Environmental Impacts of Biodiesel Production Cycle from Farm to Manufactory: An Application of Sustainable Systems Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. The Life Cycle Assessment
2.2.1. Definition of Goal and Scope
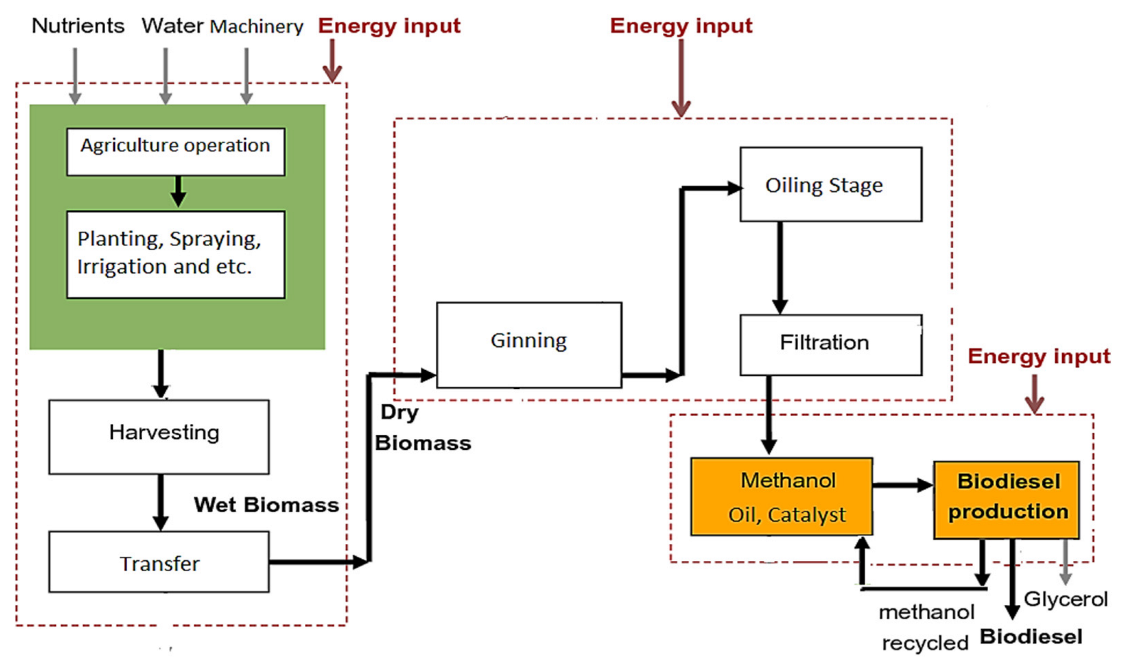
2.2.2. List Cycle Inventory
Inventorying in the Agricultural Stage
Inventorying in the Ginning and Oiling Stage
Inventorying in the Biodiesel Production Stage
2.3. Assessment of Life Cycle Effects
2.4. Interpretation of the Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inputs and Outputs in Three Different Biodiesel Production Processes
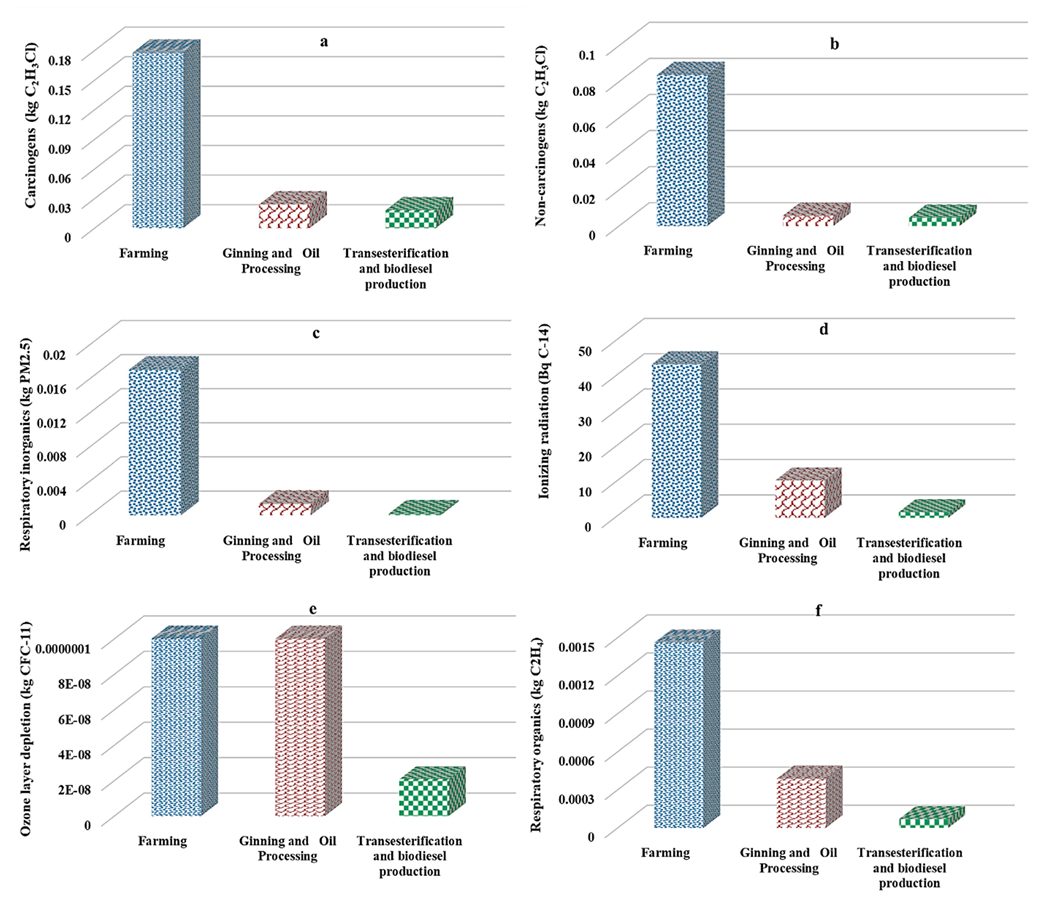
3.2. Comparing the Intermediate Indicators Affecting Human Health in Different Stages of Biodiesel Production
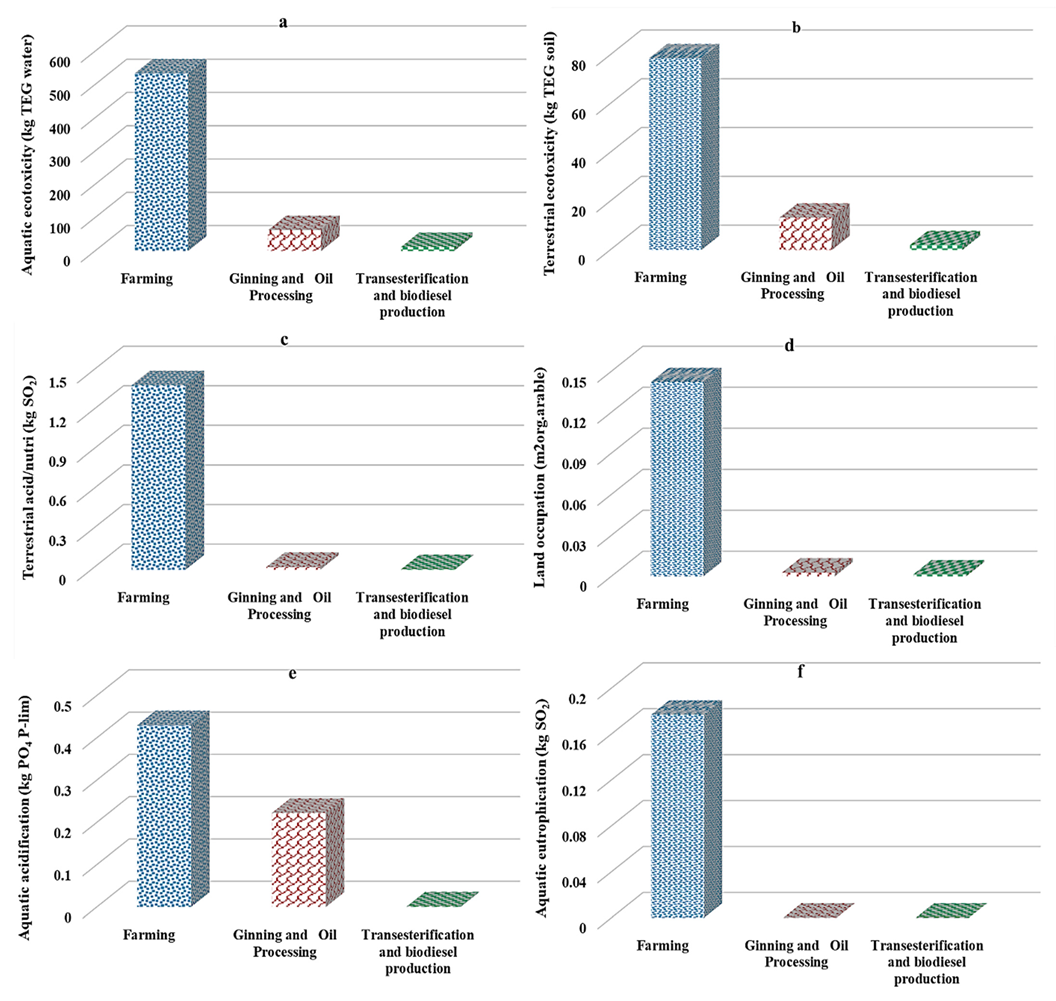
3.3. Comparing the Intermediate Indicators Affecting Ecosystem Quality in Different Stages of Biodiesel Production
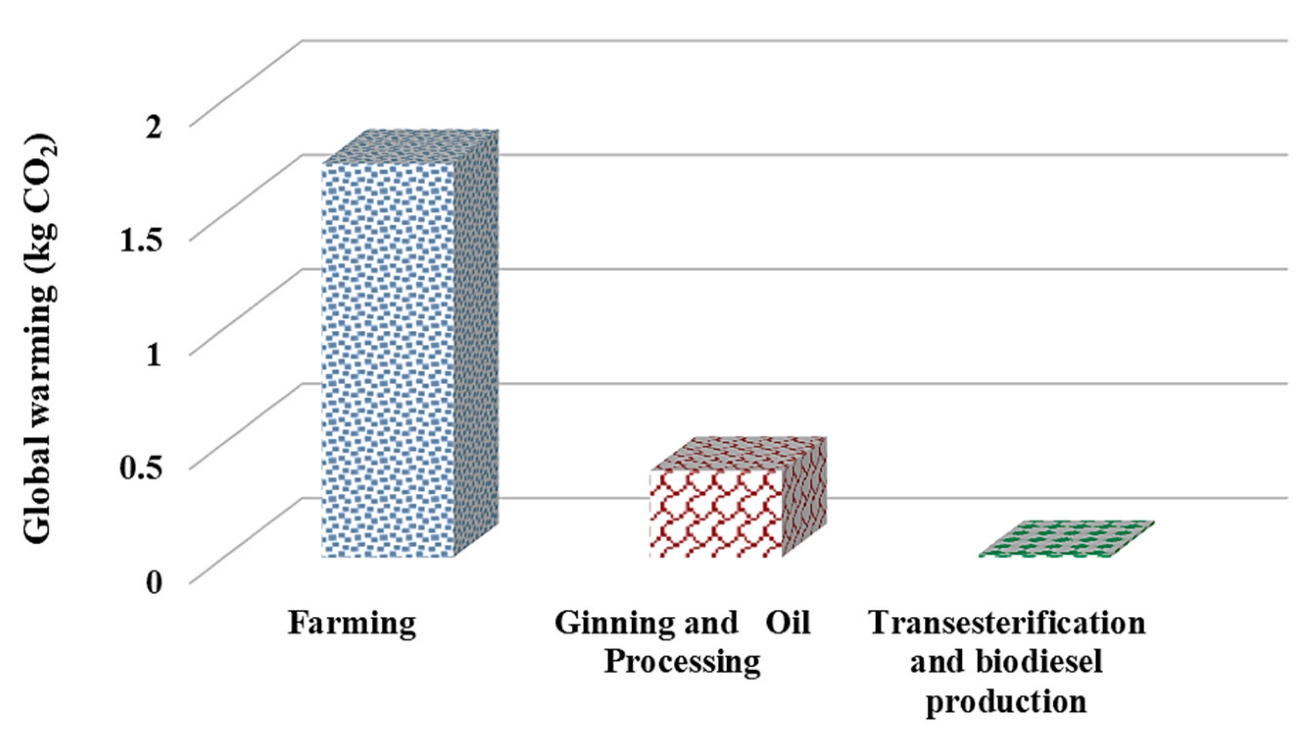
3.4. Comparing the Intermediate Indicators Affecting Climate Change in Different Stages of Biodiesel Production
3.5. Comparing the Intermediate Indicators Affecting Depletion of Resources in Different Stages of Biodiesel Production
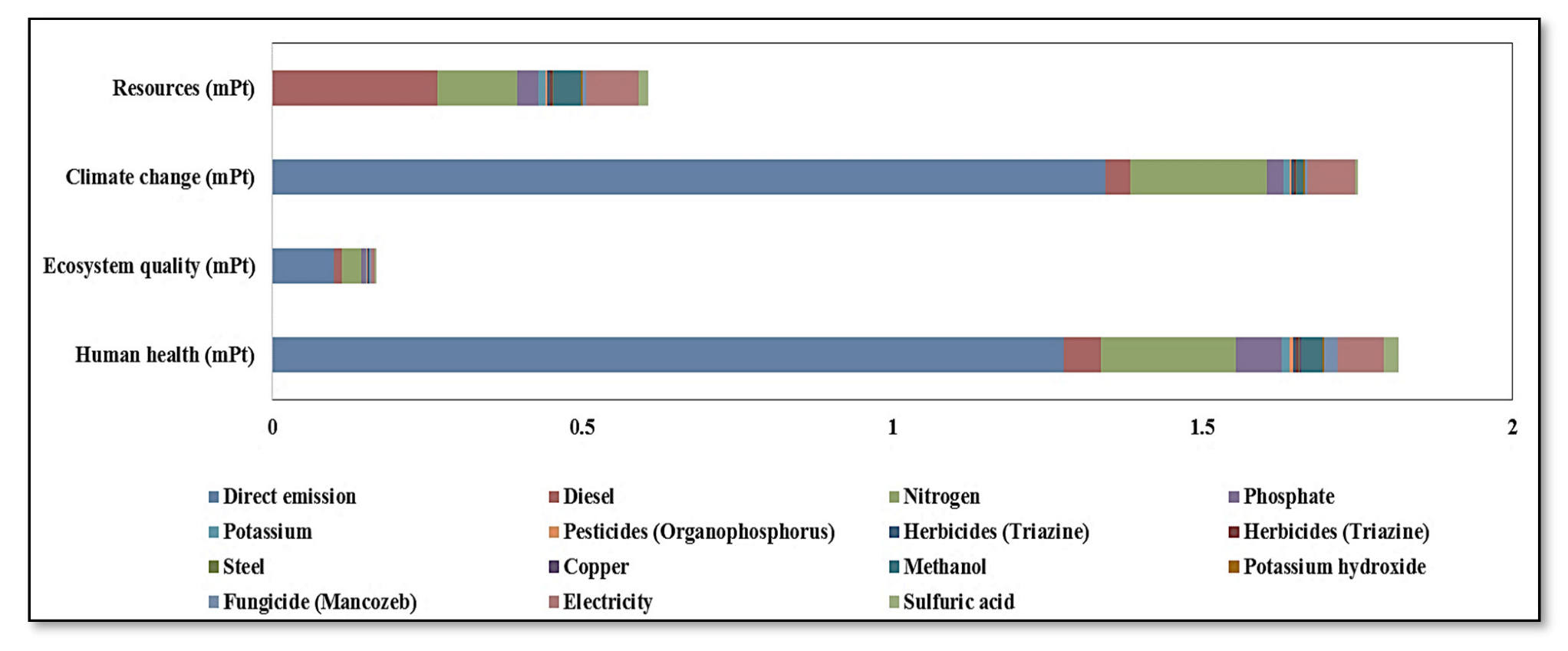
3.5.1. Evaluation of Damage Category
3.5.2. Human Health
3.5.3. Ecosystem Quality
3.5.4. Resources
3.5.5. Climate Change
3.6. Evaluation of Damage Category
3.7. Comparison of the Results of the Present Study with Other Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Energy and Air Pollution, World Energy Outlook Special Report; International Energy Agency 9 rue de la Federation 75739: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, A.; Mehregan, M.R.; Shakouri, H.G. An Energy Supply Model of Iran Aiming to Reduce Greenhouse Gases. J. Indust. Engin. 2012, 46, 63–75. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Das, L.M. Biodiesel development and characterization for use as a fuel in compression ignition engine. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power. 2001, 123, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.; Babapoor, A. Using of renewables energies such as effective way to reduce environmental pollution. Renew. Energy Quart. 2018, 5, 40–50. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Rajaeeifar, M.A.; Akram, A.; Ghobadian, B.; Rafiee, S.; Abdi, R. Energy and economic assessment of biodiesel production from olive pomace oil: A lifecycle approach. Biosys. Eng. 2015, 46, 209–218. (In Persian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makareviciene, V.; Skorupskaite, V.; Levisauskas, D.; Andruleviciute, V.; Kazancev, K. The optimization of biodiesel fuel production from microalgae oil using response surface methodology. Int. J. Green Energy 2014, 11, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, E.M.; Jamal, Y. Production of biodiesel: A technical review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4732–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Mirabdoli, M.; Shayan Nezhad, A. Commercial optimization of biodiesel production from rapeseed oil as a clean fuel for thermal power plants. Modares Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 135–142. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Enweremadu, C.C.; Mbarawa, M.M. Technical aspects of production and analysis of biodiesel from used cooking oil-A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2205–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.A.; Haddad Khodaparast, M.H. Production of edible Cottonseed protein concentrates by Mixed Solvent (Water: Acetone: Hexane). Agriculture 2005, 7, 45–51. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture Jihad. Statistics of Agricultural Products; Ministry of Agriculture Jihad: Tehran, Iran, 2015. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Nabi, N.; Rahman, M.; Akhter, S. Biodiesel from cotton seed oil and its effect on engine performance and exhaust emissions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Agha Alikhani, M. Energy use analysis of cotton production in Golestan Province and a few strategies for increasing resources productivity. Agroecology 2012, 4, 151–158. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Mosier, A.R.; Smith, K.A.; Winiwarter, W. N2O release from agro-biofuel production negates global warming reduction by replacing fossil fuels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, M.J.; Kraus, J.L.; Parker, D.R. Life-Cycle Assessment as a Sustainability, Management Tool: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Other Considerations. Environ. Quality Manag. 2010, 20, 20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040; International Standard, Environmental Management- Life Cycle Assessment- Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Jolliet, O.; Margni, M.; Charles, R.; Humbert, S.; Payet, J.; Rebitzer, G.; Rosenbaum, R. Impact 2002: A new life cycle impact assessment methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2003, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; McRoberts, R.; Yu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sloan, W.; You, S. Life cycle assessment of biodiesel production from rapeseed oil: Influence of process parameters and scale. Biores. Technol. 2022, 360, 127532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mawali, K.; Osman, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.; Mehta, N.; Jamila, F.; Mjallia, F.; Vakili-Nezhaad, R.; Rooney, D. Life cycle assessment of biodiesel production utilising waste date seed oil and a novel magnetic catalyst: A circular bioeconomy approach. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolghadr, M.; Hassan-beigi, S.R.; Kianmehr, M.H. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Biodiesel Production from Date Pit Oil. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Internal Combustion Engines, Tehran, Iranian Society of Engines Sciences, Tehran, Iran, 13–15 February 2017. (In Persian). [Google Scholar]
- Khojastehpour, M.; Taheri-Rad, A.; Nikkhah, A. Life cycle assessment of cotton production in Golestan province based on the production of biomass, energy and net income. Biosys. Eng. 2015, 46, 95–104. (In Persian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.S.; Fornasier, F.; Leitao, J.O.M.; Moraes, J.A.R.; Schneider, R.C.S. Life cycle assessment of biodiesel production from solaris seed tobacco. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 230, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y. Life cycle assessment of biodiesel from soybean, jatropha and microalgae in China conditions. Renew Sust. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 5081–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, D.; Jez, S.; Basosi, R. Integrated Environmental Assessment of sunflower oil production. Process. Biochem. 2011, 47, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Requena, J.F.; Guimaraes, A.C.; Quirós Alpera, S.; Relea Gangas, E.; Hernandez-Navarro, S.; Navas Gracia, L.M.; Martin-Gil, J.; Fresneda Cuesta, H. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of the biofuel production process from sunflower oil, rapeseed oil and soybean oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.M.F.; Torres, E.A.; Kiperstok, A.; De Freitas Moreira Santos, G. Environmental impacts of the biodiesel production chain of cotton seed in Bahia, Brazil. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.B.; Muñoz, E. Life cycle assessment of second generation ethanol derived from banana agricultural waste: Environmental impacts and energy balance. J. Cleaner Prod. 2018, 174, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Emanuele Ciarapica, F.; Mazzuto, G.; Paciarotti, C. Environmental analysis of a cotton yarn supply chain. J. Cleaner Prod. 2014, 82, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.; Nalley, L.; Clayton-Niederman, Z. Carbon Life Cycle Assessment of United States Cotton: A View of Cotton Production Practices and Their Associated Carbon Emissions for Counties in 16 Cotton Producing States; Cotton Incorporated, Center for Agricultural and Rural Sustainability University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture: Arkansas, AR, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, S.; Chen, G.; Baillie, C.; Symes, T. Energy uses for cotton ginning in Australia. Biosys. Eng. 2011, 109, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Guo, Y. Life Cycle Assessment of Rapeseed Biodiesel. World Elec. Vehicle J. 2010, 4, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomelli Luiz, G.; Barreta Pedro, T.; Lacava Dermeval Carinhana, J. Study of the Influence of Biodiesel in Soot Emissions of Diesel Laminar Diffusion Flames. J. Brazilian Chem. Soci. 2017, 28, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, C.X.; He, L.; Nie, H.T.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, J.C.; Fan, B.G.; et al. Regeneration mechanism of a novel high-performance biochar mercury adsorbent directionally modified by multimetal multilayer loading. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 15, 326–116790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyono, Y.; Hadiyanto, H.; Budihardjo, M.A.; Adiansyah, J.S. Assessing the Environmental Performance of Palm Oil Biodiesel Production in Indonesia: A Life Cycle Assessment Approach. Energies 2020, 13, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, L.F.A.; da Costa, R.B.R.; de Souza, T.A.Z.; Coronado, C.J.R.; Pinto, G.M.; Cintra, A.J.A.; Raats, O.O.; Oliveira, B.M.; Frez, G.V.; Alves, L.F.R. Experimental analysis and life cycle assessment of green diesel (HVO) in dual-fuel operation with bioethanol. J. Cleaner Prod. 2023, 389, 135989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, N.; Biswas, W.; Mazhar, I.; Howard, I. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Alternative Fuels for Western Australia’s Transport Sector. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, T.; Kagi, T. Life cycle inventories of agricultural production system. Final. Rep. Ecoinvent 2007, 15, 1–360. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg, F.; Kubiak, B.W.G.; Majewski, M.S.; Yates, S.R.; Reeves, G.L.; Van der Linden, A.M.A. Emission of pesticides into the air. Water Air Soil Poll. 1999, 115, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, H.S.; Miwa, K.; Ngara, T.; Tanabe, K. (Eds.) IPCC, Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. In Eggleston, Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; IGES: Kanagawa, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi-Avval, S.H.; Rafiee, S.; Sharifi, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Shah, A. Combined application of Life Cycle Assessment and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System for modeling energy and environmental emissions of oilseed production. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.T.; Hermansen, J.E. System expansion for handling co-products in LCA of sugar cane bio-energy systems: GHG consequences of using molasses for ethanol production. Appl. Energy 2012, 89, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyazi, E.; Ghobadian, B.; Mousavi, S.M.; Najafi, G. Intensification of continues biodiesel production process using a simultaneous mixer-separator reactor. Energy Sources Part A: Rec. Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farvardin, M.; Hosseinzadeh Samani, B.; Rostami, S.; Abbaszadeh-Mayvan, A.; Najafi, G.; Fayyazi, E. Enhancement of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: Ultrasonic-hydrodynamic combined cavitation system. Energy Sources Part A: Rec. Utilize. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 5065–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyazi, E.; Ghobadian, B.; Najafi, G.; Hosseinzadeh, B. Genetic algorithm approach to optimize biodiesel production by ultrasonic system. Chem. Prod. Process Model. 2014, 9, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Motevali, A.; Keikha, M. The life cycle assessment of subsurface drainage performance under rice-canola cropping system. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, Z.; Esmaeili, M.; Pirdashti, H.; Motevali, A.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A. Exergoenvironmental-Life cycle cost analysis for conventional, low external input and organic systems of rice paddy production. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 263, 121529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Fashami, F.; Motevali, A.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A.; Hashemi, S.J.; Chau, K.-W. Energy-Life cycle assessment on applying solar technologies for greenhouse strawberry production. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, A.; Motevali, A.; Tabatabaeekoloor, R.; Hashemi, S.J. Multiyear life energy and life cycle assessment of orange production in Iran. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2019, 26, 32432–32445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevali, A.; Hashemi, S.J.; Tabatabaeekoloor, R. Environmental footprint study of white rice production chain-case study: Northern of Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, O.; Knol, A.B.; Jantunen, M.; Lim, T.-A.; Conrad, A.; Rappolder, M.; Carrer, P.; Fanetti, A.-C.; Kim, R.; Buekers, J.; et al. Environmental burden of disease in Europe: Estimates for nine stressors in six countries. Environ. Health Perspec. 2014, 122, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, G.A.; Granvold, P.W.; Hoats, A.S.; Nazaroff, W.; Nazaroff, W.W. Intake fraction assessment of the air pollutant exposure implications of a shift toward distributed electricity generation. Atm. Environ. 2006, 40, 7164–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurun, N.; Mustafizur, R.; Shamim, A. Biodiesel from cotton seed oil and its effect on engine performance and exhaust emissions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Commercial fertilizers and soil amendments. Nutr. Manag. Module 2009, 10, 4410–4449. [Google Scholar]
- Permadi, D.A.; Sofyan, A.; Kim Oanh, N.T. Assessment of emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants in Indonesia and impacts of national policy for elimination of erosene use in cooking. Atm. Environ. 2017, 154, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bare, J. TRACI 2.0: The tool for the reduction and assessment of chemical and other environmental impacts 2.0. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2011, 13, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, L.; Hermansen, J.E.; Halberg, N.; Dalgaard, R.; Vis, J.; Smith, B.G. Life cycle assessment across the food supply chain. Sust. Food Ind. 2009, Chapter 5, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, B. The Causes of Soil Acidity. New South Wales Acid Soil Action Program. New South Wales Department of Agriculture: Orange, NSW, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brentrup, F.; Küsters, J.; Kuhlmann, H.; Lammel, J. Environmental impact assessment of agricultural production systems using the life cycle assessment methodology: I. Theoretical concept of a LCA method tailored to crop production. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 20, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentrup, F.; Palliere, C. GHG Emissions and Energy Efficiency in European Nitrogen Fertilizer Production and Use; International Fertilizer Society: York, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Greenhouse Gas Bulletin (GHG Bulletin)—No. 3: The State of Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere Using Global Observations through 2006. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Annual greenhouse gas index (AGGI). Available online: https://library.wmo.int/index.php?lvl=notice_display&id=3030#.Y1JBvkxBzIU (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Keikha, M.; Darzi- Naftchali, A.; Motevali, A.; Valipour, M. Effect of nitrogen management on the environmental and economic sustainability of wheat production in different climates. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 276, 108060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.A.; Zaki, N.A.M.; Narashid, R.H.; Talib, N.; Manokaran, J.; Arshad, F.C.; Fauzi, S.S.M.; Dom, N.C.; Valipour, M.; Dambul, R.; et al. COVID-19 Restriction Movement Control Order (MCO) Impacted Emissions of Peninsular Malaysia Using Sentinel-2a and Sentinel-5p Satellite. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 7, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.R.; Mustafa, A.; Hyder, S.; Valipour, M.; Rizvi, Z.F.; Gondal, A.S.; Yousuf, Z.; Iqbal, R.; Daraz, U. Bacillus spp. as Bioagents: Uses and Application for Sustainable Agriculture. Biology 2022, 11, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ditta, A.; Valipour, M.; Aslam, S. Microcosm Study on the Potential of Aquatic Macrophytes for Phytoremediation of Phosphorus-Induced Eutrophication. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

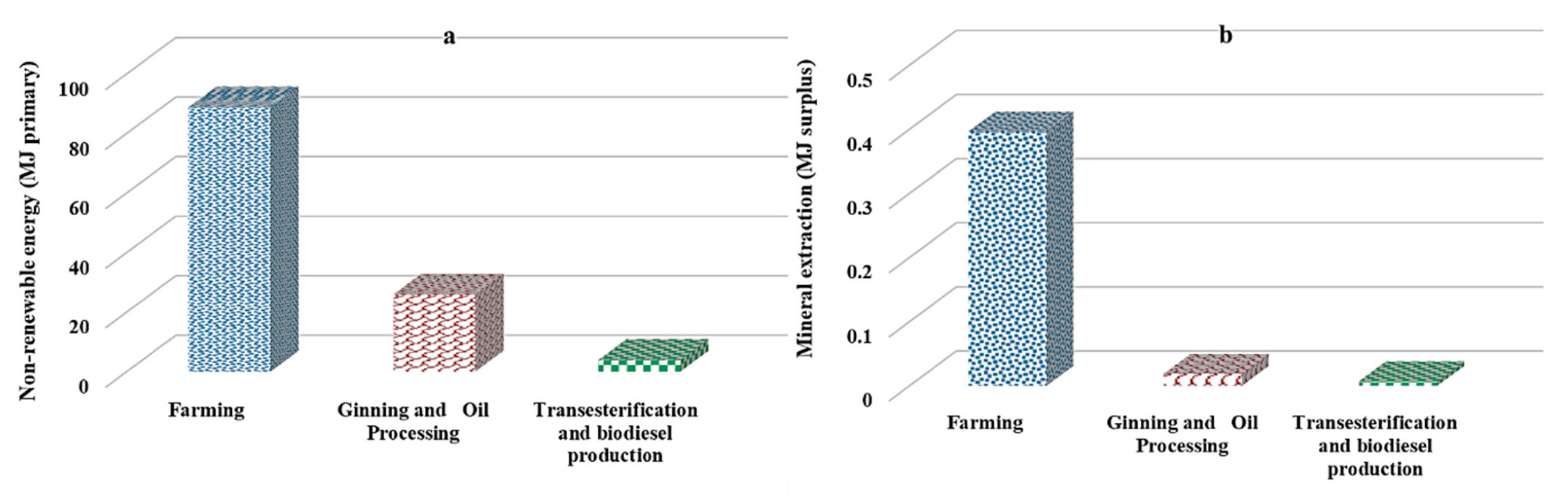
| Input | Consumption Level | Input | Consumption Level | Input | Consumption Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Operations | Diesel fuel (L) | 0.247 | Ginning Operation | Diesel fuel (L) | 0.456 | Biodiesel Production | Methanol (kg) | 0.250 |
| Nitrogen (kg) | 0.259 | Electricity (kWh) | 0.257 | Potassium hydroxide (kg) | 0.011 | |||
| Phosphorus (kg) | 0.142 | Labor force (h) | 0.090 | Electricity (kWh) | 0.28 | |||
| Potassium (kg) | 0.183 | Electro motor (kg) | 0.001 | Steel (kg) | 0.001 | |||
| Herbicides (kg) | 0.004 | Steel (kg) | 0.004 | Electro motor (kg) | 0.0001 | |||
| Fungicides (kg) | 0.008 | Sulfuric acid (kg) | 0.320 | Labor Force (h) | 0.065 | |||
| Pesticides (kg) | 0.003 | |||||||
| Electricity (kWh) | 0.299 | |||||||
| Labor force (h) | 0.615 | |||||||
| Agricultural machinery (kg) | 0.00365 | |||||||
| Agricultural Pollutants | Emission to Air (kg) | |||||||
| CO2 | 2.873 | Ginning and Oiling Pollutants | CO2 | 1.386 | Biodiesel Production Pollutants | CO2 | 0.023 | |
| N2O | 0.008 | N2O | 8.82 × 10−2 | N2O | 1.31 × 10−5 | |||
| CH4 | 0.011 | CH4 | 7.72 × 10−3 | CH4 | 8.35 × 10−3 | |||
| PM 10 | 1.50 × 10−2 | PM 10 | 2.75 × 10−3 | PM 10 | 6.79 × 10−7 | |||
| NOx | 0.005 | NOx | 2.66 × 10−3 | NOx | 91.0 × 10−5 | |||
| SO2 | 0.019 | SO2 | 0.011 | SO2 | 1.00 × 10−3 | |||
| CO | 2.12 × 10−2 | CO | 3.86 × 10−3 | CO | 2.75 × 10−6 | |||
| NH3 | 0.053 | NH3 | 0 | NH3 | 0 | |||
| Herbicides | 0.51 × 10−2 | |||||||
| Fungicides | 1.80 × 10−2 | |||||||
| Pesticides | 0.50 × 10−2 | |||||||
| Emission toWater (kg) | ||||||||
| NO3- | 0.158 | - | - | |||||
| Phosphate | 0.175 | - | - | |||||
| Emission toSoil (kg) | ||||||||
| Herbicides | 1.97 × 10−2 | - | - | |||||
| Fungicides | 4.20 × 10−2 | - | - | |||||
| Pesticides | 1.16 × 10−2 | - | - | |||||
| Damage Category | Human Health | Ecosystem Quality | Climate Changes | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Daily | PDF*m2*year | kg CO2 eq | MJ Primary |
| Total | 1.27 × 10−5 | 2.257 | 17.247 | 89.116 |
| Direct emission | 9.05 × 10−6 | 1.369 | 13.302 | 0 |
| Diesel | 4.27 × 10−7 | 0.175 | 0.393 | 40.550 |
| Nitrogen fertilizer | 1.54 × 10−6 | 0.422 | 2.170 | 19.521 |
| Phosphate fertilizer | 5.26 × 10−7 | 0.097 | 0.281 | 5.159 |
| Potassium fertilizer | 8.76 × 10−8 | 0.026 | 0.095 | 1.674 |
| Pesticides | 3.78 × 10−8 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.501 |
| Herbicides | 3.10 × 10−10 | 0.005 | 0.035 | 0.675 |
| Fungicides | 1.48 × 10−7 | 0.045 | 0.047 | 0.993 |
| Steel | 1.56 × 10−8 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.103 |
| Copper | 1.58 × 10−8 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.054 |
| Methanol | 2.47 × 10−7 | 0.019 | 0.104 | 6.788 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 2.01 × 10−8 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.327 |
| Sulfuric acid | 1.77 × 10−7 | 0.036 | 0.048 | 2.278 |
| Electricity | 5.27 × 10−7 | 0.072 | 0.758 | 12.768 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motevali, A.; Hooshmandzadeh, N.; Fayyazi, E.; Valipour, M.; Yue, J. Environmental Impacts of Biodiesel Production Cycle from Farm to Manufactory: An Application of Sustainable Systems Engineering. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020399
Motevali A, Hooshmandzadeh N, Fayyazi E, Valipour M, Yue J. Environmental Impacts of Biodiesel Production Cycle from Farm to Manufactory: An Application of Sustainable Systems Engineering. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotevali, Ali, Niusha Hooshmandzadeh, Ebrahim Fayyazi, Mohammad Valipour, and Jun Yue. 2023. "Environmental Impacts of Biodiesel Production Cycle from Farm to Manufactory: An Application of Sustainable Systems Engineering" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020399
APA StyleMotevali, A., Hooshmandzadeh, N., Fayyazi, E., Valipour, M., & Yue, J. (2023). Environmental Impacts of Biodiesel Production Cycle from Farm to Manufactory: An Application of Sustainable Systems Engineering. Atmosphere, 14(2), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020399







