Investigation and Evaluation of Flue Gas Pollutants Emission in Waste-to-Energy Plant with Flue Gas Recirculation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
2.1. Materials
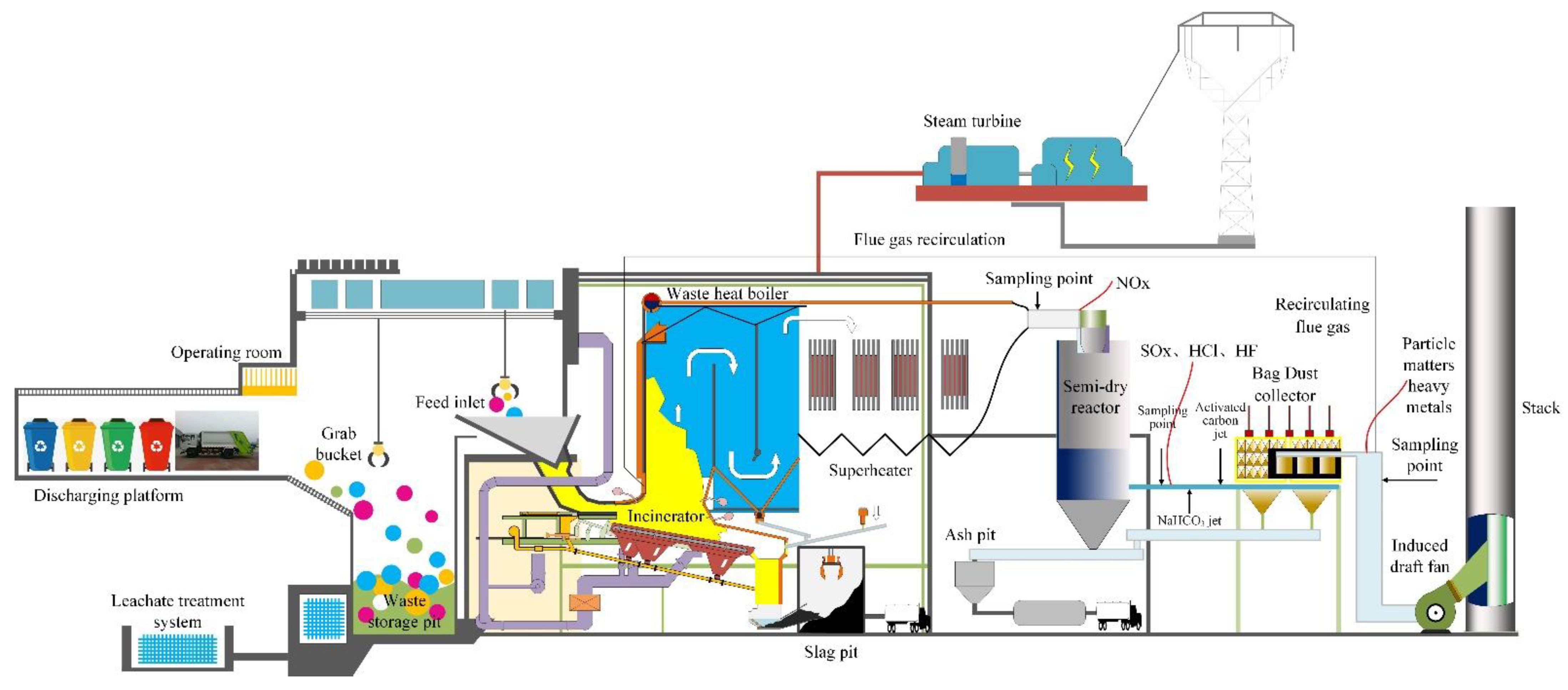
2.2. Plant Description
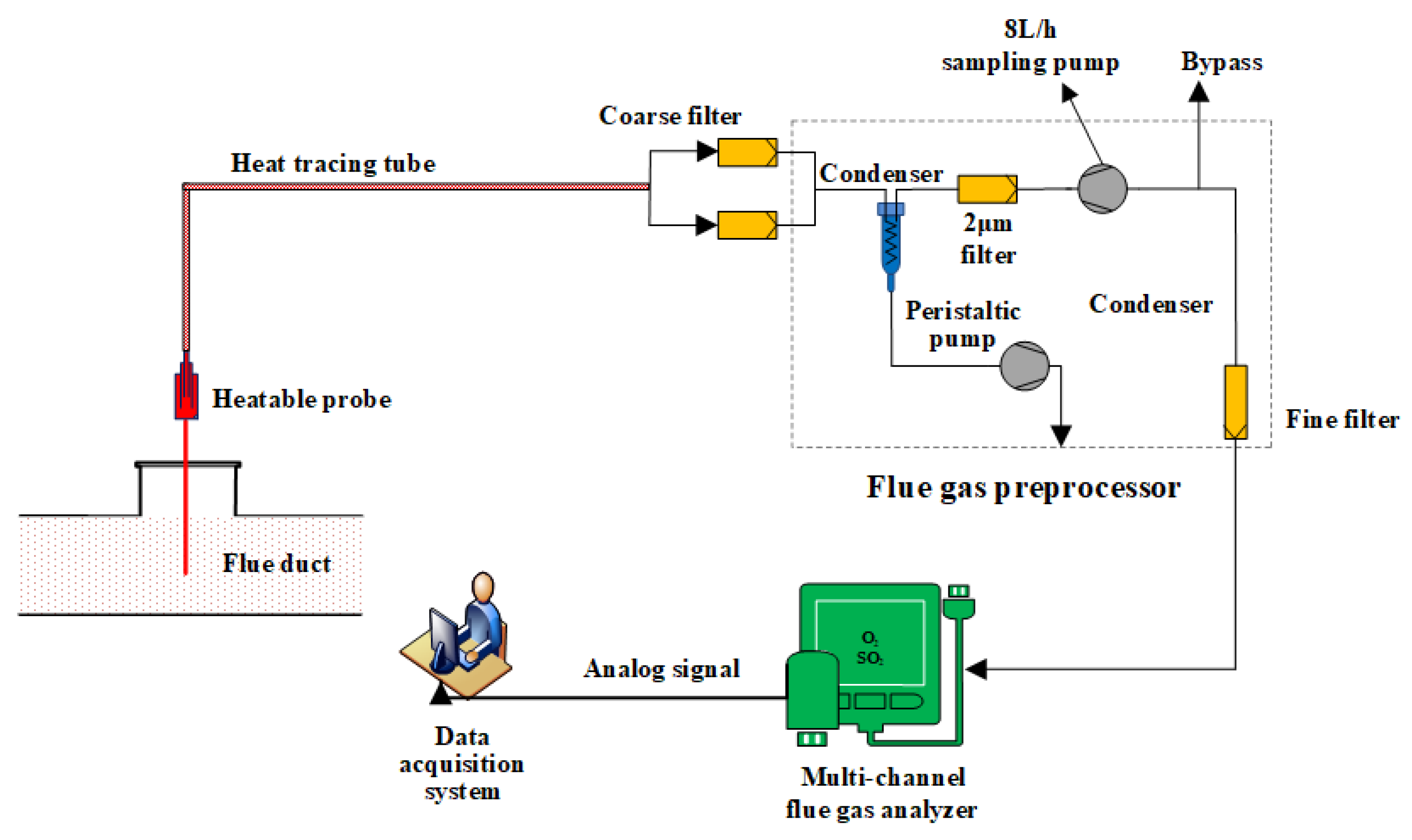
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Emission Level of NOx
3.2. Emission Levels of Other Acid Gases
3.3. PM Emission Levels
3.4. Emission Levels of Heavy Metals
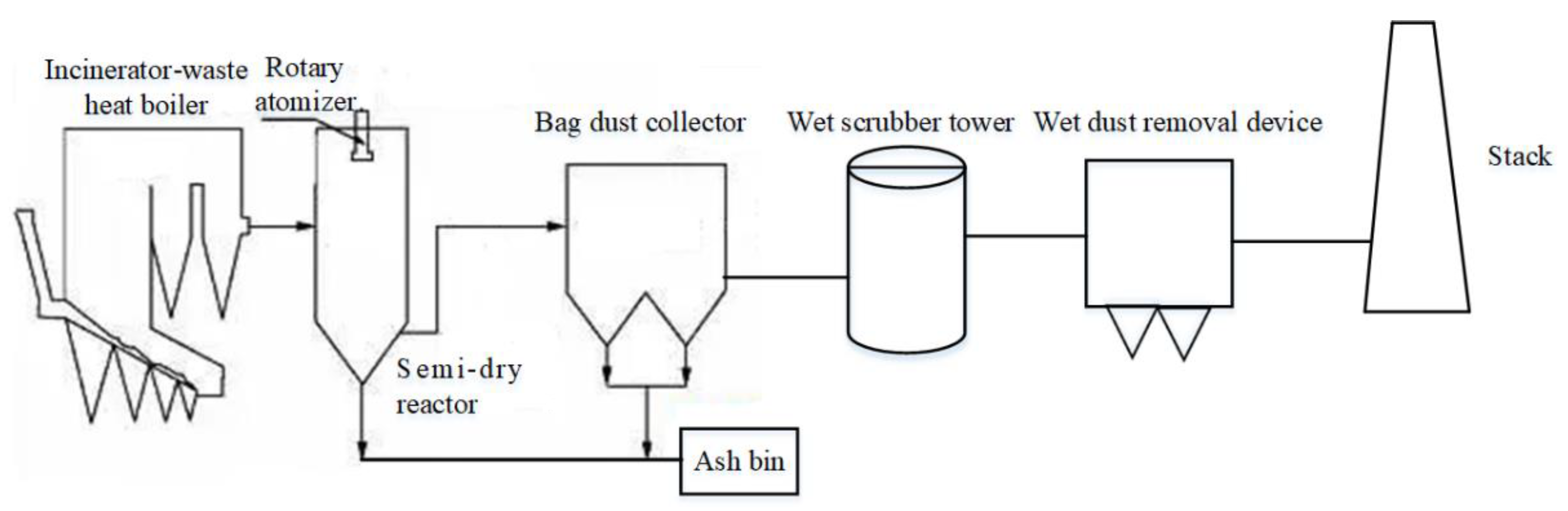
3.5. Improvement in Flue Gas Cleaning System
4. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Full Names | Abbreviation | Full Names | Abbreviation | Full Names | Abbreviation | Full Names | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nitrogen oxide | NOx | Carbon dioxide | CO2 | Cadmium | Cd | Cuprum | Cu |
| sulfur dioxide | SO2 | Nitric oxide | NO | Titanium | Ti | Manganese | Mn |
| hydrogen chloride | HCl | Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)2 | Lead | Pb | Nickel | Ni |
| hydrogen fluoride | HF | Sodium bicarbonate | NaHCO3 | Chromium | Cr | Vanadium | V |
| methane | CH4 | Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 | Antimony | Sb | Mercury | Hg |
| oxygen | O2 | Nitric acid | HNO3 | Arsenic | As | ||
| carbon monoxide | CO | Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | Cobalt | Co |
References
- Wang, Z.D.; Teng, Y.; Hui, Q.; Chen, Z. A Sustainable Development Multi-energy System Planning Method Incorporating the Demand of Waste Disposal and Peak Shaving. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 3781–3797. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Ma, Z.; Hao, J.; Jiang, J. Characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter emitted from two waste incineration power plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, M.; Gao, X.; Su, J. Evaluation of a flue gas cleaning system of a circulating fluidized bed incineration power plant by the analysis of pollutant emissions. Powder Technol. 2015, 286, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.F.; Jiang, E.C.; Ma, X.Q. Numerical simulation on NOx emissions in a municipal solid waste incinerator. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, C.T.; Sam, K.C.; Tan, S.T. Waste Management Pinch Analysis (WAMPA): Application of Pinch Analysis for greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction in municipal solid waste management. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Shi, Z.Q. How China views the EU in global energy governance: A norm exporter, a partner or an outsider? Comp. Eur. Polit. 2017, 15, 80–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, H.Z.; Hossain, Q.H.; Monir, M.M.U.; Ahmed, M.T. Municipal solid waste (MSW) as a source of renewable energy in Bangladesh: Revisited. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.P. Address at the General Debate of the seventy-fifth Session of the United Nations General Assembly. In Proceedings of the 75th Session of the United Nations General Assembly, New York, NY, USA, 23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jia, M.; Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Kao, C.M.; Chen, S. A comparison of CH4, N2O and CO2 emissions from three different cover types in a municipal solid waste landfill. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafari, N.H.; Stark, T.D.; Thalhamer, T. Spatial and temporal characteristics of elevated temperatures in municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Duan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mustafa, M.F.; Lu, W.; Wang, H. Characteristics of volatile compound emission and odor pollution from municipal solid waste treating/disposal facilities of a city in Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18383–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edjabou, M.E.; Takou, V.; Boldrin, A.; Petersen, C.; Astrup, T.F. The influence of recycling schemes on the composition and generation of municipal solid waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.L.; Zhong, L.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.W. Analysis on Calorific Value of Municipal Solid Waste as Fired in China. Adv. New Renew. Energy 2021, 9, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.; He, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Su, L.; Duan, Z.; Song, J.; Tong, W.; Li, X. Process simulation and optimization of municipal solid waste fired power plant with oxygen/carbon dioxide combustion for near zero carbon dioxide emission. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 157, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhou, X.-y.; Wu, Y.-w.; Mi, T.-g.; Liu, J.; Hu, B.; Zhao, L. Interaction mechanism between cadmium species and SiO2 of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: Effect of HCl. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.; Abis, M.; Kuchta, K.; Simon, F.-G.; Grönholm, R.; Hoppe, M.; Fiore, S. Material flow, economic and environmental assessment of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash recycling potential in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, M.-Y.; Ou, W.-Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Tseng, H.-H.; Yang, W.-Y.; Chiang, B.-C. Pollutants in incineration flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 82, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Yao, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, W. Influence of flue gas recirculation on the performance of incinerator-waste heat boiler and NOx emission in a 500 t/d waste-to-energy plant. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.Y.; Ma, X.Q. Mathematical modeling of MSW combustion and SNCR in a full-scale municipal incinerator and effects of grate speed and oxygen-enriched atmospheres on operating conditions. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2520–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CJJ 90-2009; Technical Code for Projects of Municipal Waste Incineration. State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Yi, H.; Hao, J.; Duan, L.; Tang, X.; Ning, P.; Li, X. Fine particle and trace element emissions from an anthracite coal-fired power plant equipped with a bag-house in China. Fuel 2008, 87, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CJ/T 531-2018; Testing, Sampling and Sample Preparation of Slag and Ash from Waste Incinerator. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- HJ 57-2017; Stationary Source Emission. Determination of Sulfur Dioxide. Fixed Potential by Electrolysis Method. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- EPA method 26A; Determination of Hydrogen Halide and Halogen Emissions from Stationary Sources–Non-Isokinetic Method. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- GB/T 16157-1996; Determination of Particulates and Sampling Methods of Gaseous Pollutants Emitted from Exhaust Gas of Stationary Source. State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1996.
- EPA Method 29; Determination of Metals Emissions from Stationary Sources. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2017.
- HJ 501-2009; Water Quality. Determination of Total Organic Carbon. Combustion Oxidation Nondispersive Infrared Absorption Method. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Jepsen, M.S.; Jensen, P.A.; Clausen, S.; Fateev, A.; Glarborg, P.; Norman, T. Measurements of the NOx precursors and major species concentrations above the grate at a waste-to-energy plant. Fuel 2018, 222, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, B.; Lei, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, T.; Song, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L. Combustion optimization and NOx reduction of a 600 MWe down-fired boiler by rearrangement of swirl burner and introduction of separated over-fire air. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2000/76/EC; Directive 2000/76/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Incineration of Waste. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- GB18485-2014; Standard for Pollution Control on the Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Takaoka, M.; Shiota, K.; Imai, G.; Oshita, K. Emission of particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) and elements from municipal solid waste incinerators. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju Elizbath, P.; Shiva, N.S.M.; Indumathi, M.N. Comprehensive analysis of inhalable toxic particulate emissions from an old municipal solid waste dumpsite and neighborhood health risks. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Fu, J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Q. Environmental and human health risk evaluation of heavy metals in ceramsites from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3779–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.M.; Liao, Y.F.; Ma, X.Q. Heavy metals volatilization characteristics and risk evaluation of co-combusted municipal solid wastes and sewage sludge without and with calcium-based sorbents. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2019, 182, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASME PTC 4.3-2017; Air Heaters Performance Test Codes. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
| MSW | Proximate Analysis (wt%) a | Ultimate Analysis (wt%) b | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Combustible Matter | Ash | LHV (kJ/kg) | C | H | O | N | S | Cl | |
| Received | 44.31 | 35.38 | 20.31 | 6699 | 54.55 | 7.72 | 34.62 | 1.90 | 0.31 | 0.90 |
| Name of Facility | Item | Unit | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incinerator and waste heat boiler | Type of incinerator | - | Reciprocating mechanical grate furnace |
| Daily waste treatment capacity | t/d | 500 | |
| Boiler rated evaporating capacity (MCR) | t/h | 51.80 | |
| Rated steam pressure | MPa | 4.00 | |
| Main steam temperature | °C | 400 | |
| Denitrification system | Type of denitrification system | - | SNCR + flue gas recirculation |
| Flow of recirculating flue gas | m3/h | 0~26,240 | |
| Reagents of SNCR | - | Urea | |
| Number of nozzle | - | 12 (three layers arrangement) | |
| Flow rate of urea (per nozzle) | L/min | 3.2 | |
| Deacidification system | Type | - | Semi-dry method (rotating spray reaction towers) + dry method (NaHCO3 injection) + activated carbon injection |
| Inlet temperature of semidry reactor | °C | 190 | |
| Consumption of Ca(OH)2 (semidry method) | kg/t MSW | 8.0 | |
| Consumption of NaHCO3 (dry method) | kg/t MSW | 2.5 | |
| Consumption of activated carbon | kg/t MSW | 0.5 | |
| Dust collector | Type | - | Bag dust collector |
| Flue gas temperature | °C | 155 | |
| Removal efficiency | % | >99.80 | |
| Dust content at outlet (11% O2, dry basis) | mg/m3 | <8.00 | |
| Air leakage rate | % | 2% |
| Item | Unit | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opening of recirculating flue gas damper | % | 100 | 50 | 0 |
| Flow rate of recirculating flue gas | m3/h | 16,163.93 | 9345.65 | 0.00 |
| Flue gas temperature at outlet of economizer | °C | 193 | 195 | 198 |
| CO2 emission concentration | % | 14.07 | 14.13 | 13.92 |
| CO emission concentration | mg/m3 | 11.48 | 11.30 | 9.56 |
| NOx emission concentration | mg/m3 | 126.15 ± 5.60 | 178.90 ± 6.23 | 209.54 ± 6.45 |
| NOx emission limit of plant (daily average) | mg/m3 | 180.00 | ||
| CNS emission limit [31] (daily average) | mg/m3 | 250.00 | ||
| EC emission limit [30] (daily average) | mg/m3 | 200.00 | ||
| Acid Gas | SO2 | HCl | HF | TOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 |
| Value | 23.65 ± 2.31 | 16.90 ± 2.52 | 0.58 ± 0.06 | 0.62 ± 0.03 |
| Emission limit of the plant (daily average) | 30.00 | 8.00 | 1.00 | 10.00 |
| CNS emission limit [31] (daily average) | 80.00 | 50.00 | - | - |
| EC emission limit [30] (daily average) | 50.00 | 10.00 | 1.00 | 10.00 |
| Element | Hg | Cd + Ti | Pb + Cr |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 |
| Value | 1.45 × 10−4 | 3.90 × 10−3 | 0.21 |
| Emission limit of plant (daily average) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.50 |
| CNS emission limit [31] (daily average) | 0.05 | 0.10 a | 1.00 b |
| EC emission limit [30] (daily average) | 0.05 | 0.05 c | 0.50 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Tian, S.; Long, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Z. Investigation and Evaluation of Flue Gas Pollutants Emission in Waste-to-Energy Plant with Flue Gas Recirculation. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071016
Wang W, Tian S, Long J, Liu J, Ma Q, Xu K, Zhang Z. Investigation and Evaluation of Flue Gas Pollutants Emission in Waste-to-Energy Plant with Flue Gas Recirculation. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071016
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weishu, Shujian Tian, Jisheng Long, Jun Liu, Qinhui Ma, Kai Xu, and Zhen Zhang. 2022. "Investigation and Evaluation of Flue Gas Pollutants Emission in Waste-to-Energy Plant with Flue Gas Recirculation" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071016
APA StyleWang, W., Tian, S., Long, J., Liu, J., Ma, Q., Xu, K., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Investigation and Evaluation of Flue Gas Pollutants Emission in Waste-to-Energy Plant with Flue Gas Recirculation. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071016






