Abstract
Understanding precipitation chemistry is highlighted as important worldwide due to its close relationship with air quality and impacts on ecosystems. However, the chemical composition of precipitation is limited in Tibet, where alpine ecosystems are sensitive to global change. Here, rainwater samples were collected in Nyingchi city from January 2021 to December 2021, and a total of 44 samples were obtained. Major ions (NO3−, NH4+, Cl−, SO42−, Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) were analyzed. Results showed that the predominant ions in the precipitation were Ca2+, Na+, SO42−, and Cl−. Precipitation was mainly concentrated in summer, accounting for 65.2% of all samples collected during the monitoring period. As a result, ion deposition fluxes were mainly concentrated in summer, accounting for 55%, 53%, 84%, 82%, 61%, 63%, 75.8%, and 37.8% of the annual Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, Na+, NH4+, Cl−, SO42−, and NO3−, respectively. Backward trajectory analysis revealed that airmasses were mainly from the southern direction, but the sources varied widely. In addition, Na+ and Cl− ions were dominated by the sea source fraction; the ions of Ca2+ and K+ were dominated by crustal fraction sources. The NH4+ and NO3− ions were mainly influenced by local pollution. However, SO42− was mainly from long distance transports. Our results suggest that ions abundance was varied largely in different direction airmasses in southeast Tibet. Considering that ion deposition fluxes were mainly concentrated in the summer and the airmasses were mainly from the southern direction in this season, the pollutants from the southern direction the environmental effects of those ions should be given more attention in the future.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric precipitation can effectively scavenge pollutants from the atmosphere and is the most effective method of air purification [1,2]. Precipitation chemistry is commonly used to estimate air pollutants at regional scales or the national scale [2,3,4]. Usually, the chemical characteristics of precipitation are affected by both natural and anthropogenic sources [4]. However, in some regions, this situation has changed in recent decades due to human activities. With the intensification of anthropogenic activities, the ionic composition of precipitation has largely depended on anthropogenic sources in human-concentrated areas [1,5,6,7]. Meanwhile, studies on chemical characteristics of precipitation have focused on local and regional areas, especially cities [1,8].
Aerosol sources and the migration and removal processes of chemical substances can affect the chemical concentration of rainwater [9]. The different atmospheric chemical reactions that occur within and below clouds are also important [2]. The chemical composition of rainfall water is influenced by several factors, such as local emissions, pollution sources, meteorological conditions, and process of transportation [4,10,11,12,13]. The chemical composition of atmospheric precipitation reveals the characteristics of regional air pollution to some extent [10,14]. In addition, knowledge of the chemical composition of rainfall not only indirectly reflects the atmospheric quality of specific regions but also provides useful information to help us understand the impact on ecosystems through deposition processes [10]. To date, studies that have focused on precipitation chemistry have been conducted in human-concentrated areas [15,16]. However, the precipitation chemistry in background sites is interesting and useful [17]. The Qinghai–Tibet Plateau is considered to be an area of low human disturbance and low nitrogen deposition, yet it is an area sensitive to global change [18]. To date, the research focused on the chemistry of the Qinghai–Tibet plateau has been relatively limited to areas in China [18,19].
The status of the Tibetan Plateau is unique as it is the highest geographical unit in the world. Thus, it plays an important role in evaluating long-term changes in ecological conditions and environmental status [18]. Human activities on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau are increasing rapidly. This situation may change the composition of air pollutants and ions in precipitation in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau. Consequently, potential impacts of pollutant and nutrient deposition on local ecosystems are unpredictable. Thus, understanding the precipitation chemistry and quantification of ion deposition fluxes is crucial in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau. To our knowledge, the seasonal variations and potential original sources of precipitation chemistry have not been completely quantified in southeast Tibet. Therefore, the present study sampled precipitations in Nyingchi city, Tibet, with the aim to: (1) quantify the major water-soluble ion deposition fluxes in precipitation and clarify the dominant ions, (2) investigate whether the major ions have the same source in all seasons, and (3) understand if the ion pollution is mainly from local pollution or long-distance transports in those area.
2. Experiments
2.1. Sampling Location
The sampling site was located at Xizang Agriculture and Animal Husbandry College (29.66° N 94.34° E 2990 m a.s.l.), Nyingchi city (Figure 1). Nyingchi city is in southeast Tibet and is mainly influenced by the Indian Ocean and the Pacific warm current. It has a population of approximately 200,000. In addition, Nyingchi city is a tourist city, with no large pollution sources nearby. The potential emission sources were small villages and agricultural fields. The regional climate is that of a cold, temperate, humid, subalpine zone. The monthly mean temperature is in the range of 1–16.2 °C; the annual precipitation amount is in the range of 600–800 mm.
Figure 1.
Location of the monitoring site.
2.2. Precipitation Collection
Bulk deposition samples were collected. Bulk deposition is defined as the amount of wet deposition plus dry particles that sediment during sampling into the collector located in an air environment [2]. As a result, the ion deposition fluxes were slightly higher than the wet deposition fluxes.
Rain samples were collected from January 2021 to December 2021 via continuously open rain gauges (SDM6A, Kailongda Inc., Tianjin, China). All parts are made of stainless steel except the glass water collection bottle. Considering that rainfall events mainly occurred at night, rainfall water samples were collected in the morning of the next day. If rainfall events continued into the morning, we collected samples the next morning. In addition, according to a previous study [18], samples were not collected when the sample’s volume was less than 10 mL. Unfortunately, we did not obtain enough rainfall samples for determination because there were limited rainfall events in January, February, and December. Precipitation was only 6.7mm throughout the whole of winter in Nyingchi city (http://data.cma.cn/data/weatherBk.html, accessed on 30 April 2022). As a result, rainfall samples were analyzed from March 2021 to November 2021. Precipitation samples were collected by hand, and a total of 44 samples were obtained during the monitoring period. After each precipitation event, the samples were thoroughly stirred and immediately transferred to clean polyethylene bottles. The rainwater collection bottle was rinsed with deionized water to eliminate cross-event contamination.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
After each sample collection, rainfall water samples were immediately taken to the laboratory, filtered with 0.45 μm cellulose acetate filter (Tengda Inc., Tianjin, China), and then saved in polyethylene bottles at −18 °C. Water-soluble ions were analyzed by ion chromatography (IC, Dionex Corporation, Idstein, Germany). Three blank samples were measured before samples measurement to eliminate contamination. Anions (Cl−, NO2−, NO3−, F−, Br−, PO43−, and SO42−) were analyzed via an ICS-2100 ion chromatograph that consisted of a separation column (Dionex Ionpac AS11) and guard column (Dionex Ionpac AG11). Cations (Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+) were analyzed on a DX-600 ion chromatograph that consisted of a separation column (Dionex CS12A) and a guard column (Dionex AG12A), and the detection limit was 0.1 μg/L. The amount of HCO3− was estimated using the following equation: HCO3− = 10 (pH−5.05) [20].
2.4. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
The wet deposition fluxes of ionic constituents and volume-weighted mean (VWM) concentrations in rainwater were calculated via the following equations:
where Ci is the concentration of a particular ion in the ith sample (mg L−1); Pi is the precipitation amount collected within the ith sampling period (mm); and n is the total number of precipitation events. F represents the seasonal and/or annual bulk deposition flux (kg N ha−1); 100 is the unit conversion factor.
Cvwm = 10,000 × V/M × F/Pt
Cvwm is the VWM concentration (μeq L−1); M is the molecular weight of ion; V is the valence of ion (absolute value); and Pt is total amount of rainfall per season/year(mm). The unit conversion factor is 10,000.
The Enrichment Factor (EF) is commonly used to estimate the source contributions in rainfall water [18]. In general, Na+ can be considered as a typical marine source tracer, whereas Ca2+ derives mainly from the continental crust. The EF of an ion concentration in rain relative to the concentration in sea was estimated as follows [20]:
EFsea = (X/Na+)rain/(X/Na+)sea
EFsoil = (X/Ca2+)rain/(X/Ca2+)soil
EFsea is the EF of an ion in rainfall relative to in the sea; X is an ion in precipitation; (X/Na+)sea is referenced from Keene et al. [21]; and (X/Ca2+)soil is referenced from Taylor et al. [22].
Sources of ions can be divided into ocean, land, and human activities. We used the following equations to estimate the sources of ionic components from previous studies [18]:
SSF(%) = (X/Na+)sea/(X/Na+)rain × 100
CF(%) = (X/Ca2+)soil/(X/Ca2+)rain × 100
AF(%) = 100% − SSF(%) − CF(%)
SSF represents the sea fraction, CF represents the crustal fraction, and AF represents the anthropogenic fraction; if the SSF (CF) ratio is greater than 1, SSF (CF) is calculated as 1 minus CF (SSF).
The Pearson correlation was calculated based on Σanions and Σcations. Σanions and Σcations in each precipitation samples were calculated via the following equation.
where i is the numbers of different anions; t is the numbers of different cations; Ci is the concentrations of ith anions; Mi is the molecular weight of the ith anions; Vi is the valence of anions (absolute value); Ct is the concentrations of tth cations; Mt is the molecular weight of the tth cations; and Vt is the valence of cations (absolute value).
2.5. Backward Trajectory Analysis
Air mass back-trajectory analysis was performed by HYSPLIT 5.2.0 (the Hybrid-Single Particle Integrated Trajectory Model) (http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php; Last accessed on 9 May 2022). The program was provided by the Air Resource Laboratory of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA, College Park, MD, USA). Meteorological data were input from the Global Data Assimilation System (ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives/gdas1, accessed on 9 May 2022). Then, 72-h backward trajectories were calculated on sampling days, with an arrival height of 1000 m [1]. Cluster analysis was performed using the trajectories based on the total spatial variance (TSV) method [23].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Precipitation
The VWM concentrations of total cations was 132.8 μeq L−1, whereas the value of the total anions (except for HCO3−) was 63.4 μeq L−1. The estimated VWM of HCO3− was 66.6 μeq L−1. This result agreed that HCO3− was the dominant anion species in Tibet [18,19,20]. The Pearson correlation value between the sum of total cations (Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+) and sum of total anions (Cl−, NO3−, NO2−, NO3−, F−, Br−, PO43−, and SO42−) was 0.812 precipitations, suggesting that the measured ion balance in this experiment was credible.
The VWM ionic concentrations for Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, NO2−, NO3−, F−, Br−, PO43−, and SO42− were 30.5, 15.0, 2.5, 14.7, 70.1, 25.6, 0.3, 6.4, 0.29, 0.01, 0.8, and 29.9 μeq L−1, respectively. In addition, the order of concentration abundance of cation concentrations was Ca2+ > Na+ > NH4+ > Mg2+ > K+, whereas the order of concentration abundance of anions was SO42− > Cl− > NO3− > PO43− > NO2− > F− > Br−. Obviously, Ca2+ was the dominant cation, accounting for 52.8% of the total cations; SO42− was the dominant anion, accounting for 47.2% of the total cations. Those results agreed with previous studies that focused on southeast Tibet [20]. In addition, both Na+ and Cl− concentrations were at a high level (Figure 2). The reason might be that airmasses are mainly influenced by the Indian Ocean and the Pacific warm current (Figure 3). In general, air masses mainly came from the south in different seasons. In addition, the southern trajectory was the only one in the spring, whereas there were three southern trajectory in the summer. In autumn, air masses came mainly from the southeast direction. Moreover, air masses were dominated by long-distance transports in the southern direction in the summer (Figure 3).
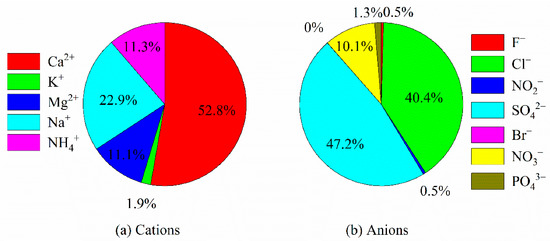
Figure 2.
Comparison of the percentage of cations (a) and anions (b) based on equivalents.
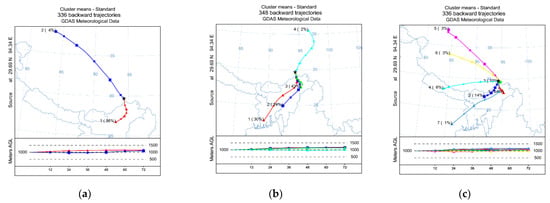
Figure 3.
The 72-h backward trajectories in the research area in different seasons. (a)—spring; (b)—summer; (c)—autumn. Cluster analysis was performed using the trajectories based on the total spatial variance (TSV) method.
3.2. Seasonal Variations in the Ion Concentrations
Due to various pollutant sources in different seasons, seasonal variations of ion concentrations in precipitation are widespread in different regions [5,24,25]. Seasonal variations in cations’ and anions’ concentrations existed within the research area (Figure 4). The VWM cations were 306.4, 132.5, and 64.9 μeq L−1 in spring, summer, and autumn, respectively, whereas the averaged anion concentrations were 126.3, 65.0, and 34.4 μeq L−1 in spring, summer, and autumn, respectively. Both cations’ and anions’ concentrations were the highest in the spring and lowest in autumn. Commonly, the dilution effect of rainwater on precipitation chemistry is present. In this work, both ion concentrations and deposition fluxes had seasonal variations (Figure 3). Interestingly, low concentrations of both cations and anions were observed in autumn, whereas precipitation was concentrated in the summer. One reasonable explanation for this is that the original airmasses’ directions were different between the summer and autumn (Figure 4). India, located in the direction of the source of the air mass, is a human-concentrated area, and ion concentrations in precipitation there are relatively high [26]. During airmass transportation, the air mass may be polluted by sources from India in the southern direction (Figure 4). As a result, high ion concentrations were observed in the summer. In contrast, ion concentrations were relatively low in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau because of its low human activity [18]. As a result, precipitation caused by other airmass directions showed relatively low ion concentrations, and those airmasses contributed low amounts in autumn (Figure 4). In addition, the relationships between precipitation amounts and cations, precipitation amounts and anions, and cations and anions were all calculated (Figure 5). There is no conflict regarding the fact that ion concentrations in rainfall water are negatively correlated with precipitation amount. Considering that bulk deposition was collected in this work, the chemistry of rainfall water may be influenced by the residence time of particles floating in the air [5]. Consequently, ion concentrations were relatively high in some cases (Figure 5).
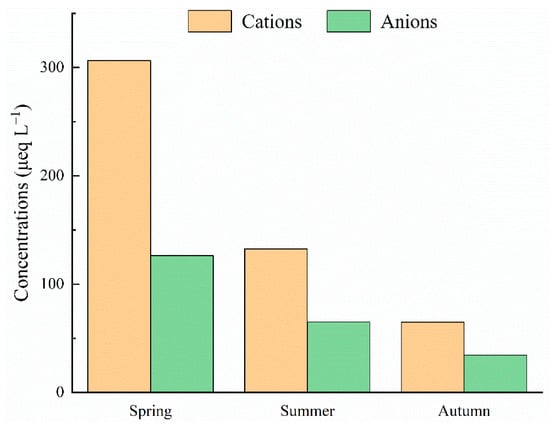
Figure 4.
Comparison of VWM cations and anions concentrations in different seasons.
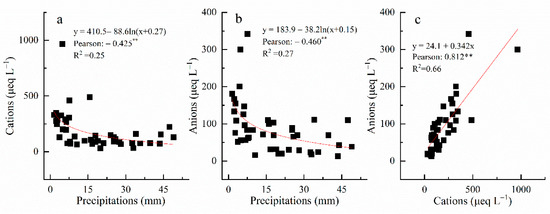
Figure 5.
Relationship between precipitation amounts and cations (a), precipitation amounts and anions (b), and cations and anions (c). The symbol ** represents significance at 0.01 level.
3.3. Source Assessment
EFsea values of NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− were 55.5, 3.77, 2.17, 52.8, 0.72, 33.9, and 6.93, respectively, which means that these ions, except for Cl−, were all enriched by a sea source. EFsoil values of NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− were 400.2, 0.14, 0.23, 207.5, 592.9, and 164.2, respectively, which means that ions of NH4+, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− were enriched by a soil source. In addition, the ions of NH4+, NO3−, and SO42− were enriched relative to both marine and soil reference sources, which means that those ions were mainly from anthropogenic sources. Those results agree with a previous study that focused on Tibet [18]. Moreover, the ions of Na+ and Cl− dominated SSF sources. The K+ and Ca2+ ions dominated AF sources. Anthropogenic sources contributed at least 97.9% of the NH4+ and of 96.9% of the NO3− in precipitation (Table 1). It should be pointed out that the CF source of Mg2+ was greater than one. Based on the calculation method, the contributions of CF and SSF sources to Mg2+ were comparable.

Table 1.
Source contributions (%) for major ions in precipitation.
3.4. Ions Deposition Fluxes and Correlations among Different Components
During our experiment, the precipitation was 782.4 mm. In the same period, the deposition fluxes were 5.48, 2.12, 0.76, 1.38, 11.0, 7.12, 0.12, 3.12, 0.01, 0.21, and 11.2 kg ha−1 for Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, NO2−, NO3−, F−, Br−, PO43−, and SO42−, respectively. Moreover, the deposition fluxes of NH4+-N, NO3−-N, PO43−-P, and SO42−-S were 1.65, 0.713, 0.07, and 3.73 kg ha−1 during our monitoring periods. NH4+-N was the dominant from, and the results agreed with previous studies [27]. In addition, the amounts of precipitation were 75.3, 510.0, and 197.1 mm in spring, summer, and autumn, respectively, and the percentage of precipitation that occurred in the summer was 65.2%.
The deposition fluxes of different ions showed different seasonal variations. Considering that the precipitation was mainly concentrated in the summer, deposition fluxes of different ion species were all highest in this season. In addition, the deposition fluxes were accounting for 55%, 53%, 84%, 82%, 61%, 63%, 75.8%, and 37.8% of the annual Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, Na+, NH4+, Cl−, SO42−, and NO3− deposition fluxes (Figure 6). The deposition flux percentages of Mg2+, Na+, and SO42− were higher than the precipitation percentages in the summer, whereas NO3−, Ca2+, and K+ were lower than the precipitation percentages in the same period. The reason might be that ions of Mg2+, Na+, and SO42− were mainly from the southern direction, and those ions were abundant in the airmasses from the southern direction (Figure 3). Based on the Pearson correlation analysis, we had been found that a positive correlation was observed between Na+ and Mg2+, Na+, and SO42− (Table 2). Ca2+ and K+ were mainly from terrestrial sources (Table 1), and a high positive correlation has also been found between Ca2+ and K+. Caused by dilution effect of rainwater on precipitation chemistry, the deposition flux percentages of Ca2+ and K+ were slightly lower than the precipitation percentages in the summer. Compared to other ions, high NH4+ deposition fluxes were observed in the spring. This might be because local agriculture activities can influence atmospheric NH4+ concentrations, and atmospheric NH4+ concentration was at a high level from May to Sep [27]. As a result, the deposition fluxes were high in the spring and summer. Interestingly, the deposition flux percentages of SO42− were higher than the precipitation percentages in the summer, and NO3− was lower than the precipitation percentages in the same period. However, both SO42− and NO3− were significantly positively correlated with Ca2+. Acid deposition was mainly caused by the ions of atmospheric SO42− and NO3− [28], and the acid neutralization in the atmosphere was dominated by Ca2+ in China [29]. In this work, Ca2+ was the dominant cation and neutralizing ion (Figure 2). SO42− sourced from long distance transports was neutralized by Ca2+, and a high positive correlation was observed between Ca2+ and SO42−. In addition, a high positive correlation between Ca2+ and SO42− was observed in previous studies [30]. NO3− sourced from the local environment was neutralized by Ca2+, and a high positive correlation was observed between Ca2+ and NO3− (Table 2). In addition, there are often valley winds in autumn afternoons in Nyingchi city. NO3− may drift into the air, coupling with the ions from terrestrial sources, with the wind and then sediment via dry deposition. In addition, a large contribution of Ca2+ and K+ to the annual precipitation in comparison with other ions of the autumn period was observed. The ions NO2−, F−, Br−, and PO43− were not measured in some samples, and as a result, we have not calculated their percentages.
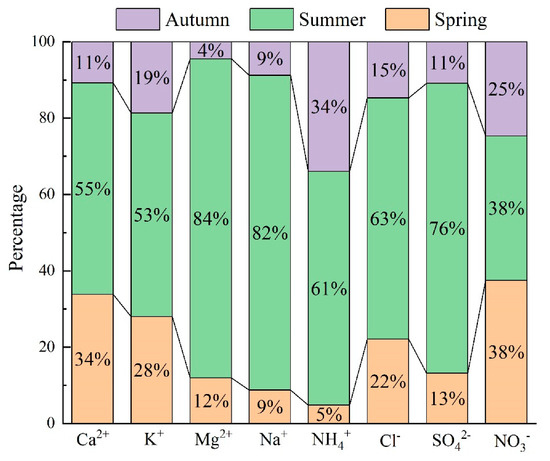
Figure 6.
The percentage in different seasons of different ion species deposition fluxes.

Table 2.
The Pearson correlation of different ion deposition fluxes in precipitation.
3.5. Comparison with Other Research in Other Regions
Compared to the ion concentrations in the precipitation in the other areas, the values were commonly relatively low in Nyingchi city (Table 3), which agrees with previous studies [31]. This can be explained by the fact that low human activity and few anthropological ion pollution sources exist in Tibet. Interestingly, Na+ concentrations were higher than in most areas in China. The reason is that Nyingchi city is mainly influenced by the Indian Ocean and airmasses mainly from the south (Figure 3). Correspondingly, high Na+ deposition fluxes were observed in summer in this work (Figure 6). Similarly, the concentrations of Cl− coupled with Na+, mainly from SSF sources, were all at a high level (Figure 2). Due to the airmasses being mainly derived from the Indian Ocean, ion species that were mainly from CF sources were all at a low level (Table 2 and Table 3). In addition, Ca2+ was the dominant cation species in Nyingchi city, but the Ca2+ concentration in rainfall water was found to be relatively low. Ca2+ is a typical crustal ion. However, airmasses came mainly from the southern direction in the summer, when precipitation mainly occurred (Figure 6). This means that the precipitation events were dominated by sea-source airmasses. As a result, low VWM Ca2+ concentrations were observed in other research areas. It should be pointed out that, although the concentrations of ion species (NH4+, SO42−, and NO3−) that are mainly from human activities were all at a relative level, their concentrations were higher than in a previous study that focused on southeast Tibet [18]. Our monitoring sites were located in a city, whereas in previous studies they were located in remote areas. Our results reveal that the deposition fluxes of NH4+, SO42−, and NO3− might increase with intensifying human activities in Tibet.

Table 3.
Comparison of major ion concentrations (in μeq L−1) at sampling sites with other sites.
4. Conclusions
Ion concentrations and deposition fluxes were measured in Nyingchi city, Tibet. The results showed that Ca2+ and Na+ were the dominant cations, and their deposition fluxes were 11.2 and 5.48 kg ha−1 in a year, respectively; SO42− and Cl− were the dominant anions, and their deposition fluxes were 11.2 and 7.12 kg ha−1, respectively. Due to precipitation being mainly concentrated in the summer, ions deposition fluxes were all the highest in this season. Considering that atmospheric SO42− is an ion that causes acid deposition, and the deposition fluxes were relatively high in Nyingchi city, the environmental effects should be given more attention. In addition, the pollutants from southern direction need be further studied in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.W.; methodology, W.W. and L.G.; software, W.W. and Z.S.; validation, W.W.; formal analysis, W.W., J.Z. and L.G.; investigation, W.W., J.Z. and L.G.; resources, W.W., J.Z. and L.G.; data curation, W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W.; writing—review and editing, W.W.; visualization, W.W. and Z.S.; supervision, W.W. and J.F.; project administration, W.W.; funding acquisition, W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42067036) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tibet Autonomous Region Department and Agriculture and Animal Husbandry University (XZ202101ZR0023G).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the monitoring site is located close to the border. As a result, it may not suitable to disclose it to everyone. If the data is used for scientific research on request, I will provide it.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, X.D.; Xu, Z.F.; Liu, W.J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.C. Chemical composition of precipitation in Shenzhen, a coastal mega-city in South China: Influence ofurbanization and anthropogenic activities on acidity and ionic composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Baez, A.P. Chemical composition of bulk precipitation in the metropolitan area of Costa Rica, Central America. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, M.; Sinisi, R.; Mancusi, C.; Pilat, K.; Sabia, A.; Mongelli, G. Natural versus anthropogenic influences on the chemical composition of bulk precipitation in the southern Apennines, Italy: A case study of the town of Potenza. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztesi, G.; Nita, I.A.; Boga, R.; Birsan, M.V.; Bodor, Z.; Szep, R. Spatial and long-term analysis of rainwater chemistry over the conterminous United States. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Y.; Xu, Y.G.; Peng, P.A.; Zhang, H.H.; Lan, J.B. Chemical composition and seasonal variation of acid deposition in Guangzhou, South China: Comparison with precipitation in other major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wen, Z.; Shang, B.; Dore, A.J.; Tang, A.; Xia, X.; Zheng, A.; Han, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Precipitation chemistry and atmospheric nitrogen deposition at a rural site in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.F.; Liu, W.J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Yu, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.D. Chemical compositions ofprecipitation at three non-urban sites of Hebei Province, North China: Influence of terrestrial sources on ionic composition. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Gao, Y. Chemical characteristics of precipitation at metropolitan Newark in the US East Coast. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4903–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hélène, C.; Travi, Y.; Loyee-Pilot, M.D.; Huneau, F.; Bertrand, G. Rainwater chemistry at a Mediterranean inland station (Avignon, France): Local contribution versus long-range supply. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.I.; Olmo, F.J.; Lyamani, H.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Castro, A.; Fernández-Raga, M.; Fraile, R. Chemical composition of wet precipitation at the background EMEP station in Víznar (Granada, Spain) (2002–2006). Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wang, H.S.; Zhang, Z.F.; Jin, X.; Li, W. Trends in chemical composition of precipitation in Nanjing, China, during 1992–2003. Atmos. Res. 2005, 73, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Tian, L.D.; Fischer, E.; Li, Z.Q.; Jiao, K.Q. Study of chemical composition of precipitation at an alpine site and a rural site in the Urumqi River Valley, Eastern Tien Shan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8934–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.R.; Fracassi, D.; Lago, C.L.; Fornaro, A.; Gutz, I. Wet deposition and related atmospheric chemistry in the So Paulo metropolis, Brazil: Part 1. Major inorganic ions in rainwater as evaluated by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduber, F.; Calvo, A.I.; Castro, A.; Blanco-Alegre, C.; Alves, C.; Barata, J.; Nunes, T.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; et al. Chemical composition of rainwater under two events of aerosol transport: A Saharan dust outbreak and wildfires. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.Y.; Qiu, C.C.; Ding, C.; Wang, G.Z.; Yu, X.N. Analysis on chemical composition of precipitation and its source apportionment in Xi’an City. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 2384–2394, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; He, X.B.; Wu, J.K.; Ding, Y.J.; Hu, Z.F.; Wang, L.H.; Yang, G.S. Chemical Characteristics and Ionic Sources of Precipitation in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4431–4439, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Das, R.; Chaudhury, G.R.; Das, S. Chemical composition of precipitation at background level. Atmos. Res. 2010, 95, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Xu-Ri; Wang, Y.S.; Pan, Y.P.; Piao, S.L. Wet deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen at five remote sites in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11683–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.J.; Liu, J.Q.; Di, Y.A.; Yang, J.; Wen, T.X.; Li, Y.W.; Shi, Y.Q. Major ionic composition of precipitation in the Shigatse region, Southern Tibetan Plateau. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2012, 347–353, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Liu, D.; Zheng, A.; Dore, A.J.; Liu, X. Chemical compositions of fog and precipitation at Sejila Mountain in the southeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, W.C.; Pszenny, A.A.P.; Galloway, J.N.; Hawley, M.E. Sea-Salt Corrections and Interpretation of Constituent Ratios in Marine Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1986, 91, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of Chemical Elements in the Continental Crust—A New Table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.; Stunder, B.; Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Taylor, A. HYSPLIT4 User’s Guide; Version 4, Report; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Singla, V.; Pandithurai, G.; Safai, P.D.; Meena, G.S.; Dani, K.K.; Kumar, V.A. Seasonal variability in chemical composition and source apportionment of sub-micron aerosol over a high altitude site in Western Ghats, India. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 180, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpo, A.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Laouali, D.; Delon, C.; Liousse, C.; Adon, M.; Gardrat, E.; Mariscal, A.; Darakpa, C. Precipitation chemistry and wet deposition in a remote wet savanna site in West Africa: Djougou (Benin). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Tiwari, S.; Sarkar, C.; Das, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Raha, S. Precipitation chemistry over urban, rural and high altitude Himalayan stations in eastern India. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Wen, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Atmospheric Reactive Nitrogen Deposition in Nyingchi City. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Xu, Z.F.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhou, L. Multiple isotopic tracing for sulfate and base cation sources of precipitation in Hangzhou city, Southeast China: Insights for rainwater acidification mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhu, J.X.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, J.F.; He, N.P. Spatiotemporal variability, source apportionment, and acid-neutralizing capacity of atmospheric wet base-cation deposition in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, T.T.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, A.F.; Guo, X.Y.; Guo, R.; Jia, B.; Song, Y.X.; Han, C.T.; et al. Composition of wet deposition in the central Qilian Mountains, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7315–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Duan, D.; Lu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wen, X.; Guo, X.; Boman, B.J. Inorganic pollution around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An overview of the current observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouali, D.; Delon, C.; Adon, M.; Ndiaye, O.; Saneh, I.; Gardrat, E.; Dias-Alves, M.; Tagesson, T.; Fensohlt, R.; Galy-Lacaux, C. Source contributions in precipitation chemistry and analysis of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in a Sahelian dry savanna site in West Africa. Atmos. Res. 2021, 251, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduber, F.; Calvo, A.I.; Blanco-Alegre, C.; Castro, A.; Alves, C.; Cerqueira, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Martin-Villacorta, J.; et al. Towards a model for aerosol removal by rain scavenging: The role of physical-chemical characteristics of raindrops. Water Res. 2020, 190, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasereka, M.M.; Cuoco, E.; Zabene, F.Z.; Balagizi, C.M. Baseline for rainwater chemistry and quality as influenced by Nyiragongo volcano permanent plume, East Africa. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 130859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztesi, A.; Nita, I.A.; Birsan, M.V.; Bodor, Z.; Pernyeszi, T.; Micheu, M.M.; Szép, R. Assessing the variations in the chemical composition of rainwater and air masses using the zonal and meridional index. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, Z.; Ayitken, M.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Chemical Composition Characteristics and Source Contributions of Precipitation in Typical Cities on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountain in Xinjiang during 2010–2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.N.; Luo, X.C.; Liu, D.Y.; Su, Y.; Wu, Z.Y. The effect of construction dust and agricultural fertilization on the precipitation chemical composition during summer in the Yangtze River Delta area, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. The Chemical Characteristics and Environmental Significance of Atmospheric Precipitation in Shanghai Area. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Relationship between the Characteristics of Precipitation and Air Quality in Nanjing. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural university, Nanjing, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. The Chemical Characteristics and Nitrate Sources Analysis of Precipitation in Typical Cities in Southeast China. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang university of technology, Zhejiang, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ai, D.S. Chemical Characteristics of Wet Precipitation in Shanghai and Its Source Analysis. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.A.; Lin, T.J.; He, L. Chemical compositions and sources of precipitation in Shenzhen from 2010 to 2017. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 1872–1881, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.l.; Wu, Q.X.; Tang, Y. Effects of agricultural alkaline substances on reducing the rainwater acidification: Insight from chemical compositions and calcium isotopes in a karst forests area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 290, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J. The Characteristic Change of Atmospheric Precipitation and Indicative Significance of Dust Weather in Shiyang River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Gansu, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).