Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
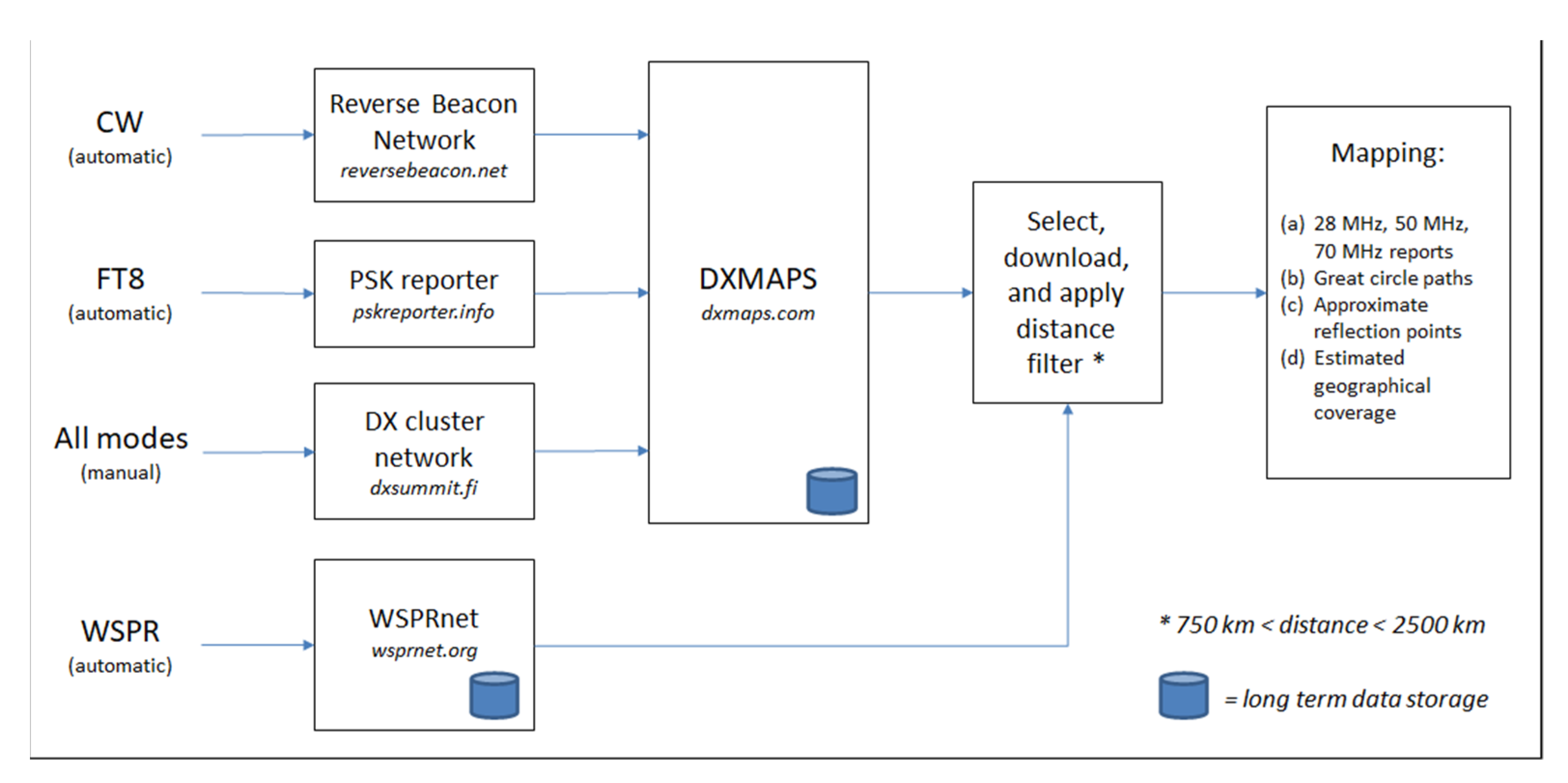
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Es Detection Using Amateur Data
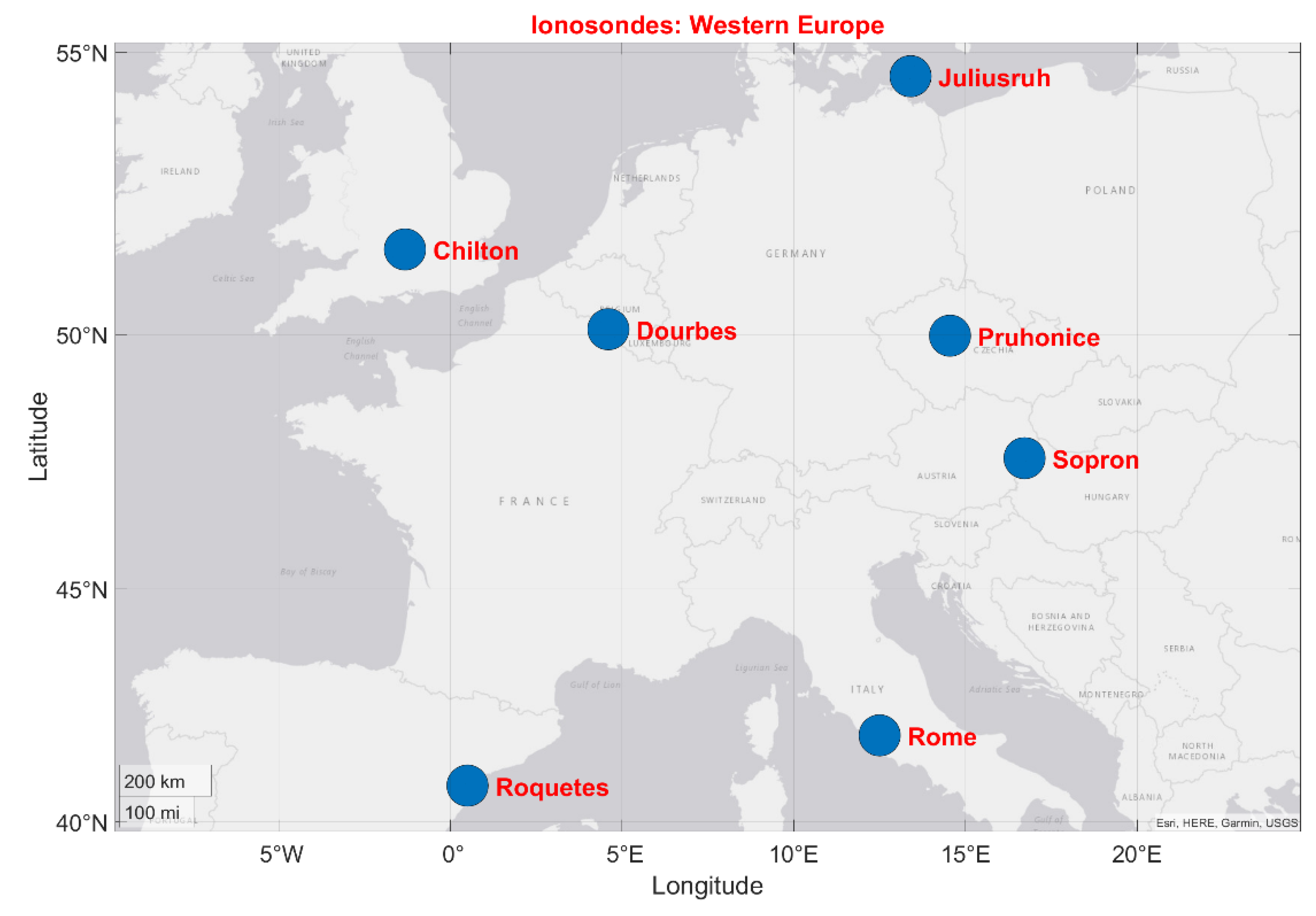
2.2. Validation against Ionosonde Data
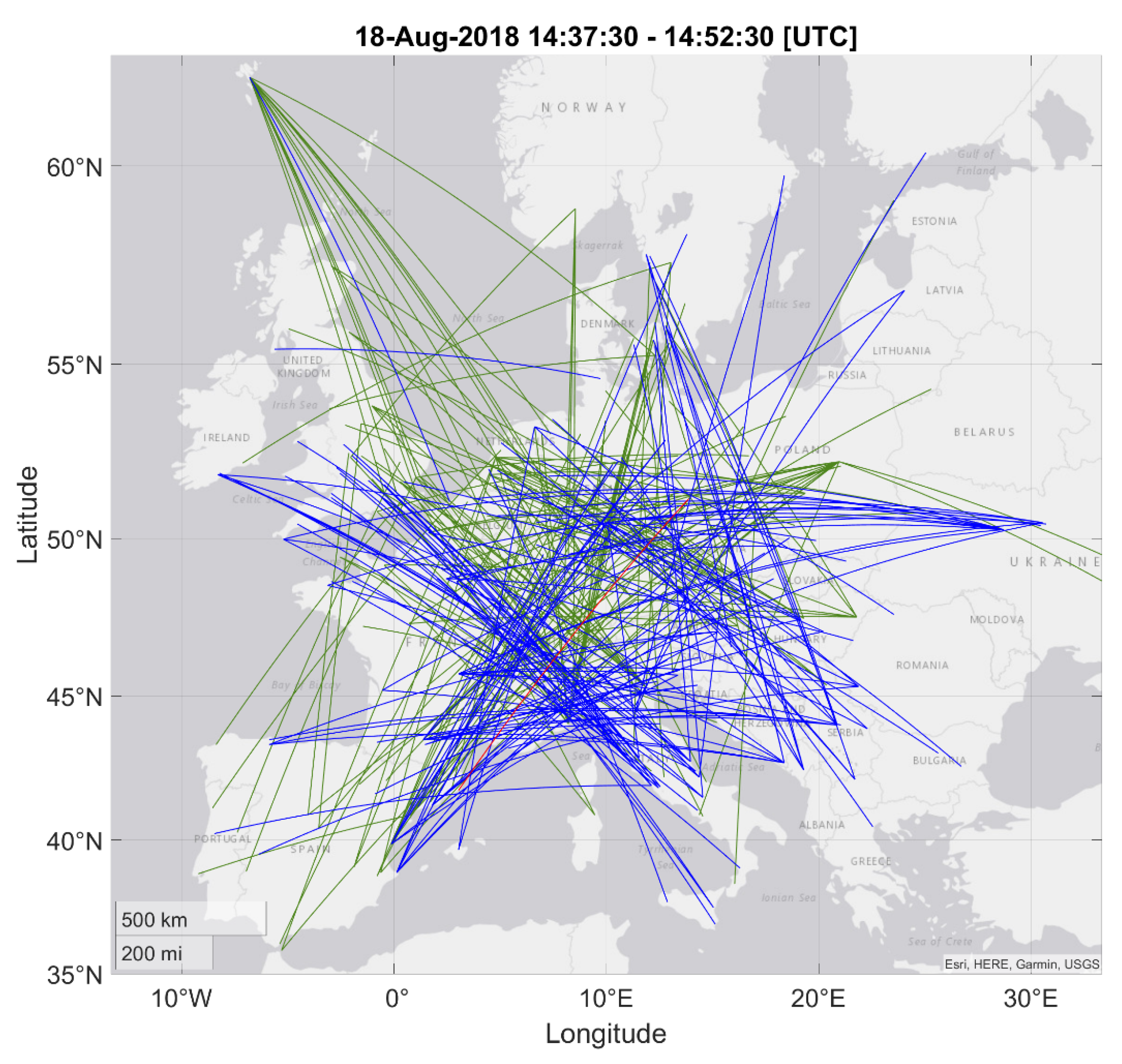
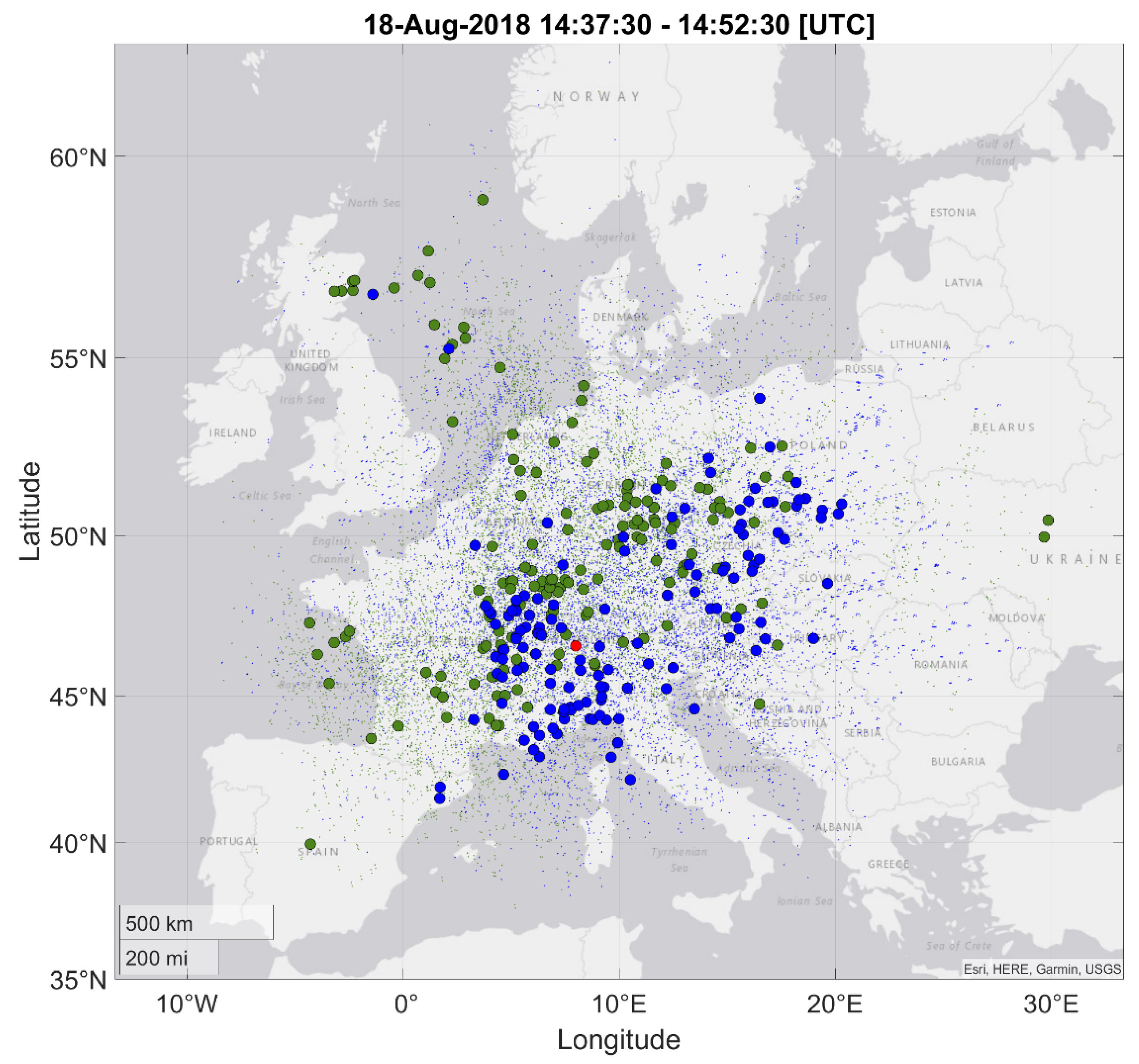
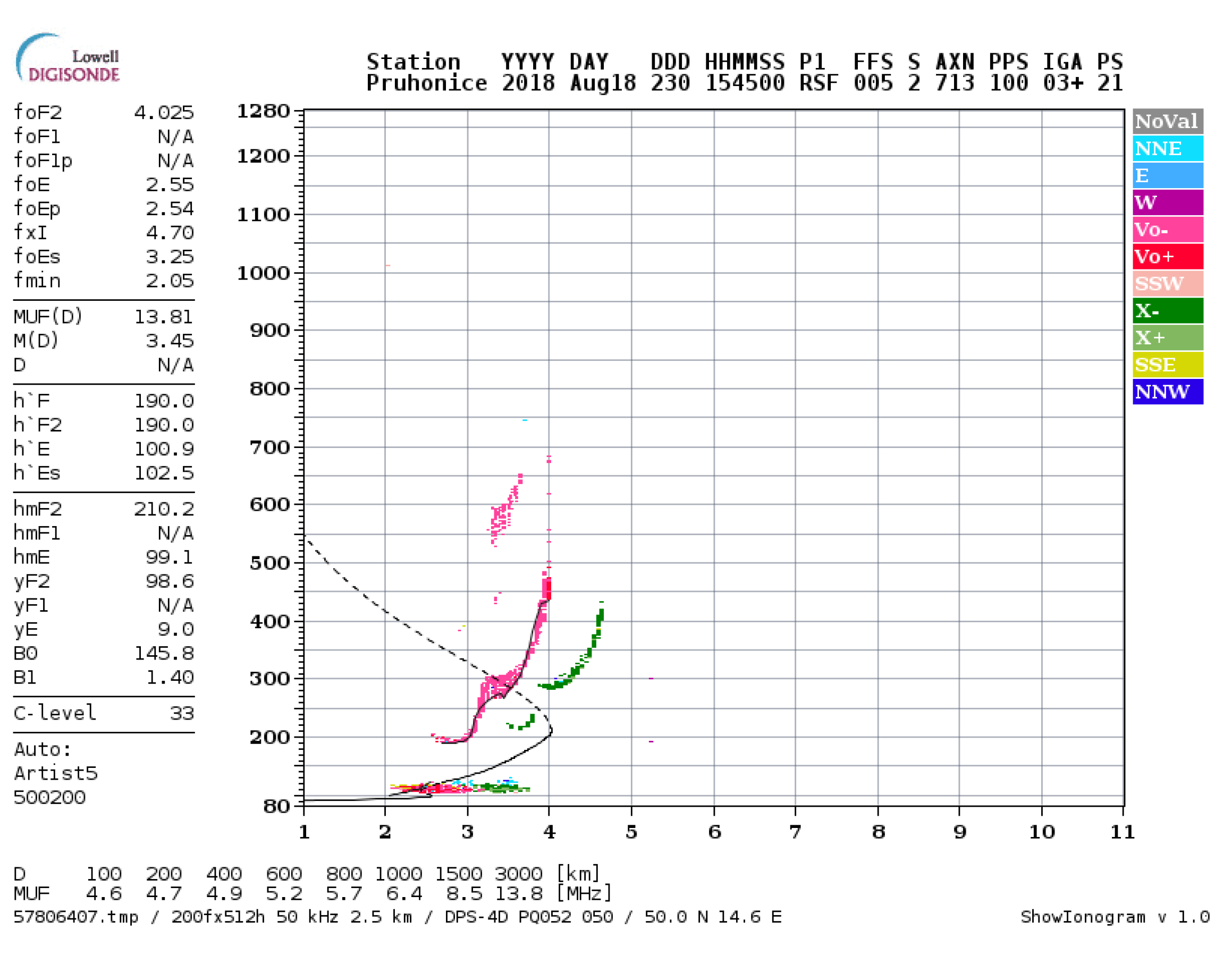
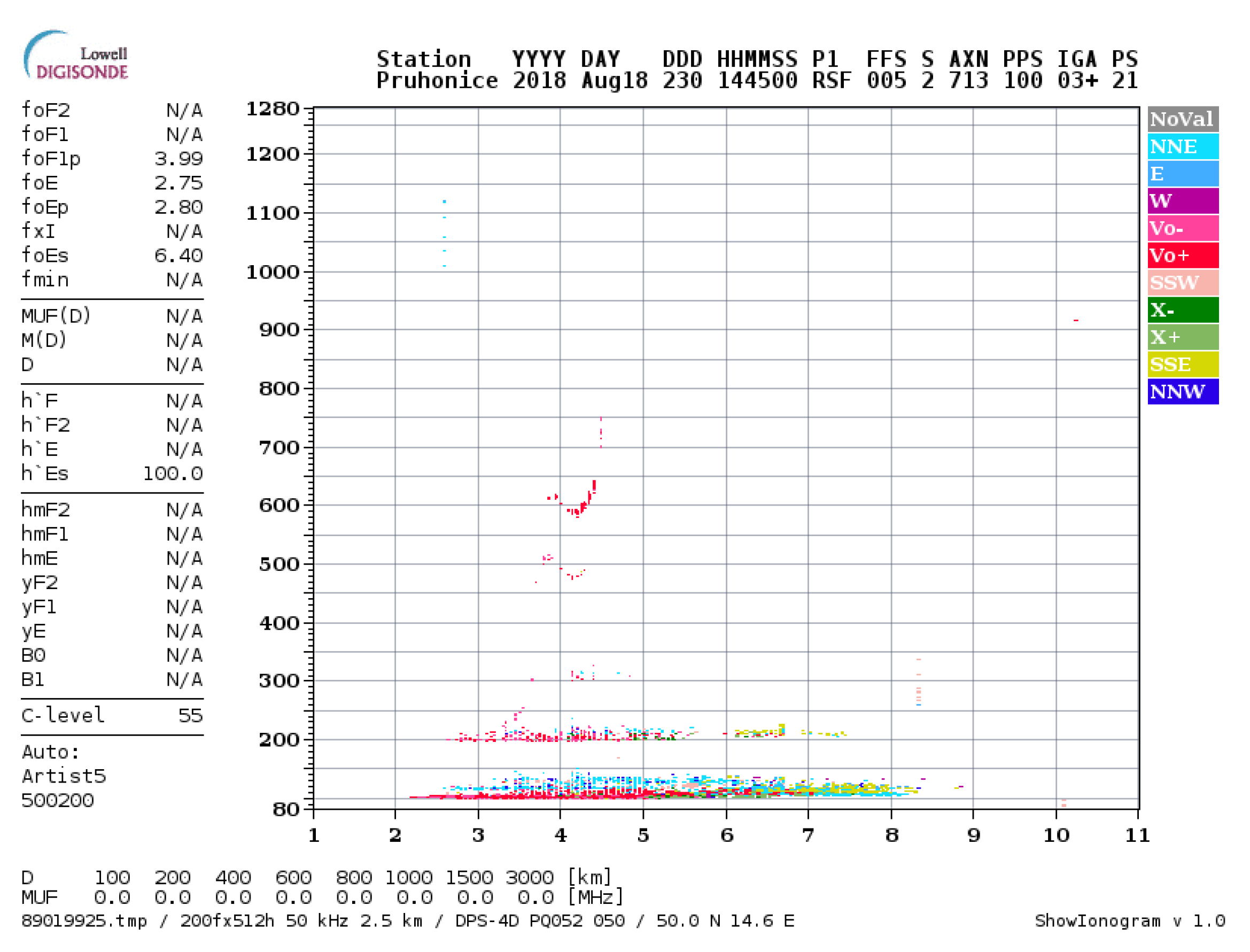
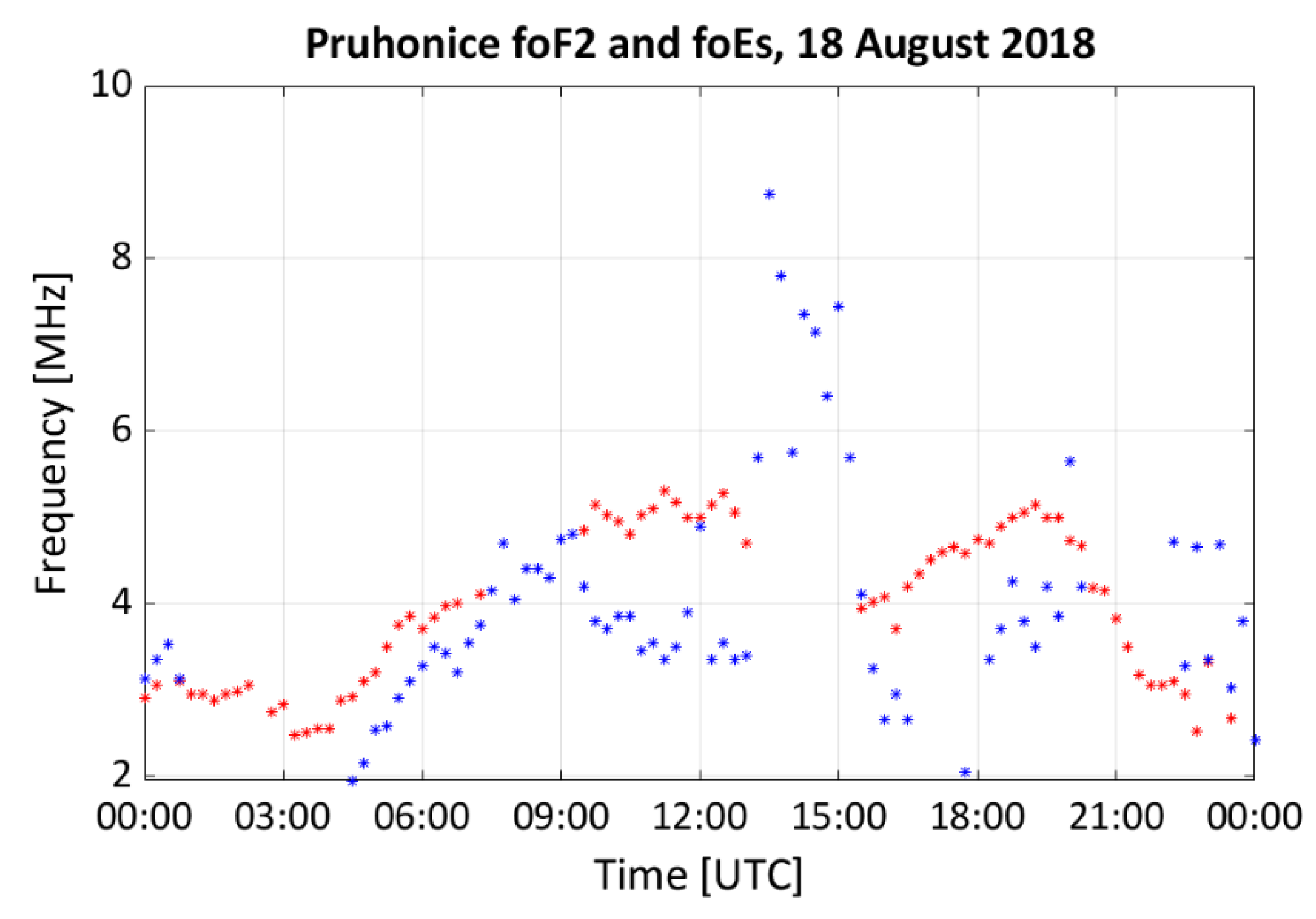
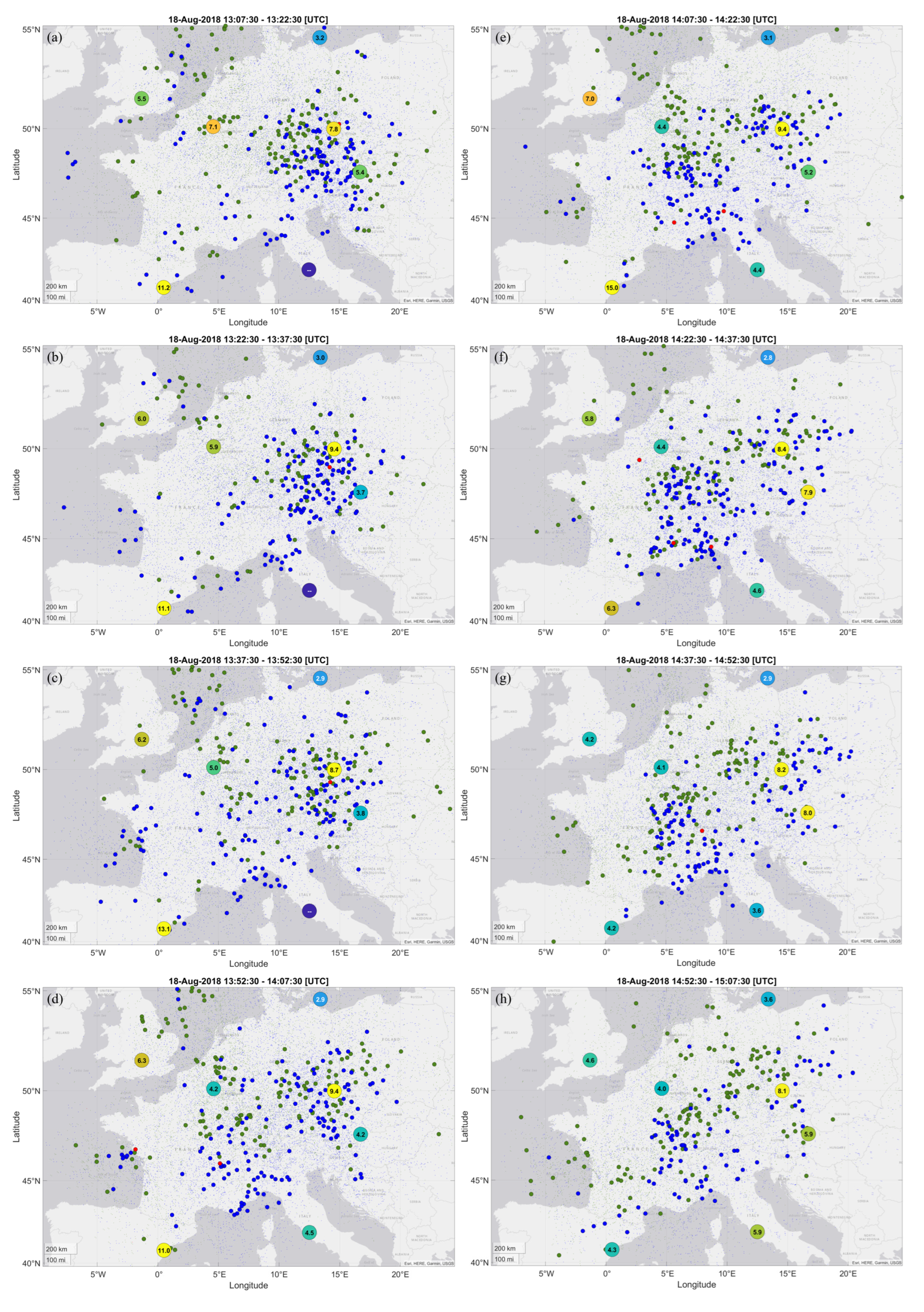
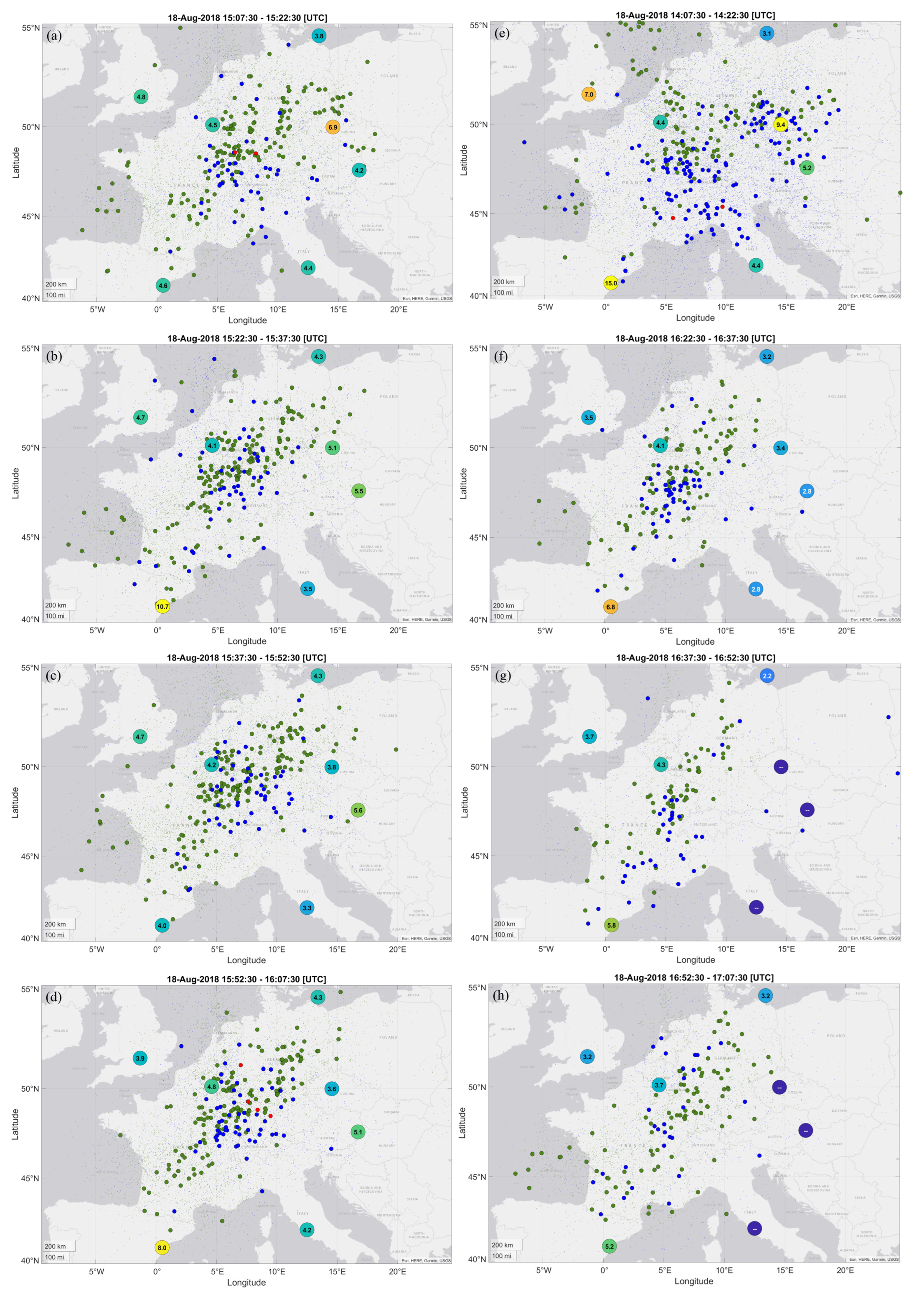
3. Case Study Results
4. Case Study Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vincent, R.A. The dynamics of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere: A brief review. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.M.; Killeen, T.L. The Upper Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere: A Review of Experiment and Theory; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.D. Recent work on mid-latitude and equatorial sporadic-E. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1989, 51, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D. Sporadic E: Current views and recent progress. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 1998, 60, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C. A tutorial review on sporadic E layers. In Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere; Abdu, M., Pancheva, D., Eds.; IAGA Special Sopron Book Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K. Temperate zone sporadic-E maps (foEs > 7 MHz). Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakis, N.; Haldoupis, C.; Zhou, Q.; Meek, C. Seasonal variability and descent of mid-latitude sporadic E layers at Arecibo. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grebowsky, J.M.; Bilitza, D. Sounding rocket data base of E-and D-region ion composition. Adv. Space Res. 2000, 25, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K. Worldwide Occurrence of Sporadic E; US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1957; Volume 582, pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.G.; Mechtly, E.A. Rocket observations of sporadic-E layers. Radio Sci. 1972, 7, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From, W.R.; Whitehead, J.D. On the peculiar shape of sporadic-E clouds. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1978, 40, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, E. On the abundance of metal ions in the lower ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 9667–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D.; Zhou, Q.; Philbrick, C.R.; Morton, Y.T.; Gardner, C.S. Observations of ion and sodium layer coupled processes during AIDA. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1993, 55, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Sojka, J.; Rice, D.; Oberheide, J.; Criddle, N. Investigation of the seasonal and local time variations of the high-altitude sporadic Na layer (Nas) formation and the associated midlatitude descending E layer (Es) in lower E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 5985–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Eccles, J.V.; Raizada, S. Investigation on the distinct nocturnal secondary sodium layer behavior above 95 km in winter and summer over Logan, UT (41.7° N, 112° W) and Arecibo Observatory, PR (18.3° N, 67° W). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 9610–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.D. The formation of the sporadic-E layer in the temperate zones. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1961, 20, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C.; Pancheva, D.; Singer, W.; Meek, C.; MacDougall, J. An explanation for the seasonal dependence of midlatitude sporadic E layers. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zuo, X.; Yu, T.; Sun, Y.; Qi, Y. Comparison of global morphologies of vertical ion convergence and sporadic E occurrence rate. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 3606–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Arras, C.; Andoh, S.; Miyoshi, Y.; Shinagawa, H.; Harding, B.J.; Englert, C.R.; Immel, T.J.; Sobhkhiz-Miandehi, S.; Stolle, C. Examining the wind shear theory of sporadic E with ICON/MIGHTI winds and COSMIC-2 Radio 2 occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, K. My memory of efforts in developing CCIR Recommendation 534-3: Method for calculating sporadic-E field strength. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1996, 38, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K.; Igarashi, K. VHF sporadic E—A significant factor for EMI. Proc. Int. Symp. EMC 1997, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Schreiner, W.S.; Pedatella, N.M.; Kuo, Y.H. Characterizing GPS radio occultation loss of lock due to ionospheric weather. Space Weather 2016, 14, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arras, C.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Heise, S.; Schmidt, T.; Jacobi, C. A global climatology of ionospheric irregularities derived from GPS radio occultation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, C.; Wickert, J. Estimation of ionospheric sporadic E intensities from GPS radio occultation measurements. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2018, 171, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.C.; Su, S.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Schuh, H.; Wickert, J.; Alizadeh, M.M. Global morphology of ionospheric sporadic E layer from the FormoSat-3/COSMIC GPS radio occultation experiment. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinisch, B.W.; Galkin, I.A. Global ionospheric radio observatory (GIRO). Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haldoupis, C.; Meek, C.; Christakis, N.; Pancheva, D.; Bourdillon, A. Ionogram height–time–intensity observations of descending sporadic E layers at mid-latitude. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Ning, B.; Yue, X.; Li, G.; Hu, L.; Chang, S.; Lin, J. Strong sporadic E occurrence detected by ground-based GNSS. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 3050–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, W.J. Seasonal characteristics of daytime Es occurrence in the southern hemisphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1985, 47, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBU Technical Centre. Ionospheric propagation in Europe in VHF television band I. In EBU Technical Document TECH 3214; European Broadcasting Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, C.J.; Witvliet, B.A.; Mitchell, C.N. Investigation of the polarization of 50 MHz signals via Sporadic-E reflection. In Proceedings of the Nordic HF Conf (August 2019). Nordic Shortwave Conference, Fårö, Sweden, 12–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, C.J.; Witvliet, B.A.; Steendam, S.N.; Mitchell, C.N. Rapid and accurate measurement of polarization and fading of weak VHF signals obliquely reflected from sporadic-E Layers. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 69, 4033–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, J.; Saito, S.; Hosokawa, K.; Tomizawa, I. Anomalous propagation of radio waves from distant ILS localizers due to ionospheric sporadic-E. Space Weather 2020, 18, e2020SW002517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, K.; Kimura, K.; Sakai, J.; Saito, S.; Tomizawa, I.; Nishioka, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Ishii, M. Visualizing sporadic E using aeronautical navigation signals at VHF frequencies. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2021, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kojima, T. Oblique-incidence sporadic-E propagation and its ionospheric attenuation. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frissell, N.A.; Miller, E.S.; Kaeppler, S.R.; Ceglia, F.; Pascoe, D.; Sinanis, N.; Smith, P.; Williams, R.; Shovkoplyas, A. Ionospheric sounding using real-time amateur radio reporting networks. Space Weather 2014, 12, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frissell, N.A.; Katz, J.D.; Gunning, S.W.; Vega, J.S.; Gerrard, A.J.; Earle, G.D.; Moses, M.L.; West, M.L.; Huba, J.D.; Erickson, P.J.; et al. Modeling amateur radio soundings of the ionospheric response to the 2017 Great American Eclipse. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4665–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frissell, N.A.; Vega, J.S.; Markowitz, E.; Gerrard, A.J.; Engelke, W.D.; Erickson, P.J.; Miller, E.S.; Luetzelschwab, R.C.; Bortnik, J. High-frequency communications response to solar activity in September 2017 as observed by amateur radio networks. Space Weather 2019, 17, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frissell, N.A.; Kaeppler, S.R.; Sanchez, D.F.; Perry, G.W.; Engelke, W.D.; Erickson, P.J.; Coster, A.J.; Ruohoniemi, J.M.; Baker, J.B.; West, M.L. First Observations of Large Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Using Automated Amateur Radio Receiving Networks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL097879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://reversebeacon.net/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Available online: https://pskreporter.info/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Available online: https://www.wsprnet.org/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Available online: http://www.dxsummit.fi/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Available online: https://www.dxmaps.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Miya, K.; Sasaki, T. Characteristics of ionospheric Es propagation and calculation of Es signal strength. Radio Sci. 1966, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.J. Data and code for “Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers”. Bath Univ. Bath Res. Data Arch. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deacon, C.; Mitchell, C.; Watson, R. Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060906
Deacon C, Mitchell C, Watson R. Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060906
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeacon, Chris, Cathryn Mitchell, and Robert Watson. 2022. "Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060906
APA StyleDeacon, C., Mitchell, C., & Watson, R. (2022). Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers. Atmosphere, 13(6), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060906





