Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of Winter Fog in Amritsar: An Urban City of North-Western India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
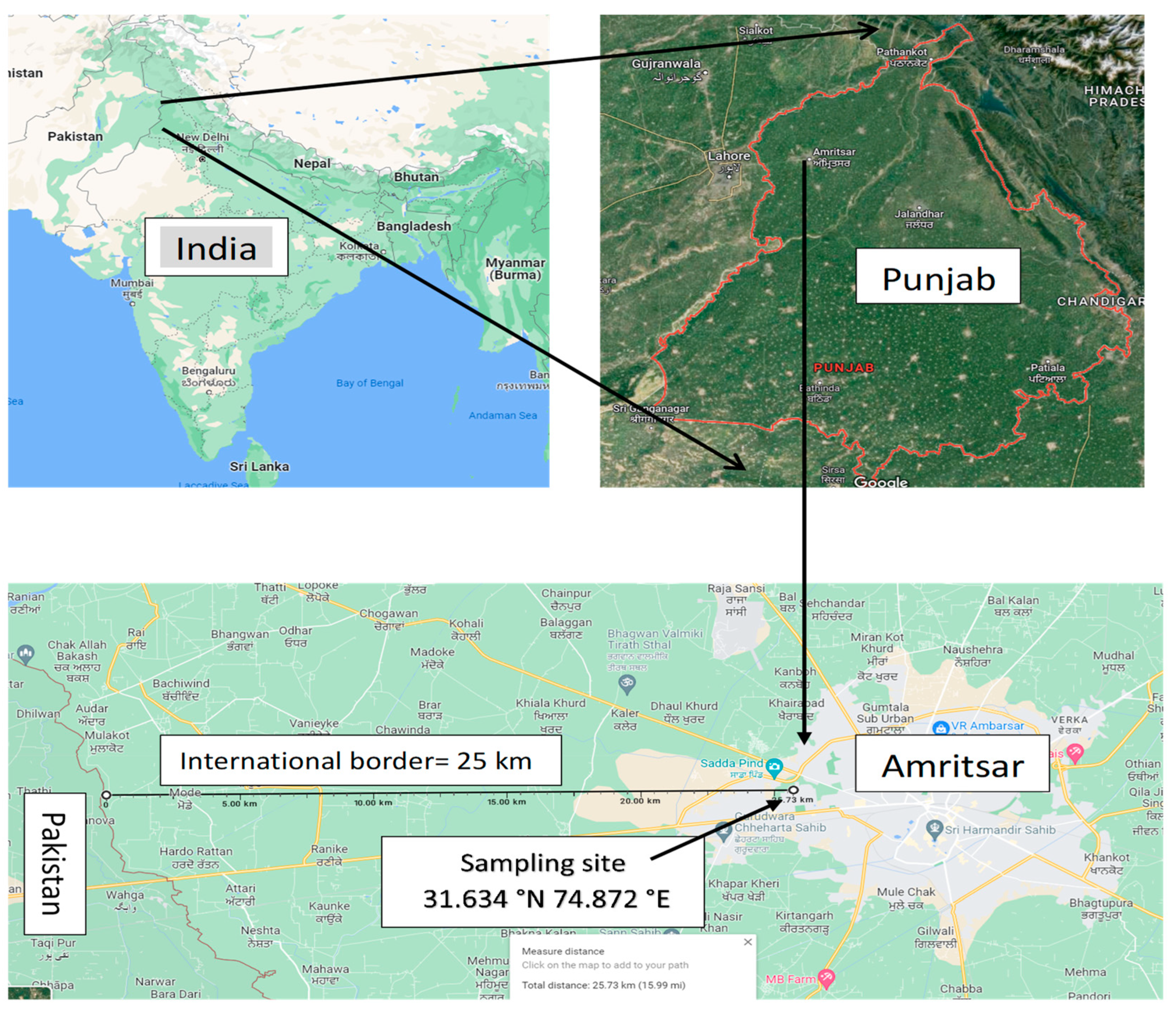
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Ionic Composition of Fog Samples and Anion–Cation Balance Check
2.4. Neutralization Factor (NF)
2.5. Enrichment Factor (EF)
2.6. Principal Component Analysis
2.7. Air Mass Back Trajectories
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH
3.2. Electrical Conductivity
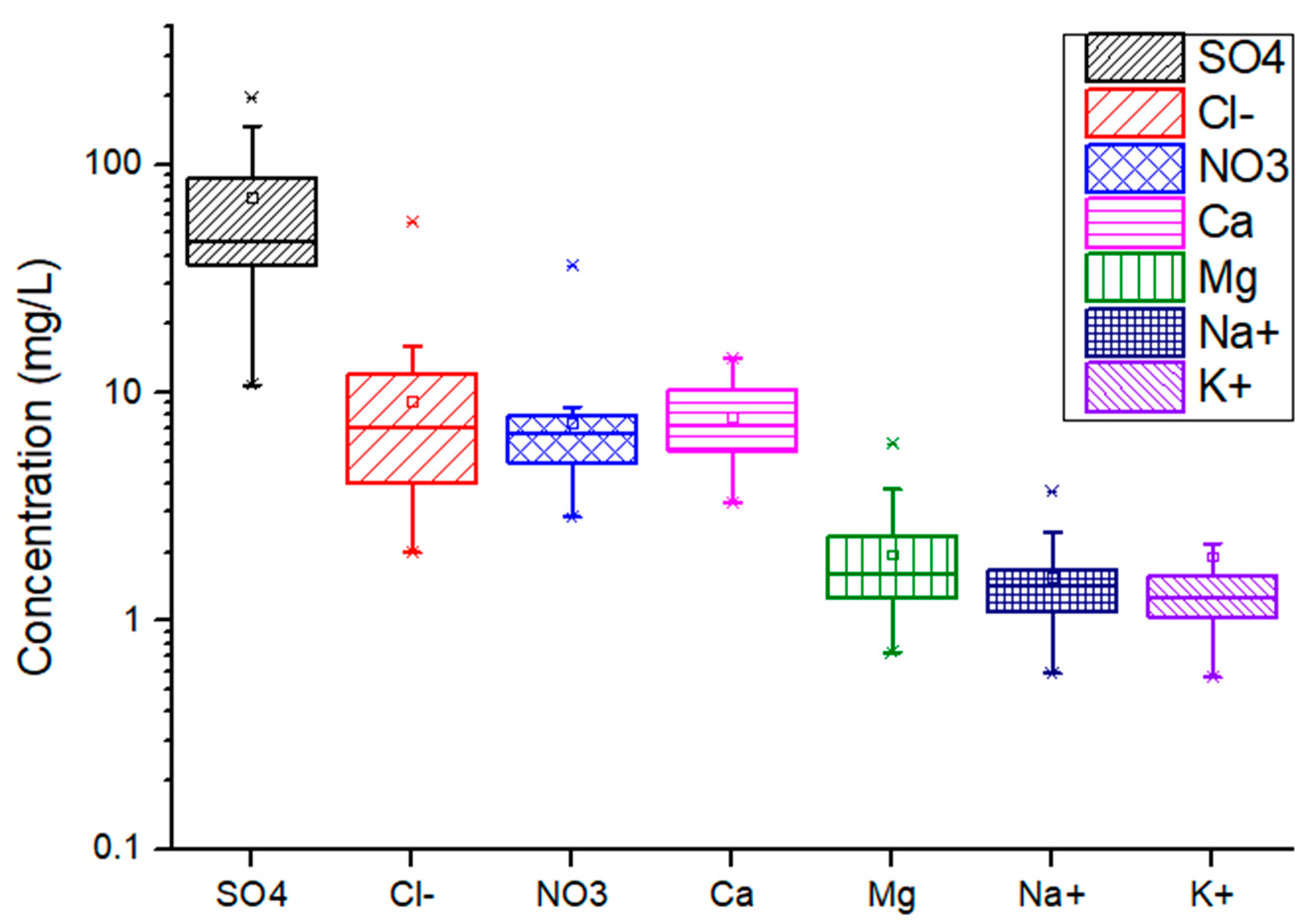
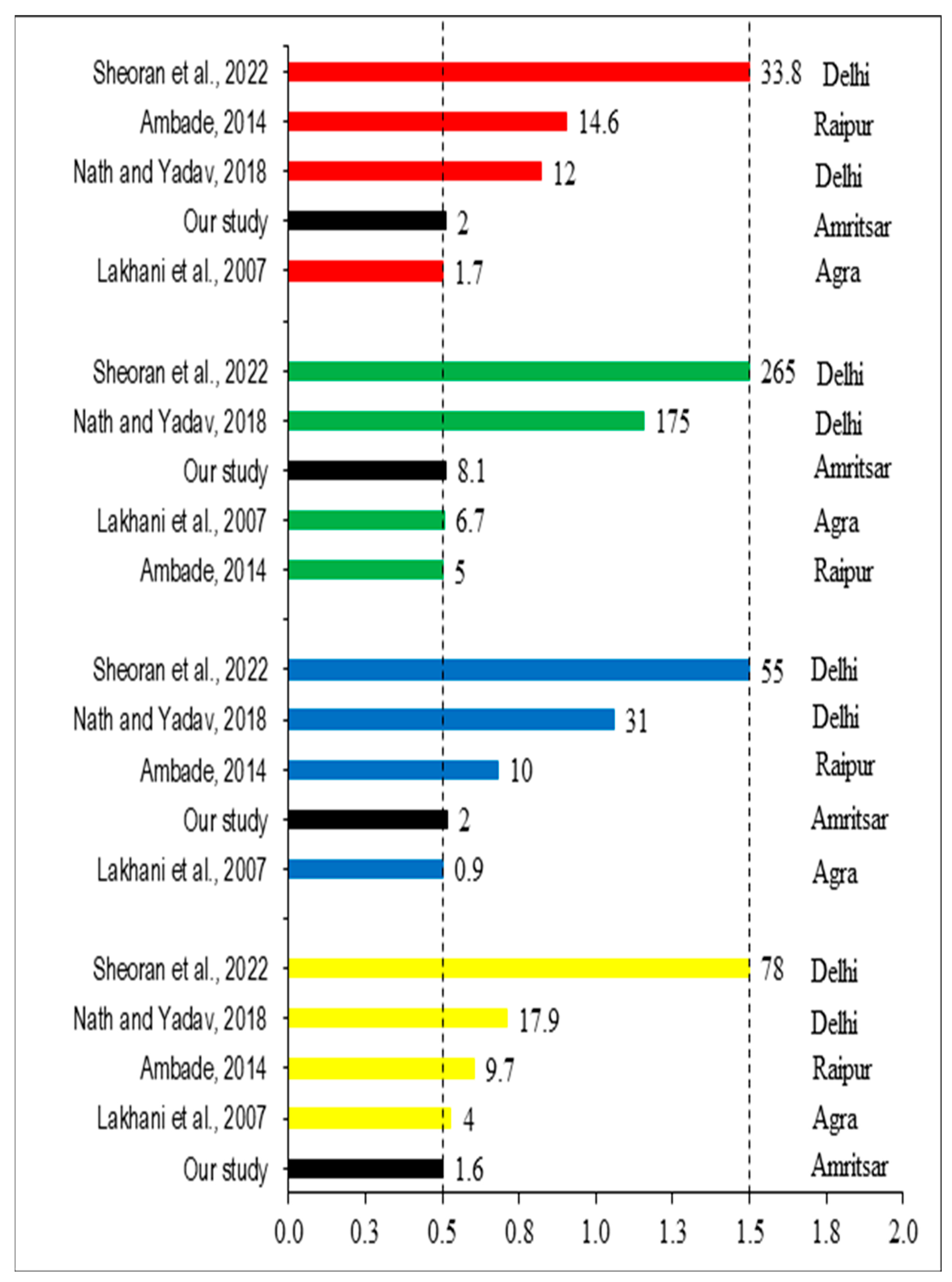
3.3. Ionic Composition and Trace Metals in Fog Water
3.4. Neutralization Factor
3.5. Source Identification Studies
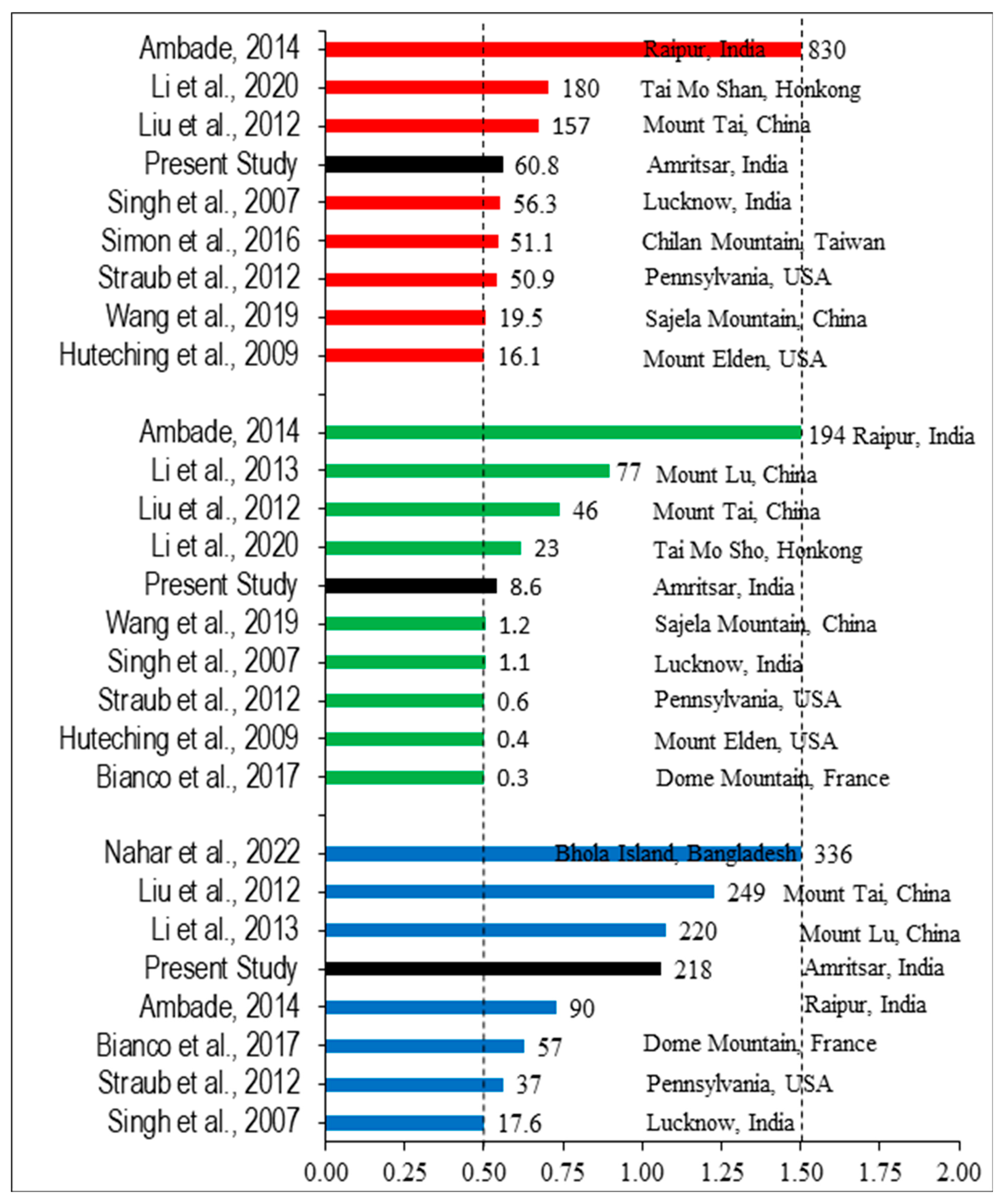
3.5.1. Enrichment Factor
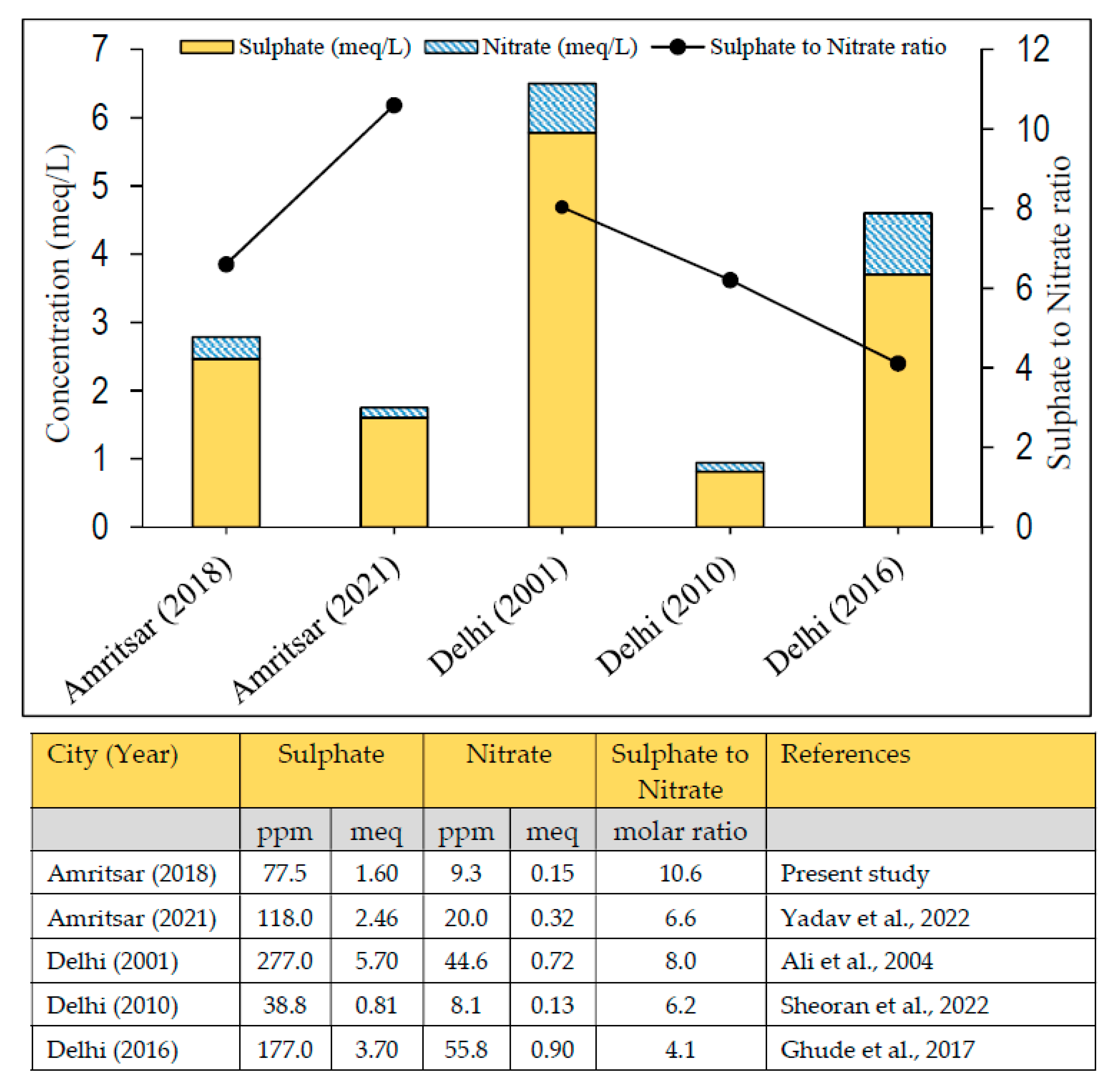
3.5.2. Sulphate to Nitrate Ratio
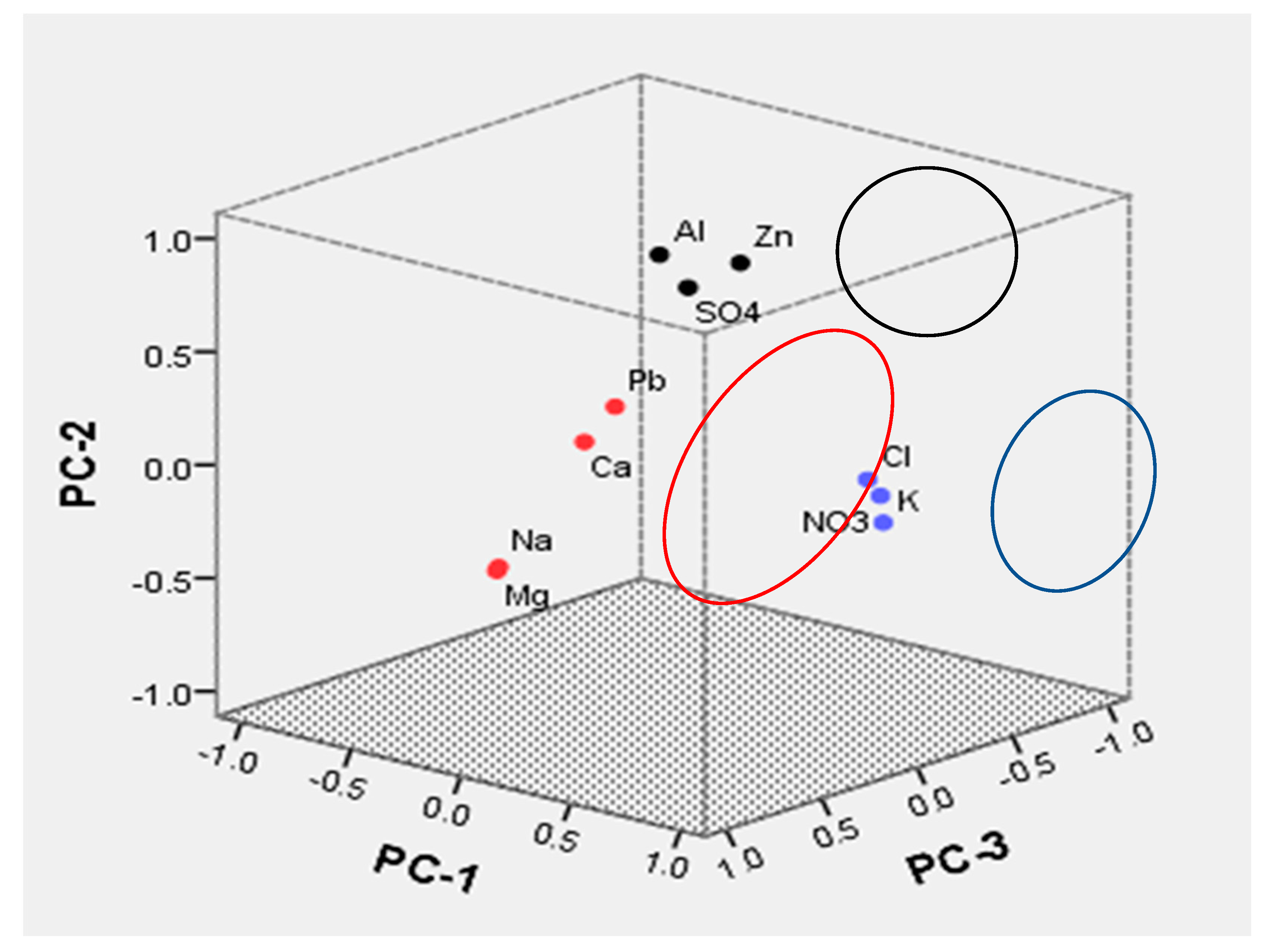
3.5.3. Principal Component Analysis
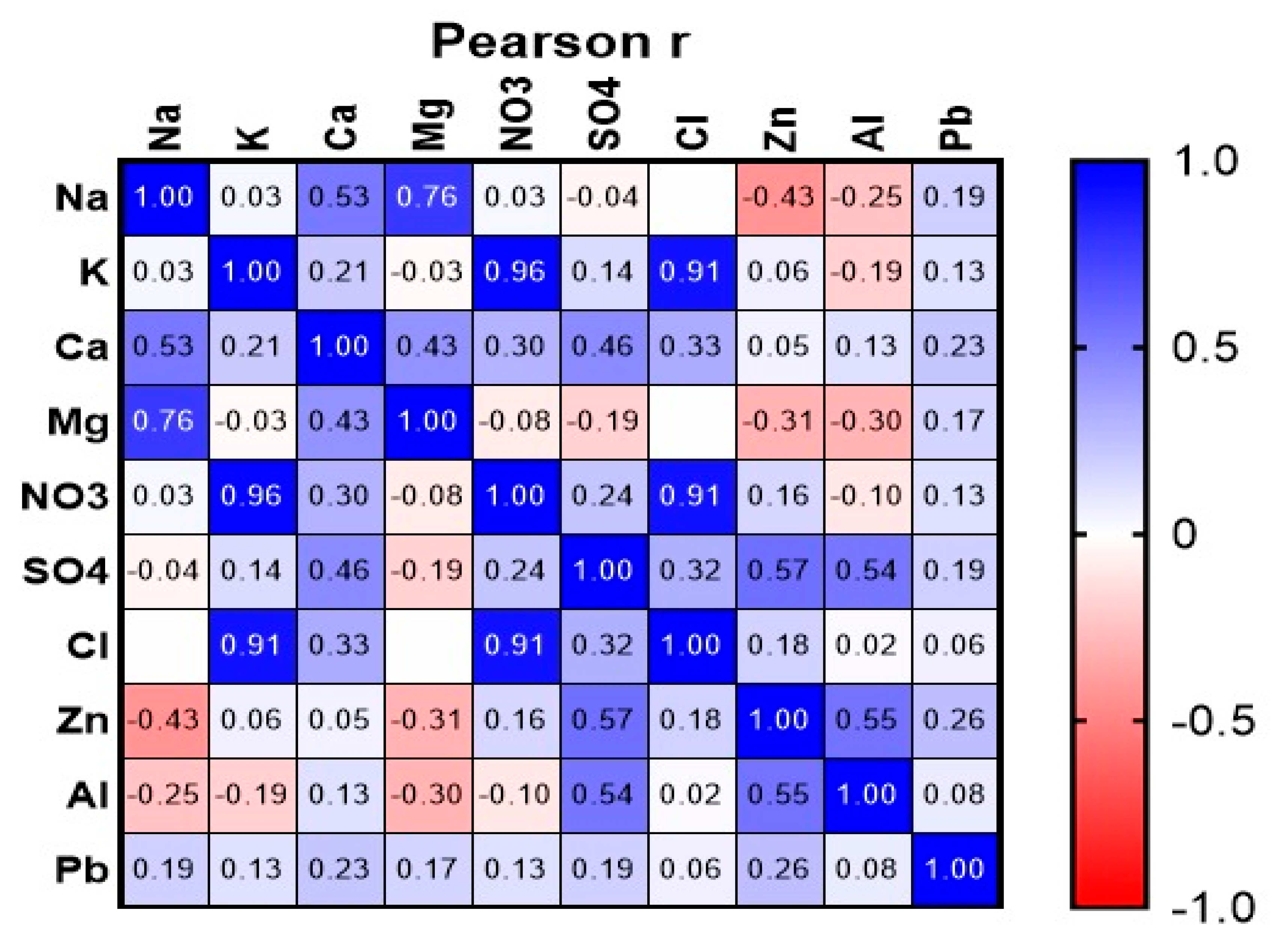
3.5.4. Multiple Correlation Analysis
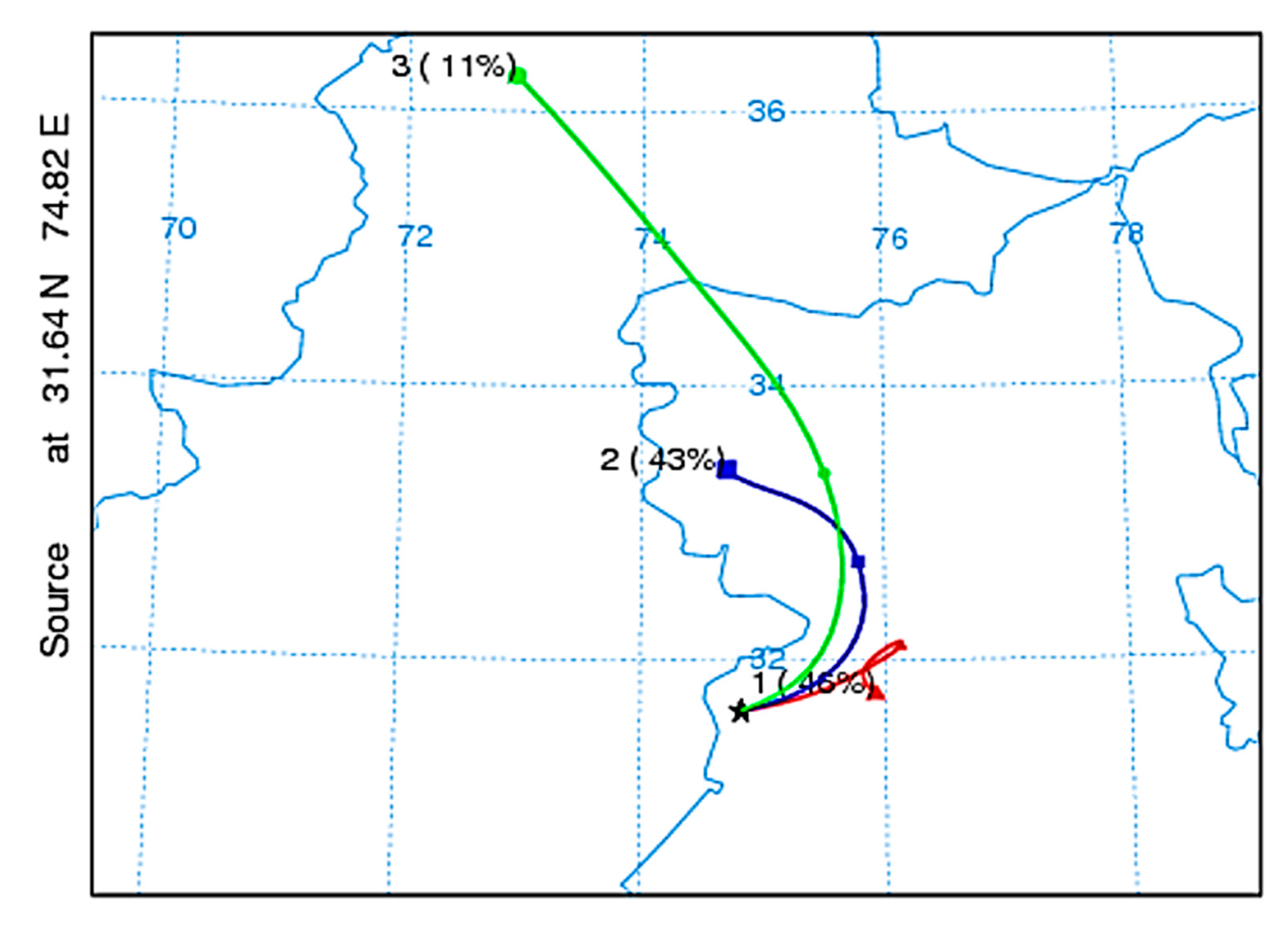
3.5.5. Air Mass Back Trajectory
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Che, H.; Zhong, J.; Chu, Y.; Cheng, L. Temporal and spatial variations of haze and fog and the characteristics of PM2.5 during heavy pollution episodes in China from 2013 to 2018. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Chaudhuri, S. Nowcasting visibility during wintertime fog over the airport of a metropolis of India: Decision tree algorithm and artificial neural network approach. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1349–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, O.; Todorov, P.; Gultepe, I. Investigations on the influence of chemical compounds on fog microphysical parameters. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Hu, Z. Influence of air pollutants on fog formation in urban environment of Nanjing, China. Procedia Eng. 2011, 24, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohan, M.; Payra, S. Influence of aerosol spectrum and air pollutants on fog formation in urban environment of megacity Delhi, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Kang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhu, T. To what extents do urbanization and air pollution affect fog? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5559–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar, S.; Gupta, T.; Minz, A.P.; Senapati, S.; Panday, A.K. Influence of regional and long range transport air masses on fog water composition, contribution and toxicological response at Indo Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghude, S.D.; Bhat, G.S.; Prabhakaran, T.; Jenamani, R.K.; Chate, D.M.; Safai, P.D.; Karipot, A.K.; Konwar, M.; Pithani, P.; Sinha, V.; et al. Winter fog experiment over the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.S.; Moorthy, K.K.; Alappattu, D.P.; Kunhikrishnan, P.K.; George, S.; Nair, P.R.; Babu, S.S.; Abish, B.; Satheesh, S.K.; Tripathi, S.N. Wintertime aerosol characteristics over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP): Impacts of local boundary layer processes and long-range transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Liu, D.; Zheng, A.; Dore, A.J.; Liu, X. Chemical compositions of fog and precipitation at Sejila Mountain in the southeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Microscopic evaluation of trace metals in cloud droplets in an acid precipitation region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Vaïtilingom, M.; Bridoux, M.; Chaumerliac, N.; Pichon, J.M.; Piro, J.L.; Deguillaume, L. Trace metals in cloud water sampled at the puy de Dôme station. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ge, B.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z. Impact of water vapor content on visibility: Fog-haze conversion and its implications to pollution control. Atmos. Res. 2021, 256, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Okochi, H.; Igawa, M. Characteristics of fog and fog collection with passive Collector at Mt. Oyama in Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M. Multiple Regression Analysis of low visibility focusing on severe haze-fog pollution in various regions of China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, D.; Mora-Carreño, M.; Sandoval, C.; Espinoza, S. Assessing fog water collection in the coastal mountain range of Antofagasta, Chile. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 198, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Wai, K.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, P.H.; Guo, J.; Xu, P.J.; Wang, W.X. Evaluation of trace elements contamination in cloud/fog water at an elevated mountain site in Northern China. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nath, S.; Bhatti, M.S.; Yadav, S. Chemical characteristics of fine and coarse particles during wintertime over two urban cities in North India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1573–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Mor, S.; Singh, V.; Mandal, T.K.; Bhatti, M.S.; Gahlawat, S.K.; Dhankar, R.; Mor, S.; Beig, G. Real-time monitoring of air pollutants in seven cities of North India during crop residue burning and their relationship with meteorology and transboundary movement of air. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Bhatti, M.S.; Kansal, S.K.; Das, L.; Gilhotra, V.; Sugha, A.; Sugha, A.; Hingmire, D.; Yadav, S.; Tandon, A.; et al. Comparison of ambient air pollution levels of Amritsar during foggy conditions with that of five major north Indian cities: Multivariate analysis and air mass back trajectories. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Nahian, S.; Jeba, F.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Choudhury, T.R.; Fatema, K.J.; Salam, A. Characterization and Source Discovery of Wintertime Fog on Coastal Island, Bangladesh. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Yadav, S. Factors and sources influencing ionic composition of atmospheric condensate during winter season in lower troposphere over Delhi, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2795–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Sugha, A.; Bhatti, M.S.; Kansal, S.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. The role of particulate matter in reduced visibility and anionic composition of winter fog: A case study for Amritsar city. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11104–11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Momin, G.A.; Tiwari, S.; Safai, P.D.; Chate, D.M.; Rao, P.S.P. Fog and precipitation chemistry at Delhi, North India. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Klemm, O.; El-Madany, T.; Walk, J.; Amelung, K.; Lin, P.H.; Chang, S.C.; Lin, N.H.; Engling, G.; Hsu, S.C.; et al. Chemical composition of fog water at four sites in Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Joshi, H.; Ram, K.; Singh, N.; Naja, M.; Tiwari, S. Chemical characterization of rainwater at a high-altitude site “Nainital” in the central Himalayas, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohel, M.; Simol, H.A.; Reid, E.; Reid, J.S.; Salam, A. Dew water chemical composition and source characterization in the IGP outflow location (coastal Bhola, Bangladesh). Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, J.; Lu, S. Chemical characteristics of wet precipitation at an urban site of Guangzhou, South China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, L.Y.; Li, N.; Yang, G.; Luo, D.; Chen, J. Chemical characteristics of spring rainwater of Xi’an city, NW China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5058–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Ri, X.; Wang, Y.S.; Pan, Y.P.; Piao, S.L. Wet deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen at five remote sites in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11683–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A.; Sharma, N.; Murthy, R.C.; Kumar, R. Hydrochemistry of wet atmospheric precipitation over an urban area in Northern Indo-Gangetic Plains. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, A.; Parmar, R.S.; Satsangi, G.S.; Prakash, S. Chemistry of fogs at Agra, India: Influence of soil particulates and atmospheric gases. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekouch, I.; Muselli, M.; Kabbachi, B.; Ouazzani, J.; Melnytchouk-Milimouk, I.; Beysens, D. Dew, fog, and rain as supplementary sources of water in south-western Morocco. Energy 2011, 36, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysens, D.; Ohayon, C.; Muselli, M.; Clus, O. Chemical and biological characteristics of dew and rain water in an urban coastal area (Bordeaux, France). Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3710–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.S.; Gupta, T.; Tripathi, S.N.; Tare, V.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Secondary organic aerosol: A comparison between foggy and nonfoggy days. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7307–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, A.J.; Napolitano, D.C.; Herckes, P.; Clements, A.L.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Fogs and air quality on the southern California coast. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Kulshrestha, U.C. Extreme air pollution events spiking ionic levels at urban and rural sites of Indo-Gangetic plain. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1266–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Yadav, S. A comparative study on fog and dew water chemistry at New Delhi, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B. Characterization and source of fog water contaminants in central India. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 1535–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Fog water chemistry in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4034–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaś, M.; Polkowska, Ż.; Sobik, M.; Klimaszewska, K.; Nowiński, K.; Namieśnik, J. Fog water chemical composition in different geographic regions of Poland. Atmos. Res. 2010, 95, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Niu, S.; Tang, L.; Lv, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, B. Chemical composition of fog water in Nanjing area of China and its related fog microphysics. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Marcotte, A.R.; Karl, M.; Dye, C.; Herckes, P. Fog chemistry at three sites in Norway. Atmos. Res. 2015, 151, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Sui, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, J. Fog composition along the Yangtze River basin: Detecting emission sources of pollutants in fog water. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiderwieden, E.; Wrzesinsky, T.; Klemm, O. Chemical characterization of fog and rain water collected at the eastern Andes cordillera. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Lee, B.K.; Kim, H.J. Cloud/fog water chemistry at a high elevation site in South Korea. J. Atmos. Chem. 2006, 55, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberding, F.; Breuer, B.; Braeckevelt, E.; Klemm, O.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Y. Fog water chemical composition on ailaoshan mountain, Yunnan province, SW China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, A.J.; Lee, T.; Park, T.; Choi, J.; Seo, S.J.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Fog composition at Baengnyeong Island in the eastern Yellow Sea: Detecting markers of aqueous atmospheric oxidations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, D.J.; Hutchings, J.W.; Herckes, P. Measurements of fog composition at a rural site. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, R.; Dumka, U.C.; Sowmya, H.N.; Bisht, D.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Tiwari, S.; Attri, S.D.; Hopke, P.K. Changes in inorganic chemical species in fog water over Delhi. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 16, 2021092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Xia, M.; Yu, C.; Yun, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Chemical characteristics of cloud water and the impacts on aerosol properties at a subtropical mountain site in Hong Kong SAR. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS-10500; Indian Standards-Drinking Water Specifications. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2012.
- Hutchings, J.W.; Robinson, M.S.; McIlwraith, H.; Triplett Kingston, J.; Herckes, P. The chemistry of intercepted clouds in Northern Arizona during the North American monsoon season. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 199, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, W.C.; Pszenny, A.A.; Galloway, J.N.; Hawley, M.E. Sea-salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 1986, 91, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.P.; Tiwari, S.; Matwale, J.L.; Pervez, S.; Tunved, P.; Safai, P.D.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Singh, S.; Hopke, P.K. Sources of chemical species in rainwater during monsoon and non-monsoonal periods over two mega cities in India and dominant source region of secondary aerosols. Atmospheric Environment. 2016, 146, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Kumar, P. Pollutant scavenging in dew water collected from an urban environment and related implications. Air Quality, Atmosphere Health 2014, 7, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobre, T.; Salve, P.R.; Krupadam, R.J.; Bansiwal, A.; Shastry, S.; Wate, S.R. Chemical composition of precipitation in the coastal environment of India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y. Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in southeastern China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, G.A.; Ali, K.; Rao, P.S.P.; Safai, P.D.; Chate, D.M.; Praveen, P.S.; Rodhe, H.; Granat, L. Study of chemical composition of rainwater at an urban (Pune) and a rural (Sinhagad) location in India. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D08302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, V.; Prakash, J.; Soni, A.; Madhwal, S.; Shridhar, V. Atmospheric aerosols and inhalable particle number count during Diwali in Dehradun. City Environ. Interact. 2019, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 0.98 | ||
| NO3− | 0.98 | ||
| Cl− | 0.94 | ||
| SO42− | 0.83 | ||
| Al | 0.81 | ||
| Zn | 0.81 | ||
| Ca2+ | 0.75 | ||
| Na+ | 0.89 | ||
| Mg2+ | 0.83 | ||
| Eigenvalue | 3.2 | 2.5 | 1.9 |
| Variance explained (%) | 29.8 | 24.2 | 23.2 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 29.8 | 54.0 | 77.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asif, M.; Yadav, R.; Sugha, A.; Bhatti, M.S. Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of Winter Fog in Amritsar: An Urban City of North-Western India. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091376
Asif M, Yadav R, Sugha A, Bhatti MS. Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of Winter Fog in Amritsar: An Urban City of North-Western India. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(9):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091376
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsif, Mohammad, Rekha Yadav, Aditi Sugha, and Manpreet Singh Bhatti. 2022. "Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of Winter Fog in Amritsar: An Urban City of North-Western India" Atmosphere 13, no. 9: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091376
APA StyleAsif, M., Yadav, R., Sugha, A., & Bhatti, M. S. (2022). Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of Winter Fog in Amritsar: An Urban City of North-Western India. Atmosphere, 13(9), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091376







