-Binding Properties of Mature Fully Active Der p 1, a Clinically Relevant Major Allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meno, K.; Thorsted, P.B.; Ipsen, H.; Kristensen, O.; Larsen, J.N.; Spangfort, M.D.; Gajhede, M.; Lund, K. The Crystal Structure of Recombinant ProDer p 1, a Major House Dust Mite Proteolytic Allergen. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Chruszcz, M.; Lasota, P.; Lebioda, L.; Minor, W. Data Mining of Metal Ion Environments Present in Protein Structures. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Maduka, T.; Wang, Q.; Islam, M.R. In Silico Screening of Active Compounds in Garri for the Inhibition of Key Enzymes Linked to Diabetes Mellitus. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivashankar, S.; Sangeetha, M.K. The Natural Ligand for Metalloproteinase—A Multifaceted Drug Target. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 1716–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Wang, Q.; Ovuoraye, P.E.; Maduka, T.O. Toxicity Evaluation of Microplastics to Aquatic Organisms through Molecular Simulations and Fractional Factorial Designs. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbaghzadeh, A.; Ghaffari, J.; Feridoni, M.; Alipour, A. House Dust Mite Allergen Levels of Der p1 and Der f1 in Houses of Asthmatic Children. J. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidouni, M.; Fereidouni, F.; Hadian, M.; Hasankiadeh, S.N.; Mazandarani, M.; Ziaee, M. Evaluation of the Level of House Dust Mite Allergens, Der p 1 and Der f 1 in Iranian Homes, a Nationwide Study. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2013, 41, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, R.H.; Akhter, S.; Abbas, S.; Ismail, M. Sensitivity to House Dust Mite Allergens and Prevalence of Allergy-Causing House Dust Mite Species in Pothwar, Pakistan. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 74, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Pedrosa, M.M.; Rodríguez, J.; González, Á.; Muzquiz, M.; Cuadrado, C.; Crespo, J.F.; Burbano, C. Effects of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Lentil Allergenicity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Qu, X.; Yang, N.; Ahmed, I. The Conformational Structural Change of β-Lactoglobulin via Acrolein Treatment Reduced the Allergenicity. Food Chem. X 2021, 10, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhao, H.; Peng, J.; Hong, Q.; Xiao, K.; Shang, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; et al. Size Distribution of Platanus Acerifolia Allergen 3 (Pla A3) in Shanghai Ambient Size-Resolved Particles and Its Allergenic Effects. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1263, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, C.E.; Umar, H.I.U.; Duru, I.A.; Enenebeaku, U.E.; Ngozi-Olehi, L.C.; Enyoh, C.E. Blocking the Interactions between Human Ace2 and Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein by Selected Drugs: A Computational Perspective. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2021, 36, e2021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, C.E.; Duru, I.A.; Enyoh, C.E. In Silico Binding Affinity Analysis of Microplastic Compounds on PET Hydrolase Enzyme Target of Ideonella Sakaiensis. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuro, O.; Naoyuki, M.; Toshihiko, K.; Yuichi, T.M.E. Efficient Extraction of Essential Oil from Woody Materials Using Vaccume Microwave Assisted Steam Distillation. Aroma Res. 2010, 11, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappé, A.K.; Casewit, C.J.; Colwell, K.S.; Goddard, W.A.; Skiff, W.M. UFF, a Full Periodic Table Force Field for Molecular Mechanics and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand-Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. Ligplot: A Program to Generate Schematic Diagrams of Protein-Ligand Interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Chandar, N.B.; Lo, R.; Ganguly, B. Effective Docking Program for Designing Reactivator for Treating Organophosphorus Inhibited AChE. JSM Chem. 2016, 4, 1032. [Google Scholar]
- Iman, M.; Saadabadi, A.; Davood, A. Molecular Docking Analysis and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Ameltolide Analogous as a Sodium Channel Blocker. Turk. J. Chem. 2015, 39, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavan, N.V.; Ha, C.E. Chapter 4—Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins and Disorders of Protein Misfolding. In Essentials of Medical Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.L.; Rose, G.D. How the Hydrophobic Factor Drives Protein Folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12462–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, C.; Tooze, J. Introduction to Protein Structure, 2nd ed.; Garland Publishing: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth, R.J.; Chua, K.Y.; Thomas, W.R. Sequence Analysis of CDNA Coding for a Major House Dust Mite Allergen, Der f I. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1991, 21, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach, M.; Fabian, P.; Stapor, K.; Konieczny, L.; Roterman, I. Structure of the Hydrophobic Core Determines the 3d Protein Structure—Verification by Single Mutation Proteins. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, G.W.; Thomas, E.W.; Topham, M.; Brocklehurst, K. Ionization Characteristics of the Cys-25/His-159 Interactive System and of the Modulatory Group of Papain: Resolution of Ambiguity by Electronic Perturbation of the Quasi-2-Mercaptopyridine Leaving Group in a New Pyrimidyl Disulphide Reactivity Probe. Biochem. J. 1993, 296, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, L.E.; Werneck, A.S.; De Oliveira Neto, M.; Bisch, P.M. Electrostatic Properties in the Catalytic Site of Papain: A Possible Regulatory Mechanism for the Reactivity of the Ion Pair. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2003, 52, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil (Relative Proportion) | PubChem CID | Chemical Formula | Chemical Structure | Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil (Relative Proportion) | PubChem CID | Chemical Formula | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-carene (0.50%) | 26049 | C10H16 | 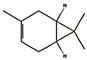 | limonene (5.75%) | 22311 | C10H16 | 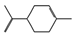 |
| α-terpinolene (0.95%) | 11463 | C10H16 | 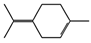 | β-pinene (7.55%) | 14896 | C10H16 | 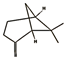 |
| borneol (1.00%) | 64685 | C10H18O | 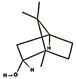 | β-phellandrene (12.05%) | 11142 | C10H16 | 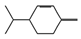 |
| β-maaliene (1.25%) | 101596917 | C15H24 | 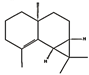 | α-pinene (18.25%) | 6654 | C10H16 | 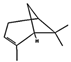 |
| tricyclene (2.25%) | 79035 | C10H16 | 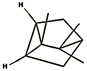 | camphene (20.25%) | 6616 | C10H16 | 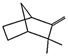 |
| β-myrcene (4.45%) | 31253 | C10H16 | 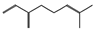 | bornyl acetate (25.75%) | 6448 | C12H20O2 | 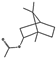 |
| Group 1 Allergens | PDB ID | 3D structure | Enzymatic Activity | Organism | Mutations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Der f 1 | 5vpk |  | Cysteine protease | Dermatophagoides farinae | No |
| Der p 1 | 5vph | 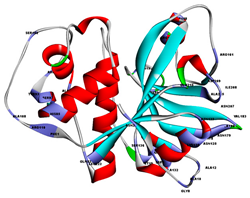 | Cysteine protease | Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus | No |
| Ingredients of Todomatsu Oil | 3D Complex Representation | 2D Complex Representation | Docking Amino Acid Residues | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | Der f 1 | Der p 1 | |
| β-maaliene | 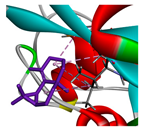 | 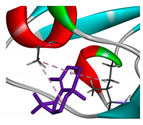 | 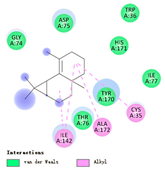 |  | AHI: CYS35 ILE142 ALA172 | AHI: ALA149 ILE159 |
| bornyl acetate |  | 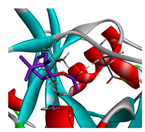 | 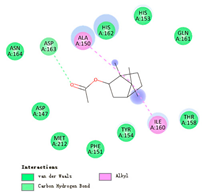 | 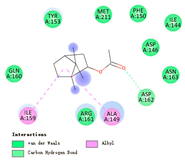 | AHI: ALA150 ILE160 CHB: ASP163 | AHI: ALA149 ILE159 CHB: ASP162 |
| α-terpinolene |  | 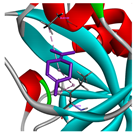 | 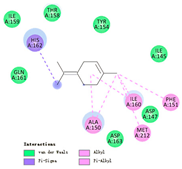 |  | AHI: ALA150 PHE151 ILE160 MET212 PS: HIS162 | AHI: ALA149 ILE159 |
| β-phellandrene | 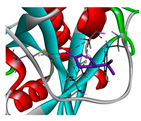 |  |  | 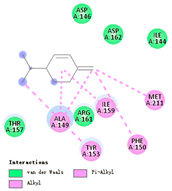 | AHI: ALA150 TYR154 ILE160 MET212 | AHI: ALA149 PHE150 TYR153 ILE159 MET211 |
| limonene | 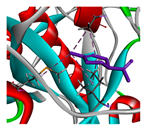 | 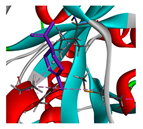 | 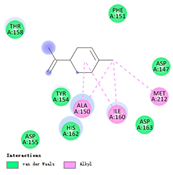 | 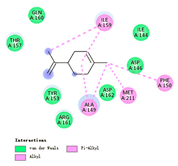 | AHI: ALA150 ILE160 MET212 | AHI: ALA149 PHE150 ILE159 MET211 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, Q. Study on Lowering the Group 1 Protease Allergens from House Dust Mites by Exposing to Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030548
Lin Y, Xiao K, Wang W, Lu S, Wang Q. Study on Lowering the Group 1 Protease Allergens from House Dust Mites by Exposing to Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030548
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yichun, Kai Xiao, Weiqian Wang, Senlin Lu, and Qingyue Wang. 2023. "Study on Lowering the Group 1 Protease Allergens from House Dust Mites by Exposing to Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030548
APA StyleLin, Y., Xiao, K., Wang, W., Lu, S., & Wang, Q. (2023). Study on Lowering the Group 1 Protease Allergens from House Dust Mites by Exposing to Todomatsu Oil Atmosphere. Atmosphere, 14(3), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030548









