High-Resolution Ammonia Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application in China during 2005–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
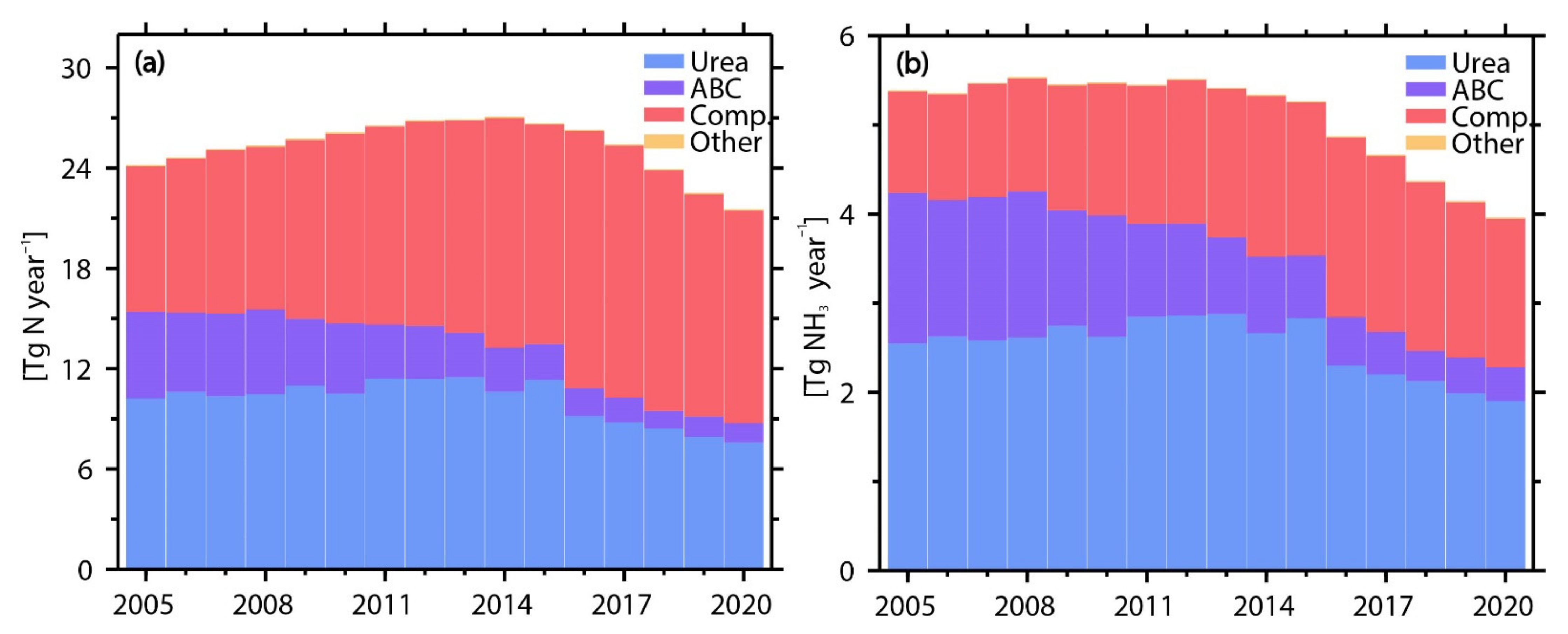
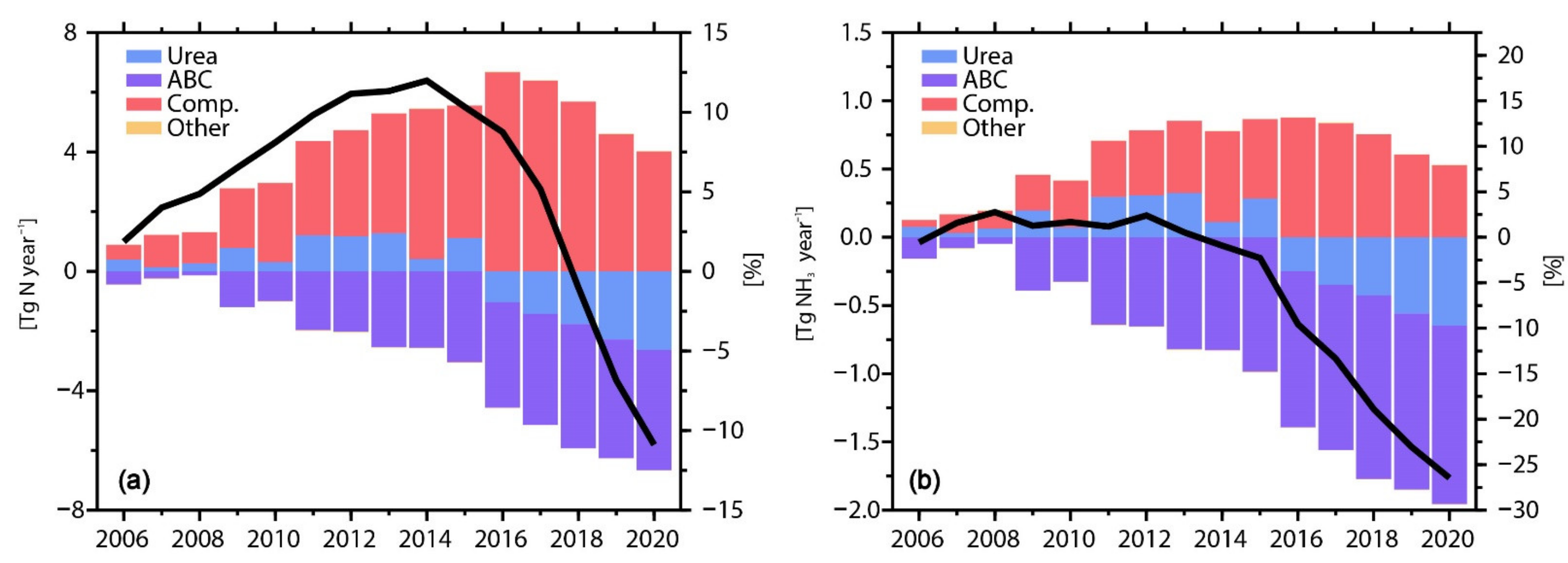
3.1. Annual Changes in NH3 Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application
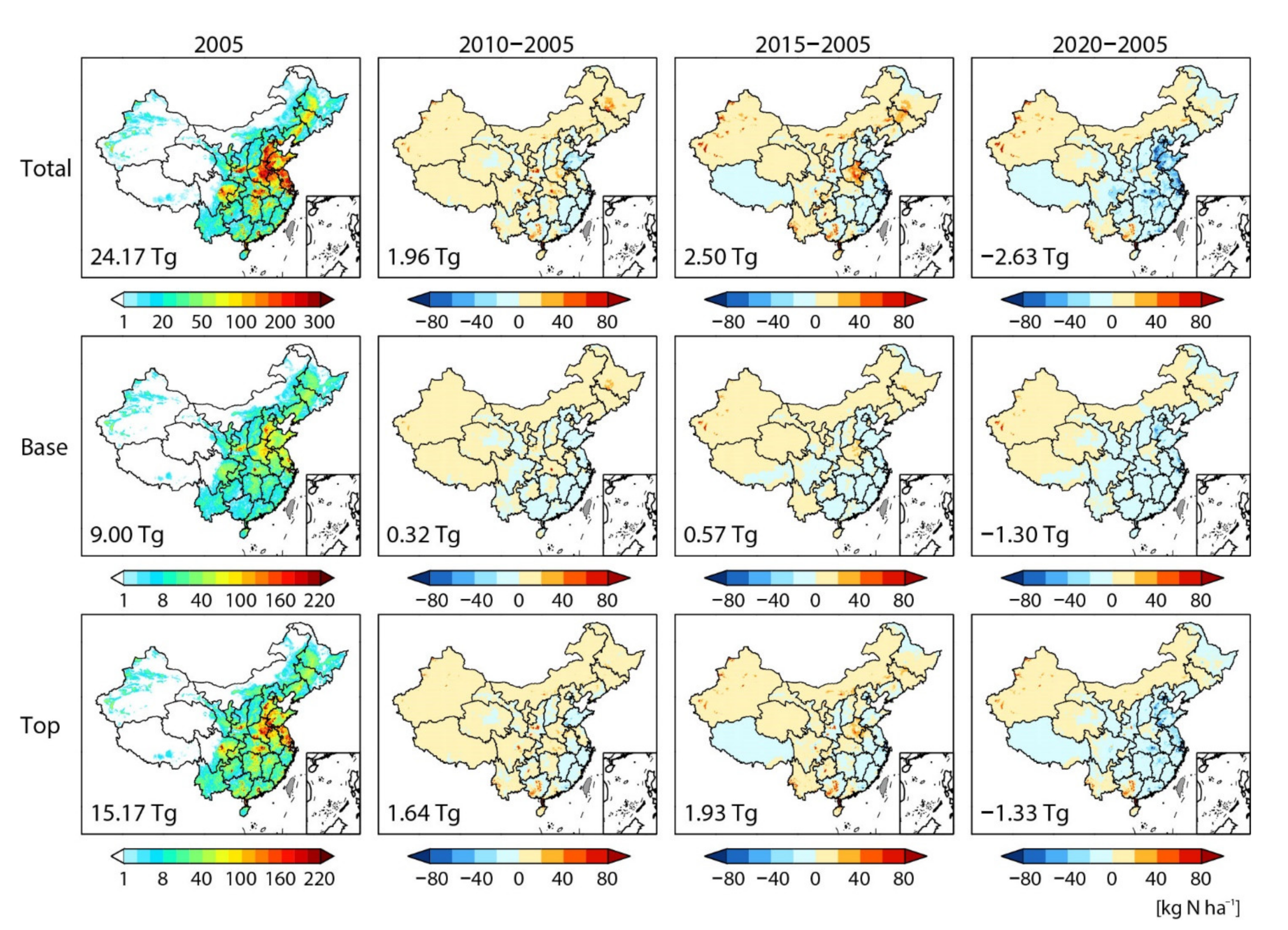
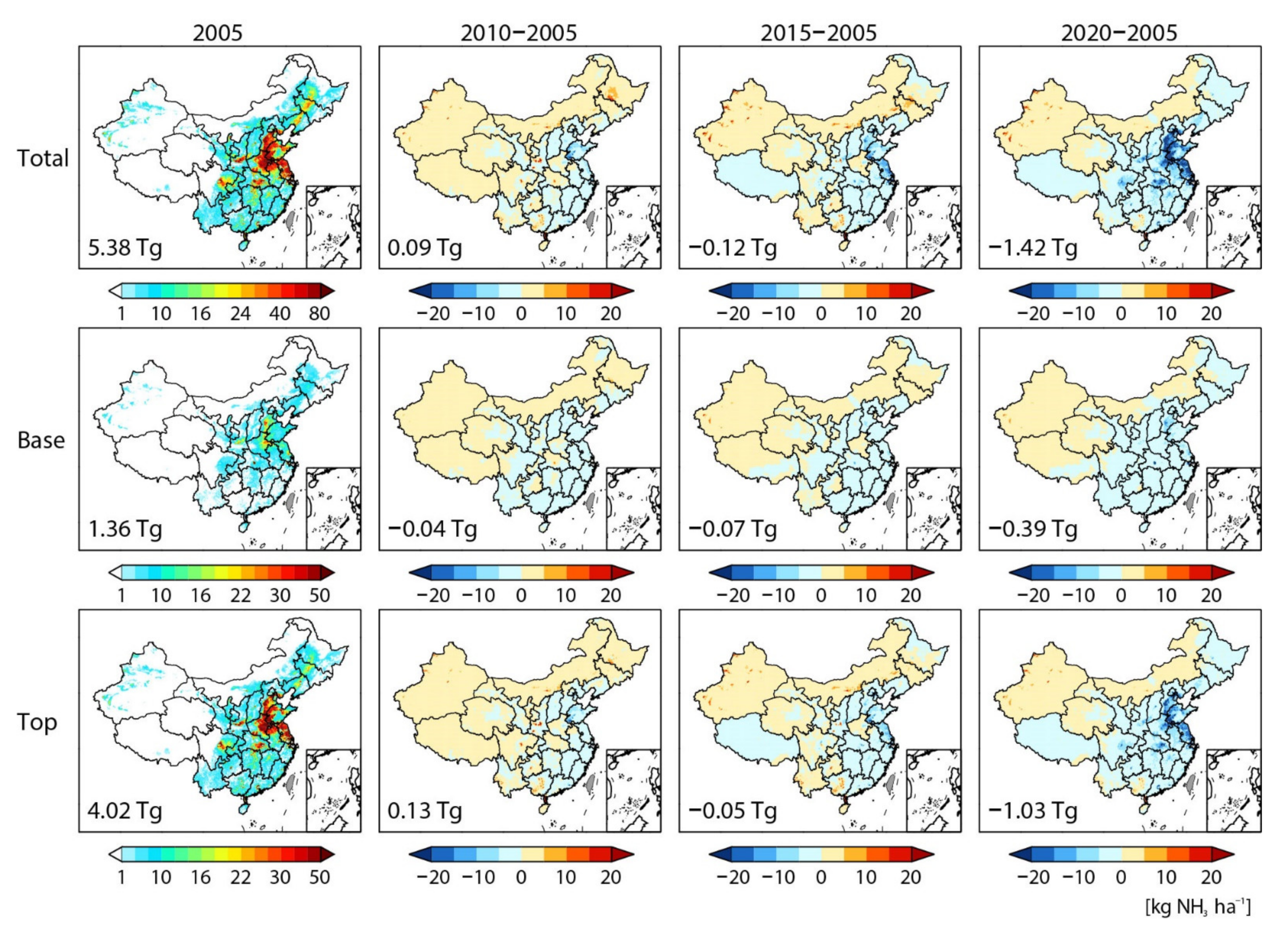
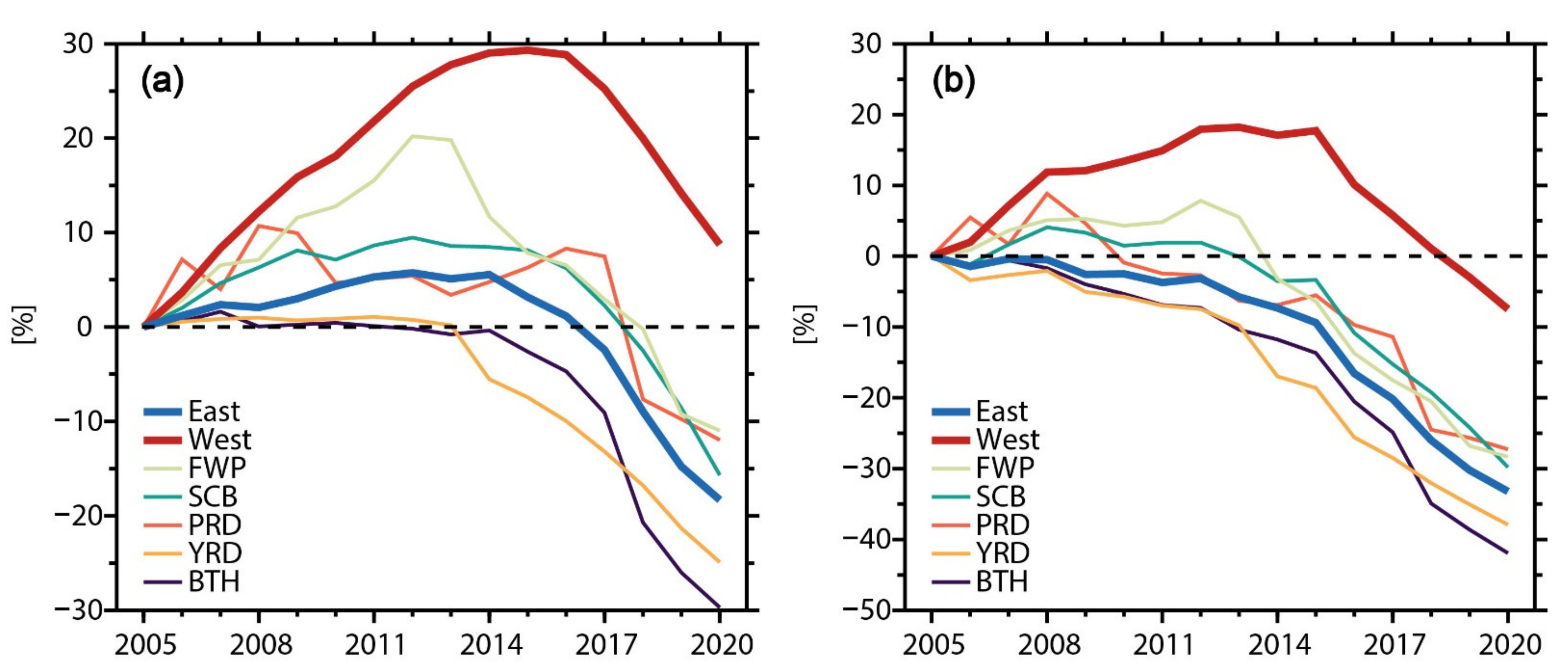
3.2. Changes in Spatial Distribution of NH3 Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application
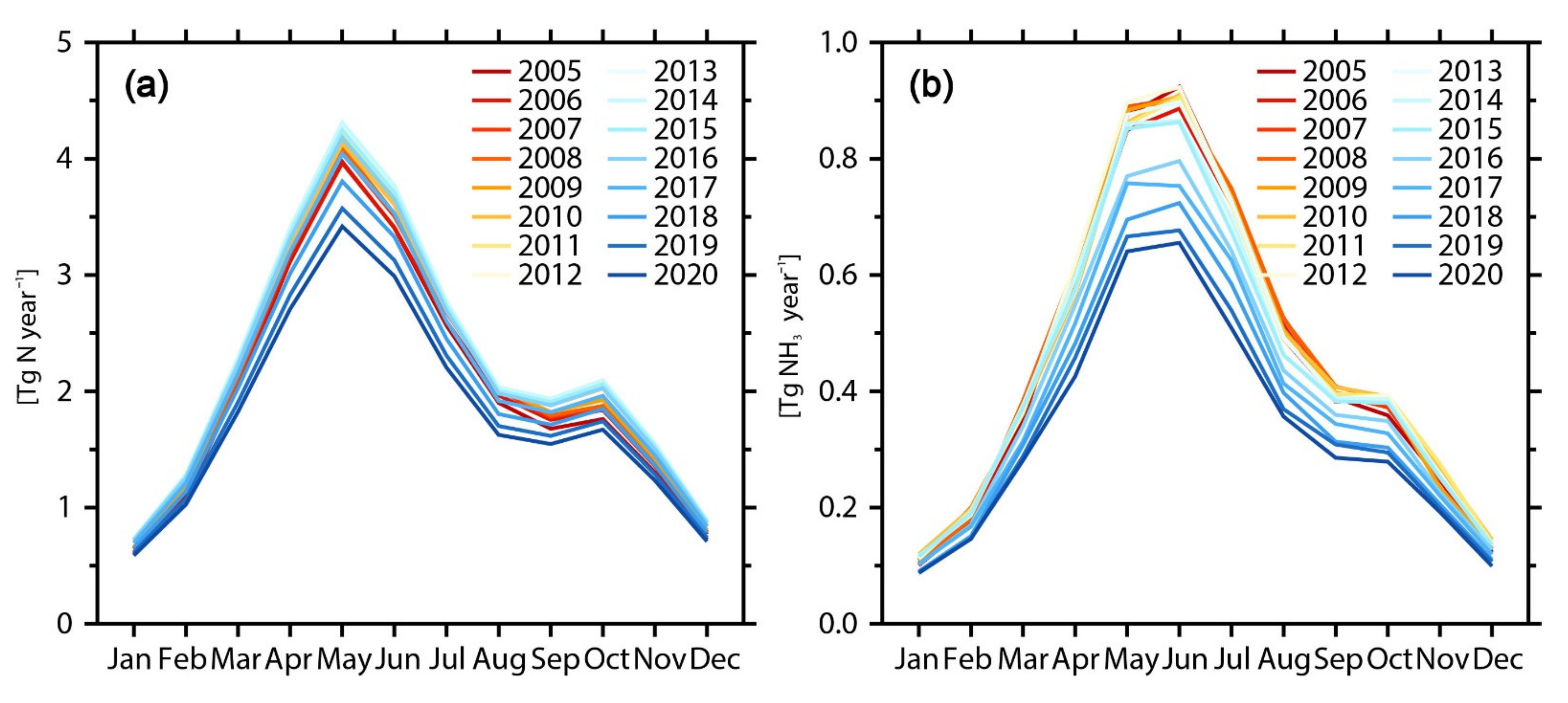
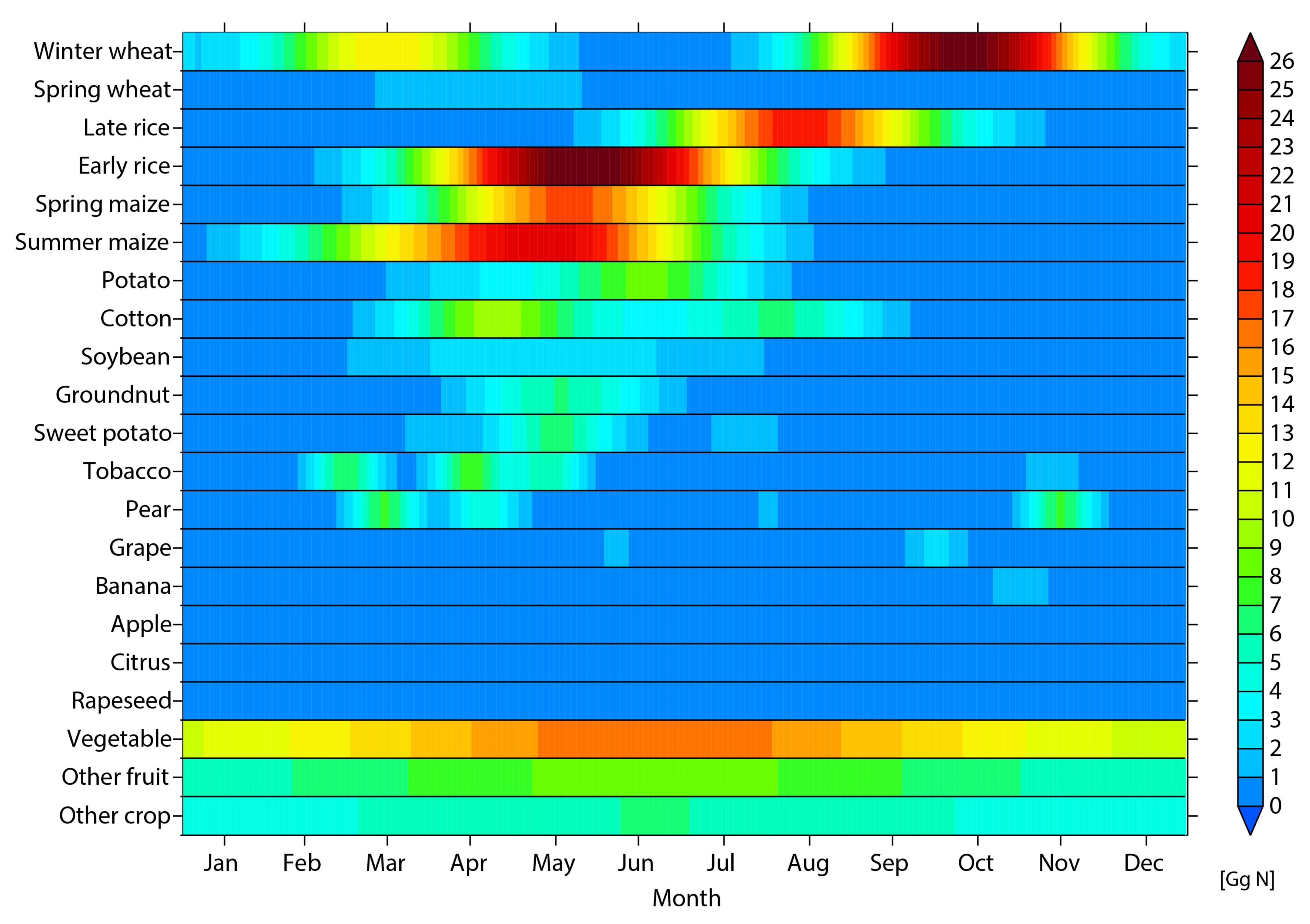
3.3. Monthly Variation of NH3 Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application
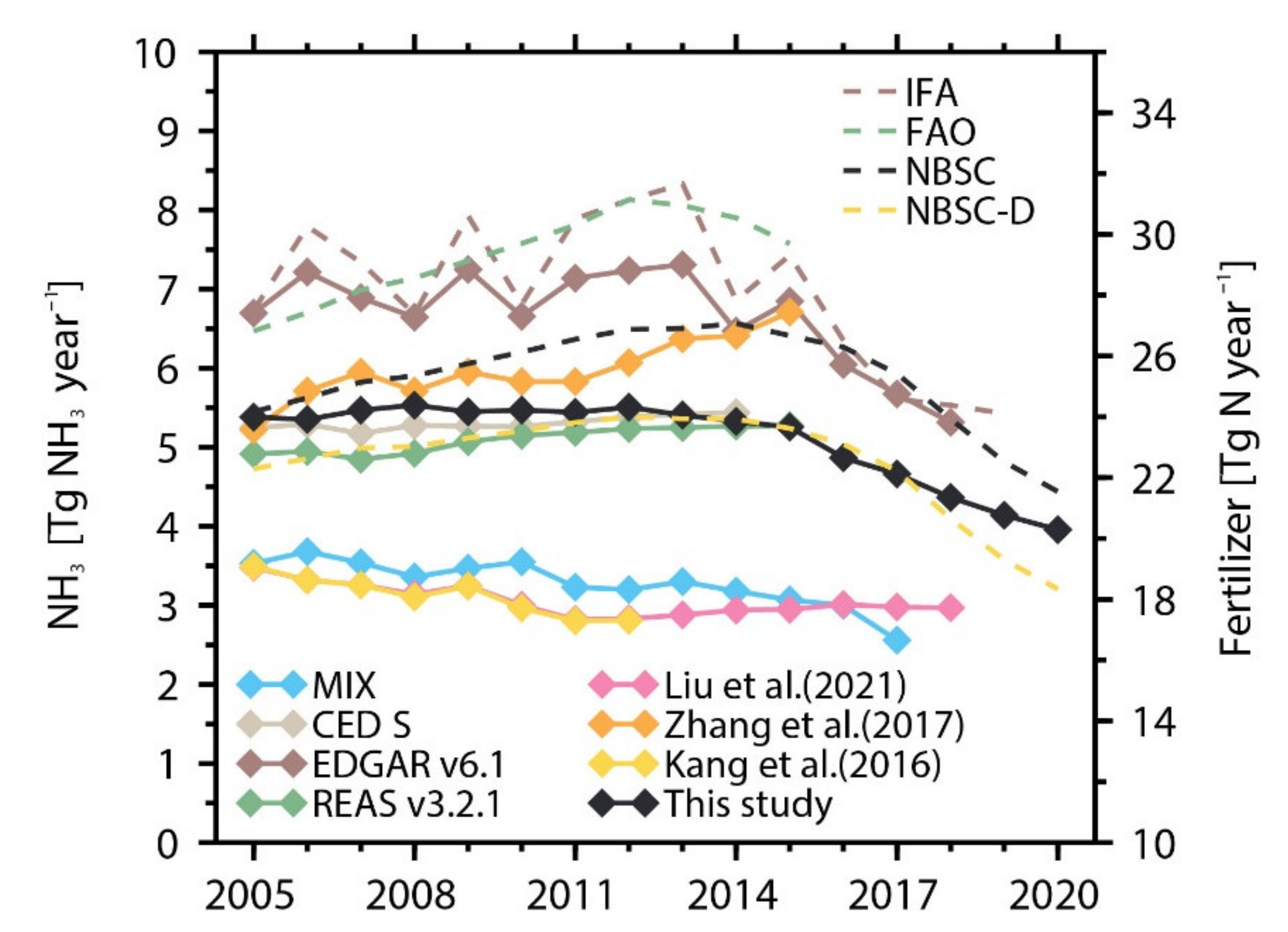
3.4. Comparison with Previous Studies
3.5. Uncertainty
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the atmosphere: A review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulot, F.; Jacob, D.J.; Pinder, R.W.; Bash, J.O.; Travis, K.; Henze, D.K. Ammonia emissions in the United States, European Union, and China derived by high-resolution inversion of ammonium wet deposition data: Interpretation with a new agricultural emissions inventory (MASAGE_NH3). J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 4343–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Huo, Q.; Cai, X.; Zhu, T.; Hu, M.; Zhang, H. A high-resolution ammonia emission inventory in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, GB1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Henze, D.K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Paulot, F.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Agricultural ammonia emissions in China: Reconciling bottom-up and top-down estimates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Benedict, K.B.; Tang, A.; Sun, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, X. Persistent nonagricultural and periodic agricultural emissions dominate sources of ammonia in urban Beijing: Evidence from 15N stable isotope in vertical profiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, A.J.; Harley, R.A.; Littlejohn, D.; Kendall, G.R. On-road measurement of ammonia and other motor vehicle exhaust emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3535–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tao, L.; Miller, D.J.; Pan, D.; Golston, L.M.; Zondlo, M.A.; Griffin, R.J.; Wallace, H.W.; Leong, Y.J.; Yang, M.M.; et al. Vehicle emissions as an important urban ammonia source in the United States and China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.E.; Dammers, E.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Werf, G.R.v.d. Satellite evidence of substantial rain-induced soil emissions of ammonia across the Sahel. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16713–16727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kumar, M.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, J.; Francisco, J.S.; Zeng, X.C. Near-Barrierless ammonium bisulfate formation via a loop-structure promoted proton-transfer mechanism on the surface of water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Penner, J.E. Global simulations of nitrate and ammonium aerosols and their radiative effects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9479–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kong, W.; Marten, R.; He, X.C.; Chen, D.; Pfeifer, J.; Heitto, A.; Kontkanen, J.; Dada, L.; Kurten, A.; et al. Rapid growth of new atmospheric particles by nitric acid and ammonia condensation. Nature 2020, 581, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Air Quality Criteria for Particulate Matter. Citeseer Princet. 2004, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Jang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J.S.; Hao, J. Impact assessment of ammonia emissions on inorganic aerosols in East China using response surface modeling technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9293–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.; Kan, H. Heavy smog and hospital visits in Beijing, China. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care. 2013, 188, 1170–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokstad, E. Ammonia pollution from farming may exact hefty health costs. Science 2014, 343, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N. Acidification of the world: Natural and anthropogenic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Aber, J.D.; Erisman, J.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Howarth, R.W.; Cowling, E.B.; Cosby, B.J. The nitrogen cascade. BioScience 2003, 53, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickenscheidt, N.; Brumme, R.; Veldkamp, E. Direct contribution of nitrogen deposition to nitrous oxide emissions in a temperate beech and spruce forest—A 15N tracer study. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilegaard, K.; Skiba, U.; Ambus, P.; Beier, C.; Brüggemann, N.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dick, J.; Dorsey, J.; Duyzer, J.; Gallagher, M.; et al. Factors controlling regional differences in forest soil emission of nitrogen oxides (NO and N2O). Biogeosciences 2006, 3, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Heald, C.L.; Hurtmans, D.; Ngadi, Y.; Clerbaux, C.; Dolman, A.J.; Erisman, J.W.; Coheur, P.F. Global distributions, time series and error characterization of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) from IASI satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Dammers, E.; Liu, X.; Nowak, J.B.; Clerbaux, C.; Flechard, C.R.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Xu, W.; Neuman, J.A.; et al. Towards validation of ammonia (NH3) measurements from the IASI satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammers, E.; Palm, M.; Van Damme, M.; Vigouroux, C.; Smale, D.; Conway, S.; Toon, G.C.; Jones, N.; Nussbaumer, E.; Warneke, T.; et al. An evaluation of IASI-NH3 with ground-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10351–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.X.; Wei, Z.; Strow, L.L.; Dickerson, R.R.; Nowak, J.B. The global tropospheric ammonia distribution as seen in the 13-year AIRS measurement record. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5467–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank Group. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?locations=CN (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- IFA. Fertilizer Consumption. Available online: https://www.ifastat.org/ (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Warner, J.X.; Dickerson, R.R.; Wei, Z.; Strow, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Increased atmospheric ammonia over the world’s major agricultural areas detected from space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; et al. Rapid SO2 emission reductions significantly increase tropospheric ammonia concentrations over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17933–17943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Zhang, L.; Dingenen, R.V.; Vieno, M.; Grinsven, H.J.V.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, C.; et al. Abating ammonia is more cost-effective than nitrogen oxides for mitigating PM2.5 air pollution. Science 2021, 374, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Heal, M.R.; Reis, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, S.; Li, P.; et al. Trends in secondary inorganic aerosol pollution in China and its responses to emission controls of precursors in wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 6291–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, A.M.; Aulinger, A.; Bieser, J.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M. Ammonia emissions in Europe, part II: How ammonia emission abatement strategies affect secondary aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Akimoto, H.; Ohara, T. Estimation of nitrous oxide, nitric oxide and ammonia emissions from croplands in East, Southeast and South Asia. Glob. Change Bilo. 2003, 9, 1080–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, J.S.; Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Fu, X.; Hao, J. Impact of national NOx and SO2 control policies on particulate matter pollution in China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Dentener, F.; Bergamaschi, P.; Pagliari, V.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Peters, J.A.H.W.; et al. EDGAR v4.3.2 Global Atlas of the three major greenhouse gas emissions for the period 1970–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 959–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Bond, T.C.; Carmichael, G.R.; Fernandes, S.D.; Fu, Q.; He, D.; Klimont, Z.; Nelson, S.M.; Tsai, N.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; et al. An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2003, 108, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSC (China State Council). Notice of the State Council on Issuing the Three-Year Action Plan for Winning the Blue Sky Defense Battle. 2018. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-07/03/content_5303158.htm (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- CSC (China State Council). Further Promoting the Nationwide Battle to Prevent and Control Pollution. 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-11/07/content_5649656.htm (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Kang, Y.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, H.; Cai, X.; Zhang, H.; Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Yan, X.; et al. High-resolution ammonia emissions inventories in China from 1980 to 2012. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2043–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalibieke, W.; Zhan, X.; Cui, X.; Reis, S.; Winiwarter, W.; Zhou, F. Decoupling between ammonia emission and crop production in China due to policy interventions. Glob. Change Bilo. 2021, 27, 5877–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Henze, D.K.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Winiwarter, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Wen, Z.; Pan, Y.; et al. Interannual variation of reactive nitrogen emissions and their impacts on PM2.5 air pollution in China during 2005–2015. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.-i.; Woo, J.-H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesly, R.M.; Smith, S.J.; Feng, L.; Klimont, Z.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Pitkanen, T.; Seibert, J.J.; Vu, L.; Andres, R.J.; Bolt, R.M.; et al. Historical (1750–2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 369–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuffie, E.E.; Smith, S.J.; O’Rourke, P.; Tibrewal, K.; Venkataraman, C.; Marais, E.A.; Zheng, B.; Crippa, M.; Brauer, M.; Martin, R.V. A global anthropogenic emission inventory of atmospheric pollutants from sector- and fuel-specific sources (1970–2017): An application of the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3413–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR) v6.1 Air Pollutants. Available online: https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/index.php/dataset_ap61 (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Regional Emission Inventory in ASia (REAS). 2022. Available online: https://www.nies.go.jp/REAS/index.html#REASv3.2.1 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T. Long-term historical trends in air pollutant emissions in Asia: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 3. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12761–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sha, Z.; Song, Y.; Dong, H.; Pan, Y.; Gao, Z.; lI, Y.; Ma, L.; Dong, W.; Hu, C.; et al. China’s atmospheric ammonia emission characteristics, mitigation options and policy recommendations. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Reis, S.; Jin, J.; Dragosits, U.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Whitburn, S.; Coheur, P.F.; et al. Ammonia emissions may be substantially underestimated in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12089–12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Estimation of global NH3 volatilization loss from synthetic fertilizers and animal manure applied to arable lands and grasslands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 8-1–8-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfreda, C.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Farming the planet: 2. Geographic distribution of crop areas, yields, physiological types, and net primary production in the year 2000. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, GB1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EarthStat: University of Minnesota’s Institute on the Environment and the Ramankutty Lab at the University of British Columbia, V Harvested Area and Yield for 175 Crops Year 2000. Available online: http://www.earthstat.org/ (accessed on 25 December 2015).
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MCD12C1 MODIS/Terra+Aqua Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG V006. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MCD12C1.006. [CrossRef]
- Sacks, W.J.; Deryng, D.; Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N. Crop planting dates: An analysis of global patterns. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBSC). China Rural Statistical Yearbook, 2006–2021. Available online: https://ghdx.healthdata.org/organizations/national-bureau-statistics-china (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Søgaard, H.T.; Sommer, S.G.; Hutchings, N.J.; Huijsmans, J.F.M.; Bussink, D.W.; Nicholson, F. Ammonia volatilization from field-applied animal slurry—The ALFAM model. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3309–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyldenkærne, S.; Ambelas Skjøth, C.; Hertel, O.; Ellermann, T. A dynamical ammonia emission parameterization for use in air pollution models. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2005, 110, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, L.; de Sousa, L.M.; Batjes, N.H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Ribeiro, E.; Rossiter, D. SoilGrids 2.0: Producing soil information for the globe with quantified spatial uncertainty. Soil 2021, 7, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Soil Reference and Information Centre(ISRIC)—World Soil Information, SoilGrids. Available online: https://files.isric.org/soilgrids/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land Monthly Averaged Data from 1981 to Present. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Li, B.; Chen, L.; Shen, W.; Jin, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y.; Liao, H. Improved gridded ammonia emission inventory in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 15883–15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Cai, G.X.; Simpson, J.R.; Zhang, S.L.; Chen, D.L.; Jackson, A.V.; Freney, J.R. Processes of nitrogen loss from fertilizers applied to flooded rice fields on a calcareous soil in north-central China. Fertil. Res. 1989, 18, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.X.; Zhu, Z.L.; Zhu, Z.W.; Trevitt, A.C.F.; Freney, J.R.; Simpsom, J.R. The research of nitrogen losses from ammonium bicarbonate and urea in rice paddy field. Soils 1985, 17, 225–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Cai, G.X.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, S.L. Ammonia volatilization and its significance to the losses of fertilizer nitrogen applied to paddy soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1985, 22, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.D.; Zhang, J.S.; Ren, S.R.; Zhou, Y.M. The Nitrogen balance of crop field soil in north area of China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1988, 3, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.X.; Xin, J.; Wang, S.X. Temporal and spatial distribution of anthropogenic ammonia emissions in China: 1994–2006. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar]
- MARA (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs). Implementation Plan for Soil Testing and Formulation Fertilization for 10 Million Farms. 2005. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2005/dliuq/201806/t20180618_6152460.htm (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Hao, J. Increasing ammonia concentrations reduce the effectiveness of particle pollution control achieved via SO2 and NOx emissions reduction in East China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Multi-Resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC). Available online: http://meicmodel.org/ (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Van der Hoek, K.W.; Berdowski, J.J.M. Global air emission inventories for anthropogenic sources of NOx, NH3 and N2O in 1990. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F.; Heuberger, P.S.C.; Van Drecht, G.; Van Der Hoek, K.W. Bottom-up uncertainty estimates of global ammonia emissions from global agricultural production systems. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6067–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, X.; Yu, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of adding proportions of functional absorption materials on performance of new slow-release urea. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 740–748. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Dong, W.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Hu, C. Effect of continuously appling controlled-release fertilizers on nitrogen balance and utilization in winter wheat-summer maize cropping system. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- An, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zou, G.; Yang, J. Effects of different slow/controlled release fertilizers on yield, quality of fresh maize and ammonia emissions. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Dong, W.; Wang, W.; Gaudel, G.; Mosongo, P.; Hu, C. The effects of deep application of nitrogen fertilization on ammonia volatilization in a winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in the North China Plain. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhou, M.; Luo, B. High-Resolution Ammonia Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application in China during 2005–2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081297
Chen Y, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Liu M, Zhou M, Luo B. High-Resolution Ammonia Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application in China during 2005–2020. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081297
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Youfan, Lin Zhang, Yuanhong Zhao, Lijuan Zhang, Jingwei Zhang, Mengyao Liu, Mi Zhou, and Bin Luo. 2022. "High-Resolution Ammonia Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application in China during 2005–2020" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081297
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., Liu, M., Zhou, M., & Luo, B. (2022). High-Resolution Ammonia Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Application in China during 2005–2020. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081297







