Spatio-Temporal Changes and Contribution of Human and Meteorological Factors to Grassland Net Primary Productivity in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 2000 to 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
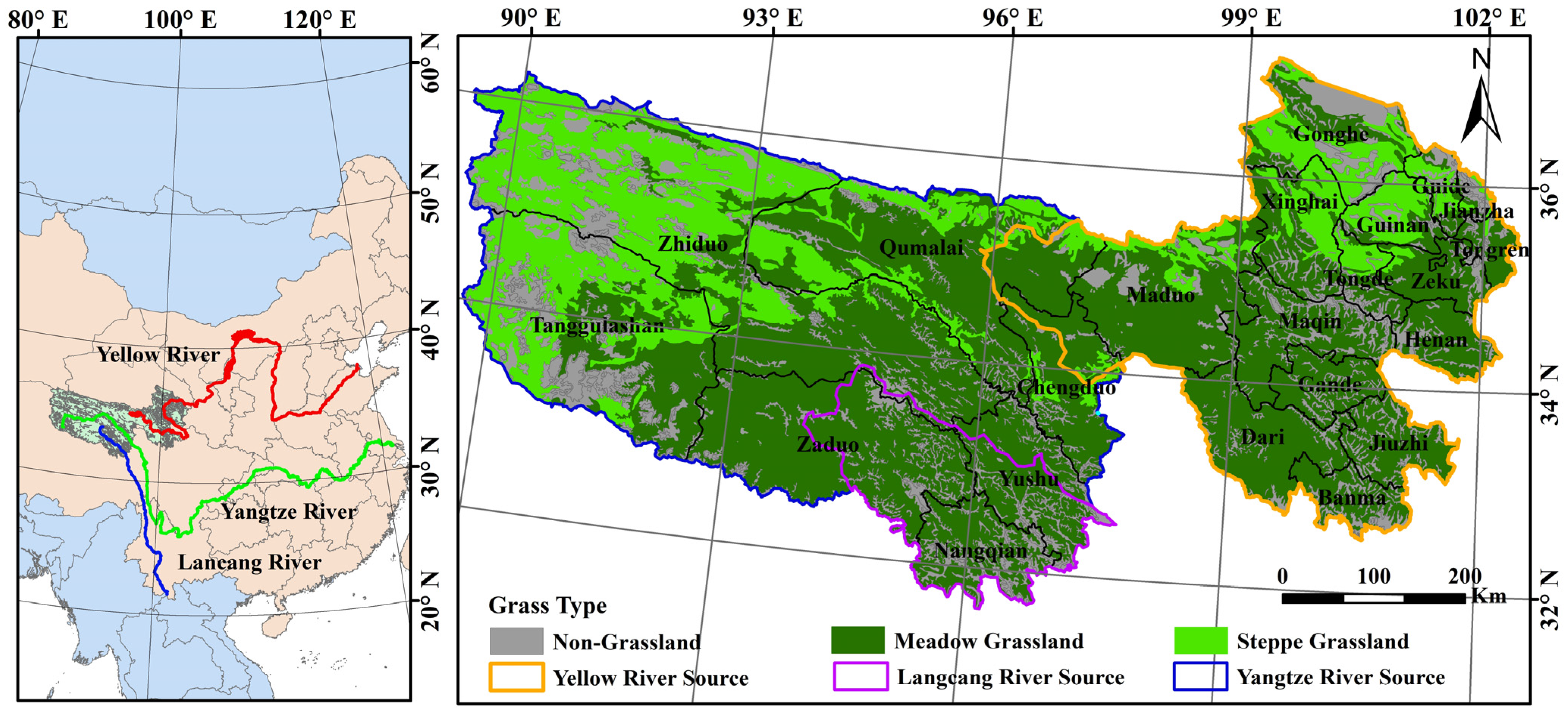
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
2.2.3. Data on the Type of Vegetation
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. NPP Estimation
2.3.2. Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Analysis of Abrupt Changes
2.3.4. Contribution Degree Analysis of the Abrupt Change in NPP
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Variation of Grassland NPP
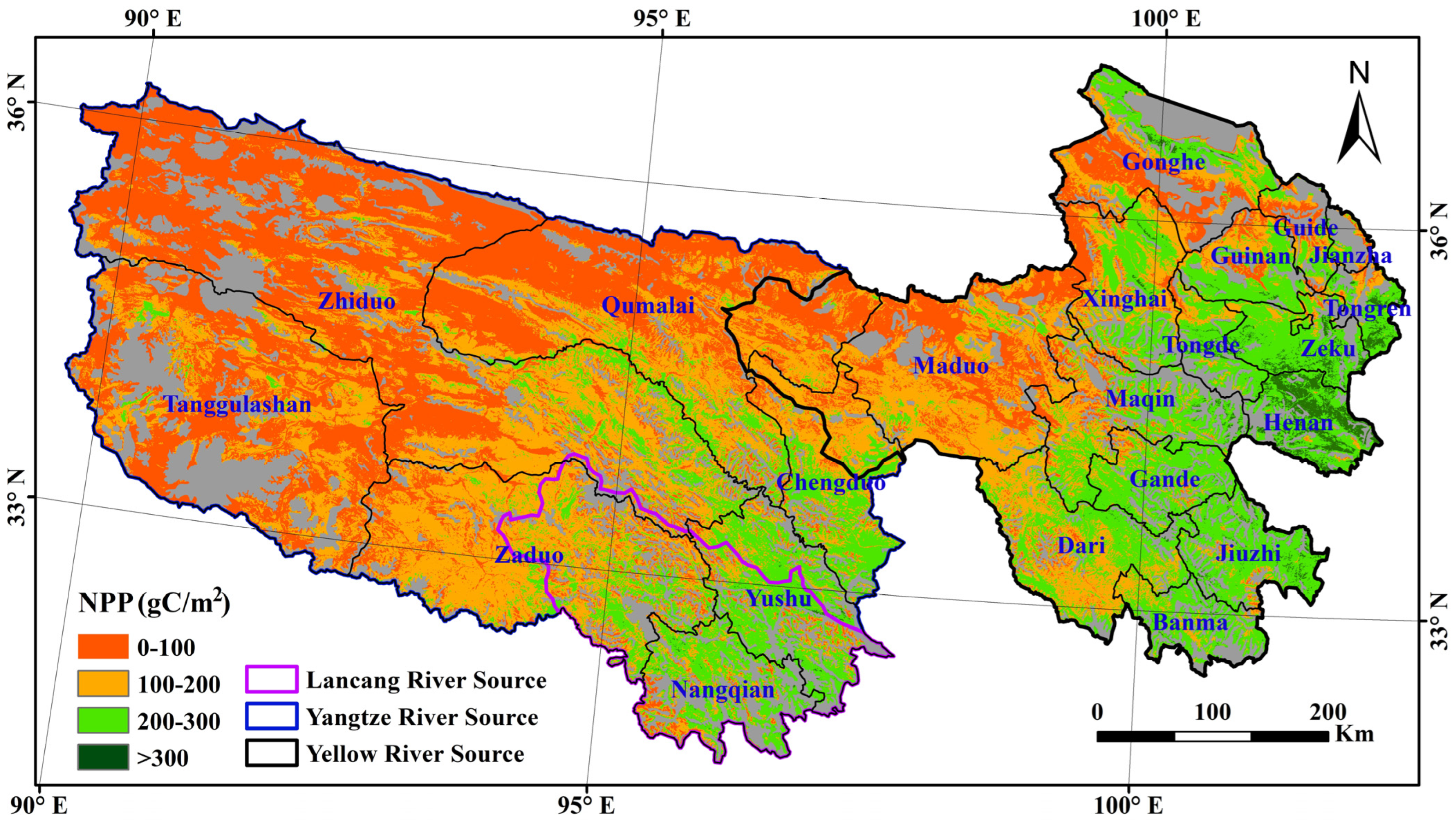
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution of NPP from 2000 to 2019
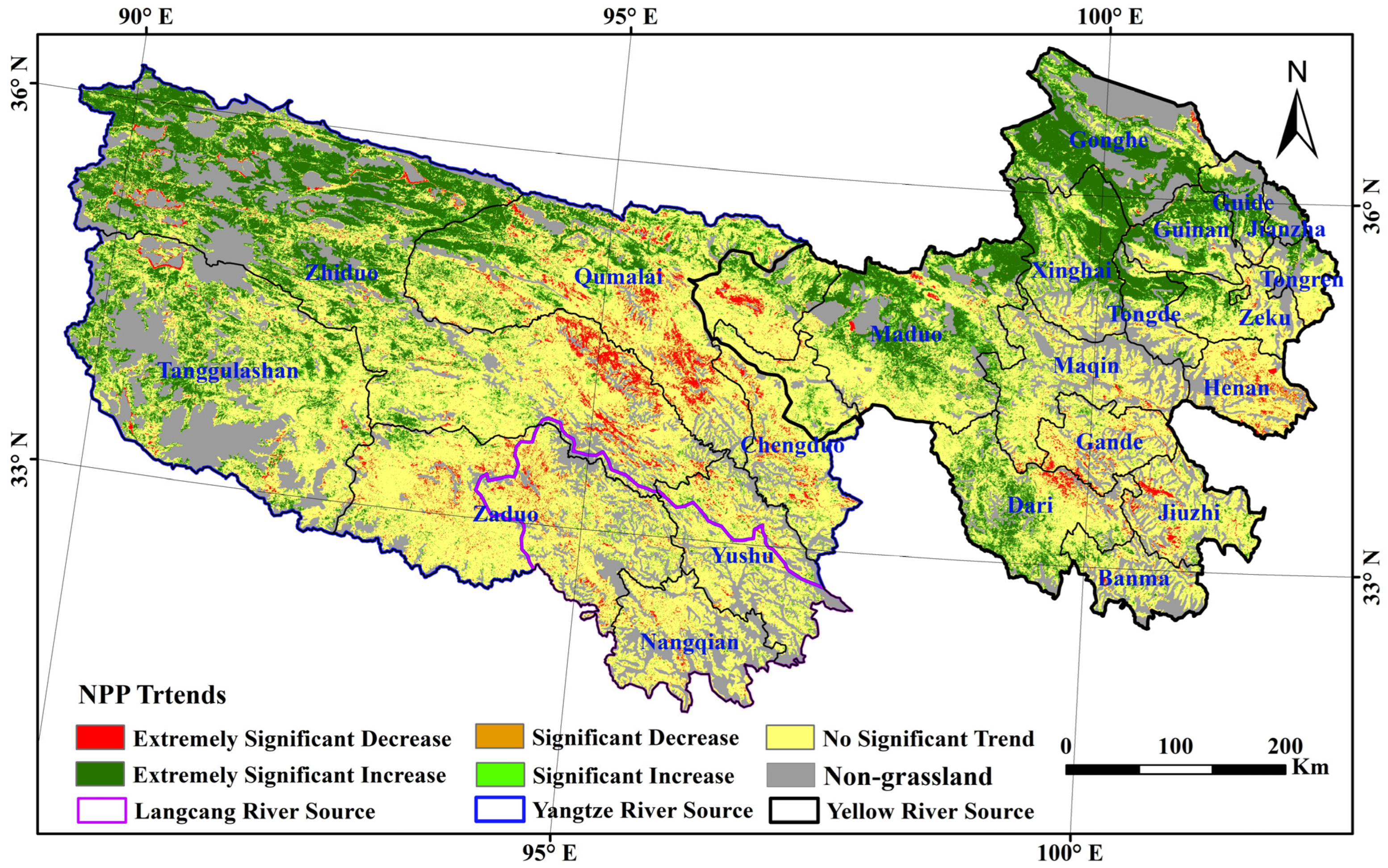
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution of NPP Changes from 2000 to 2019
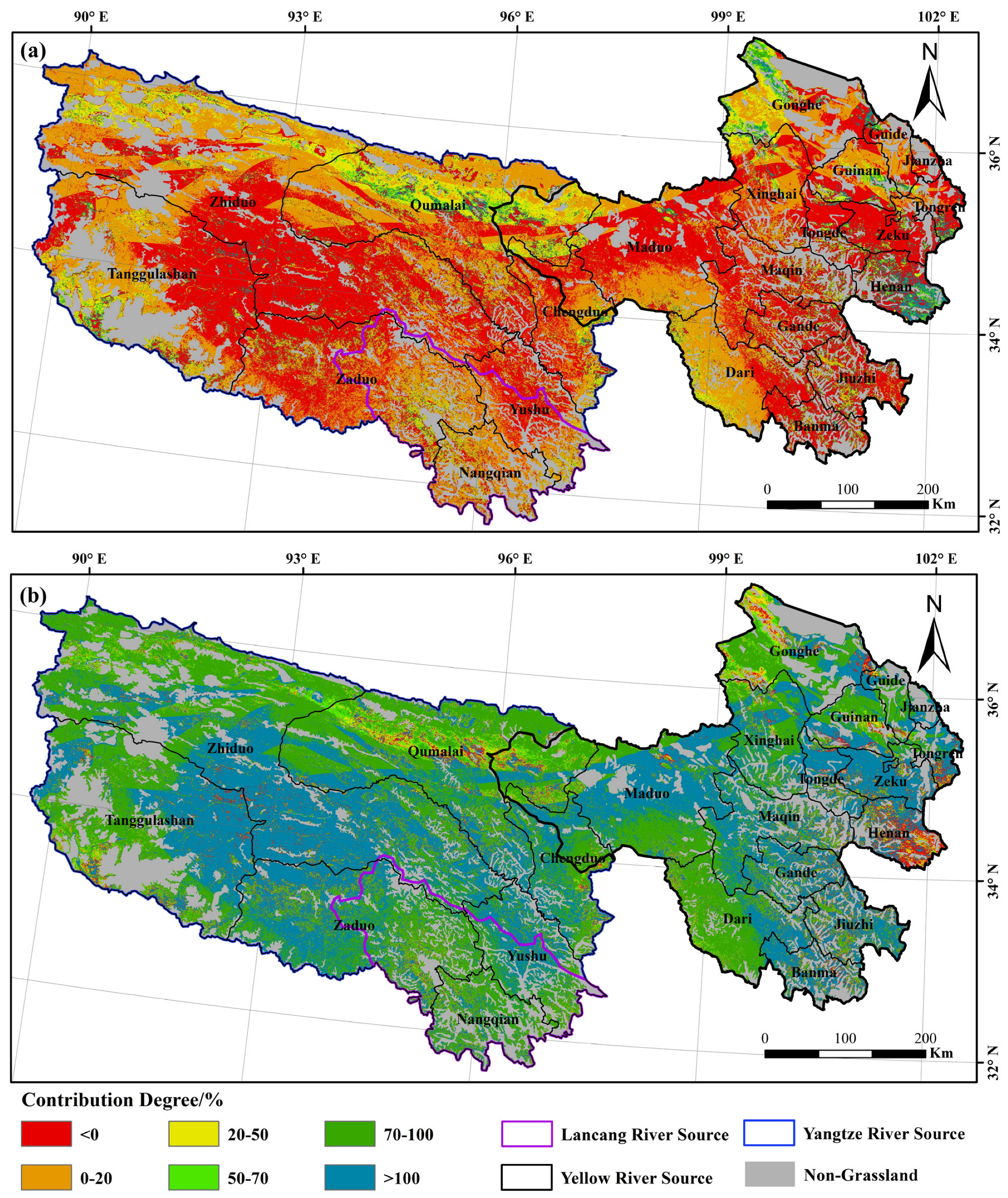
3.2. Analysis of the Degree of Contribution to the Change in NPP of Grassland
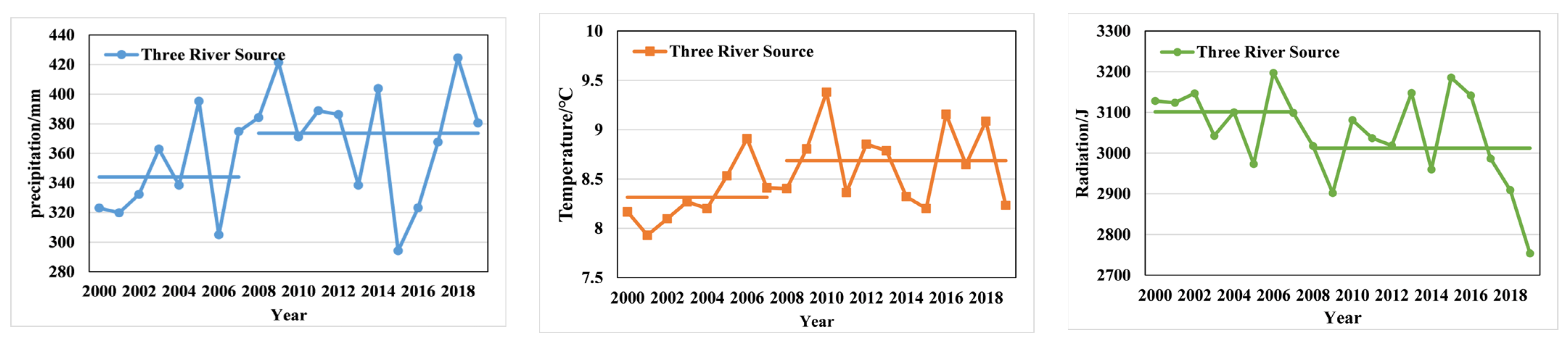
3.2.1. Abrupt Change Analysis of NPP and Meteorological Factors
3.2.2. Analysis of the Human and Meteorological Contribution to the Change of Grassland NPP
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of NPP
4.2. Influence of Meteorological Factors on NPP
4.3. Influence of Ecological Engineering and Policy on NPP
5. Conclusions
- (1)
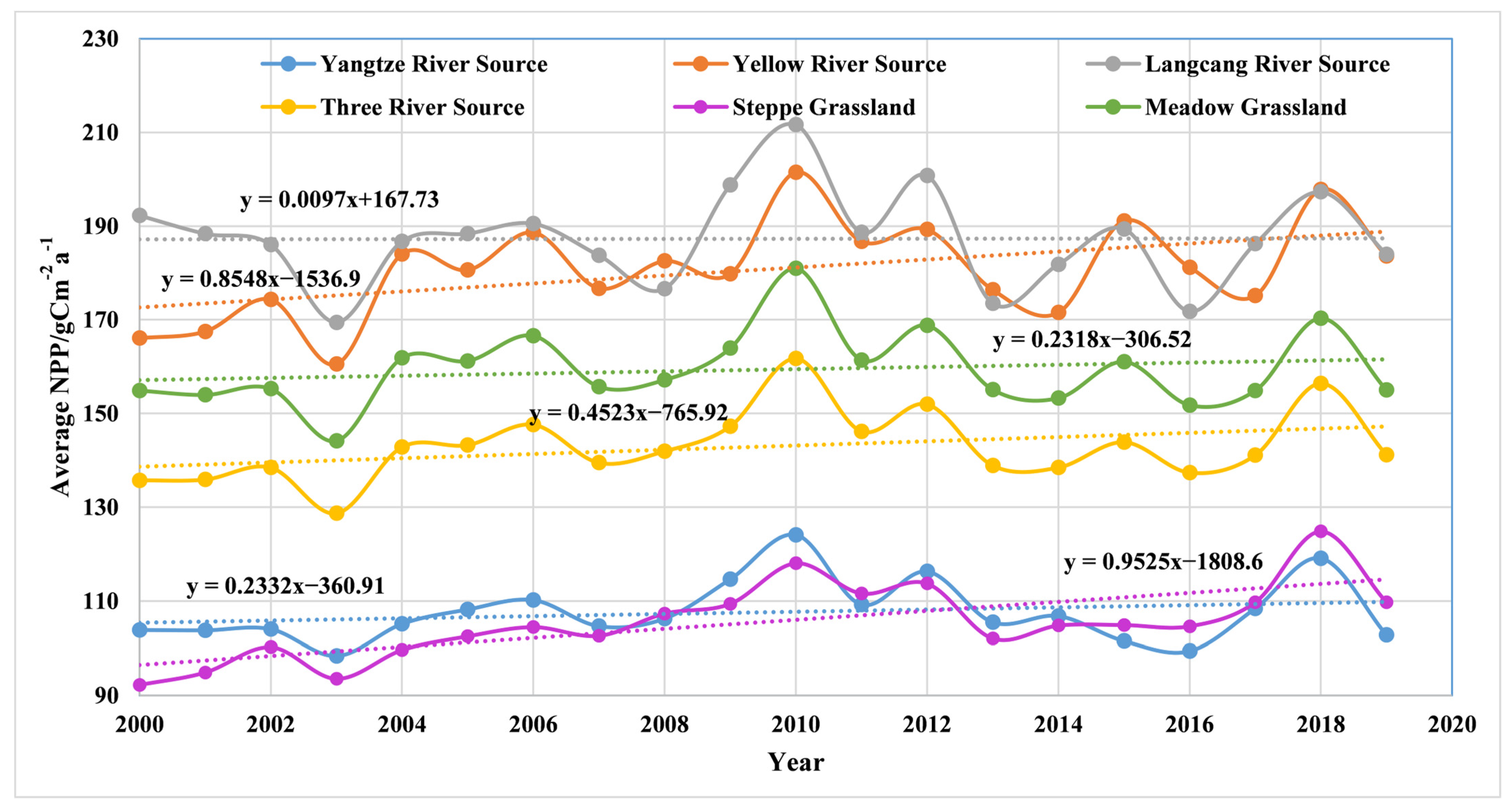
- The grassland NPP in the TRH region showed an overall increasing trend, but the trend was not significant. The average grassland NPP of the TRH region was about 142.90 gC/m−2a−1. The NPP values of the Yellow River Source and the Lancang River Source were higher than the average NPP of the TRH region, while the NPP of the Yangtze River Source was significantly lower than the average value. The annual average grassland NPP of the TRH region and three sub-regions showed an alternating increase-decrease-increase fluctuation, but the overall increasing trend was not significant in more than 60% of the TRH region. Only about 30% of the regions in the Yellow River Source and the Yangtze River Source had a significant increase.
- (2)
- Human factors were the determining factors for the abrupt increase in grassland NPP in the TRH region. Abrupt increases in precipitation, temperature, and radiation in the TRH region and sub-regions mostly occurred around 2005, while abrupt increases in NDVI and NPP, which reflected the impact of human activities, occurred in 2008. The difference in the timing of the abrupt increases between meteorological and human factors indicated that human factors were the decisive factors for the abrupt increase in grassland NPP in the study area.
- (3)
- The contribution of human factors to the abrupt increase in grassland NPP in the TRH region was significantly higher than that of the meteorological factors. The contributions of human factors to the abrupt increase in NPP in three sub-regions were generally above 98%. The contributions of human factors generally exceeded 100% in the eastern part of Tanggulashan County, the southeastern part of Zhiduo County, and the western part of Zaduo County in the Yangtze River Source and most areas in the Yellow River Source.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, J.Z.; Lin, H.L. Assumed plan on grassland ecological reconstruction in the source region of Yangtse River, Yellow River and Lantsang River. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2005, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hong, F.Z.; Zong, J.Y. Resource and their sustainable utility in the “Three-River Headwaters” Region. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2005, 13, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Doris, C.; Cristan, S.K.; Marcus, J.L.; Raudsepp-Hearne, C. Ecosystems and Human Well Being: Multiscale Assessment s1 Volume 4; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 16–301. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37717295_Ecosystems_and_Human_Well-Being_Multiscale_Assessments_Findings_of_the_Sub-Global_Assessments_Working_Group (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Liu, X.D.; Chen, B.D. Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Y.; Chu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Xu, M.Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.L.; Zhai, P.M.; Shao, X.M.; Zhang, A.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; et al. Recent progresses in studies of regional temperature changes in China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.M.; Wu, G.X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.M. New proofs of the recent climate warming over the Tibetan Plateau as a result of the increasing greenhouse gases emissions. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Ma, Y.S.; Bai, Y.F. An analysis of the impact of climate change on vegetation succession in Qinghai Province. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Dong, W.J.; Yu, Y.Q.; Feng, J.M. A pre-diction of trend of the future climate change in the western China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Ren, G.Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Gong, P.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhai, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.C.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, H.J.; et al. National assessment report of climate change (I): Climate change in China and its future trend. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2006, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, L.S.; Bai, W.Q.; Shen, Z.X.; Yan, J.Z.; Ding, M.J.; Li, S.C.; Zheng, D. Grassland degradation in the source region of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xie, G.D.; Shen, Z.X. Analysis of formation causes of grassland degradation in Maduo County in the source region of Yellow River. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 823–826. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.F.; Liu, F.G. Spatial dis-parity of NDVI response in vegetation growing season to climate change in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.Y.; Xiao, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J.M. Vegetation change and its response to climate change in Three-River Source Region. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2006, 2, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Sun, X.Q. Research about analysis of the causes of ecological degradation of the pastoral areas in Qinghai- with the case study of the grassland degradation in the three rivers. Qinghai Prataculture 2009, 18, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Waiz, R. Development of environmental indicator systems: Experiences from Germany. Environ. Manag. 2000, 25, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.S.; Zhao, M.C.; Zheng, J.Y.; Fang, X.Q. Study on division of the terrestrial system in China. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2002, 57, 515–522. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.M.; Wang, T.; Xie, C. Eco-environmental degradation in the source region of the Yellow River, Northeast Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 122, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Shao, Q.Q. Grassland degradation in the “Three-River Headwaters”region, Qinghai Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Liu, R. Changing inland lakes responding to climate warming in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Li, B.L.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Ding, L.L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, L.L. Review on the estimation of net primary productivity of vegetation in the Three-River Headwater Region, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1596–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.C.; Fan, J.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.L. Effects of an ecological conservation and restoration project in the Three-River Source Region, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 27, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Y.; Chen, K.L. Study on dynamic change of vegetation coverage in Sanjiangyuan National Park from 2005 to 2015. Qinghai Prataculture 2019, 28, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.X.; Jiao, J.; Pan, J.H.; Song, J.Y.; Che, Y.D.; Li, L.R. Spatial and temporal patterns of planting NPP and its driving factors in Qinghai Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5306–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, B.; Tamura, M. Integrating remotely sensed data with an ecosystem model to estimate net primary productivity in East Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P.G. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, W.; Noble, I.; Canadell, J.; Apps, M.; Schulze, E.D.; Jarvis, P.G. The terrestrial carbon cycle: Implications for the Kyoto Protocol. Science 1998, 280, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, Q.H. Application of CASA model to the estimation of Chinese terrestrial Net Primary Productivity. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2001, 25, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.P.; Qin, Z.H.; Xie, W. A research of monitoring grassland degradation based on mono temporal MODIS data. Chin. J. Grassl. 2007, 29, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Xin, X.P.; Wang, D.L. Application of improved CASA model in productivity evaluation of grassland in Inner Monglia. Chin. J. Ecol. 2007, 26, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hua, T. Roles of climate changes and human interventions in land degradation: A case study by net primary productivity analysis in China’s Shiyanghe Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Sun, Z.G.; Li, J.L.; Gang, C.C.; Zhang, C.B. Desertification dynamic and the relative roles of climate change and human activities in desertification in the Heihe River Basin based on NPP. J. Arid Land 2013, 5, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.J.; Zhou, S.X.; Chen, Y.Z.; Li, J.L.; Ju, W.M.; Odeh, I. Assessing the impact of restoration-induced land conversion and management alternatives on net primary productivity in Inner Mongolian grassland, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 108, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Shao, Q.Q. A simulation on changes in vegetation productivity in Three River Sources Nature Reserve, Qinghai Province over past 20 years. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Sun, Y.X.; Zhao, H.D.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, M.Q. Grassland dynamics and their driving factors associated with ecological construction projects in the Three-River Headwaters Region based on multi-source data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.J.; Xu, Y.J. Using NPP and EVI to assess the ecological status of the Sanjiangyuan area. Grassl. Turf 2021, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Lu, G.X.; Ye, H.; Wang, C.Y. Changes and influencing factors of vegetation net primary productivity in the Sanjiangyuan National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5559–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhai, Y.H.; Zhou, X.P. Spatial variation of long-term runoff trends and response to precipitation change in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Li, B.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Ding, L.L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, L.L. A systematic review of research studies on the estimation of net primary productivity in the Three-River Headwater Region, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 27, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Long, R.J.; Lin, H.L.; Ren, J.Z. Study on pastoral ecosystem security and its assessment. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2008, 17, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bai, W.Q.; Yan, J.Z.; Ding, M.J.; Shen, Z.X.; Li, S.C.; Zheng, D. Characteristics of grassland degradation and driving forces in the source region of the Yellow River from 1985 to 2000. J. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Piao, S.L. Variations in grassland vegetation cover in relation to climatic factors on the Tibetan plateau. J. Plant Ecol. 2006, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.G.; Veroustraete, F. Interannual change trend of NDVI from 1981 to 2001 in the Heihe River Basin, China. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Vegetation User Conference, Antwerp, Belgium, 24–26 March 2004; pp. 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.L.; Ding, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.F.; Yan, J.Z.; Bai, W.Q.; Zheng, D. Spatial charac-teristic of vegetation change in the source regions of the YangtzeRiver, Yellow River and Lancang River in China. Geo-Graph. Res. 2007, 26, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Tan, H.C.; Deng, Y.C.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Tang, Y.H.; Higashi, T.; Cui, X.Y. Partitioning patttern of carbon flux in a Kobresia grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau revealed by field 13C pulse-labeling. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 2322–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Lu, L. Comparison study of spatial interpolation methods of air temperature over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2003, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, L.T.; Mcvicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Yang, Q.K. Introduction of the professional interpolation software for meteorology data: ANUSPLINN. Meteorol. Mon. 2008, 34, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.T.; Mckenney, D.W.; Nalder, I.A.; Hutchinson, J.L.; Kesteven, J.L. A comparison of two statistical methods for spatial interpolation of Canadian monthly mean climate data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 101, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.L.; Lv, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.H. Application and assessment of spatial interpolation method on daily meteorological elements based on ANUSPLIN software. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2010, 26, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.L.; Liu, F.; Duo, H.R.; Li, D.Q. The comparison of spatial interpolation methods on temperature and precipitation of Sanjiangyuan area. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2010, 1, 7–11+57. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Shao, H.B.; Zhu, W.Q.; Pan, Y.Z. Modeling net primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems in East Asia based on an improved CASA ecosystem model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4851–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Q.; Pan, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.S. Estimation of net primary productivity of Chinese terrestrial vegetation based on remote sensing. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 31, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, H.L.; Yao, S.B. Spatial and temporal response of vegetation cover to climate change in different zones of Sichuan-Shaanxi area during growing season. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 5218–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.L.; Wei, J.H.; Xie, H.W. Characteristics of wetness dryness variation and their influences in the Three-River Headwaters region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 8397–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Q.; Li, Q.J.; Liu, X.S.; Tang, H.B.; Li, Y. Variation Characteristics of Runoff Time Series in the Source Region of Three Rivers. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2017, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Gu, S.; Xu, W.J.; Jiang, S.; Xiao, R.X.; Xiao, J.S.; Zhang, J. Spatial pattern and its variations of aridity/humidity during 1971–2010 in Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Arid Land Geogr. 2012, 35, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.T.; Yang, W.D.; Gao, B.; Yang, H.B.; Hu, H.P. Hydrological trend analysis in the Yellow River basin using a distributed hydrological model. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W00A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.; Adhikari, P.; Li, L.; Su, F.G. Quantitative assessment of climate change and human impacts on long-term hydrologic response: A case study in a sub-basin of the Yellow River, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L.; Yong, B.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.L. Analyzing the effects of climate variability and human activities on runoff from the Laohahe basin in northern China. Hydrol. Res. 2012, 43, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Tang, W.J.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.Y.; Xie, J.L.; Ma, C.; Yan, C.Z. Change in grassland productivity in Qinghai Province and its driving factors. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2022, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, J.B. Analysis of net primary productivity of terrestrial vegetation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, based on MODIS remote sensing data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y. Terrestrial net primary production and its spatio-temporal patterns in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China during 1982–1999. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 17, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.P.; Ou, Y.H.; Wang, Q.X.; Masatak, W.; Sun, Q.Q. Estimation of Net Primary Production in Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2004, 59, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Tong, L.J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, J.L. Spatiotemporal dynamics of China’s grassland NPP and its driving factors. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.F.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of vegetation Net Primary Productivity and its carbon sequestration value in Three-River Headwater Region during 1999–2012. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, X.; Wu, L.C.; Zhang, J.P. Estimation of net primary production in the Three-River headwater region using CASA model. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.B.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, R.Y. Responses of Net Primary Productivity of natural vegetation to climatic change over source regions of yangtze river in 1959–2008. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.R.; Zhu, S.C.; Li, H.M. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity and Its Responses to Climate Change in Three-river Headwaters Region. J. Arid Meteorol. 2016, 34, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischnewski, J.; Kramer, A.; Kong, Z.; Mackay, A.W.; Simpson, G.L.; Mischke, S.; Herzschuh, U. Terrestrial and aquatic responses to climate change and human impact on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau during the past two centuries. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3376–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.Y. The climate change and adaptation strategies for sustainable development in the Three-River Headwaters Region in Qinghai Province in recent half century. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 32, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C. Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trends | Sen Slope (β) | MK Test (Z) |
|---|---|---|
| Extremely significant increase | β > 0 | Z > 2.58 |
| Significant increase | β > 0 | 1.96 < Z ≤ 2.58 |
| No significant trend | --- | −1.96 ≤ Z ≤ 1.96 |
| Significant decrease | β < 0 | −2.58 ≤ Z < −1.96 |
| Extremely significant decrease | β < 0 | Z < −2.58 |
| Region | NPP Grade Proportion/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–100 gC/m−2a−1 | 100–200 gC/m−2a−1 | 200–300 gC/m−2a−1 | >300 gC/m−2a−1 | |
| TRH | 36.81 | 36.58 | 25.04 | 1.57 |
| Yangtze River Source | 52.92 | 37.11 | 9.90 | 0.07 |
| Yellow River Source | 20.54 | 35.06 | 40.62 | 3.78 |
| Lancang River Source | 12.27 | 39.95 | 46.92 | 0.87 |
| Steppe grassland | 58.94 | 27.49 | 13.38 | 0.20 |
| Meadow grassland | 27.06 | 40.59 | 30.18 | 2.17 |
| Region | NPP Change Trend Ratio/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extremely Significant Decrease | Significant Decrease | No Significant Trend | Significant Increase | Extremely Significant Increase | |
| TRH | 4.00 | 2.05 | 62.51 | 6.46 | 24.99 |
| Yangtze River Source | 4.85 | 2.24 | 60.39 | 6.50 | 26.02 |
| Yellow River Source | 2.75 | 1.52 | 59.92 | 7.17 | 28.64 |
| Lancang River Source | 4.38 | 3.18 | 85.92 | 3.18 | 3.35 |
| Steppe grassland | 2.35 | 0.97 | 39.37 | 8.16 | 49.14 |
| Meadow grassland | 4.72 | 2.52 | 72.70 | 5.71 | 14.35 |
| Region | Index | Detection Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK Test | Cumulative Departure | Pettitt Test | ||
| Yangtze River Source | Precipitation | --- * | 2005 ↑ * | 2007 ↑ |
| Radiation | 2005 ↑ | 2005 ↑ | 2007 ↑ | |
| Temperature | 2003 ↑ | 2004 ↑ | 2004 ↑ | |
| NDVI | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | |
| NPP | 2003 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | |
| Yellow River Source | Precipitation | 2003 ↑ | 2003 ↑ | 2004 ↑ |
| Radiation | 2005 ↑ | 2005 ↑ | 2002 ↑ | |
| Temperature | 2005 ↑ | 2005 ↑ | 2004 ↑ | |
| NDVI | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | |
| NPP | 2003 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | |
| Lancang River Source | Precipitation | --- | 2014 ↓ * | 2014 ↓ |
| Radiation | --- | 2005 ↑ | 2016 ↑ | |
| Temperature | 2005 ↑ | 2005 ↑ | 2005 ↑ | |
| NDVI | --- | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | |
| NPP | 2008 ↑ | 2008 ↑ | 2012 ↑ | |
| NPP | TRH | Yangtze River Source | Yellow River Source | Lancang River Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Period | 141.87 | 107.09 | 178.9 | 186.8 |
| Change Period | 149.39 | 112.76 | 189.57 | 191.69 |
| Simulation | 141.63 | 107.1 | 178.06 | 187.75 |
| Region | Factors | Contribution Degree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0 * | 0–20 | 20–50 | 50–70 | 70–100 | >100 * | Mean | ||
| TRH | Meteorology | 46.92 | 30.29 | 12.6 | 2.86 | 2.22 | 5.11 | 1.8 |
| Human | 5.11 | 1.29 | 3.79 | 6.13 | 36.76 | 46.92 | 98.2 | |
| Yangtze River Source | Meteorology | 47.35 | 31.25 | 13 | 2.58 | 1.81 | 4 | −0.37 |
| Human | 4 | 1.04 | 3.36 | 6.23 | 38.02 | 47.35 | 100.37 | |
| Yellow River Source | Meteorology | 48.66 | 26.6 | 11.81 | 3.28 | 2.83 | 6.83 | 2.41 |
| Human | 6.83 | 1.66 | 4.44 | 5.96 | 32.45 | 48.66 | 97.59 | |
| Lancang River Source | Meteorology | 36.91 | 40.47 | 13.67 | 2.7 | 1.99 | 4.28 | 4.43 |
| Human | 4.28 | 1.14 | 3.54 | 6.33 | 47.8 | 36.91 | 95.57 | |
| Steppe grassland | Meteorology | 36.88 | 40.84 | 14.44 | 2.51 | 1.79 | 3.55 | 4.25 |
| Human | 3.55 | 1.00 | 3.30 | 6.28 | 49.00 | 36.88 | 95.75 | |
| Meadow grassland | Meteorology | 51.30 | 25.68 | 11.80 | 3.02 | 2.41 | 5.80 | −0.24 |
| Human | 5.80 | 1.42 | 4.01 | 6.07 | 31.40 | 51.30 | 100.24 | |
| Scholars | Grassland NPP | Study Area | Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piao, S.L. (2002) | 121.39 | Qinghai Plateau | CASA |
| Zhou, C.P. (2001) | 161.4 | Qinghai Plateau | TEM |
| Zhao, G.S. (2011) | 102 | Qinghai Province | NPP—EMSC |
| Chen, Z.Q. (2012) | 135 | Qinghai Plateau | GLO—PEM |
| Wo, X. (2014) | 162.87 | Three River Source | CASA |
| Wang, Y.H. (2022) | 138.5 | Qinghai Province | CASA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hao, C.; Wang, H. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Contribution of Human and Meteorological Factors to Grassland Net Primary Productivity in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 2000 to 2019. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020278
Song Y, Liang T, Zhang L, Hao C, Wang H. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Contribution of Human and Meteorological Factors to Grassland Net Primary Productivity in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 2000 to 2019. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020278
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yang, Tian Liang, Linbo Zhang, Chaozhi Hao, and Hao Wang. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Changes and Contribution of Human and Meteorological Factors to Grassland Net Primary Productivity in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 2000 to 2019" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020278
APA StyleSong, Y., Liang, T., Zhang, L., Hao, C., & Wang, H. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Changes and Contribution of Human and Meteorological Factors to Grassland Net Primary Productivity in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 2000 to 2019. Atmosphere, 14(2), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020278






