Comparison of Fluorescent Techniques Using Two Enzymes Catalysed for Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
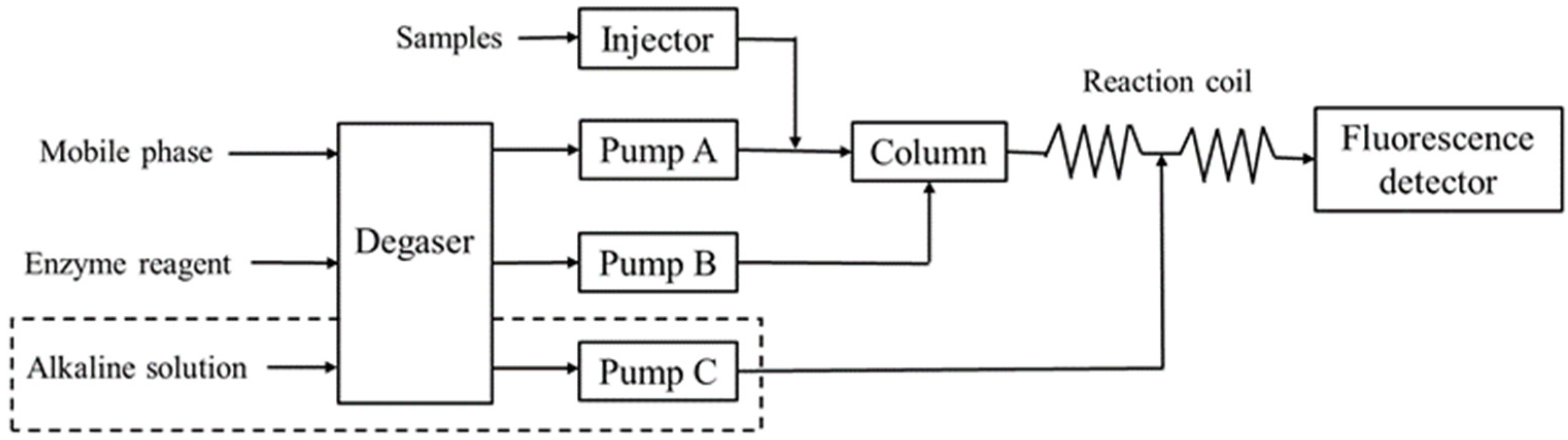
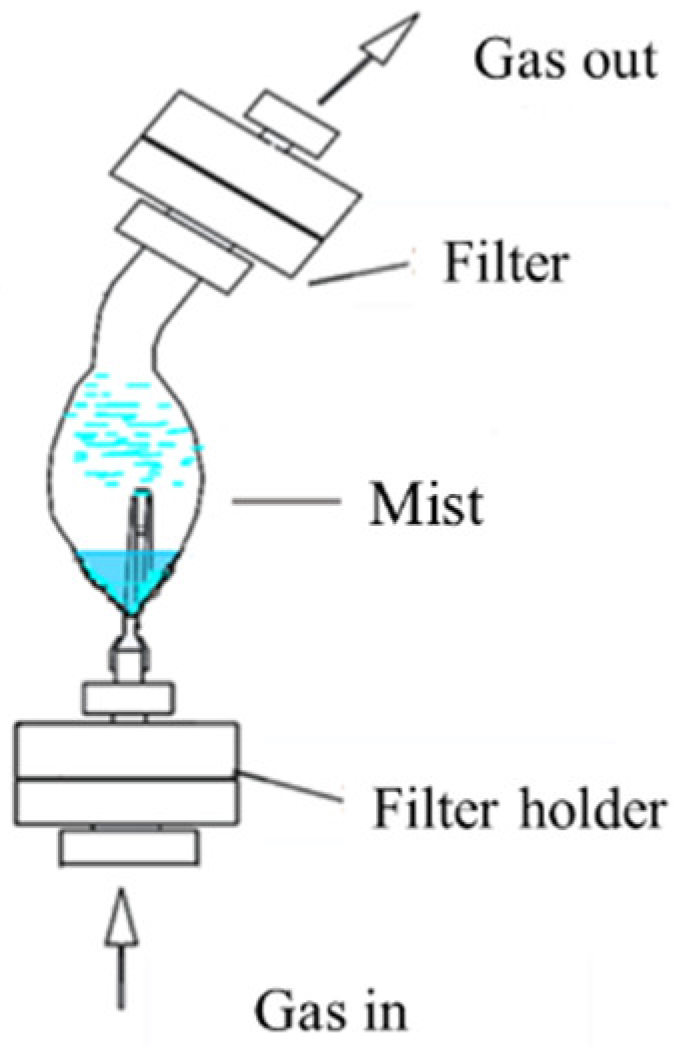
2.1. Experimental Methods
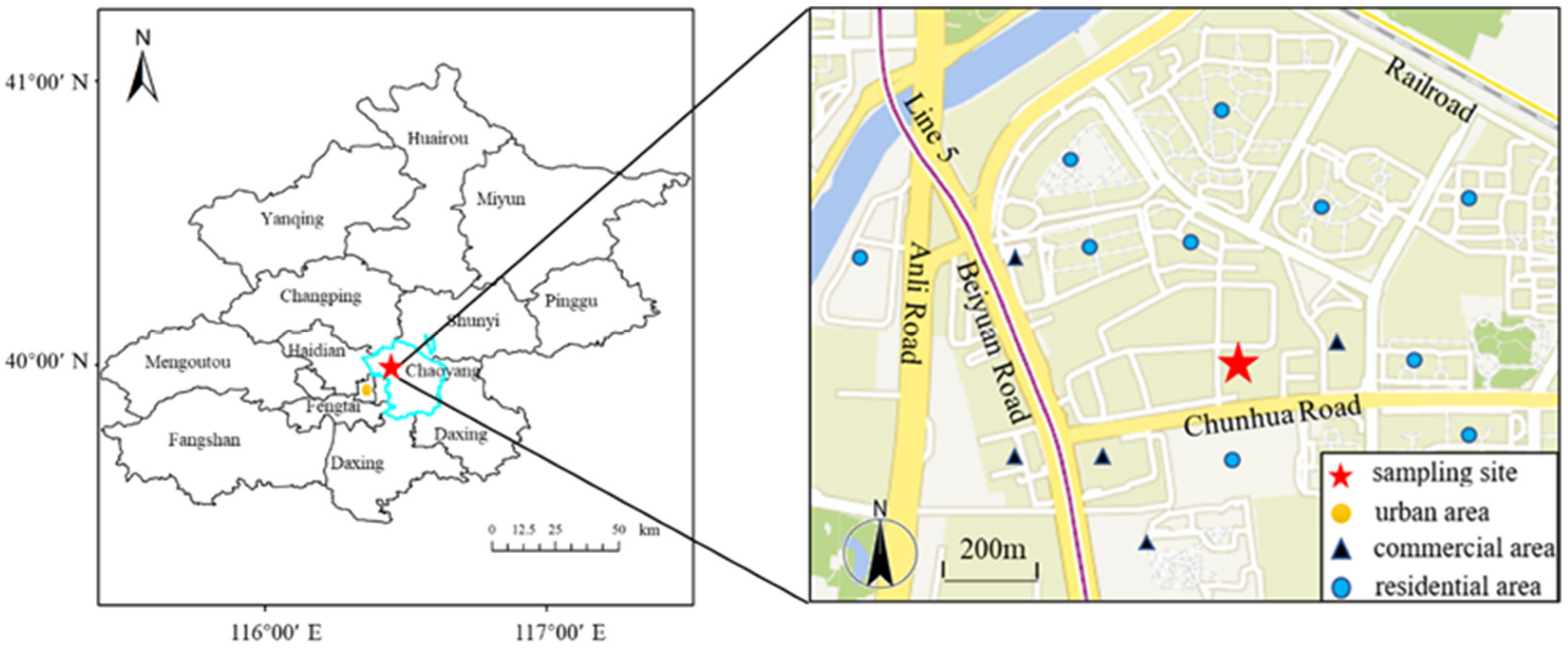
2.2. Field Observation
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
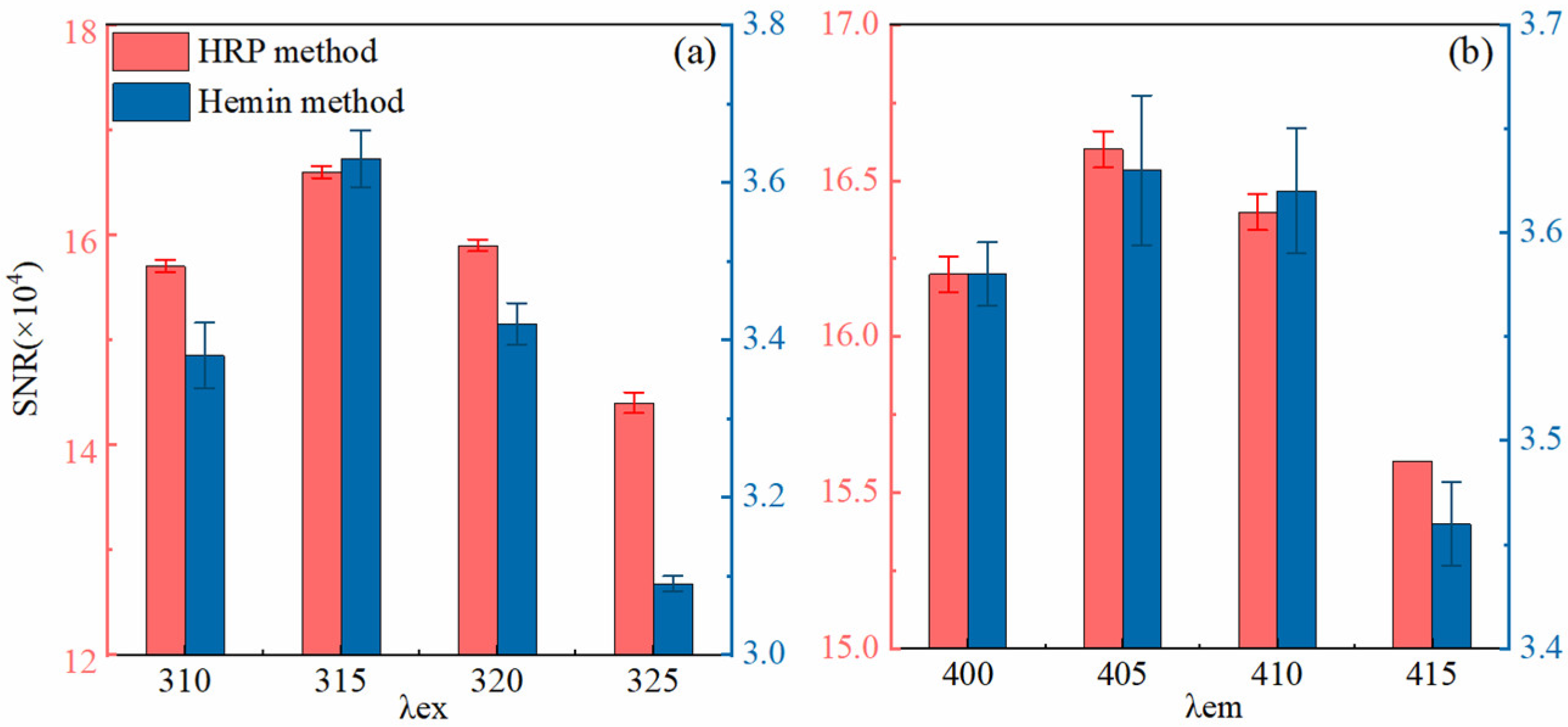
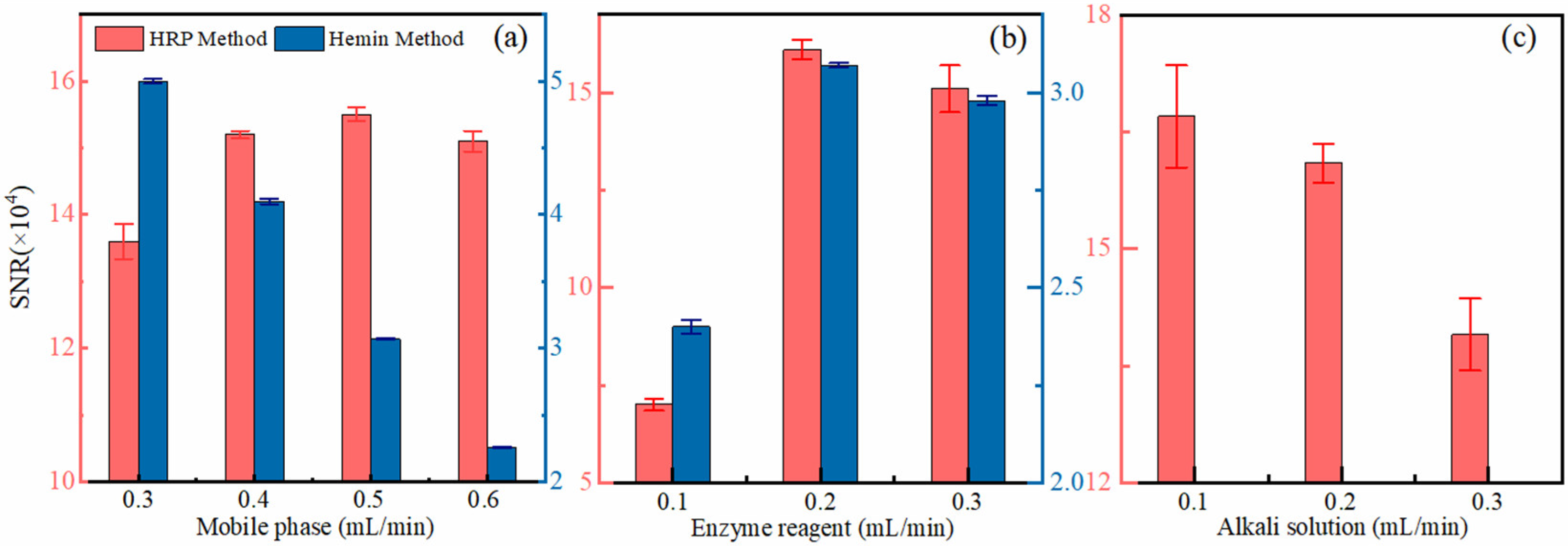
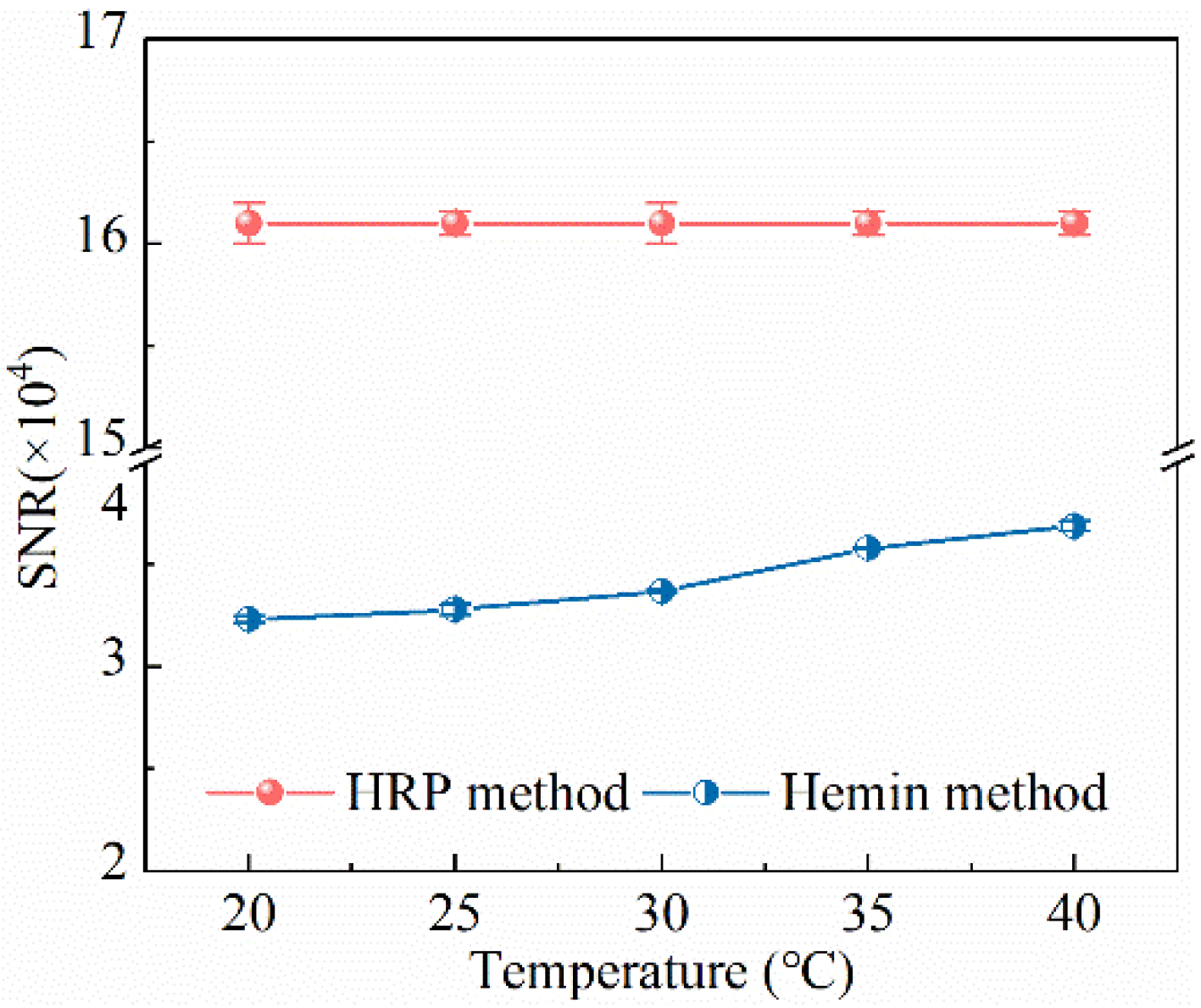
3.1. Optimum Analysis Conditions of Two Methods
3.2. Comparison of Two Methods
3.2.1. Detection Limit
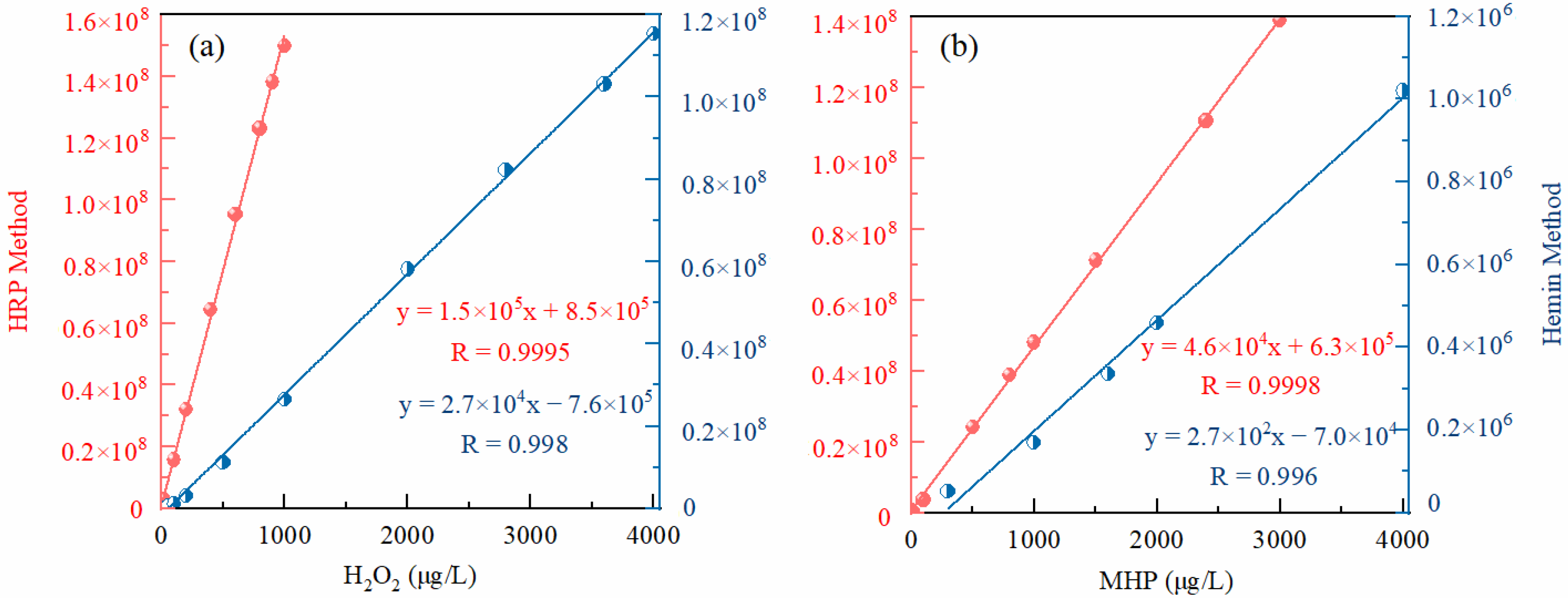
3.2.2. Calibration Curve and Sensitivity
3.2.3. Precision
3.2.4. Accuracy
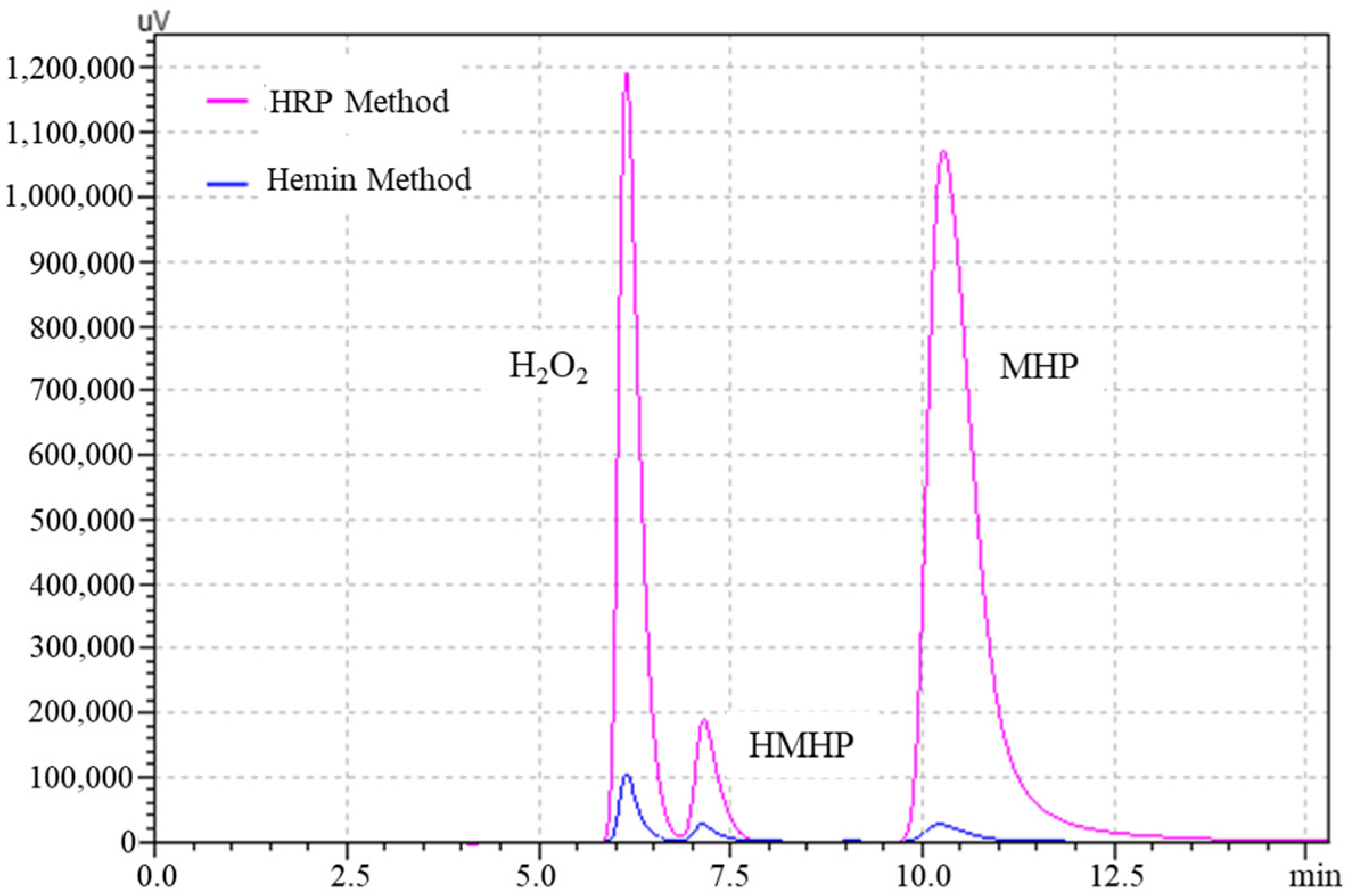
3.2.5. Applicability of Methods
3.3. Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunz, D.W.; Hoffmann, M.R. Atmospheric chemistry of peroxides: A review. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 7, 1601–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Aoki, M.; Takami, A.; Chai, F.; Hatakeyama, S. Effect of ambient-level gas-phase peroxides on foliar injury, growth, and net photosynthesis in Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.F.; Zheng, Z.W.; Xu, S. Measuring Method for Hydrogen Peroxide in Liquid Phase and Its Progress at Home and Abroad. China Saf. Sci. J. 2007, 3, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.V.; Hewitt, C.N. Hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxide concentrations in air in a eucalyptus forest in central Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 6, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Aoki, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Nozoe, S.; Komori, D.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S. Observation of hydrogen peroxide concentrations in a Japanese red pine forest. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 60, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Chen, Z.; Jie, C.; Kondo, Y.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Takegawa, N.; Chang, C.; Lu, K., III; Miyazaki, Y.; Kita, K.; et al. Atmospheric hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxides during PRIDE-PRD’06, China: Their concentration, formation mechanism and contribution to secondary aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6755–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, A.; Shiratori, N.; Yonekura, H.; Hatakeyama, S. Measurement of hydroperoxides and ozone in Oku-Nikko area. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3861–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakugawa, H.; Kaplan, I.R. Observation of the Diurnal Variation of Gaseous H2O2 in Los Angeles Air Using a Cryogenic Collection Method. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1990, 12, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zika, R.G.; Saltzman, E.S. Interaction of ozone and hydrogen peroxide in water: Implications for analysis of H2O2in air. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1982, 9, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazrus, A.L.; Kok, G.L.; Gitlin, S.N.; Lind, J.A.; McLaren, S.E. Automated fluorimetric method for hydrogen peroxide in atmospheric precipitation. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbault, G.G.; Kramer, D.N.; Hackley, E.B. New substrate for fluorometric determination of oxidative enzymes. Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellpointner, E.; Gäb, S. Detection of methyl, hydroxymethyl and hydroxyethyl hydroperoxides in air and precipitation. Nature 1989, 337, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dasgupta, P.K. Hematin as a peroxidase substitute in hydrogen peroxide determinations. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, K.H.; Hu, M.; Chen, Z.M. Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydrophilic Organic Peroxides by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Hemin as a Peroxidase Substitute. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 26, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, G.L.; McLaren, S.E.; Stafflbach, T.A. HPLC Determination of Atmospheric Organic Hydroperoxides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Noone, B.C.; O’Sullivan, D.; Heikes, B.G. Method for the collection and HPLC analysis on hydrogen peroxide and C1 and C2 hydroperoxides in the atmosphere. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.R.; Chen, Z.M. Determination of Peroxides in Environmental Samples by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2005, 23, 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kurth, H.H.; Gaeb, S.; Turner, W.V.; Kettrup, A. A high-performance liquid chromatography system with an immobilized enzyme reactor for detection of hydrophilic organic peroxides. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 2586–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffelbach, T.A.; Kok, G.L. Henry’s Law Constants for Aqueous Solutions of Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydroxymethyl Hydroperoxide. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 12713–12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghjiani, G.L.; Ravishankara, A.R. Absorption Cross Sections of CH3OOH, H2O2, and D2O2Vapors between 210 and 365 nm at 297 K. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1989, 94, 3487–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofer, W.R.; Collins, V.G.; Talbot, R.W. Improved aqueous scrubber for collection of soluble atmospheric trace gases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, F.; Limbach, S.; Moortgat, G.K. Measurement of hydrogen peroxide and individual organic peroxides in the marine troposphere. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Su, W.H. Determination of hydrogen peroxide in air and precipitation by automatic fluorescence method. Environ. Chem. 1987, 6, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Z.; Xie, C.X.; Shi, N.; Xu, W. Research on decomposition behavior of hydrogen peroxide solution. Qilu Petrochem. Technol. 2009, 37, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W.; Chen, X. Measurement of hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxide concentrations during autumn in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, F.; Beck, J.; Schuster, G.; Moortgat, G.K. Hydrogen peroxide, organic peroxides and organic acids in a forested area during FIELDVOC’94. Chemosphere-Glob. Chang. Sci. 2001, 3, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Liquid Phase (μg/L) | Gas-Phase (ppt) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 | MHP | H2O2 | MHP | |
| HRP method | 0.04 | 0.64 | 0.4 | 4.5 |
| Hemin method | 0.61 | 61 | 4 | 282 |
| Compounds | Method | Linear Range (μg/L) | Equation of Linear Regression | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 | HRP method | 0.2~1000 | y = 152,324x + 847,775 | >0.999 |
| Hemin method | 3~4000 | y = 27,129x − 759,287 | 0.99~0.999 | |
| MHP | HRP method | 3~3000 | y = 46,232x + 625,650 | >0.999 |
| Hemin method | 300~4000 | y = 268x − 70,175 | 0.99~0.999 |
| Items | Area | RSD (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| Slop (×105) | 1.52 | 1.51 | 1.53 | 1.51 | 1.52 | 1.52 | 1.49 | 1.52 | 0.774 |
| 100 (×107 μg/L) | 1.59 | 1.61 | 1.61 | 1.51 | 1.58 | 1.59 | 1.54 | 1.58 | 2.22 |
| 600 (×107 μg/L) | 9.53 | 9.28 | 9.55 | 9.16 | 9.36 | 9.46 | 9.36 | 9.40 | 1.35 |
| Items | Present Study | Ref. [14] |
|---|---|---|
| HRP concentration in enzyme reagent (U/mL) | 6.25 | 6.0 |
| Flow rate of enzyme reagent (mL/min) | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Flow rate of reaction solution (mL/min) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| HRP concentration in reaction solution (U/mL) | 1.8 | 0.86 |
| H2O2 (μg/L) | Area (×106) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRP Method | Hemin Method | |||
| Mean ± SD | RSD (%) | Mean ± SD | RSD (%) | |
| 20 | 3.03 ± 0.0133 | 0.44 | 0.142 ± 0.00138 | 0.97 |
| 400 | 65.8 ± 3.22 | 0.49 | 7.85 ± 0.389 | 0.49 |
| 800 | 125 ± 4.38 | 0.35 | 21.3 ± 1.00 | 0.47 |
| Analytical Method | Recovery Rates (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Mean | RSD (%) | |
| HRP Method | 97.1 | 96.5 | 99.7 | 97.8 | 1.7 |
| Hemin Method | 102 | 99.0 | 103 | 102 | 2.2 |
| Air Pollutions | Mean | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 | 0.60 ± 0.37 | 0.13 | 1.6 |
| MHP | 0.081 ± 0.039 | 0.020 | 0.21 |
| Air Pollutions | Mean | Min. | Max. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny | Cloudy | Sunny | Cloudy | Sunny | Cloudy | |
| H2O2 | 0.69 ± 0.37 | 0.30 ± 0.089 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 1.6 | 0.49 |
| MHP | 0.089 ± 0.039 | 0.047 ± 0.015 | 0.020 | 0.021 | 0.21 | 0.081 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Ning, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, B. Comparison of Fluorescent Techniques Using Two Enzymes Catalysed for Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050659
Sun J, Ning Y, Chen X, Zhang X, Ren Y, Li B. Comparison of Fluorescent Techniques Using Two Enzymes Catalysed for Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050659
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jieya, Yi Ning, Xuan Chen, Xinlu Zhang, Yanjun Ren, and Bin Li. 2022. "Comparison of Fluorescent Techniques Using Two Enzymes Catalysed for Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050659
APA StyleSun, J., Ning, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, X., Ren, Y., & Li, B. (2022). Comparison of Fluorescent Techniques Using Two Enzymes Catalysed for Measurement of Atmospheric Peroxides. Atmosphere, 13(5), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050659






