Near-Road Traffic Emission Dispersion Model: Traffic-Induced Turbulence Kinetic Energy (TKE) Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Program
2.2. Traffic-Induced TKE
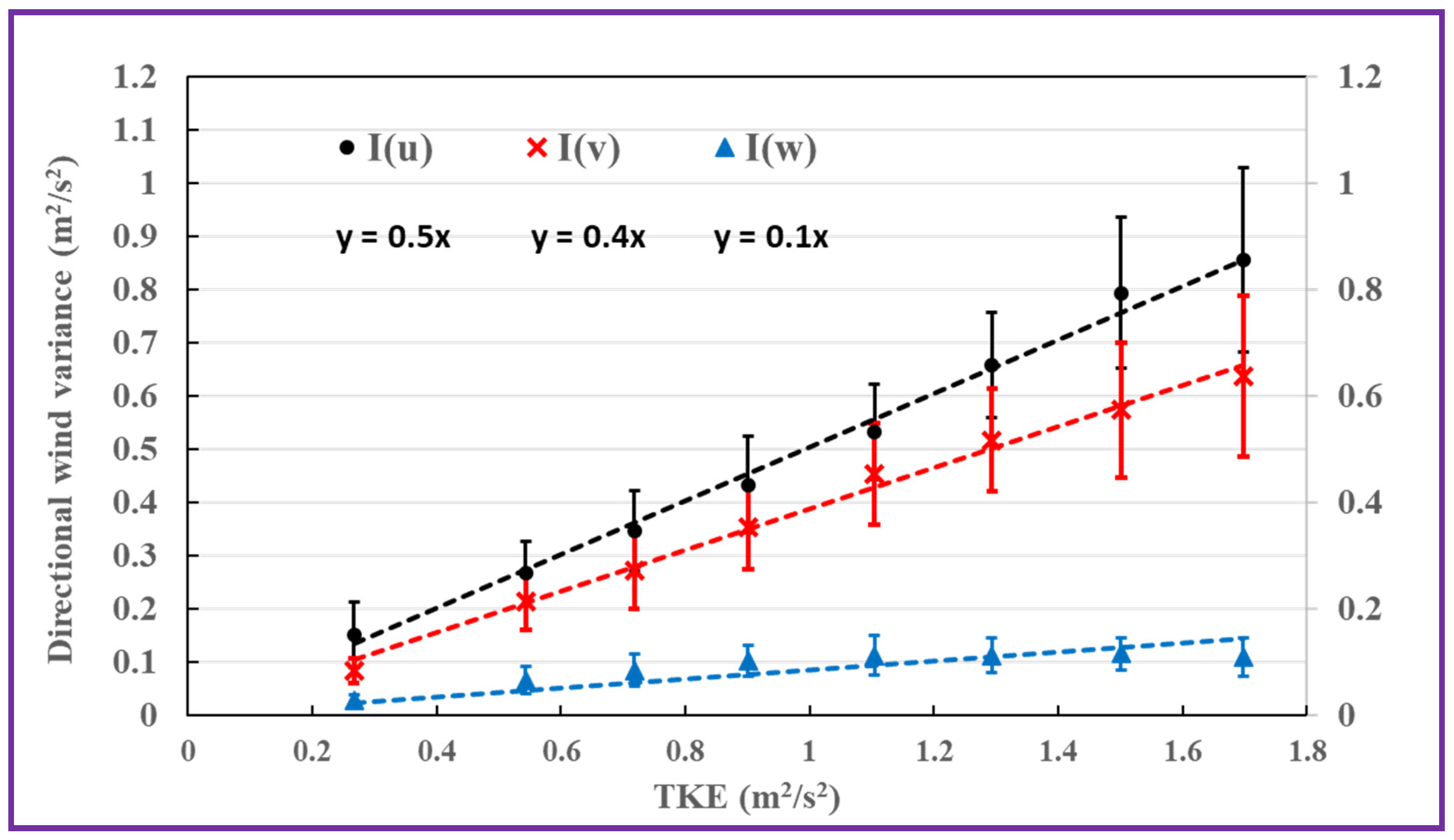
2.3. Near-Road Characterization of TKE and Three-Dimensional Wind STD
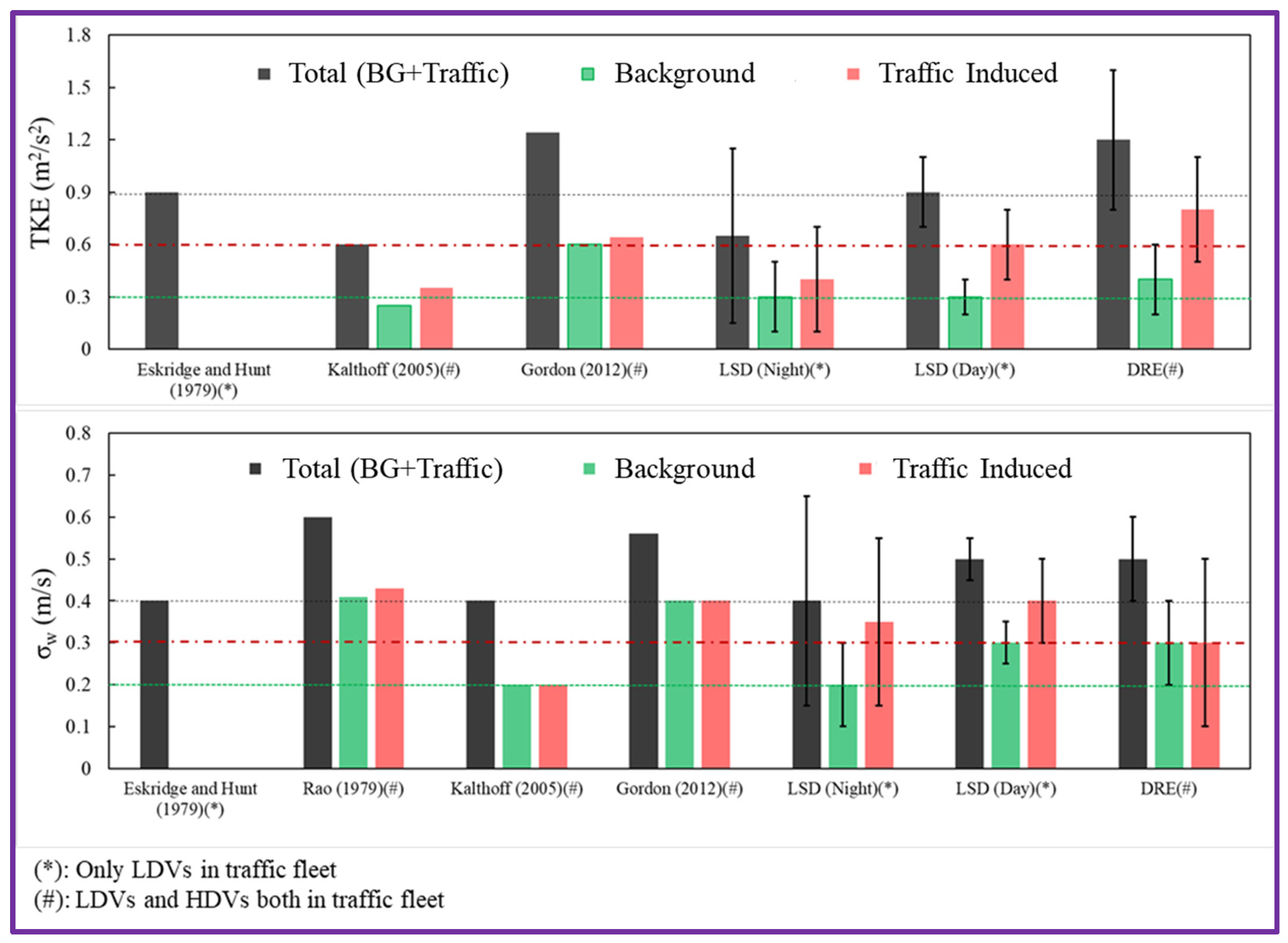
3. Results
3.1. TKE and Wind STD
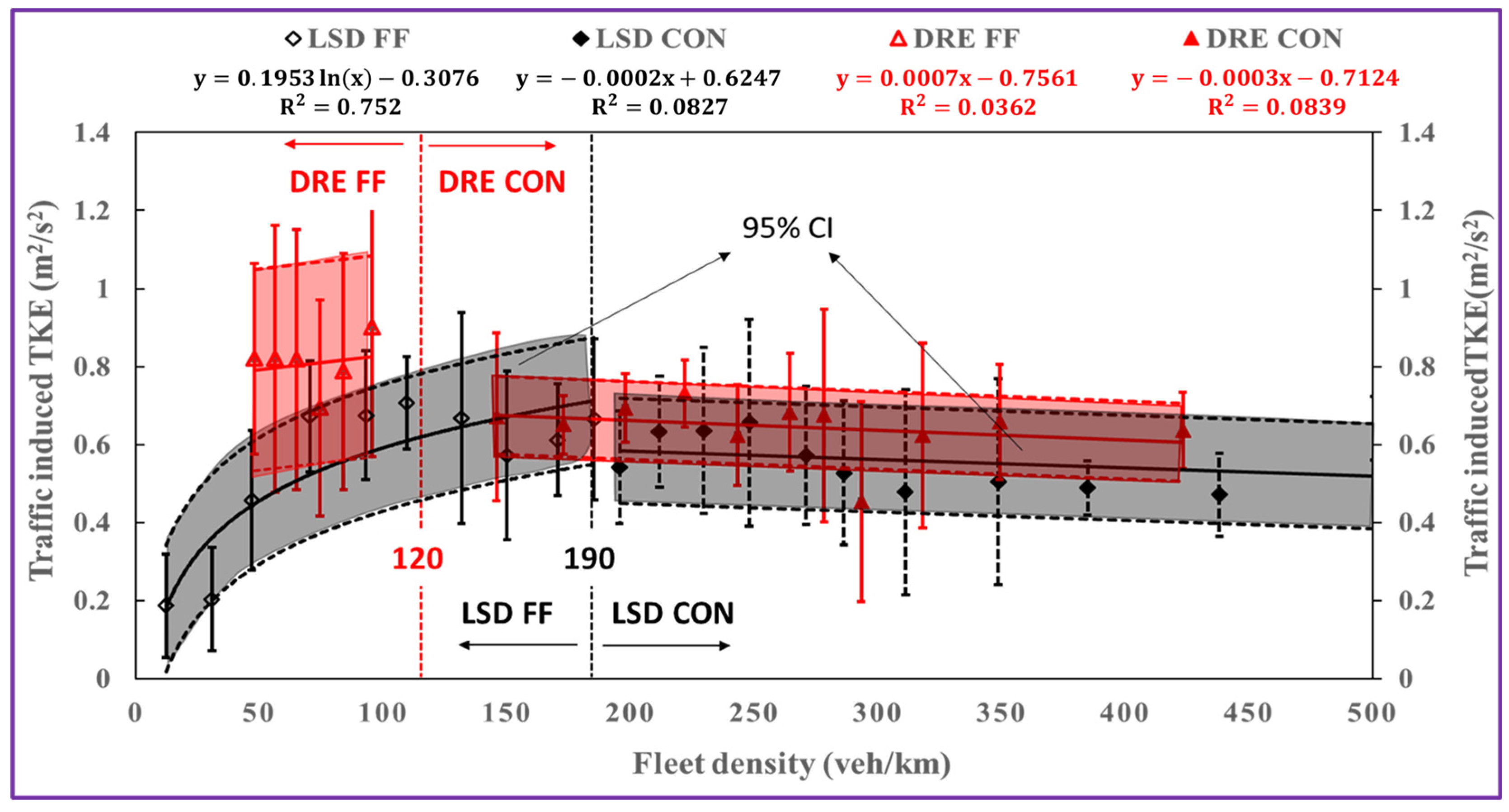
3.2. TKEtr as a Function of Traffic Conditions
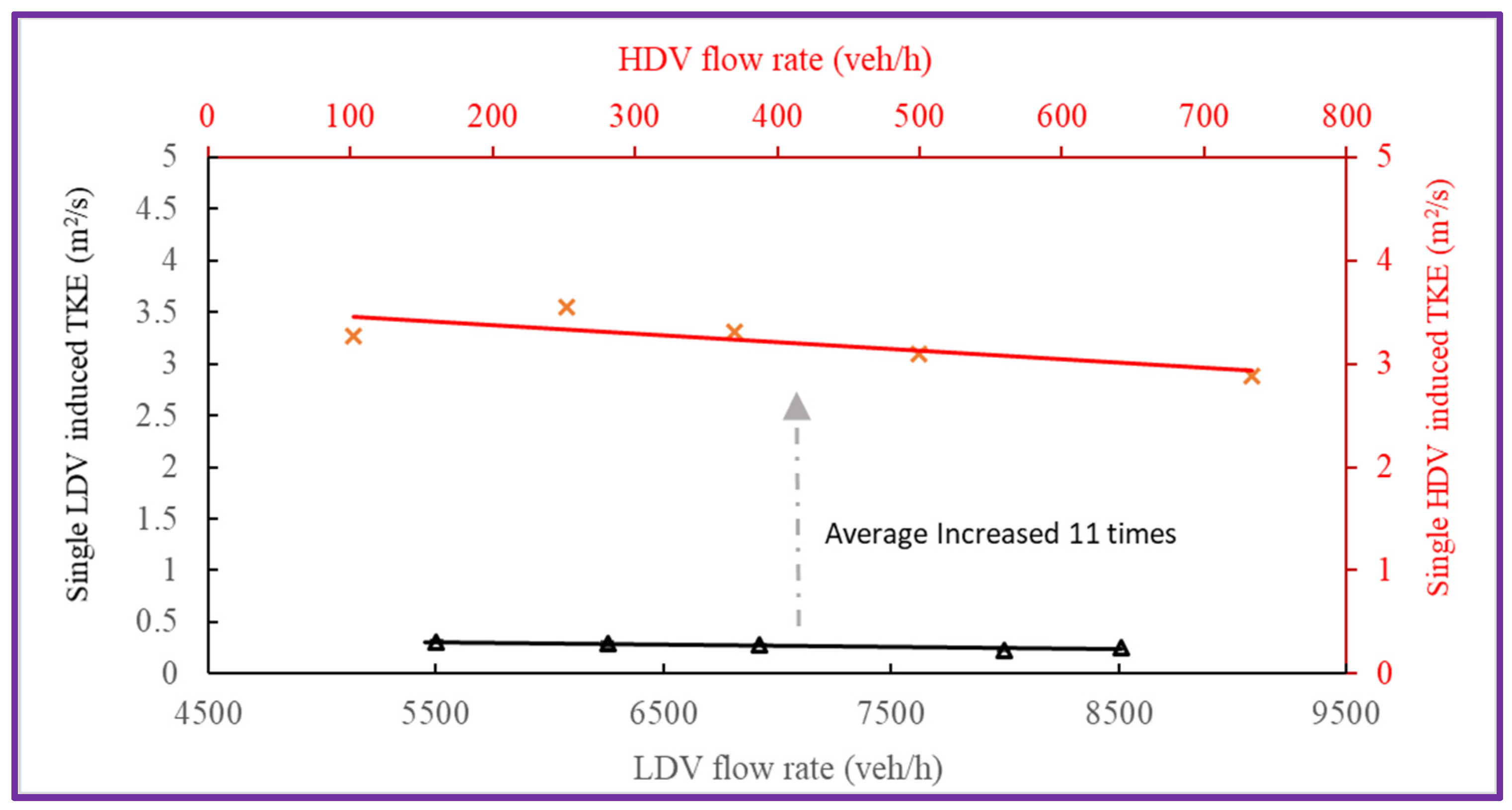
3.3. The Influence of HDV on Near-Road TKEtr
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, C. Outline of a Novel Method for the Prediction of Atmospheric Pollution Dispersal from Road Vehicles. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1996, 65, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumer, D.; Vogel, B.; Fiedler, F. A New Parameterisation of Motorway-Induced Turbulence and Its Application in a Numerical Model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, R.E.; Rao, S.T. Measurement and Prediction of Traffic-Induced Turbulence and Velocity Fields Near Roadways. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Gunter, R.; White, J.; Hosker, R. Turbulence and Dispersion Modeling Near Highways. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4337–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatram, A.; Isakov, V.; Thoma, E.; Baldauf, R. Analysis of Air Quality Data near Roadways Using a Dispersion Model. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9481–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Jamriska, M.; Thomas, S.; Ferreira, L.; Mengersen, K.; Wraith, D.; McGregor, F. Quantification of Particle Number Emission Factors for Motor Vehicles from On-Road Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9130–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamriska, M.; Morawska, L. A model for determination of motor vehicle emission factors from on-road measurements with a focus on submicrometer particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 264, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, R.E.; Petersen, W.B.; Rao, S.T. Turbulent Diffusion Behind Vehicles: Effect of Traffic Speed on Pollutant Concentrations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1991, 41, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, R.E.; Hunt, J.C.R. Highway Modeling. Part I: Prediction of Velocity and Turbulence Fields in the Wake of Vehicles. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1979, 18, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Dhaniyala, S. A Dispersion Model for Traffic Produced Turbulence in a Two-Way Traffic Scenario. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2011, 11, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.; Saunders, J.W.; Hoffmann, P.H. Turbulence Experienced by Moving Vehicles. Part I. Introduction and Turbulence Intensity. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1995, 57, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, P. Wind Spectrum and Correlation Characteristics Relative to Vehicles Moving through cross Wind Field. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 133, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidhagen, L.; Johansson, C.; Omstedt, G.; Langner, J.; Olivares, G. Model Simulations of NOx and Ultrafine Particles Close to a Swedish Highway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6730–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, S.; Jia, C.Q. A New Approach to Quantifying Vehicle Induced Turbulence for Complex Traffic Scenarios. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlodin, A.M.; Sotudeh-Gharebagh, R.; Zhu, Y. Modeling of Dispersion near Roadways Based on the Vehi-cle-Induced Turbulence Concept. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Steffens, J.T.; Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhang, K.M. Modeling Multi-Scale Aerosol Dynamics and Micro-Environmental Air Quality near a Large Highway Intersection Using the CTAG Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, K.M. Coupled Turbulence and Aerosol Dynamics Modeling of Vehicle Exhaust Plumes Using the CTAG model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, M.; Kumar, P.; Robins, A. Wind Tunnel Measurements for Dispersion Modelling of Vehicle Wakes. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheli, F.; Corradi, R.; Sabbioni, E.; Tomasini, G. Wind Tunnel Tests on Heavy Road Vehicles: Cross Wind Induced Loads—Part 1. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheli, F.; Ripamonti, F.; Sabbioni, E.; Tomasini, G. Wind Tunnel Tests on Heavy Road Vehicles: Cross Wind Induced Loads—Part 2. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, R.E.; Thompson, R.S. Experimental and Theoretical Study of the Wake of a Block-Shaped Vehicle in A Shear-Free Boundary Flow. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 2821–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heist, D.K.; Perry, S.G.; Brixey, L.A. A Wind Tunnel Study of the Effect of Roadway Configurations on the Dispersion of Traffic-Related Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5101–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner-Klein, P.; Fedorovich, E.; Rotach, M. A Wind Tunnel Study of Organised and Turbulent Air Motions in Urban Street Canyons. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2001, 89, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.H.; Kontis, K. Flow around an Articulated Lorry Model. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 406, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, B.R.; Belluz, L.; Belzile, M. Measurement of the On-Road Turbulence Environment Experienced by Heavy Duty Vehicles. SAE Int. J. Commer. Veh. 2014, 7, 685–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, D.; Burton, D.; Thompson, M.; Sheridan, J. On the near Wake of a Simplified Heavy Vehicle. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 66, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Estébanez, A.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Yagüe, C.; Laina, R.; Castro-Fresno, D. Field Experimental Study of Traffic-Induced Turbulence on Highways. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belušić, D.; Lenschow, D.H.; Tapper, N.J. Performance of a Mobile Car Platform for Mean Wind and Turbulence Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Staebler, R.M.; Liggio, J.; Makar, P.; Li, S.M.; Wentzell, J.; Lee, P.; Brook, J.R. Measurements of En-hanced Turbulent Mixing near Highways. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1618–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.T.; Sedefian, L.; Czapski, U.H. Characteristics of Turbulence and Dispersion of Pollutants near Major Highways. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1979, 18, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sedefian, L.; Rao, S.T.; Czapski, U. Effects of Traffic-Generated Turbulence on Near-Field Dispersion. Atmos. Environ. 1981, 15, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadle, S.H.; Chock, D.P.; Monson, P.R.; Heuss, J.M. General Motors Sulfate Dispersion Experiment: Ex-Perimental Procedures and Results. J. Air Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1977, 27, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chock, D. General Motors Sulfate Dispersion Experiment—An Overview of the Wind, Temperature, and Concentration Fields. Atmos. Environ. 1977, 11, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solazzo, E.; Vardoulakis, S.; Cai, X. Evaluation of Traffic-Producing Turbulence Schemes within Operational Street Pollution Models Using Roadside Measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5357–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthoff, N.; Bäumer, D.; Corsmeier, U.; Kohler, M.; Vogel, B. Vehicle-Induced Turbulence near a Motor-way. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5737–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wen, D.; Xiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Ultrafine-Particle Emission Factors as a Function of Vehicle Mode of Operation for LDVs Based on Near-Roadway Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-Roadway Monitoring Part I: Light Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-Roadway Monitoring Part II: Heavy Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expressway Atlas Annual Average Daily Traffic on Northeastern Illinois Expressways. 2016. Available online: https://www.cmap.illinois.gov/documents/10180/24491/ExpresswayAtlas2016_v1.pdf/56dbf264-8a52-45c0-a5adadcec64a52c1#:~:text=Overall%2C%20on%20IDOT%20facilities%20equipped,region’s%20expressway%20system%20since%202014 (accessed on 20 August 2023).
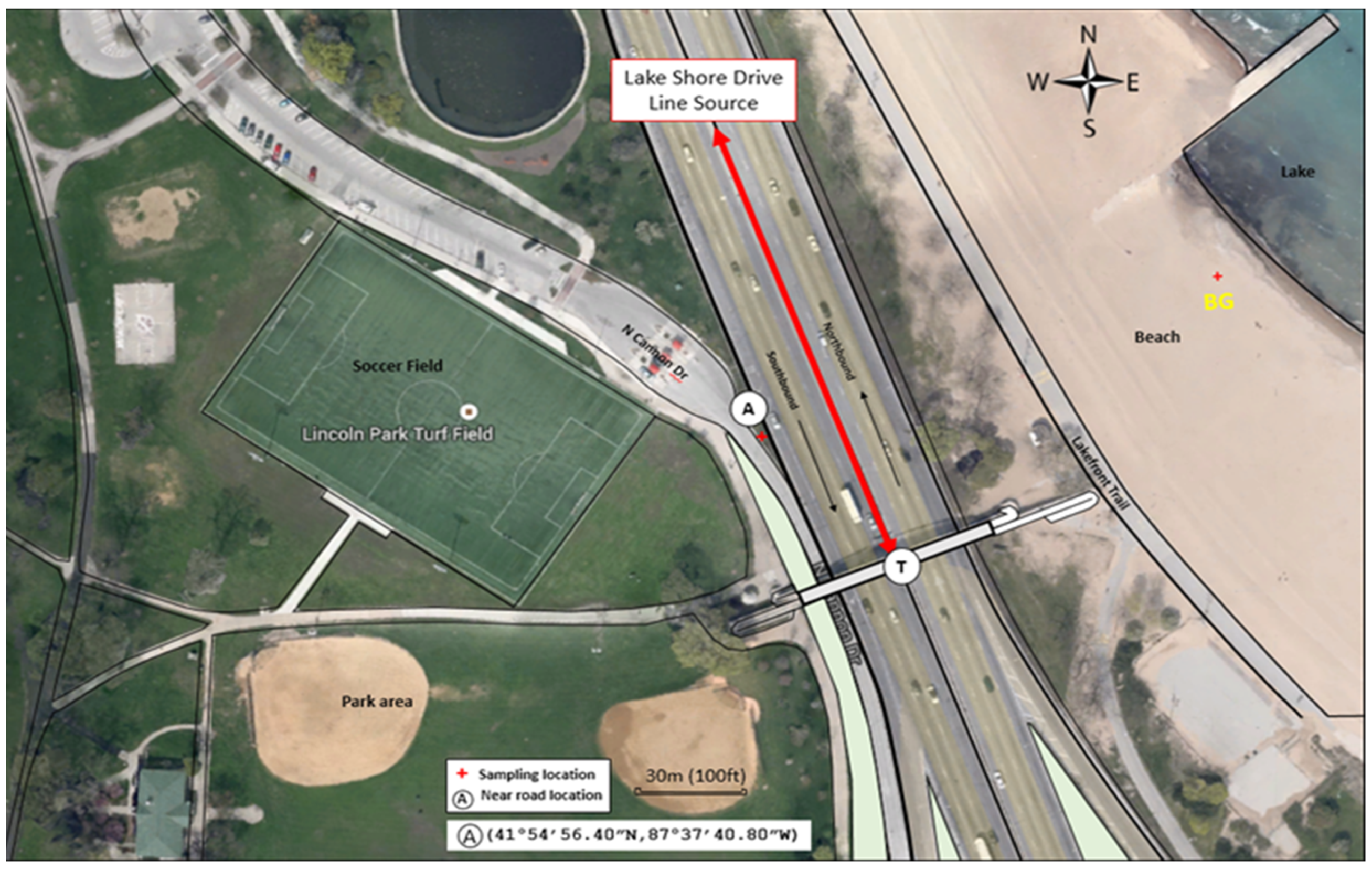
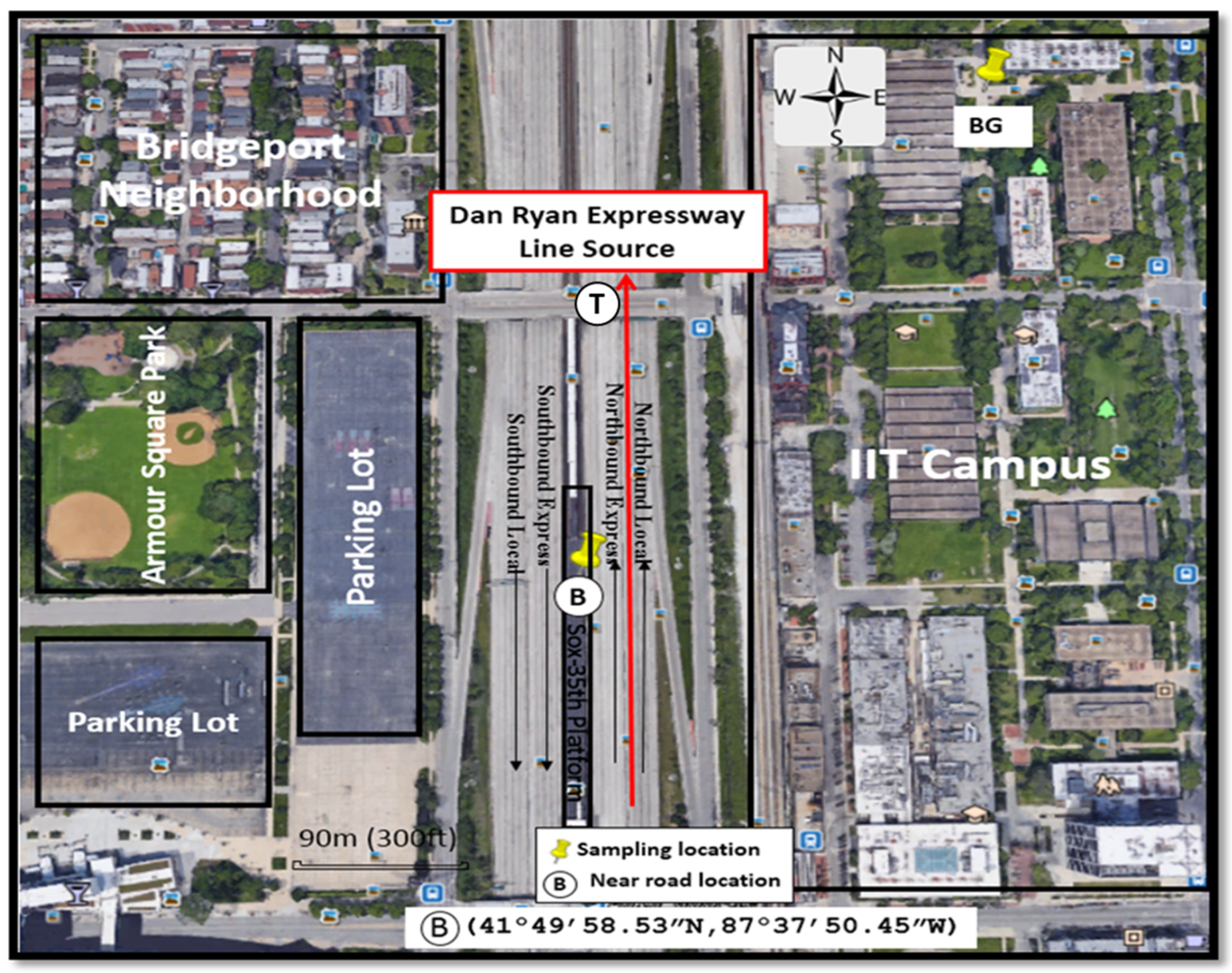
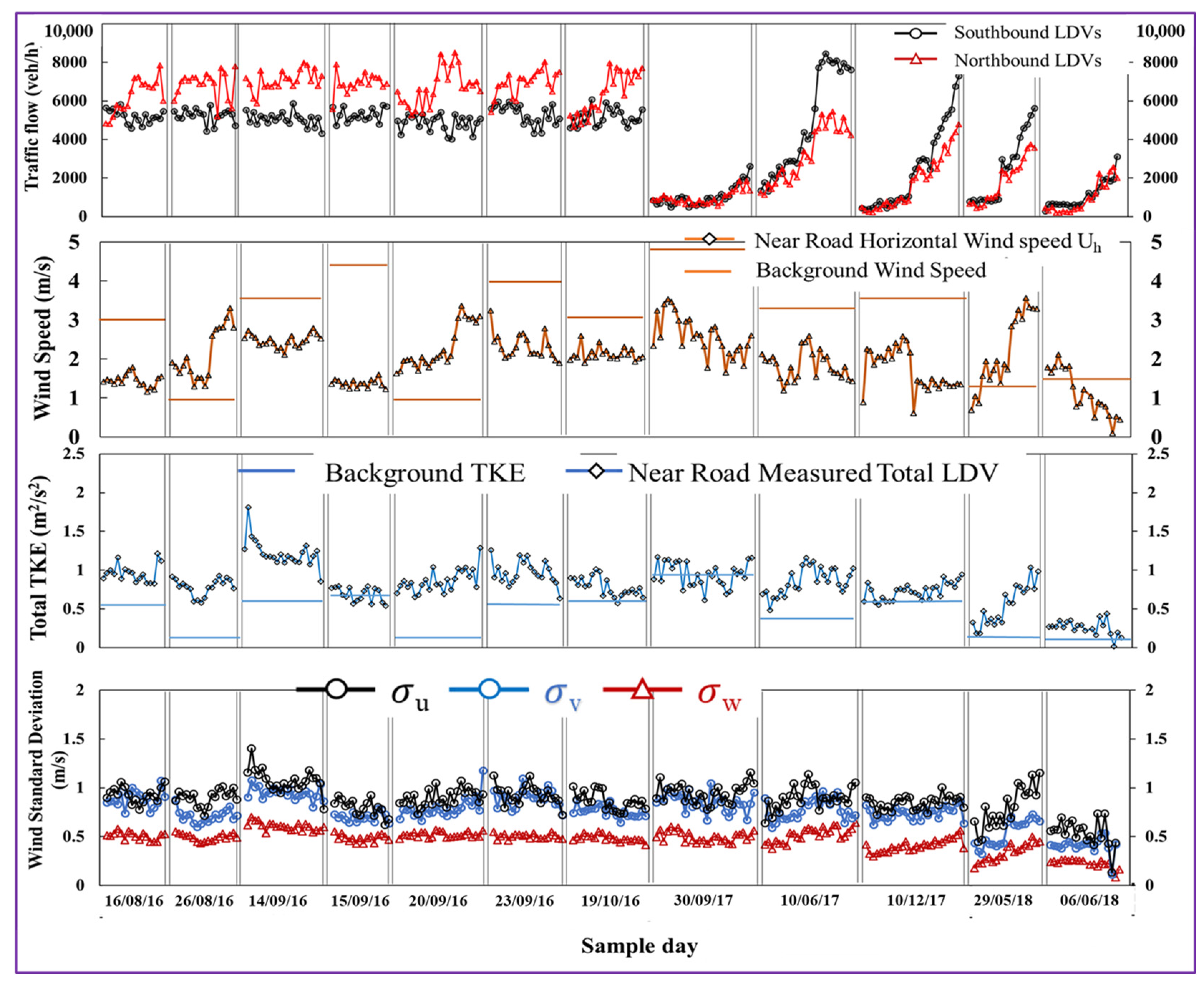

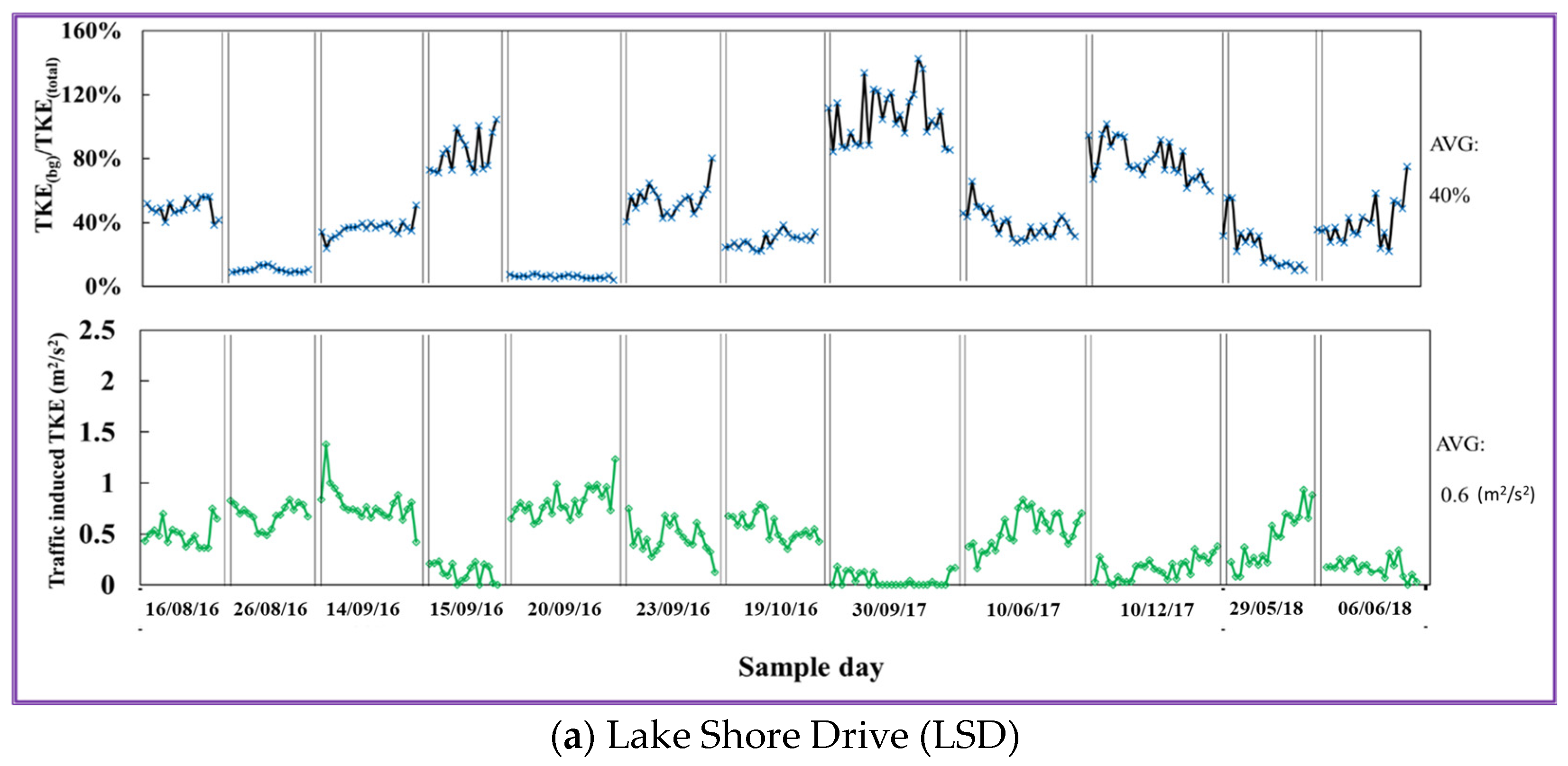

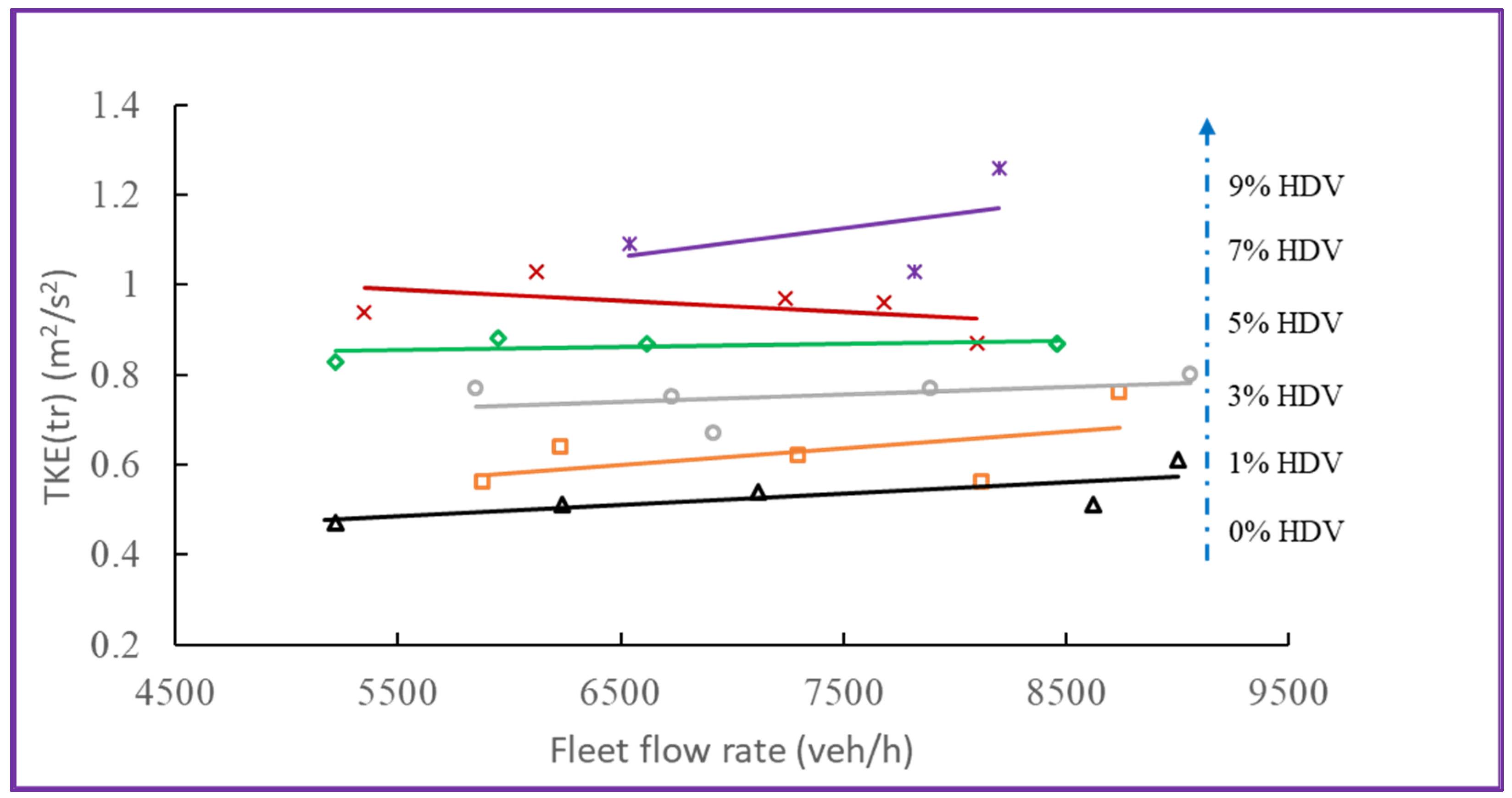
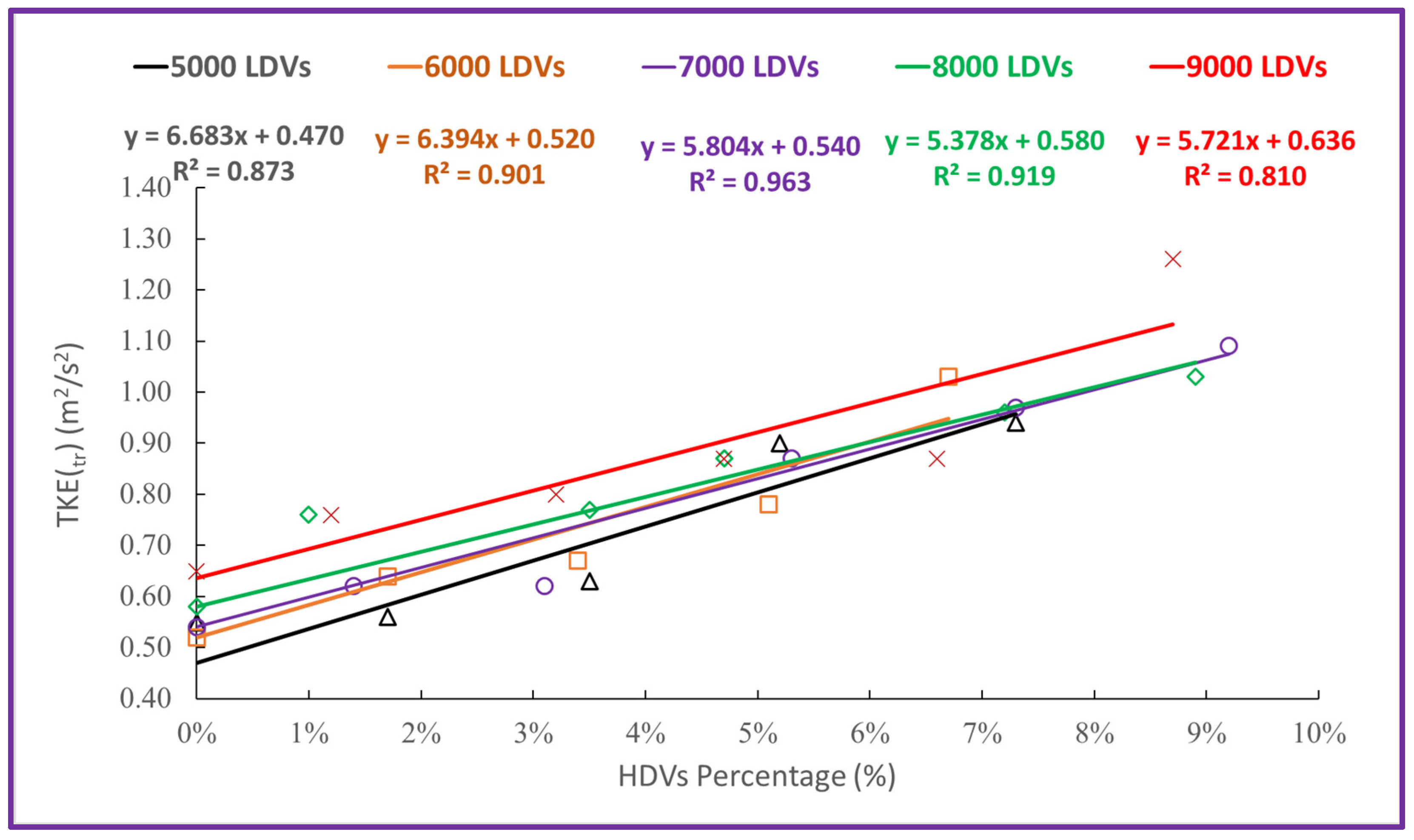
| Roadway | Date | TKEtr | TKELDV (a) | TKEHDV (b) | LDV Normalized TKEtr (c) | HDV Normalized TKEtr (d) | Normalized TKEHDV/TKELDV (e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2/s2 | m2/s2 | m2/s2 | |||||
| LSD | 6 October 2017 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0 | 0.22 | N/A | N/A |
| DRE | 1 October 2016 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 1.8 | 7.83 |
| DRE | 3 May 2017 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 3.11 | 7.57 |
| DRE | 13 June 2017 | 0.87 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 2.92 | 10.93 |
| DRE | 13 June 2017 | 0.97 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 2.35 | 10.68 |
| DRE | 11 July 2017 | 1.09 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 2.13 | 10.09 |
| Average | 0.84 ± 0.2 | 0.54 | 0.31 ± 0.2 | 0.28 | 2.82 ± 0.4 | 10.05 ± 1.6 |
| Roadway | Date | HDV Vehicle Flow | HDV Percentage | LDV Vehicle Flow | HDV Vehicle Speed | LDV Vehicle Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Veh/h | % | Veh/h | Km/h | Km/h | ||
| LSD | 6 October 2017 | 0 | 0% | 7120 | N/A | 93 |
| DRE | 1 October 2016 | 100 | 1.4% | 7300 | 91 | 112 |
| DRE | 3 May 2017 | 220 | 3.1% | 6920 | 93 | 118 |
| DRE | 13 June 2017 | 370 | 5.3% | 6620 | 87 | 114 |
| DRE | 13 June 2017 | 540 | 7.3% | 7240 | 89 | 109 |
| DRE | 11 July 2017 | 660 | 9.2% | 6540 | 85 | 98 |
| Average | 378 ± 228 | 89 ± 3 | 110 ± 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Near-Road Traffic Emission Dispersion Model: Traffic-Induced Turbulence Kinetic Energy (TKE) Measurement. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101485
Hu Z, Noll KE. Near-Road Traffic Emission Dispersion Model: Traffic-Induced Turbulence Kinetic Energy (TKE) Measurement. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(10):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101485
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhice, and Kenneth E. Noll. 2023. "Near-Road Traffic Emission Dispersion Model: Traffic-Induced Turbulence Kinetic Energy (TKE) Measurement" Atmosphere 14, no. 10: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101485
APA StyleHu, Z., & Noll, K. E. (2023). Near-Road Traffic Emission Dispersion Model: Traffic-Induced Turbulence Kinetic Energy (TKE) Measurement. Atmosphere, 14(10), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101485








