Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1).
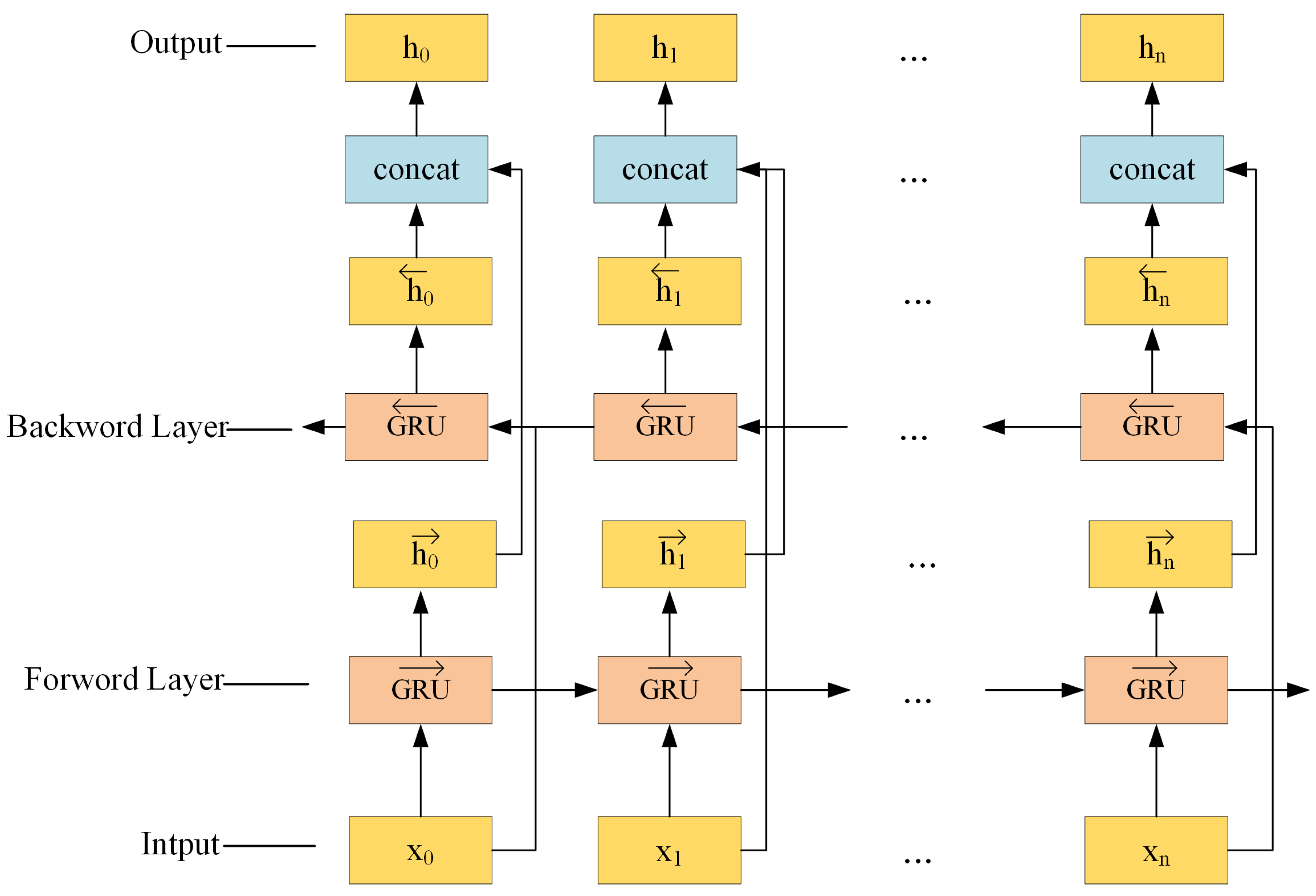
- For the first time, both past and future time-step were used in Ionospheric TEC prediction. We present BiGRU, which contains a forward-propagated GRU unit and a backward-propagated GRU unit. Therefore, the output layer contains both past information and future information.
- (2).
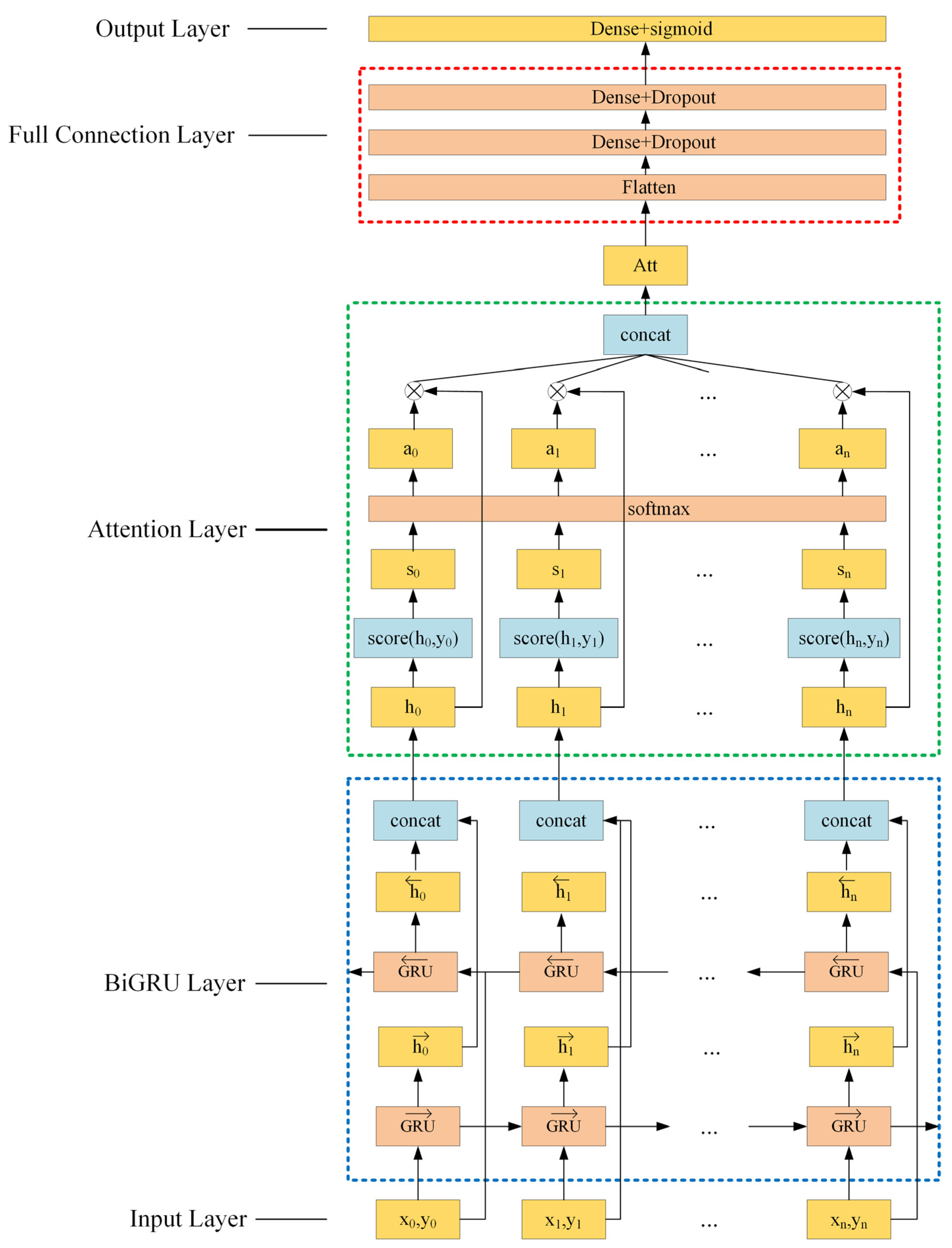
- For the first time, the attention mechanism is introduced into the Ionospheric TEC prediction to highlight critical time-step information.
2. Data and Proposed Model
2.1. Data Description
2.2. Data Preprocessing
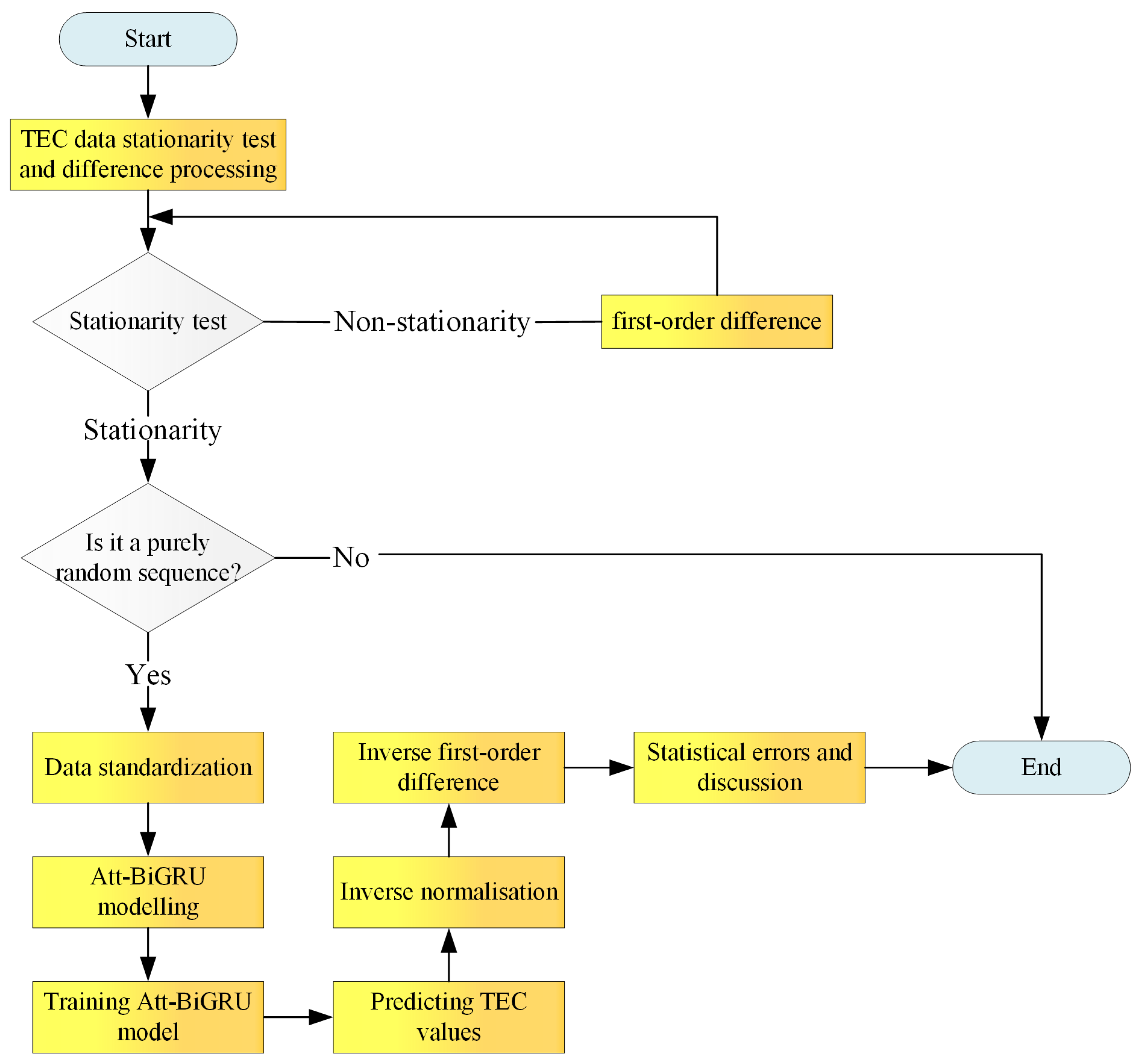
2.2.1. TEC Data Stationary Test and Difference Processing
2.2.2. Pure Randomness Test
2.2.3. Data Standardization
2.2.4. Samples Making
2.3. Evaluation Indexes
2.4. Our Proposed Model
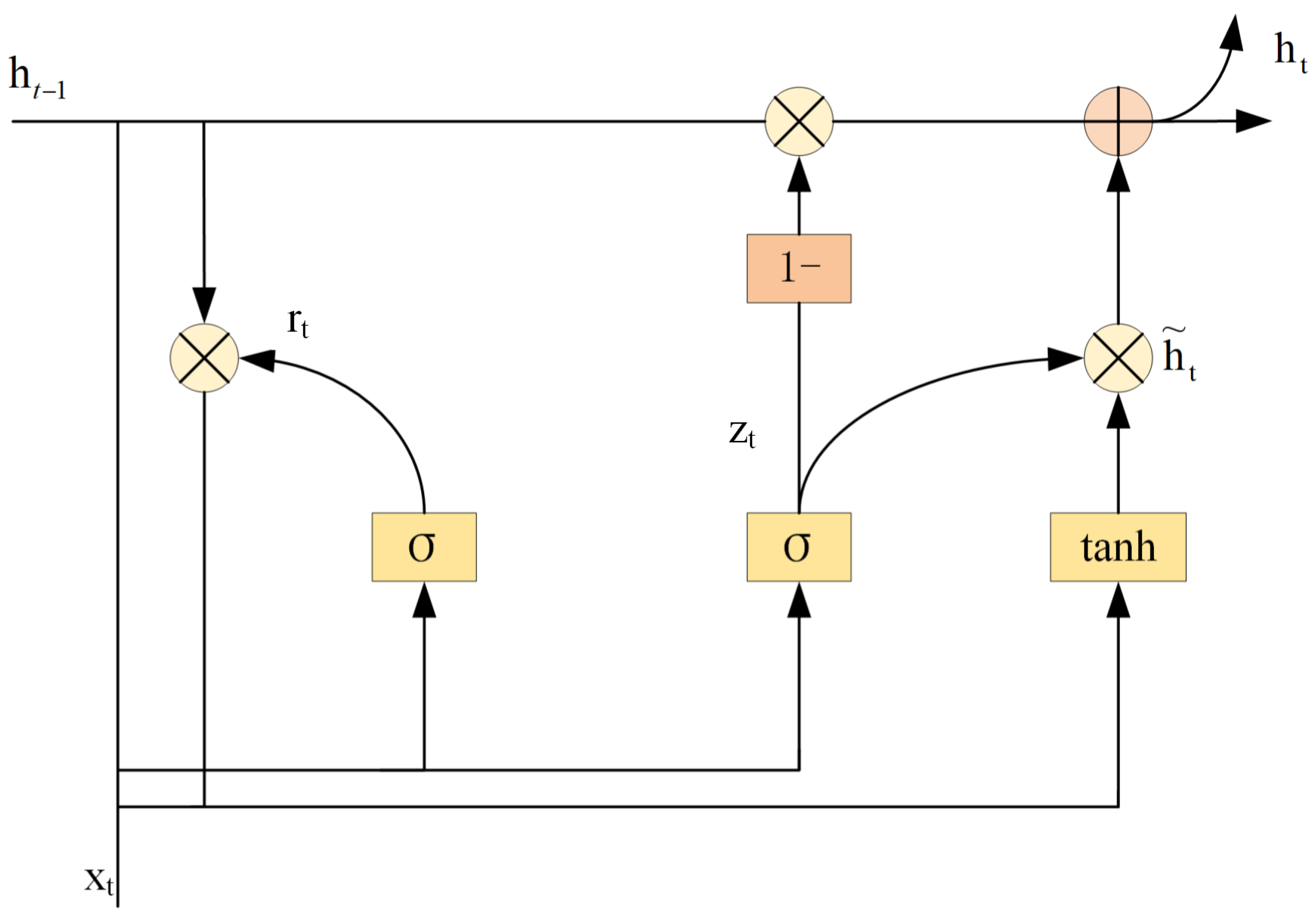
2.4.1. The BiGRU Model
2.4.2. The Proposed Attentional BiGRU Model for TEC Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Parameters of the Proposed Attentional BiGRU Model
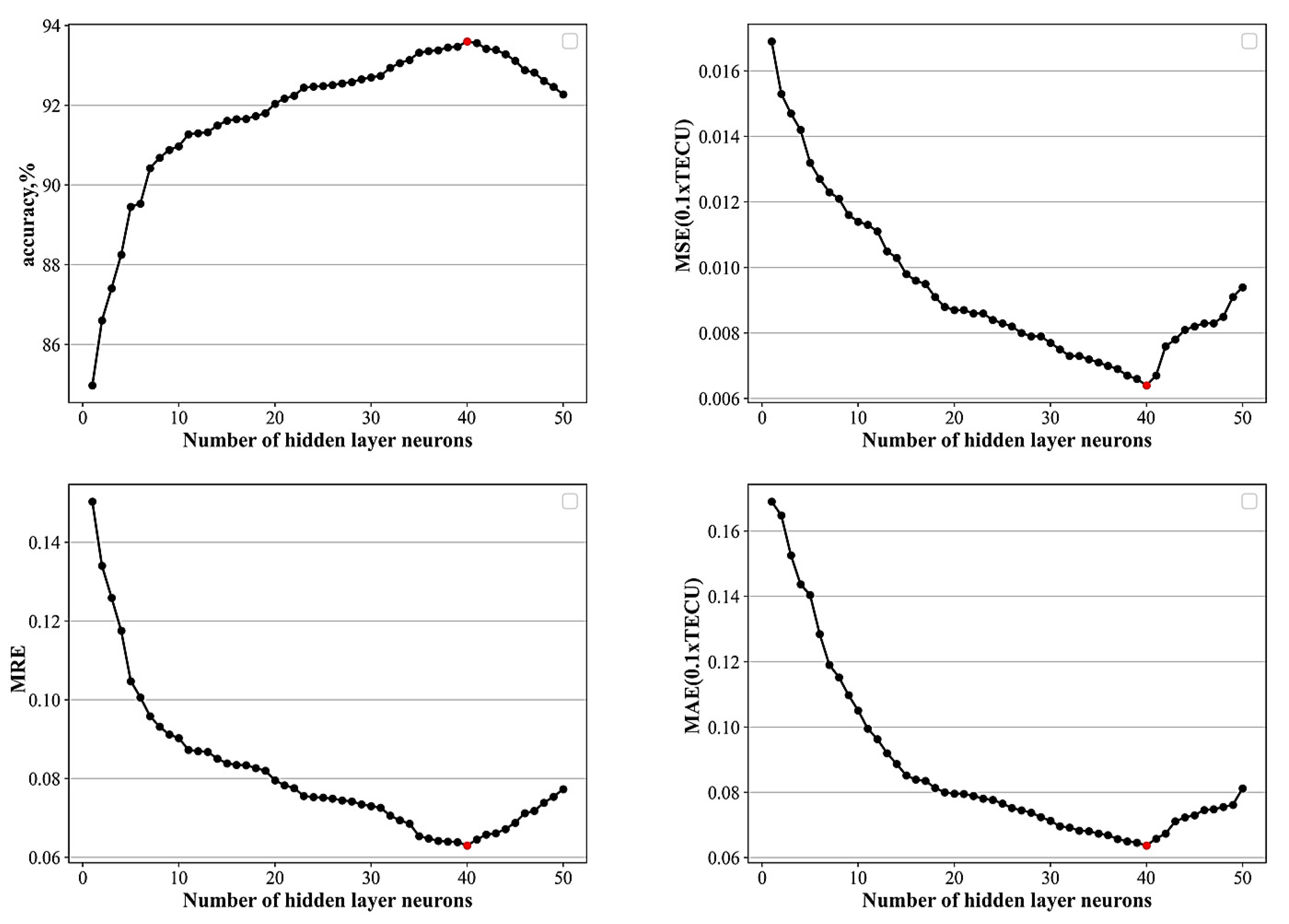
3.1.1. Effect of Model Parameters on Prediction Performance
Number of Hidden Layer Neurons
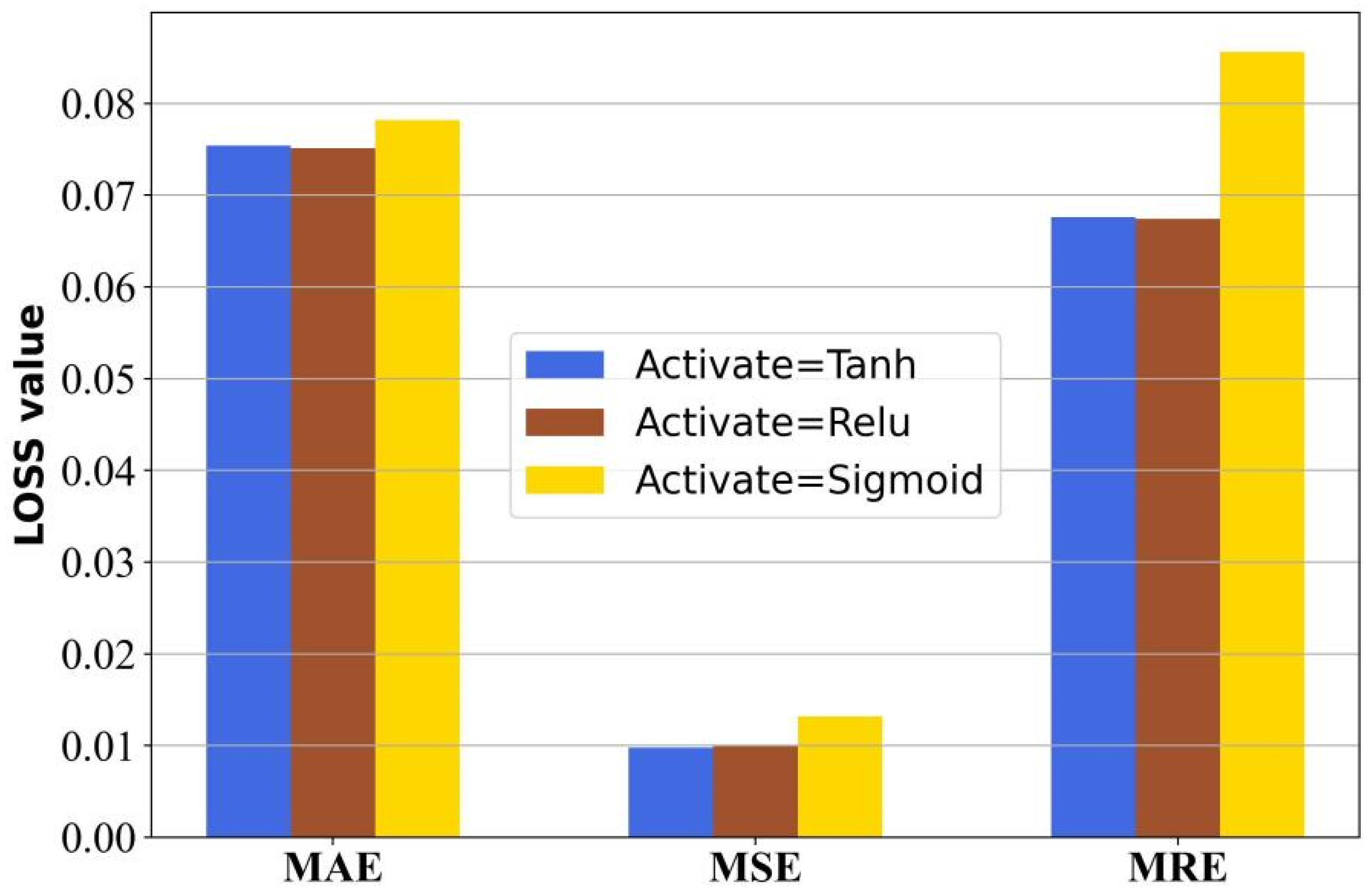
Activation Function
3.1.2. Effect of Training Parameters on Prediction Performance
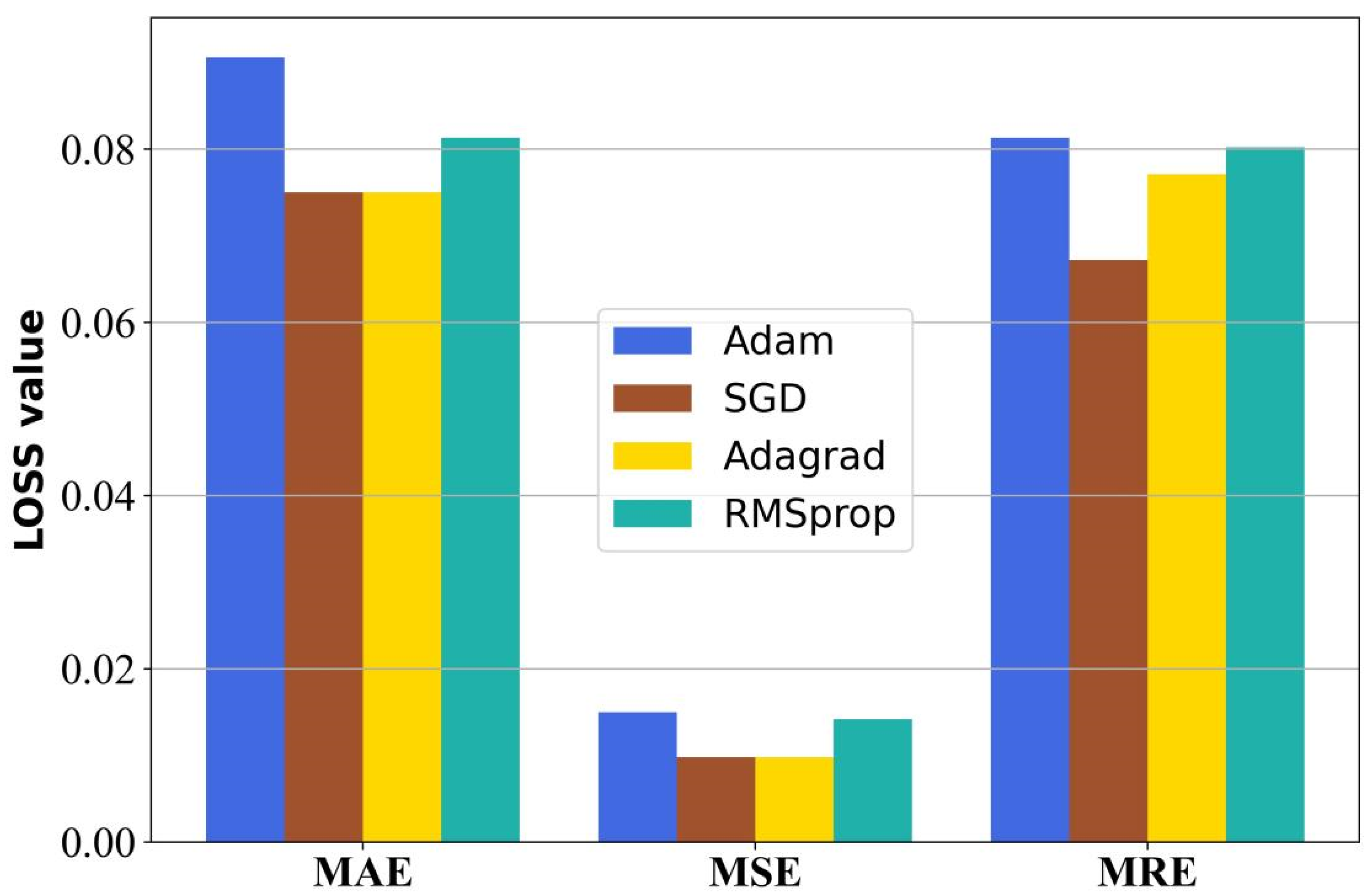
Optimizer Javascript: Void (0)
Influence of Batch_Size
Influence of Learning Rate (LR)
3.2. Comparison with DNN, ANN, RNN, LSTM, GRU, and BiLSTM on Different Latitudes
3.3. Experiments in High and Low Solar Activity Year
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaselimi, M.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Delikaraoglou, D. A causal long short-term memory sequence to sequence model for TEC prediction using GNSS observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhou, B.; Guo, S.; Liu, Z. Research on COMPASS navigation signals of China. Chin. Space Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Mohanty, S.; Kannaujiya, S. Ionospheric TEC modelling for earthquakes precursors from GNSS data. Quat. Int. 2017, 462, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, A.; Gende, M.; Brunini, C.; Radicella, S.M. Evaluating the accuracy of ionospheric range delay corrections for navigation at low latitude. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 36, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, I.V.; Karpov, M.I.; Borchevkina, O.P.; Yakimova, G.A.; Koren’Kova, N.A. Spatial and temporal variations of the ionosphere during meteorological disturbances in December 2010. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 13, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; An, J.; Ou, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, N. Assessment of spatial and temporal TEC variations derived from ionospheric models over the polar regions. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Yin, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Lu, H. Analysis of Pre-Earthquake Space Electric Field Disturbance Observed by CSES. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivavaraprasad, G.; Deepika, V.S.; Rao, D.S.; Kumar, M.R.; Sridhar, M. Performance evaluation of neural network TEC forecasting models over equatorial low-latitude Indian GNSS station. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 11, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; He, F.; Zhou, C.; Qing, H.; et al. Ionospheric TEC data assimilation based on Gauss–Markov Kalman filter. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4189–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.A.; Wan, W.X.; Liu, L.B.; Le, H.J.; Chen, Y.D.; Yu, T. Development of a middle and low latitude theoretical ionospheric model and an observation system data assimilation experiment. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. A MLP neural network as an investigator of TEC time series to detect seismo-ionospheric anomalies. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, I.; Ziggah, Y.Y.; Asafo-Agyei, D. Appraisal of ANN and ANFIS for Predicting Vertical Total Electron Content (VTEC) in the Ionosphere for GPS Observations. Ghana Min. J. 2017, 17, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthanasangmechai, K.; Supnithi, P.; Lerkvaranyu, S.; Tsugawa, T.; Nagatsuma, T.; Maruyama, T. TEC prediction with neural network for equatorial latitude station in Thailand. Earth Planets Space 2012, 64, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inyurt, S.; Sekertekin, A. Modeling and predicting seasonal ionospheric variations in Turkey using artificial neural network (ANN). Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yuan, H. Ionospheric single-station TEC short-term forecast using RBF neural network. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habarulema, J.B.; McKinnell, L.A.; Cilliers, P.J. Prediction of global positioning system total electron content using neural networks over South Africa. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent neural network regularization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, J. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural networkormalsize. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2018, 38, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Srivani, I.; Prasad, G.S.V.; Ratnam, D.V. A deep learning-based approach to forecast ionospheric delays for GPS signals. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Shen, Y. A novel deep learning prediction model for concrete dam displacements using interpretable mixed attention mechanism. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2021, 50, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, A.; Lu, X. Vision-to-language tasks based on attributes and attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Anomaly detection in quasi-periodic time series based on automatic data segmentation and attentional LSTM-CNN. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 2626–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. A hybrid VMD–BiGRU model for rubber futures time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 84, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04747. [Google Scholar]
- Duchi, J.; Hazan, E.; Singer, Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2121–2159. [Google Scholar]
- McMahan, B.; Streeter, M. Delay-tolerant algorithms for asynchronous distributed online learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Man, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, M.; Cui, P. A deep learning based dynamic COD prediction model for urban sewage. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicella, S.M.; Adeniyi, J.O. Equatorial ionospheric electron density below the F 2 peak. Radio Sci. 1999, 34, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.G.; Sharma, R.P. Ionospheric electron content at Ahmedabad (near the crest of equatorial anomaly) by using beacon satellite transmissions during half a solar cycle. Planet. Space Sci. 1971, 19, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
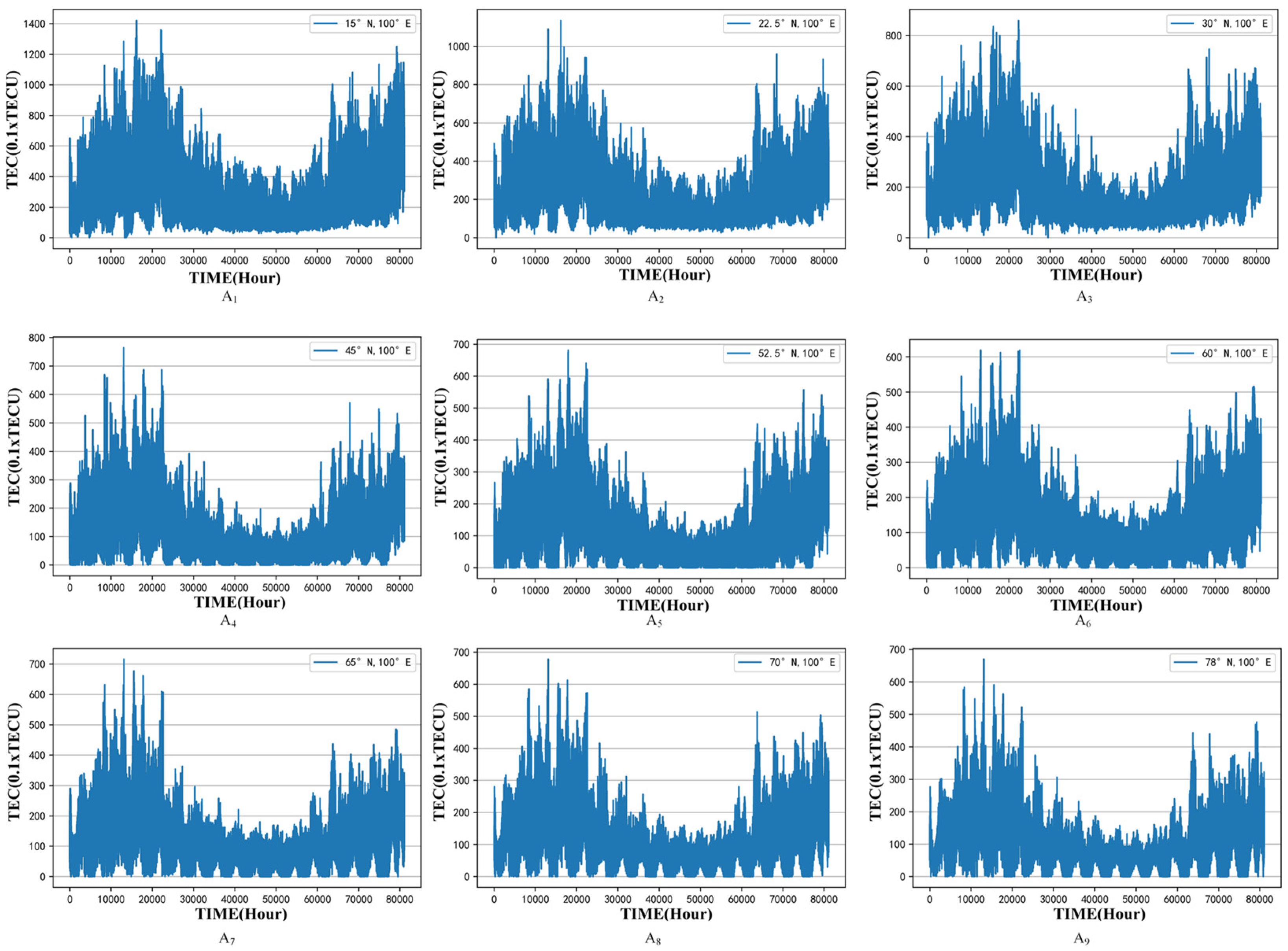
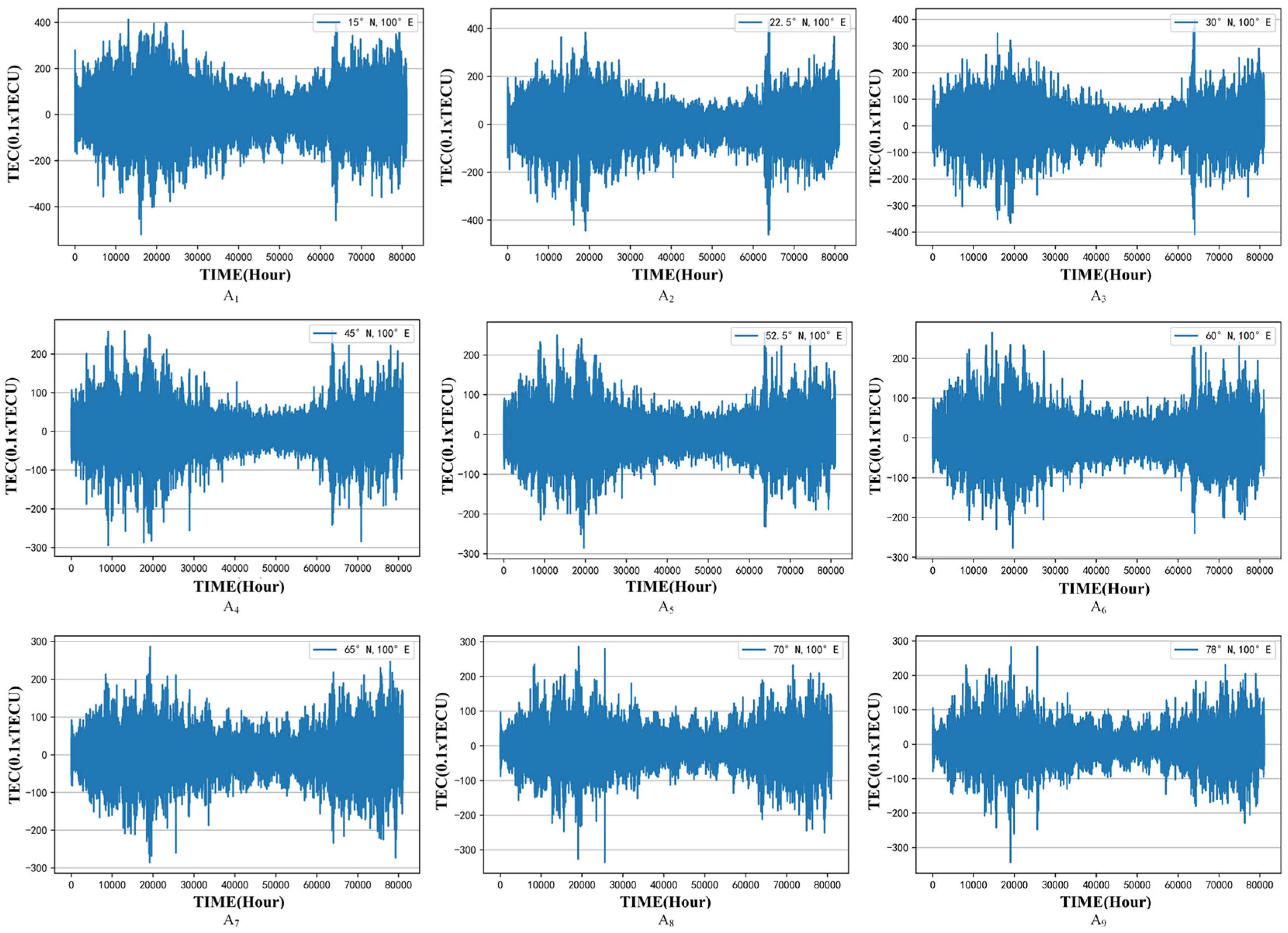


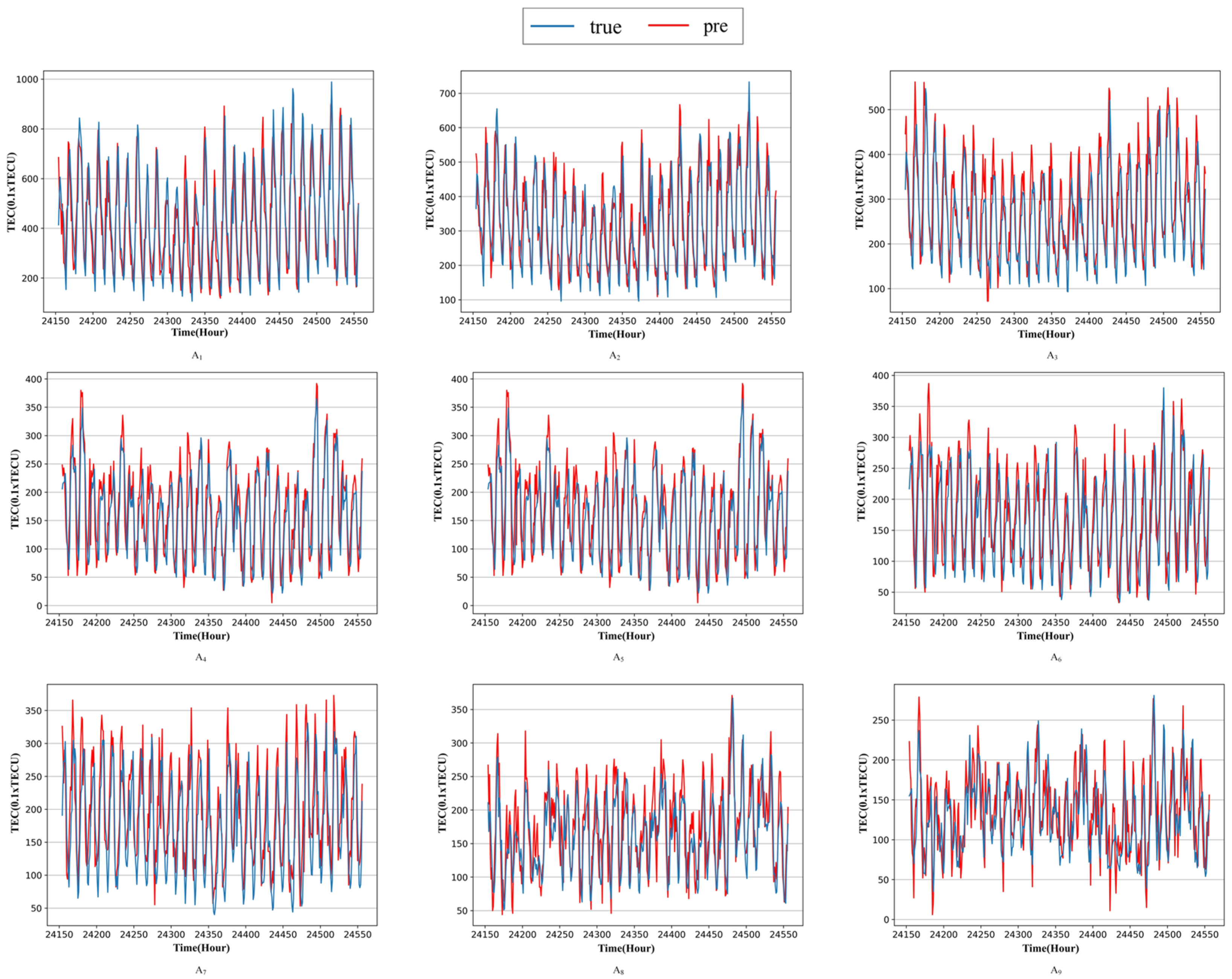

| Study Area Number | Longitude and Latitude Coordinates | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | Bangkok (15° N, 100° E) | low latitude regions |
| A2 | Lincang (22.5° N, 100° E) | |
| A3 | Ganzi (30° N, 100° E) | |
| A4 | Bogdo (45° N, 100° E) | middle latitude regions |
| A5 | Ojinsky (52.5° N, 100° E) | |
| A6 | Keremsky (60° N, 100° E) | |
| A7 | Ewenki (65° N, 100° E) | high latitude regions |
| A8 | Krasnoyarsk (70° N, 100° E) | |
| A9 | Arctic ocean (78° N, 100° E) |
| Activation | MAE | MSE | MRE | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanh | 0.0754 | 0.0098 | 0.0676 | 93.24% |
| Relu | 0.0751 | 0.0099 | 0.0674 | 93.26% |
| Sigmoid | 0.0782 | 0.0126 | 0.0856 | 92.44% |
| Optimizer | MAE | MSE | MRE | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adam | 0.0906 | 0.015 | 0.0813 | 91.87% |
| SGD | 0.0750 | 0.0098 | 0.0672 | 93.28% |
| Adagrad | 0.0750 | 0.0098 | 0.0771 | 92.29% |
| RMSprop | 0.0813 | 0.0142 | 0.0802 | 91.98% |
| Batch_Size | MAE | MSE | MRE | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch_Size = 16 | 0.0750 | 0.0098 | 0.0772 | 92.28% |
| Batch_Size = 32 | 0.0736 | 0.0098 | 0.0653 | 93.47% |
| Batch_Size = 64 | 0.0801 | 0.0116 | 0.0701 | 92.99% |
| Batch_Size = 128 | 0.0826 | 0.0142 | 0.0766 | 92.34% |
| LR | MSE | MAE | MRE | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR = 0.1 | 0.0126 | 0.0847 | 0.1076 | 89.24% |
| LR = 0.05 | 0.0105 | 0.0820 | 0.0926 | 90.74% |
| LR = 0.01 | 0.0097 | 0.0761 | 0.0915 | 90.85% |
| LR = 0.005 | 0.0092 | 0.0660 | 0.0678 | 93.22% |
| LR = 0.001 | 0.0088 | 0.0637 | 0.0546 | 94.54% |
| Algorithm | Indicator | A1 (15° N, 100° E) | A2 (22.5° N, 100° E) | A3 (30° N, 100° E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNN | 0.0135 | 0.0113 | 0.0270 | |
| ANN | 0.0132 | 0.0130 | 0.0127 | |
| RNN | 0.0142 | 0.0123 | 0.0103 | |
| LSTM | MSE | 0.0075 | 0.0154 | 0.0082 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0082 | 0.0119 | 0.0065 | |
| GRU | 0.0098 | 0.0126 | 0.0088 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0062 | 0.0060 | 0.0045 | |
| DNN | 0.0739 | 0.1198 | 0.0955 | |
| ANN | 0.0796 | 0.0768 | 0.0743 | |
| RNN | 0.0832 | 0.0819 | 0.0802 | |
| LSTM | MAE | 0.0754 | 0.0938 | 0.0782 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0609 | 0.0719 | 0.0565 | |
| GRU | 0.0725 | 0.0854 | 0.0673 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0572 | 0.0654 | 0.0472 | |
| DNN | 0.0965 | 0.0946 | 0.0823 | |
| ANN | 0.0849 | 0.0825 | 0.0819 | |
| RNN | 0.0842 | 0.0820 | 0.0784 | |
| LSTM | MRE | 0.0696 | 0.0640 | 0.0673 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0639 | 0.0603 | 0.0672 | |
| GRU | 0.0696 | 0.0693 | 0.0646 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0634 | 0.0598 | 0.0597 | |
| DNN | 90.35% | 90.54% | 91.77% | |
| ANN | 91.51% | 91.75% | 91.81% | |
| RNN | 91.58% | 91.80% | 92.16% | |
| LSTM | accuracy | 93.04% | 93.60% | 93.27% |
| BiLSTM | 93.61% | 93.97% | 93.28% | |
| GRU | 93.04% | 93.07% | 93.54% | |
| Att-BiGRU | 93.66% | 94.02% | 94.03% |
| Algorithm | Indicator | A4 (45° N, 100° E) | A5 (52.5° N, 100° E) | A6 (60° N, 100° E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNN | 0.0124 | 0.0092 | 0.0083 | |
| ANN | 0.0122 | 0.0117 | 0.0109 | |
| RNN | 0.0093 | 0.0087 | 0.0082 | |
| LSTM | MSE | 0.0098 | 0.0075 | 0.0067 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0082 | 0.0072 | 0.0064 | |
| GRU | 0.0086 | 0.0074 | 0.0069 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0058 | 0.0068 | 0.0053 | |
| DNN | 0.0972 | 0.0915 | 0.0830 | |
| ANN | 0.0739 | 0.0721 | 0.0704 | |
| RNN | 0.0791 | 0.0746 | 0.0723 | |
| LSTM | MAE | 0.0784 | 0.0645 | 0.0673 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0673 | 0.0657 | 0.0642 | |
| GRU | 0.0740 | 0.0620 | 0.0691 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0570 | 0.0618 | 0.0533 | |
| DNN | 0.1155 | 0.0886 | 0.0901 | |
| ANN | 0.0803 | 0.0782 | 0.0774 | |
| RNN | 0.0764 | 0.0738 | 0.0715 | |
| LSTM | MRE | 0.0788 | 0.0661 | 0.0652 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0725 | 0.0623 | 0.0647 | |
| GRU | 0.0633 | 0.0621 | 0.0620 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0504 | 0.0563 | 0.0539 | |
| DNN | 88.45% | 91.14% | 90.99% | |
| ANN | 91.93% | 92.18% | 92.26% | |
| RNN | 92.36% | 02.62% | 92.85% | |
| LSTM | accuracy | 92.12% | 93.39% | 93.48% |
| BiLSTM | 92.75% | 93.77% | 93.53% | |
| GRU | 93.67% | 93.79% | 93.80% | |
| Att-BiGRU | 94.35% | 94.37% | 94.61% |
| Algorithm | Indicator | A7 (65° N, 100° E) | A8 (70° N, 100° E) | A9 (78° N, 100° E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNN | 0.0257 | 0.0114 | 0.0091 | |
| ANN | 0.0104 | 0.0096 | 0.0090 | |
| RNN | 0.0076 | 0.0071 | 0.0070 | |
| LSTM | MSE | 0.0065 | 0.0047 | 0.0036 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0074 | 0.0051 | 0.0034 | |
| GRU | 0.0067 | 0.0045 | 0.0057 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0058 | 0.0045 | 0.0033 | |
| DNN | 0.0843 | 0.0961 | 0.0998 | |
| ANN | 0.0674 | 0.0661 | 0.0652 | |
| RNN | 0.0704 | 0.0659 | 0.0624 | |
| LSTM | MAE | 0.0586 | 0.0528 | 0.0551 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0567 | 0.0519 | 0.0532 | |
| GRU | 0.0578 | 0.0615 | 0.0547 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0535 | 0.0494 | 0.0408 | |
| DNN | 0.0838 | 0.0861 | 0.0828 | |
| ANN | 0.0729 | 0.0699 | 0.0672 | |
| RNN | 0.0684 | 0.0649 | 0.0630 | |
| LSTM | MRE | 0.0610 | 0.0528 | 0.0543 |
| BiLSTM | 0.0587 | 0.0491 | 0.0502 | |
| GRU | 0.0563 | 0.0468 | 0.0495 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.0548 | 0.0464 | 0.0378 | |
| DNN | 91.62% | 91.39% | 91.72% | |
| ANN | 92.71% | 93.01% | 93.28% | |
| RNN | 93.16% | 93.51% | 93.70% | |
| LSTM | accuracy | 93.90% | 94.72% | 94.57% |
| BiLSTM | 94.13% | 95.09% | 94.98% | |
| GRU | 94.37% | 95.32% | 95.05% | |
| Att-BiGRU | 94.52% | 95.36% | 96.22% |
| Indicator | A1 15° N | A2 22.5° N | A3 30° N | A4 45° N | A5 52.5° N | A6 60° N | A7 65° N | A8 b70° N | A9 78° N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 0.0174 | 0.0113 | 0.0114 | 0.0103 | 0.0097 | 0.0089 | 0.0072 | 0.0065 | 0.0041 |
| MAE | 0.1033 | 0.0869 | 0.0913 | 0.0891 | 0.0853 | 0.0807 | 0.0610 | 0.0534 | 0.0433 |
| MRE | 0.0924 | 0.0891 | 0.0864 | 0.0839 | 0.0826 | 0.0782 | 0.0685 | 0.0526 | 0.0416 |
| accuracy | 90.76% | 91.09% | 91.36% | 91.61% | 91.74% | 92.18% | 93.15% | 94.74% | 95.84% |
| Indicator | A1 15° N | A2 22.5° N | A3 30° N | A4 45° N | A5 52.5° N | A6 60° N | A7 65° N | A8 70° N | A9 78° N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 0.0195 | 0.0126 | 0.0118 | 0.0116 | 0.0109 | 0.0104 | 0.0089 | 0.0077 | 0.0052 |
| MAE | 0.1048 | 0.0934 | 0.0926 | 0.0917 | 0.0870 | 0.0827 | 0.0681 | 0.0567 | 0.0459 |
| MRE | 0.0953 | 0.0936 | 0.0911 | 0.0864 | 0.0835 | 0.0820 | 0.0703 | 0.0581 | 0.0468 |
| accuracy | 90.47% | 90.64% | 90.89% | 91.36% | 91.65% | 91.80% | 92.97% | 94.19% | 95.32% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, D.; Liu, H.; Le, H.; Huang, J.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071039
Lei D, Liu H, Le H, Huang J, Yuan J, Li L, Wang Y. Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071039
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Dongxing, Haijun Liu, Huijun Le, Jianping Huang, Jing Yuan, Liangchao Li, and Yali Wang. 2022. "Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071039
APA StyleLei, D., Liu, H., Le, H., Huang, J., Yuan, J., Li, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071039







