Emissions and Control Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from a Typical Chemical Enterprise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Sites Description and VOCs Measurement
2.2. Emission Amount Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. VOCs Characteristics
3.1.1. Organized Emission
3.1.2. Leakage of Production Units
3.1.3. Storage Tank Breathing Emissions
3.1.4. Product Filling Release
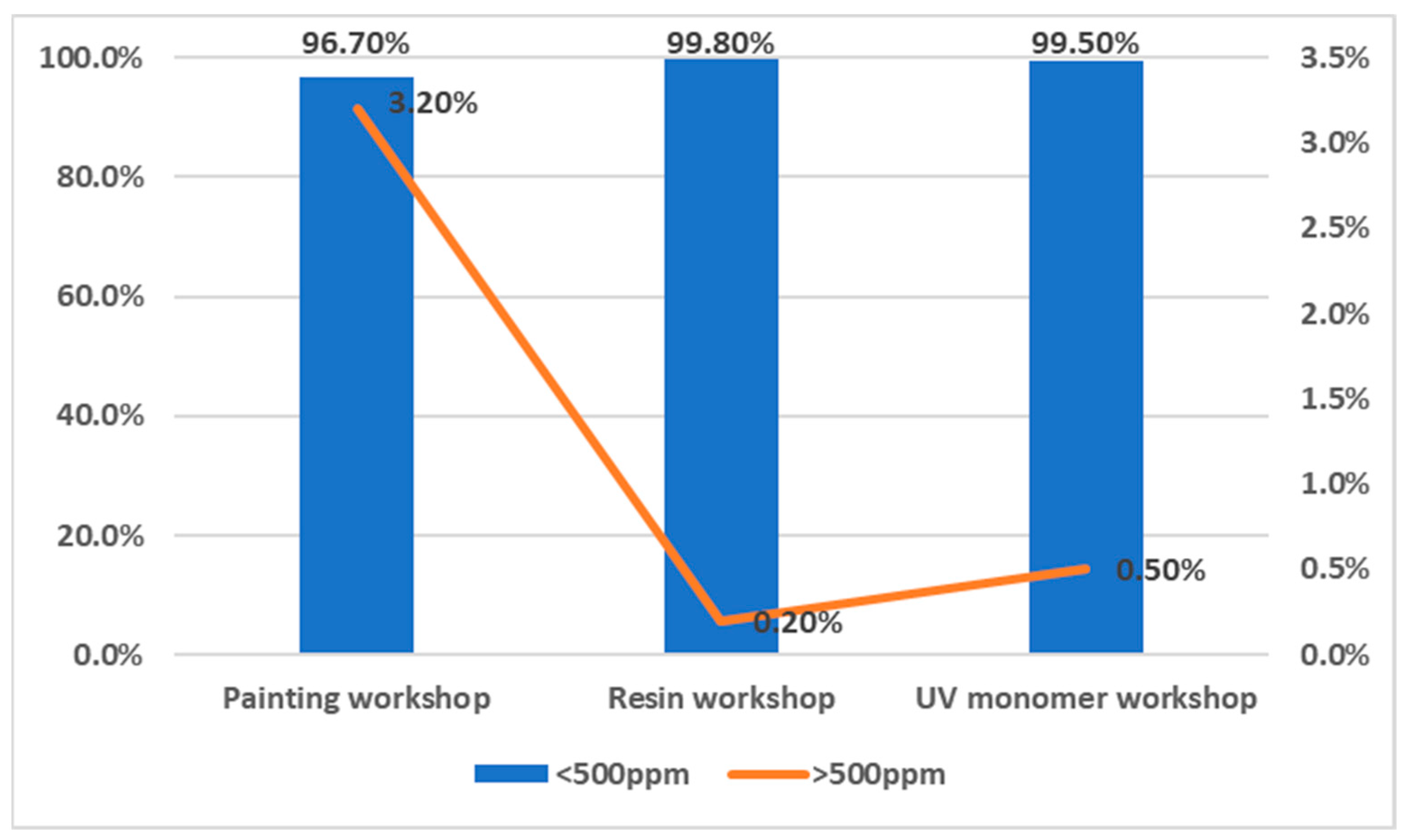
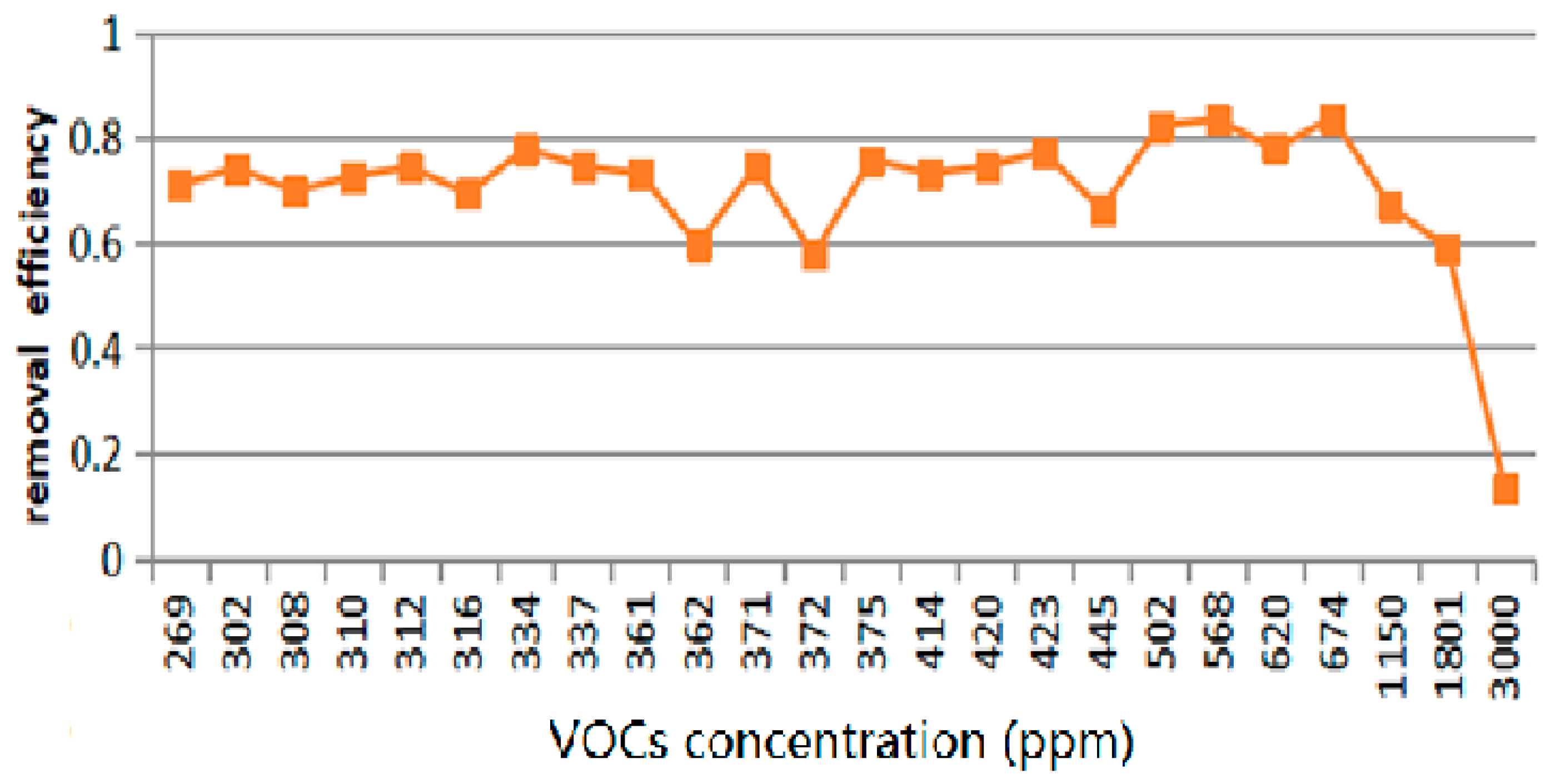
3.1.5. Assessment of VOC Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Jing, K.; Wang, Q.; An, X.; Liu, B. Characteristics of VOCs concentrations and active species in a petrochemical industrial area in the summer of 2018. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Su, R.; Dong, H.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Exploring ozone pollution in Chengdu, southwestern China: A case study from radical chemistry to O3-VOC-NOx sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillman, S.; Vautard, R.; Menut, L.; Kley, D. O3-NOx-VOC sensitivity and NOx-VOC indicators in Paris: Results from models and Atmospheric Pollution Over the Paris Area (ESQUIF) measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, A.G.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Kroll, J.H. A review of Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) formation from isoprene. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4987–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Xin, D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Situation and countermeasures of volatile organic compounds in Wuhan chemical industrial park. Mod. Chem. Res. 2022, 15, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ho, S.S.H.; Gong, S.; Ni, J.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Yang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, D. Characterization of VOCs and their related atmospheric processes in a central Chinese city during severe ozone pollution periods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xie, S. Spatial distribution of ozone formation in China derived from emissions of speciated volatile organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2574–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; An, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, N. VOC characteristics, sources and contributions to SOA formation during haze events in Wuhan, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2624–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Ye, D. Improved emissions inventory and VOCs speciation for industrial OFP estimation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. Characteristics of Industrial VOCs Emissions and Evaluation of Control Technology in China. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W. Application status and discussion of chemical industry VOCs waste gas treatment technology. Resour. Econom. Environ. Prot. 2019, 10, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, G. Discussion on the treatment of VOC waste gas in chemical industry. Resour. Econom. Environ. Prot. 2018, 7, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Control of VOC emission in the treatment of wastewater from chemical process plants. Sichuan Chem. Ind. 2019, 22, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Discussions on the treatment technology of industrial organic waste gas pollution. Constr. Des. Eng. 2019, 8, 150–151. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Sun, Y. Countermeasures of emission reduction of fugitive emission in petrochemical industry. China Environ. Prot. Ind. 2016, 3, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. Unorganized emission control of VOCs by a coal chemical enterprise. Energy Energy Conserv. 2021, 7, 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Shao, Q. Discussion on the principle and method of health protection distance standard for multi-source emission industrial enterprises. J. Hyg. Res. 1985, 5, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Du, S. Leak detection and repair (LDAR) technologies, applications and trends. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences, Chengdu, China, 22–23 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE, PRC); Ministry of Environmental Protection. Technical Guidelines for the Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted from Leakage and Open Liquid Level: HJ 733-2014; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Qu, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, H.; Jin, L.; Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Shu, S. Vehicle exhaust detection method based on portable FTIR. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 2021, 41, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 320: Measurement of Vapor Phase Organic and Inorganic Emissions by Extractive Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE, PRC); Ministry of Environmental Protection. Emission from Stationary Cources-Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds-Bags Method: HJ 732-2014; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Feng, Y.X.; Xiao, A.S.; Li, B.; Dong, R.; Jia, R.Z.; Li, M.J. Effects of sampling conditions on composition and emission characteristics of volatile organic compounds in process units from different Refineries. China Pet. Process. Petrochem. Technol. 2020, 22, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, L.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; An, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhai, R.; Wang, Z. VOC characteristics, chemical reactivity and sources in urban Wuhan, central China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, D.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Shao, X.; Nie, L. Source profiles of volatile organic compounds(VOCs) from typical solvent-based industries in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4395–4403. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Xu, K.; Jing, C. Analysis of technical status of portable VOCs testing gas chromatographs. Anal. Instrum. 2021, 6, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Demuth, C.; Hecq, P.; Berger, A. Dispersion from fugitive sources. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application II; Wispelaere, C., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 459–472. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Li, S.; Barnett, A.G.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Huxley, R.; Chen, W.; Williams, G. The association between lung cancer incidence and ambient air pollution in China: A spatiotemporal analysis. Environ. Res. 2016, 144, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P. Discussion on estimation of emission sources and quantity of voc from petrochemical enterprises. Petrochem. Saf. Environ. Prot. Technol. 2013, 29, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. AP-42, Fifth Edition Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factors, Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/chief/ap42/index.html#toc (accessed on 25 November 2022).
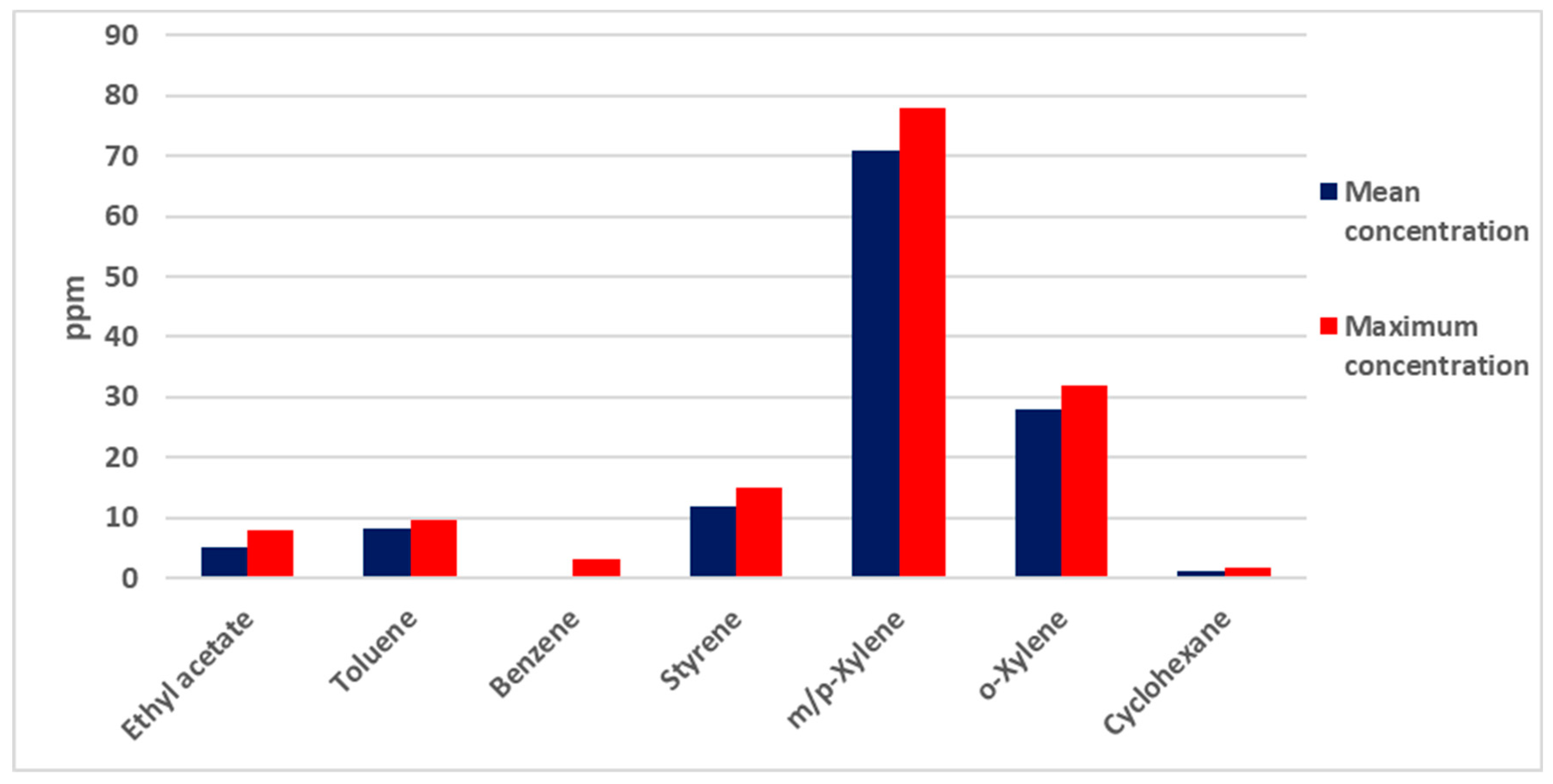
| No. | Testing Items | Concentration (mg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acetone | 0.24 |
| 2 | Isopropyl alcohol | 0.28 |
| 3 | 1,3-Pentadiene | 0.45 |
| 4 | 2-Methyl-dipropanol | 0.92 |
| 5 | Trichloromethane | 5.35 |
| 6 | Methylcyclopentane | 0.67 |
| 7 | Cyclohexane | 27.05 |
| 8 | Methylcyclohexane | 0.87 |
| 9 | Benzene | 0.29 |
| 10 | Ethyl acetate | 4.50 |
| 11 | Toluene | 5.99 |
| 12 | Butyl acetate | 7.45 |
| 13 | Tetrachloroethylene | 3.79 |
| 14 | Styrene | 5.69 |
| 16 | m/p-Xylene | 19.33 |
| 17 | o-Xylene | 9.51 |
| 18 | Phenol | 1.89 |
| 19 | Phenylacetate | 1.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Lin, D.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Emissions and Control Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from a Typical Chemical Enterprise. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020206
Wang L, Lin D, Liu R, Li J, Xu X. Emissions and Control Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from a Typical Chemical Enterprise. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lin, Dong Lin, Rui Liu, Jing Li, and Xiuyan Xu. 2023. "Emissions and Control Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from a Typical Chemical Enterprise" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020206
APA StyleWang, L., Lin, D., Liu, R., Li, J., & Xu, X. (2023). Emissions and Control Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds from a Typical Chemical Enterprise. Atmosphere, 14(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020206




