A Contrast of the Monsoon–Tropical Cyclone Relationship between the Western and Eastern North Pacific
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Contrasting the Monsoon–TC Relationship between the WNP and ENP
4. Possible Explanations for Different Monsoon–TC Relationships over the WNP and ENP
4.1. Monsoon-Associated Changes in the Environmental Factors Defined in the GPI
4.1.1. The Modified GPI
4.1.2. Vertical Wind Shear
4.1.3. Mid-Level Atmospheric Relative Humidity
4.1.4. Other Related Environmental Factors
4.2. Influences from SST Anomalies across Tropical Ocean Basins
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q. Changes in global monsoon precipitation over the past 56 years. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L06711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maue, R.N. Recent historically low global tropical cyclone activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L14803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.L. Interannual and interdecadal variations of tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Lau, K.M. Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific–East Asian monsoons. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 4073–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, B. A review on the western North Pacific monsoon: Synoptic-to-interannual variabilities. Terr. Atmos. Ocean Sci. 2005, 15, 286–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.F.; Boucharel, J.; Lin, I.I. Eastern Pacific tropical cyclones intensified by El Niño delivery of subsurface ocean heat. Nature 2014, 516, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.K.; Comrie, A.C. The north American monsoon. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2197–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, W.R.; Pascale, S. Mechanical forcing of the North American monsoon by orography. Nature 2021, 599, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, R. Possible linkage between the monsoon trough variability and the tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, B.J.; Zhang, R.; Park, K.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Cha, Y.; Nam, J.C. Possible relation of the western North Pacific monsoon to the tropical cyclone activity over western North Pacific. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3334–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Klotzbach, P.J. Recent strengthening of the relationship between the western north Pacific monsoon and western north Pacific tropical cyclone activity during the boreal Summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 8283–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, W.M. Tropical cyclone formation. In A Global View of Tropical Cyclones; Elsberry, R.L., Ed.; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1987; pp. 53–90. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, J.L. Tropical cyclone formation. In Global Perspectives on Tropical Cyclones; Elsberry, R.L., Ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 63–105. [Google Scholar]
- Harr, P.A.; Chan, J.C.L. Monsoon impacts on tropical cyclone variability. In The Global Monsoon System: Research and Forecast; Chang, C.P., Wang, B., Lau, N.C.G., Eds.; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 512–542. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, J.; Vollaro, D. What percentage of western North Pacific tropical cyclones form within the monsoon trough? Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basconcillo, J.; Cha, E.J.; Moon, I.J. Characterizing the highest tropical cyclone frequency in the western North Pacific since 1984. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbach, H.M.; Bourassa, M.A. The effects of gap-wind-induced vorticity, the monsoon trough, and the ITCZ on east Pacific tropical cyclogenesis. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, T.; Zhou, W. Drier North American monsoon in contrast to Asian–African monsoon under global warming. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9801–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kurk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The international best track archive for climate stewardship (IBTrACS) unifying tropical cyclone data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Thorne, P.W.; Banzon, V.F.; Boyer, T.; Chepurin, G.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Menne, M.J.; Smith, T.M.; Vose, R.S.; Zhang, H.M. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature, version 5 (ERSSTv5): Upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8179–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.A. A comparison of regional monsoon variability using monsoon indices. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Wang, B.; Kitoh, A. Future change of western North Pacific typhoons: Projections by a 20-km-mesh global atmospheric model. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bister, M.; Emanuel, K.A. Dissipative heating and hurricane intensity. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 65, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, M.; Waliser, D.E. Modulation of tropical cyclones over the eastern Pacific by the intraseasonal variability simulated in an AGCM. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6524–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Yuan, J.; Duan, X.; Feng, D. Seasonal variation of tropical cyclone genesis and the related large-scale environments: Comparison between the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea sub-basins. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. What controls the interannual variation of tropical cyclone genesis frequency over Bay of Bengal in the post-monsoon peak season? Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2015, 17, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Geng, X.; Stuecker, M.F.; Jin, F.F. Modulation of tropical cyclones in the southeastern part of western North Pacific by tropical Pacific decadal variability. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4475–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. Global view of the origin of tropical disturbances and storms. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 669–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.L.; Zehr, R. Observational analysis of tropical cyclone formation. Part II: Comparison of non-developing versus developing systems. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 1132–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lee, S.K. Co-variability of tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic and the eastern North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L24702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, L. North-south variations of tropical storm genesis locations in the Western Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11367–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lau, K.H.; Zhang, Q.H.; Fung, C.H. Observation of non-developing and developing tropical disturbances over the South China Sea using SSM/I satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakmi, H.; Wang, B. Patterns and frequency of projected future tropical cyclone genesis are governed by dynamic effects. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lau, K.H.; Fung, C.H.; Gan, J.P. The relative vorticity of ocean surface winds from the QuikSCAT satellite and its effects on the geneses of tropical cyclones in the South China Sea. Tellus A. 2007, 59, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Tu, C.; Li, W. Effects of environmental relative vorticity and seasonal variation on tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S. The controlling of the subtropical high leading modes on the spatial pattern of tropical cyclone genesis in the western North Pacific and tracks landing on the east coast of China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L. Enhanced correlation between ENSO and western North Pacific monsoon during boreal summer around the 1990s. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2019, 12, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Guo, P.; Hameed, S.N.; Jin, D. The role of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies in modulating western North Pacific tropical cyclone genesis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2378–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, T.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, Z. Effects of tropical North Atlantic SST on tropical cyclone genesis in the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, X.; Xue, H.; Sun, Q. Contribution of major SSTA modes to the climate variability of tropical cyclone genesis frequency over the western North Pacific. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 2016, 142, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Contrasting two spring SST predictors for the number of western North Pacific tropical cyclones. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Gan, Q. A contrast of recent changing tendencies in genesis productivity of tropical cloud clusters over the western North Pacific in May and October. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, R.; Xiao, X. A new perspective of intensified impact of El Niño-Southern Oscillation Modoki on tropical cyclogenesis over the western North Pacific around 1990s. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4262–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.C.; Chang, T.C.; Hsu, H.H. Enhanced relationship between the tropical Atlantic SST and the summertime western North Pacific subtropical high after the early 1980s. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Huo, L. Influence of tropical Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies on the East Asian summer monsoon. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 2018, 144, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, J.Y. A recent shift in the monsoon centers associated with the tropospheric biennial oscillation. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, J.Y.; Paek, H. Enhanced biennial variability in the Pacific due to Atlantic capacitor effect. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.M.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.Y. Recent weakening in interannual variability of mean tropical cyclogenesis latitude over the western North Pacific during boreal summer. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Ha, K.J.; Jhun, J.G. Interdecadal changes in interannual variability of the global monsoon precipitation and interrelationships among its subcomponents. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2585–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Weng, H. Recurrent teleconnection patterns linking summertime precipitation variability over east Asia and north America. J. Meteorolog. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, S.; Kousky, V.E. South Asian high and Asian-Pacific-American climate teleconnection. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 22, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, T. A new paradigm for continental U.S. summer rainfall variability: Asia-North America teleconnection. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7313–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J. Impact of the spring North Atlantic Oscillation on the northern hemisphere tropical cyclone genesis Frequency. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 829791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Luo, J.J. A seesaw variability in tropical cyclone genesis between the western North Pacific and the North Atlantic shaped by Atlantic multidecadal variability. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


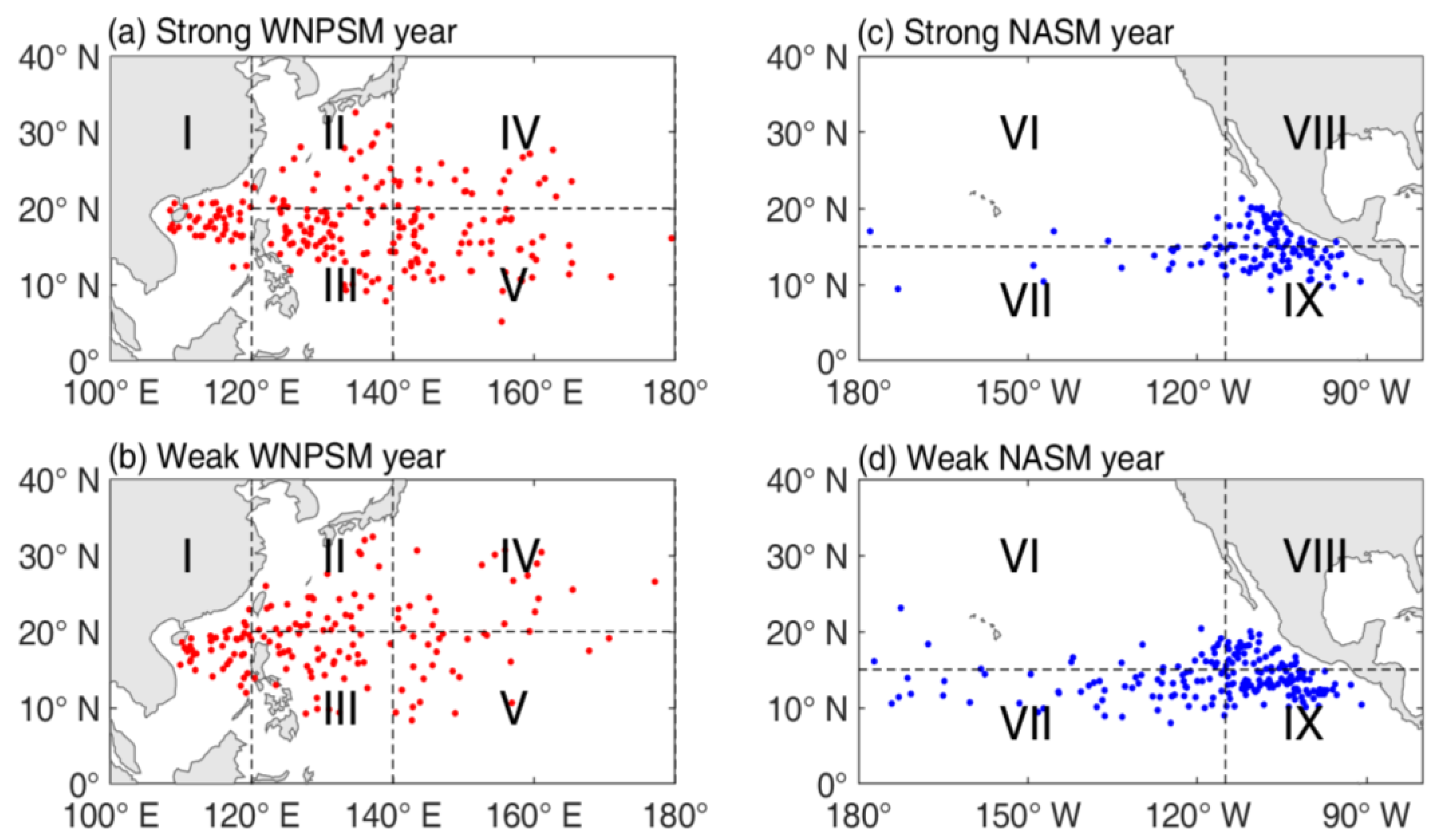
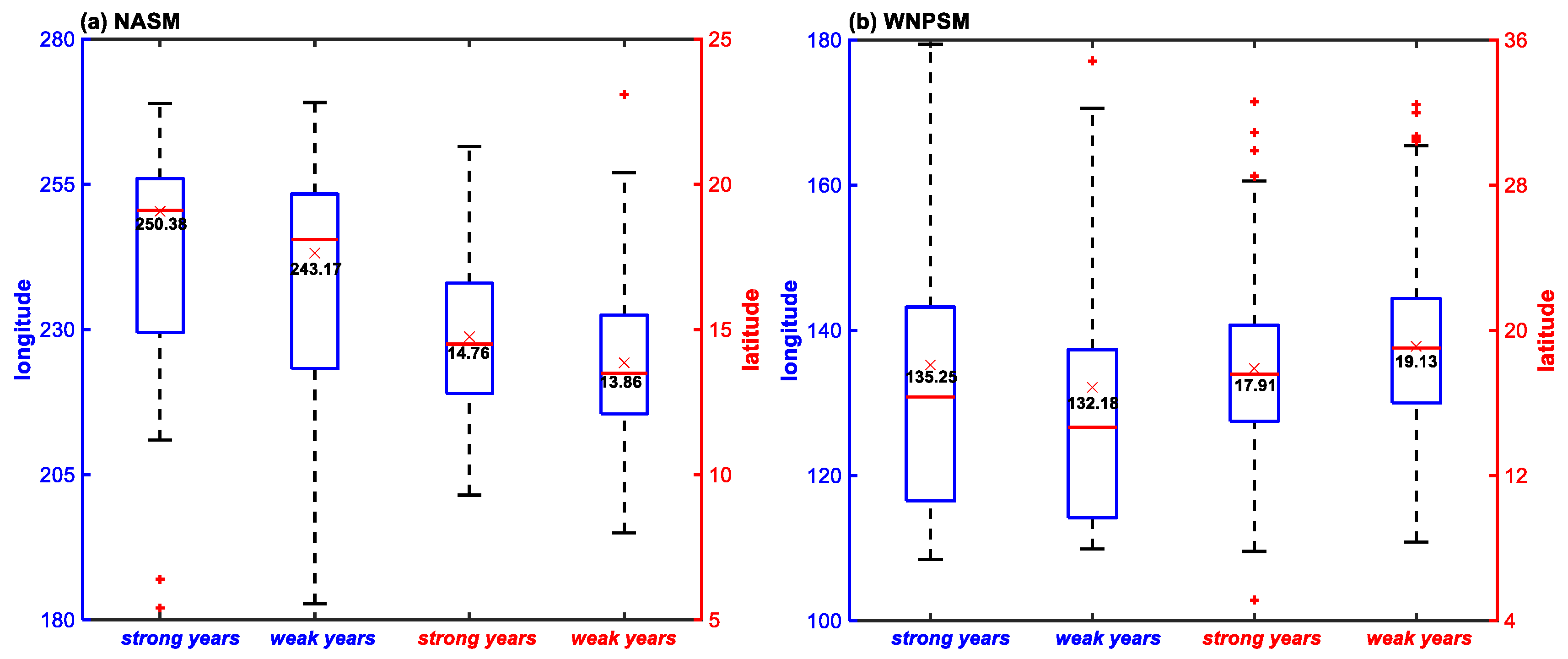
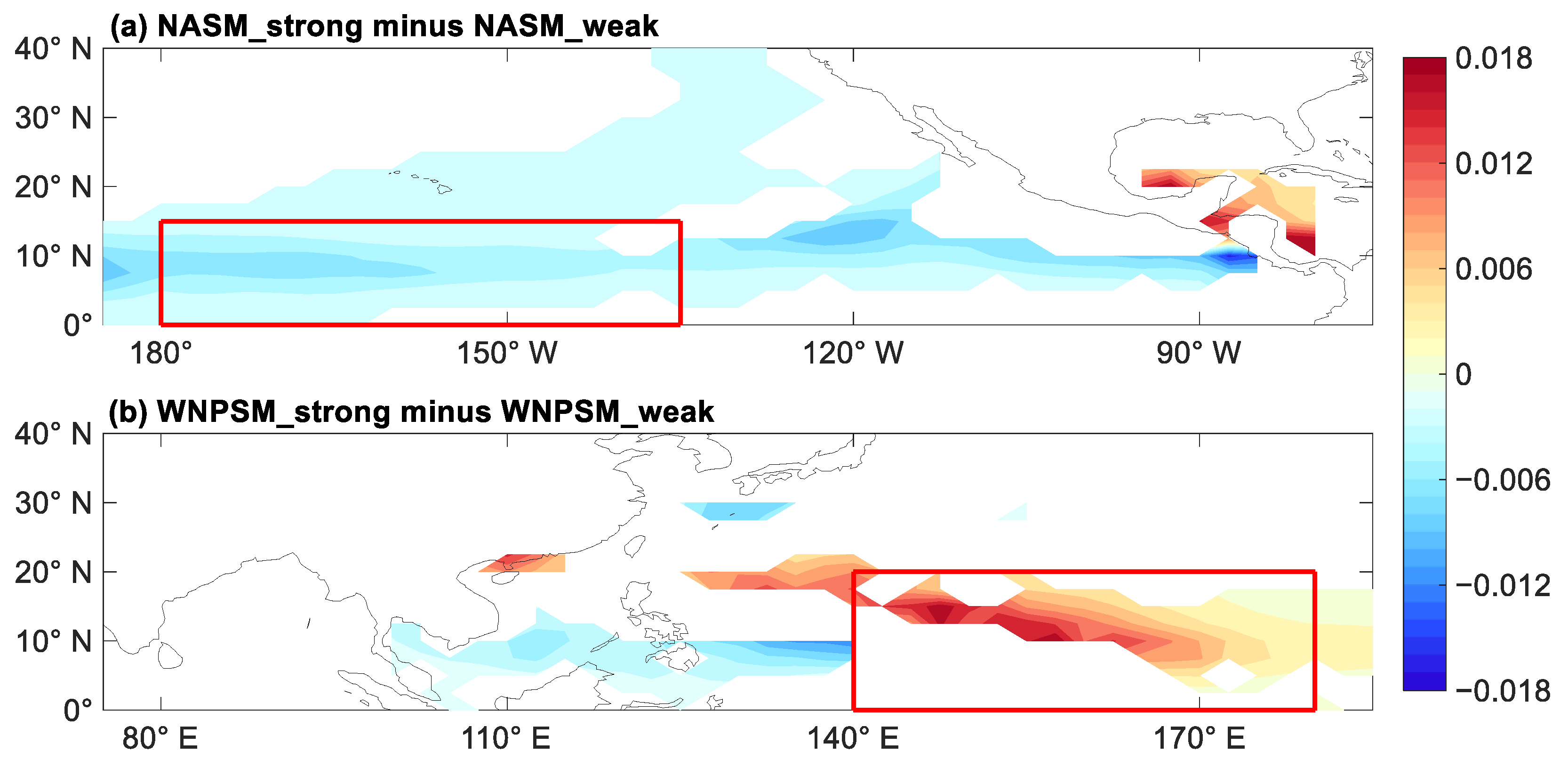
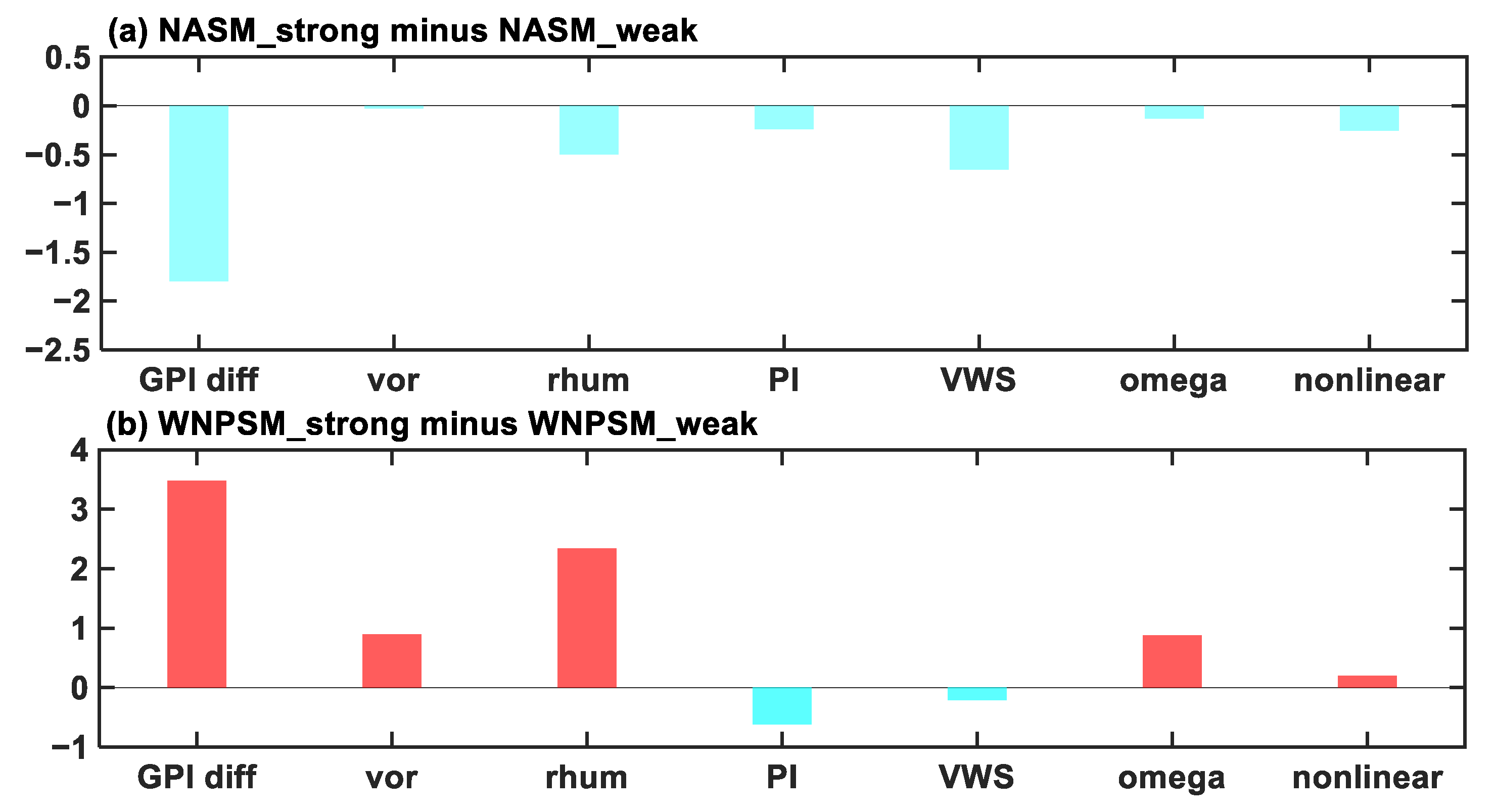
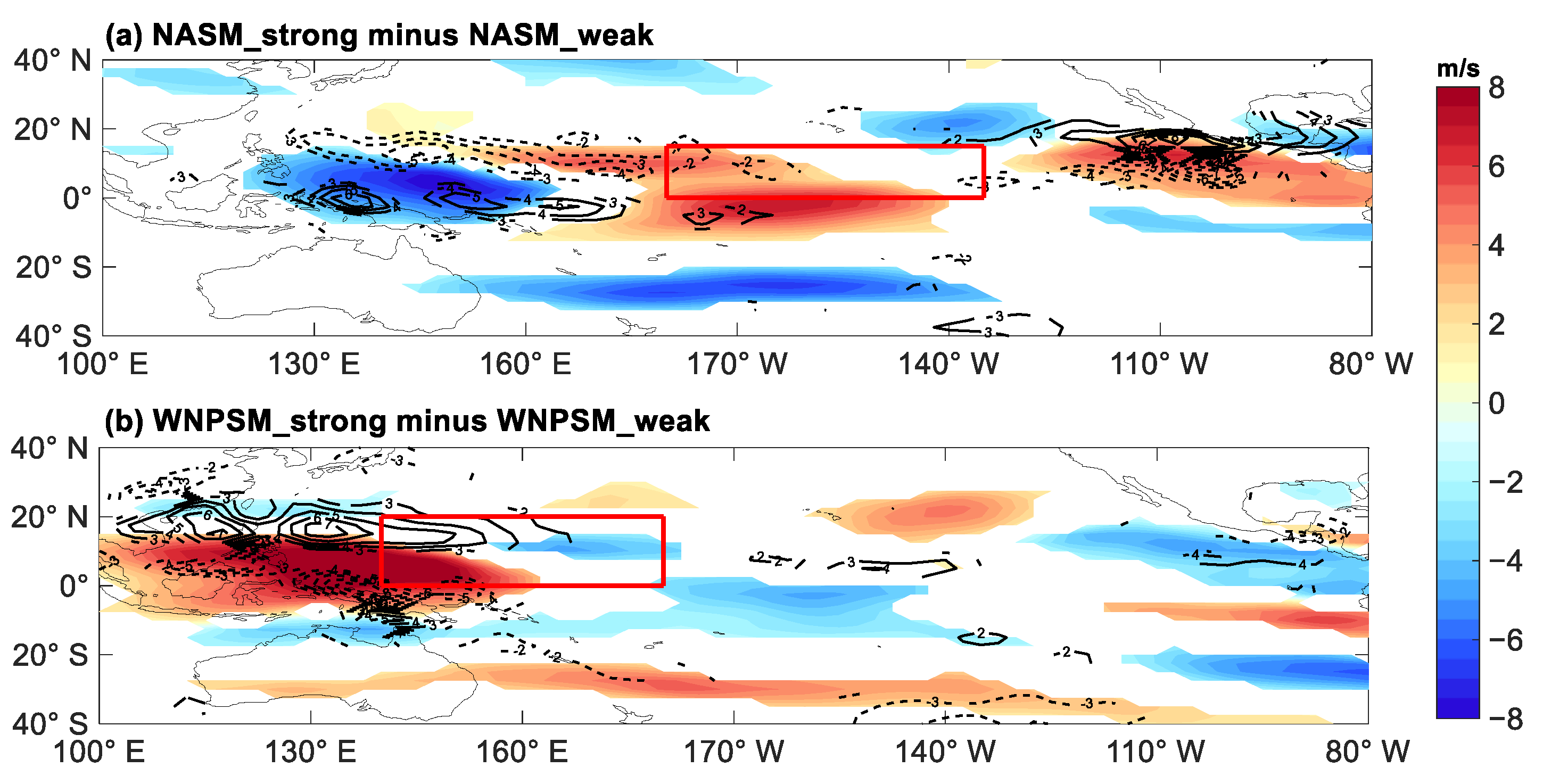
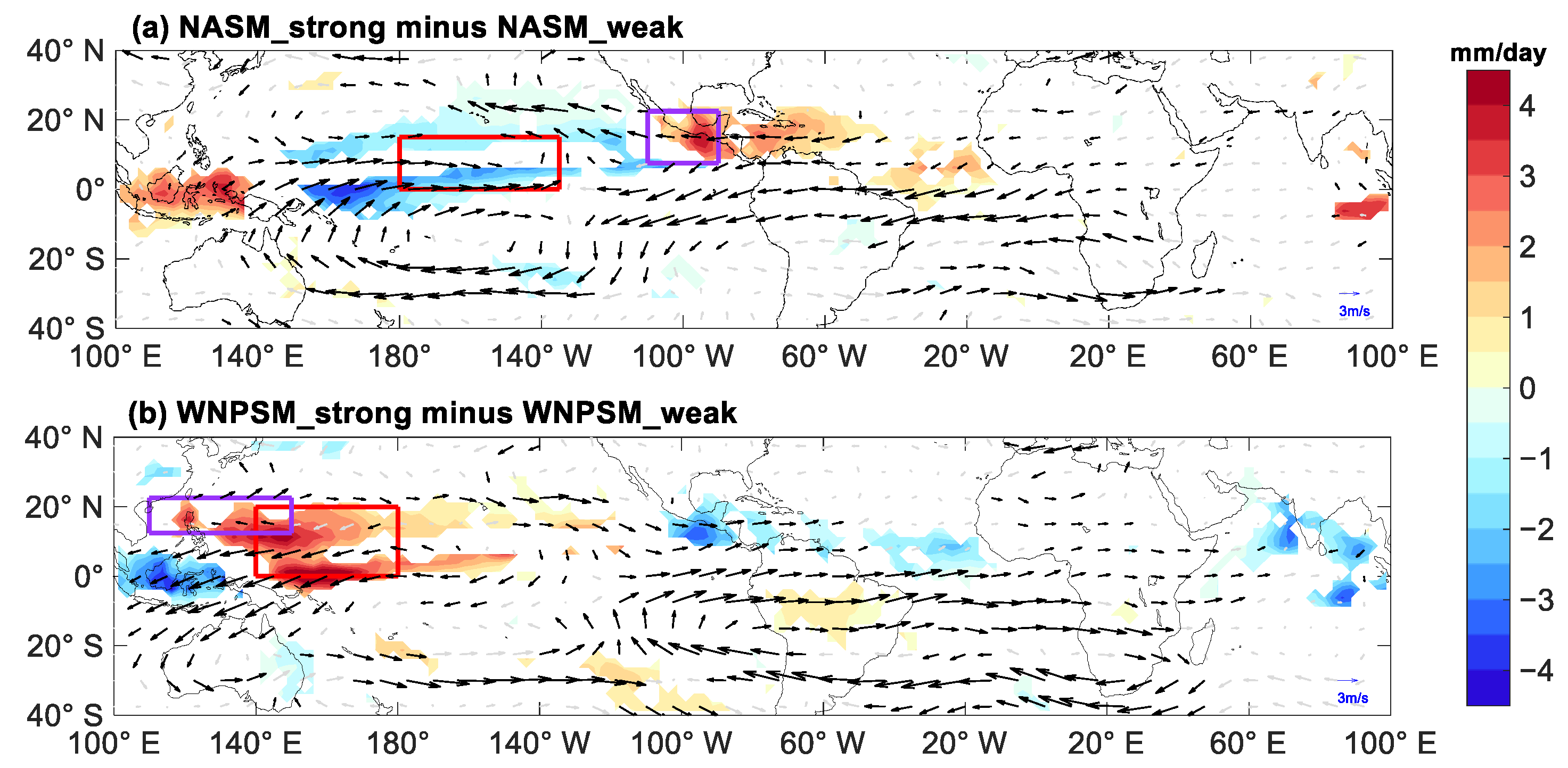
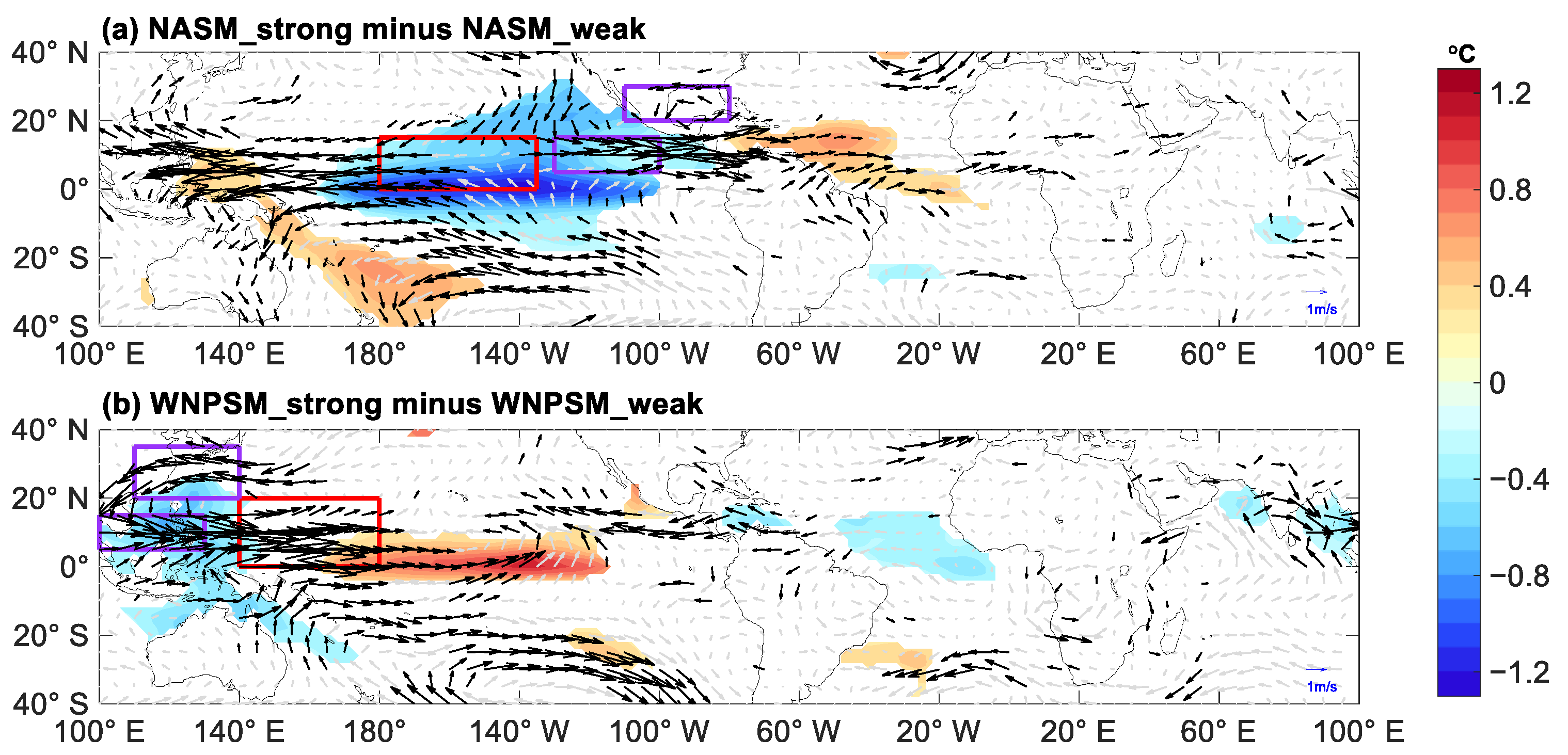
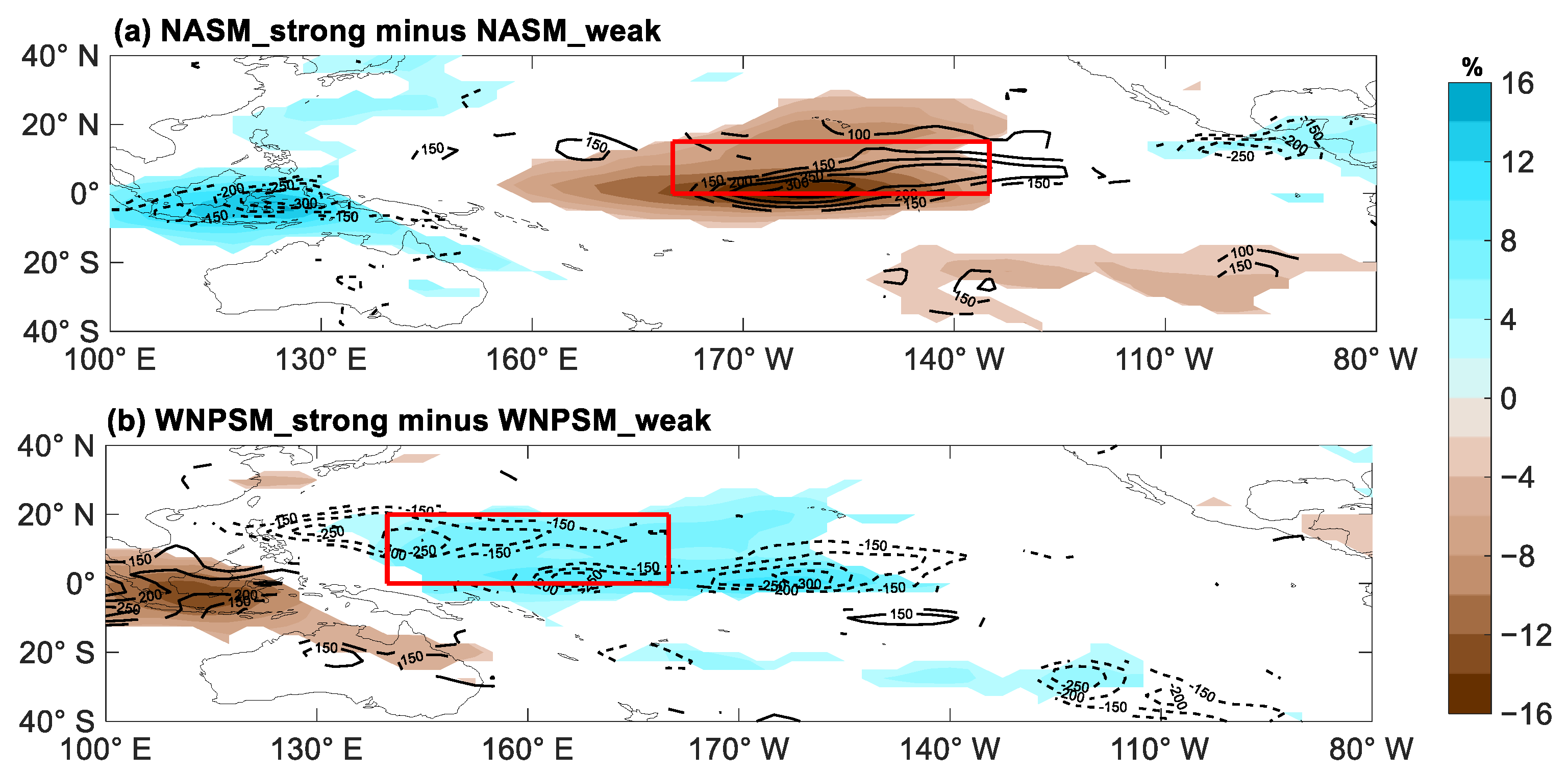
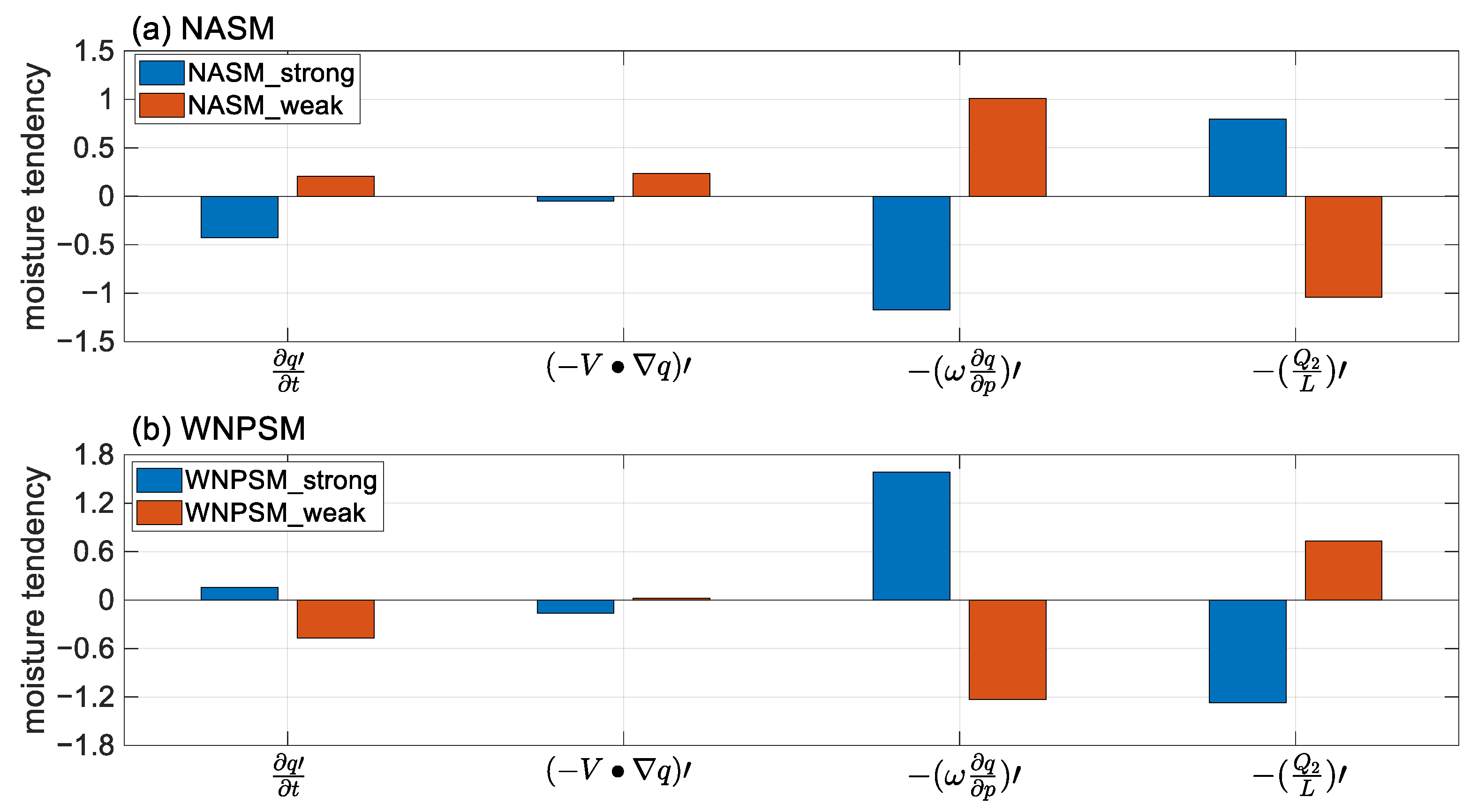
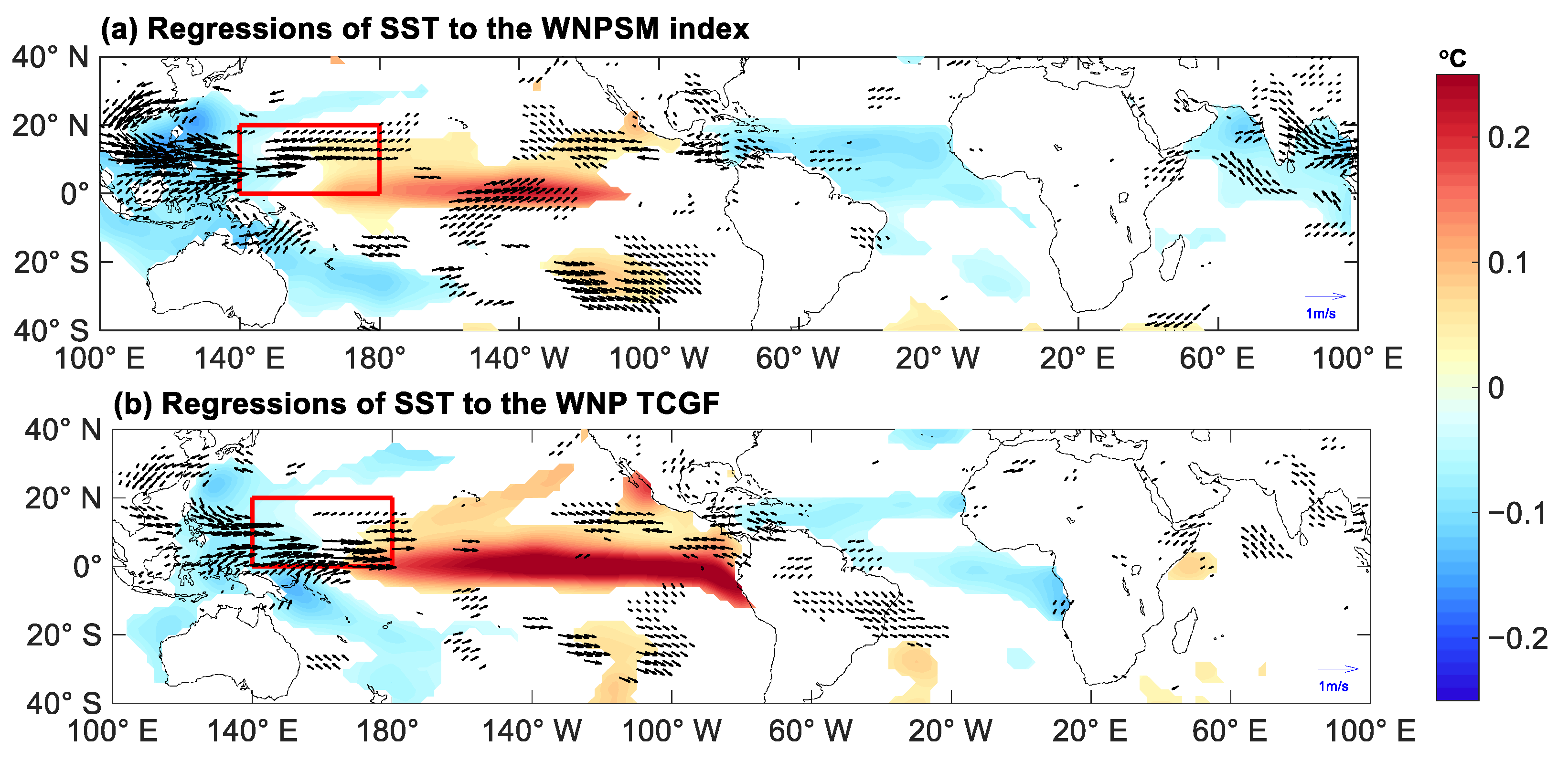


| Sub-Region | Strong Monsoon Years | Weak Monsoon Years | The Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 3.54 | 3.64 | −0.10 |
| II | 2.15 | 2.91 | −0.76 |
| III | 4.92 | 3.27 | 1.65 |
| IV | 1.85 | 1.91 | −0.06 |
| V | 4.69 | 2.09 | 2.60 * |
| VI | 0.50 | 1.69 | −1.19 |
| VII | 1.50 | 4.38 | −2.88 * |
| VIII | 3.83 | 2.92 | 0.91 |
| IX | 4.75 | 6.54 | −1.78 |
| Sub-Region | Local Monsoon Index and GPI | TCGF and GPI |
|---|---|---|
| V | 0.69 * | 0.49 * |
| VII | −0.58 * | 0.72 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Chen, B.; Peng, X.; Gan, Q. A Contrast of the Monsoon–Tropical Cyclone Relationship between the Western and Eastern North Pacific. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091465
Weng J, Wang L, Luo J, Chen B, Peng X, Gan Q. A Contrast of the Monsoon–Tropical Cyclone Relationship between the Western and Eastern North Pacific. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(9):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091465
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Jinwen, Lei Wang, Jianzhou Luo, Baiyang Chen, Xugang Peng, and Qiuying Gan. 2022. "A Contrast of the Monsoon–Tropical Cyclone Relationship between the Western and Eastern North Pacific" Atmosphere 13, no. 9: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091465
APA StyleWeng, J., Wang, L., Luo, J., Chen, B., Peng, X., & Gan, Q. (2022). A Contrast of the Monsoon–Tropical Cyclone Relationship between the Western and Eastern North Pacific. Atmosphere, 13(9), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091465








