Optimization Study of Sampling Device for Semi-Volatile Oil Mist in the Industrial Workshop
Abstract
:1. Introduction
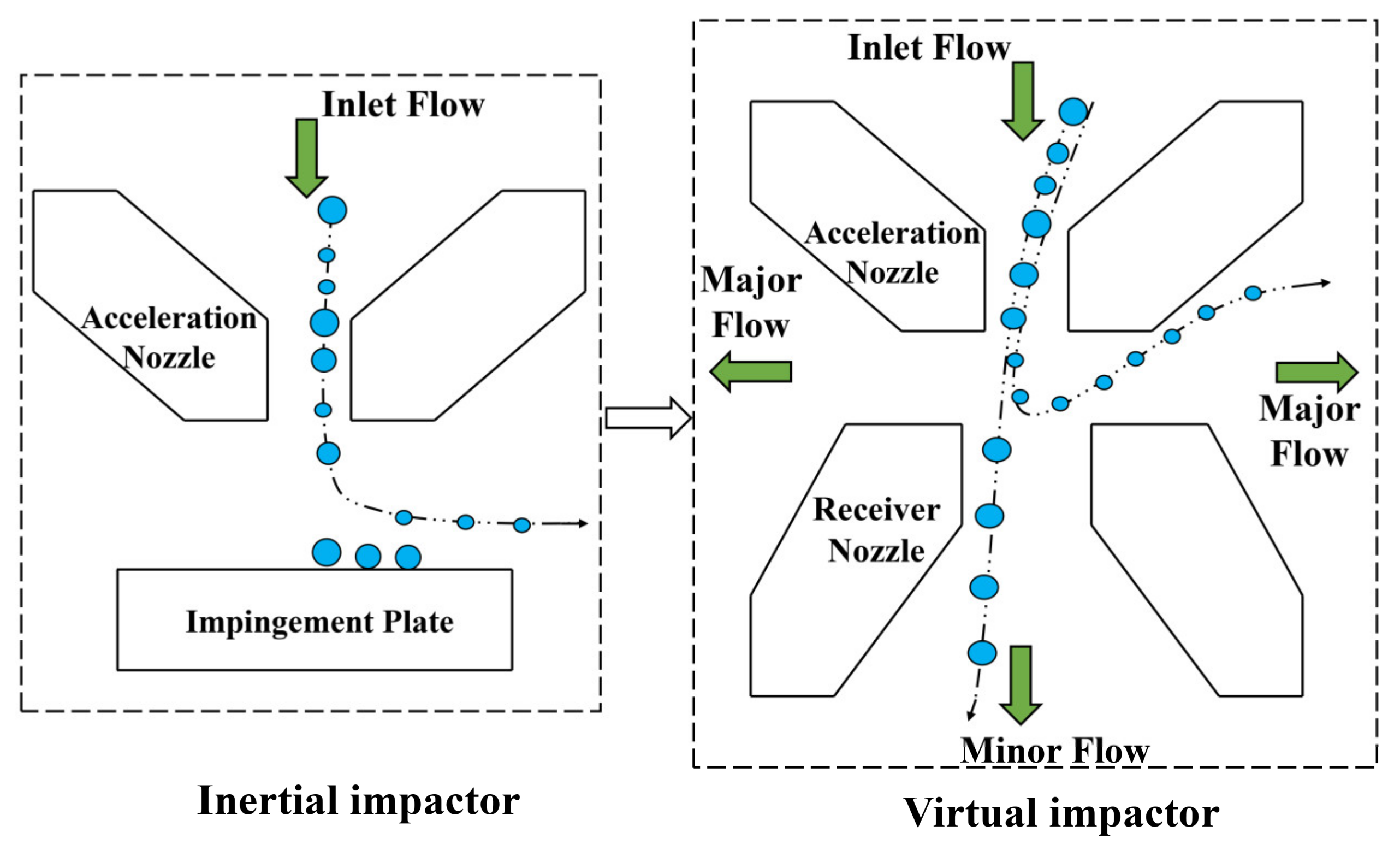
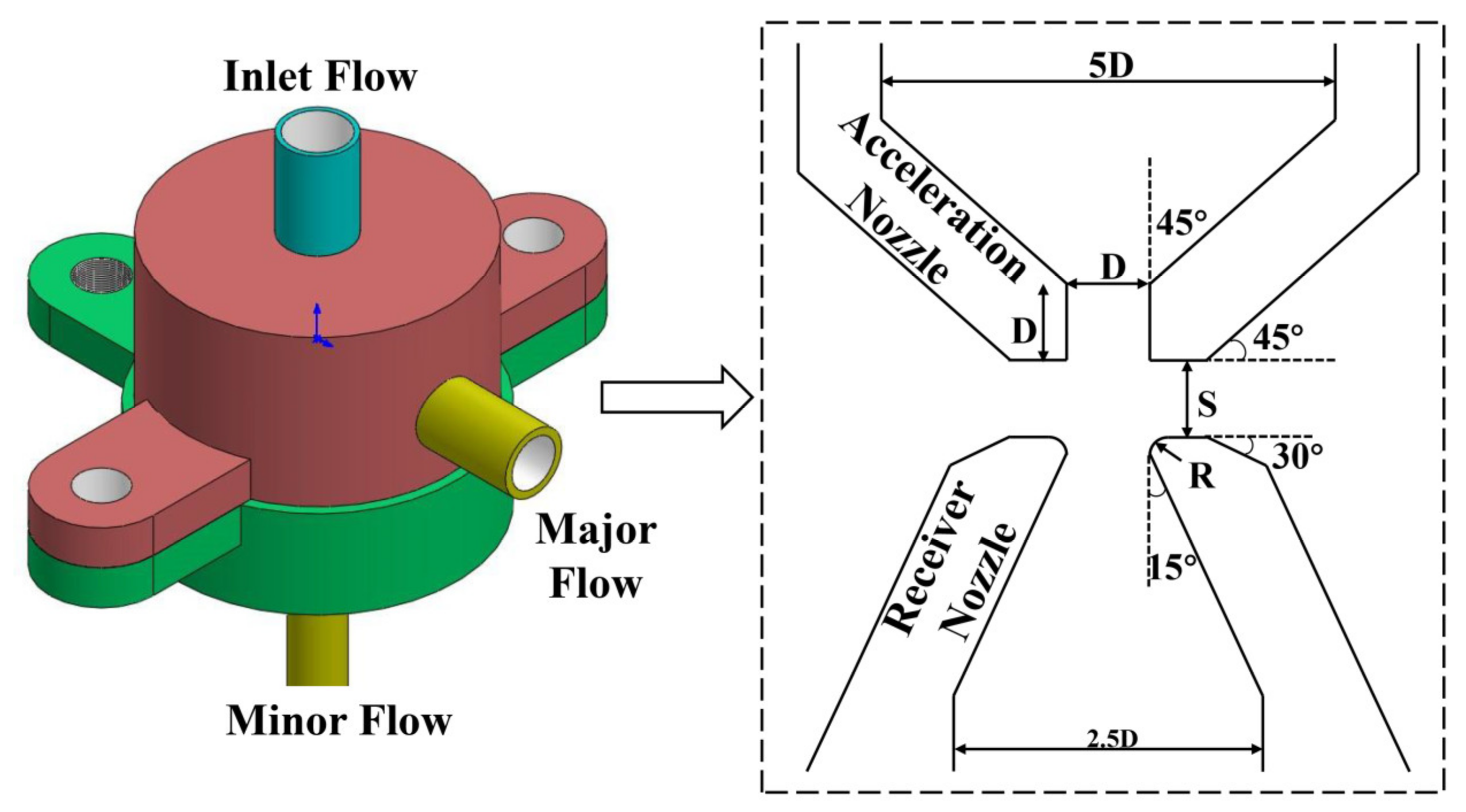
2. Sampling Device Design
3. Numerical Optimization Method
3.1. Physical Model
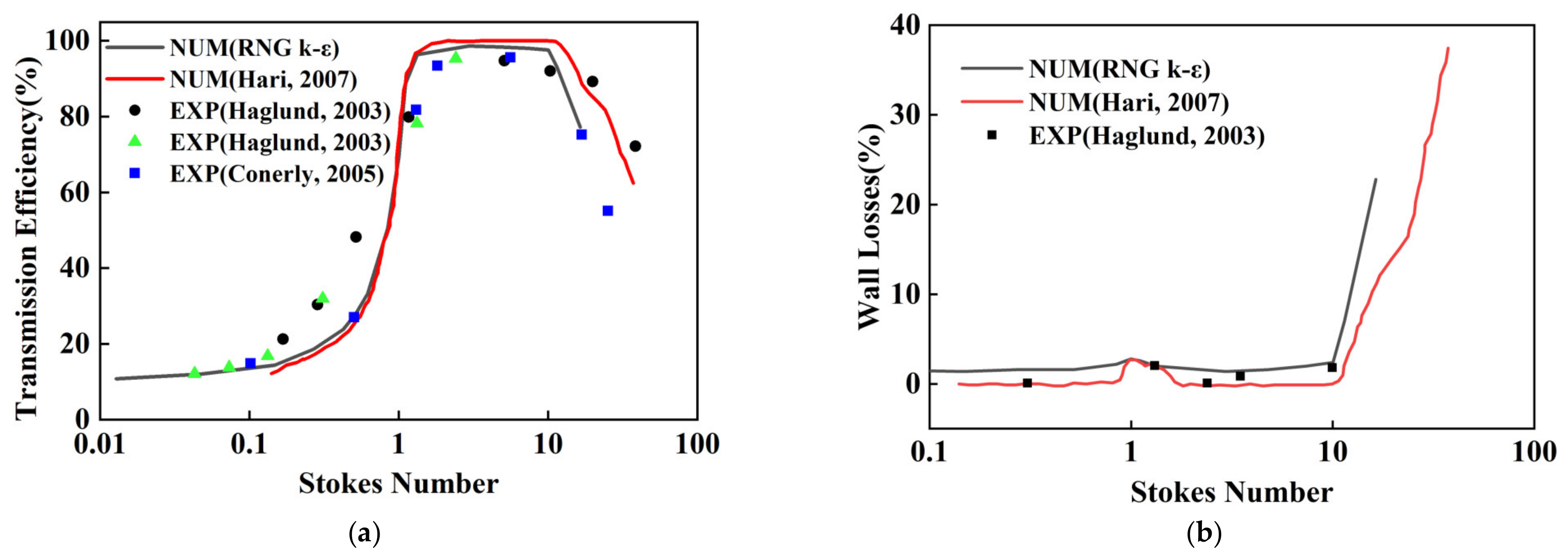
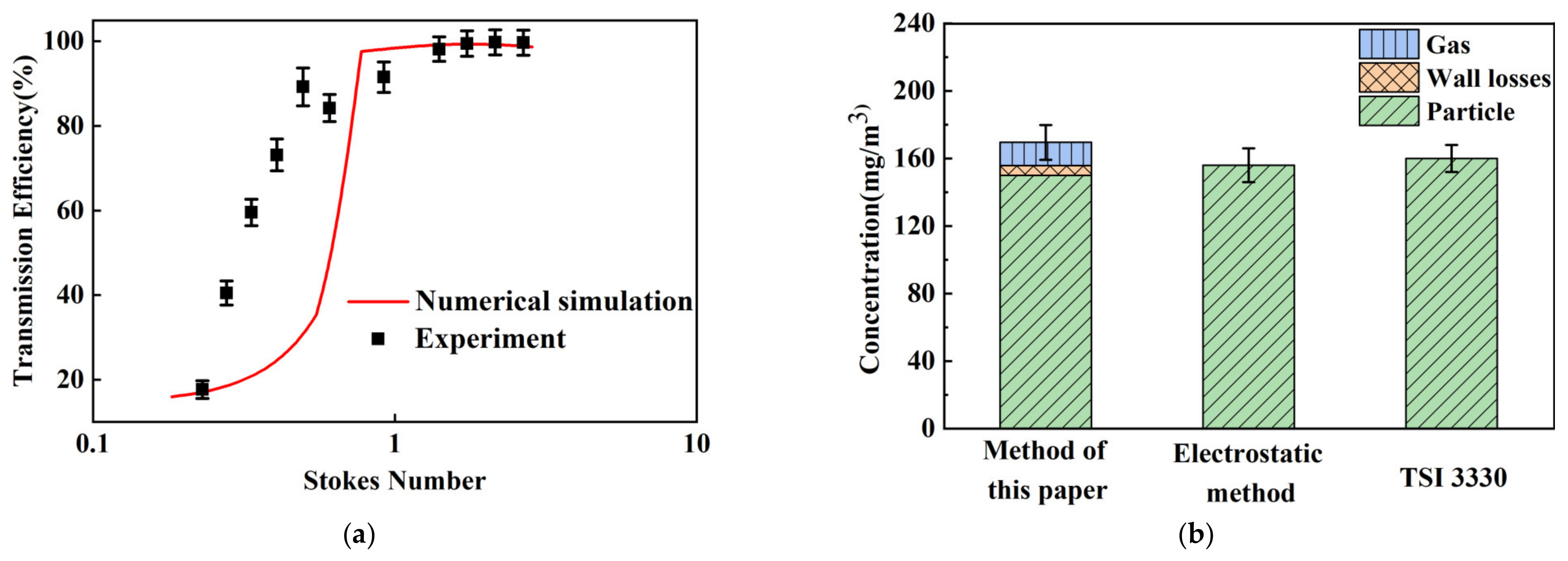
3.2. Numerical Method and Validation
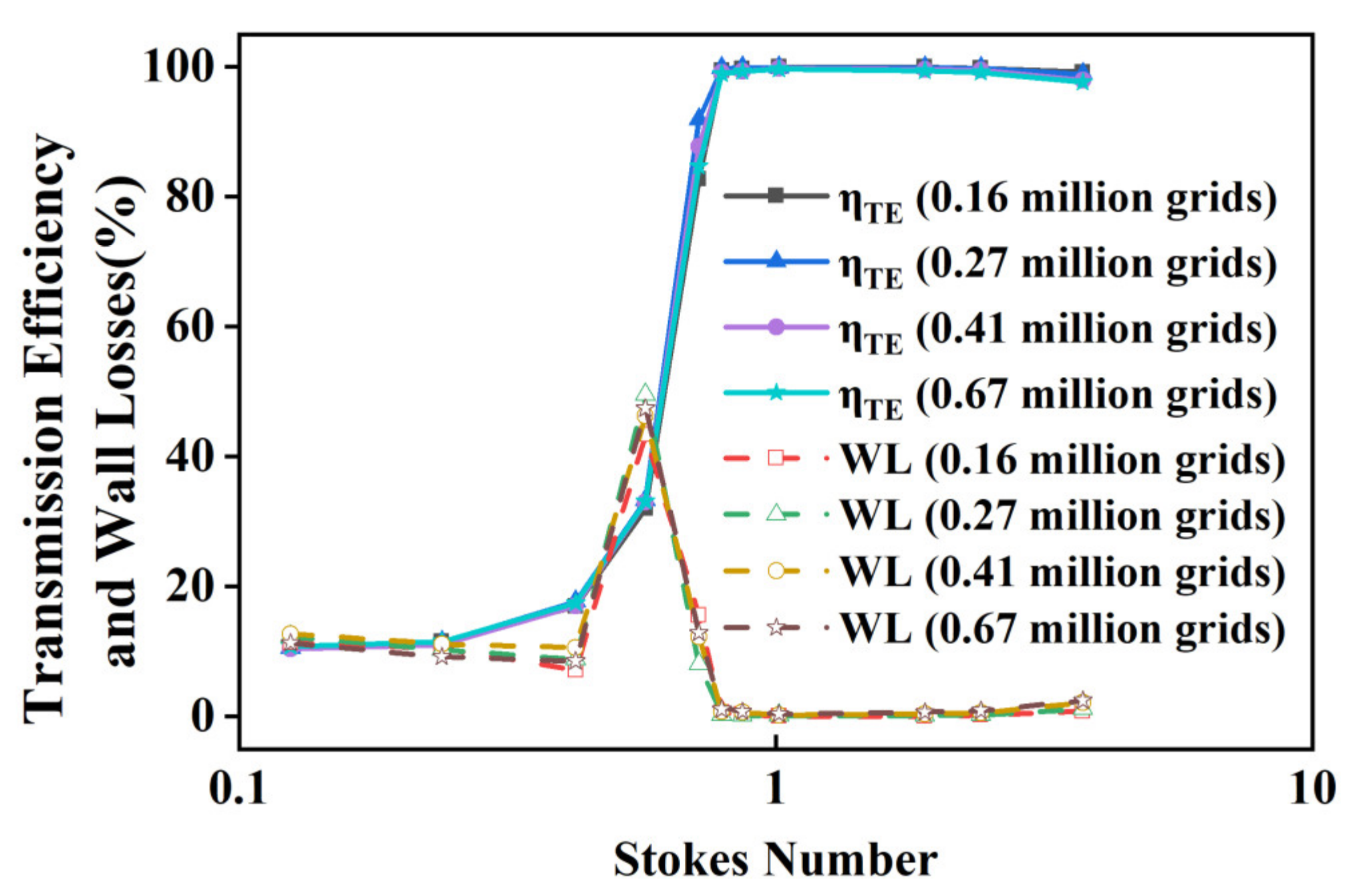
3.3. Grid Division and Verification of Grid Independence
3.4. Boundary Conditions
4. Full-Scale Experimental Evaluation
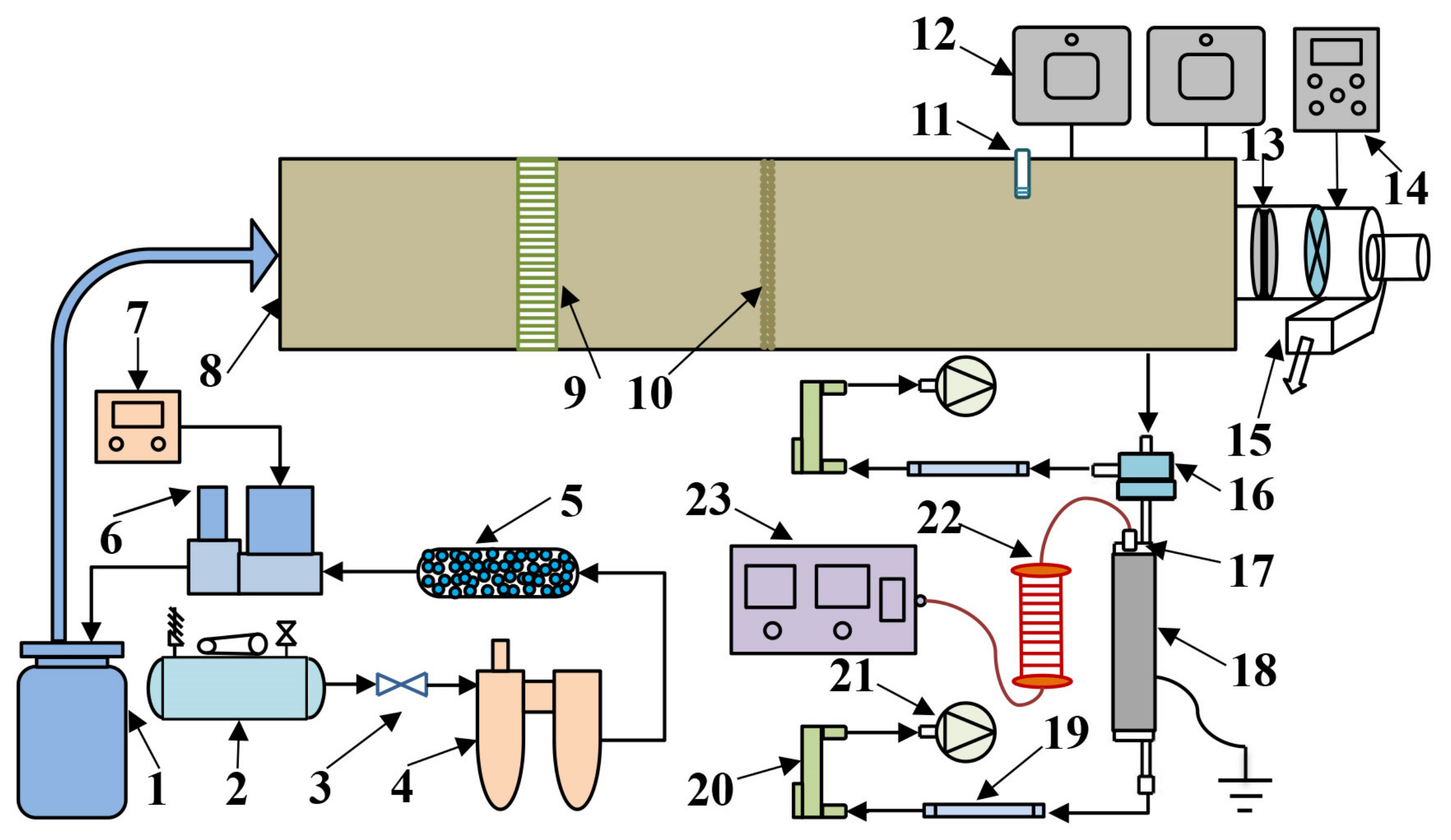
4.1. Experimental System
4.2. Experimental Method
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Numerical Optimization of the Sampler Design
5.1.1. Influence of Geometric Factors on Performance
- A.
- The influence of the nozzle fillet radius on the performance of the impactor
- B.
- The effect of nozzle spacing on performance
- C.
- The impact of throat size on performance
5.1.2. The Impact of Reynolds Number on Performance
5.1.3. The Impact of Split Ratio on Performance
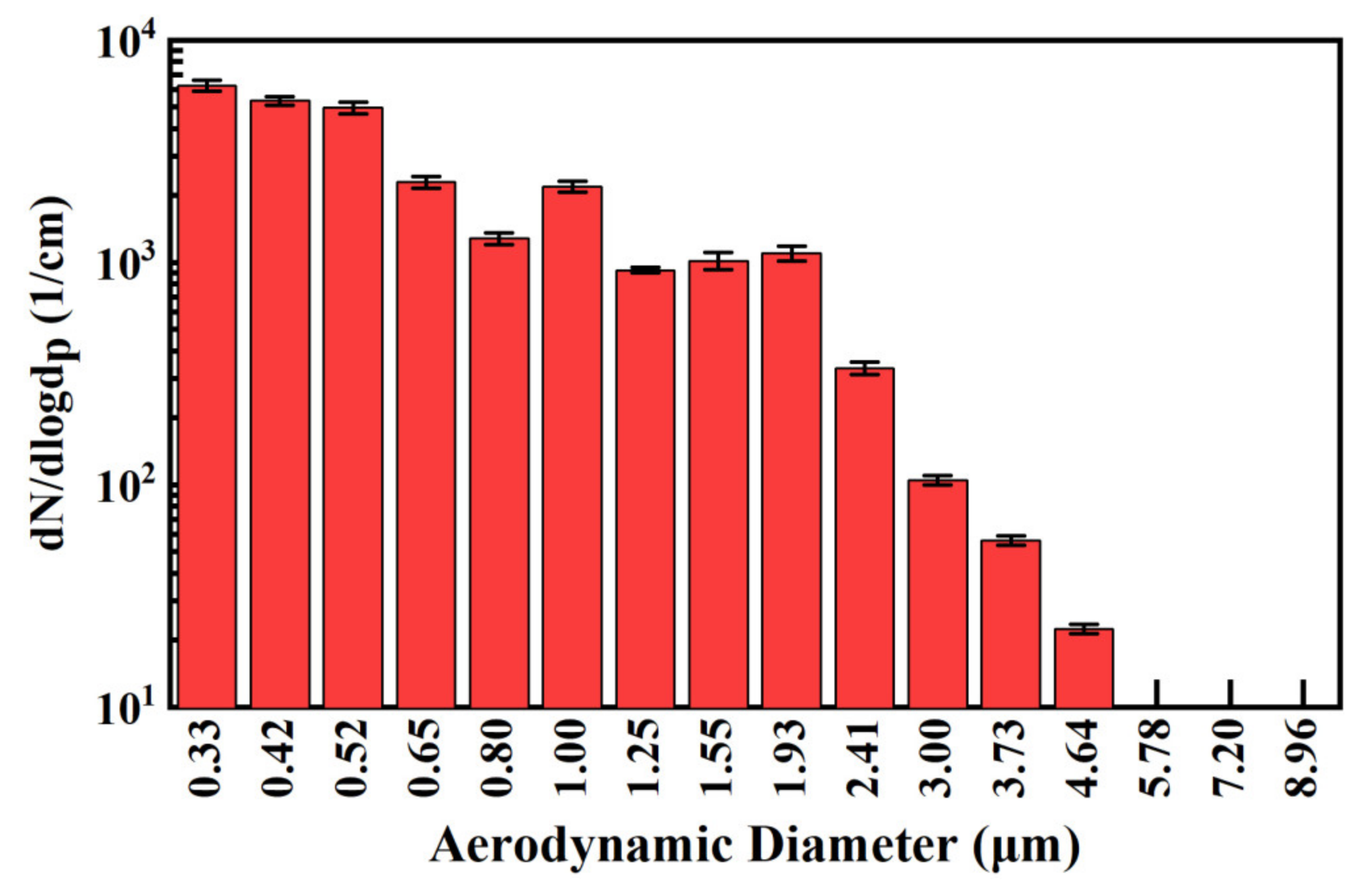
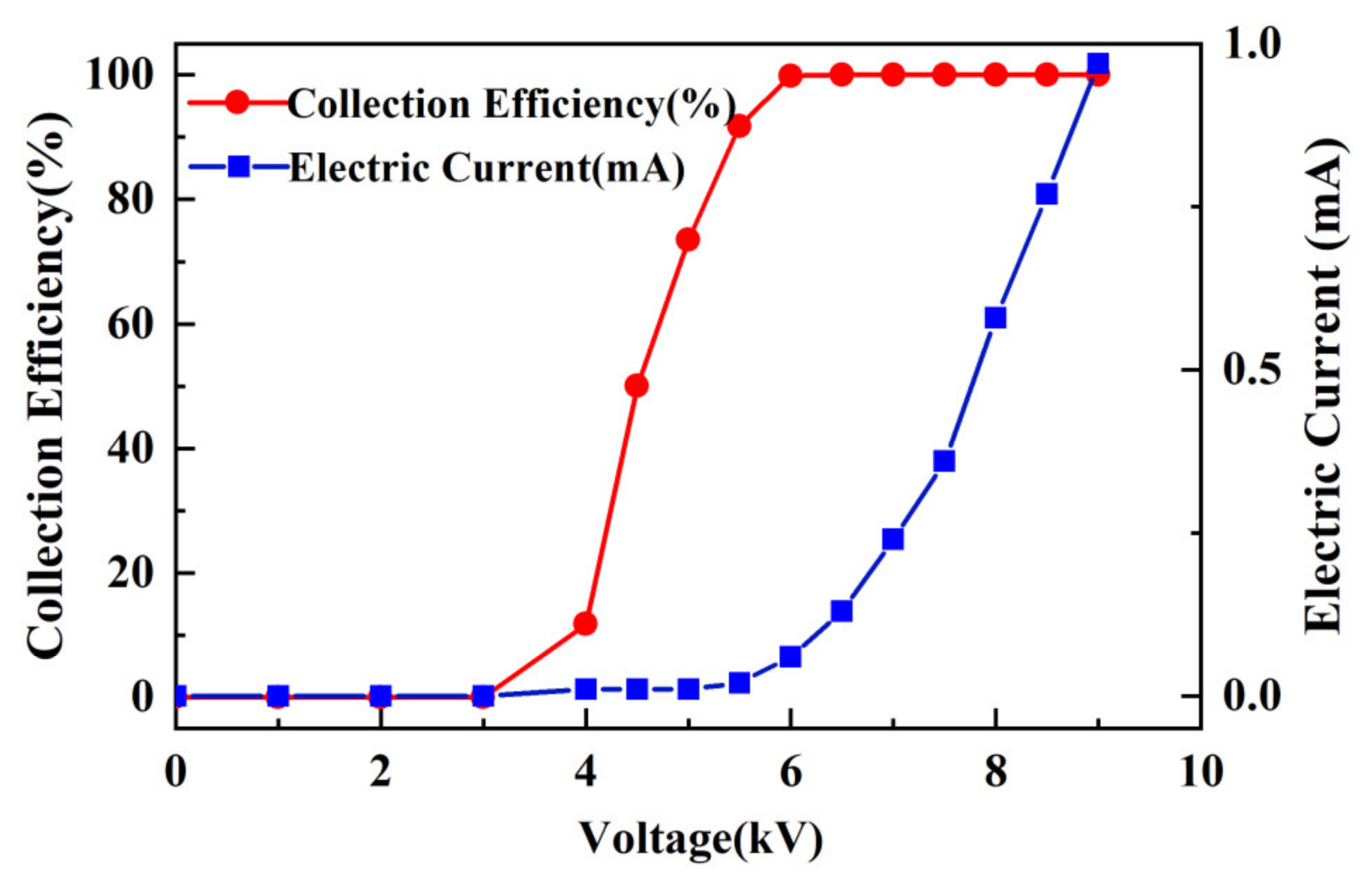
5.2. Experimental Evaluation of the Performance of the Sampler
6. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacasse, Y.; Girard, M.; Cormier, Y. Recent advances in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 2012, 142, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Driving forces of chinese primary air pollution emissions: An index decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoci, A.; Galeotti, M.; Sordi, S. Environmental pollution as engine of industrialization. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 58, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirer, F.E. New evidence on the health hazards and control of metalworking fluids since completion of the osha advisory committee report. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, K.T.; Lim, C.H. Biologically hazardous agents at work and efforts to protect workers’ health: A review of recent reports. Saf. Health Work 2014, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, E.; Xia, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Mo, J. electrostatic air filtration by multifunctional dielectric heterocaking filters with ultralow pressure drop. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 29383–29392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Long, Z. Physicochemical characterization of oily particles emitted from different machining processes. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitbrink, W.A.; Yacher, J.M.; Deye, G.J.; Spencer, A.B. Mist control at a machining center, part 1: Mist characterization. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 2000, 61, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Murga, A.; Long, Z.; Yoo, S.J.; Ito, K. Experimental study of oil mist characteristics generated from minimum quantity lubrication and flood cooling. Energy Built Environ. 2021, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Chen, B.; Lai, D.; Chen, Q. An improved displacement ventilation system for a machining plant. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 228, 117419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Y. Exposure levels of oil mist particles under different ventilation strategies in industrial workshops. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Mo, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. Indoor particle age, a new concept for improving the accuracy of estimating indoor airborne svoc concentrations, and applications. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, R.E.; Camann, D.E.; Morello-Frosch, R.; Brody, J.G.; Rudel, R.A. Semivolatile organic compounds in homes: Strategies for efficient and systematic exposure measurement based on empirical and theoretical factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okeme, J.O.; Saini, A.; Yang, C.; Zhu, J.; Smedes, F.; Klánová, J.; Diamond, M.L. Calibration of polydimethylsiloxane and XAD-pocket passive air samplers (pas) for measuring gas- and particle-phase SVOCS. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Okeme, J.O.; Mark Parnis, J.; McQueen, R.H.; Diamond, M.L. From air to clothing: Characterizing the accumulation of semi-volatile organic compounds to fabrics in indoor environments. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.C.; Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Liu, Z.; Cohen Hubal, E.A. Rapid methods to estimate potential exposure to semivolatile organic compounds in the indoor environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11171–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.L.; Hubbard, J.A.; Dellinger, J.G.; Servantes, B.L. Experimental study of electrostatic aerosol filtration at moderate filter face velocity. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Pan, W.; Long, Z.; Yu, T. Experimental and theoretical study of the collection efficiency of the two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamov, R.S. Influence of gas velocity on the particle collection and reentrainment in an air-cleaning electrostatic precipitator. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistrom, A.O.; Khachatourian, A.V. Electrostatic interaction between unlike aerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Woo, J.H.; Ra, Y.M.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Ahn, S.; Yun, J.H.; Gwak, J.; Yoon, K.; James, S.C. Electrostatic spray deposition of copper-indium thin films. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leith, D.; Leith, F.A.; Boundy, M.G. Laboratory measurements of oil mist concentrations using filters and an electrostatic precipitator. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1996, 57, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volckens, J.; Boundy, M.; Leith, D.; Hands, D. Oil Mist concentration: A comparison of sampling methods. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1999, 60, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, P.C.; Leith, D. Evaporation of accumulated multicomponent liquids from fibrous filters. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1999, 43, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.T.; Groves, J.A.; Unwin, J.; Piney, M. Mineral oil metal working fluids (MWFs)-development of practical criteria for mist sampling. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2000, 44, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.T.; Wright, M.D. Diffusive sampling of C7-C16 hydrocarbons in workplace air: Uptake rates, wall effects and use in oil mist measurements. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2008, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, S.S.; de Carvalho, J.A.; Costa, M.A.M.; Pinheiro, C. An overview of particulate matter measurement instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1327–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hari, S.; Hassan, Y.A. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of virtual impactor performance: Comparison to experiment. powder technol. Powder Technol. 2008, 188, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan Zahir, M.; Lim, J.H.; Noh, S.Y.; Yook, S.J. Development of electric virtual impactor with variable sampling particle size range. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 3456–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yuan, S.; Oppong, P.K.; Yang, N. A Sheathed virtual impactor—Microseparator for improved separation of sub- and supercritical sized particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2022, 164, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, N.H.; Park, G.S.; Maeng, J.S.; Yook, S.J. Development of three-stage bioaerosol sampler for size-selective sampling. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 071008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngagine, S.H.; Deboudt, K.; Flament, P.; Choël, M.; Kulinski, P.; Marteel, F. Development and characterization of a time-sequenced cascade impactor: Application to transient pm2.5 pollution events in urbanized and industrialized environments. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, C.C.; Kohlmeier, V.; Breuer, D.; Blaskowitz, M.; Karg, E.; Zimmermann, R. On the challenges of measuring semi-volatile organic compound aerosols using personal samplers. Gefahrst. Reinhalt. Luft 2017, 77, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Jo, D.H.; Kim, W.G.; Yook, S.J.; Ahn, K.H. Effect of an orifice on collection efficiency and wall loss of a slit virtual impactor. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Raynor, P.C. A new semivolatile aerosol dichotomous sampler. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 53, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Raynor, P.C. Optimization of the design of a semivolatile aerosol dichotomous sampler. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Raynor, P.C. Experimental evaluation of oil mists using a semivolatile aerosol dichotomous sampler. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2010, 7, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, S.; McFarland, A.R.; Hassan, Y.A. CFD study on the effects of the large particle crossing trajectory phenomenon on virtual impactor performance. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K.; Hsiao, T.C.; Engling, G.; Chen, J.C. Computational fluid dynamics study of the effects of flow and geometry parameters on a linear-slit virtual impactor for sampling and concentrating aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 131, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; McFarland, A.R.; Hu, S. Circumferential-slot virtual impactors with stable flow. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, S.; Hassan, Y.A.; Mcfarland, A.R. computational fluid dynamics simulation of a rectangular slit real impactor’s performance. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2005, 235, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standard; High Efficiency Air Filters (EPA, HEPA and ULPA) Part 3: Testing Flat Sheet Filter Media; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.



| Equation or Model | ϕ | Гϕ | Sϕ | Constants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuity | 1 | 0 | ||
| Momentum | uj | μeff | μeff=μ+μt | |
| Temperature | T | ST | Cμ= 0.0845 | |
| RNG k-ε | k | αk = 1.0, αε = 1.3, C1ε = 1.42, C2ε = 1.68, η0 = 4.377, β = 0.012 | ||
| ε |
| Geometric Features (mm) | Reynolds Number (Re) | Split Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throat Size (D) | Nozzle Spacing (S) | Collecting Nozzle Radius (R) | ||
| 0.8 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 1766 | 9:1 |
| 0.15 | 3531 | 6:1 | ||
| 1.0 | 1.20 | 1:6 | ||
| 0.40 | 7062 | 1:9 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Long, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Yu, T. Optimization Study of Sampling Device for Semi-Volatile Oil Mist in the Industrial Workshop. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071048
Wang Y, Long Z, Zhang H, Shen X, Yu T. Optimization Study of Sampling Device for Semi-Volatile Oil Mist in the Industrial Workshop. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071048
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yukun, Zhengwei Long, Hongsheng Zhang, Xiong Shen, and Tao Yu. 2022. "Optimization Study of Sampling Device for Semi-Volatile Oil Mist in the Industrial Workshop" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071048
APA StyleWang, Y., Long, Z., Zhang, H., Shen, X., & Yu, T. (2022). Optimization Study of Sampling Device for Semi-Volatile Oil Mist in the Industrial Workshop. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071048







