Abstract
Better understanding of the spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation is essential in developing the best management practices for ecological restoration and soil erosion control on China’s Loess Plateau, an arid and semiarid region with severe soil erosion. This study aimed to explore the spatiotemporal trends of precipitation using long-term precipitation data from 1957 to 2018 from the 100 national standard meteorological stations across the Loess Plateau. The nonparametric Mann–Kendall statistical test and geospatial interpolation were used to detect the trends and to analyze spatial patterns of annual and seasonal precipitation. Wavelet analysis was applied to examine periodical variation across the plateau. The results reveal that regional annual precipitation over the Loess Plateau decreased during the 62 years of the study at a mean rate of −1.05 mm/10 years (p > 0.1). The changes in annual precipitation showed a periodical fluctuation with an increasing trend from 1957 to 1969, a decreasing trend from 1970 to 1999, and an increasing trend again in the first 18 years of the 21st century. The annual precipitation decreased in all eight sub-annual periods except for winter. Spatially, a decreasing trend occurred in the southern and eastern parts of the Loess Plateau, whereas a slight increase existed in the northwest in all periods. The decrease in six stations was statistically significant (p < 0.05), and a significant increase occurred in four stations (p < 0.1). These changes can be explained by an evident southward shift of the precipitation isohyets especially for 350 mm, 450 mm and 550 mm from the 1960s to the 1990s, and a clearly northward shift after the 1990s. Findings from this study facilitate an understanding of the spatial temporal trends of precipitation so appropriate countermeasures can be developed for effective vegetation restoration and soil erosion control across the Loess Plateau.
1. Introduction
With global warming, precipitation in China over the past 50 years has been well documented to have a slightly increasing trend, but the climatic variables show considerable spatial variation and uncertainty [1,2]. Global warming can simultaneously intensify the hydrological cycle at local and regional scales, especially in arid and semi-arid regions such as the Loess Plateau in northern China [3,4]. The distribution of precipitation can be consequently altered and may have great impacts on the regional ecosystems [5]. Understanding the trend and the periodic variation of precipitation have important implications to ecological restoration, soil erosion assessment and water resource regulation in the arid and semi-arid area.
Numerous studies on precipitation have been implemented on the Loess Plateau [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Ref. [16] showed that a signal of climate transition from warm-dry to warm-humid was detected in northwest China, and the transformation may be on a century time scale, but it was not yet possible to determine the speed and extent of its change. Ref. [9] analyzed the annual precipitation across the Loess Plateau using 214 meteorological stations revealing that about 83% of the total stations had a decreasing trend. Ref. [17] reported that the annual rainfall decreased gradually from southeast to northwest with great spatial variability over the Loess Plateau. Ref. [11] reported that annual precipitation showed a decreasing trend from 1961 to 2014 (p > 0.05) and the region with the largest decreasing rate was in the southeastern Loess Plateau, whereas the changes in the northwestern Loess Plateau were not obvious. Ref. [18] found that there was no significant trend of annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau and the climate tended to be humid in the western part (approximately 7.98% of the total area) from 1901 to 2014 by using the delta downscaling method. Ref. [14] found the annual extreme precipitation from seven indices (including maximum one-day precipitation, maximum five-day precipitation, erosive precipitation, heavy precipitation, rainstorm, very wet day precipitation and extremely wet day precipitation) all exhibited decreases on the Loess Plateau. These previous studies were useful to understand the large-scale change in precipitation of the Loess Plateau before 2010. However, in the last 10 years, several extreme rainstorms with a return period of once in a century occurred in some places on the Loess Plateau (e.g., 2012, 2013 and 2017), which resulted in serious flooding and soil erosion and consequently catastrophic disasters for the local residents. Thus, it is urgent and important to know the new patterns and trends of precipitation changes over the Loess Plateau using longer and more recent data.
In the study of climate change, the nonparametric Mann–Kendall (MK) method is widely used to detect the significance of monotonic trends in climatological time series [19,20]. Due to its fine structure in precipitation time series, the application of wavelet transform for climate variability assessment and ecological pattern analysis has been widely studied [21,22]. Ref. [23] analyzed the correlation between the time series of temperature in Tomsk and solar activity using the wavelet transform method and found a significant correlation between the periodicities in the time series of temperature and individual solar activity indexes. Ref. [24] used the wavelet transform method to study the temporal variability of precipitation of five precipitation series in northern California, U.S.A. in the past 96 years and found that the dominant period is about 16 years in the area. Additionally, this method was used to study the characteristics of precipitation changes in Northeast China [25]. The trends of precipitation, especially its periodic variation, are of great significance for understanding the interaction among atmosphere, vegetation, soil and hydrology on the Loess Plateau.
Water resources are scarce in the Loess Plateau, most of which covered arid and semi-arid area, with the most severe soil erosion in the world [26]. To reduce the source of sediment in the downstream Yellow River, many soil and water conservation practices have been introduced since 1949 including the conversion of slope farming land to forest and grassland or ‘Grain for Green’ project implemented since 1999, resulting in changes in surface hydrology [27]. The change of precipitation in space and time is expected to affect the water discharge and sediment yield by influencing the vegetation distribution and community composition [28]. The spatiotemporal trend of precipitation especially for the last 60 years over the Loess Plateau can help in understanding the regional vegetation restoration and sediment reduction, however, there is still a knowledge gap in understanding these recent trends [29]. Therefore, we conducted this study to (1) assess the trend and spatial distribution of annual and eight sub-annual precipitation series over the Loess Plateau, (2) determine how precipitation isohyets shift on the Loess Plateau during the study period, and (3) identify the period characteristics of annual precipitation on the Plateau. The findings from this study will help us to understand the climate impact on the local ecological environment and develop adaptation measures to these changes.
2. Study Site and Data Source
2.1. Study Site
The Loess Plateau is bounded by 100.8°–114.6° E, 33.7°–41.3° N, covering approximately 6.24 × 105 km2. Most parts of the Loess Plateau range from 800 to 2000 m a.s.l. (Figure 1a,b). The soil is mainly wind-deposited loess with an average thickness of approximately 100–200 m [30]. Precipitation on the Loess Plateau shows a clear zonal variation with a high value in the southeast and a low value in the northwest, about 440 mm per year on average (Figure 1c). However, the variation coefficient () of annual precipitation in this area is characterized by an opposite change trend compared to the precipitation, and the in the northwestern part of the Loess Plateau is approximately two times greater than that in the southeast (Figure 1d).
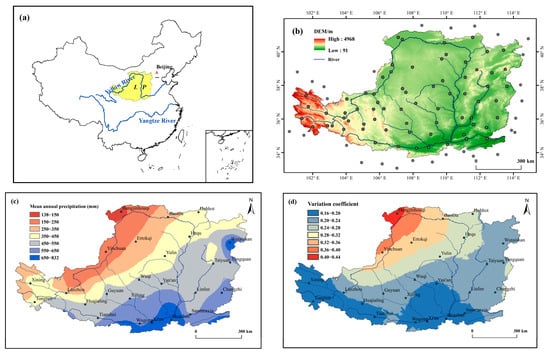
Figure 1.
(a) The geographical location of the Loess Plateau, (b) the digital elevation model map of the study area, (c) the distribution of mean annual precipitation, and (d) the distribution characteristics of variation coefficient of annual precipitation across the Loess Plateau from 1957 to 2018.
The precipitation is highly uneven in seasons affected by the East Asian monsoons. About 70–80% of the precipitation was concentrated from June to September, and the intense rainfall is the main cause of runoff and soil erosion in this area. The total area affected by soil erosion was 4.3 × 105 km2 and 65% of that area (2.8 × 105 km2) suffered severe erosion [26,31]. More than 90% of the sediment in the lower reaches of the Yellow River was sourced from the Loess Plateau. The area with the mean annual soil erosion modulus between 5000 and 10,000 t·km−2·a−1 is generally covered by the annual precipitation of 350–450 mm due to the intense rainstorms and wind erosion there [26].
2.2. Data Source and Processing
In accordance with the data in [29], a total of 100 meteorological stations comprising 62 years of monthly precipitation recordings in the period of 1957–2018 were analyzed. The Loess Plateau and the adjacent areas cover 68 and 35 national standard meteorological stations, respectively. The monthly precipitation observation data of stations that were obtained from the China meteorological data sharing network (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 10 November 2022) were checked and compiled to the seasonal and annual total.
In this study, the basic information of the meteorological stations (station name, longitude and latitude coordinates, elevation and precipitation data) was input into ArcGIS to create a point shape file with attribute information. The annual precipitation data of most meteorological stations passed the normal distribution test (p < 0.05); therefore, the ordinary kriging interpolation method was applied for spatial interpolation. The missing values of annual and monthly precipitation at partial meteorological stations were interpolated and extended to 1957 using the regression analysis method. Simultaneously, the anomalous values were detected and eliminated.
The regional precipitation estimated from the 100 meteorological stations for each year and the long-term average over the Loess Plateau during 1957–2018 were obtained by the ordinary kriging interpolation method. The isohyets of 250 and 450 mm were widely used to divide the climate zones, such as the arid, semi-arid and semi-humid regions over the Loess Plateau by considering annual, seasonal distribution of rainfall as well as actual evapotranspiration and drought index [29]. Therefore, the shifts of isohyets including 250 and 450 mm were examined in decadal scale by using surface analysis and resampling tools.
The East Asian summer monsoon index (EASMI) is a good indicator of climate change and can reflect the phased characteristics of climate change in China. Previous research [32] found that EASMI began to decline in the late 1960s and again increased in the late 1990s. Accordingly, three stages were identified, namely stage Ⅰ from 1957 to 1969, stage Ⅱ from 1970 to 1999, and stage Ⅲ from 2000 to 2018.
We further separated each year into eight periods to better detect and describe the trends of precipitation based on [29]. These periods are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The eight sub-annual periods used in this study.
3. Methods
3.1. Mann–Kendall Trend Test
The nonparametric MK method was chosen [19,20] to detect the significance of monotonic trends in hydrological and climatological time series considering its simplicity, reliability and ability to handle missing values and extreme values. It is one of the most appropriate time series trend analysis methods extensively used in the world [33,34].
The null hypothesis is the observed sample data. The values () are independent of each other and identically distributed. The alternative hypothesis indicates a monotonic trend in . The Mann–Kendall test statistic is derived as follows:
where and are the statistical values (), respectively. The n indicates the record length of the data series and is the return function. For the cases where , the statistic denotes normal distribution and . The variances are calculated based on the following formula:
where and are the number of tied groups and data values, respectively. The standard test statistic is calculated as:
where the statistical value possesses the characteristics of standard normal distribution. The will be rejected if at the level of significance in bilateral trend detection. A positive value denotes an upward trend and a negative value denotes a downward trend. When the ≥ 1.28, 1.64, and 2.32, it means passing the significance tests of 90%, 95%, and 99%.
3.2. Sen’s Slope Estimator
The Sen’s estimator can be used to estimate the slope of detected data under the condition that the meteorological and hydrological elements exhibit a linear trend [35]. Fortunately, the estimator is insensitive to abnormal values and can accurately calculate the magnitude of a trend in time series [36]. The is given by:
In the given Equation (5), indicates the magnitude of the trend and denotes a constant. Estimated slope of all detected data are calculated using the following formula:
where , denote the data values (). In case there are n values, during the study period, then and slope estimates, will be calculated. The median of slope depends on the following situation:
3.3. The Variation Coefficient of Annual Precipitation
The variation coefficient () of annual precipitation is an index used to denote the volatility of the precipitation at the annual scale which has a high relation with annual precipitation and elevation [2,37]. The greater the , the more obvious the fluctuation of annual precipitation with a smaller annual precipitation. The is determined as follows:
where and denote the standard deviation and the mean value of selected data series, respectively.
3.4. The Wavelet Analysis
The Morlet wavelet in Matlab wavelet analysis toolbox was used as the generating function to analyze the periodic variations of annual precipitation over the Plateau. Its advantages in both the local time and frequency domain showing the fine structure of precipitation time series are noticeable [21]. It provides a new way to analyze the multiple time scales variation of hydrological and meteorological elements. The function is:
where denotes unreliable number and is a constant.
Wavelet transformation is essential to wavelet analysis. The characteristics of wavelet change in the wavelet change domain are acquired by analyzing wavelet transformation parameter graph. The wavelet transformation of time series of detected data is determined as:
where means wavelet transformation coefficient, indicates the length of wavelet period and denotes the transformation time [23,38].
Wavelet variance shows the distribution of signal fluctuating energy in precipitation series and each significant period can be detected in each peak value. The existing main period can be conveniently diagnosed in the process of precipitation change to the typical meteorological stations. Wavelet variance can be calculated as follows [22].
where denotes the number of sample data and means module square of wavelet transformation coefficient.
4. Results
4.1. Trend of Annual Precipitation over the Loess Plateau
The mean annual precipitation over the Loess Plateau during 1957–2018 was 440 mm, which was slightly greater than 434 mm from 1957 to 2009 [29]. The annual precipitation over the Loess Plateau showed an extremely slight decreasing trend (p > 0.1) and possessed a declining rate of −1.05 mm/10 a, which approximately accounted for 0.024% of the mean annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau. The trend of annual precipitation was consistent with the results of previous research [9,11,29,39], but with some differences in magnitude of decrease.
The annual precipitation showed a significant fluctuation with 470, 441, 430, 411, 419, and 465 mm corresponding to the periods of 1957–1969, 1970s, 1980s, 1990s, 2000s and 2010–2018, respectively. Based on the fluctuation characteristics, annual precipitation can be divided into three stages (Table 2). Stage Ⅰ (1957–1969): the mean annual precipitation reached the maximum value and the variation coefficient in this stage was also the largest, 0.20, implying a high fluctuation rate of annual precipitation. Stage Ⅱ (1970–1999): precipitation began to decline since 1970s and fell to the lowest level in the late 1990s. The variation coefficient is significantly lower than that of the first stage. Stage Ⅲ (2000–2018): an increasing trend occurred in recent 20 years of the 21st century. In this stage, the fluctuation range of annual precipitation was the lowest with of 0.07. Table 2 also shows that the annual precipitation during 1957–2018 exhibited a periodic fluctuation of increasing-decreasing-increasing pattern, while exhibited a stable decreasing trend due to the expansion of the range between maximum precipitation and minimum precipitation on the Loess Plateau.

Table 2.
The stage variation of annual precipitation across the Loess Plateau, China during 1957–2018.
Figure 2 shows the spatial trend of annual precipitation across the Loess Plateau. During 1957–2018, there were 65 meteorological stations within and around the Plateau exhibiting a negative trend, and six of them were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Nevertheless, 38 meteorological stations covering the Plateau and the adjacent areas exhibited a positive trend with four stations statistically significant on the Plateau (p < 0.1). From Figure 2, the area with an increasing rate of 0.8–5 mm/10 a during the study period was primarily situated in the northwestern part of the Plateau. However, a much greater increasing rate of 5–15 mm/10 a was detected in northeastern Qinghai Province that would lead to a more obvious ecological restoration process. The areas with a significant decreasing trend (p < 0.05) are mainly located at places like Wutai Mountain station and Hua Mountain station, where the annual precipitation was detected with a decreasing rate of −30 to −44 mm/10 a. Overall, 34% of the total area of the Plateau (about 2.18 × 105 km2), including 45 stations, exhibited an increasing trend. Nevertheless, the area covered by a decreasing trend was mainly situated in the eastern and southeastern part of the Plateau, approximately 66% of the total area of the Plateau or 4.06 × 105 km2 (Figure 2). The area with an increasing trend increased by 1.25 × 105 km2, which mainly covered the northwestern part of the Plateau.
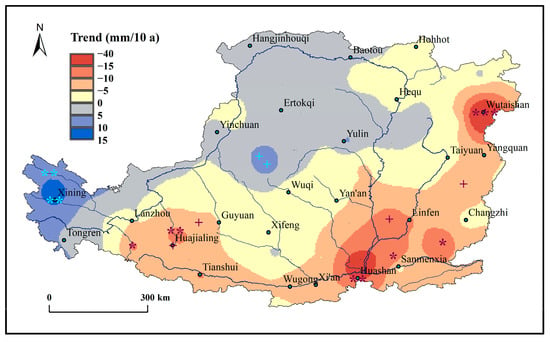
Figure 2.
Spatial trend of annual precipitation (mm/10 a) across the Loess Plateau during 1957–2018. The blue symbols represent increasing trend and the red represent decreasing trend. The symbols of +, *, **, *** mean passing the significance level of 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively.
4.2. Trend of Seasonal Precipitation over the Loess Plateau
Table 3 and Table 4 show the seasonal precipitation and the change intensities. A non-significant decreasing trend was detected in all the sub-annual periods except winter (Table 3). There were noticeable differences in the mean annual change rates among different periods. The mean annual change rates of summer, and LFP were relatively higher than that of spring, autumn, winter, wet season, EFP, and dry season by nearly 2–10 times.

Table 3.
The mean annual change trend of seasonal rainfall (mm/a) over the Loess Plateau, China.

Table 4.
The seasonal precipitation (mm) and Cv in different time periods over the Loess Plateau.
The variation of the seasonal precipitation (mm) in different periods reveals that of annual precipitation was generally lower than that of the eight sub-annual series (Table 2 and Table 4). The of precipitation in winter, dry season, spring and autumn was greater than that of other sub-annual series during 1957–2018, which showed the climatic nature of the arid region. The of precipitation in seven out of eight sub-annual seasons showed a decreasing trend in decadal scale (Table 4), which resulted in the same change direction in as of annual precipitation (Table 2).
Overall, the precipitation in summer, wet season, dry season and LFP showed a decreasing trend from 1957 until 2018 on the Loess Plateau, but the precipitation demonstrated an increasing trend in winter, particularly in the western Loess Plateau (Figure 3). Moreover, the areas with a tendency of increasing and decreasing in precipitation were basically consistent in spring, autumn and EFP. As shown in Figure 3, the areas with a decreasing trend account for orderly 47%, 72%, 46%, 11%, 65%, 75%, 49.6% and 85% of the total area of the Plateau from spring to LFP, respectively.
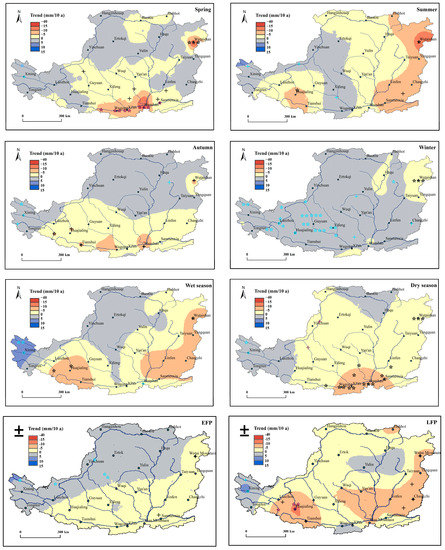
Figure 3.
Spatial trends in precipitation for the eight sub-annual periods, namely spring, summer, autumn, winter, wet season, dry season, EFP and LFP. The blue symbols represent increasing trend and the red represent decreasing trend. The symbols of +, *, **, *** mean passing the significance level of 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. The symbols of ***** represents the significance of the two adjacent stations.
Figure 3 also shows that the decreasing trend in precipitation mainly covered the eastern and southern parts of the Loess Plateau. However, the area with an increasing trend in precipitation mainly included the western part of the Plateau. Further analysis indicated that an increasing trend always occurred in the western part of the Plateau for all the sub-annual periods. Similarly, the decreasing trend appeared in the local meteorological stations, such as Wutai Mountain and Hua Mountain for the entire period, which is consistent with that in Figure 2 and Table 2.
4.3. Shifts of Isohyets across the Loess Plateau
In this section, shifts of the isohyets (e.g., 150, 250, 350, 450 and 550 mm) in terms of a decadal scale were examined to estimate the variation of the annual precipitation across the Loess Plateau. As shown in Figure 4, the movement of all isohyets was generally along the direction from northwest to southeast before the 1990s, but the opposite direction after the 1990s. In general, the 150, 250 and 350 mm isohyets experienced no obvious shifts and moved less than 30 km except for the 150 mm isohyet from the 1980s to the 2000s (Figure 4a,b,e). Nevertheless, the 450 and 550 mm isohyets witnessed more significant shifts (Figure 4c–e). The centroids of the 450 and 550 mm isohyets moved nearly 105 and 60 km eastward, 95 and 70 km southward from 1957 to the 1990s, respectively. After the 1990s, they reversed by almost 141 and 105 km westward, 107 and 106 km northward, respectively (Figure 4e). Figure 5 indicates that the areas covered by annual precipitation less than 150, 350–450, and 450–550 mm over the Loess Plateau exhibited an increasing trend, and 150–250 mm remained the same, while the area covered by 250–350 mm and larger than 550 mm had a downward trend.
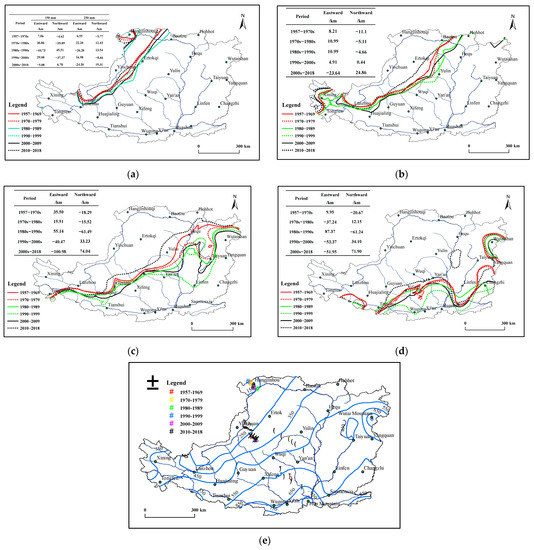
Figure 4.
Isohyets and centroids at decade-scale between 1957 and 2018 over the Loess Plateau, China. The centroids of isohyets of the 150, 250, 350, 450 and 550 mm are expressed by the triangle, star, diamond, circle and square, respectively. (a) The 150 and 250 mm isohyets and shift distance; (b) the 350 mm isohyet and shift distance; (c) the 450 mm isohyets and shift distance; (d) the 550-mm isohyets and shift distance; (e) the isohyets of mean annual precipitation and locations of the centroids of isohyets.
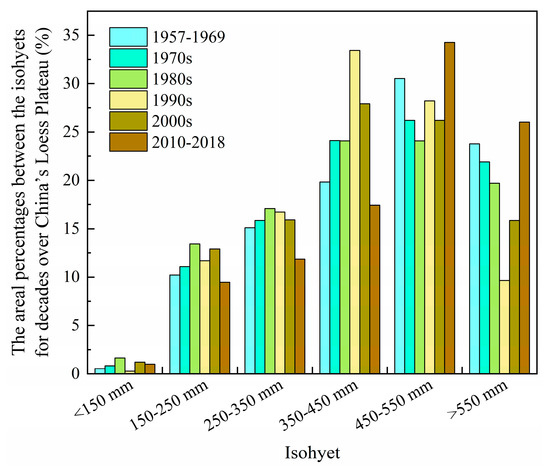
Figure 5.
The areal percentages between the isohyets for decades over China’s Loess Plateau.
Generally, the areas covered by annual precipitation of less than 250 mm kept steady along the decades with the mean rate of only 0.06%/10 a. The area covered by 250–450 mm showed a faster decreasing trend with a rate of −0.22%/10 a, which is due to the much faster decreasing trend (−0.47%/10 a) of the areas covered by 250–350 mm, and simultaneously increasing trend (0.25%/10 a) by 350–450 mm. The areas covered by annual precipitation of greater than 450 mm kept an increasing trend by 0.16%/10 a, which resulted from the fairly quick increasing trend of the areas covered by 450–550 mm with the rate of 0.65%/10 a and dramatic decreasing rate of −0.49%/10 a in the areas covered by greater than 550 mm (Figure 5). The changes for these isohyet areas, especially the isohyets of greater than 350 mm, could be well explained by the southeast moving trend of 450 mm and 550 mm in the previous 40 years and the greater northwest moving back in the later 20 years as shown in Figure 4. The results derived from this study are consistent with the findings in [29], and confirms the humidifying trend after 2000 on the Loess Plateau.
The spatial variation patterns of precipitation in China’s Loess Plateau were mainly affected by the annual fluctuation of the East Asian monsoon [40]. [32] found that the EASMI began to decline in the late 1960s and remained at a lower level in 1980s. In general, the climate of the Loess Plateau has been characterized by a dry trend from the 1960s to the end of 1990s, but precipitation increased again in the 21st century. The areas bounded by the isohyets of 450 and 550 mm increased significantly from 2010 to 2018, whereas the areas covered by the isohyets of 150–250, 250–350 and 350–450 mm retreated northwestward and decreased evidently, particularly in the 350–450 mm. These findings implied that rainfall conditions were generally favorable to vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau after the 2000s.
4.4. Periodical Analysis of Annual Precipitation
To better understand the periodic feature across the Loess Plateau, we chose and analyzed precipitation data from five typical stations at Taiyuan, Lanzhou, Wugong, Etuokeqi and Wuqi stations representing east, west, south, north, and the center, respectively (Figure 1).
The Taiyuan, Wuqi and Lanzhou are three typical meteorological stations representing the eastern, central and western Loess Plateau in the longitude direction, respectively. There were stable period variations of 4–7 years, 2–6 years and 3–9 years at Taiyuan station, Wuqi station and Lanzhou station, respectively, with quasi-eight oscillations in the annual precipitation during the study period (Figure 6a–c). The results illustrate that the three typical stations generally had a significant period at 2–7 years scale, which indicates that precipitation exhibited a short and consistent period variation over the Loess Plateau from east to west.
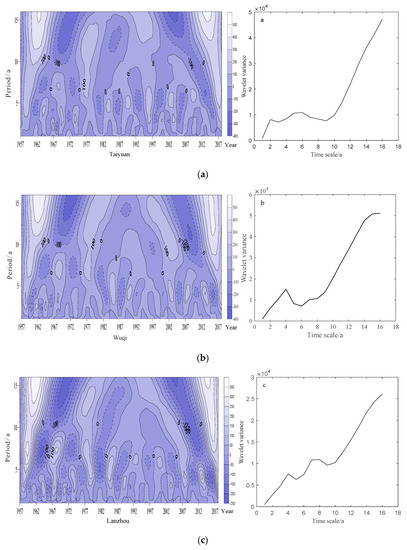
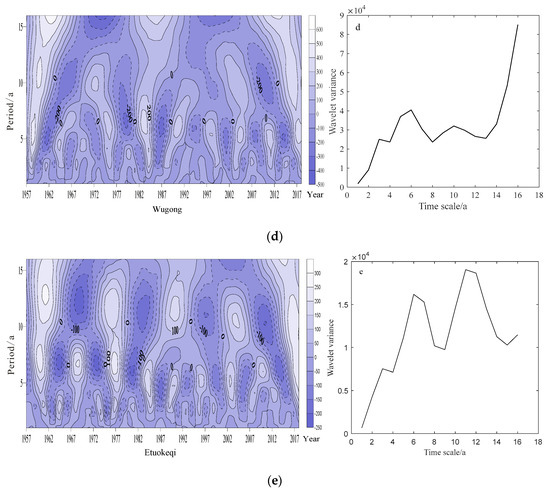
Figure 6.
Transform coefficient of Morlet wavelet real contour and wavelet variance of Taiyuan (a) Wuqi (b), Lanzhou (c), Wugong (d), and Etuokeqi (e) stations.
Additionally, the Wugong, Wuqi and Etuokeqi stations represent the southern, central, and northern parts of the Plateau in the latitude direction by turn. Complex-value Morlet wavelets showed there was obvious period variation in the three typical stations, but the difference existed between each station. Shorter period variation of annual precipitation was detected at Wugong, Wuqi and Eketuoqi stations at the 4–8 years, 2–6 years, and 4–8 years scales, respectively, but Etuokeqi station had a longer period of 9–14 years (Figure 6). The intensity of oscillation of shorter period scale in the annual precipitation gradually decreased for the entire study period. Moreover, these findings suggest that the period variation scale of annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau possibly exhibited the characteristic of the higher the latitude, the longer the period. The periodic variation of precipitation at typical stations on the Loess Plateau is mainly in short scale.
5. Discussion
5.1. Causes of Spatiotemporal Variation in Precipitation
In this paper, the spatiotemporal trends of precipitation were analyzed across 1957–2018 over the Loess Plateau. The causes of change in precipitation across the Loess Plateau have been the focus of widespread attention in the past several decades. Numerous studies pointed out that natural climate variability was the dominant driving force for the change in precipitation across the Loess Plateau, but the effects of human activities should be further analyzed [41].
From a natural perspective, the coupling effect of oceanic evaporation and atmospheric circulation played a critical role in climate change in large scale areas. The decreasing trend in annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau was affected by atmospheric circulation systems [42]. Ref. [32] pointed out that EASMI began to decline in the late 1960s, with the lowest value in the late 1990s, and increased again after 2000. It was found that the trend of annual precipitation and the moving characteristics of precipitation isohyets across the Loess Plateau in different decades were intrinsically related to the change of EASMI in the past half century. The decreasing rate of annual precipitation was tested to be −1.05 mm/10 a (p > 0.1) across the Loess Plateau from 1957 to 2018, while the average rates of −11.5 mm/10 a (p < 0.1) between 1957 and 2009 and −7.51 mm/10 a (p > 0.05) during 1961–2014 on the Plateau have been reported by [11] and [29]. The difference indicates that the annual precipitation in the study area witnessed an obvious increasing trend in the last 10 years. Ref. [43] reported that the Yellow River experienced severe drought from 1983 to the late 1990s, which caused a decrease in runoff and sediment transportation to the Yellow River Delta. This also explains the fact that annual precipitation decreased in stage Ⅱ on the Loess Plateau.
In the past half century, the decreasing trend of the summer precipitation may be attributed to the weakened southeast monsoon and reduced water vapor transport capacity in regions [44]. Furthermore, a decreasing trend of detected in annual precipitation in seven of eight sub-annual series on the Plateau was cause by the decrease of the maximum value of precipitation and the increase of the minimum value at decadal scales from 1957 to 2018.
In the past decades, we found that the variations of precipitation were characterized by an increasing trend in the western margin of the Loess Plateau, but a decreasing trend in central and eastern regions. The average wind speed near the ground in mainland China has decreased significantly [12,45,46,47], and the enhanced North wind in eastern China weakened the transportation of water vapor from the northwest Pacific Ocean, which was likely to be one of the reasons for detected variations of precipitation over the Loess Plateau [16]. The increase of net water vapor budget accounts for the obvious increases of annual precipitation in the Northwest dry area [41]. In addition, the increasing of annual and seasonal precipitation in the western Loess Plateau may be related to increased water vapor content from atmosphere and intensified water cycle driven by global climate warming [3,4,48]. Ref. [49] revealed that North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) and El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) are the main reasons for affecting precipitation change in northeast Qinghai Province. The shift of climate pattern from warm-dry to warm-humid was preliminarily verified in Northwest China [16], but a non-uniformity of trend in spatial scale was revealed [12]. Moreover, the strong extent of decreasing trend in annual and seasonal precipitation always occurred in the meteorological stations, such as Wutai Mountain and Hua Mountain, which was probably affected by the local topographical factors and atmospheric circulation condition due to the high elevation of 2000 m a.s.l. at these stations.
In addition, it cannot be ignored that increasing human activities have intensified greenhouse gas and aerosol concentrations, and altered land use and land cover conditions on the underlying surface, which probably have a certain impact on the climate system, rainfall intensify and its spatiotemporal distribution pattern [41,50,51,52].
Similar to previous research results in [53], the quasi-period of 2–7 a in the five typical stations of this paper may be affected by the ENSO and quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) [54]. Ref. [11] reported period variations of 5–7 a and 12–14 a for annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau. Ref. [55] also pointed that the annual precipitation has a dry and wet change of 2–4 a and 11–18 a on the Loess Plateau. Two obvious periods were detected in these studies, among which the shorter period is basically consistent with this study. However, the longer period, as discovered in Etuokeqi station, can be affected by solar activity [56].
5.2. The Implication of Precipitation Variation on Soil Erosion
The annual precipitation on the Loess Plateau generally showed a slightly decreasing trend (−1.05 mm/10 a) while an evident increasing trend occurred after 2000. It was expected that the rainfall erosivity of the Loess Plateau would fluctuate at the same pace [57]. However, a terrace and wrap dam can hold water and sediment directly and restored vegetation can actively enhance evapotranspiration and increase soil infiltration capacity by improving soil physical and chemical properties [58], which can result in an evident reduction in the runoff and sediment generation in the catchment and the Plateau [59].
An increasing trend of precipitation in the 21st century was detected, especially with an accelerated increasing rate since 2010. The increasing precipitation does not mean sediment transportation increases into the Yellow River. The results showed that the areas covered by 250–450 mm and greater than 450 mm with a faster decreasing trend (−0.22%/10 a) and an increasing trend (0.17%/10 a), respectively, which demonstrated that the climatic conditions on the Loess Plateau are basically conducive to local vegetation restoration. It is reported that the total vegetation cover increased significantly on the Loess Plateau from 56% to 76.8% during 2001–2017 [60]. Compared to the 1952–1979 period, average annual runoff and annual sediment transportation from the Loess Plateau decreased from 171.46 × 108 m3 and 14.99 × 108 t to 81.75 × 108 m3 and 2.37 × 108 t during 2000–2015, respectively [61]. The soil erosion area on the Loess Plateau decreased from 4.3 × 105 km2 in the early 1980s [26] to 2.14 × 105 km2 in 2018 [62]. A great number of studies proved that soil erosion control measures implemented by the nation exert a major role in the reduction of runoff and sediment in the different regions, such as the catchments and the Loess Plateau [59,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72].
However, it is well known that soil erosion on the Loess Plateau is mainly caused by heavy rainfall, especially extreme rainstorms. Changes in extreme precipitation across the Loess Plateau have been deeply discussed by [73]. Flood events with a return period of 10 years or more and extreme precipitation events were proposed to be the dominant erosion risk factors on the Loess Plateau [71]. For instance, the model of rill erosion on slope farmland was up to 20 × 103 t/km2 in the extreme rainstorm with a return period of once in 200 years in Suide, Shaanxi Province in 2017, resulting in road damage and the town being inundated [74]. This suggests that the impact on soil erosion caused by extreme rainfall events over the loess plateau cannot be ignored.
The variation coefficient of annual precipitation is helpful to the analysis of regional flood and drought disasters [75]. For areas with severe soil erosion, of the precipitation well explains the impact of extreme precipitation on the ecological environment. The of annual precipitation and seven of eight sub-annual series on the Plateau showed a decreasing trend in decadal scales, indicating that the change amplitude of precipitation was weakened and its distribution is more uniform. As presented in Table 2 and Table 4, the precipitation of annual and wet season on the Plateau have been increasing since 2000. The of annual precipitation and precipitation in most sub-annual seasons showed a decreasing trend, indicating that the fluctuation magnitude of precipitation exhibited a decreasing trend on the Loess Plateau, especially in the wet season. Overall, favorable climate conditions can promote vegetation restoration and availably play its role in conserving soil in this area.
The obvious periodical change in the typical stations helps to understand the variation characteristics of vegetation cover, runoff discharge and sediment transportation from a climatological point of view [76]. For instance, there was a return period of 4 a in annual precipitation from 1957 to 2018 at Wuqi station, the hinterland of the Loess Plateau, which had similar characteristics with the vegetation cover variability during 2001–2017 [77]. Further research was conducted and discovered that annual rainfall erosivity approximately possesses a return period of 4 a at this station throughout the study period. However, a return period of 6 a in runoff discharge and sediment transportation was detected from 1969 to 1996 and no obvious return period after the mid-1990s. There were basically consistent return periods of annual precipitation, annual rainfall erosivity, runoff discharge and sediment transportation before 1996. Since the late 1990s, runoff discharge and sediment transportation have reduced sharply in Wuqi hydrological station. Therefore, it was the effect of vegetation construction and restoration on soil and water loss since 1998.
6. Conclusions
This study used the monthly precipitation data of 100 meteorological stations within and around the Loess Plateau and analyzed the spatiotemporal trends of precipitation between 1957 and 2018 using the nonparametric Mann–Kendall method, Sen’s slope estimator and kriging interpolation method.
Temporally, a slightly decreasing trend in annual precipitation was detected for the entire period (p > 0.1), with a mean decreasing rate of −1.05 mm/10 a. Along the decades the trends were different, and three stages were classified: an increasing trend from 1957 to 1969, a decreasing trend from 1970 to 1999, and an increasing trend again in the 21st century, especially with an accelerated increasing rate since 2010. The precipitation in the sub-annual periods except for winter decreased slightly, whereas the winter increased slightly over the 62 years. The of annual precipitation was generally lower than that of the eight sub-annual series. Like the trend of annual precipitation, the of precipitation in seven of eight sub-annual seasons also showed a decreasing trend in decadal scale. The annual precipitation in the typical stations of four directions and the center generally exhibited a period of 2–7 years.
Spatially, the annual precipitation was characterized by a decreasing trend from southeast to northwest, but the trend of variation coefficient was opposite. Noticeably, a decreasing trend in annual precipitation and eight sub-annual series except for winter was detected in the southern and eastern parts of the Plateau. Additionally, there was an obvious southward shift for the 450 and 550 mm isohyets from the 1960s to the 1990s, while there was a faster northward shift after 1990s. However, the shifts of isohyets, such as the 150, 250 and 350 mm were not evident between the decades. The area covered by 250–450 mm showed a faster decreasing trend followed by a rate of −0.22%/10 a. Nevertheless, the areas covered by the annual precipitation of greater than 450 mm kept an increasing trend by 0.17%/10 a.
In summary, better understanding the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of precipitation in annual and seasonal periods is greatly helpful for comprehensive watershed management and ecological construction. The effective and reasonable measures adapting to local conditions such as engineering measures (terracing, check dams as well as reservoirs), tillage measures (adjusting crop types, agricultural planting structures, and tillage measures) and biological measures (afforestation and pasture improvement) were expected to be given more attention by local governments to reduce the threat of soil erosion during flooding season. Simultaneously, the management and maintenance of implemented measures in the treated area were suggested to be strengthened. Understanding the spatiotemporal characteristics and variations of precipitation over the Loess Plateau assists the development of cost-effective soil erosion control practices to reduce soil loss and other adverse effects at specific locations and times across the region.
Author Contributions
X.X. came up with the study idea, gathered, processed and analyzed the most meteorological data, generated maps with ArcGIS, and wrote the original draft. T.H. provided constructive suggestions for this article and did language polishing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
“Not applicable” for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
“Not applicable” for studies not involving humans.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets associated with this article can be found at http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 20 June 2019.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Zhang Xiaoping of Northwest A & F University, Yang Xihua of New South Wales Department of Planning, Industry and Environment for their assistance in data processing and analysis, language polishing, and revised draft.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ji, Y.H.; Zhou, G.S.; Wang, S.D.; Zhao, J. Warm-wet climate trend enhances net primary production of the main ecosystems in China during 2000–2021. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Y.; Zhan, Y.J.; Ren, Y.Y.; Yu, C.; Sun, X.B. Spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation variability over mainland China: I Climatology. Advanc. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 299–310, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; D’Odorico, P.; Evans, J.P.; Eldridge, D.J.; Mccabe, M.F.; Caylor, K.K.; King, E.G. Dryland ecohydrology and climate change: Critical issues and technical advances. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2585–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, D.; Favis-Mortlock, D.; Fealy, R. Addressing key limitations associated with modelling soil erosion under the impacts of future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 156, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, B.S. Spatial and temporal variability of annual precipitation during 1961—2006 in Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, F.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Flanagan, D.C. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of extreme temperature and precipitation events on the Loess Plateau of China during 1961–2007. Quat. Int. 2010, 226, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, C.M. Long-term trend analysis for major climate variables in the Yellow River basin. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 21, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.X.; Fan, X.H. Precipitation trends during 1961—2010 in the Loess Plateau region of China. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 5512–5523, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Q.; Wu, P.T.; Zhao, X.N.; Gao, X.D. Spatiotemporal analysis of climate variability (1971–2010) in spring and summer on the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.B. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation on the Loess Plateau from 1961 to 2014. J. Earth. Environ. 2015, 6, 276–282, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.Y.; Sun, Q.H.; Duan, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.F. Joint analysis of changes in temperature and precipitation on the Loess Plateau during the period 1961–2011. Clim. Dynam. 2016, 47, 3221–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cui, L.L.; Wang, J.B.; Du, H.Q.; Wen, K.M. Changes in the temperature and precipitation extremes in China during 1961–2015. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Lyu, D.; Lei, X.J.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.L.; Yi, H.J.; Guo, J.W.; He, L.; He, J.; Yang, X.H.; et al. Variability of extreme precipitation and rainfall erosivity and their attenuated effects on sediment delivery from 1957 to 2018 on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Soil Sediment. 2021, 21, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal changes of sc-PDSI and its dynamic drivers in Yellow River Basin. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Shen, Y.P.; Hu, R.X. Preliminary study on signal, impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in Northwest China. J. Glac. Geocry. 2002, 24, 219–226, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Z.B.; Lu, X.X. Spatiotemporal variation in rainfall erosivity on the Chinese Loess Plateau during the period 1956—2008. Reg. Environ. Change 2011, 11, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Peng, S.Z.; Yang, C.; Huo, X.Y.; Chen, Y.M. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Climate Change in the Loess Plateau from 1901 to 2014. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 621–633, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climate Statistics Diagnosis and Prediction Technology, 2nd ed.; Meteorological Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.C.; Ren, H.B.; Ouyang, Z.S.; Wei, W.; Ma, K.P. The use of the Mexican Hat and the Morlet wavelets for detection of ecological patterns. Plant. Ecol. 2005, 179, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolitov, I.I.; Kabanov, M.V.; Loginov, S.V. Wavelet analysis of hidden periodicities in some indexes of solar activity. Russ. Phys. J. 2002, 45, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangdan, K. Wavelet analysis of precipitation variability in Northern California, U.S.A. Ksce. J. Civ. Eng. 2004, 8, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, E.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Quan, L.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, M. Spatiotemporal variations of extreme climate events in Northeast China during 1960–2014. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Kong, X.L.; Shi, D.Y.; Huang, S.Y. Preliminary report on soil erosion and soil degradation in the Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. 1984, 5, 5–10, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Zheng, F.L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the loess plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Ecohydrology: A hydrologic perspertive of climatesoil-vegetation dynamics. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, X.P.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Ma, T.Y.; Sun, Y.P. Spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation and extreme events on the Loess Plateau of China between 1957 and 2009. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Xiong, G.S.; Liang, J.Y.; Jing, K. Erosion and Runoff Sediment Variation in the Yellow River Basin; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1993; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Wei, W.; Fu, B.J.; Lu, Y.H. Soil and water conservation on the Loess Plateau in China: Review and perspective. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2007, 31, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.H.; Ding, Y.J.; Mu, M. Climate and Environmental Evolution in China: 2012 Comprehensive Volume; Meteorological Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 22, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, C.; Berger, A. Annual and seasonal climatic variations over the Northern Hemisphere and Europe during the last century. Ann. Geophys. 1986, 4, 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Rustomji, P.; Zhang, X.P.; Hairsinen, P.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J. River sediment load and concentration responses to changes in hydrology and catchment management in the Loess Plateau region of China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 45, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B.; Cavadias, G. The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.H.; Zhang, X.W. Some results of variation coefficient of annual rainfall in XingJiang, China. J. Meteorol. Res. 1993, 7, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Subasi, A.; Kiymik, M.K.; Akin, M.; Erogul, O. Automatic recognition of vigilance state by using a wavelet-based artificial neural network. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2005, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.B.; Chen, S.L.; Liu, C.M.; Shepard, D. Hydro-climatic trends of the Yellow River Basin for the last 50 years. Clim. Chang. 2004, 65, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Ying, S.; Song, Y.F. Weakening of the Asian summer monsoon and its impact on the precipitation pattern in China. Int. J. Water Resour. D 2010, 26, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Sun, X.B.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.Y.; Ying, X.U.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, Y.J.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.J. Spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation variability over mainland China: III: Causes for recent trends. Advanc. Water Sci. 2016, 26, 451–465, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, W.J.; Sun, C.F.; Song, H.M.; Cobb, K.M.; Li, J.P.; Leavitt, S.W.; Wu, L.X.; Cai, Q.F.; Liu, R.S.; et al. Anthropogenic aerosols cause recent pronounced weakening of Asian summer monsoon relative to last four centuries. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 5469–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.X.; Miao, C.Y.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Duan, Q.Y.; Hao, L.; Sun, Q.H.; Ye, A.Z.; Di, Z.H.; Wei, G. Evolution of the Yellow River Delta and its relationship with runoff and sediment load from 1983 to 2011. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chang, C.P.; Fu, C.; Qi, Y.; Robock, A.; Robinson, D.; Zhang, H.M. Steady decline of east Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: Evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, Q. Changes in near-surface wind speed in China: 1969–2005. Int. J. Climato. 2015, 31, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.C.; Tao, S.W. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956–2004. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yang, K.; Qin, J. Observed surface and upper-air wind speed changes over China since 1960. J. Clim. 2012, 26, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers of Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group into the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Lu, R.J.; Liu, C.; Duan, C.X. Temporal change characteristics of climatic and its relationships with atmospheric circulation patterns in Qinghai Lake Basin. Advanc. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 281–293, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn, S.; Graham, F. Untangling aerosol effects on clouds and precipitation in a buffered system. Nature 2009, 461, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.J.; Zhang, D.F.; Chen, Z.X.; Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F. Land use effects on climate in China as simulated by a regional climate model. Sci. Chin. (Earth Sci). 2007, 50, 620–628, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A.S.; Adegoke, J.; BeltraáN-Przekurat, A.; Hiemstra, C.A.; Lin, J.; Nair, U.S.; Niyogi, D.; Nobis, T.E. An overview of regional land-use and land-cover impacts on rainfall. Tell. Seri. B-Chem. Phys. Mete. 2010, 59, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, Z.M.; Xu, L. Rainfall characteristics research of spatial and temporal variation in the middle of the Loess Plateau. J. Sichuan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2011, 34, 724–728, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson, E.M.; Wang, X.L.; Ropelewski, C.F. The biennial component of ENSO variability. J. Marine Syst. 1990, 1, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, Y.R. Spatial-temporal evolution of precipitation in China Loess Plateau. J. Des. Res. 2007, 27, 502–508, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Precipitation Reconstruction and Muti-Scales Variations of North China over the Past 400 Years; Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soksamnang, K.E.O.; He, H.M.; Zhao, H.F.; Jing, S.W. Analysis of rainfall erosivity change and its impacts on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau over more than 50 years. Res. Soil Water Cons. 2018, 25, 1–7, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of paired catchment studies for determining changes in water yield resulting from alterations in vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Xie, M.L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, T.T.; Guo, M.J. Hydrologic responses to vegetation restoration and their driving forces in a catchment in the Loess hilly-gully area:a case study in the upper Beiluo River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 622–629, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Lv, D.; Yin, S.Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Zhu, Q.G.Z.; Yu, Q. Remote sensing estimation of the soil erosion cover-management factor for China’s Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1942–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Tang, K.L.; Jiao, J.Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Cao, Q.; Xiao, P.Q.; Wei, X.; Fu, S.H.; Miu, C.Y.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Altas of Water and Sediment in the Yellow River; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Announcement on Soil and Water Conservation in China. Available online: http://www.swcc.org.cn/gglm/2019/0820/38773.html (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Castillo, V.M.; Martinez-Mena, M.; Albaladejo, J. Runoff and soil loss response to vegetation removal in a semiarid environment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.L.; Fu, Y.L.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, J.X.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.P. Trends of streamflow, sediment load and their dynamic relations for the catchments in the middle reaches of the Yellow River in the past five decades. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 9, 5487–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.B.; Zhang, L.; Gallichand, J. Runoff responses to afforestation in a watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu. Precipitation-vegetation coupling and its influence on erosion on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2006, 64, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Rustomji, P.; Hairsine, P. Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Wen, Z.M.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and Eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.l.; Lv, Y.H.; Ciais, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosi. 2015, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, R.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, P.F. Did streamflow or suspended sediment concentration changes reduce sediment load in the middle reaches of the Yellow River? J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Lin, P.F.; Chen, H.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.J.; Yu, Y.P.; Liu, E.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Lv, D. Understanding land use/cover change impacts on runoff and sediment load at flood events on the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.R.; Hou, P.; Gao, J.X.; Wan, H.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Sun, C.X. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics and influencing factors of vegetation in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2019. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Mu, X.M.; Song, X.Y.; Dan, W.; Cheng, A.F.; Bing, Q. Changes in extreme temperature and precipitation events in the Loess Plateau (China) during 1960–2013 under global warming. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, Q.K.; Zhang, X.P.; Cao, W.; Dang, W.Q. Investigation report on storm resistance ability of comprehensive control of soil and water loss in small watershed of loess plateau. Bull. Soil Water Cons. 2017, 34, 349–350, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, C.M.; Xu, D.Y.; Lei, R.D.; Wang, Y.H. Forest Hydrology; China Forestry Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Podlasly, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Feger, K.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Kai, S. Separating the effects of changes in land management and climatic conditions on long-term streamflow trends analyzed for a small catchment in the Loess Plateau region, NW China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Lv, D.; Guo, J.W.; Lei, S.Y.; He, J.; Zhang, X.P. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of photosynthetic vegetation cover in Beiluo River Basin from 2001 to 2017 based on MODIS products. Yellow River 2020, 42, 67–71, 76, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).