Hybrid Post-Processing on GEFSv12 Reforecast for Summer Maximum Temperature Ensemble Forecasts with an Extended-Range Time Scale over Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data Used
2.2. Calibration Methods
2.2.1. Quantile Mapping
2.2.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
2.2.3. Hybrid Post-Processing
2.3. Analysis Procedure
3. Results
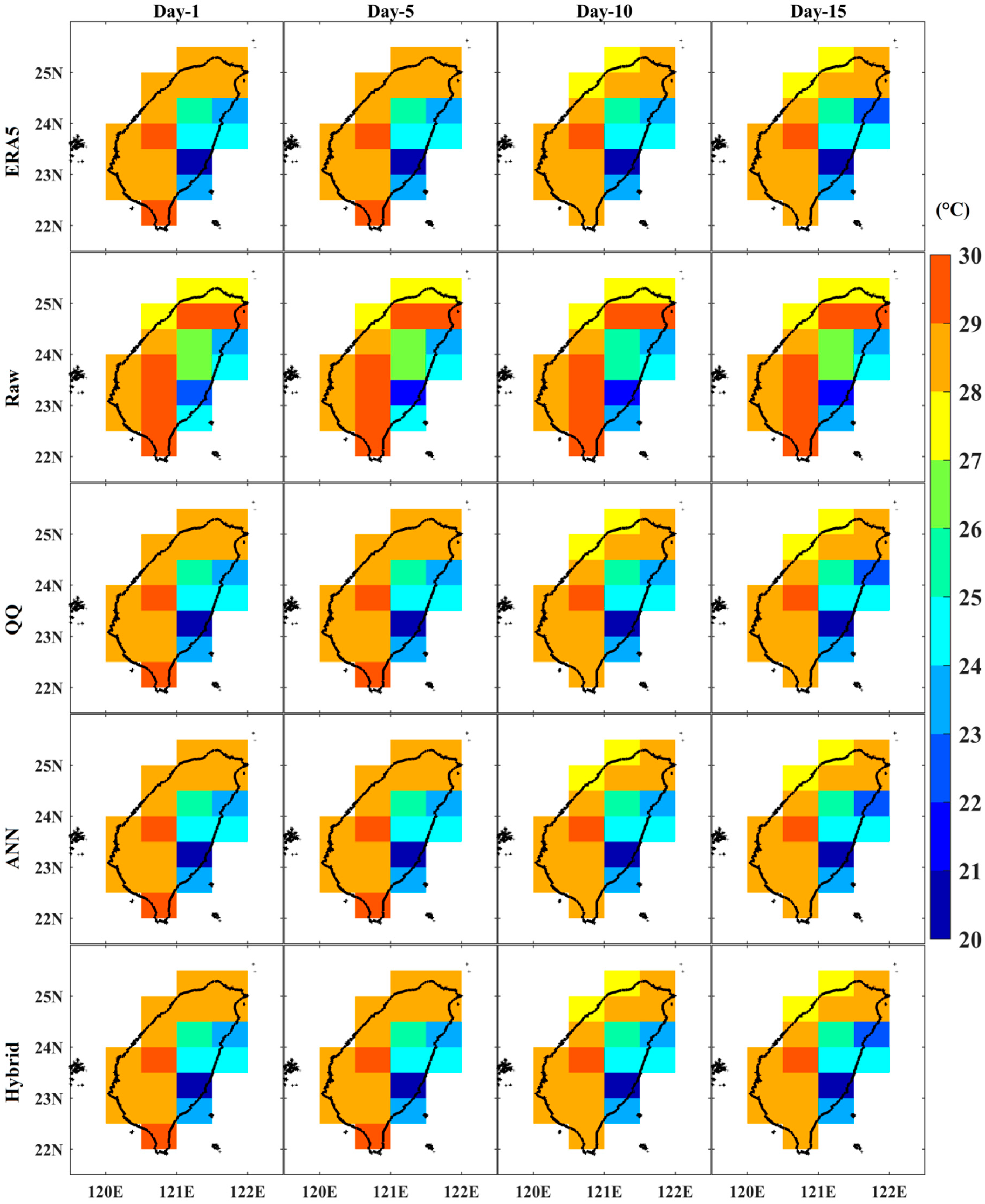
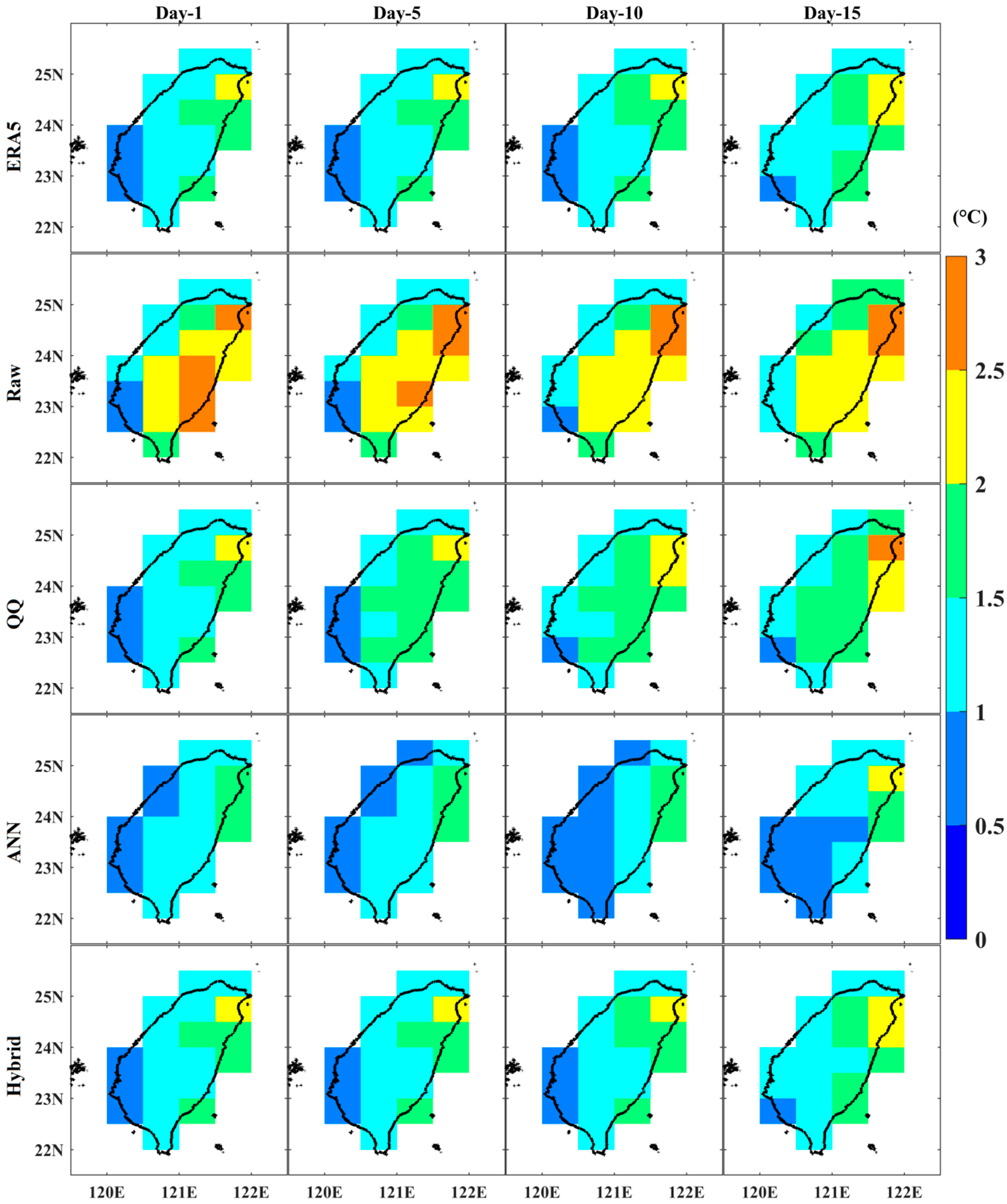
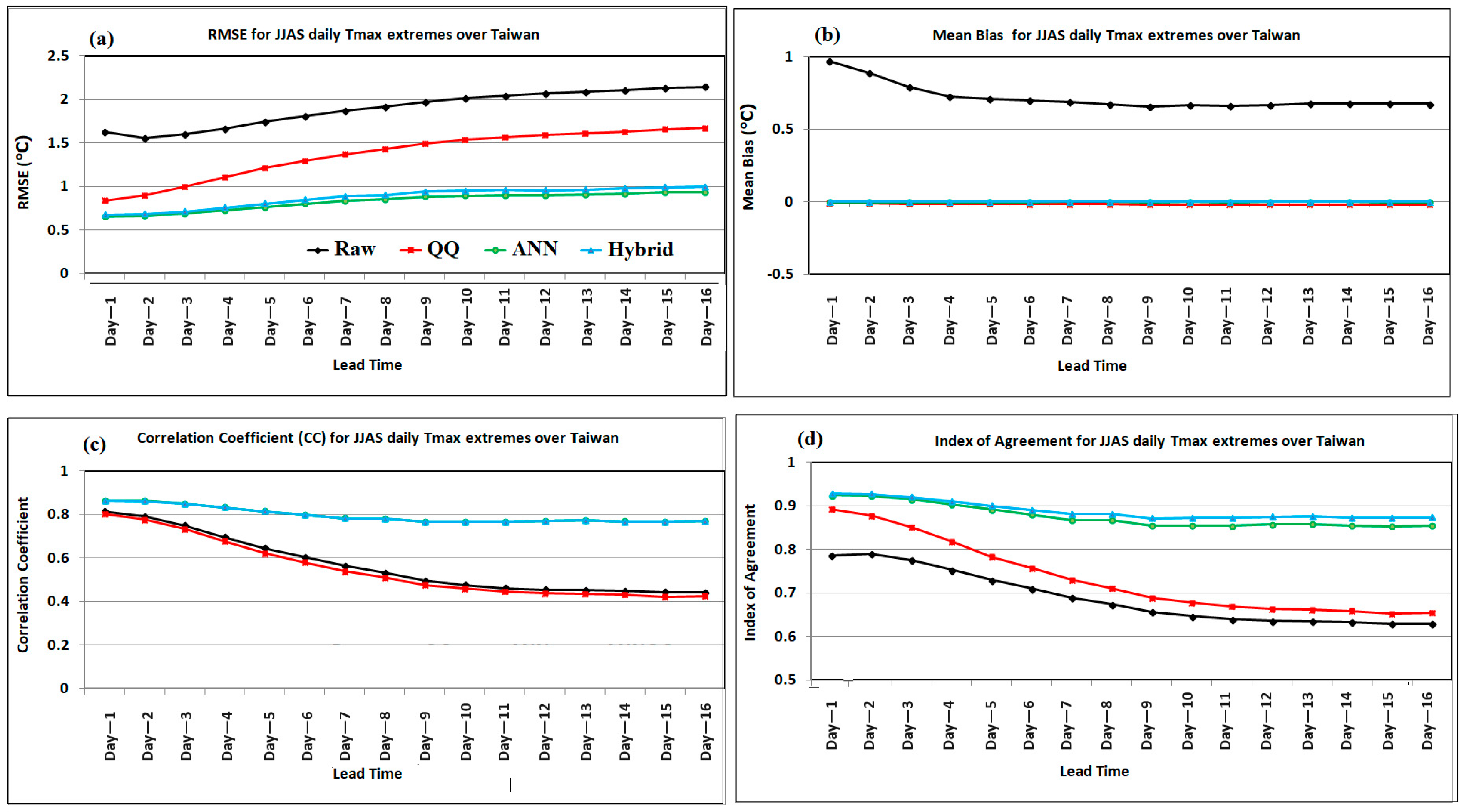
3.1. Prediction Skill of Raw, QQ, ANN, and Hybrid Post-Processing Methods for Summer Daily Tmax over Taiwan
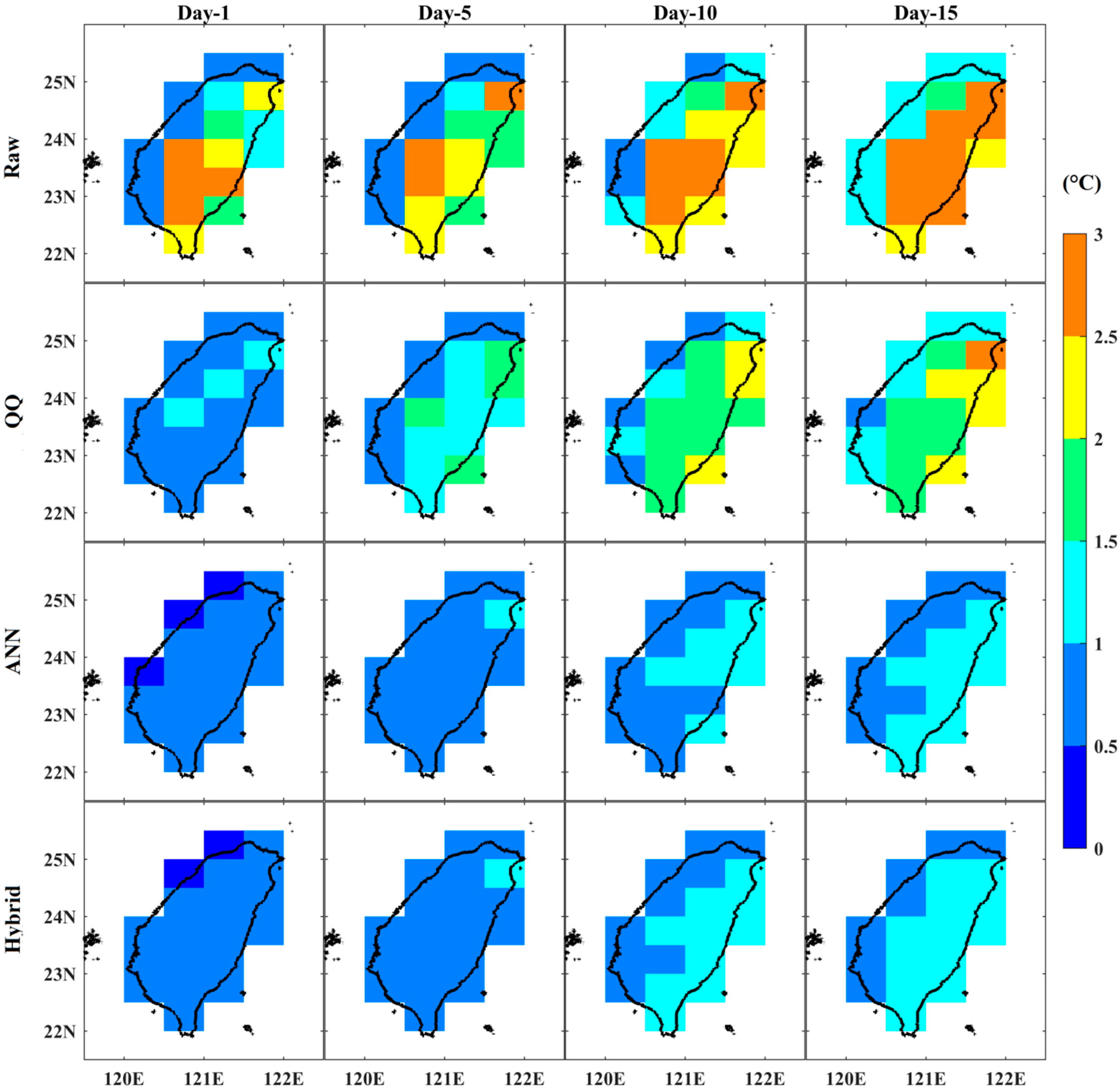
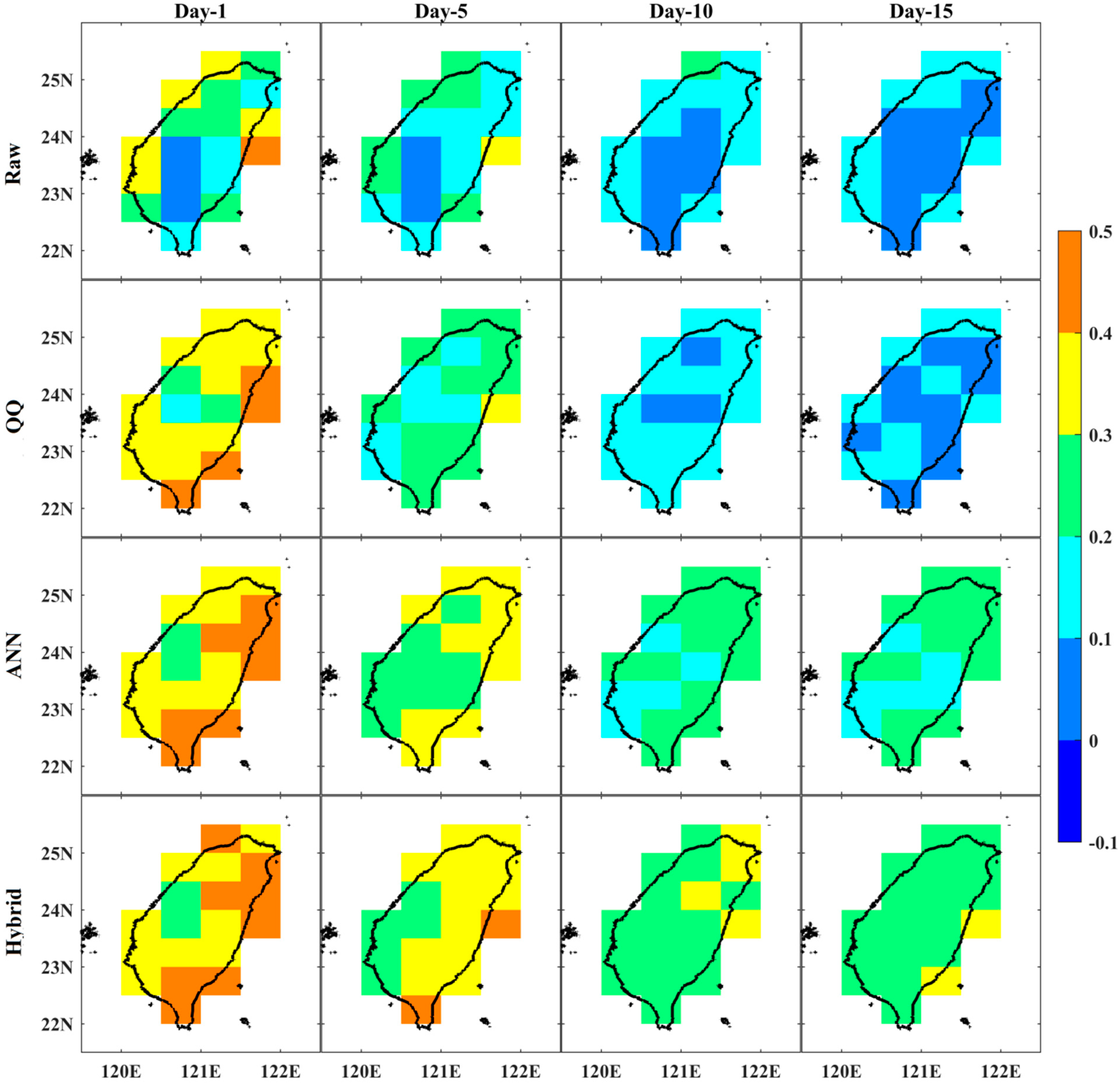
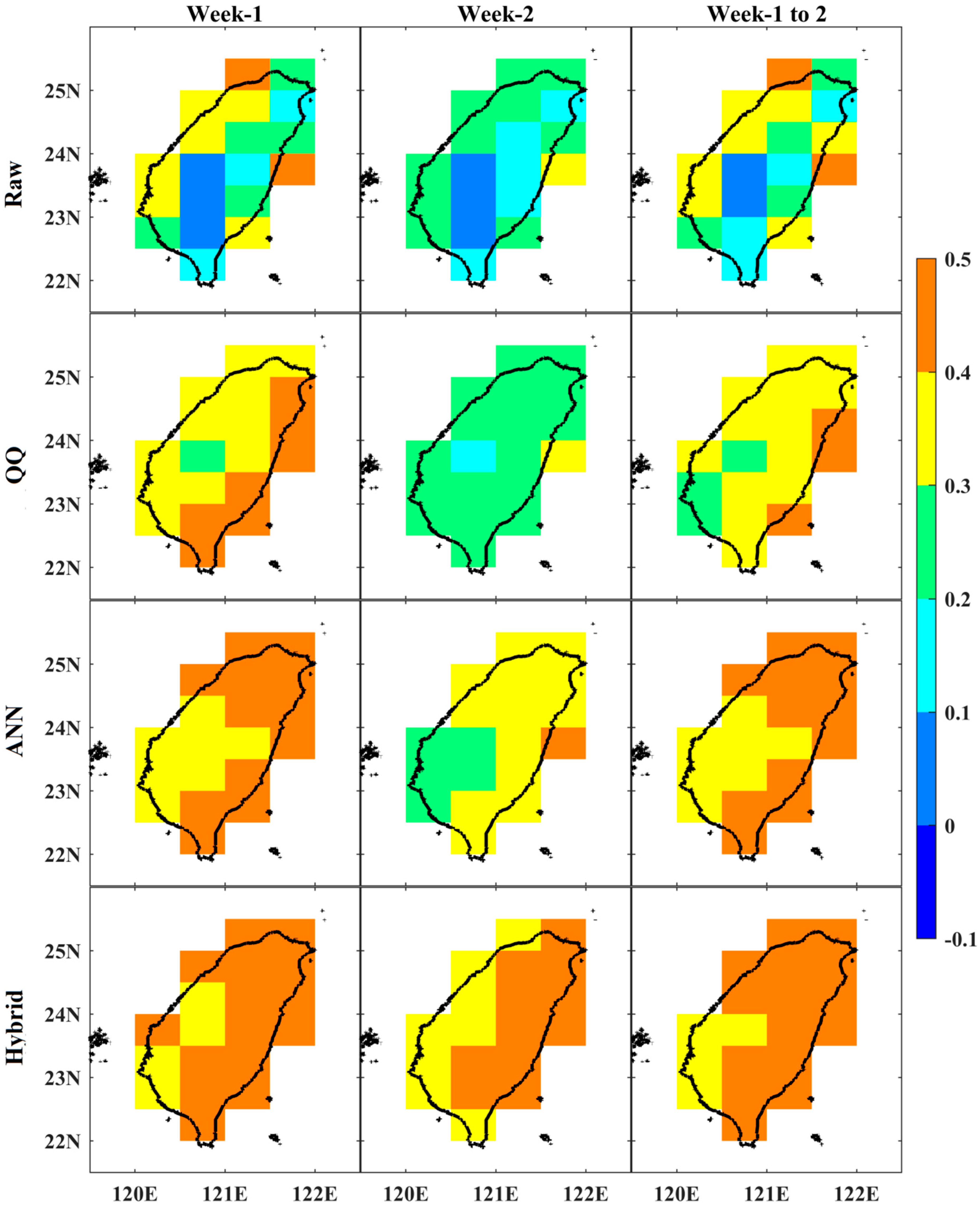
3.2. Statistical Categorical Skill Scores for Summer Daily Tmax Extremes over Taiwan from Raw, QQ, ANN, and Hybrid Methods
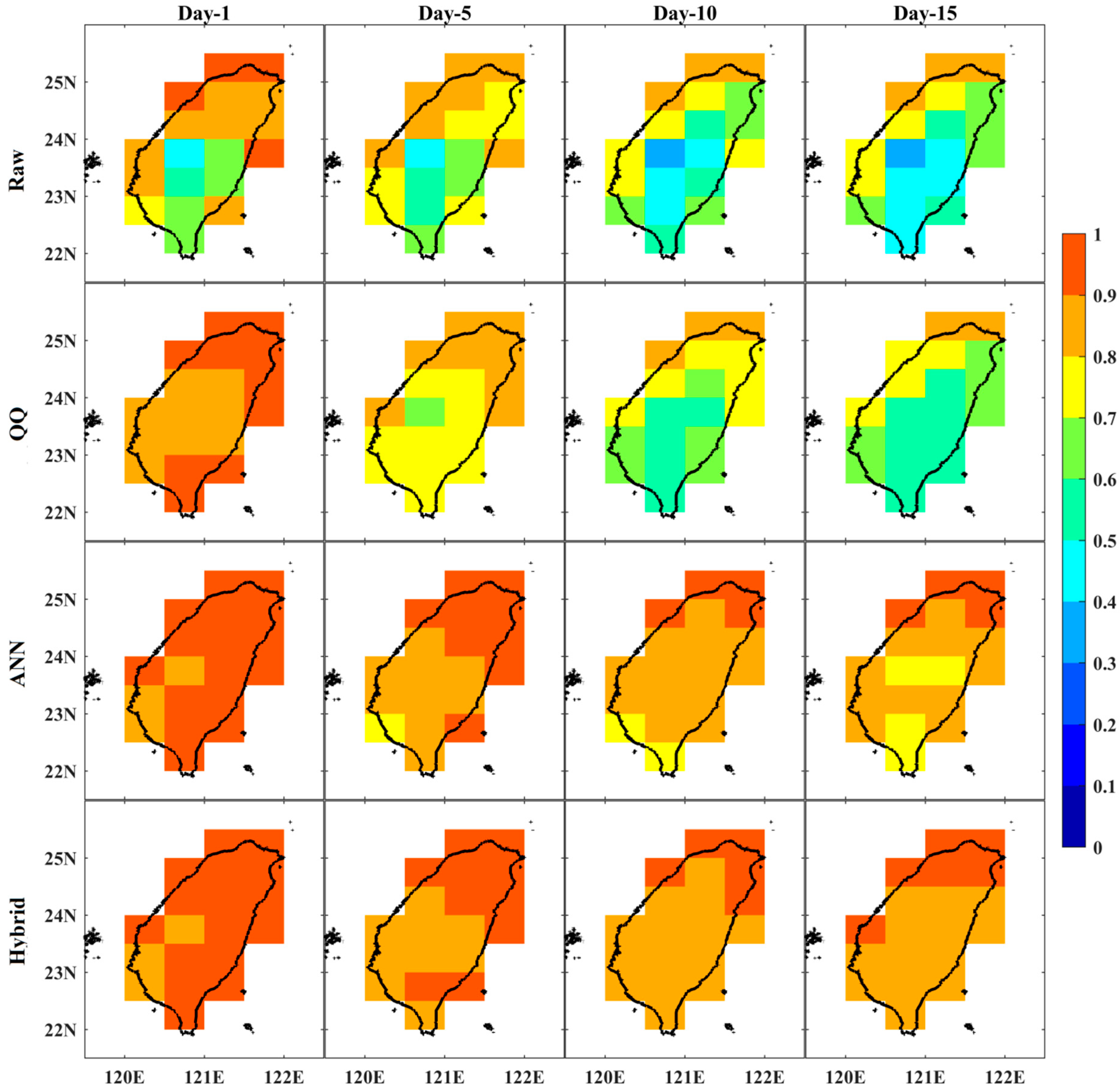
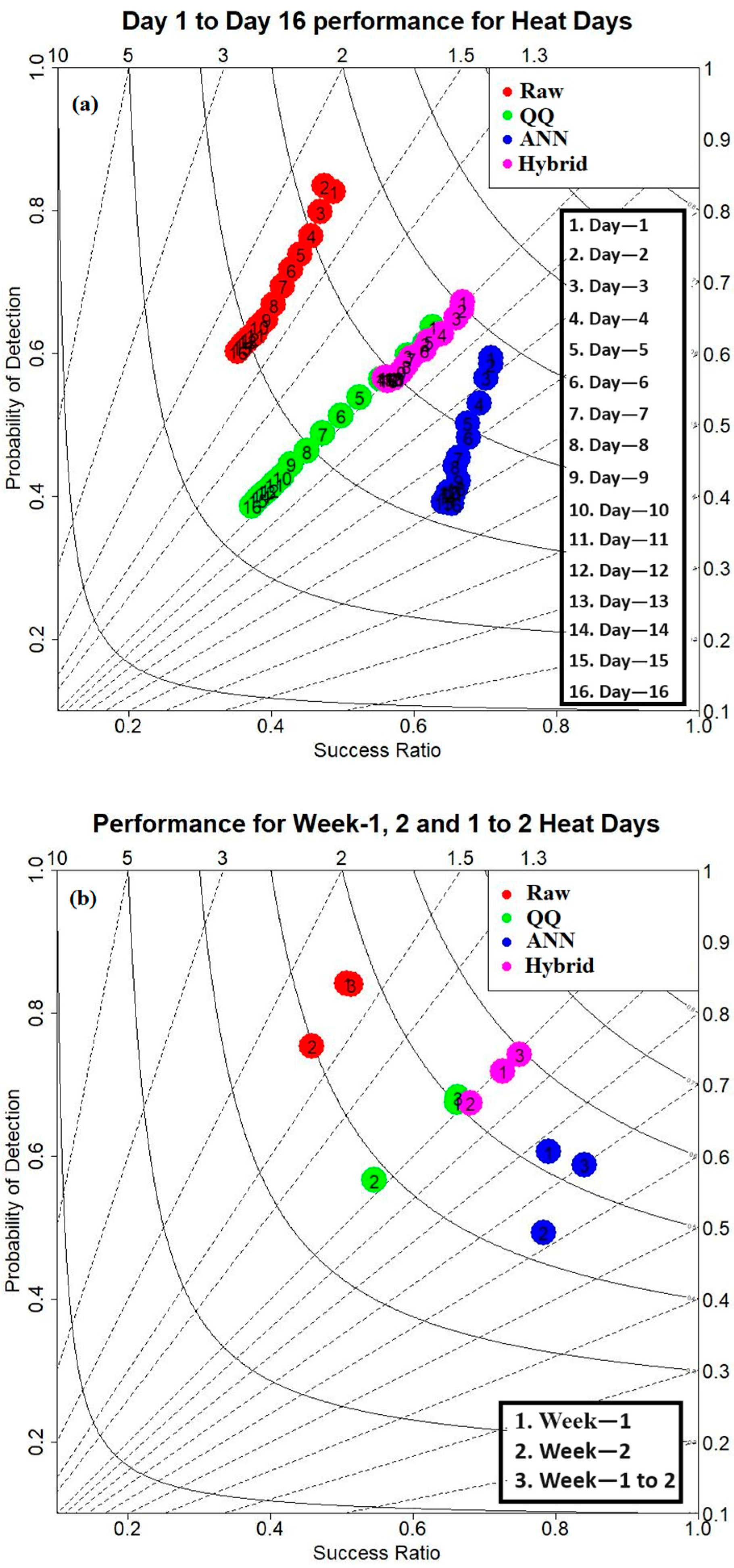
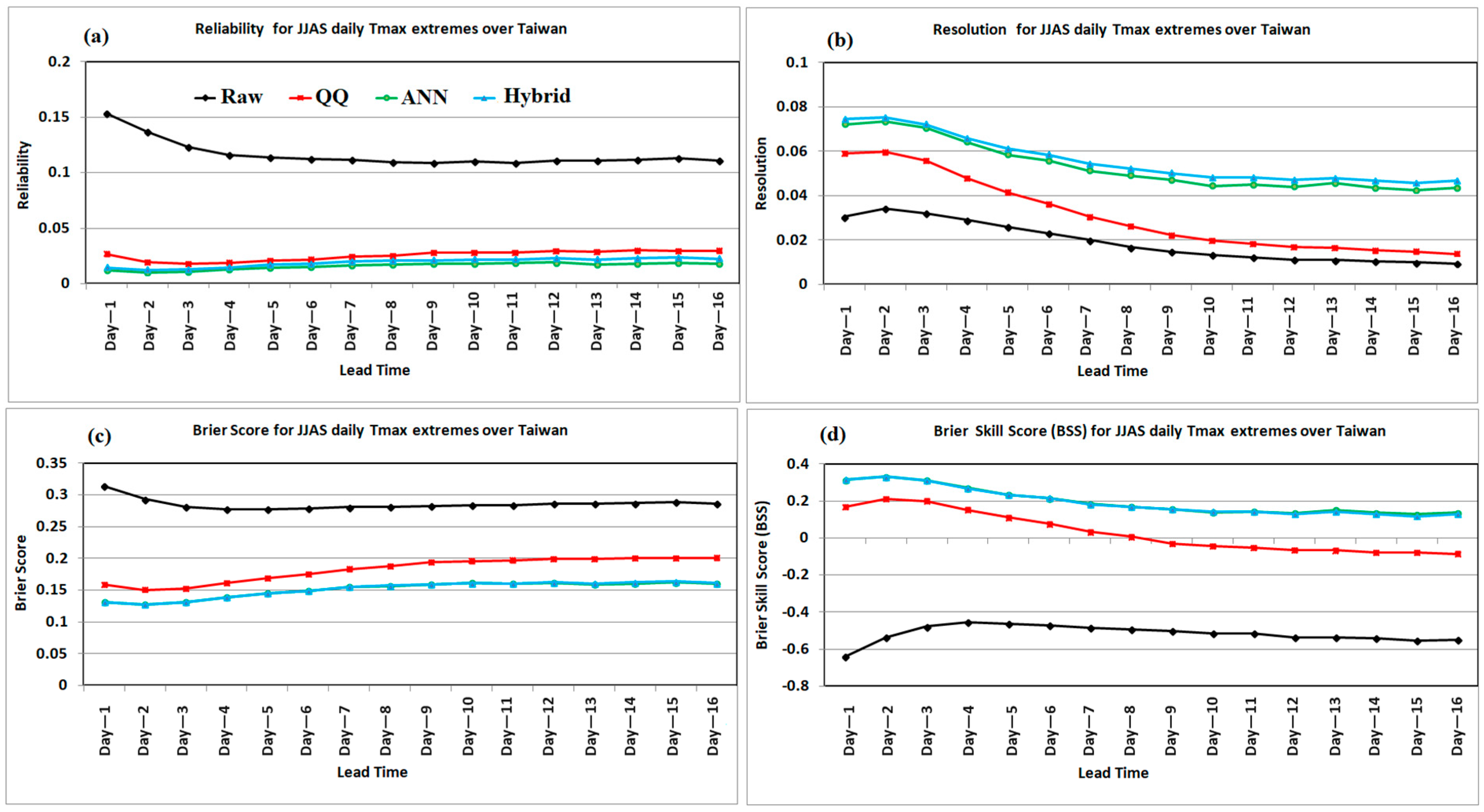
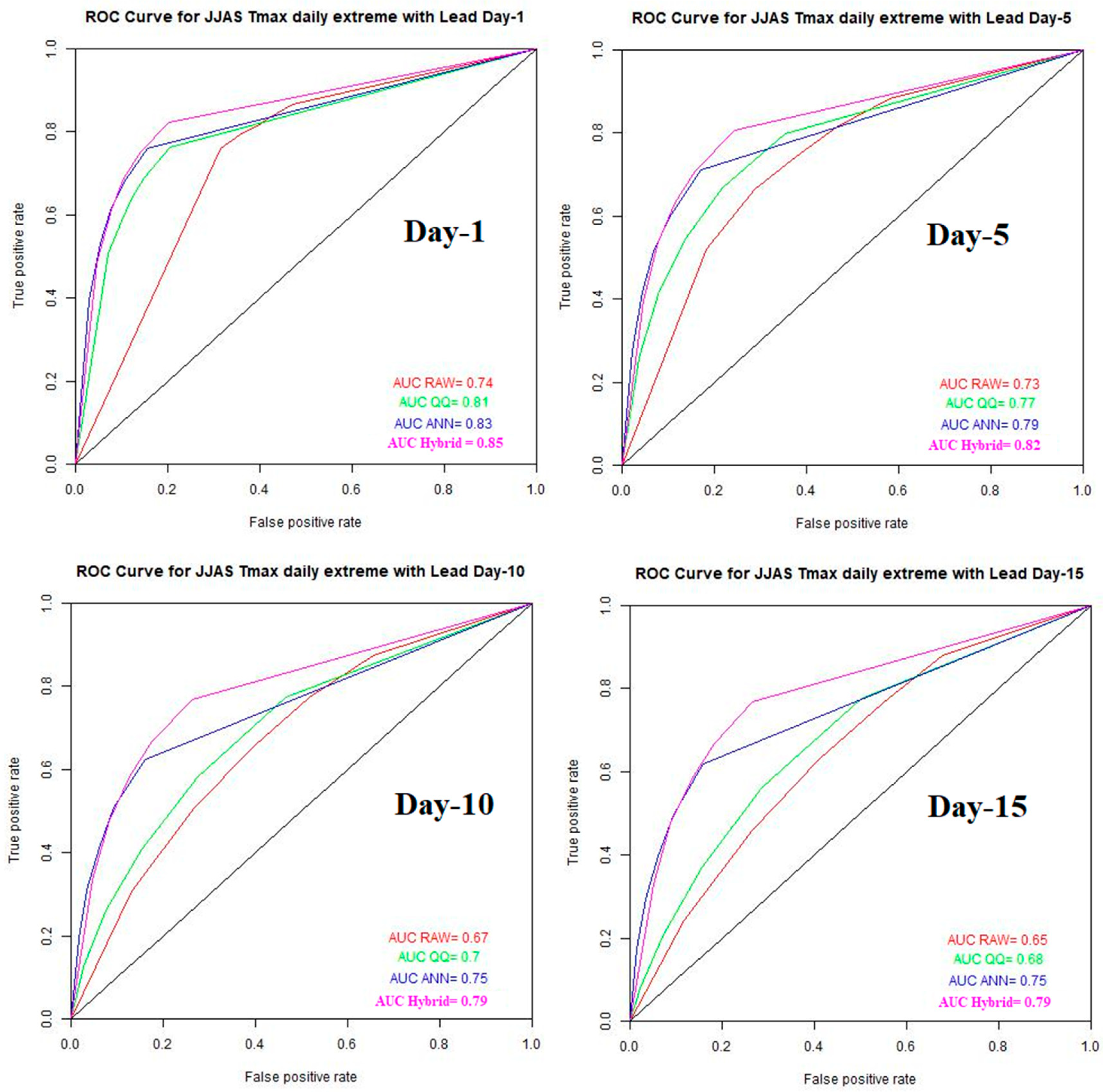
3.3. Probabilistic Prediction Skill Scores of Raw, QQ, ANN, and Hybrid Methods for Summer Daily Tmax Extremes
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Ono, M. Adaptation to Climate Change at Population Level in Japan. Epidemiology 2011, 22, S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswararao, M.M.; Mohanty, U.C.; Prasad, S.K.; Osuri, K.K.; Ramakrishna, S.S.V.S. Performance evaluation of NCEP climate forecast system for the prediction of winter temperatures over India. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2016, 126, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswararao, M.M.; Sinha, P.; Mohanty, U.C.; Mishra, S. Occurrence of More Heat Waves Over the Central East Coast of India in the Recent Warming Era. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrevula, N.R.; Ramu, D.A.; Nageswararao, M.M.; Rao, A.S. Inter-annual variability of pre-monsoon surface air temperatures over India using the North American Multi-Model Ensemble models during the global warming era. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2023, 151, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, D.; Lehner, F.; Ashfaq, M. Revisiting Recent U.S. Heat Waves in a Warmer and More Humid Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.M.; Schär, C. Consistent geographical patterns of changes in high-impact European heatwaves. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Tebaldi, C. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 2004, 305, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoyer-Tomic, K.E.; Kuhn, R.; Hudson, A. Heat Wave Hazards: An Overview of Heat Wave Impacts in Canada. Nat. Hazards 2003, 28, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Quan, X.-W.; Feng, J. Urban warming in the 2013 summer heat wave in eastern China. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 3015–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswararao, M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Tallapragada, V.; Chen, M.-S. Prediction Skill of GEFSv12 in Depicting Monthly Rainfall and Associated Extreme Events over Taiwan during the Summer Monsoon. Weather Forecast. 2022, 37, 2239–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.H.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z.D. Characteristics, processes, and causes of the spatio-temporal variabilities of the East Asian monsoon system. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 910–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chua, Y.J.; Sheng, Y.F.; Hsu, H.H.; Cheng, C.T.; Lin, Y.Y. Altitudinal and latitudinal dependence of future warming in Taiwan simulated by WRF nested with ECHAM5/MPIOM. Int. J. Clim. 2014, 35, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Fourth Assesment Report: Climate Change 2007; IPPC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.-Y.; Honda, Y.; Hong, Y.-C.; Pan, X.-C.; Guo, Y.-L.; Kim, H. Ambient temperature and mortality: An international study in four capital cities of East Asia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 408, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, A.; Ruti, P.M.; Rixen, M. Progress in subseasonal to seasonal prediction through a joint weather and climate community effort. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Robertson, A.W. Evaluation of Submonthly Precipitation Forecast Skill from Global Ensemble Prediction Systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 2871–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Ardilouze, C.; Bonet, A.; Brookshaw, A.; Chen, M.; Codorean, C.; Déqué, M.; Ferranti, L.; Fucile, E.; Fuentes, M.; et al. The sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction project (S2S) and the prediction of extreme events. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswararao, M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Tallapragada, V. Prediction Skill of GEFSv12 for Southwest Summer Monsoon Rainfall and Associated Extreme Rainfall Events on Extended Range Scale over India. Weather Forecast. 2022, 37, 1135–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.-S.; Jin, K.; Wang, B.; Lau, K.M.; Shukla, J.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Schubert, S.; Wailser, D.; Stern, W.; Kitoh, A.; et al. Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 19, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, H.R.; Lowry, D.A. The use of model output statistics (MOS) in objective weather forecasting. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1972, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, T.M.; Colucci, S.J. Evaluation of Eta–RSM Ensemble Probabilistic Precipitation Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagli, G.M.; Yang, D.; Srinivasan, D. Ensemble solar forecasting using data-driven models with probabilistic post-processing through GAMLSS. Sol. Energy 2020, 208, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Robertson, D.E.; Bennett, J.C. Improved error modelling for streamflow forecasting at hourly time steps by splitting hydrographs into rising and falling limbs. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannitsem, S.; Wilks, D.S.; Messner, J.W. (Eds.) Chapter 3: Univariate ensemble forecasting. In Statistical Postprocessing of Ensemble Forecasts; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128123720. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, E.E. Ability of a Poor Man’s Ensemble to Predict the Probability and Distribution of Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2461–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, T.M.; Whitaker, J.S. Probabilistic Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Based on Reforecast Analogs: Theory and Application. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 3209–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Precipitation Calibration Based on the Frequency-Matching Method (FMM). Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sinsky, E.; Fu, B.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Xue, X.; Hou, D.; Peng, J.; Nageswararao, M.M.; et al. GEFSv12 Reforecast Dataset for Supporting Subseasonal and Hydrometeorological Applications. Mon. Weather Rev. 2022, 150, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Bennett, J.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Schepen, A.; Wood, A.W.; Robertson, D.E.; Ramos, M.-H. How Suitable is Quantile Mapping For Postprocessing GCM Precipitation Forecasts? J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkade, J.; Brown, J.; Reggiani, P.; Weerts, A. Post-processing ECMWF precipitation and temperature ensemble reforecasts for operational hydrologic forecasting at various spatial scales. J. Hydrol. 2013, 501, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Song, Y.; Schepen, A.; Robertson, D.E.; Ryu, D.; Pappenberger, F. An evaluation of ECMWF SEAS5 seasonal climate forecasts for Australia using a new forecast calibration algorithm. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, B.; Hou, D.; Peng, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, W. The development of the Next NCEP Global Ensemble Forecast System. Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin, NOAA’s National Weather Service. In Proceedings of the 43rd NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop (CDPW), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 23–25 October 2019; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, D.; Fu, B.; Li, W.; Guan, H.; Sinsky, E.; Kolczynski, W.; Xue, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. The Development of the NCEP Global Ensemble Forecast System Version 12. Weather Forecast. 2022, 37, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, T.M.; Whitaker, J.S.; Shlyaeva, A.; Bates, G.; Fredrick, S.; Pegion, P.; Sinsky, E.; Zhu, Y.; Tallapragada, V.; Guan, H.; et al. The Reanalysis for the Global Ensemble Forecast System, Version 12. Mon. Weather Rev. 2022, 150, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.M.; Lin, S.-J. A Two-Way Nested Global-Regional Dynamical Core on the Cubed-Sphere Grid. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, W.; Kwon, Y.C.; Hong, S.-Y.; Tallapragada, V.; Yang, F. Updates in the NCEP GFS Cumulus Convection Schemes with Scale and Aerosol Awareness. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, K.-S.S.; Han, J. Sensitivity of a Cumulus Parameterization Scheme to Precipitation Production Representation and Its Impact on a Heavy Rain Event over Korea. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.; Shephard, M.; Mlawer, E.; Delamere, J.; Iacono, M.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Boukabara, S.; Brown, P. Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: A summary of the AER codes. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.-Y.; Baik, J.-J. Momentum Flux by Thermally Induced Internal Gravity Waves and Its Approximation for Large-Scale Models. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 55, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, J.C.; Kanamitsu, M.; Caplan, P.M.; Sela, J.G.; White, G.H.; Kalnay, E. Mountain induced gravity wave drag parameterization in the NMC medium-range forecast model. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–26 February 1988; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Peña, M.; Li, W.; Melhauser, C.; Hou, D. Impact of Sea Surface Temperature Forcing on Weeks 3 and 4 Forecast Skill in the NCEP Global Ensemble Forecasting System. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 2159–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Hou, D.; Melhauser, C.; Sinsky, E.; Peña, M.; Fu, B.; Guan, H.; Kolczynski, W.; et al. Toward the Improvement of Subseasonal Prediction in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction Global Ensemble Forecast System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6732–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hou, D.; Sinsky, E.; Melhauser, C.; Peña, M.; Guan, H.; Wobus, R. Evaluating the MJO prediction skill from different configurations of NCEP GEFS extended forecast. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 4923–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutts, G. A kinetic energy backscatter algorithm for use in ensemble prediction systems. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 3079–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutts, G.; Palmer, T.N. The use of high-resolution numerical simulations of tropical circulation to calibrate stochastic physics schemes. In Proceedings of the ECMWF/CLIVAR Workshop on Simulation and Prediction of Intra-Seasonal Variability with Emphasis on the MJO, Reading, UK, 3–6 November 2004; pp. 83–102. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/12212 (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Buizza, R.; Milleer, M.; Palmer, T.N. Stochastic representation of model uncertainties in the ECMWF ensemble prediction system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 2887–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N.; Buizza, R.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Jung, T.; Leutbecher, M.; Shutts, G.J.; Steinheimer, M.; Weisheimer, A. Stochastic parametrization and model uncertainty. ECMWF Tech. Memo. 2009, 598, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1959 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2018. Available online: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.adbb2d47 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Lee, C.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Lo, T.-T. A Revised Meiyu-Season Onset Index for Taiwan Based on ERA5. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikou, K.; Lazoglou, G.; Tolika, K.; Anagnostopoulou, C. Reliability of the ERA5 in Replicating Mean and Extreme Temperatures across Europe. Water 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholl, B.; Lee, Y.H.; Campbell, A.G.; Dev, S. Evaluating the reliability of air temperature from ERA5 reanalysis data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1004505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Haerter, J.O.; Coppola, E. Statistical bias correction for daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2010, 99, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Verma, N.; Tripathi, K.C. A review study of weather forecasting using artificial neural network approach. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Matarneh, L.; Sheta, A.; Bani-Ahmad, S.; Alshaer, J.; Al-Oqily, I. Development of Temperature-based Weather Forecasting Models Using Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic. Int. J. Multimedia Ubiquitous Eng. 2014, 9, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Lu, S. Performance Analysis of Various Activation Functions in Artificial Neural Networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1237, 022030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, J.; Marohasy, J. Input selection and optimisation for monthly rainfall forecasting in Queensland, Australia, using artificial neural networks. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Imteaz, M.; Jenkins, G. Catchment flow estimation using Artificial Neural Networks in the mountainous Euphrates Basin. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Lazin, N.M.; Samsuri, S.F.M. Neural network modeling and identification of naturally ventilated tropical greenhouse climates. Wseas Trans. Syst. Control 2014, 9, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Mcculloch, W.S.; Pitts, W.H. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausett, L. Fundamentals of Neural Network; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Panda, R.K. Daily sediment yield modeling with artificial neural network using 10-fold cross validation method: A small agricultural watershed, Kapgari, India. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Panda, R.K. Bootstrap-based artificial neural network analysis for estimation of daily sediment yield from a small agricultural watershed. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht-Nielsen, R. Kolmogorov’s mapping neural network existence theorem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 1 October 1987; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 3, pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Singh, G.; Mohanty, U.C. Prediction of Monthly Summer Monsoon Rainfall Using Global Climate Models Through Artificial Neural Network Technique. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, C.; Sulungu, E.D. Application of neural network in prediction of temperature: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 11487–11498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebber, P.J. Visualizing Multiple Measures of Forecast Quality. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brier, G.W. Verification of forecasts expressed in terms of probability. Mon. Weather Rev. 1950, 78, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, Z.; Talagrand, O.; Candille, G.; Zhu, Y. Probability and ensemble forecasts. Forecast Verification: A Practitioner’s Guide in Atmospheric Science; Jolliffe, I.T., Stephenson, D.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 137–163. [Google Scholar]
- Weijs, S.V.; van Nooijen, R.; van de Giesen, N. Kullback–Leibler Divergence as a Forecast Skill Score with Classic Reliability–Resolution–Uncertainty Decomposition. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, C. The ROC Curve and the Area under It as Performance Measures. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. of Hidden Layers: | 1 |
| No. of nodes/neurons in the hidden layer | 7 |
| Neural Network used | Feed-forward network |
| Neural Network processing functions | Map matrix row minimum and maximum values to [−1, 1] |
| Data divided function | 70% data for training and 30% data for validation |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Max number of iterations/epochs used | 1000 |
| Error tolerance for stopping criterion | 1 × 10−14 |
| Training function used | Supervised weight/bias training function with sequential order weight/bias training (trains) |
| Neural Network performance functions used | Mean squared error performance function |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nageswararao, M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Tallapragada, V.; Chen, M.-S. Hybrid Post-Processing on GEFSv12 Reforecast for Summer Maximum Temperature Ensemble Forecasts with an Extended-Range Time Scale over Taiwan. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111620
Nageswararao MM, Zhu Y, Tallapragada V, Chen M-S. Hybrid Post-Processing on GEFSv12 Reforecast for Summer Maximum Temperature Ensemble Forecasts with an Extended-Range Time Scale over Taiwan. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(11):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111620
Chicago/Turabian StyleNageswararao, Malasala Murali, Yuejian Zhu, Vijay Tallapragada, and Meng-Shih Chen. 2023. "Hybrid Post-Processing on GEFSv12 Reforecast for Summer Maximum Temperature Ensemble Forecasts with an Extended-Range Time Scale over Taiwan" Atmosphere 14, no. 11: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111620
APA StyleNageswararao, M. M., Zhu, Y., Tallapragada, V., & Chen, M.-S. (2023). Hybrid Post-Processing on GEFSv12 Reforecast for Summer Maximum Temperature Ensemble Forecasts with an Extended-Range Time Scale over Taiwan. Atmosphere, 14(11), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111620









