The Impact of Scale-Aware Parameterization on the Next-Generation Global Prediction System in Taiwan for Front Predictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Descriptions and Experimental Design
3. Scale-Aware Parameterization in NSAS Scheme
4. Results
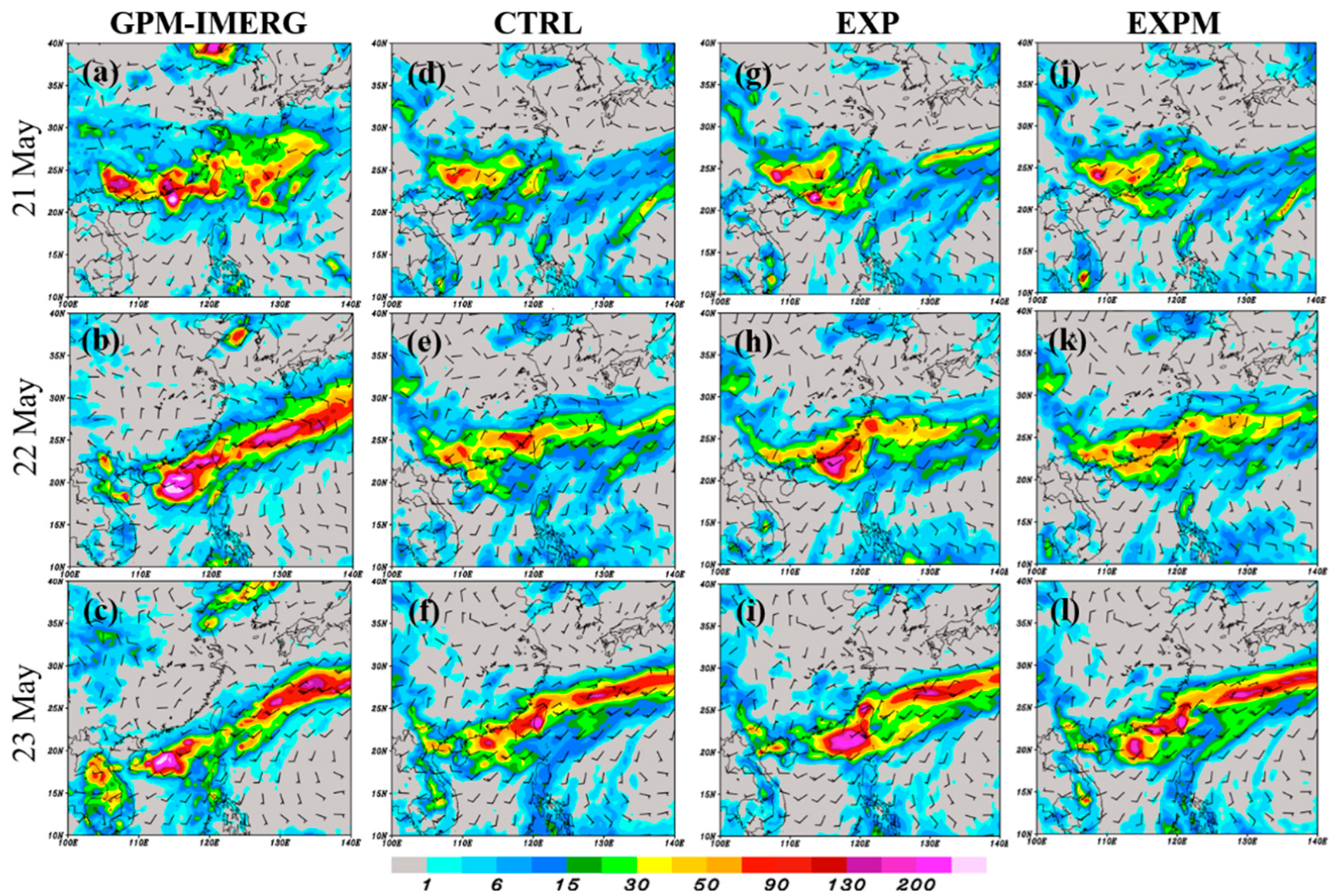
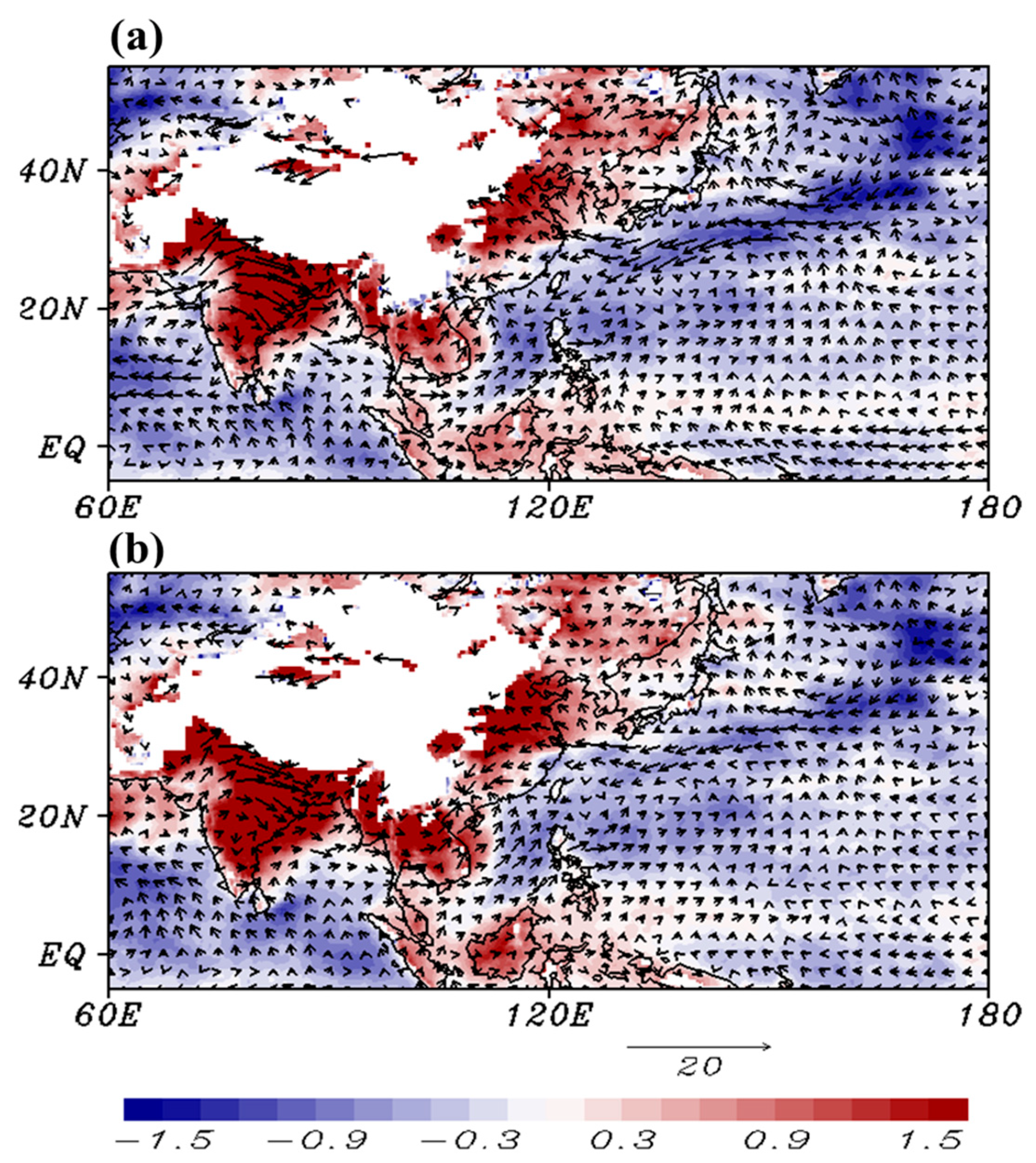
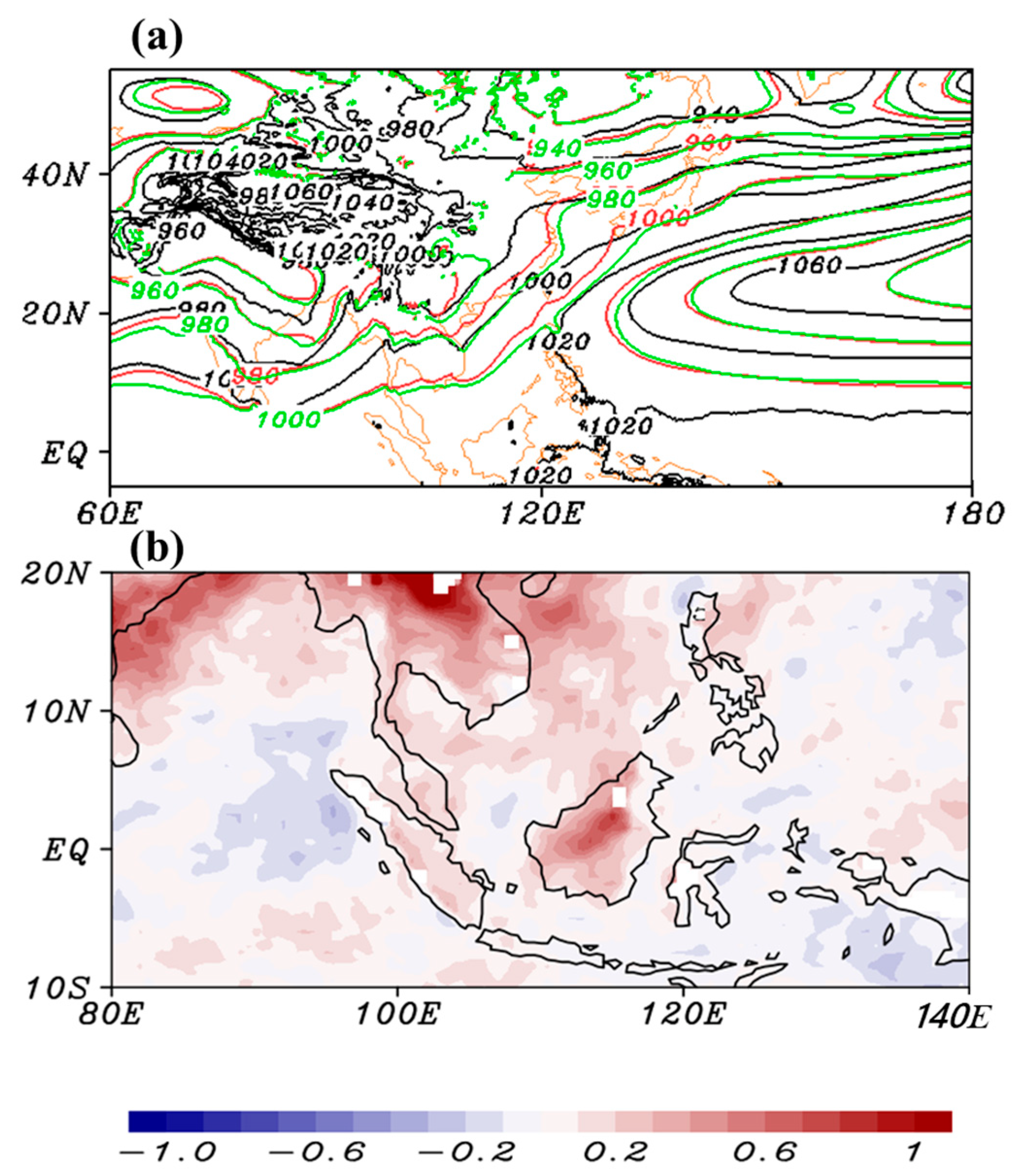
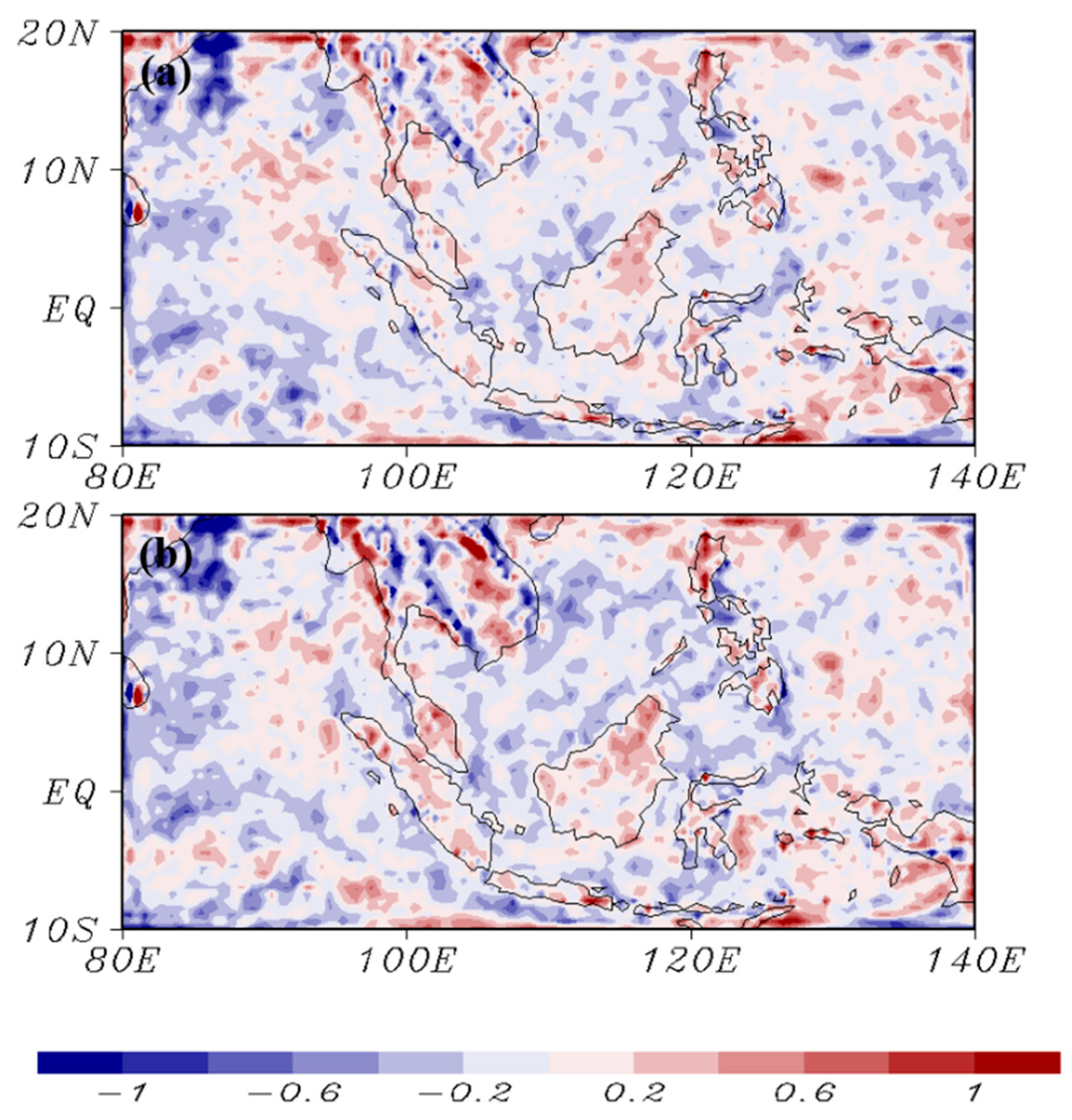
4.1. Mei-Yu Precipitation
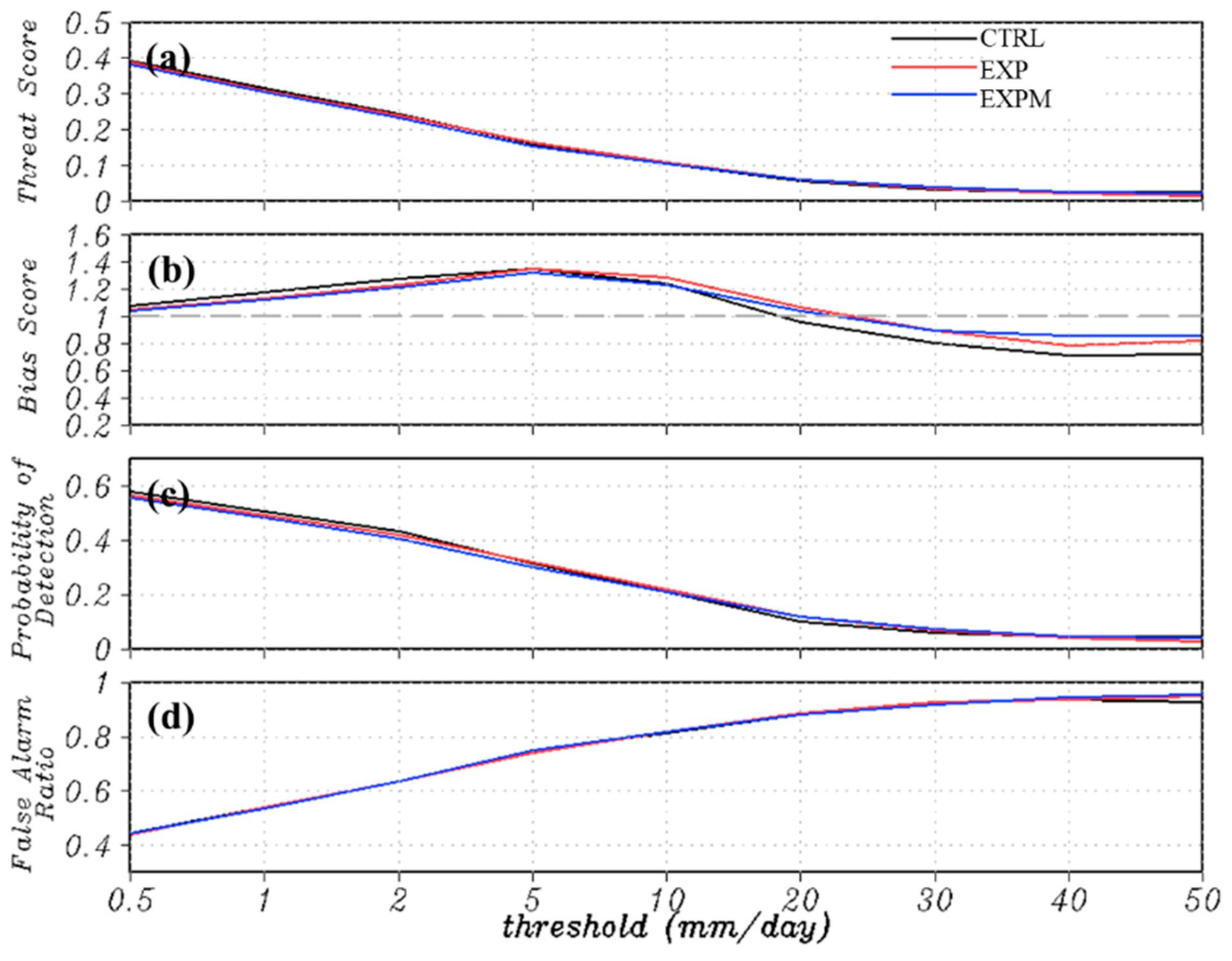
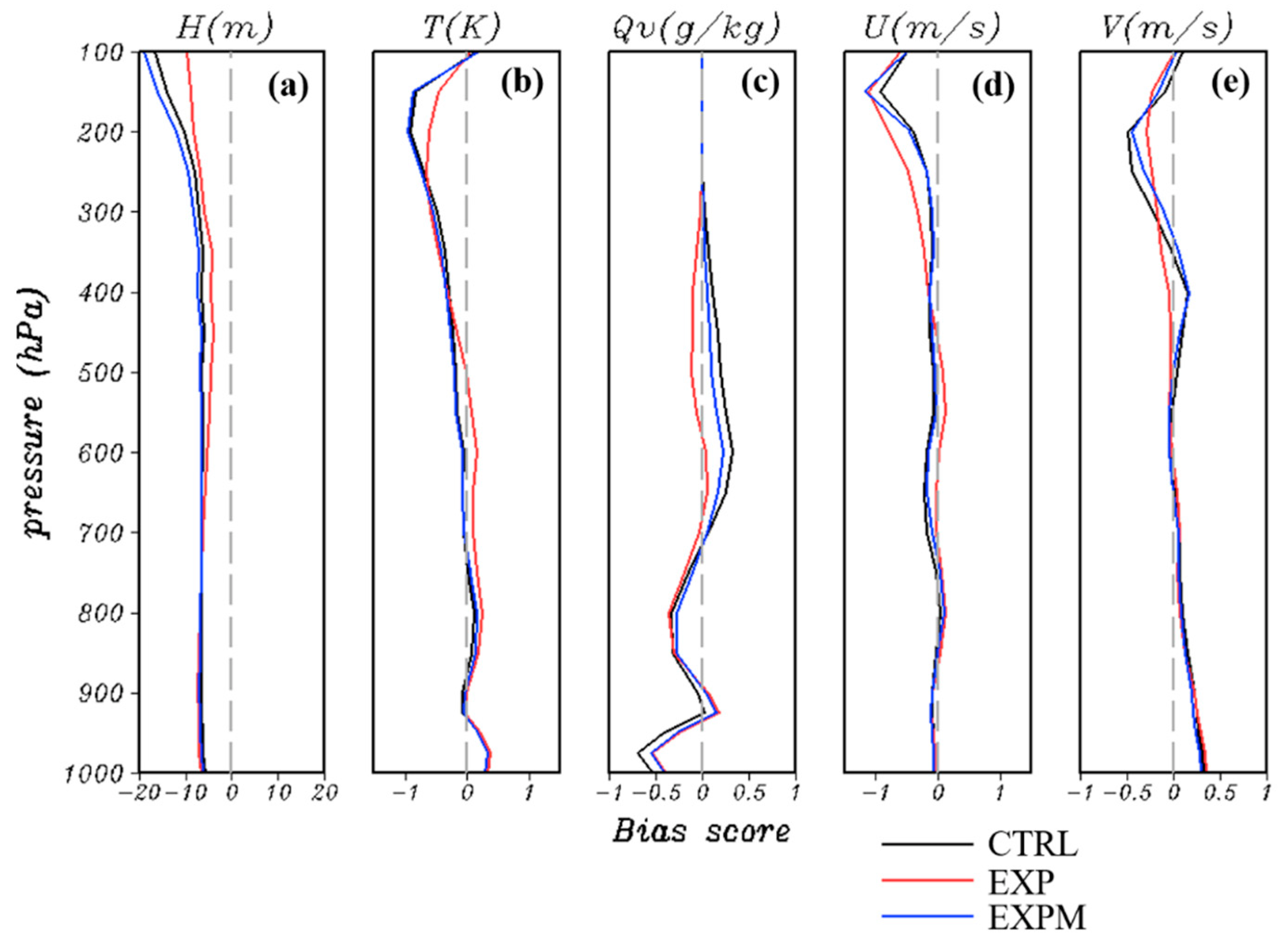
4.2. Large-Scale Verifications
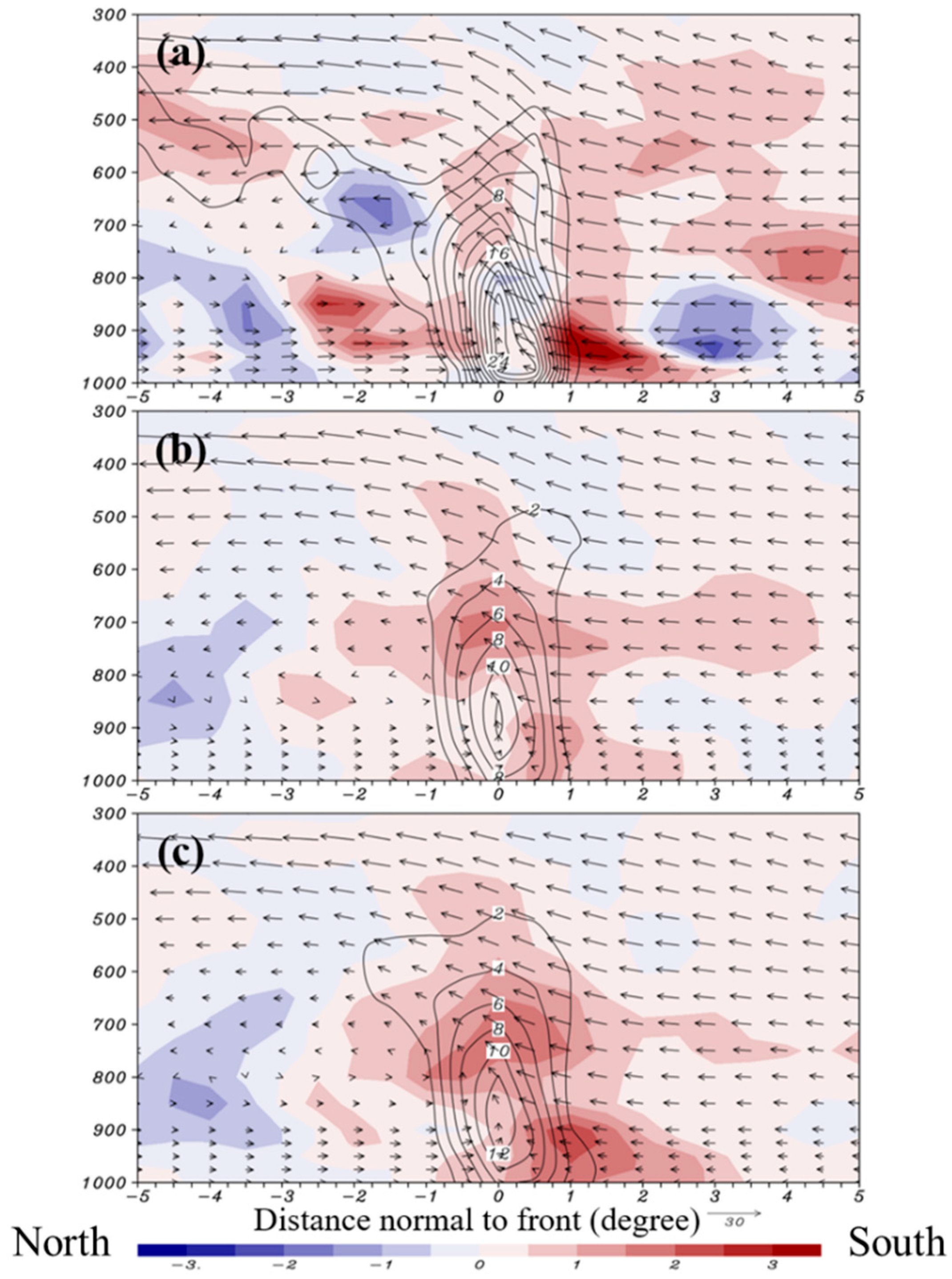
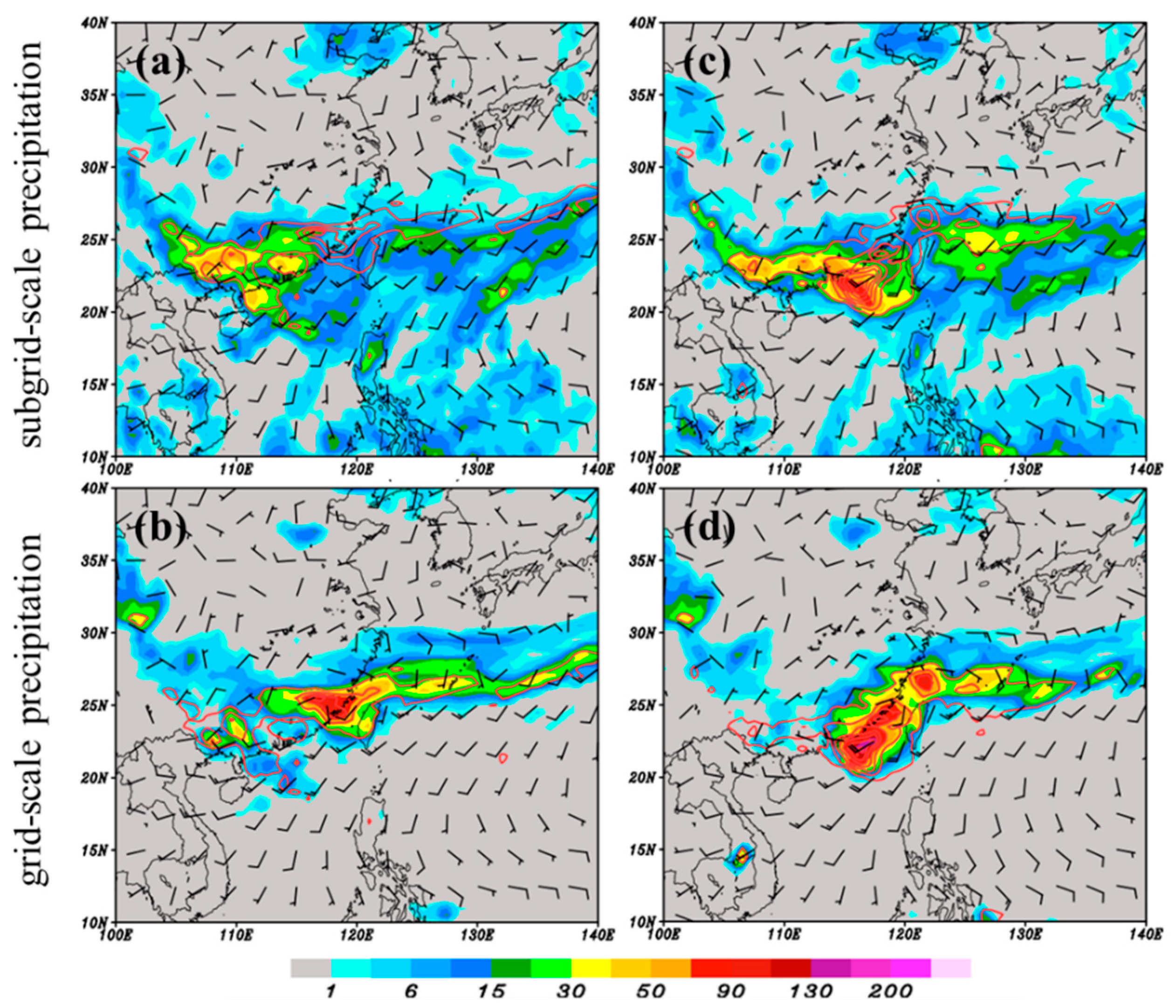
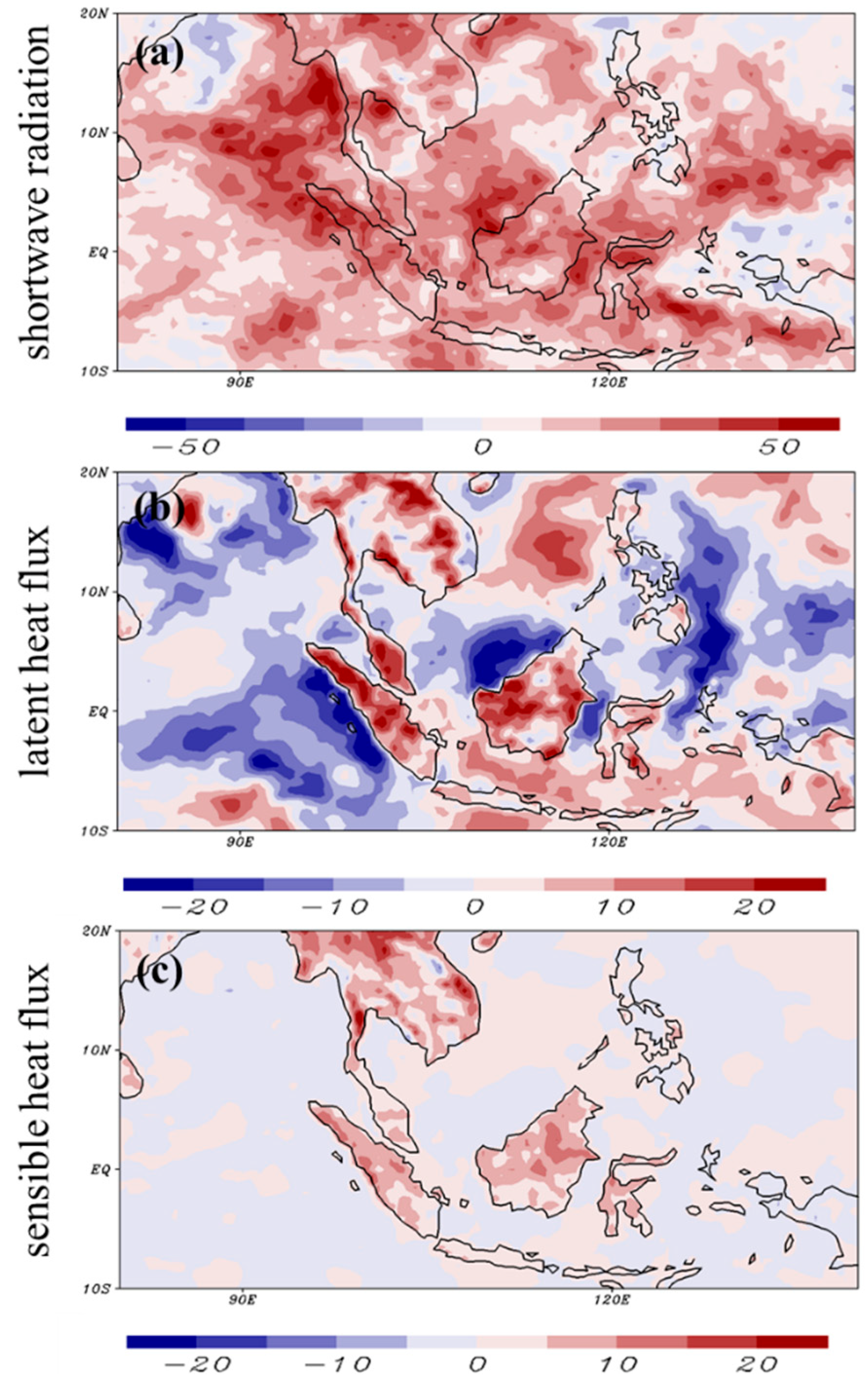
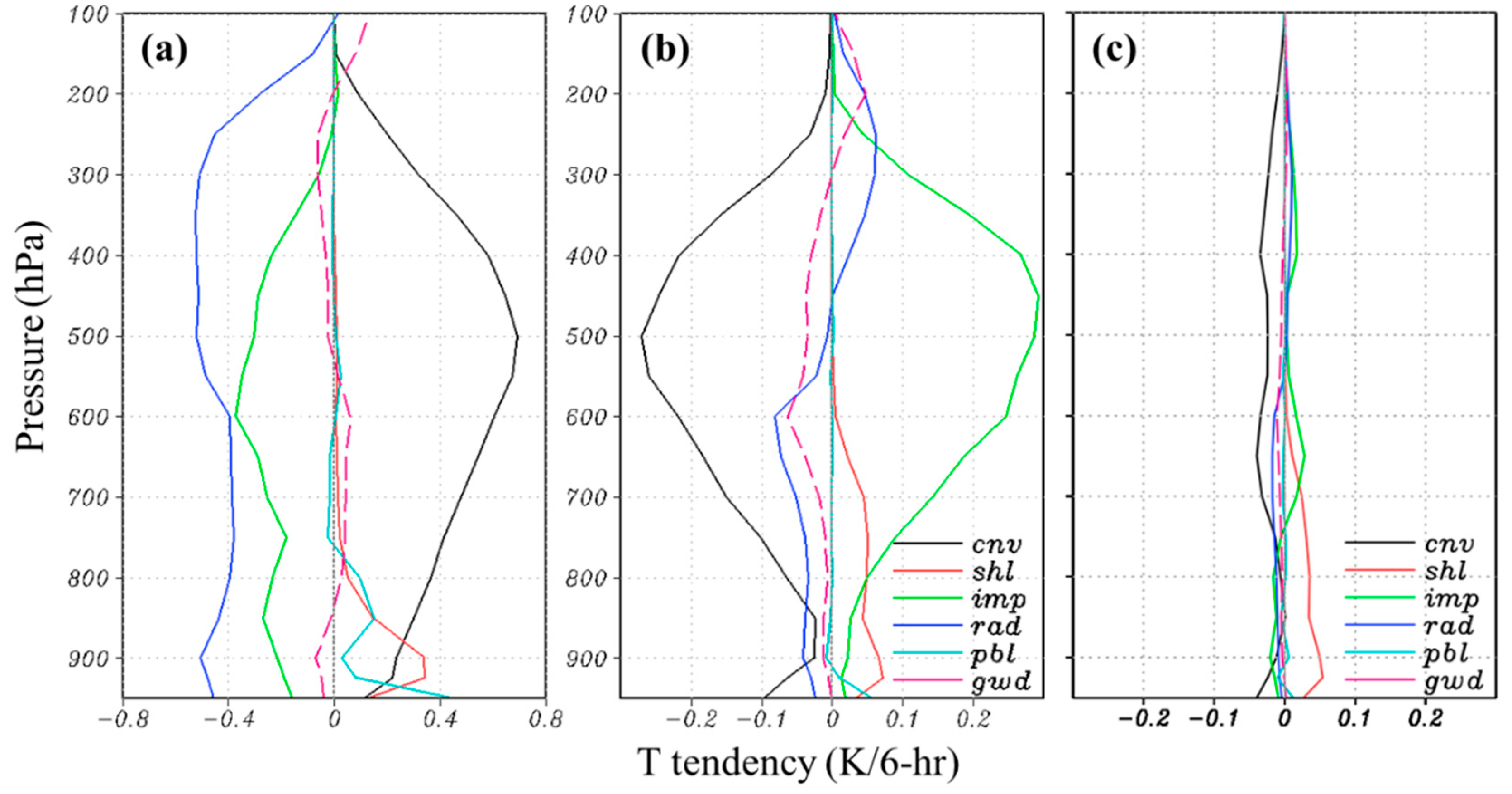
4.3. Further Modification of NSAS Scheme
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIAS | Bias Score |
| CFL | Courant–Friedrichs–Lewy |
| DISC | Data and Information Services Center |
| DTR | Convective Cloud Water Detrainment |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| FAR | False Alarm Ratio |
| FV3 | Finite-Volume Cubed-Sphere Dynamical Core |
| GES | Goddard Earth Sciences |
| GFDL | Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory |
| GFS | Global Forecast System |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement |
| GSM | Global Spectral Model |
| IMERG | Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement |
| KH | Kwon and Hong 2017 |
| KIM | Korean Integrated Model |
| MCS | Mesoscale Convective System |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| NGGPS | Next Generation Global Prediction System |
| NCEP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| NSAS | New Simplified Arakawa-Schubert |
| POD | Probability of Detection |
| SAS | Simplified Arakawa–Schubert |
| TRG | Convective Trigger Function |
| TS | Threat Score |
References
- Randall, D.A.; Abeles, J.A.; Corsetti, T.G. Seasonal simulations of the planetary boundary layer and boundary-layer stratocumulus clouds with a general circulation model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 42, 641–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Steinheimer, M.; Hantel, M.; Bechtold, P. Convection in Lorenz’s global energy cycle with the ECMWF model. Tellus 2008, 60, 1001–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensrud, D.J. Effects of a persistent, midlatitude mesoscale region of convection on the large-scale environment during the warm season. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 3503–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensrud, D.J.; Anderson, J.L. Is midlatitude convection an active or a passive player in producing global circulation patterns? J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2222–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedtke, M. Parameterization of cumulus convection in large-scale models. In Physically-Based Modelling and Simulation of Climate and Climatic Change; Schlesinger, M.E., Ed.; D. Reidel: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1988; pp. 375–431. [Google Scholar]
- LeMone, M.A. Momentum Transport by a Line of Cumulonimbus. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moncrieff, M.W.; Liu, C. Representing Convective Organization in Prediction Models by a Hybrid Strategy. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 3404–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badlan, R.L.; Lane, T.P.; Moncrieff, M.W.; Jakob, C. Insights into convective momentum transport and its parametrization from idealized simulations of organized convection. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 143, 2687–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Fan, J.; Xu, K.-M.; Zhang, G.J. Analysis of Cloud-Resolving Model Simulations for Scale Dependence of Convective Momentum Transport. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 2445–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedtke, M. A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1779–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, W.; Kwon, Y.C.; Hong, S.-Y.; Tallapragada, V.; Yang, F. Updates in the NCEP GFS Cumulus Convection Schemes with Scale and Aerosol Awareness. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, H.-L. Revision of convection and vertical diffusion schemes in the NCEP global forecast system. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, P.; Semane, N.; Lopez, P.; Chaboureau, J.-P.; Beljaars, A.; Bormann, N. Representing equilibrium and nonequilibrium convection in large-scale models. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 734–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Hong, S.-Y. A Mass-Flux Cumulus Parameterization Scheme across Gray-Zone Resolutions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, J.G. Spectral modeling at the National Meteorological Center. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Carr, F.H. A prognostic cloud scheme for operational NWP models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 1931–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Lin, S.J. The remarkable predictability of inter-annual variability of Atlantic hurricanes during the past decade. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Lin, S.J. Seasonal predictions of tropical cyclones using a 25-km-resolution general circulation model. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, J.-H.; Harris, L.M.; Chen, X.; Rees, S. Toward convective-scale prediction within the Next Generation Global Prediction System. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2019, 100, 1225–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, A.; Schubert, W.H. Interaction of a Cumulus Cloud Ensemble with the Large-Scale Environment, Part I. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A. Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 764–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, C.; Siebesma, A.P. A new subcloud model for mass-flux convection scheme: Influence on triggering, updraft properties, and model climate. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, P.; Kohler, M.; Jung, T.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Leutbecher, M.; Rodwell, M.; Vitart, F.; Balsamo, G. Advances in simulating atmospheric variability with the ECMWF model: From synoptic to decadal time-scales. Quart. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2008, 134, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-Y.; Kwon, Y.C. The performance of a revised simplified Arakawa-Schubert (SAS) convection scheme in the medium-range forecasts of the Korean Integrated Model (KIM). Weather Forecast. 2020, 35, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, A.; Wu, C.-M. A Unified representation of deep moist convection in numerical modeling of the Atmosphere. Part I. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5233–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.-Y.; Baik, J.-J. Weakly nonlinear response of a stably stratified atmosphere to diabatic forcing in a uniform flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 3109–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Arakawa, A. Improvement of orographic gravity wave parameterization using a mesoscale gravity wave model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1875–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Doyle, J.D. Extension of an orographic-drag parameterization scheme to incorporate orographic anisotropy and flow blocking. Quart. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2005, 131, 1893–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Witek, M.L.; Teixeira, J.; Sun, R.; Pan, H.L.; Fletcher, J.K.; Bretherton, C.S. Implementation in the NCEP GFS of a hybrid eddy-diffusivity mass-flux (EDMF) boundary layer parameterization with dissipative heating and modified stable boundary layer mixing. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.A.; Shephard, M.W.; Mlawer, E.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Iacono, M.J.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Boukabara, S.; Brown, P.D. Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: A summary of the AER codes. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-L.; Liu, Q.; Han, J.; Sun, R. Extending the Simplified Arakawa-Schubert Scheme for Meso-Scale Model Applications. NCEP Off. Note 2014, 10, 479. Available online: http://www.lib.ncep.noaa.gov/ncepofficenotes/files/on479.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1979 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2018. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds633.0 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Adler, R.F. TRMM (TMPA) Precipitation L3 1 Day 0.25 Degree × 0.25 Degree V7; Andrey Savtchenko, A., Ed.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| EXP. | Description |
|---|---|
| CTRL | The operational version of the NSAS scheme in CWB FV3GFS. |
| EXP | The algorithm of scale-aware parameterization in the NSAS scheme is based on KH instead. |
| EXPM | As in the EXP experiment but the scale dependency of the amount of convective cloud water detrained into grid-scale condensate is ignored. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-H.; Yang, M.-J.; Hsiao, L.-F.; Chen, J.-H. The Impact of Scale-Aware Parameterization on the Next-Generation Global Prediction System in Taiwan for Front Predictions. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071063
Lin C-H, Yang M-J, Hsiao L-F, Chen J-H. The Impact of Scale-Aware Parameterization on the Next-Generation Global Prediction System in Taiwan for Front Predictions. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071063
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chang-Hung, Ming-Jen Yang, Ling-Feng Hsiao, and Jen-Her Chen. 2022. "The Impact of Scale-Aware Parameterization on the Next-Generation Global Prediction System in Taiwan for Front Predictions" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071063
APA StyleLin, C.-H., Yang, M.-J., Hsiao, L.-F., & Chen, J.-H. (2022). The Impact of Scale-Aware Parameterization on the Next-Generation Global Prediction System in Taiwan for Front Predictions. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071063





