Abstract
With the rapid development of soil moisture estimation techniques involving remote sensing technology, the sampling designs used in soil moisture research are very important. To estimate the rational sample number for measuring near-surface soil moisture (0–20 cm), a random combination method was used to study the relationship between the average measured soil moisture contents and the true values at given scales. Compared to classic statistics and stratified sampling, the random combination method easily obtained precision estimates from a small number of samples. Moreover, the random combination method was upscaled to further discuss the influence of the coefficient of variation and study-region scale on the rational sample numbers at different scales (2, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 m). The results showed that the rational sample numbers for measuring near-surface soil moisture at the 2, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 m scales were 2, 5, 5, 8, 20, and 42, respectively, under the relative error of 10% at the 95% confidence level. The rational sample numbers at different scales were proportional to the coefficient of variation and the regional scale.
1. Introduction
The concept of regional scale should be considered when performing qualitative and quantitative soil analyses. Generally, soil moisture studies require large-scale information to obtain substantive significance [1]. Regional soil moisture, especially the distribution of surface soil moisture, is an important factor affecting surface runoff, groundwater recharge, and the feedback relationship between the land surface system and the atmospheric system [2,3]. Soil moisture drought is one of the key prerequisites for the development of extremely high temperatures, whereas atmospheric dynamics control the onset of such extremes. However, to date, researchers have used only neutron probes, time-domain reflectometry (TDR), or Earth-boring tools and other instrument equipment to accurately observe soil moisture in small areas; in addition, the collected data can represent the soil moisture conditions only in a small range [2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. With the increasing observation scale required in experiments, manual measurement methods have difficulty meeting the experimental requirements [11]. In recent years, with the development and application of remote sensing technologies, such technologies have become an important way to express the regional distribution information of soil moisture [2,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. The retrieval of surface soil moisture conditions from remote sensing data has become an important research topic in the field of soil sciences.
In the process of retrieving surface-layer soil moisture from remote sensing data, it is often necessary to establish and to verify various models with as much ground observation data as possible [2,4,5,11,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Due to the spatial variability in surface soil moisture, and the constraints of human and material resources, the amount of ground-measured data is often limited [2,22]. Ensuring that the most accurate average soil moisture conditions in a specific area can be effectively determined using the fewest possible reasonable sampling points under a certain error range and confidence level is the first problem to be solved in remote sensing inversions of surface soil moisture; this issue is of great significance for ensuring that basic research and production practices can be performed [27].
To date, many scholars have discussed the problem of selecting a reasonable sampling number when making sampling schemes. At present, traditional statistical methods are the most widely used and are suitable for simple random sampling. Cochran [28] and Warrick [29] described such methods in detail. However, traditional statistical methods are limited, in that the data errors generally conform to a normal distribution, and the sample points are mutually independent [24]. When the preconditions are violated, the reasonable number of samples calculated using traditional methods is often inconsistent with the actual needs [23,25]. Stratified sampling is another accurate sampling strategy that has been applied in different research fields, such as census, environmental analysis, and soil science research. This method can effectively reduce the number of samples required [26,28,29,30], but the calculation process is cumbersome, and there are many restrictions, such as the need for prior data support and a consideration of the impacts of stratified methods [31]. Although a small number of samples can be used to represent the mean of the sample area through stable sampling, a large number of long-time-series ground observation data sets are required [30,31,32,33,34].
In general, the sample number depends mainly on the degree of spatial variations in the measurement parameters; the higher the degree of variation is, the more samples are needed. The degree of variation is often characterized by the coefficient of variation. According to the traditional statistical principle, when the error population is normally distributed and the samples are mutually independent, the reasonable sample number is proportional to the square of the coefficient of variation (assuming that the population variance is approximately equal to the sample variance) under a certain confidence level and error conditions [23]. In the actual process, the above assumptions are difficult to fully satisfy [23], so it is necessary to further analyze the relationship between the number of sampling points and the coefficient of variation. In addition, the relationships among the regional scale, the number of samples, and the coefficient of variation are also very close. At the regional scale, it is relatively difficult to obtain the coefficient of variation. Therefore, it may be more practical to study the relationship between the reasonable sample number and the regional scale. The reasonable ground sampling method of soil moisture has great significance for the precise verification of the soil moisture inversion algorithm and the truth testing of the product [19]. With the launch of high spatial resolution satellites at home and abroad in recent years, especially the GaoFen series and space-based system satellites launched by China, there is an urgent need to build an optimal sampling analysis aiming at the validation and development of high-resolution soil moisture remote sensing products. In this paper, based on the effectiveness of the random combination method, we analyzed the reasonable sampling numbers of the surface soil moisture contents at different scales, and the relationships between the sample number and the coefficient of variation and between the sample number and the regional scale using the random combination method, to provide reference methods and a theoretical basis for the inversion of surface remote sensing data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis Method
The measured soil moisture points can represent a small area by obtaining the average value over the basic unit; this differs from the “point” concept applied in mathematics. Based on the actual situation of several existing soil moisture-measuring instruments or means, in this study, we assumed that the basic unit had a size of 0.4 m × 0.4 m. If a plot could be divided into m units (the area of each unit must be not greater than the area of the basic unit), then the soil moisture status of the plot could be understood by placing a measured point on each unit. The real average soil moisture of the plot could be considered to be equal to the average soil moisture value among the m measured points. The basic idea of applying the random combination method to determine the reasonable sampling number of surface soil moisture is as follows: first, we randomly selected N points (N = 1, 2, 3…, m) from all measured data, calculated the relative error (RE) between the mean soil moisture value and the true average soil moisture value within the plot, obtained the average value of all m measuring points, and calculated all combination numbers s with respect to specific n values and combination numbers p and q when RE was not greater than 10% and 5%, respectively. Then, p/s and q/s were set as the confidence levels under 10% and 5% errors, respectively. In this study, the relative errors of 10% and 5% under the condition of a 95% confidence level were proposed as the benchmark for determining the reasonable number of sampling points in the plot.
Theoretically, the above method can be used to determine the reasonable sampling point number in an area of any scale. However, because surface soil moisture is affected by various factors and rapid changes, remote sensing data should be continuous over time. If the selected plot area were too large, it would be impossible to obtain soil moisture measurements within all small-area basic units over a short period of time. Considering that large-scale areas can be composed of several small-scale areas, it was thus necessary to set a basic scale and to perform the analysis of reasonable sampling points based on that basic scale. In view of the above requirements of basic units and remote sensing measurement times, it was obvious that the basic scale could not be exceedingly large. In contrast, a small basic scale was not conducive to scale upgrading or amplification. The research of Sadden et al. [35] showed that soil moisture changes are relatively stable within the field scale range of 4 m × 4 m. Therefore, the basic scale was set as 2 m × 2 m (hereafter referred to as the 2 m plot or 2 m scale; the other scales were set similarly to this scale); on the basis of obtaining basic-scale analysis results, the scale expansion task was then carried out step-by-step. For example, 10 m × 10 m cells could be composed of 25 2 m × 2 m cells, 20 m × 20 m cells could be composed of four 10 m × 10 m cells, 40 m × 40 m cells could be composed of four 20 m × 20 m cells, 80 m × 80 m cells could be composed of four 40 m × 40 m cells, and 160 m × 160 m cells could be composed of four 80 m × 80 m cells. After the sampling number was determined at the 2 m scale, at the 10 m scale, random sampling was carried out in 25 2 m × 2 m cells according to the reasonable sampling number obtained above. Then, a reasonable sampling number was obtained at the 10 m scale by applying the random combination method. Subsequently, we analyzed reasonable sample numbers at higher scales via analogy. The coefficient of variation was obtained as the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean value; when M soil moisture data points were measured at a certain scale θ1, θ2… θM, the coefficient of variation CV could be expressed as follows:
In soil science [36], CV reflects the variation degree of soil properties, and it is an important parameter that is used in traditional statistical methods to estimate the reasonable sample number [29]. In this study, the standard deviation and mean value of the soil moisture measurements obtained at different scales were calculated to obtain the CV at each scale; then, the relationships among the CVs at different scales, and the area (scale) and the number of samples were analyzed.
2.2. Experimental Data
The study area was located in Hengshui city, Hebei Province, in northwestern China (38°3′00″ N, 115°27′54″ E). The region is a typical agricultural area, with only a few types of land cover (bare soils, maize, orchards, and grass areas) and a homogeneous soil texture. The area has a typical continental monsoon climate characterized by high temperatures and rainfall in summer, and cold, dry winters [23]. The average annual temperature is 12.6 °C, with an average temperature of minus 4.1 °C in the coldest month (January) and 26.8 °C in the hottest month (July). The average annual precipitation is 510 mm, 80% of which falls between June and August. Therefore, the SM content plays an important role in agricultural production, particularly in summer. To measure the SM content, field experiments were conducted for 20–21 July 2018. The location of the experimentation area is shown in Figure 1. Maize, cotton, and peanut are the main crops grown at these sites. The main soil type is loamy, including approximately 44.6% silt, 17.5% clay, and 37.9% sand [23].
Figure 1.
Location of the experimentation area.
In the first experiment, the effectiveness of the random combination method was discussed. An area with a scale of 55 m × 55 m was selected in the experiment. According to the preliminary sampling detection analysis, grid sampling was conducted at 5 m intervals. Then, the reasonable sampling number was estimated using the random combination method according to the measured data, and the results were analyzed and compared with the estimation results obtained through the traditional statistical method [29] and the stratified sampling method [28] (the calculation methods involved in the traditional statistics and stratified sampling methods are detailed in the literature and are not described in this paper).
The second experiment mainly involved the use of a random combination method to scale-up and to analyze the reasonable surface-soil-moisture sampling numbers at different scales. Nested cells with different scales of 2, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 m were established to study the reasonable surface-soil-moisture sampling number. The 2 m cells were sampled using the grid method: each 2 m cell was divided into 25 0.4 m grid cells (basic cells). A hydro sense portable soil moisture meter (CS620, USA Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA) was used to measure the volume moisture content of the surface soil (0–20 cm) at the center of each grid cell. A total of 4 repetitions were set, and the measurement of each cell took approximately 10 min (using 1 set of instruments). The 10 m scale tests were conducted on the basis of the analysis results of the reasonable sampling number at the 2 m scale. Assuming that the reasonable sampling number of 2 m × 2 m cells was n under the condition of a 95% confidence level and 10% (or 5%) error, first, we divided the 10 m × 10 m area into 25 2 m × 2 m cells, randomly measured the soil moisture in each cell n times, and obtained a total of 25 × n soil moisture data points. Similarly, the reasonable sampling number at the 10 m scale was analyzed according to the above random combination method. By analogy, the tests at the 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales were conducted on the basis of the analysis results obtained at the 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, and 80 m scales, respectively. The only exceptions were for the 80 m and 160 m scales, where the analysis was completed only once; the other scales were assessed twice.
With the expansion of the measurement scale, the number of points to be measured increased exponentially. To ensure that the measurement time of each scale was as short as possible, multiple instrument sets were used to complete the “synchronous” measurement of each scale. Considering the requirements of remote sensing technology and the practical operation potential, the measurement time at each scale was limited to 30 min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effectiveness Analysis of the Random Combination Method
For the specific calculation process of traditional statistical methods and stratified sampling methods, the studies by Cochran [28] and Warrick [29] can be used as references. In the paper, the stratified sampling was divided into four strata according to the spatial distribution of soil moisture. The weight coefficient was set as the ratio between the area of each stratum and the total area. The reasonable sampling numbers of traditional statistical methods, stratified sampling methods, and random combination methods under different error and confidence level conditions are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Reasonable sampling numbers obtained for different methods at certain confidence levels and error ranges.
Table 1 shows that under the same confidence level and error conditions, the number of reasonable samples is highest when using traditional statistical methods. The main reason for this result is that the test samples are not all mutually independent, and that this violates the basic assumption of traditional statistics. Therefore, the number of samples obtained in traditional statistical methods is higher than the number of samples actually needed [29,37,38].
In this experiment, the stratified sampling method required the fewest samples, requiring only approximately half of the number of samples taken by the traditional method; this finding was consistent with the research conclusion of Park et al. [26]. In conclusion, stratified sampling is more effective than traditional sampling in reducing the number of required samples under certain accuracy requirements. Interestingly, the sampling results of the random combination and stratified sampling methods were very similar; especially when the accuracy requirements were high (when the relative error was within 5%), the relative error of the random combination method and stratified sampling method was approximately 10%. Then, the available random combination method could be used to obtain the estimations at the same precision with a relatively small number of samples. Moreover, the random combination calculation method is simple and is not limited by the layering method or by the independent status of the samples. This method is thus a relatively feasible sampling method.
3.2. Analysis of the Reasonable Sampling Number Results at Different Scales
The relationship between the sampling number and the confidence level is shown in Figure 2 when the REs of the surface soil moisture at the 2 m scale are 5% and 10%. As the number of samples increased, the confidence level gradually increased. At the same confidence level, an accuracy improvement (a decrease in the relative error) resulted in an increased sample number. The error line in Figure 2 shows that the results of four repetitions were nearly the same. In addition, the deviation between the confidence level and the average value was slightly larger (5.7%) when the number of samples was 1 at the 10% error level, and the remaining deviation was almost zero. These results shows that the changes in the confidence level with a change in the sampling number were relatively stable in the study area, and that the results were thus reliable. Under the 95% confidence level, when the numbers of samples was no less than 2 and 7, the error requirements of 10% and 5% could be met, respectively.
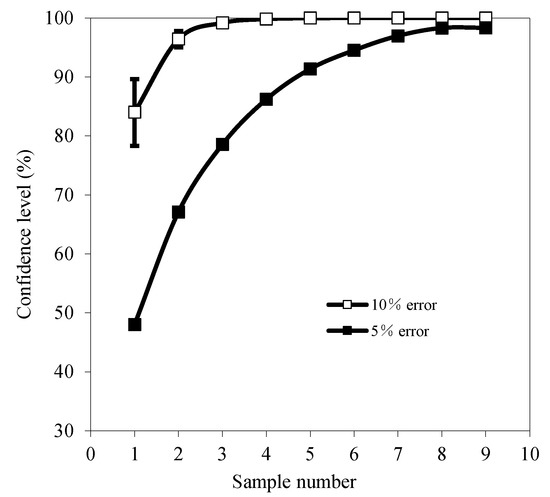
Figure 2.
Relationships between the sample number and the confidence level at the 2 m scale at REs of 5% and 10%.
On the basis of the 2 m scale analysis results, the relationship between the number of randomly combined samples and the confidence levels at the 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales under the conditions of 10% and 5% errors was further amplified iteratively, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Similar to the 2 m scale, the sampling number derived at each scale increased as the confidence level was improved. When the error and confidence level were required to be certain, the larger the scale was, the stronger the spatial variability in soil moisture, and thus, the more samples were needed. At the same scale and the same confidence level, the smaller the error requirement was, the more sampling points were needed. In addition, the graphical results also showed that the variation rule of the 10 m scale and 20 m scale confidence levels was consistent with the number of samples required in the test area. The variation from the 10 m scale to the 20 m scale in the test area was negligible and within the constant range of variation.
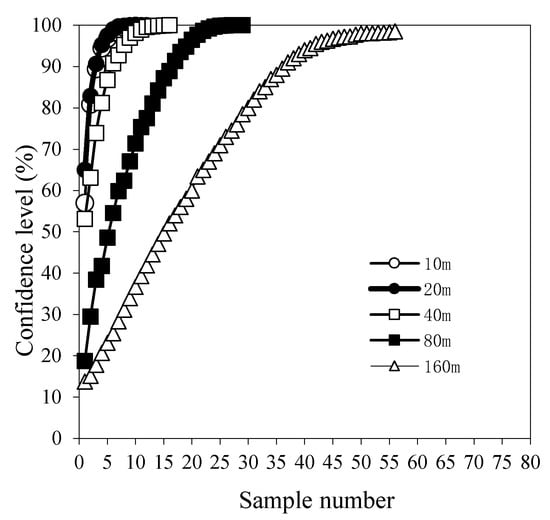
Figure 3.
Relationship between the sample number and the confidence level at the 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales at a relative error of 10%.
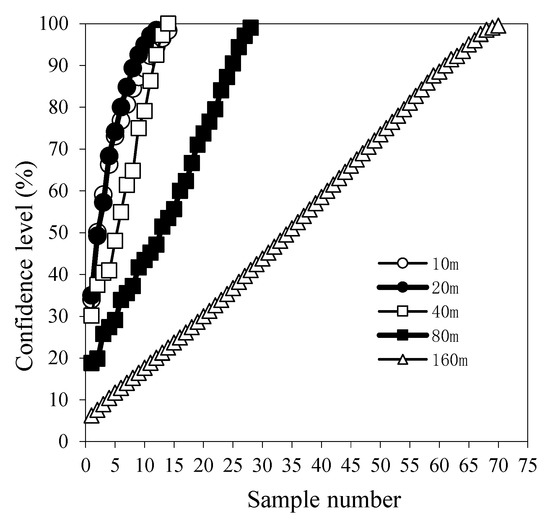
Figure 4.
Relationship between the sample number and the confidence level at the 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales at a relative error of 5%.
In the iterative scaling-up process, errors may accumulate gradually. With an increase in the number of samples, if the confidence level can gradually approach 100%, or if the confidence level of 100% is the progressive line of the relationship curve (consistent with the theoretical rule), it can be considered that the number of samples selected at a certain confidence level is reasonable. In terms of the research results obtained in this paper, under the condition of a 10% error, as the number of samples increased, the corresponding confidence level at each scale exhibited a rule of gradually approaching 100% (Figure 3). However, under the condition of a 5% error, the results obtained at each scale were quite different: the scales of 20 m and below were acceptable, and the asymptotic process did not occur at all at the 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales (Figure 4), indicating that when the relative error of 5% was taken as the standard, the accumulation of errors had a significant impact on the sampling results at the 40 m scale and above, and it was thus necessary to increase the sampling amount to eliminate this effect and to obtain more reliable results. In view of this finding, the following analysis was based on the 95% confidence and 10% error levels. When the 95% confidence level and 10% relative error were taken as the criteria for determining the number of required samples at each scale, the number of samples required at the 2 m, 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales were 2, 5, 5, 8, 20, and 42, respectively.
3.3. Relationship between the Coefficient of Variation (CV) and the Reasonable Number of Samples (Rn)
The size of the coefficient of variation critically impacts on the sampling process. Generally, the larger the coefficient of variation is, the more samples are needed. Traditional statistics estimates the reasonable sample number based on the size of the coefficient of variation. However, since the overall error may not meet the requirements of a normal distribution and mutual independence, the conclusion that the reasonable number of samples must be proportional to the square of the coefficient of variation [23,24] may not be reliable in the actual calculation process. In the following text, we perform a preliminary analysis of the relationship between the reasonable sampling number determined via the random combination method and the coefficient of variation.
The coefficients of variation (CVs) at the 2 m, 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m scales were obtained using formulas (1)–(2) and the water content values measured at each scale, as shown in Table 2. Considering the small number of CV sample points (only six) and the small variation between the 10 m and 20 m scales in the test area, to better understand the relationship between the CV and the reasonable sampling number (Rn), the measurement and analysis processes were additionally performed in areas of 50 m × 50 m and 100 m × 100 m, and the Rn determination method was the same as that described above (the 50 m scale analysis was based on 25 10 m × 10 m cells, and the 100 m scale analysis was based on 4 50 m × 50 m cells).

Table 2.
Surface soil moisture statistics at different scales.
Under the condition of a 95% confidence level and 10% error, the variation law of the CV with Rn within the 160 m range is shown in Figure 5. Since the results obtained at the 10 m and 20 m scales were almost the same, it was difficult to distinguish between the points corresponding to these two scales in the figure. The results show that the CV values within the range of 160 m in the test area were all within 0.80. With the expansion of the scale, the Rn and CV values gradually increased, and both exhibited good linear relationships. The fitting results (setting the intercept as 0) show the following expressions:
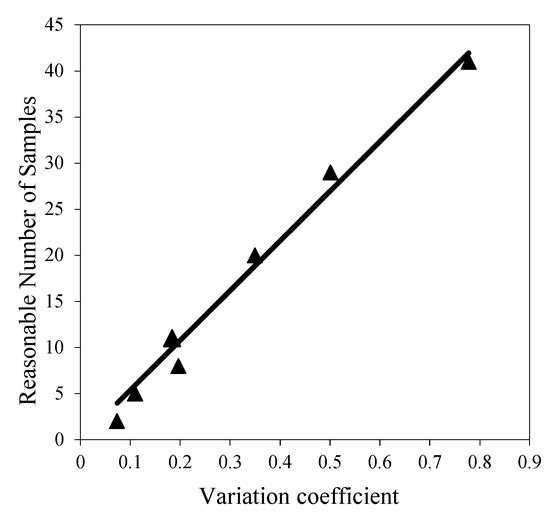
Figure 5.
Relationship between Rn and CV at a relative error of 10% and a confidence level of 95%.
In the study area considered herein, this formula could best describe the quantitative relationship between CV and Rn within the 160 m scale.
3.4. Regional Scale () and Reasonable Number of Samples (Rn)
When performing actual sampling, the reasonable number of samples can be estimated according to the CV [23,24] of the parameters provided in the literature. However, when assessing a specific region [35], it is often difficult to determine the CV of the parameters. In addition, the requirements of a normally distributed overall error and the mutual independence of the samples are not always met. Therefore, applying the estimated CV to estimate the Rn often results in relatively large errors. Generally, when the underlying surface is relatively uniform, the variation degree of the investigated parameters may increase as the size of the study area increases [39,40,41,42].
A change in the regional scale also affects the sampling design of the parameters. Moreover, compared to the CV [37], the regional area (A) or scale () is easier to determine. Therefore, it may be more practical to consider the quantitative relationship between the regional area (or scale) and the Rn. Figure 6 displays the relationships between the 2 m, 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 50 m, 80 m, 100 m, and 160 m scales () and the Rn under the conditions of a 95% confidence level and 10% error. As the regional scale increases in size, the number of reasonable samples (Rn) also gradually increases. Interestingly, within the range of 160 m, the Rn in the test area still exhibits a good linear relationship with the regional scale (); this relationship can be described using the following equation (setting the intercept as 0):
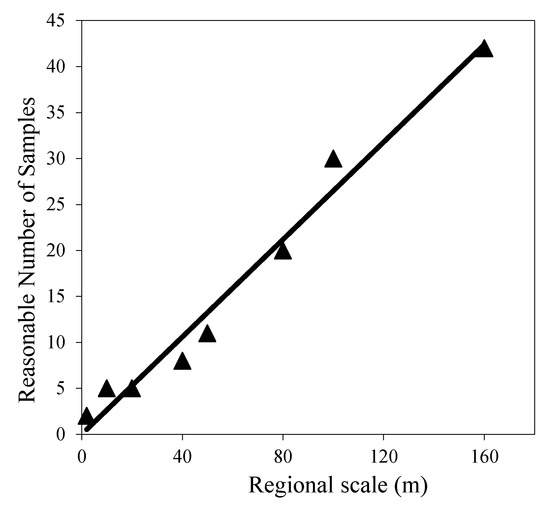
Figure 6.
Relationship between the Rn and the regional scale at a relative error of 10% and a confidence level of 95%.
To test the reliability of regression equation (4), the two scales of 60 m × 60 m and 120 m × 120 m were measured and analyzed using the random combination method (the 60 m scale analysis was based on nine 20 m × 20 m cells, and the 120 m scale analysis was based on four 60 m × 60 m cells). The reasonable sampling numbers at the 60 m and 120 m scales were found to be 14 and 33, respectively, and the relative errors with the results calculated using formula (4) were approximately 14% and 4%, respectively. It can be seen that in the test area, the established regression equation can be used to indirectly estimate the reasonable number of samples within the 160 m scale, thus providing a basis for the ground sampling design when monitoring the surface soil moisture content using medium-resolution remote sensing images (from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), Thermal Mapper (TM), etc.).
4. Conclusions
In this study, the reasonable number of surface soil moisture sampling sites was determined using the traditional statistical method, stratified sampling method, and random combination method, with the aim of analyzing the effectiveness of the random combination method in determining the reasonable sampling number. On this basis, we further applied the random combination method to analyze and to discuss the reasonable sampling numbers for assessing surface soil moisture at different scales, the relationship between the reasonable sampling number, and the coefficient of variation and the relationship between the reasonable sampling number and the regional scale. In the scaling-up process, the variations within 10 m and 20 m in the study area were small and basically within the constant range of variation. Under the condition of a 95% confidence level and 10% error, when the sampling points of 2 m, 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 80 m, and 160 m were set as 2, 5, 5, 8, 20, and 42, respectively, the surface soil moisture at the corresponding scale in the study area could be best characterized. Good linear relationships were observed between the reasonable surface soil moisture sampling number within the 160 m range in the study area, and the coefficient of variation and between the reasonable sampling number and the regional scale. These relational expressions could be used to effectively formulate surface soil moisture sampling designs [38,43,44].
The random combination method does not only effectively determine the reasonable surface soil moisture sampling numbers at various scales, but it can also determine the reasonable sampling number at different scales from scaling up. However, due to the limitations of the test area, the scale was enlarged only to 160 m in this work using the random combination method under the condition of a 95% confidence level and 10% error. Considering the sampling design requirements of different resolution remote sensing images, when the regional scale and variation intensity continued to increase, the effectiveness of this scaling-up method, and the relationships between the number of samples and the coefficient of variation and between the number of samples and the regional scale still require further study. Potentially, besides surface soil moisture, the random combination method can be used to estimate the necessary sampling number of other soil properties, such as pH, texture, porosity, and bulk density. As a key parameter of estimating the necessary sampling number using the random combination method, the ranges of CV for soil properties may be obtained through preliminary sampling investigations or retrieval from the literature. In this study, the sampling domain was limited to within the 160 m scale, and the research field was with relatively homogeneous soils and a single crop. In future studies, the application potential of the random combination method in areas with mixed crops or uneven soil texture also needs further experimental research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.W. (Chunmei Wang) and X.G.; methodology, C.W. (Chunnuan Wang); validation, C.W. (Chunmei Wang); project administration, J.Y.; format modification, Z.C.; software, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Common Application Support Platform for Land Observation Satellites of China’s Civil Space Infrastructure (Y930280A2F).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Renhua, Z.; Xiaomin, S.; Hongbo, S.; Xinzhai, T.; Zhilin, Z. Remote sensing and scale transfering of levity parameters on earth surface. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 1999, 41, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangyun, L. Simulation and correction of spatial scaling effects for leaf area index. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 18, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Mohanty, B.P.; Hsu, E.-C.; Miller, D. SMEX02: Field scale variability, time stability and similarity of soil moisture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingzhu, X.; Guoce, X.; Yuting, C.; Zhiqiang, M.; Peng, L.; Binhua, Z.; Peng, S.; Lie, X. Soil moisture estimation and its influencing factors based on temporal stability on a semiarid sloped forestland. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 629826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakakos, K.P.; Baumer, O.W. Measurement and utilization of on-site soil moisture data. J. Hydrol. 1996, 184, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal variability of soil–water content at different depths in fields mulched with gravel for different planting years. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Desai, A.R.; Zhu, J.; Hartemink, A.E.; Stoy, P.C.; Ii, S.P.L.; Bogena, H.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Arriaga, F. Retrieving heterogeneous surface soil moisture at 100 m across the globe via fusion of remote sensing and land surface parameters. Front. Water 2020, 2, 578367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingting, J.; Haitang, H.; Chunxia, Q.; Cunjun, L.; Jingping, Z.; Qiaoling, Z.; Cui, B. Spatial variability and Its controlling topographic factors of soil moisture during spring plowing season in black soil hilly region of Northeast China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guohua, W.; Qianqian, G.; Yulian, H.; Huimin, Z.; Xiafang, Z. Dynamics of soil water content across different landscapes in a typical desert-oasis ecotone. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 577406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Jones, S.B.; Montzka, C.; Vereecken, H.; Tuller, M. Ground, proximal, and satellite remote sensing of soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 530–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Panda, R.K.; Mohanty, B.P. Spatiotemporal analysis of soil moisture and optimal sampling design for regional-scale soil moisture estimation in a tropical watershed of India. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 2057–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, P.; Tian, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, L. Spatial pattern and temporal stability of root-zone soil moisture during growing season on a larch plantation hillslope in northwest China. Forests 2018, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Saxtonn, K.E. Estimation of soil water properties. Trans. ASABE 1982, 25, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Peng, Y.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y. Improving estimation of soil moisture content using a modified soil thermal inertia model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Qin, Q.; Ghulan, A.; Wang, D. NIR-red spectral space based new method for soil moisture monitoring. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, M. Using soil surface gray level to determine surface soil water content. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Research on the method for retrieving soil moisture using thermal inertia model. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xia, X. Study on remote sensing monitoring model of agricultural drought based on random forest deviation correction. Inmateh-Agric. Eng. 2021, 64, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, B.H. Methods of soil analysis agronomy monograph number Part 1, Physical and mineralogical methods. Catena 1988, 15, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenying, H.; Yongqin, L. Review of agricultural drought monitoring models. Yunnan Geogr. Environ. Res. 2013, 25, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Z.; Jianli, D.; Peng, Z. Model algorithm of soil moisture retrieval base on microwave remote sensing in arid regions. Arid. Land Geogr. 2011, 34, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, R. Estimating the necessary sampling size of surface soil moisture at different scales using a random combination method. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiuxia, X.; Jiahui, Z.; Kun, L.; Yunxiao, S.; Linlin, Z. Research and application of flood submerged information precise extraction based on typical remote sensing image fusion method. J. Catastrophology 2017, 32, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, N.F.; Carr, J.R. The use of geostatistics in relating soil moisture to RADARSAT-1 SAR data obtained over the Great Basin, Nevada, USA. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, N.; Niu, Z.; Raghavan, V.; Song, X. Soil moisture retrieval in farmland using C-band SAR and optical data. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 25, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; van de Giesen, N. Soil–landscape delineation to define spatial sampling domains for hillslope hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K. Soil Physics; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2013; p. 478. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1977; p. 428. [Google Scholar]
- Warrick, A.W. Soil Water Dynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chunmei, W.; Yulin, Z.; Xiangqin, W.; Juan, L.; Lingling, L.; Miao, L. Ground sampling strategy for surface soil moisture in heterogeneous remote sensing pixels. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2016, 47, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingting, L.; Xiang, Z.; Zui, T.; Xiaoyu, S.; Jin, W.; Ruoxi, L.; Futai, X. Remote Sensing-Guided Spatial Sampling Strategy over Heterogeneous Surface Ground for Validation of Vegetation Indices Products with Medium and High Spatial Resolution. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, Z. Horizontal variability of soil water content, evaporation an d throughfall in corn row. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Cieszewski, C.J.; Zasada, M.; Lowe, R.C. Applying geostatistics for investigations of forest ecosystems using remote sensing imagery. Silva Fenn. 2005, 39, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Haining, R.; Cao, Z. Sample surveying to estimate the mean of a heterogeneous surface: Reducing the error variance through zoning. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiq, M.H.; Wierenga, P.J.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Hussain, M.Y. Spatial variability of soil water tension in an irrigated soil. Soil Sci. 1985, 140, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, W. Soil Science. Botanical Gazette 1916, 62, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Webster, R. How many observations are needed for regional estimation of soil properties? Soil Sci. 1983, 135, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Chong, S.-K.; Varsa, E.C. Sampling strategies for fertility on a stoy silt loam soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1995, 26, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shao, M.; Han, F.; Reichardt, K.; Tan, J. Watershed scale temporal stability of soil water content. Geoderma 2010, 158, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G. Temporal Stability and the Spatial Scaling of Soil Moisture in a Small Watershed in the Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Research Center of Soil and Water Conservation and Ecological Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Education, Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhua, J. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Soil Water Content on a Loessial Slope. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Water Resources, Xi’an, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xuemei, M. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Soil Water and Its Effect Mechanism on the Loess Hillslope. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Dapeng, Y.; Jinpu, L.; Qile, C.; Shutao, W. Study on the layout of sample plots for soil investigation. For. Ecol. Sci. 2019, 34, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.O.D.J.; Gontijo, I.; Da Silva, M.B.; Partelli, F.L. Sampling design of soil physical properties in a conilon coffee field. Rev. Bras. De Ciência Do Solo 2017, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).