Abstract
In recent years, vehicle emissions have become one of the important pollutant sources of the urban atmosphere. Scholars and decision-makers are constantly expected to accurately grasp the dispersion of vehicle pollutants to formulate a series of policies and strategies which can facilitate a friendly and sustainable urban environment, such as controlling the total number of vehicles, requiring higher emission standards, promoting new energy vehicles, improving public transit service, and optimizing non-motorized transportation systems. This paper provides a review of the mechanism research methods and mathematical modeling approaches for urban vehicle pollutant dispersion. The mechanism research methods reviewed include field measurements, wind tunnel experiments, and numerical simulations. The modeling approaches involve two kinds of popular models: Box models (STREET, CPBM, AURORA, PBM) and Gaussian models (CALINE, HIWAY, OSPM, CALPUFF, R-LINE, ADMS series, EPISODE, CityChem, SIRANE, MUNICH). Moreover, this paper clarifies the basic assumption, fundamental principle, related research, applicable conditions, and limitations of these mechanism research methods and modeling approaches.
1. Introduction
As an essential travel mode for urban residents, motor vehicles generate large amounts of air pollutants, especially during congestion. The layout of dense high-rise buildings in large cities further hinders the spread of vehicle pollutants to the surrounding areas, resulting in a noticeable impact on urban air quality. Unhealthy effects have been linked to high concentrations of designated pollutants generated through mobile-source emissions, e.g., hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, lead compounds, benzopyrene, and solid particles [1].
Some cities have begun to take a series of governance measures to make urban traffic more environmentally friendly and sustainable, such as controlling the total number of motor vehicles, requiring higher emission standards, promoting new energy vehicles, improving public transit service, and optimizing non-motorized transportation systems [2,3,4].
To hammer out more effective policies and strategies, it is essential to accurately predict the impact of vehicle emissions on air quality in different areas. The spatial and temporal distribution of vehicle pollutant concentrations can be calculated according to the pollutant source strength and dispersion state. In recent years, scholars have continued to study the mechanism of pollutant dispersion and model the relationship between the traffic state and the pollutant concentration distribution [5,6]. Despite the emergence of many enlightening works, there are still problems to be solved because of complex impact factors and the surrounding environment. For example, there will be a significant difference in the concentration of pollutants in open terrain and street canyons. The geometry of buildings and streets, meteorological environment, and wind speed are all significant impact factors to be considered [7]. One needs to carefully choose the corresponding models and methods to obtain plausible results with limited input data and computational resources. Therefore, this paper reviews the mechanism research methods and mathematical modeling approaches for urban vehicle pollutant dispersion. Moreover, the basic assumptions, fundamental principles, related research, applicable conditions, and limitations of these mechanism research methods and modeling approaches are clarified. For convenience, the associated model acronyms mentioned in this paper are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Acronyms of models.
2. Research Methods for Urban Vehicle Pollutant Dispersion Mechanism
The dispersion mechanism of urban vehicle pollutants refers to the movement status and distribution law of vehicle pollutants in various dispersion environments. Currently, the main analysis methods for dispersion mechanism research include field measurement, wind tunnel experiments, and numerical simulations.
2.1. Field Measurement
Field measurement refers to directly monitoring the dispersion and distribution of pollutants at specific locations by arranging multiple pollutant concentration detection devices in actual scenarios. Normally, concentration monitoring is carried out continuously along with building height, street width, wind speed, azimuth angle, etc., and could be applied to transportation arterials. Although field measurement can obtain accurate concentration values, it is costly and time consuming, and the data collected are relatively limited. Therefore, the method is mainly employed to study the dispersion mechanism in small-scale environments (e.g., tunnels, simple streets) or as a verification method for the results of dispersion models [8].
2.2. Wind Tunnel Experiment
The wind tunnel experiment is based on the principle of motion similarity. By constructing a miniature model of the vehicle pollutant dispersion scene, the dispersion mechanism of vehicle pollutants can be analyzed according to the movement trajectory of the traceable gas under the action of the wind field. For example, Wedding et al. built a 400:1 dispersion model to simulate the dispersion process of vehicle pollutants in a real street environment, which was described by an aerodynamically rough turbulent boundary layer of neutral thermal stratification. The results showed that a single isolated building is prone to mixing pollutants downwind and forming a high concentration area on the leeward side of the building (see Figure 1 taken from [9]).
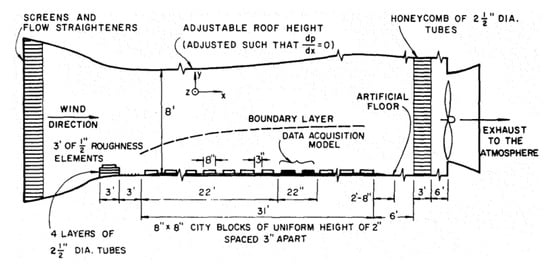
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a typical wind tunnel experiment [9].
The wind tunnel method can also ensure simulation accuracy and is convenient for replicated field tests. Sometimes, the method is also used to verify other dispersion models. However, the strict experimental conditions and the considerable cost make it only suitable for researching some representative dispersion scenarios.
2.3. Numerical Simulation
Numerical simulation is one of the critical methods for studying the mechanism of vehicle pollutants dispersion, typically based on CFD, taking the atmospheric turbulent fluid dynamics as the theoretical basis. Atmospheric turbulence is widely formulated by the RANS and LES models. By solving fluid flow differential equations with the three-dimensional (3D) finite difference and finite volume methods, the discrete distribution of the flow field in continuous space can be obtained, and the pollutant concentration can be calculated (see Figure 2 taken from [10]).
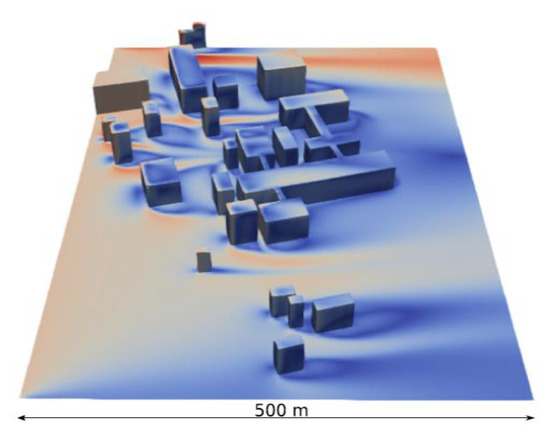
Figure 2.
Building scale flow field over a set of buildings simulated using CFD software [10].
Since the 1990s, numerical simulation methods have been used to study vehicle pollutant dispersion [10,11,12,13,14]. Chang et al. considered both physical and numerical urban street canyon modeling, assuming the buildings on both sides of the street to be symmetrical, and analyzed the sensitivity of important factors, such as the location of emission sources and the impact of different turbulence models. They found that numerical simulation could accurately describe the vehicle pollutant dispersion compared to wind tunnel experiments according to a series of measurements and experimental data comparison [15]. Kim et al. developed a 3D CFD using the k-ε turbulence model. They systematically analyzed the street canyon’s wind flow and pollutant concentration distribution under various flow modes and concluded that variation in ambient wind direction can greatly affect flow circulation and spatial distribution of passive pollutants [16]. Salim et al. discuss the application of RANS and LES models in detail. The prediction accuracy of pollutant dispersion was estimated from the perspective of average concentration distribution, time evolution, and 3D diffusion. The results show that the performance of RSM is better than the standard k-ε model. Although LES is more computationally extensive, it performs better than RANS in simulating concentration distributions [17].
Since numerical simulation methods are more flexible, affordable, and able to overcome the disadvantages of field measurement and wind tunnel experiments, a variety of mature commercial CFD software has been developed to further reduce the research threshold, such as PHOENICS [18,19,20], FLUENT [21,22], STAR-CD [23,24,25], etc. However, CFD requires a large amount of computation resource and is generally used for pollutant dispersion studies at the street or micro-district level. More macroscopic models are essential to meet actual requirements for large-scope scenarios, such as vehicle pollutant dispersion in regional and urban areas.
3. Urban Vehicle Pollutant Dispersion Models
Vehicle pollutant dispersion models simulate the dispersion process of vehicle-source air pollutants in the atmospheric environment quantitively to calculate the concentrations of the pollutants at an arbitrary geographic location. Relevant research with multiple perspectives has been launched since the 1960s, accompanied by rapid urbanization and the increase in mobility. Dispersion models that are compatible with multiple scenarios have been proposed and modified for decades.
Mainstream integrated models can be divided into several types according to their application scenarios, research scope, and fundamental principles. Based on application scenarios, models are designed to calculate dispersion at intersections, road segments, and street canyons. According to the research scope, they can be divided into street-level, block-level, urban-level, and regional-level [26]. According to the fundamental principle, the dispersion model is mainly divided into the Box dispersion model, Gaussian plume and puff models, CFD model, etc. In this paper, the Box and Gaussian models are discussed in detail regarding principles, applicability, and deficiencies as influencing conditional factors like thermodynamics, chemistry, heat transfer, aerosol loading, dense gas effects, etc.
3.1. Box Model
The box model considers the study area (e.g., the whole city, urban district, or urban street) as a closed space. Generally, it is assumed that air pollutants in the study area are thoroughly mixed and evenly distributed after chemical and physical reactions. The model is set up to follow the principle of mass conservation. The inputs required for the model mainly include simple meteorological data, emission source strength, and the pollutants in and out of the study area. The box model includes STREET, CPBM, AURORA, PBM, and others. Due to the concise assumption of the box model, these models are suitable for formulating the air pollutant dispersion of closed streets and macroscopic and mesoscopic areas.
The STREET model was first developed by Johnson et al. in 1973, which considers the initial dispersion of pollutants from road traffic and the turbulent effect caused by the driving process of vehicles [27]. They estimated the pollutant concentration in two parts, the environmental background value of the urban environment and the concentration caused by the emission of pollutants from road vehicles. For the basic intraurban model, they treated road segments as line sources of emission pollutants, and the diffusion was calculated based on annular area segments that overlay the road segments of the traffic network. A simple box model was developed to formulate the contribution of CO concentration from each area segment to receptors individually. Moreover, the box model derives a street canyon sub-model to simulate the aerodynamic effects of structures on both sides of the street. The concentration of pollutants on the leeward side of the canyon is inversely proportional to the distance between the receptor and the line source, while the concentration on the windward side is only related to the vertical height of the receptor and the line source (see Figure 3 taken from [27]).
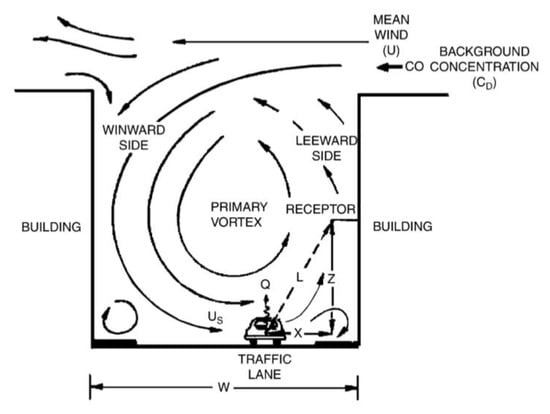
Figure 3.
Cross-street dispersion circulation between buildings [27].
The model can handle the pollutant concentration of receptor points at different heights from the road surface and at different distances from the road shoulder. However, the parameters in the model are calculated based on uniform canyon characteristics and a certain wind speed, which has limitations for formulating pollutants in the case of irregular canyons and the slight angle between the street and the wind direction. Further modifications to the model parameters are required to simulate the dispersion of pollutants in low wind speeds and irregular canyons.
Nicholson [28] proposed a scalar budget-box diffusion model in 1975. The average concentration of pollutants in the street canyon was calculated based on the emission source intensity in the box, the input wind direction, and wind speed. Whether the roof-level winds are perpendicular to or parallel to the street, their models perform well in predicting street-level pollution concentrations. In perpendicular cases, wind profiles were formulated as logarithmic contour lines to calculate vortex velocity above buildings and street canyons with continuity equations, i.e., the average downdraft volume within the canyons on the windward side is equal to the updraft volume on the leeward side. In parallel cases, air pollution transport is primarily horizontal, and the diffusion speed was modeled by integration of the exponential profile law.
Yamartino et al. [29] proposed an urban CPBM based on mass-measured data, which considered the initial dispersion of vehicle emissions, the transmission and dispersion of plumes on the leeward side of canyons, advection and turbulence exchange at the top of the canyon, pollutant circulation, and other factors. A Gaussian plume model and a box model were combined to estimate the street direct diffusion and vertical recirculation of the wind vortex within the canyon. Because canyon parallel and transverse flows are decoupled from one another, transverse flows were formulated following the H-H equations [30] and parallel flows were simulated with the logarithmic-type profiles. The thermal effect of solar radiation and the turbulence caused by moving vehicles were also considered using an empirical model. The pollutant concentration was calculated following the mass conservation rule, and the CPBM is mainly suitable for diffusing pollutants in urban street canyons with height-to-width ratios from 0.5 to 2.
Recently, Sobottka [31] evaluated and compared the performance of CPBM, STREET, and MAPS models with measured carbon monoxide data. Gualtieri [32] applied the STREET, CPBM, and OSPM models to calculate the hourly carbon monoxide concentration on streets. These models were verified with measured data, and the results showed that the STREET model has a better prediction effect on pollutant concentration than other models.
The AURORA model [33] is a comprehensive air quality model for simulating the concentration of inert and reactive gas particles in urban environments based on a steady-state box model to calculate pollutant concentrations in street canyons. The model assumes a uniform distribution of concentration across the street. Different from the CPBM, the AURORA considers the turbulent intermittency in the shear flow from the upwind roof as a driving force. The characteristic length for the vertical pollutant exchange is related to a typical mixing length created by turbulent eddies shedding off at the roof level, constructing the exchange of mass and momentum with the urban canopy flow above the street.
Based on the AURORA, Lefebvre [34] constructed a model chain to support policies within the EU Air Quality Directive Framework. The empirical results show that the model chain can adequately simulate the spatial variability of average EC concentrations over more extended periods. Beckx et al. [35] integrated the activity-based model ALBATROSS with emissions modeling. The resulting emissions are used as input to the AURORA to predict hourly concentrations of different pollutants in the Netherlands, showing that the model could accurately predict the changing trend of the average organic matter concentration in this area.
The above four box models are adequate for simulating a specific street. However, the PBM [36] model is based on an extended version of the box model to simulate urban-wide pollutant concentrations. The PBM divides the urban space (i.e., ranging from 10–50 km) into cubes with heights of 0.1 to 2 km, assuming that air pollutants from the point, line, and area sources are homogeneous within each cube. The input parameters include initial pollutant concentration, wind speed, pollutant flow rate, etc. The pollutant concentration in each hour is calculated considering chemical reactions and photochemical rates.
3.2. Gaussian Model
The basic Gaussian model makes the following assumptions: (1) atmospheric stability and other meteorological parameters are uniform constants in the entire atmosphere and do not change with time, especially for the wind speed and direction; (2) turbulent flow is a random movement, so the time-averaged pollutant concentrations can be described by Gaussian or normal distribution in both horizontal and vertical directions (see Figure 4 taken from [37]); (3) the concentrations from a continuously emitting source are inversely proportional to the wind speed; (4) the plume will be reflected back into the atmosphere when it reaches the ground; (5) the plume only moves physically in the atmosphere without chemical and biological changes. Generally, because of turbulent reflections from the ground and the boundary atmosphere layer, the Gaussian distribution of the plume needs to be modified when the mixing height is low, and the plume’s width is determined by the parameter of σy and σz, i.e., the standard deviation of plume diffusion in the horizontal and vertical direction [38].
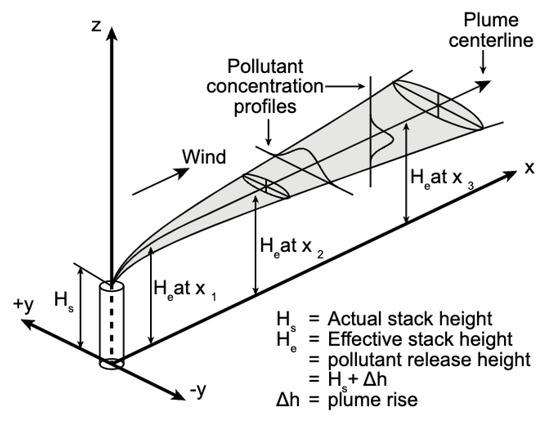
Figure 4.
Gaussian structure of a plume [37] (Wikimedia Commons contributors, 2020).
Moreover, the Gaussian model can be divided into Gaussian plume and puff models according to the assumption about dispersion conditions and forms. The plume model mainly simulates continuous source dispersion, and the puff model simulates discrete source dispersion.
In vehicle emission dispersion research, dispersion models based on the Gaussian model are mainly recommended by most environmental protection ministries worldwide, including CALINE, HIWAY, OSPM, CALPUFF, ADMS series, and SIRANE.
3.2.1. Classical Street-Emission Dispersion Models
CALINE4 and HIWAY2 are the most widely used dispersion models for highway vehicle emissions. HIWAY2 [39] is modified based on HIWAY, which is the first highway dispersion model developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). CALINE4 [40] is based on the CALINE from the California Department of Transportation. These two models divide highway links into multiple adjacent line source elements and determine the influence elements of a receptor according to the wind direction and plume dispersion parameters, then calculate the pollutant concentration contribution of influence elements to different receptors. CALINE4 comprehensively considers the mixing area and pollutant deposition rate. It is assumed that there is a mixed zone at a certain distance on both sides of the highway when the pollutants emitted by vehicles diffuse. The Gaussian model is used to calculate the diffusion outside the mixing zone, while the vertical dispersion parameters in CALINE4 incorporate vehicles’ thermal and mechanical turbulence in the mixing zone, which are not considered in HIWAY2. These two models are mainly used to estimate the concentration of vehicle pollutants around open terrains such as highways and urban expressways [41,42]. Considering the pollution sources’ strength, meteorology, and site geometry, the two models can also predict pollution concentration within 500 m, such as intersections, bridges, and parking facilities. However, these two models are relatively simple to deal with pollutant dispersion in the complex environment of many buildings within the urban.
Sharma and Broderick et al. evaluated the prediction accuracy of the CALINE4 based on the measured carbon monoxide data along a corridor expressway and obtained well results [43,44]. Marmur et al. evaluated the performance of CALINE4 and HIWAY2 in predicting nitrogen dioxide concentration under different fleet compositions and physical layout conditions. The results show that the HIWAY2 can better estimate the average concentration of pollutants under unstable conditions, while CALINE4 performs better in average and peak pollutant concentrations under stable states [45].
OSPM [46,47] is a semi-empirical model developed by the Danish National Environmental Research Institute. The OSPM model divides the pollutant concentration into three parts: the direct contribution from the wind at the bottom of the canyon to receptors, the circulating part caused by the turbulence and dispersion in the canyon, and the urban background concentration value. Specifically, the model uses the Gaussian plume equation to formulate the direct contribution of pollution sources and combines the box model to calculate the effect of turbulence on pollutant concentrations. The model describes the pollutant source as infinite line sources. The crosswind effect on plume dispersion is not explicitly modeled. Instead, it uses the relationship between parameters to describe the vehicle emissions, the backflow and atmospheric disturbance caused by vehicle movement, etc., integrating the line source elements along the wind direction to obtain the pollutant concentration.
Compared to CALINE4 and HIWAY2, OSPM has more precise requirements for wind direction and other diffusion parameters in road sections, mainly used to calculate the dispersion concentration in street canyons at the micro level. The model has been widely verified and applied internationally [48]. Kakosimos summarized the application performance of the OSPM in many countries and suggested future research directions for traffic pollution dispersion [49]. Based on the detected data, Ketzel et al. verified and analyzed the prediction accuracy of the OSPM [50]. The results showed that the calculated results are highly consistent with the measured data. However, OSPM assumes that vehicle emissions are uniformly distributed in the canyon and empirically derives the effect of turbulence caused by vehicles, resulting in invalidation to simulate intermittent fluctuations in airflow. Therefore, OSPM is unsuitable for calculating short-term pollutant concentrations in less than one hour.
CALPUFF is a Gaussian puff dispersion model operating in the Lagrangian coordinate system [an urban scale application, the first page]. It is a non-steady state multi-layer model based on similarity equations to simulate the dispersion of gases and particles. The model considers the geophysical data and spatial-temporal variability of meteorological conditions. The mechanism is to evaluate the contribution of puff concentration for a certain receptor by the “snapshot” method, freezing the movement of the puff within a fixed interval time (sampling step). The puff can change its intensity, size, or moving trajectory before the next interval time, and the pollutant concentration can be calculated by summing the average values of all sampling steps near the certain receptor. CALPUFF can formulate different source types (e.g., point, line, volume, and area) with four main processes: emission strengths, turbulence, transformation, and removal. CALPUFF is widely used to simulate the atmospheric environment in regional and urban areas, but it is not recommended for the environment where dispersion is severely affected by turbulence [51,52,53,54,55,56].
Joo et al. combined the MOVES model with the CALPUFF model to calculate the dispersion concentration of highway vehicle pollutants, simulated the significant impact of traffic accident collisions on the pollutant dispersion area, and proposed associated public safety strategies [57]. Moreover, the validation of CALPUFF is often compared to that of AERMOD in recent studies. Both models show good characteristics in odor dispersion, urban pollutant dispersion, and winter validation tracer studies. However, Dresser and Huizer compared the short-term and annual average predictions of SO2 with measured data. The result shows that the performance of CALPUFF is better than that of AERMOD. Tartakovsky concluded that AERMOD has better prediction accuracy for TSP dispersion in complex terrains than CALPUFF. Specifically, some literature points out that CALPUFF has strong over-predictions in short-term dispersion cases.
In 1991, the American Meteorological Society (AMS) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) jointly established the AMS and EPA Regulatory Model Improvement Committee (AERMIC) to develop the AERMOD model system cooperatively [58]. Different from CALPUFF, AERMOD is a steady-state dispersion model that considers dispersion effects from vertical variations in the planetary boundary layer. In the stable boundary layer, the concentration distribution in the vertical and horizontal directions follows the Gaussian distribution. In the convective boundary layer, only the horizontal distribution is Gaussian distribution, while the vertical distribution is described by the probability density function. In addition, AERMOD also considers the phenomenon of buoyant plumes, i.e., part of the plume first rises near the top of the boundary layer and stays for a period, and then mixes into the interior of the convective boundary layer. AERMOD formulates the portion of the plume that penetrates the stable layer, allowing it to re-enter the boundary layer under certain circumstances. Moreover, AERMOD can formulate different types of sources and can handle both simple and complex terrain. The plume is formulated as a combination of terrain-following and terrain-impacting states for complex terrain in the AERMOD model.
For the AERMOD application, Misra combined a microscopic traffic simulation and a vehicle pollutant emission model to estimate the concentrations of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides during the morning peak hour of urban transportation networks [59]. Askariyeh et al. used vehicle pollutant tracer data to evaluate the performance of the AERMOD model in different source types and low-wind scenarios. The results show that the estimated concentration is lower than the measurements because of the lack of handling lateral plume tortuosity in the AERMOD model.
In contrast to AERMOD, the R-LINE model was specially developed to simulate primary and chemically inert pollutants, emphasizing near-surface releases and near-source dispersion [60]. The numerical line source approximation was also driven by the Gaussian plume formulation. More particularly, based on historical field data, tracer field studies, and wind tunnel studies, new dispersion formulations were designed and incorporated into the model to calculate the vertical and horizontal plume dispersion of near-surface releases. Moreover, a wind meander algorithm was developed for the dispersion simulation in all directions during light and variable winds. However, the R-LINE model has its limitation in simulating chemically reactive species such as NO2, which is an important component of motor vehicle emissions. To compensate, Valencia et al. [61] developed three methods driven with R-LINE to simulate chemically reactive species: a linear regression method based on the Dixon–Middleton–Derwent (DMD) method [62], a simplified chemistry scheme from Hess and Cope [63], and a robust approach using the Generic Reaction Set (GRS).
3.2.2. Urban-Scale Systematic Models
The ADMS model series was developed by the Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants (CERC) [64,65], which can be applied in various conditions to simulate the emission dispersion and transmission of point, line, volume, and area sources. The analysis scope can reach regional and urban scales, up to hundreds of kilometers. It is a steady-state model and assumes Gaussian distribution based on the Monin-Obukhov length and the boundary layer height. Two different Gaussian models are used to approximate the vertical concentration distribution under the convective boundary layer. The process of handling plume reflections on the planetary boundary layer is similar to other Gaussian models. According to different application scenarios, ADMS can be divided into sub-models: ADMS-Screen, ADMS-Roads, ADMS-Industrial, and ADMS-Urban.
Specifically, the ADMS-Roads model is mainly suitable for highways or urban roads in a simple dispersion environment [66,67,68]. ADMS-Urban is the most complex dispersion model with complete geographic information system functions and photochemical reaction modules, which can simulate the pollutant concentrations for the entire city or larger areas [69,70]. Moreover, the OSPM is embedded into the ADMS-Urban model to calculate the effect of traffic pollutant dispersion in the street canyon. The influence of vehicle-caused turbulence is also considered. For the dispersion process to the peripheral area of the street, ADMS-Urban considers the impact of the spatial distribution of surrounding buildings and optimizes the dispersion model according to different street aspect ratios and building gap ratios.
The ADMS series models have been widely used in many countries and achieved satisfying verification effects [71,72,73]. Ellis et al. verified ADMS-Roads and CALINE4 based on the measured pollutant concentration data near expressways in open terrain. The results show that the direction and width of the expressway affect the concentration from the road section to its peripheral area [74]. Righi et al. used measured data from air quality monitoring stations to test the accuracy of ADMS-Urban in predicting regional traffic pollutant concentrations. The results showed that the model could well simulate the traffic-related carbon monoxide concentrations but tended to produce low estimates. The research also proposed a model modification method to solve this problem and verified its performance [75].
To overcome the limitation of regional-scale models, another urban-scale model, EPISODE, was developed to consider details of the urban topography, wind flow field characteristics, land use information, and the geometry of local pollution sources [76]. Eulerian 3D sub-grid-scale modules are incorporated in EPISODE to represent line and point source emissions, Gaussian dispersion, and local photochemistry. Generally, the horizontal resolution of grids is 1 × 1 km2 over an entire city with domains of up to 2500 km2, and the EPISODE model allows users to specify the estimation of concentrations at the sub-gird scale. The subsequent CityChem expansion model based on the EPISODE model further refines the simulation of complex atmospheric chemistry in urban areas and the near-field dispersion in proximity to emission sources within the sub-gird components [77]. The EPISODE–CityChem model system is powerful to simulate the photochemical transformation of multiple reactive pollutants within atmospheric diffusion. The concentration fields can be analyzed on a horizontal resolution of 100 m or even finer and a vertical resolution of 24 layers up to 4000 m in height.
3.2.3. Street-Network Models
SIRANE is the first pollutant dispersion model based on the concept of the street-network. By simplifying the urban road network structure, the SIRANE model abstracts the vehicle pollutant diffusion into continuous point sources at the top of the street [78]. The building environment is not formulated into the model specifically. Instead, the impact of buildings is considered by two input parameters, the aerodynamic roughness length and the displacement height. Streets are classified into the canyon and open terrain according to their width-to-height ratio. The pollutant dispersion in the urban boundary layer and the urban canopy is calculated based on parametric relations, i.e., the advection along the street, the intersection, and the transfer of pollutants between the street and the overlying atmosphere. The Gaussian plume model is adopted to simulate the dispersion from road sections to peripheral areas, and improved box models are used for the dispersion simulation inside streets. The chemical reaction of nitrogen oxides, pollutant sedimentation, and other function modules are also included in the model.
The model is suitable for calculating district or regional scale pollutant concentrations. However, SIRANE does not provide any specific concentration simulation module for low wind conditions and is not recommended when building density is low.
Since SIRANE was proposed, many scholars have applied and improved the model [79,80]. Soulhac et al. analyzed the SIRANE model with measured data from air quality monitoring stations and portable detect equipment. The SIRANE model performs well, except for NO and some of BTX. New photochemical models need to be tested to improve the performance on NO, and the BTX problem can be improved by correcting vehicular emissions factors.
Recently, another street-network model, MUNICH, with updates from version 1.0 to 2.0 is getting scholars’ attention [81,82]. In MUNICH v1.0, the street network is divided into street segments and intersections. Specifically, street segments are formulated as cuboid-type boxes with homogeneous concentration assumptions, while intersections are only treated as spaces for the advective transfer of pollutants among streets and part of the exchanges with the overlying atmosphere. Compared to SIRANE, MUNICH v1.0 combined the advantages of 3D-gridded Eulerian models and street-network models to better simulate the concentrations of air pollutants in complex urban canopy configurations.
Because the wind velocity at the roof level has effects on pollutants’ advection from street to street, MUNICH v2.0 developed a new formulation to calculate the wind profile within the street, instead of the SIRANE method, which can be calculated depending on the street characteristics using a logarithmic wind profile above buildings. Chemical transformations of the pollutants in both the gas and particle phases are modeled, i.e., a chemical kinetic mechanism for the gas phase and the mass transfer between the gas and particle phases. Moreover, MUNICH v2.0 added an approach from Lugon et al. [83] to estimate resuspension.
Gavidia-Calderón et al. demonstrated the great potential of MUNICH to estimate the concentrations of pollutants from a fleet close to the streets [84]. Moreover, street-level transport emission models are emerging with open-source packages, such as the Vehicular Emission Inventory (VEIN) [85] and Yeti [86], alleviating the collection difficulty and poor accuracy of front-end data. Because the VEIN model, which is an open-source model to provide high-resolution vehicular emissions inventories for different fields of study, has the advantage of presenting compatibility with MUNICH, they combined these two models to simulate ozone (O3) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) concentrations within the urban street canyons in the São Paulo metropolitan area. The results show that NO2 is better simulated in both urban zones than O3, and O3 is overpredicted because it is highly dependent on the background concentration.
4. Conclusions
This paper provides a review of the mechanism research methods and modeling approaches for urban vehicle pollutant dispersion. The mechanism research methods reviewed include field measurements, wind tunnel experiments, and numerical simulations. The modeling approaches involve two kinds of popular models: Box models (STREET, CPBM, AURORA, PBM) and Gaussian models (CALINE, HIWAY, OSPM, CALPUFF, R-LINE, ADMS series, EPISODE, CityChem, SIRANE, MUNICH). The basic assumptions, fundamental principles, related research, applicable conditions, and limitations of these mechanism research methods and modeling approaches are clarified in this paper. Although the atmosphere pollutant dispersion problem has been studied systematically and deeply for decades, there are still deficiencies when considering the urban vehicle pollutant effects, which are manifested in the following aspects.
Urban roads traverse through complex and diverse built environments. Existing studies mostly focus on the microscopic street and local block. Even though some studies simulate vehicle pollutant dispersion across entire regional and urban areas, the built environment is usually roughly assumed without actual building profile data. CFD is capable of incorporating detailed building profile data, but it is arduous to implement large-scope numerical simulations because of computing power limitations. According to version 5.0 of the ADMS-Urban user guide, up to 25 buildings may be modeled in a model run, and the effect of buildings on dispersion can only be modeled for point sources. In the future, it is an essential research direction to systematically analyze large-scope building effects on vehicle pollutant dispersion with limited computing resources, including the spatial distribution and building profile description.
Moreover, most previous works model pollutant dispersion in particular wind speeds and directions, but they are not recommended for low-wind scenarios. For example, Gaussian plume canyon models are unsuitable for low-wind dispersion scenarios because the basic assumption is that the pollutant diffusion patterns of each hour are independent of each other. When the wind speed is low, the vehicle pollutants cannot be completely dispersed outside the study area within one hour, which contradicts the basic assumption. Gaussian puff models can simulate low wind dispersion, but the model requires very refined meteorological conditions and related background data, resulting in high computational complexity and substantial computational resource requirements.
In future research, it is necessary to improve modeling approaches considering low wind conditions and complex building environments. Furthermore, thermal effects, dispersion around moving obstacles, and other complex environments are all subtle problems expected to be systemically considered. Overall, there is a trade-off between prediction accuracy, research scope, and computational complexity. Both the numerical simulation and mathematical models depend heavily on input data, e.g., emission factors of vehicles, traffic flow state, the geometry of buildings and streets, meteorological environment, etc. Using limited data sources and computational resources to accurately approximate the actual pollutant dispersion is an unavoidable problem for both users and researchers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and Y.T.; formal analysis, M.L.; resources, Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L. and Y.C.; writing—review and editing, T.X.; project administration, M.L. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tu, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jin, K. Investigating the impacts of driving restriction on NO2 concentration by integrating citywide scale cellular data and traffic simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 265, 118721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Barman, S.; Levin, M.W.; Chen, R.; Li, T. Integrating public transit signal priority into max-pressure signal control: Methodology and simulation study on a downtown network. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 138, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Levin, M.W.; Cieniawski, M. A Zone-Based Dynamic Queueing Model and Maximum-Stability Dispatch Policy for Shared Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation System Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3827–3832. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, T.; Li, X. Longitudinal safety impacts of cooperative adaptive cruise control vehicle’s degradation. J. Saf. Res. 2019, 69, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forehead, H.; Huynh, N. Review of modeling air pollution from traffic at street-level. State Sci. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah-Shorshani, M.; Shekarrizfard, M.; Hatzopoulou, M. Evaluation of regional and local atmospheric dispersion models for the analysis of traffic-related air pollution in urban areas. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Visscher, A. Air Dispersion Modeling: Foundations and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Leelőssy, Á.; Molnár, F.; Izsák, F.; Havasi, Á.; Lagzi, I.; Mészáros, R. Dispersion modeling of air pollutants in the atmosphere: A review. Open Geosci. 2014, 6, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedding, J.B.; Lombardi, D.J.; Cermak, J.E. A wind tunnel study of gaseous pollutants in city street canyons. J. Air. Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1977, 27, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadaverugu, R.; Sharma, A.; Matli, C.; Biniwale, R. High resolution urban air quality modeling by coupling CFD and mesoscale models: A review. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 55, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Ito, S. A micro-scale dispersion model for motor vehicle exhaust gas in urban areas—OMG volume-source model. Atmos. Environ. Part B. Urban Atmos. 1990, 24, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.Y.; Park, H.M. Comparison of microphysics parameterizations in a three-dimensional dynamic cloud model. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, J.F.; Anquetin, S.; Mestayer, P.G. Pollutant dispersion and thermal effects in urban street canyons. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2659–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroney, R.; Ohba, R.; Leitl, B.; Kondo, H.; Grawe, D.; Tominaga, Y. Review of CFD guidelines for dispersion modeling. Fluids 2016, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Meroney, R.N. Numerical and physical modeling of bluff body flow and dispersion in urban street canyons. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2001, 89, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Baik, J.J. A numerical study of the effects of ambient wind direction on flow and dispersion in urban street canyons using the RNG k–ε turbulence model. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.M.; Buccolieri, R.; Chan, A.; Sabatino, S.D. Numerical simulation of atmospheric pollutant dispersion in an urban street canyon: Comparison between RANS and LES. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, P. Air Quality Estimation and Error Analysis. Innov. Mech. Eng. 2022, 1, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ehm, C.; Frohmüller, M.O.; Flassak, T.; Stephan, D. On-site reduction of nitrogen oxides at an emission hotspot using actively vented photocatalytic reactors in a highway tunnel. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hong, B.; Jiang, R. Are green walls better options than green roofs for mitigating PM10 pollution? CFD simulations in urban street canyons. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.J.; Wu, S.; Shen, S.; Xu, T. Simulation and assessment of traffic pollutant dispersion at an urban signalized intersection using multiple platforms. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriks, T.; Longo, R.; Baetens, D.; Derudi, M.; Parente, A.; Bellemans, A.; van Beeck, J.; Denys, S. Application of improved CFD modeling for prediction and mitigation of traffic-related air pollution hotspots in a realistic urban street. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aris, M.H.M.; Darlis, N.; Ishak, I.A.; Sulaiman, S.; Jaat, N.; Hakim, A.F. HVAC CFD Analysis of Air Flow and Temperature Distribution Inside Passenger Compartment. J. Automot. Powertrain Transp. Technol. 2021, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.; ElGammal, T.; Amano, R.S.; Khalil, E.E. Flow Patterns and Temperature Distribution in an Underground Metro Station. Energy Sustainability. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2018, 51418, V001T06A004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; He, C. Prediction of Transient NOx Emission from Diesel Vehicles Based on Deep-Learning Differentiation Model with Double Noise Reduction. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ketzel, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Pirjola, L.; Britter, R. Dynamics and dispersion modeling of nanoparticles from road traffic in the urban atmospheric environment—A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.B.; Ludwig, F.L.; Dabberdt, W.F.; Allen, R. An urban diffusion simulation model for carbon monoxide. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1973, 23, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.E. A pollution model for street-level air. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1975, 9, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamartino, R.J.; Wiegand, G. Development and evaluation of simple models for the flow, turbulence and pollutant concentration fields within an urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1986, 20, 2137–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchklss, R.S.; Harlow, F.H. Air Pollution Transport M Street Canyons; United States Environmatal Protection Agency: Wasington, DC, USA, 1973; EPA-R4-73-029. [Google Scholar]
- Sobottka, H. Air Pollution Impact in Streets with Heavy Traffic and the Effects of the Dominant Parameters. In Studies in Environmental Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; Volume 8, pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, G. A street canyon model intercomparison in Florence, Italy. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, C.; Colles, A.; Janssen, L.; Cornelis, J. Integrated air quality modeling for the assessment of air quality in streets against the council directives. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5177–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, W.; Vercauteren, J.; Schrooten, L.; Janssen, S.; Degraeuwe, B.; Maenhaut, W.; de Vlieger, I.; Vankerkom, J.; Cosemans, G.; Mensink, C.; et al. Validation of the MIMOSA-AURORA-IFDM model chain for policy support: Modeling concentrations of elemental carbon in Flanders. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6705–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckx, C.; Panis, L.I.; Van De Vel, K.; Arentze, T.; Lefebvre, W.; Janssens, D.; Wets, G. The contribution of activity-based transport models to air quality modeling: A validation of the ALBATROSS–AURORA model chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3814–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. A Comparison of Calpuff Modeling Results to Two Tracer Field Experiments [EB/OL]. 1998. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/scram001/7thconf/calpuff/tracer.pdf. (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Wikimedia Commons Contributors, "File:Gaussian Plume (SVG).svg," Wikimedia Commons, the Free Media Repository. 2020. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Gaussian_Plume_(SVG).svg&oldid=495553766 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Holmes, N.S.; Morawska, L. A review of dispersion modeling and its application to the dispersion of particles: An overview of different dispersion models available. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5902–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, W.B. User’s Guide for HIWAY-2: A Highway Air Pollution Model; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, P.E. Caline 4-A Dispersion Model for Predicting Air Pollutant Concentrations Near Roadways; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kenty, K.L.; Poor, N.D.; Kronmiller, K.G.; McClenny, W.; King, C.; Atkeson, T.; Campbell, S.W. Application of CALINE4 to roadside NO/NO2 transformations. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, R.; Sharma, N. Sensitivity analysis of CALINE4 model under mix traffic conditions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Gulia, S.; Dhyani, R.; Singh, A. Performance evaluation of CALINE 4 dispersion model for an urban highway corridor in Delhi. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2013, 72, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, B.M.; Budd, U.; Misstear, B.D.; Ceburnis, D.; Jennings, S. Validation of CALINE4 modeling for carbon monoxide concentrations under free-flowing and congested traffic conditions in Ireland. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 24, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.; Mamane, Y. Comparison and evaluation of several mobile-source and line-source models in Israel. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2003, 8, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, O.; Berkowicz, R.; Larssen, S. The operational street pollution model (OSPM). In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application VIII; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowicz, R. OSPM-A parameterized street pollution model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2000, 65, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.; Valkonen, E.; Walden, J.; Koskentalo, T.; Aarnio, P.; Karppinen, A.; Berkowicz, R.; Kartastenpää, R. A measurement campaign in a street canyon in Helsinki and comparison of results with predictions of the OSPM model. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakosimos, K.E.; Hertel, O.; Ketzel, M.; Berkowicz, R. Operational Street Pollution Model (OSPM)—A review of performed application and validation studies, and future prospect. Environ. Chem. 2010, 7, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzel, M.; Jensen, S.S.; Brandt, J.; Ellermann, T.; Olesen, H.R.; Berkowicz, R.; Hertel, O. Evaluation of the street pollution model OSPM for measurements at 12 streets stations using a newly developed and freely available evaluation tool. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2012, S1, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwine, K.J.; Dabberdt, W.F.; Simmons, L.L. Peer Review of the CALMET/CALPUFF Modeling System; EPA Contract No. 68-D-98-092; The KEVRIC Company Inc.: Durham, North Carolina, 1998. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ttn/scram/7thconf/calpuff/calpeer.pdf. (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Holnicki, P.; Kałuszko, A.; Trapp, W. An urban scale application and validation of the CALPUFF model. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, T. Comparison of model predictions with the data of an urban air quality monitoring network in Izmir, Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, M.G.; Gimson, N.R. Dispersion modeling of a wintertime particulate pollution episode in Christchurch, New Zealand. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3531–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivančič, M.; Vončina, R. Determinating the influence of different PM10 sources on air quality in Ljubljana basin with CALPUFF dispersion model. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 54, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, W. The application of CALMET/CALPUFF models in air quality assessment system in Poland. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2010, 36, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.; Oh, C.; Lee, S.; Lee, G. Assessing the impact of traffic crashes on near freeway air quality. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimorelli, A.J.; Perry, S.G.; Venkatram, A.; Weil, J.C.; Paine, R.J.; Wilson, R.B.; Lee, R.F.; Peters, W.D.; Brode, R.W. AERMOD: A dispersion model for industrial source applications. Part I: General model formulation and boundary layer characterization. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Roorda, M.J.; MacLean, H.L. An integrated modeling approach to estimate urban traffic emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 73, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelle, G.S.; Akula, V.; David, K.H.; Perry, S.G.; Petersen, W.B.; Isakov, V. RLINE: A line source dispersion model for near-surface releases. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 748–756. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia, A.; Venkatram, A.; Heist, D.; Carruthers, D.; Arunachalam, S. Development and evaluation of the R-LINE model algorithms to account for chemical transformation in the near-road environment. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.; Middleton, D.R.; Derwent, R.G. Sensitivity of nitrogen dioxide concentrations to oxides of nitrogen controls in the United Kingdom. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, G.; Cope, M. A note on subgrid-scale processes in photochemical modelling. Atmos. Environ. 1989, 23, 2857–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.A.; Carruthers, D.J.; Edmunds, H.A. Adms and adms–urban. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 8, 438–440. [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers, D.J.; Holroyd, R.J.; Hunt, J.C.R.; Weng, E.S.; Robins, A.G.; Apsley, D.D.; Thompson, D.J.; Smith, F.B. UK-ADMS: A new approach to modeling dispersion in the earth’s atmospheric boundary layer. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1994, 52, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADMS—Urban C, U. ADMS—Roads and the latest government guidance. In UK Tools for Modelling NOX and NO2. ADMS—Urban and Roads User Group Meeting; CERC: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hirtl, M.; Baumann-Stanzer, K. Evaluation of two dispersion models (ADMS-Roads and LASAT) applied to street canyons in Stockholm, London and Berlin. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5959–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CERC. ADMS-Roads: An Air Quality Management System, User Guide Version 3.1.; CERC: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, C.A.; Carruthers, D.J.; Edmunds, H.A. ADMS–Urban: An air quality management system for traffic, domestic and industrial pollution. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 8, 666–674. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, J.; Hood, C.; Carruthers, D.; McHugh, C. ADMS–Urban: Developments in modelling dispersion from the city scale to the local scale. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 50, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, P.; Nagendra, S.M.; Gulia, S.; Khare, M.; Bell, M.; Namdeo, A. Performance Evaluation of UK ADMS-Urban Model and AERMOD Model to Predict the PM 10 Concentration for Different Scenarios at Urban Roads in Chennai, India and Newcastle City, UK. In Urban Air Quality Monitoring, Modelling and Human Exposure Assessment; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Badamfirooz, J.; Rahmati, A.; Daneshpajooh, N.; Mousazadeh, R.; Mirzaei, R. Investigating the impact of existing and under construction industries on the air quality of Arak City using ADMS model. Environ. Sci. 2021, 20, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, V.; Torre, M.; Tratzi, P.; Fazzini, P.; Tomassetti, L.; Cozza, V.; Naso, F.; Marcozzi, D.; Petracchini, F. Effects of deployment of electric vehicles on air quality in the urban area of Turin (Italy). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.; McHugh, C.; Carruthers, D.; Stidworthy, A. Comparison of ADMS-Roads, CALINE4 and UK DMRB Model Predictions for Roads; CERC Documentation: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Righi, S.; Lucialli, P.; Pollini, E. Statistical and diagnostic evaluation of the ADMS-Urban model compared with an urban air quality monitoring network. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3850–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, P.D.; Walker, S.E.; Sousa-Santos, G.; Vogt, M.; Vo-Thanh, D.; Aparicio-Lopez, S.; Ramacher, M.O.P.; Karl, M. The urban dispersion model EPISODE. Part 1: A Eulerian and subgrid-scale air quality model and its application in Nordic winter conditions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 13, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, M.; Walker, S.E.; Solberg, S.; Ramacher, M.O. The Eulerian urban dispersion model EPISODE—Part 2: Extensions to the source dispersion and photochemistry for EPISODE–CityChem v1.2 and its application to the city of Hamburg. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 3357–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Cierco, F.X.; Perkins, R. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; part I, presentation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Didier, D.; Rios, I. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; PART II, validation of the model on a real case study. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Nguyen, C.V.; Volta, P.; Salizzoni, P. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion. PART III: Validation against NO2 yearly concentration measurements in a large urban agglomeration. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wu, Y.; Seigneur, C.; Roustan, Y. Multi-scale modeling of urban air pollution: Development and application of a Street-in-Grid model (v1.0) by coupling MUNICH (v1.0) and Polair3D (v1.8.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lugon, L.; Maison, A.; Sarica, T.; Roustan, Y.; Valari, M.; Zhang, Y.; André, M.; Sartelet, K. MUNICH v2.0: A street-network model coupled with SSH-aerosol (v1.2) for multi-pollutant modelling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 7371–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugon, L.; Vigneron, J.; Debert, C.; Chrétien, O.; Sartelet, K. Black carbon modeling in urban areas: Investigating the influence of resuspension and non-exhaust emissions in streets using the Street-in-Grid model for inert particles (SinG-inert). Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 7001–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavidia-Calderón, M.; Ibarra-Espinosa, S.; Kim, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Andrade, M.D.F. Simulation of O3 and NOx in Sao Paulo street urban canyons with VEIN (v0.2.2) and MUNICH (v1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2020, 14, 3251–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Espinosa, S.; Ynoue, R.; O’Sullivan, S.; Pebesma, E.; Andrade, M.D.F.; Osses, M. VEIN v0.2.2: An R package for bottom-up Vehicular Emissions Inventories. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2018, 11, 2209–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.C.; Leitao, J.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Butler, T.M. Yeti 1.0: A generalized framework for constructing bottom-up emission inventory from traffic sources. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).