Analysis and Evaluation of the Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Data from the FENGYUN-4A/AGRI over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Research Data
2.2.1. FY-4A/AGRI LPW
2.2.2. Radiosonde Observation Data
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Three-Dimensional Matching between FY-4A/AGRI LPW and RAOB Data
2.3.2. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The Precision of FY-4A/AGRI LPW in Vertical Height Layer
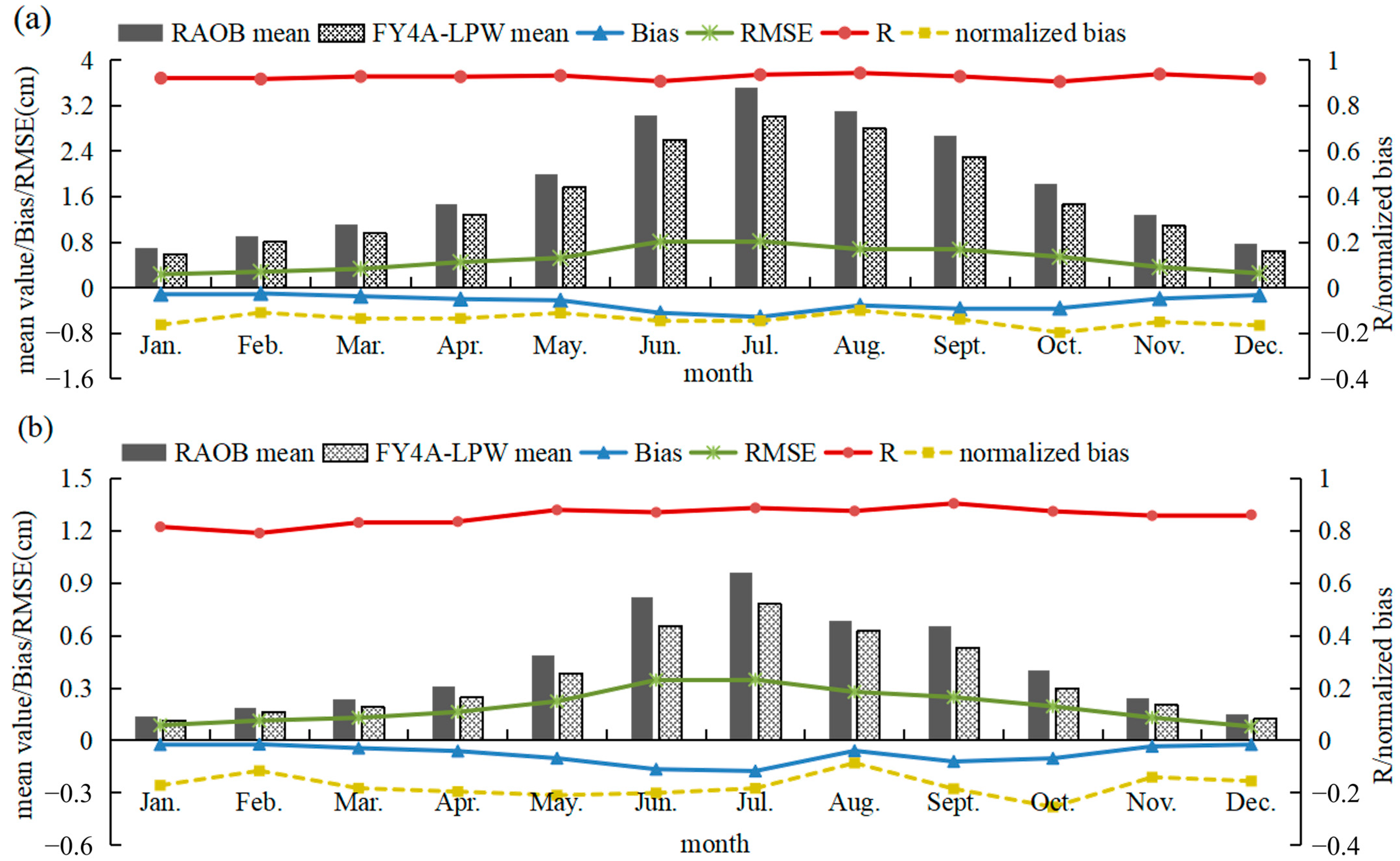
3.2. The Precision of FY-4A/AGRI LPW in Different Month
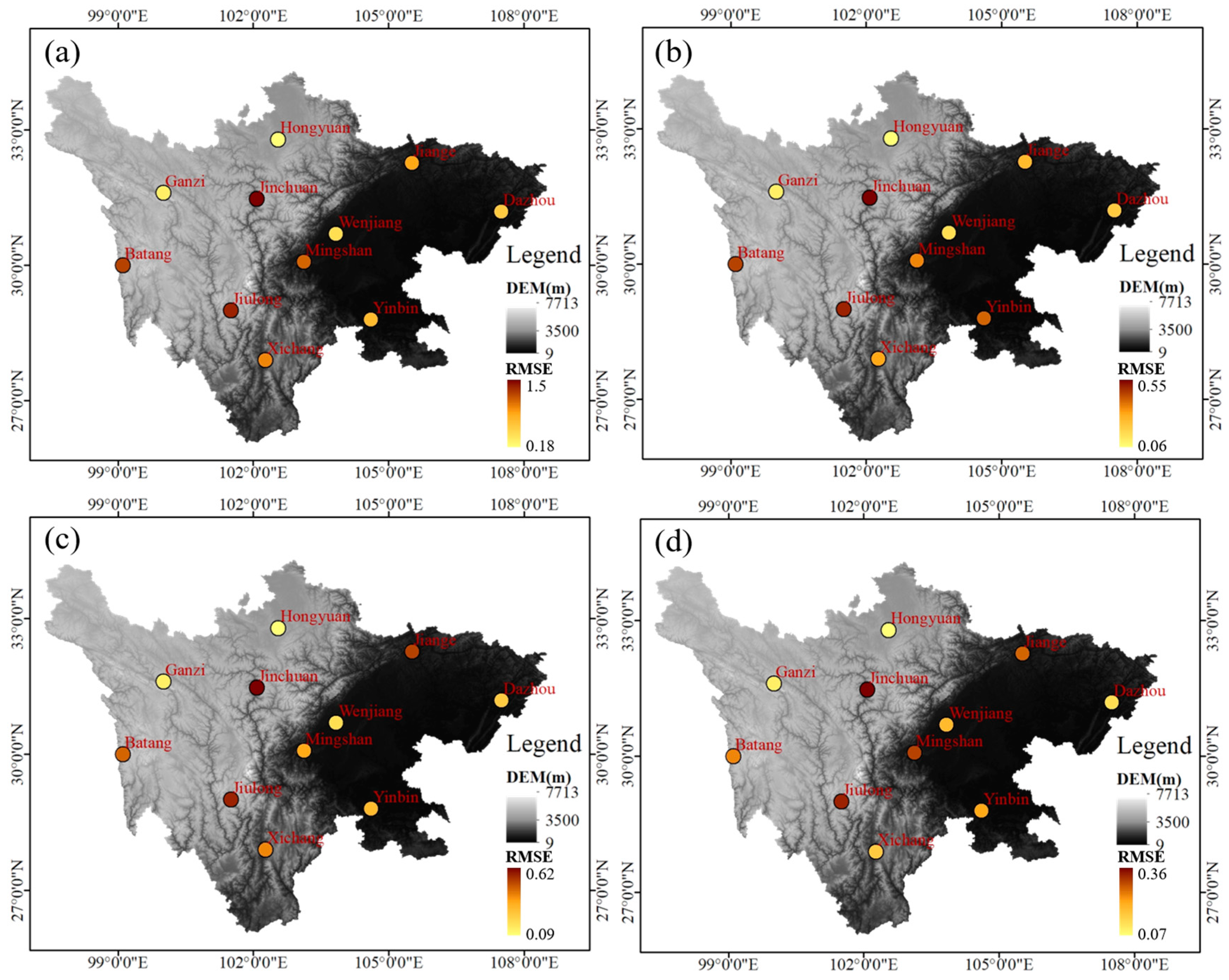
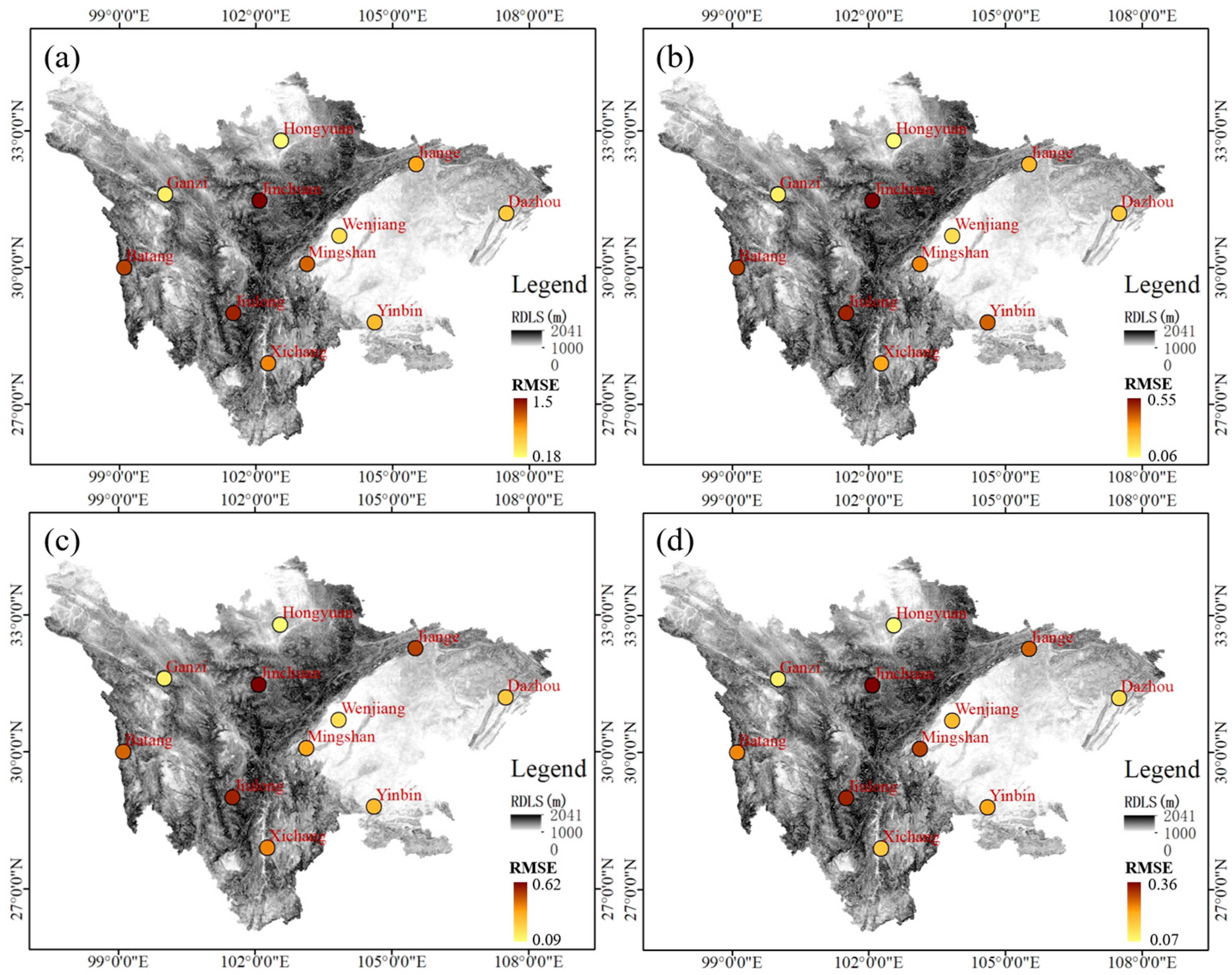
3.3. The Precision of FY-4A/AGRI LPW in Spatial Distribution
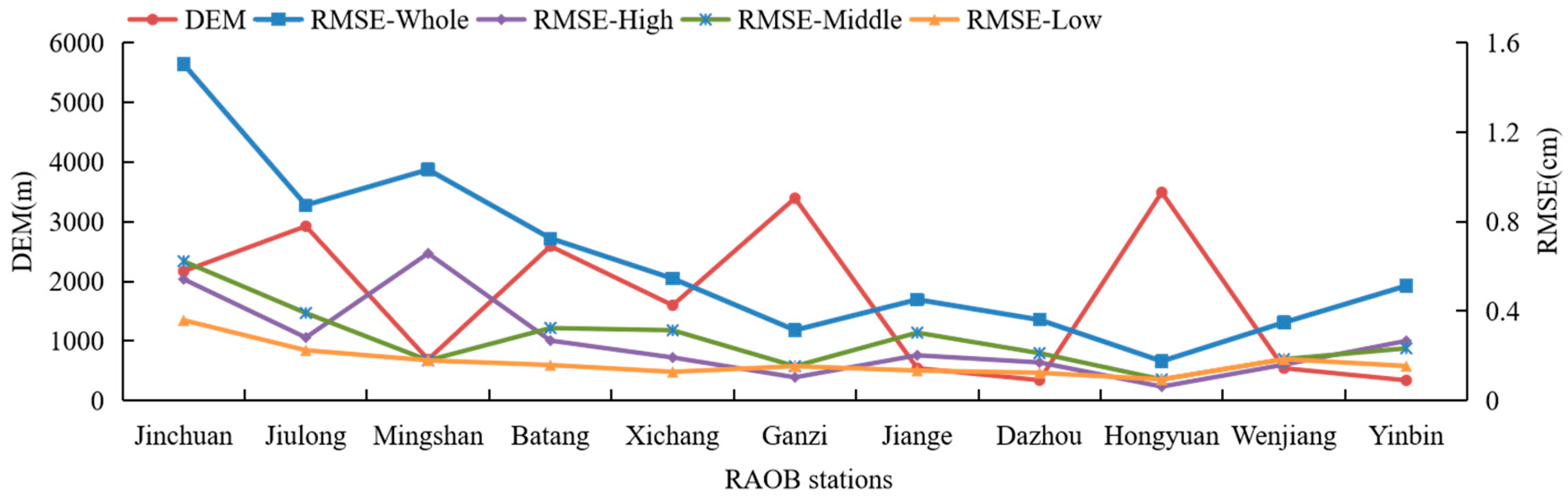
3.3.1. The Correlation between the Precision of FY-4A/AGRI LPW and DEM
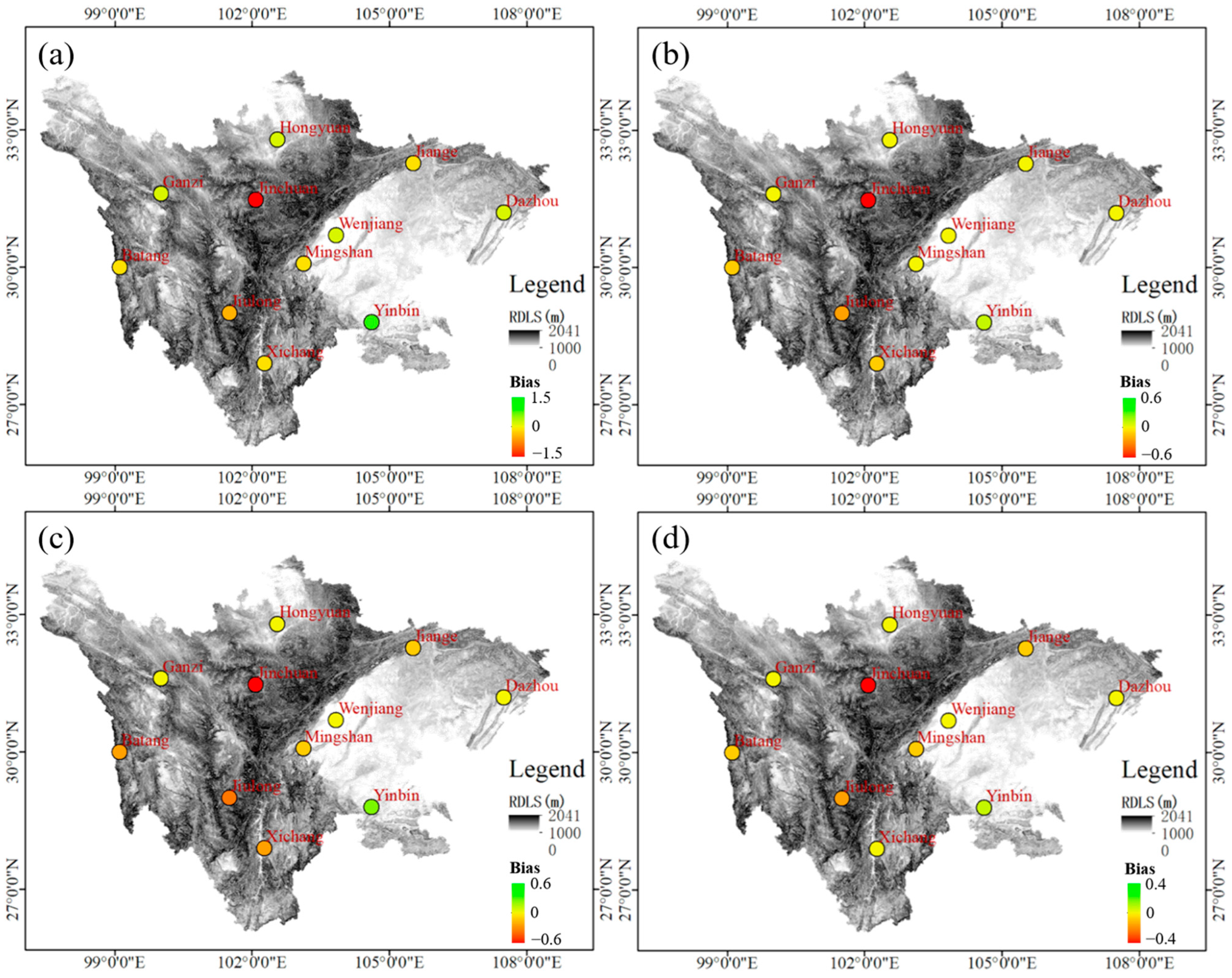
3.3.2. The Correlation between the Precision of FY-4A/AGRI LPW and Relief Degree of Land Surface
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Jin, S.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ping, F. High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, J.B. Understanding the Influence of Measurement Uncertainty on the Atmospheric Transition in Rainfall and Column Water Vapor. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Feng, G. Water Vapor Transport Related to the Interdecadal Shift of Summer Precipitation over Northern East Asia in the Late 1990s. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.; Mateus, P. A new unconstrained approach to GNSS atmospheric water vapor tomography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, ee2021GL094852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.; Smith, L.; Qian, T.; Dai, A.; Fasullo, J. Estimates of the Global Water Budget and Its Annual Cycle Using Observational and Model Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Qiu, G.; Tang, S.; Shang, L.; Dai, Q.; Hou, Y. Seasonal variation of gaseous mercury exchange rate between air and water surface over Baihua reservoir, Guizhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Shen, Z.; Wan, M.; Wan, M.; Li, L. Perceptible Water Vapor Converted from GNSS-ZTD and ERA5 Datasets for the Monitoring of Tropical Cyclones. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87275–87290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rosenlof, K.; Portmann, R.; Daniel, J.; Davis, S.; Sanford, T.; Plattner, G. Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science 2010, 5970, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Grzegorski, M.; Platt, U. Global trends (1996–2003) of total column precipitable water observed by Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME) on ERS-2 and their relation to near-surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 2193–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.; Fasullo, J.; Smith, L. Trends and variability in column-integrated atmospheric water vapor. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 24, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, Y.; Sato, K.; Yabuki, M.; Tsuda, T. Comparison of shipborne GNSS-derived perceptible water vapor with radiosonde in the western North Pacific and in the seas adjacent to Japan. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zou, R.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Xia, X. Radiative Transfer Model Simulations for Ground-Based Microwave Radiometers in North China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, P. New Gridded Product for the Total Columnar Atmospheric Water Vapor over Ocean Surface Constructed from Microwave Radiometer Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. Application of Microwave Radiometer in Monitoring Water Vapor Characteristics and Precipitation Analysis. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 44, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Validating HY-2A CMR precipitable water vapor using ground-based and shipborne GNSS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, M.; Rorland, P.; Pottiaux, E.; Stankunavicius, G.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T.; Brenot, H.; Bruyninx, C.; Jones, J. Global Spatiotemporal Variability of Integrated Water Vapor Derived from GPS, GOME/SCIAMACHY and ERA-Interim: Annual Cycle, Frequency Distribution and Linear Trends. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Galina, D.; Jens, W.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, K.; Harald, S. Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Sun, X.; Sang, J.; Wei, X. Modify the Accuracy of MODIS PWV in China: A Performance Comparison Using Random Forest, Generalized Regression Neural Network and Back-Propagation Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, H.; Li, X. Real-Time Sensing of Precipitable Water Vapor from BeiDou Observations: Hong Kong and CMONOC Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 7897–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.R.; Crisp, D.; Ott, L.E.; O’Dell, C.W. High-accuracy measurements of total column water vapor from the orbiting carbon observatory-2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12261–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Assessment of Spectra of the Atmospheric Infrared Ultraspectral Sounder on GF-5 and Validation of Water Vapor Retrieval. Sensors 2021, 21, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Z. Water vapor retrieval from MERSI NIR channels of Fengyun-3B satellite using ground-based GPS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niell, A.; Coster, A.; Solheim, F.; Mendes, V.; Toor, P.; Langley, R.; Upham, C. Comparison of measurements of atmospheric wet delay by radiosonde, water vapor radiometer, GPS, and VLBI. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, B.; Joerg, S. Analysis of water vapor over Nigeria using radiosonde and satellite data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, S.; Li, J.; Menzel, W.; Gumley, L. Operational retrieval of atmospheric temperature, moisture, and ozone from MODIS infrared radiances. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1072–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Kaufman, Y.; Menzel, W.; Tanre, D. Remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, and water vapor properties from the moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.; Gao, B. Remote sensing of water vapor in the near IR from EOS/MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, FENGYUN-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, R.; Shen, F. Impacts of FY-4A AGRI Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of the Super Typhoon “In-Fa” (2021). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, P.; Weng, F.; Huang, W.; Zhu, J. Effects of Direct Assimilation of FY-4A AGRI Water Vapor Channels on the Meiyu Heavy-Rainfall Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, W.; Leng, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wan, R.; Wang, J. Evaluation and Improvement of FY-4A AGRI Quantitative Precipitation Estimation for Summer Precipitation over Complex Topography of Western China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.; Jin, F. Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, B.; Molnar, P. Signatures of Tibetan Plateau heating on Indian summer monsoon rainfall variability. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Ding, Y.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, W. What is the relationship between China summer precipitation and the change of apparent heat source over the Tibetan Plateau? Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2013, 14, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhong, A.; Li, Y. Characteristics of the precipitation over the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2010, 106, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, D. Temporal and spatial changes in estimated near-surface air temperature lapse rates on Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2907–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jun, L. A preliminary layer perceptible water vapor retrieval algorithm for FengYun-4 advanced geosynchronous radiation imager. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 7564–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, Z.; Jiang, X. An Assessment of the Temperature and Humidity of Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) v6 Profiles Using Radiosonde Data in the Lee of the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, H. FENGYUN-4A Advanced Geosynchronous Radiation Imager Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Products’ Comprehensive Evaluation Based on Quality Control System. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Xiao, C. Relief degree of land surface and its geographical meanings in the qinghai-tibet plateau, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, W.; Song, X. Relief Degree of Land Surface and Population Distribution of Mountainous Areas in China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 2, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Sun, Y. Geographical Detection of Spatial Heterogeneity and Drivers of PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Luo, J.; Deng, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, L. Influence of Topographic Factors on the Characteristics of Gully Systems in Mountainous Areas of Ningnan Dry-Hot Valley, SW China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, K. Neighborhood Analysis-Based Calculation and Analysis of Multi-Scales Relief Amplitude. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 468–471, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Q. A study on Optimal Statistical Unit of Relief Amplitude of Land Surface in Shaanxi Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 265–270+370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, A. Study on the Optimal Scale for Calculating the Relief Amplitude in China Based on DEM. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2012, 28, 8–12. [Google Scholar]






| Radiosonde Station | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batang | 30.00 | 99.10 | 2589 |
| Dazhou | 31.20 | 107.51 | 311 |
| Ganzi | 31.62 | 100.01 | 3394 |
| Hongyuan | 32.80 | 102.56 | 3422 |
| Jiange | 32.27 | 105.51 | 522 |
| Jinchuan | 31.29 | 102.04 | 2165 |
| Jiulong | 29.00 | 101.50 | 2919 |
| Mingshan | 30.08 | 103.11 | 690 |
| Wenjiang | 30.70 | 103.84 | 541 |
| Xichang | 27.90 | 102.28 | 1592 |
| Yinbin | 28.80 | 104.61 | 342 |
| Layers | R | Slope | Intercept |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abias-whole (cm) | 0.60 * | 0.0016 | 0.2153 |
| Abias-High (cm) | 0.35 | 0.0004 | 0.1198 |
| Abias-Middle (cm) | 0.66 ** | 0.0006 | 0.0992 |
| Abias-Low (cm) | 0.71 ** | 0.0004 | 0.2650 |
| RMSE-Whole (cm) | 0.54 * | 0.0012 | 0.4308 |
| RMSE-High (cm) | 0.27 | 0.0003 | 0.0704 |
| RMSE-Middle (cm) | 0.64 ** | 0.0005 | 0.1913 |
| RMSE-Low (cm) | 0.55 * | 0.0002 | 0.1376 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Han, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, G. Analysis and Evaluation of the Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Data from the FENGYUN-4A/AGRI over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020277
Song Y, Han L, Huang X, Wang G. Analysis and Evaluation of the Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Data from the FENGYUN-4A/AGRI over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020277
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yunfan, Lin Han, Xiaolong Huang, and Ge Wang. 2023. "Analysis and Evaluation of the Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Data from the FENGYUN-4A/AGRI over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020277
APA StyleSong, Y., Han, L., Huang, X., & Wang, G. (2023). Analysis and Evaluation of the Layered Precipitable Water Vapor Data from the FENGYUN-4A/AGRI over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere, 14(2), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020277






