Diurnal Characteristics in Summer Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
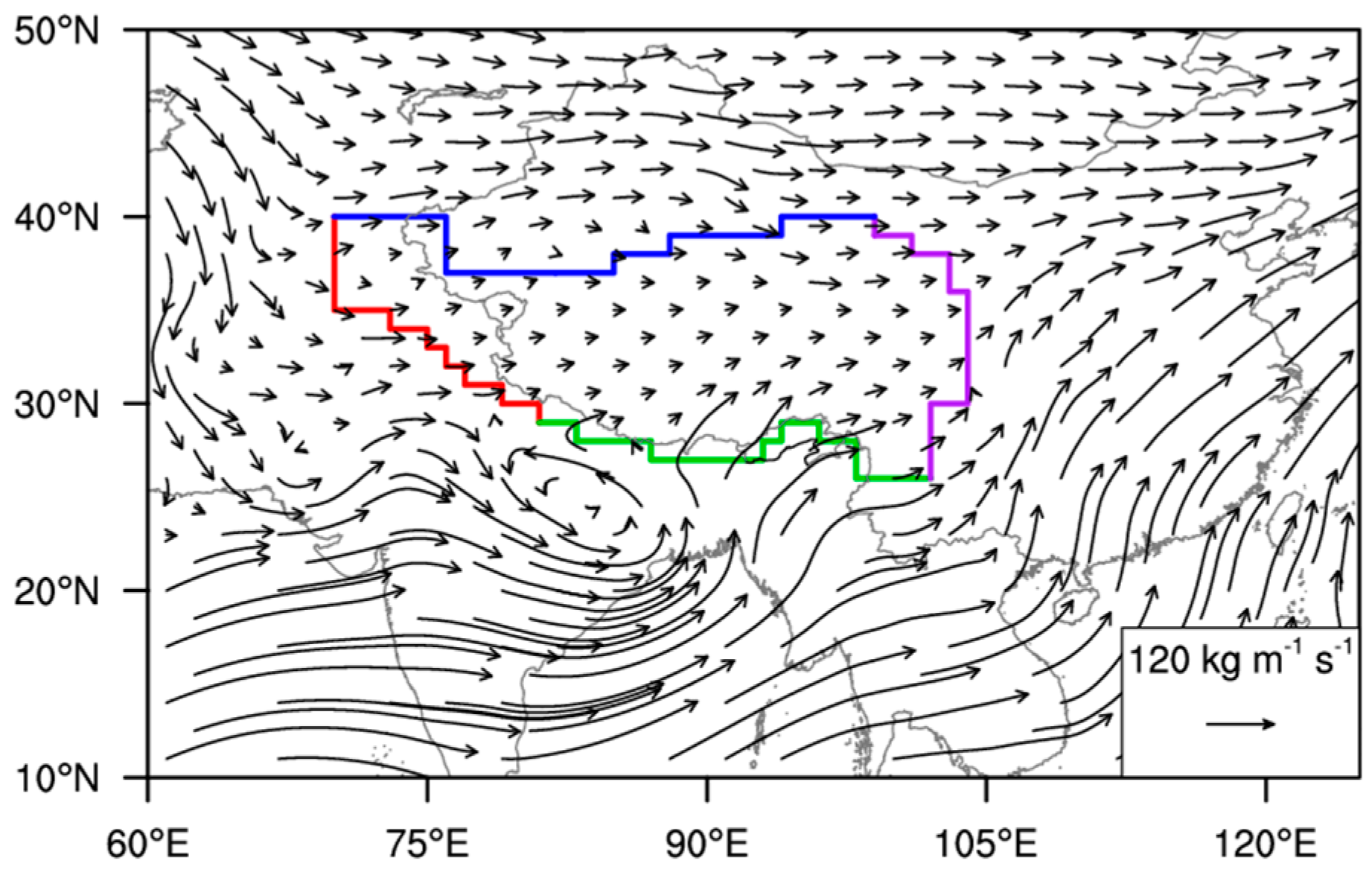
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
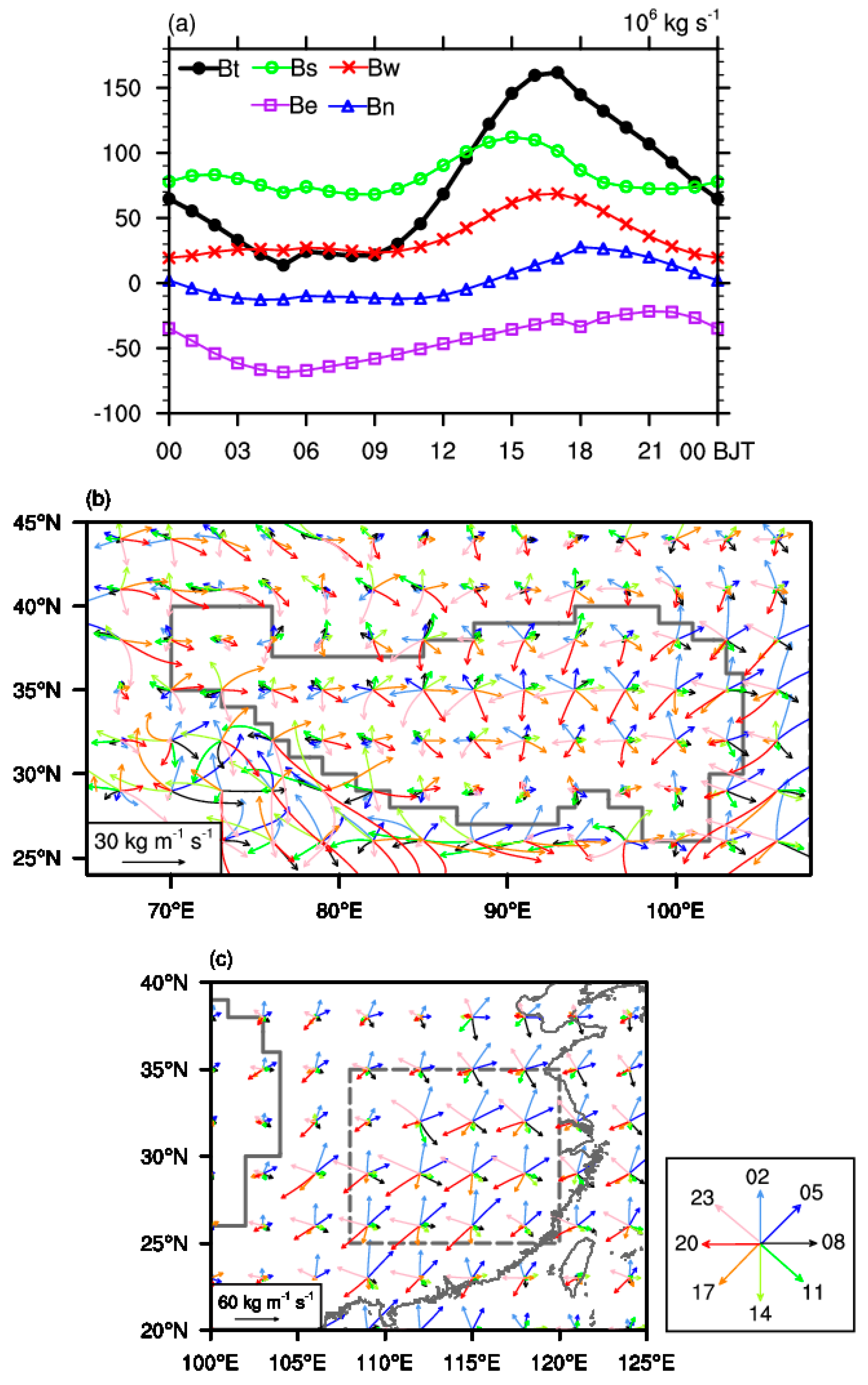
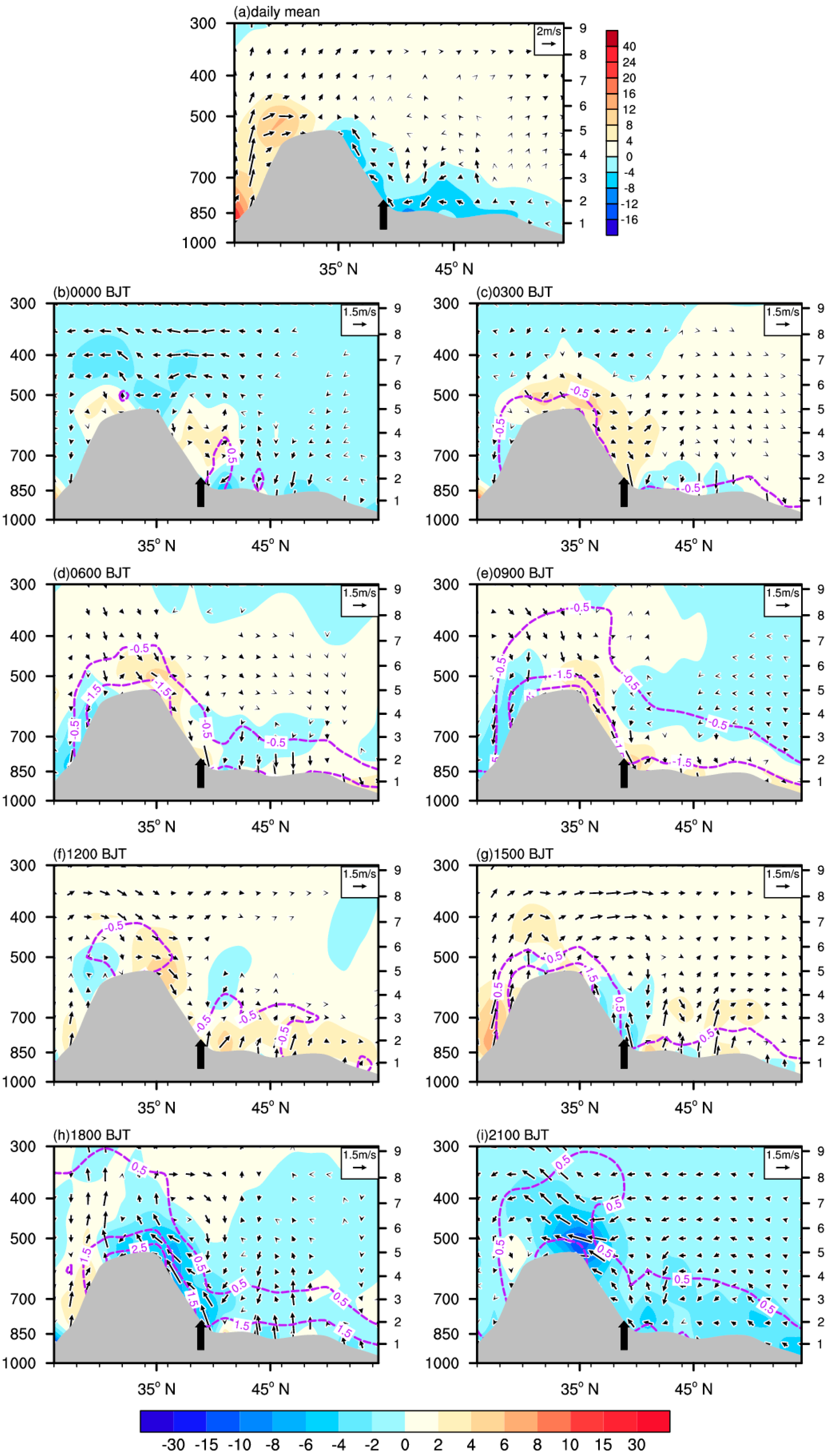
3.1. Diurnal Variation Features of the Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the TP
3.1.1. Diurnal Variation in the Bt
3.1.2. Spatial Features of Diurnal Variation in Water Vapor Transport
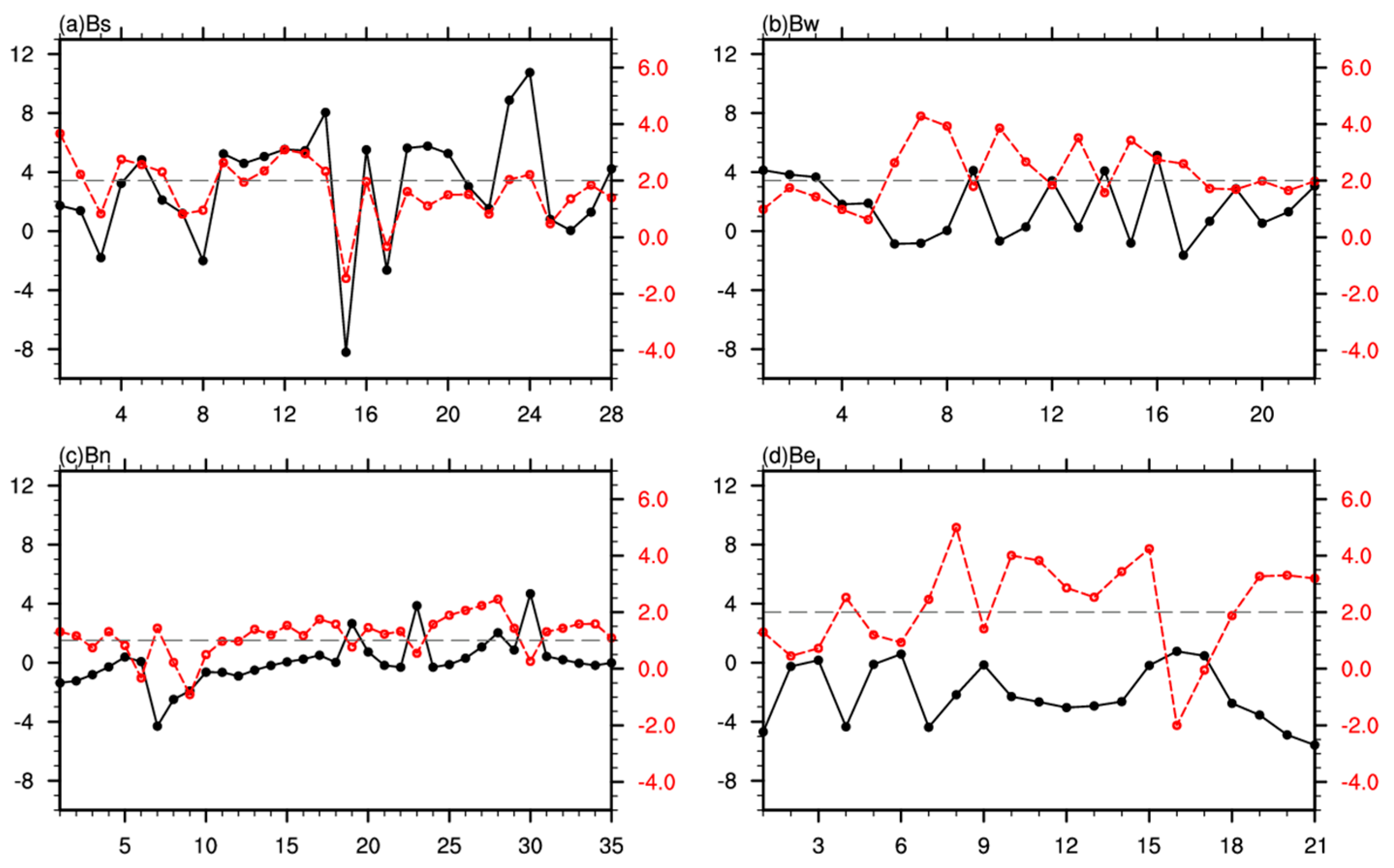
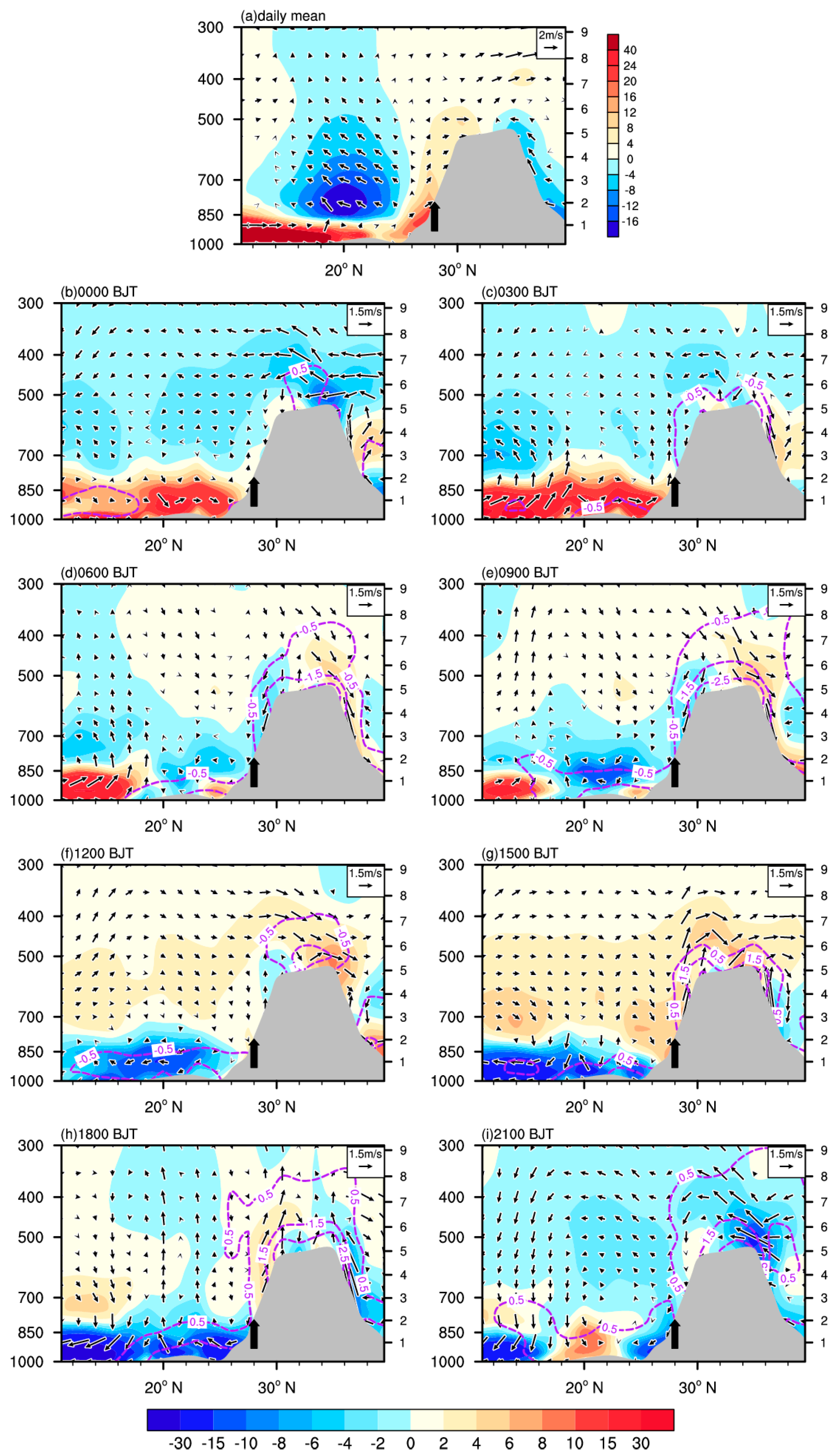
3.2. The Cause of the Diurnal Variation in the TP Bt and Its Relationship with Precipitation
3.2.1. The Cause of the Diurnal Variation in the TP Bt
3.2.2. The Relationship between the TP Bt and Precipitation
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.; Bierkens, M.F. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Shi, X.; Gao, S. World water tower: An atmospheric perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettelman, A.; Kinnison, D.E.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Brasseur, G.P. Impact of monsoon circulations on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Hu, Y.; Wright, J.S.; Jiang, J.H.; Dickinson, R.E.; Chen, M.; Filipiak, M.; Read, W.G.; Waters, J.W.; Wu, D.L. Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, X. An important mechanism sustaining the atmospheric “water tower” over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 11287–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; La, Z.; Peng, H.; et al. The third atmospheric scientific experiment for understanding the earth atmosphere coupled system over the Tibetan Plateau and its effect. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2018, 99, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, S. Attribution of the Tibetan Plateau to northern drought. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Deng, Y.; Son, S.; Wang, X.; Di, D.; Pan, M.; Ma, X. How were the eastward–moving heavy rainfall events from the Tibetan Plateau to the lower reaches of the Yangtze River enhanced? J. Clim. 2021, 34, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Tsukamoto, O.; Yao, T.; Koike, T.; Zuo, H.; Hu, Z.; Su, Z. Diurnal and inter–monthly variation of land surface heat fluxes over the central Tibetan Plateau area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2005, 80, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zipser, E.J. Diurnal variations of precipitation, deep convection, and lightning over and east of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M. Diurnal variation in the occurrence frequency of the Tibetan Plateau vortices. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2014, 125, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Y. Evaluation of simulated climatological diurnal temperature range in CMIP5 models from the perspective of planetary boundary layer turbulent mixing. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Zhao, P. Characteristics of the summer atmospheric boundary layer height over the Tibetan Plateau and influential factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5253–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yao, X. The characteristics and mechanisms on diurnal variation of summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwagata, T.; Numaguti, A.; Endo, N. Diurnal variation of water vapor over the central Tibetan Plateau during summer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Wu, P.; Kimura, F.; Yoshikane, T.; Liu, J. Drastic evening increase in precipitable water vapor over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 81, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Pan, Z.; Qin, J.; Chen, D.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Lazhu; Tang, W.; Han, M.; et al. Evaluation of precipitable water vapor from four satellite products and four reanalysis datasets against GPS measurements on the Southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5699–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhou, T. Water vapor transport for summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Multidata set analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D20114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J. The interdecadal change of summer water vapor over the Tibetan Plateau and associated mechanisms. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4103–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, P. Spatiotemporal variation of water vapor budget over the Tibetan Plateau and its regulation on precipitation. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2022, 28, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Deser, C. Diurnal and semidiurnal variations in global surface wind and divergence fields. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 31109–31125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, F. Impacts of mountain–plains solenoid on diurnal variations of rainfalls along the Mei-Yu Front over the East China plains. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackadar, A.K. Boundary layer wind maxima and their significance for the growth of nocturnal inversions. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1957, 38, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Luo, X.; Zhu, K.; Sun, Z.; Fei, J. The controlling role of boundary layer inertial oscillations in Meiyu frontal precipitation and its diurnal cycles over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5090–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Chen, G. Diurnal variations of precipitation over North China regulated by the mountain-plains solenoid and boundary-layer inertial oscillation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, H.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, N.; Sato, T.; Kanamori, H.; Sunako, S.; Kayastha, R.B. Twice-daily monsoon precipitation maxima in the Himalayas driven by land surface effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2021, 126, e2020JD034255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Fu, Y.F.; Yang, Y.; Pan, X.; Tan, R. Trumpet-shaped topography modulation of the frequency, vertical structures, and water path of cloud systems in the summertime over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: A perspective of daytime–nighttime differences. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Lou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W. On the suitability of ERA5 in hourly GPS precipitable water vapor retrieval over China. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Version 06; p. 38. Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-05/IMERG_ATBD_V06.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Kulie, M.S.; Bennartz, R. Utilizing spaceborne radars to retrieve dry snowfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2564–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulies, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, M. Temporal and spatial variations of convection, clouds and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau from recent satellite observations. Part II: Precipitation climatology derived from global precipitation measurement mission. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4858–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, A.; Wang, T.; Wan, R.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X. The influence of mechanical and thermal forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, P.; Guo, G.; Park, S.K.; Wiscombe, W.; Chen, B. Measurements of water vapor and high clouds over the Tibetan Plateau with the Terra MODIS instrument. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote 2003, 41, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Diurnal Cycle of the Asian summer monsoon: Air pump of the second kind. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 1747–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, P. Comparison of moisture transport between Siberia and Northeast Asia on annual and interannual time Scales. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 7645–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, B. What is the main cause of diurnal variation and nocturnal peak of summer precipitation in Sichuan Basin, China? The key role of boundary layer low-level jet inertial oscillations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2643–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilovich, M.G.; Akella, S.; Coy, L.; Cullather, R.; Draper, C.; Gelaro, R.; Kovach, R.; Liu, Q.; Molod, A.; Norris, P.; et al. MERRA-2: Initial Evaluation of the Climate; NASA/TM-2015-104606; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015; Volume 43, p. 139. Available online: https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/pubs/tm/docs/Bosilovich803.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2022).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhao, P. Diurnal Characteristics in Summer Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020322
Wang H, Zhao P. Diurnal Characteristics in Summer Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020322
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huimei, and Ping Zhao. 2023. "Diurnal Characteristics in Summer Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the Tibetan Plateau" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020322
APA StyleWang, H., & Zhao, P. (2023). Diurnal Characteristics in Summer Water Vapor Budget and Transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere, 14(2), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020322





