Abstract
The influence of a mesoscale convective system (MCS) in the evolution of two wildfires that started during the afternoon of 17 June 2017 in Pedrógão Grande, Central Portugal is discussed and analysed using weather radar data, weather stations, video images and fire spread analysis. As the MCS approached the region, its convectively driven flows started to influence the fires. The overturning flows were formed by two main limbs: one organised as front-to-rear deep layer inflows that propagated over the convective region of the MCS and the other as rear-to-front mid-level inflows that descended below the anvil structure of the MCS. The rear-to-front inflows, while accelerating and descending to lower levels, contributed to modify the fires’ intensity and plume characteristics. After the two fires merged, the resulting junction fire became very intense and impossible to control. Then, a firestorm was generated, causing the deaths of 66 people. The main goal of this study is to detail the influence of the MCS in the fire spread, thus contributing to the general knowledge of outstanding fire behaviour modifications due to the influence of atmospheric convective processes.
1. Introduction
The interaction between wildland fires and the atmosphere is a subject of great interest given its importance to understanding fire development and behaviour. The so- called fire–atmosphere coupling has been studied by many authors in the past [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Such interaction spans a wide range of scales. These include relatively small scales that are related to fire-induced changes in the flow and can be associated, for example, with the eruptive behaviour of fire in canyons [7,8] and larger scales that are associated, for instance, with boundary layer flows such as convective outflows, whose role in a wildfire evolution was studied by Johnson et al. [9].
This study focuses on the influence of a weather system in the evolution of two wildfires that started in Pedrógão Grande (PG), Central Portugal in the early afternoon of the 17 June 2017 (Figure 1). During this day, an ensemble of thunderstorms started to organise to the east–southeast of the fire areas. This cloud system was characterised by a horizontal extent of a few hundred kilometres and a life cycle of over 12 h, typical of a mesoscale convective system (MCS) [10]. This MCS developed in a hot and dry atmospheric environment at low levels, where instability existed only from mid-level upwards, favouring the occurrence of active convection in sections of the leading area of the system. A large number of downbursts [11,12] occurred, which were associated with the large magnitude reflectivity cores observed by radar. As a result, strong, low-level diverging flows were generated and their effects extended to ground level, as strong gusty winds were observed to the southeast and south of the fires. These diverging flows did not significantly affect the fires. Meanwhile, the MCS continued to move towards the fire areas, and it started to dissipate as reflectivity cores of relatively lower magnitude were progressively observed by radar, as well as a pattern of more homogeneous reflectivity. No discrete downbursts were generated after the MCS began to dissipate. Instead, strong flows were observed by radar, which were organised over much larger areas (when compared to the scales of single discrete downbursts) and located downwind of modest reflectivity cores. The observations showed that these flows accelerated towards the ground and interacted with the fires, modifying their behaviour, contributing to their merging and the initiation of a very violent fire storm process [13]. For three hours, the fire spread destroyed more than nine thousand hectares and killed 66 people in the Municipality of Pedrógão Grande, making it the worst and deadliest wildfire ever recorded in Portuguese history, as well as one of the most tragic fire events in all of Europe [14].
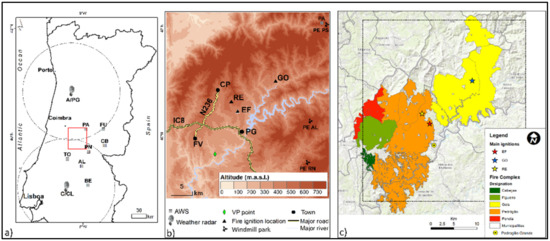
Figure 1.
(a) Map of Portugal with the location of the relevant automatic weather (AWS) and radar stations. (b) Zoom in of the fire complex area with the terrain altimetry; important locations (including the accessed video cameras in PG and windmill parks, PE RN, PE AL and PE PS); roads; vertical profile of numerical model (VP) and relevant fire ignitions (EF—Escalos Fundeiros, RE—Regadas and GO—Góis). The square in (a) marks the zoomed in area of (b). (c) Map of the complex of fires of Pedrógão Grande. The square in (c) matches the zoomed in area of (b).
In order to facilitate the follow up of the evolution that occurred during the complex influence of the MCS low-level induced flows over the fires, a timeline was organised (Figure 2). The more relevant events of the fire activity and changes in the low-level flows driven by the MCS are indicated in the diagram. All times are referenced as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).

Figure 2.
Timeline of the convectively induced flows and their influences on the evolution of the Pedrógão Grande fires on 17 June 2017. Plume orientation is expressed as the direction from which the plume is being driven by the wind. Wind orientation is expressed as the direction from which the wind is blowing. “A”, “B” and “C” refer to events of fire intensification (Section 5).
The Global Atmospheric Research Program Atlantic Tropical Experiment (GATE, 1974) prolific research activity resulted in increased knowledge about flows and thermodynamics in MCS. It became commonly accepted that the different types assumed by MCS, both linear and noncanonical convective systems [15,16,17], were strongly dependent on the balance between the environmental vertical wind shear and the storm motion [18,19,20,21,22]. It was also found that the environmental wind shear was related to several scales of flows that were organised in all those systems. On one hand, there are the convective-scale updrafts–downdrafts associated with each individual convective cell. Within this region of deeper convection, the upward air motions are much stronger than the fall velocities of hydrometeors [23]. On the other hand, there is a larger-scale overturning flow. This flow is formed by two limbs, one of them is a front-to-rear (FTR) deep layer inflow, organised as a sloping mesoscale updraft, and the other is a rear-to-front (RTF) mid-level inflow descending below the mesoscale ascent (Figure 3). As the convective-scale updrafts weaken in time and hydrometeor particles are transported to the rear of the system by this sloping updraft that ascends through the area of the more active convection, those particles descend slowly and organise a region of stratiform precipitation [23] to the back of the system. It was shown that the RTF inflow was strengthened if the environmental wind favourably fed air into the mid-levels of the storm [24] and that the direction of the inflow was associated with the system-relative wind direction [25].
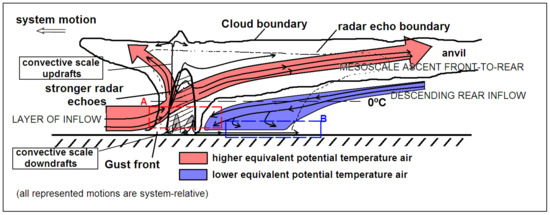
Figure 3.
A conceptual model of a kinematic, microphysical and radar echo structure of a convective line MCS with trailing-stratiform precipitation as viewed in a vertical cross-section at an angle perpendicular to the convective line with a westward propagation. Dark grey shades indicate stronger radar reflectivity. Area A (dashed red) highlights the region where the front-to-rear inflow and the rear-to-front mid-level inflow (RTF) converge. Area B (dashed blue) highlights the region where the low-level front-to-rear flow beneath the RTF is observed (adapted from Reference [23]. © American Meteorological Society. Used with permission).
The ascending mesoscale flow picks up high potential temperature air from a relatively deep layer not confined to the boundary layer and transports it to higher levels [25]. The mesoscale downdraft is fed from a mid-level inflow in the rear of the MCS that descends due to microphysical processes such as evaporation of falling hydrometeors [26] and the sublimation and melting of ice particles [27] beneath the typical anvil of the MCS (Figure 3). This mesoscale downdraft initiates above the 0 °C level and descends below it. It transports low potential temperature air to lower levels. The stronger convective-scale downdrafts are frequently generated by loading of the convective precipitation and generate density currents of colder air that propagate horizontally as convective outflows that surge with a gust front (Figure 3). On some occasions, the mesoscale downdraft arrives at low levels where, eventually, it merges with the convective scale downdrafts, and their combined effects produce a bowing gust front known as a bow echo [28].
This comprehensive knowledge about the flows in MCS points to the organisation of flows at several scales in the systems at distinct stages of their life cycles. The analysis of radar observations has suggested that the MCS that affected the fires during the afternoon of the 17 June 2017 presented a kinematic organisation consistent with this description.
This paper is organised as follows. Section 2 describes several data that were used to perform the study, namely surface and weather radar observations, as well as analyses and short-term forecasts from several operational weather forecasting models. The data included an important survey that was conducted by some of the authors [14]. Section 3 addresses the background conditions in which the events unfolded, including topography, fuel and the underlying climate and weather ingredients. Section 4 describes, in detail, the weather system that propagated over the fire areas, focusing on the airflows that were observed during its relevant life cycle. The results of a radar-based methodology that was developed to monitor the fires behaviour are presented in Section 5. In Section 6, the influence of MCS-driven flows in the course of the fires is described. Section 7 highlights the main conclusions of the study.
2. Materials and Methods
The fire of Pedrógão Grande (PG) resulted from two separate fires that started on the 17 June 2017 near the town of PG. The first ignition occurred at Escalos Fundeiros (EF) at 13:38, and an electric power line was probably the cause [14]. A second ignition attributed to the same cause, but 2.6 km away at Regadas (RE), started at about 15:15 (Figure 1b,c). An intermediate fire ignition, at 13:48, occurred in the Municipality of Góis, less than 20 km away from the PG fires. Other simultaneous fires in the region contributed to dispersing the fire suppression means.
As shown (Figure 1), there were several other significant fire events within the final fire perimeter that were controlled on 22 June 2017. The current work focuses mainly on the events of EF and RE between 18:00 and 21:00 on 17 June 2017, which originated the fatal episodes of this complex of fires.
2.1. Fire Data Survey
The Portuguese government requested a full report on the fires from some of the authors of this study, which led to a detailed investigation of the fire spread conditions. Based on an extensive field survey, an enquiry of hundreds of people and consultation with a large amount of data, it was possible to convey the fire history, as well as the details and reconstruction of each accident [14].
A set of four fixed video cameras installed at the Fire Brigade Station building of PG (Figure 1b) and owned by the local technical school (Escola Tecnológica e Profissional da Zona do Pinhal, ETPZP) recorded the evolution of the fires and several important plume patterns throughout the event. Its analysis was important to clarify doubts and consolidate ideas, as well as some arguments involved in the current study.
2.2. Surface Observations
Data from six automatic weather stations (AWS) of the Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA), the Portuguese Met Service, located in the region surrounding the fires, were available. In this study, data from the Tomar (TO), Proença-a-Nova (PN), Alvega (AL), Benavila (BE), Pampilhosa da Serra (PA) and Castelo Branco (CB) AWS were used (Figure 1a). Two-metre air temperature and relative humidity, 10-m wind gusts and average wind magnitude and direction were recorded at every 10 min. All of these AWS were farther than 40 km from the fire areas. Wind data from three windmill parks located closer to the fires were also available: Alvelos (PE AL), Rendeiros (PE RN), sited approximately 15 km to the east–southeast of the fire areas, and the Pampilhosa-da-Serra (PE PS) Park, sited 30 km to the northeast (Figure 1c), were equipped with wind sensors at 60–80 m above ground level (a.g.l.) that recorded the average wind magnitude and direction. The PE PS windmill was close to the PA station.
2.3. Weather Radar Data and Processing
Two Doppler weather radars from the IPMA network, both about 100 km away from the fire areas, were used in the analysis of the MCS and of the fire plumes. One is located to the north (Porto radar station, A/PG) and the other to the south (Lisbon radar station, C/CL). A/PG is a dual polarisation (DP) system, with a beam at around 1100 m in altitude (Figure 1a), whereas C/CL is a single polarisation system, with a beam at around 200 m in altitude (Figure 1a). For each station the observations were extracted from (i) a 300-km range scan (deep reflectivity scan, 16 tilts) every 10 min with a time stamp on the hour, from (ii) the 300-km range scan (shallow reflectivity scan, five lowest tilts) every 10 min with a time stamp on the hour + 5 min and from the 100-km range scan (Doppler velocity scan, five tilts) with a time stamp on the hour + 6 min. From the deep reflectivity scan, the echo tops (TOPS) and maximum returns of reflectivity (MAXZ) were generated, and the plane position indicators of reflectivity (PPZ) were extracted. From the A/PG radar, the plane position indicators of the correlation coefficient (ρhv) were additionally extracted. This coefficient is a correlation, in a time series, between horizontally and vertically polarised echoes and was available from both deep and shallow scans. From the velocity (V) scan of the radars, the PPZ and plane position indicator of V (PPV), as well as of storm-relative velocity (SRV), was produced. The SRV was computed by an algorithm [29] that uses cross-correlation over reflectivity data (300-km radius circle) to determine a storm translation vector. This vector was subtracted from the total velocity to retrieve SRV for each along-beam radial. Both V and SRV were used to analyse the flows. While V is used to identify wind components relative to the ground, SRV is more suitable to identify storm-relative patterns such as flow divergence and rotation that were extensively observed during this event. The divergence magnitude was computed by normalising the differential SRV across the divergence centre with the corresponding radial distance.
Within the 100-km range, the spatial resolution of radar observations was 1 km or better. The lower tilts that were used in the scans of C/CL and the A/PG radars allowed observations close to the fire site. The more relevant radar data that were used in this study are summarised (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of the radar data used in this study.
Reflectivity observations were used to monitor the behaviour of the PG fires. As fires intensify, the heat flux increases combustion processes and buoyancy increases as well, transporting more pyrometeors [30] upwards [31]. Therefore, both the magnitude of low-level reflectivity, observed close to the fire site (buoyancy source), and the vertical extent of the plume can be considered as good indicators of the general intensity of the pyroconvection (strong convective processes caused by the fire) and, therefore, of the fire. Furthermore, the fire plume mode that results from the balance between buoyancy forces and environmental wind has been acknowledged as another important element that provides useful information on fire behaviour [32]. The presence of a nearby weather system in this event modulated the plume orientation at low levels and made it relevant to its close monitoring.
The observations from the lowest tilt of C/CL reflectivity scans offered the best view of the magnitude of low-level reflectivity close to the buoyancy source due to the lower altitude of this radar, allowing for observations to be obtained as low as 400-m a.g.l. observations (900-m altitude), compared to 900-m a.g.l. observations (1400-m altitude) performed by A/PG over the fire areas. This low-level reflectivity was computed as an average of a 3 × 3 km2 matrix (in polar coordinates) centred in the maximum reflectivity value observed within the element that was identified closer to the fire. As discussed later, during this event, a convective system approached and propagated over the fire areas, which increased its overall complexity, raising an additional difficulty. In fact, the low-level reflectivity measured close to the area of active fire could be mainly the result of (1) backscatter from the larger pyrometeors [30] associated to the fire itself or (2) the result of backscatter from a mix of pyrometeors–hydrometeors from the weather system or (3) due to hydrometeors, unrelated to the fire. To determine its most likely origin, the authors applied a method based in the DP capabilities of A/PG. This radar routinely processes ρhv, which is a good particle type discriminator [33]. It was confirmed that fire particles systematically exhibited ρhv values lower than those associated with hydrometeors, due to their specific microphysical properties [34,35]. It was also found that a mixture of fire ash and rime ice exhibited ρhv ≥ 0.8, whereas pure ash was used to feature ρhv < 0.8. Recently, several smoke plumes have been observed by radar over Portugal by the authors, and those observations suggested that a tighter criterion should be applied. As such, in this study, it was considered that smoky atmospheric volumes with ρhv ≤ 0.7 would be mainly occupied by pyrometeors forming convective plumes without significant condensate. The ρhv field was then selected from the lowest tilt of A/PG (at 900 m a.g.l. or 1400-m altitude) and inspected over the exact pixels of the matrix identified by C/CL 500 m below. If the ρhv was ≤0.7, it was considered that the corresponding reflectivity at that height originated on larger pyrometeors released by the fire. Therefore, the reflectivity observed by C/CL at 400 m a.g.l. would also be due to pyrometeors. This method allowed following the maximum reflectivity in the area of active fire and its approximate location over time.
The plume orientation was also estimated from the low-level reflectivity observations, as long as a reflectivity pattern extending downwind of the buoyancy source was identifiable. The centreline of such a reflectivity pattern was taken as a reference to its orientation.
The vertical extent of the smoke plume was also estimated using A/PG but differently from the classical echo tops method. The classical method relies on the determination of hydrometeor cloud tops based on the highest level at which a certain reflectivity value (e.g., 18 dBZ) is observed. This procedure can be extended to determine smoke plume tops when the plume is isolated [32]. However, the coexistence of an MCS with the fire plume in the current event did not allow the estimation of the pyroconvective plume vertical extent with this procedure (a fire plume characterised by strong convective processes). In fact, for a substantial period, the MCS propagated over the fires, and as a result, the echo tops product targeted the anvil tops of the MCS instead of the underlying smoke plume top. Therefore, the altitude of the smoke plume was derived from the highest altitude ρhv ≤ 0.7 in a PPI. For those cases where the condensation of pyrometeors occurs in the higher portions of the pyroconvective plume, the derived top height corresponds only to the smoky part of the plume (ρhv ≤ 0.7), due to the current impossibility of discriminating the anvil material (from the original weather system) from the pyrocumulus (formed by the condensation of the convective plume, if it occurred) using ρhv alone. This method allowed monitoring the vertical extent of the plume over time.
The current knowledge on fire plume mode shows that the multicell type [36,37] is associated with a wind-driven fire phase [38]. In this case, the plume is characterised by individual pyroconvective elements that rise and expand due to buoyancy and fire combustion [39] and are transported downwind. On the other hand, the convective type is typical of a plume-dominated fire phase [38], characterised by a vertically orientated updraft driven by buoyancy, when buoyancy forces overcome the environmental winds [40]. Recent studies have shown that individual elements can be monitored downstream by the radar if high temporal resolution scanning is available [13,41]. This was not the case for the setting of the current study, but still, radar data were available every 5 min for the five lowest tilts of reflectivity scans and every 10 min for the overall volumetric scan. The horizontal distance between the maximum echo top of the plume and the low-level pyroconvective element located close to the buoyancy source was determined to classify the plume mode. To the authors’ knowledge, there are no universal quantitative criteria to classify plume mode on radar. In this study, whenever the horizontal distance between the top of the plume location and the pyroconvective element identified close to the buoyancy source was <6 km, the plume was deemed to be of a convective type.
To summarise, the evolution of the fire behaviour was monitored using radar data, including: (i) the magnitude of the reflectivity observed in the pyroconvective element located closer to the updraft source every 5 min, (ii) the orientation of the plume observed at low levels every 10 min, (iii) the vertical extent of the plume observed every 10 min and (iv) the plume mode determined every 10 min.
2.4. Numerical Model and Rawinsonde Data
The atmospheric environment was accessed and described using the analysis of the UK Met Office (Met Office of the UK) and the short-term operational forecasts of the European Centre for Medium range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model, as well rawinsonde data from the Lisbon station (17 June, 12:00, not shown). In June 2017, the ECMWF deterministic model had a spectral resolution TL 399, corresponding to a horizontal grid spacing of about 16 km and 91 vertical levels [42]. As discussed ahead, several vertical wind profiles for specific locations of interest were considered to understand the way that the MCS was organised.
3. Background Conditions
3.1. Topography and Fuel
Previous studies have clearly established that fire behaviour depends on the environmentally influenced fuel properties, topography and meteorological conditions [43]. It also depends on a great extent on the dynamics created by the fire itself.
The terrain over which the fires of PG spread exhibited a relatively complex topography, with undulating ground cut by several courses of water, having versants and canyons with slopes that can reach 40%. The altitude of the terrain varied between 300 m and 600 m, and there was no stretch of flat ground within the area (Figure 1b).
The vegetation cover consisted mainly of a mixture of Pinus pinaster and Eucalyptus globulus, with areas of Acacia dealbata, broadleaf trees and orchards (near the houses). Inside the tree stands and over a few non-cultivated areas, there were shrubs like Ericacea and Cistaceae, as well as herbaceous vegetation. Due to the extended drought, high surface temperature and low relative humidity during the previous days, the moisture content of the fine fuels (FMC) both dead and alive were low on a dry basis: 6–11% for Pinus pinaster dead needles and Eucalyptus globulus dead leaves, about 75% for Eucalyptus globulus live/green leaves and about 60% for Calluna vulgaris plant tips [14].
The low values of fine fuel moisture content indicated that any fire start, including spot fires, would have favourable conditions in terms of spread. The probability of an ember to start a new fire was greater than 90% [44]. It also indicated that much larger elements of the fuel beds were available for burning in surface or crown fires, releasing a great amount of energy. The Initial Spread Index (ISI), component of the Fire Weather Index (FWI) system, which is a key input for fire behaviour predictions, showed a maximum value of 20.5 at the PA AWS (see Figure 1) [45].
3.2. Synoptic and Mesoscale Environments
Above-average temperature and below-normal rainfall, particularly in April and May, characterised the months before the fire, aggravating the drought in the whole territory. In fact, April 2017 was the driest in Portugal since 1931. The Standardized Precipitation Index [16] and the Palmer Drought Severity Index [15] indicated that, by the end of May, 71% of the territory was in a severe drought [16]. The FWI Drought Code component values [46] for reference weather stations in the region of the fire were also much higher than the average [14], indicating favourable conditions for intense fires [47]. Starting in early June, a heatwave scorched inland regions of Portugal for more than two weeks, further exacerbating the drought [45].
On the 17 June, 12:00, the UK Met Office mean sea-level pressure analysis revealed a high-pressure system centred over Southern England (Figure 4a). To the south of it, a thermal trough was visible over Western Iberia, associated with the typical Iberian thermal low. A weak flow was settled over mainland Portugal, as shown by the 12:00 ERA5 (fifth-generation ECMWF reanalysis) hourly reanalysis 10-m wind over Iberia (Figure 4b). Offshore Northern Morocco, there was an upper-level low wind, significant just above 700 hPa. In the early afternoon, cool air advection over the 700–500 hPa layer (not shown), driven by the high-pressure system and strong low-level heating, increased the atmospheric instability. A hot and dry atmospheric environment was in place below 700 hPa. Short-range ECMWF forecasts suggested that there was some humidity convergence at mid-level over Central Portugal. The vertical atmospheric profile at 18:00, extracted from those forecasts for a location a few kilometres to the south of the fire areas (Figure 1b), confirmed a hot and dry low troposphere environment, presenting an inverted V-shaped profile (Figure S1), typical from dry downburst environments [48]. As denoted by this profile, and the atmosphere was dry up to the 700–600 hPa level, while several dry air intrusions in the sub-cloud layer were also discernible. The atmosphere was unstable aloft, and the Total Precipitable Water (TPW) was around 30 mm, consistent with an environment prone to high-level based convection. An observed profile at the Lisbon station by 12:00 (rawinsonde obtained 150 km to the southwest of the fire areas, Figure 1a) exhibited similar characteristics, although presenting much less instability (not shown).
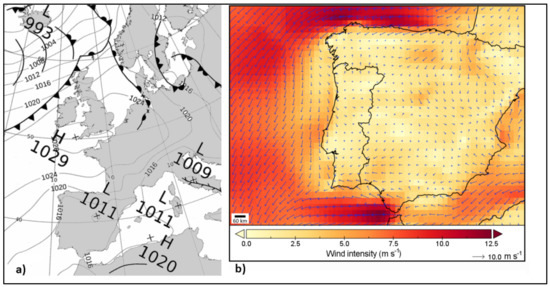
Figure 4.
(a) Mean sea-level pressure (solid contours, 4-hPa intervals) over the Northeast Atlantic (adapted from Uk Met Office), and (b) wind intensity and direction (arrows) over the Iberian Peninsula (ERA5 hourly reanalysis) at 12:00 UTC, 17 June 2017.
4. The Mesoscale Convective System of 17 June
4.1. MCS Type
During the early afternoon of 17 June, both radar and satellite data revealed that convective clouds started to build up along the central southern–eastern region of Portugal close to the Spanish border, forming an ensemble of thunderstorms that were characterised by space and time scales typical of an MCS. According to C/CL radar observations, the convective cells initially developed following a broken areal pattern [49] and a chaotic mode [50], in the sense that they formed randomly, as can be seen by 15:10 radar imagery (Figure 5).
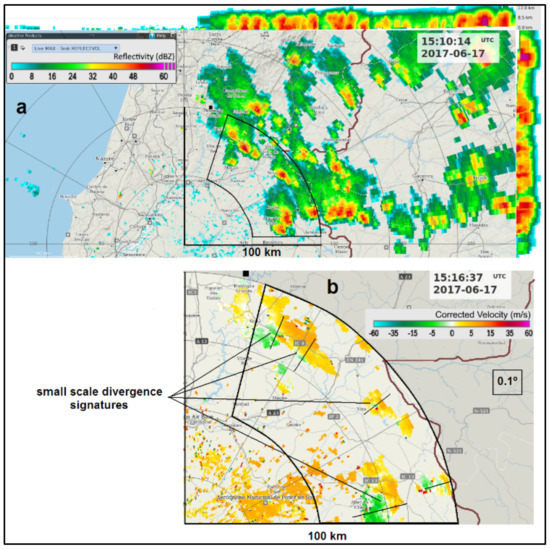
Figure 5.
(a) MAXZ at 15:10 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar. Range rings are marked every 50 km. Segments mark the 100-km range. Fire areas are represented by a black square symbol. An azimuthal sector (50–100-km range) in the north–eastern quadrant observed by radar is also defined. Around the upper and right borders of the central image, the side panels of MAXZ are represented. (b) Zoomed-in area from (a) extracted from the Doppler scan, storm-relative velocity PPI, 0.1° tilt at 15:16 UTC, 17th June 2017, C/CL radar. Small radial segments depict small-scale divergence signatures coherent with discrete downburst activity. Border with Spain is represented by the brown line.
As the system evolved into a more mature stage, deep convection occurred, and high reflectivity cores were observed more extensively at 16:30 (Figure 6a). At that time, many small-scale low-level divergence signatures were detected on Doppler radar, always close to those reflectivity cores (Figure 6a,b). Some of the more active convections occurred in a section of the leading area of the MCS, although some cells were also observed outside that area. No leading convective line was properly defined (Figure 6a,b).
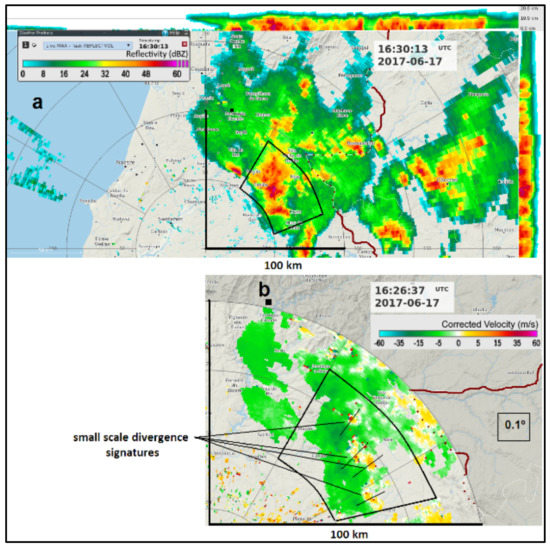
Figure 6.
(a) MAXZ at 16:30 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar. Range rings are marked every 50 km. Segments mark the 100-km range. Fire areas are represented by a black square symbol. An azimuthal sector (50–80-km range) in the north–eastern quadrant where high reflectivity cores were observed is also defined. Around the upper and right borders of the central image, the side panels of MAXZ are represented. (b) Zoomed-in area from (a) extracted from the Doppler scan, storm-relative velocity PPI, 0.1° tilt at 16:26 UTC, 17 June 2017. Small radial segments depict small-scale divergence signatures coherent with discrete downburst activity. Border with Spain is represented by the brown line.
As the system continued to evolve and propagate, it progressively exhibited less convective cores and lower reflectivity. During this dissipation stage, a more homogeneous and moderate reflectivity pattern was observed, coherent with a stratiform-dominated regime that was clear by 18:20 (Figure 7a). At this stage, the low-level Doppler patterns differed substantially from the ones of the mature stage, mainly because a strong flow signature was now observable, still organised at the mesoscale but in a much larger area than the one corresponding to single convective cells (Figure 7b). This signature was observed slightly downwind of modest reflectivity cores in the range 40–42 dBZ.
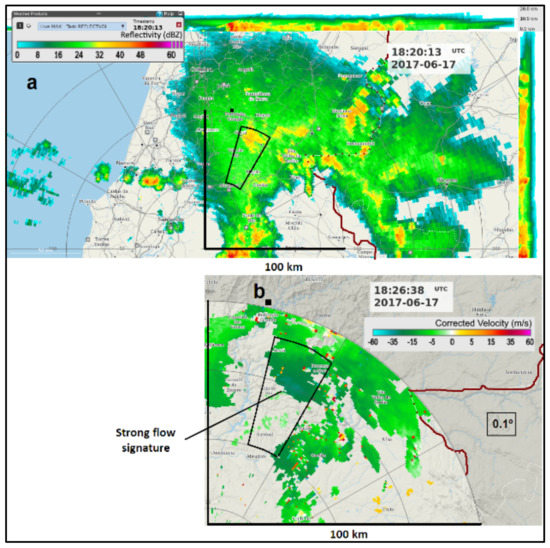
Figure 7.
(a) MAXZ at 18:20 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar. Range rings are marked every 50 km. Segments mark the 100-km range. Fire areas are represented by a black square symbol. An azimuthal sector (50–80-km range) in the north–eastern quadrant where modest reflectivity cores were observed is also defined. Around the upper and right borders of the central image, the side panels of MAXZ are represented. (b) Zoomed-in area from (a) extracted from the Doppler scan, storm-relative velocity PPI, 0.1° tilt at 18:26 UTC, 17 June 2017. Strong flow signature in a much larger scale than that of single discrete downbursts is marked. Border with Spain is represented by the brown line.
This system was not classifiable as any linear archetype proposed in the literature [15,16,17]. Indeed, while the developing stage revealed a broken areal formation, as shown before (Figure 5a), the system did not evolve into a squall line, since a leading convective line was not identified (Figure 6a). A more stratiform region in the poleward area of the MCS (Figure 6a) resembled the structure of an asymmetric system [51], but the absence of a clear leading convective line excluded such categorisation. Moreover, although the MCS developed a large, quasi-circular anvil, which resembled a mesoscale convective complex, the satellite-based criteria that are typical of this system type were also not met [52]. Therefore, this MCS was considered a chaotic convective system [50].
4.2. System-Relative Winds
The general view over the flows and thermodynamics in MCS that was described in Section 1 applies to every MCS type. Therefore, to understand the circulations in a noncanonical system such as the one observed in the current study, its direction of motion and system-relative winds must be determined.
The MCS motion results from the contribution of an advection component, due to the average motion of the individual convective cells within the system, and a propagation component, due to the new growing cells position relative to the existing cells. For typical squall lines, the movement of the leading convective line defines the motion [53]. In chaotic mesoscale convective systems, however, there is no defined convective line, the cell structure is rather complex and the discrete propagation may make estimation of the storm motion difficult [54]. The motion vector of the current noncanonical MCS was derived from an average of the advection of its cells [50] that were detected by radar during the period 14:30–16:30. After that, no more reflectivity cores were identified, as a stratiform pattern became dominant. The advection of individual cells was estimated by monitoring the convective cores in the PPI of reflectivity, layer 3.1–5.1 km a.g.l., during at least 30 min for each cell. A motion vector for this MCS of 58° at 3.6 m/s (approx. from the east–northeast) was found. During the same period, the SRV algorithm estimated a storm motion vector of 78° at 4.2 m/s.
The algorithm computed a faster motion than the manual method. The MCS expanded across a much wider area (Figure 8) than the one over which the manual method was applied. Many cells were located within the 300-km radius but beyond the 150-km range of the manual method application (namely to the south and southwest). These cells moved faster and in more westward directions than the ones observed in the relevant area. Thus, it was considered that the storm motion vector estimated by the algorithm was not as representative as the manual method, which is why the latter method was used to estimate the storm relative inflows. Despite the above-mentioned discrepancy, the SRV field presented throughout this paper was used as a reliable indicator of specific patterns such as convergence/divergence. The main conclusions will be supported both by the V and the SRV field analyses.
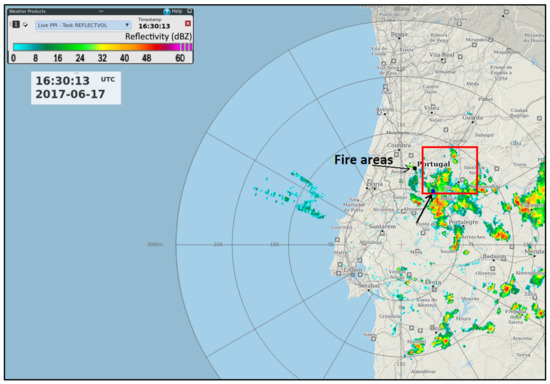
Figure 8.
PPI of reflectivity, 0.1° tilt, 16:30 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar. Range rings are marked every 75 km. The red square delimits the area where a manual method was applied to determine the storm motion of the Mesoscale Convective System during the period 14:30–16:30 UTC. Fire areas are depicted by an arrow. The location Proença-a-Nova of the sounding mentioned in Figure S2 is also depicted by an arrow to the southeast of the fire areas.
The environmental vertical wind profile ahead of the storm at an early stage was required to derive system-relative winds. A sounding was not available for that time. Nevertheless, ECMWF short-term forecasts captured the event reasonably well (not shown). At 15:00, as convective cells started to develop to the east of the fire areas (Figure 5a), ECMWF wind profiles from several locations were inspected. A detailed analysis of those profiles revealed that, in general, a light north–westerly flow was in place up to 900 hPa (approx. 600 m a.g.l.), a moderate north–north–easterly flow was veering to the east up to 600 hPa (approx. 4000 m a.g.l.) and, aloft, a moderate south–easterly flow veering to the south up to the higher levels of the troposphere. The profile extracted for Proença-a-Nova (Figure S2) was selected as a good representation of the environmental winds ahead of the storm (Figure 8). By subtracting the estimated storm motion vector from this wind, the vertical profile of the system-relative winds was computed (Figure S3).
This wind profile highlights a westerly low-level inflow layer up to 2000 m a.m.s.l., with an average magnitude of 3 m/s, an average north–easterly–easterly inflow between 2100 m and 4000 m a.m.s.l. at 2.5 m/s and a deep south–south–easterly inflow layer up to the tropopause with an average magnitude of 6 m/s. Since the environmental wind profile was extracted from a forecast and the estimate of the storm motion vector involves some uncertainty, some inaccuracy in the obtained storm-relative wind profile must be considered. The storm motion was from the northeast, so its southwestern edge was the leading part, and conversely, the north–eastern edge was the rear part of the system (Figure S4a). These relative inflows were discernible over the reflectivity pattern of the MCS, which was observed at 17:00, and at low elevation (Figure S4a). The westerly inflow layer up to 2000 m a.m.s.l. and the southerly inflow layer at higher levels were an indication that the MCS was being fed by a front-to-rear flow over a deep layer. Furthermore, the north–easterly inflow between 2000 m and 4000 m a.m.s.l. indicated that the MCS was being fed by a rear-to-front flow at mid-level. In this representation, vertical sections of reflectivity were also depicted in order to facilitate the understanding of the expected inflows across the several levels of the weather system. According to the storm relative wind profile, the rear-to-front inflow layer would be expected below the 0 °C level that was around 4300 m a.m.s.l. (Figure S4b,c).
4.3. Convective Regimes and Airflows Observed in the MCS
The MCS that developed on 17 June organised was a noncanonical, chaotic system (see Section 4.1). Following the suggestion of specific inflow layers that were deduced from the system-relative wind profile (discussed in Section 4.2), it is now important to analyse the radar observations to find if this system revealed the common features ubiquitous to every MCS, namely the organisation of a large scale overturning the flow formed by a front-to-rear deep layer inflow and by a rear-to-front descending mid-level inflow superimposed on smaller scale updrafts–downdrafts associated with individual cells.
4.3.1. Initial and Mature Stages
- (a)
- Reflectivity cores and downburst activity
The observations of 15:10–15:16 were considered as representative from the initial stage of the MCS, in which the convective activity formed a broken areal pattern that was identified in the maximum reflectivity product (Figure 5a) to the east of the fire areas. As previously documented, this system developed in an inverted V-type environment prone to downburst activity [44]. Downbursts are strong downdrafts that diverge outward and produce significant outflows at or near the ground level [11,12]. At the leading edge of such outflows, a convergence zone, known as the gust front [55], typically separates warmer and drier environmental air from cooler and moister air originated higher in the storms. This baroclinic zone manifests by turbulent flows with gusty winds.
During this early stage, downburst activity was already identifiable. Low-level radial divergence signatures were seen in PPIs of SRV (also in V, not shown) to the southeast of the fire areas, and each signature was correlated with convective cores of large magnitude (51–57 dBZ) (Figure 5b). These signatures were observed at 300–500 m a.g.l. Similar signatures were also identified at other instants at approximately the same heights. The radial divergence of the five signatures detected by 15:16 (Figure 5b) had an average magnitude of 1.8 × 10−3 s−1.
During the mature stage, well-illustrated by the 16:26–16:30 observations, a pattern suggesting more merged and extensive convection formed, with stronger cores (55–62 dBZ) identified within the leading section of the MCS (Figure 6a). These high reflectivity cores were of larger magnitude than before (Figure 5a vs. Figure 6a), although not linearly aligned, as would be the case of a classical squall line system. Furthermore, behind these stronger leading cells, moderate convective cores were still observed, some of them exceeding 50 dBZ. These comparatively weaker cores were embedded in a pattern characterised by lower and more homogeneous reflectivity typical of a stratiform-like regime (Figure 6a) that was developing. Low-level divergence signatures were identified in the area where the leading section of the system was propagating (Figure 6) and were always associated with the largest reflectivity cores (Figure 6b). The low-level signatures were captured at lower altitudes than before, since the system was approaching the radar site but were observed at the same height, due to the lower terrain altitude. The radial divergence of the four signatures that were detected by 16:26 (Figure 6b) had an average magnitude of 2.9 × 10−3 s−1. This value was larger than the one computed during the first stage. Reflectivity cores as large as 62 dBZ were detected at an altitude of 2000 m underneath the zero-degree isotherm (4300 m). The dual pol A/PG radar sampled these cores and revealed that their composition was mainly graupel and hail (not shown). According to previous studies, the combined effects of sublimation and melting of hail in the above zero-degree layer, as well as the evaporation of rain drops, can generate downbursts [56]. Thus, cores of larger reflectivity tend to be associated with stronger downbursts. The presence of a dry sub-cloud layer in the environment of 17 June must have reinforced these effects.
Many small-scale low-level divergence signatures were identified close to moderately large reflectivity cores during the initial stage (Figure 5a,b) and close to large magnitude reflectivity cores during the mature stage (Figure 6a,b). Thin reflectivity lines were detected close to those signatures, as revealed by radar reflectivity. These lines result from the local increase in reflectivity that is associated with the stacking of scatterers produced by low-level convergence in the leading edge of the outflows [55]. In the current event, the downbursts were of the discrete type, but the corresponding individual outflows merged, forming a larger outflow whose leading edge was detected by radar (Figure S5). When the thin reflectivity line propagated over a weather station, a sudden change of airmass properties was noticeable in the observations. As an example, a thin line was detected and moved westwards, to the west–southwest of the MCS front. When the line was upwind of the AL and BE weather stations (Figure S5a), the observations at these locations reflected a hot and dry environment and light environmental winds prevailing from the west–northwest (Figure S6). However, as the thin line propagated over each location, a large temperature drop and relative air humidity increase were recorded, as well as much stronger gusty winds. In AL, these winds turned to the east–northeast, and its maximum gust reached more than 21 m/s at 16:40–16:50 (Figure S6), in correlation with the thin line position over the station (Figure S5b). In BE, the effects were felt only by 17:20 (Figure S6), as the line advected later over the station (Figure S5b–d). The PN weather Station (PN in Figure S5), located more to the northeast, started to be influenced by downburst activity much earlier by 16:10–16:20 (Figure S6), due to its closer location to the leading convection of the MCS. Tomar Station (TO in Figure S5), located much more to the west, was influenced only around 17:30 (Figure S5d).
These examples confirmed that the storm was a prolific downburst producer and that the strong outflow winds influenced the ground level. However, during these initial and mature stages, the fire areas were not significantly influenced by this downburst activity, as was demonstrated with the support of a continuous smoke plume monitoring using radar observations at 500 m a.g.l. As discussed ahead in detail, the plume did not change its orientation significantly at this level, maintaining its undisturbed orientation, in accordance with prevailing northerly environmental winds that were affecting the fire areas until slightly after 17:00.
- (b) Airflows at several scales
It was already discussed (Section 1) that the current knowledge on flows and thermodynamics in MCS considers the existence of airflows at the convective scale and at the mesoscale.
In the current event, the profile of the derived storm relative motion (SRM) suggested a front-to-rear (westerly) inflow up to 2000 m a.m.s.l., a deep layer sideways (southerly) inflow from 3500 m upwards and a rear-to-front (north–easterly) inflow in the mid-level layer, 2000–4000 m a.m.s.l. (Figure S4). Two vertical sections on reflectivity across distinct areas of the system were also represented, together with the zero-degree isotherm (Figure S4).
A detailed kinematic analysis of the system was performed to evaluate the relationship between the storm-relative flows expected from the SRM profile and the storm-relative velocities (SRV) that were observed on the C/CL radar. The three lowermost tilts available from the Doppler scan were used (0.1°, 1.5° and 4.0°; upper elevations overshoot the MCS). The system was sampled at altitudes in the ranges 400–900 m (0.1° tilt), 1300–3400 m (1.5°) and 3000–7700 m (4.0°), considering the relevant atmospheric volumes at the times of the observations. A cross-section taken over the reflectivity of the deep volumetric scan, including a finer vertical sampling than the Doppler scan, shows the regions of the MCS that were sampled by each tilt of the Doppler scan, as, in example, for 15:10 (Figure S7), when the MCS was at an initial stage. A cross-section applied over the reflectivity scan was also obtained for 16:30 (Figure S8), when the system was at a mature stage.
At the initial stage, the 0.1° tilt showed several small-scale divergence signatures spatially correlated with moderate-high reflectivity cores (Figure 5b), consistent with the downburst activity that was documented. However, the 1.5° tilt showed a pattern of widespread outgoing wind components in the SRV at 2400–3300 m a.m.s.l. (Figure 9a), consistent with air currents entering the MCS from the west–south–westerly direction or even southerly direction. The same pattern was consistently found above, with a 4.0° tilt at 5200–7700 m a.m.s.l. (Figure 9b), coherent with air flows entering the MCS from the same directions. The few exceptions to this outgoing wind pattern were observed in the areas closer to the radar (thus, at a lower altitude) in the vicinity of active convective cores.
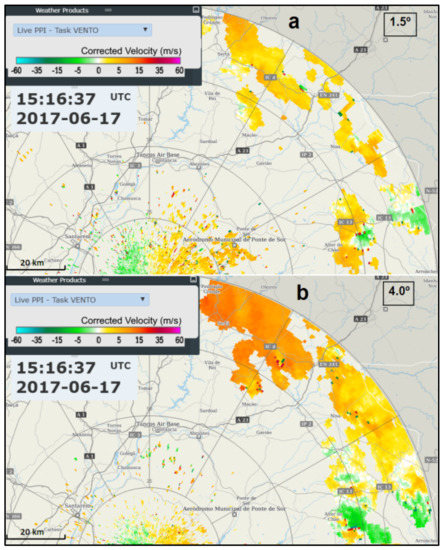
Figure 9.
PPI of the storm-relative velocity, 1.5° tilt (a) and 4.0° tilt (b), 15:16 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar.
As the system was maturing, the 0.1° tilt continued to show downburst signatures (Figure 10a). Compared to the 15:16 observation (Figure 5b), these signatures revealed larger magnitudes of incoming–outgoing components (Figure 10a) and, thus, larger divergence. The downburst strength increased until 16:26 (Figure 6b). This overall increase in the magnitude of downbursts was already documented by comparing the average values of radial divergence by 15:16 (1.8 × 10−3 s−1) with the ones observed by 16:26 (2.9 × 10−3 s−1), which as discussed above, is consistent with the increase in the magnitude of the associated reflectivity cores. However, the most remarkable fact was that, by 15:56, both upper tilts of 1.5° and 4.0° continued to show widespread outgoing SRV components, consistent with air flows entering the MCS from west–south–westerly or southerly directions. Therefore, when the system was at its mature stage, with reflectivity cores at the largest magnitude, low-level divergence signatures were identified, in association with discrete, strong downburst activity, but at higher levels were observed front-to-rear MCS inflow currents. These air flows agreed with a coherent structure of a front-to-rear ascent, similar to past studies based on Doppler radar ([15], Figure 3). By this time, there were still no visible incoming SRV components proceeding from the rear of the MCS, even at moderate-high altitudes.
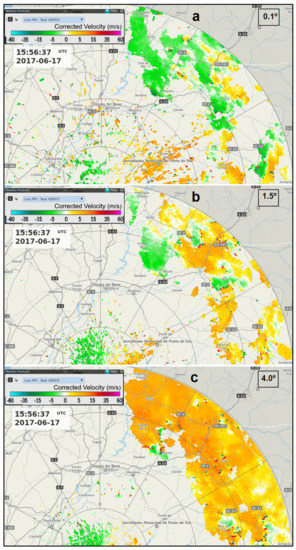
Figure 10.
PPI of the storm-relative velocity, 0.1° tilt (a), 1.5° tilt (b) and 4.0° tilt (c), 15:56 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar.
4.3.2. Dissipating Stage: The Rear Inflow Jet
Schmocker & Przybylinski [57] extended the concept of a specific Doppler velocity signature to a Quasi-Linear Convective System (QLCS) that, so far, has only been associated with isolated storms [58]. This signature, known as Mid-Altitude Radial Convergence (MARC), was identified when studying many QLCS cases, each of them involving the transition from a linear convective line into a bowing echo [57]. MARC is a strong and deep radial convergence identified on radar at the storm mid-altitudes. These authors computed MARC values by considering the maximum outbound–inbound radial storm relative velocity (SRV) differences. The areas of larger radial convergence were usually located within (or right downwind of) high reflectivity cores (typically above 50 dBZ) along the linear convective line. For systems moving toward the radar, they interpreted the outbound SRV of the MARC signatures as being associated to the deep layer front-to-rear ascent in the convective region of the MCS [18,59] (Figure 3) and the inbound SRV observed close to mature to weakening the convective cores, as associated with the middle rear-to-front descending flow [18,59] (Figure 3). The stronger inbound velocity signatures were interpreted as the origins of the mesoscale Rear Inflow Jet (RIJ) [60].
According to a study [61], the RIJ descended to the surface and was associated with the development of a Rear Inflow Notch (RIN) identifiable in the reflectivity field, behind the apex of the bowing echo. The RIN is a channel of a weak echo aligned or co-located with the RIJ [60]. It has been related to the effect of evaporating hydrometeors that cool and accelerate the jet. A region of low-level front-to-rear flow, located below the rear inflow was observed in several studies [22,53,62]. At the time of maximum intensity of convection in a squall line system it was found (BAMEX - Bow echo and Mesoscale Convective Vortex Experiment [28]) that as the rear-inflow was descending from the back of the system and the front-to-rear flow was ascending over the rear-inflow aloft, a front-to-rear flow beneath the rear-inflow was concurrently observed at low levels [53]. This low-level front-to-rear flow was observed during the entire period of observation of these studies.
In the current event, the MCS started to dissipate by mid-afternoon (16:30–17:00), as suggested by a gradual weakening of the reflectivity cores. The observations from 18:20–18:26 were selected as representative of this dissipating stage (Figure 7) and showed a reflectivity pattern comprising an area of more active (but weakening) convection in the southern section of the MCS front (Figure 7a), whereas the northern sector was characterised by low to moderate and homogeneous reflectivity, typical of a stratiform regime. By this time, the MCS resembled the asymmetric form [63]. As the system propagated over the fire areas, both reflectivity and velocity patterns showed the onset of flows distinct from the ones typical of discrete downbursts that were detected at an earlier stage. The period 16:26–18:36 was selected to analyse such emerging flows.
Doppler and reflectivity radar observations from this study showed similarities with previous findings for the Central USA [57,61] but, also, some remarkable differences. The overall length of the detected MARC signatures (30–50 km) (Figure 11 (bottom panel)) was smaller than their observed cases, due to the much larger scale of the systems typically observed in the central USA. Velocity maxima associated with MARC in their cases were located slightly downwind of high reflectivity cores, typically exceeding 50–60 dBZ, whereas in this study they were observed downwind of modest reflectivity cores, of no more than 45 dBZ (Figure 11 (top panel)). On their cases it was observed a bowing of the line convection pattern located downwind of each RIN whereas in this study that effect was very subtle and barely detected. The strongest magnitudes of MARC observed in the USA occurred at 4–7 km a.g.l. layer, whereas in this study they occurred at 2600–3100 m a.g.l. (approx. 3000–3500 m a.m.s.l.). The magnitude of the radial convergence observed in the USA was in the range 5.6 × 10−3–2.5 × 10−2 s−1 whereas in the current study it was considerably lower, 1.3 × 10−3–0.5 × 10−2 s−1. This was associated with much lower magnitude reflectivity cores in the current study. Furthermore, the MARC was computed with an unfavourable viewing angle, with the front of the MCS not perpendicular to the radar beam, which may have decreased the computed magnitudes [64]. Nevertheless, while those studies in the USA were specifically concerned with the onset of surface damaging winds, the current study also focused on winds of relatively lower magnitude, as these still can influence fires.
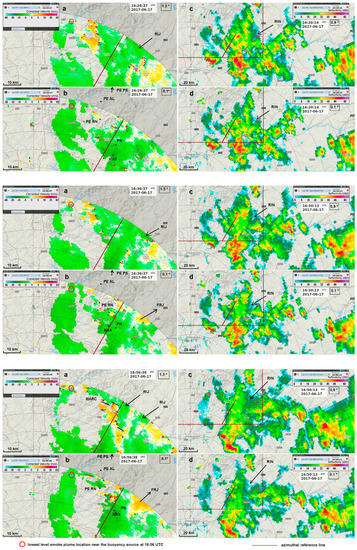
Figure 11.
PPI of storm-relative velocity, 1.5° tilt (a,e,i), 0.1° tilt (c,g,k); PPI of reflectivity, 0.9° tilt (b,f,j), 0.1° tilt (d,h,l). Lines in (b,d,f,h,j,l) delimit the insertion of the observed area in (a,c,e,g,i,k) respectively. 17th June 2017, C/CL radar. Top panel: 16:26 UTC (a,c); 16:20 UTC (b,d). Middle panel: 16:36 UTC (e,g); 16:30 UTC (f,h). Bottom panel: 16:56 UTC (i,k); 16:50 UTC (j,l).PE AL, PE RN represent Alvelos and Rendeiros Windmill Parks (PE PS Pampilhosa Park is outside the area, to the north). PN represents Proença-a-Nova AWS. MAX indicates the location of maximum inbound winds in the lowest tilt. RIJ indicates the signature of low-level inflow of a rear inflow jet. FRJ indicates the signature of a low-level front-to-rear flow located beneath the RIJ. RIN indicates the signature of a rear inflow notch. MARC stands for mid altitude radial convergence (represented by azimuthal segments in the bottom panel.
The two lowermost tilts of the velocity scan (0.1°, 1.5°) were used to describe the evolution of the SRV patterns and the two lowermost tilts available from the reflectivity scan (0.1°, 0.9°) were also accessed to identify relevant patterns of the MCS, in both scans from C/CL radar.
At 16:26, the SRV was not showing impressive MARC signatures at the higher tilt, but an inbound SRV pattern that would be continuously observed during more than two hours, started to emerge. This was the first time in the current event that a developing RIJ was observed at those levels (2700 m a.g.l.) (Figure 11a (top panel)). At the same time (slight difference in the time stamps of velocity and reflectivity scans) RIN signatures were identified in reflectivity, on both tilts (Figure 11b,d (top panel)). The RIN signature at the higher level was aligned with and upwind of the RIJ and the RIN signature at the lower tilt (collocated with the one observed higher) was aligned and upwind of the maximum inbound winds observed at the lower level (Figure 11 (top panel)). By 16:36, the RIJ signature was in the same area as before (Figure 11e (middle panel)), but the SRV values were of higher magnitude. Moreover, at low levels, a front-to-rear flow (FRJ), started to be clearly observed beneath the RIJ, in agreement with other studies [53]. The signatures of a RIN were visible in the two elevations, concurrent and upwind of the RIJ and of the maximum inbound winds in the higher and lower levels, respectively (Figure 11 (middle panel)). Ten minutes later the same setting was observed, including the presence of a FRJ signature below the RIJ and the same comments apply (Figure S9).
The PPI of SRV at 16:56 for the higher tilt revealed several MARC signatures to the east–southeast of the PG fires and downwind of relatively low reflectivity cores, at a height of 2600–2700 m a.g.l. (Figure 11i,j (bottom panel)). In the lower tilt, a maximum inbound wind was observed at a height of 400 m a.g.l. (Figure 11k (bottom panel)) and signatures of a RIN were identified on both tilts (Figure 11j,l (bottom panel)), located upwind of the MARC signatures and of the maximum inbound winds observed at a low level (Figure 11i,k (bottom panel)). Two signatures of inbound flows (marked RIJ in Figure 11i (bottom panel)) were identifiable and resulted from the interaction between the descending jet and the front-to-rear sloping ascent flow. Furthermore, a FRJ signature continued to be observed in the lower tilt, just below the RIJ (Figure 11k (bottom panel)). Similar MARC signatures were detected by 17:06 and 17:16, at similar heights (Figure S10a and S11a). Maximum inbound storm relative winds of similar magnitude than earlier were also observed in the lower tilt (15.9 m/s and 17.7 m/s, Figure S10b and S11b). At those times signatures of RIN continued to be identified on both tilts (Figure S10c,d and S11c,d) less prominently than before, but still located upwind of the identified MARC signatures and of the maximum inbound winds observed at the low level. These RIN signatures were spatially coherent between successive observations thus suggesting continuous and prolonged phenomena. Moreover, C/CL and A/PG radars, while having very different viewing angles towards the MCS, both showed the same weak channel echo signatures, at the same location and time (not shown). This argument is an additional support of their existence.
By 17:26 an inbound SRV pattern similar to those that were observed earlier, became visible in the higher elevation as an apex of incoming velocities among the outgoing flows. This signature was considered another surge of the RIJ at those levels (2700 m a.g.l.) (Figure S12a). A maximum inbound wind (11.2 m/s) in the lower tilt was roughly aligned and downwind of the apex of this pattern (Figure S12b). At that time a RIN signature was identified on both tilts (Figure S12c,d), the higher aligned and upwind of the RIJ and the lower upwind of the maximum inbound winds at low levels. Ten minutes later, the area of the RIJ pattern detected on the higher tilt of the scan had expanded, which was a clear sign that the RIJ was developing and being better resolved by radar in its westerly/south–westerly displacement (Figure 12a (top panel)). Its maximum inbound SRV winds increased slightly, and a maximum of 17.7 m/s was observed in the lower tilt, just downwind (southwest) of the apex of the RIJ pattern (Figure 12c (top panel)). Again, a signature of outbound winds (FRJ) was present in the lower tilt and these winds also increased concurrently with the RIJ. The RIN signature continued to be identified on both tilts, located upwind of the RIJ and of the maximum inbound winds (Figure 12b,d (top panel)). At 17:46 the higher tilt revealed an even more prominent RIJ signature and its maximum SRV winds increased, again. A maximum inbound wind (17.1 m/s) that was identified in the lower tilt was located, again, downwind of the apex of the RIJ pattern observed above (Figure 12g (middle panel)). The FRJ continued to be identified underneath the RIJ. The RIN signature also continued to be visible at both elevations, located upwind of the RIJ (Figure 12f,h (middle panel)) and strongest low-level inbound SRV (Figure 12g (middle panel)). Between 17:36 and 17:46 at the low levels, a displacement to the southwest of the maximum inbound wind pattern was identified (Figure 12c (top panel) versus Figure 12g (middle panel)). This displacement was noticed concurrently to the expansion of the RIJ signature to the southwest and is interpreted as a sign of spatial coherence of the flow observed at two different heights.
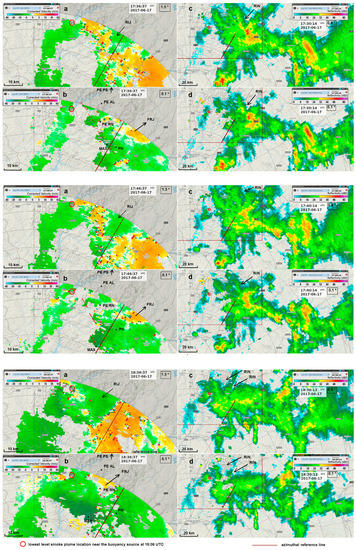
Figure 12.
PPI of storm-relative velocity, 1.5° tilt (a,e,i), 0.1° tilt (c,g,k); PPI of reflectivity, 0.9° tilt (b,f,j), 0.1° tilt (d,h,l). Lines in (b,d,f,h,j,l) delimit the insertion of the observed area in (a,c,e,g,i,k) respectively. 17th June 2017, C/CL radar. Top panel: 17:36 UTC (a,c); 17:30 UTC (b,d). Middle panel: 17:46 UTC (e,g); 17:40 UTC (f,h). Bottom panel: 18:36 UTC (i,k); 18:30 UTC (j,l). PE AL, PE RN represent Alvelos and Rendeiros Windmill Parks (PE PS Pampilhosa Park is outside the area, to the north). PN represents Proença-a-Nova AWS. MAX indicates the location of maximum inbound winds in the lowest tilt. RIJ indicates the signature of low-level inflow of a rear inflow jet. FRJ indicates the signature of a low-level front-to-rear flow located beneath the RIJ. RIN indicates the signature of a rear inflow notch. Dashed red segment depicts a pattern of enhanced low-level winds collocated with the frontal (southwestern) section of the MCS (represented in (c), Top panel and (g), Middle panel).
As the MCS continued to slowly propagate over the fire areas and the RIJ pattern was detected at the higher elevation, the maximum SRV winds of the RIJ were increasing (−10 m/s at 17:56, −11.2 m/s at 18:06, −11.2 m/s at 18:16 and −17.7 m/s at 18:26), as well as the maximum inbound winds that were detected in the lower tilt (−17.7 m/s at 17:56, −21.9 m/s at 18:06, −26.0 m/s at 18:16 and −30.7 m/s at 18:26), always in areas that were located downwind the apex of the RIJ signature (Figures S13–S16). Moreover, the FRJ signature continued to be discernible beneath the RIJ at all times. A decrease in SRV winds of the RIJ was observed only by 18:36 (−9.5 m/s), concurrent with a slight decrease in the maximum inbound winds at low levels (−28.4 m/s). The RIN signature was identified at the two elevations (Figure S13c,d and Figure 12j,l (bottom panel)), always upwind of the RIJ observed at the higher levels and of the maximum inbound winds that were observed at the lower levels.
The identification of RIN signatures upwind of RIJ signatures and the concurrent observation of an increase in the magnitude of the SRV from the higher (further to the northeast) to the lower (further to the southwest) levels reveal that these SRV signatures correspond to the onset of coherent airflows that were descending and accelerating toward the lower levels, materialising a RIJ. These findings are synthesised in Figure 13 for the period 17:26–18:36. It can be observed that higher level SRV, from 1.5° tilt, is always weaker than lower level SRV, from 0.1° tilt, and that as higher level SRV increased, lower level SRV increased accordingly. As SRV components decreased between 18:26 and 18:36 (compare Figure S16 and Figure 12 (bottom panel)), both higher and lower level SRV values responded with a decrease. After 18:06, during a period in which reflectivity at both tilts was being depleted, several RIN signatures were observed simultaneously in the back of the northern sector of the quickly dissipating MCS (Figure S16 and Figure 12 (bottom panel)).
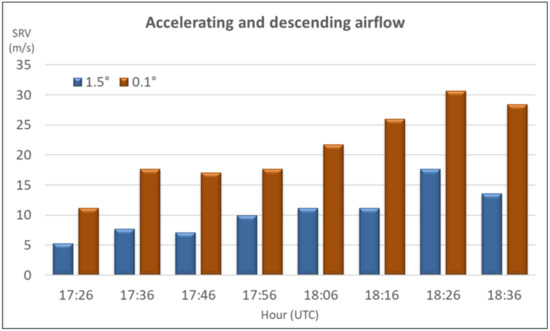
Figure 13.
Maximum inbound storm velocity at the 1.5° and 0.1° tilts, 17:26–18:36 UTC, 17 June 2017, C/CL radar.
The radar viewing angle over the maximum inbound SRV areas did not change much during the period 17:26–18:36. Moreover, as discussed ahead in more detail, a sudden shift in the fire plume orientation was observed on radar reflectivity by 17:40–17:50. Before, the smoke plume at low levels was under the influence of northerly winds but by that time onwards, it kept being forced by low level winds blowing from the east–northeast. This suggests that the C/CL radar had a viewing angle progressively less favourable toward the inbound SRV signatures, as the MCS propagated to the west. Thus, it is reasonable to assume that the larger incoming wind components would be observed at approximately the same location of the true stronger winds during that period, although being a default estimate of these winds. By 18:26 a 40 km-wide signature was detected at low levels, corresponding to incoming Doppler velocities exceeding 30 m/s at 300 m a.g.l. (Figure S16).
Range height indicator scans were not available; thus, the available PPIs of the Doppler scan were used to roughly estimate the RIJ inclination. At each instant the location of the maximum SRV value observed concurrently with the RIJ signature, at the 1.5° tilt, was combined with the location of the maximum SRV observed at the 0.1° tilt, in order to compute the inclination of maximum winds. An estimated value of 12° was obtained to the period 17:26–18:36. This value compares with the inclination of a RIJ that was observed during the BAMEX experiment over the central USA [53] (Figure 9e), slightly above 7°. Even if those cases were different, it is still interesting to note a similar inclination between the two.
During the entire period that the large-scale inbound SRV flow (the RIJ) was monitored at the higher tilt (1.5°), a large-scale outbound SRV flow was also identified in the lower tilt (0.1°), collocated with the inbound flow above (Figure S12, Figure 12 and Figures S13–S16). This outbound flow is compatible with a low-level airflow directed to the east–northeast and was interpreted as a return current of the descending rear-to-front flow. This agrees with the observations that were collected during BAMEX [53]. This type of flow was also identified in other study [59] and is represented in Figure 3. The onset of this low-level airflow was coherent with surface observations, as shown ahead.
5. Evolution of the Pyroconvective Plume: Fire Intensity, Plume Orientation, Plume Vertical Extent and Plume Mode
As discussed in 2.3, it was applied a methodology based on radar observations to monitor the evolution of fire behaviour in the period 16:00–20:00. This evolution was inferred from (i) the magnitude of the reflectivity observed in the pyroconvective element located closer to the updraft source, (ii) the orientation of the plume observed at low levels, (iii) the vertical extent of the plume and (iv) the estimated plume mode.
The overall fire intensity demanded the investigation of the type of backscatter that was causing the reflectivity observed right above the updraft source region. The 16:40 and 18:30 observations are presented here as examples of the applied methodology. On both cases it was found that the reflectivity observed close to the updraft source by the dual pol A/PG radar, at an altitude of 1400 m, originated on pyrometeors. This conclusion was drawn from the fact that the backscatter measured by A/PG above the pyroconvective element detected on reflectivity close to the updraft source by C/CL, was characterised by ρhv < 0.7 at 16:40 (Figure S17, panel b) and at 18:30 (Figure S18, panel b). Thus, smoke caused the backscatter that was observed by the C/CL radar 500 m below that altitude (Figure S17a and Figure S18a).
Results are synthesised in Figure 14, where the magnitude of reflectivity of the pyroconvective elements identified close to the updraft source as smoke, can be followed.
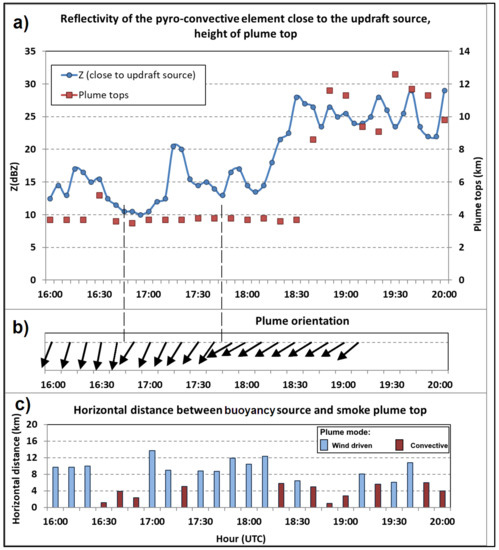
Figure 14.
(a) Reflectivity of the pyroconvective element close to the updraft source (blue line). Plume tops (red squares) (16:00–20:00 UTC). (b) Plume orientation denoted by arrows that point downwind (16:00–19:10 UTC). Dashed-lines highlight orientation changes >= 20°. (c) Bars denote the horizontal distance between buoyancy source and smoke plume top (16:00–20:00 UTC). 17 June 2017.
The low-level reflectivity of a pattern originating close to the buoyancy source and extending downwind from it was also identified at each instant, on radar. A centreline of this pattern was determined, from radar observations, for every instant of the considered period and its orientation was taken as a reference for the orientation of the plume near, but slightly above, the active fire. The orientation of this upper-level plume was derived from reflectivity patterns that were observed at 400 m a.g.l. and the short-term forecasts of the ECMWF model (Figure S2) did not suggest significant environmental wind shear in the layer below that level. However, there was a strong suggestion that vertical wind shear was, indeed, present in the layer below 400 m a.g.l in the fire areas and surroundings during the period 16:00–19:00. The evidence came from the comparison between the referred orientation observed at 400 m a.g.l. and the wind direction that was observed close to the ground (60–80 m a.g.l.) at 2 windmill parks, during the same period. This will be further discussed in Section 6.1.
Even when the plume mode transitioned into a more convective regime, it was still possible to monitor its orientation from the direction of the low-level smoke advection due to the prevailing winds at that level. This monitoring was possible until 19:10 (Figure 14).
During the same time span (16:00–20:00) a methodology to estimate the vertical extent of the smoke plume was applied. The 16:40, 18:30 and 18:40 observations are presented as examples. At 16:40 the highest altitude at which ρhv < 0.7 was observed was 3.6 km (Figure 14). The cross-section presented in Figure S19 shows a plume top above 4 km, but that was an overestimation due to interpolation between tilts. To be more accurate, PPI values were used to estimate the smoke plume top. The same considerations apply to the other examples (Figure 14 and Figure S20).
Results are synthesised in Figure 14, where the evolution of the vertical extension of the pyroconvective plume can be followed.
As discussed above, the plume mode was also identified and monitored along the same period, as multicell type versus convective type, and the results can be followed in Figure 14. To the authors’ knowledge, there are no universal quantitative criteria to classify plume mode on radar. The observations that were characterised by a distance < 6 km between the top of the plume and the pyroconvective element identified close to the buoyancy source were highlighted in the graphic as defining a convective-type plume (Figure 14) due to its approximate vertical alignment.
The evolution of the PG fires intensity revealed three periods in which the magnitude of reflectivity in the pyroconvective plume close to the updraft source reached a relative maximum: at 16:15 (17 dBZ maximum, after an increase of 4.5 dBZ in the previous 15 min), hereafter intensification A at 17:15 (20.5 dBZ maximum, after an increase of 10.5 dBZ in the previous 20 min), hereafter intensification B and at 18:30 (28 dBZ maximum after an increase of 14.5 dBZ in the previous 25 min), hereafter intensification C (Figure 14). Considering that dBZ is the unit of a logarithmic reflectivity factor, depending on the sixth power of drops diameter, a relatively small difference in dBZ values hide a countless discrepancy in the base linear reflectivity. This means that the rise of 14.5 dBZ in the last intensification (C) equates to a much larger increase in the number/size of backscatterers than that of 10.5 dBZ during the intermediate intensification (B) and 10.5 dBZ in turn, much larger than that of 4.5 dBZ in the first (A).
A shift in the orientation of the plume from northwest to north (observed slightly before 16:00, not shown) anticipated the peak of intensification A, a shift in the orientation at 16:40–16:50, from north to north–northeast (24° variation in 10 min, first orientation change denoted in Figure 14) anticipated the peak of intensification B and, finally, a shift in the orientation at 17:40–17:50, from north–northeast to northeast (20° variation in 10 min, second orientation change denoted in Figure 14) anticipated intensification C. Moreover, 10 to 20 min after the peak of each intensification process, a towering of the pyroconvective plume top was observed: a considerable rise from 3600 m to 5200 m in A, a modest rise in B and an outstanding expansion from 3700 m to 8600 m in C (Figure 14). Furthermore, analysis of the fire evolution showed that, as an intensification was occurring, the plume acquired the characteristics of a convective type, becoming approximately vertically aligned (Figure 14).
So, a substantial shift in the orientation of the plume anticipated A, B and C intensification. Since after each shift the plume maintained a relatively steady direction for subsequent times, a relatively strong and coherent airflow should be the cause for such changes. Slightly after each shift, the intensity of the fire started to increase. Such a slight delay between the shift in the orientation and the start of the intensification process is attributed to the time required for the stronger low-level winds that re-oriented the plume, increase the combustion process in the active fire area and for the heated surface airmass to be transported upwards, carrying more and larger scatterers to the lowest level that the radar can observe, thus increasing the reflectivity [31]. Soon after each of the intensification peaks, the towering of the pyroconvective plume was observed, as an effect of the intensification of the convective process that resulted from the release of more heat within the active fire area. Monitoring the evolution from A to B and C shows the culmination of continuously stronger intensification processes over progressively more intense fires.
The wind shifts and resulting fire intensification will be discussed in the context of the underlying atmospheric flows.
6. Discussion: Influence of the MCS Driven Flows in the Course of the PG Fires
6.1. MCS Driven Flows
As the MCS propagated towards and over the fires of PG (16:20–18:40) several patterns of storm-relative velocity and reflectivity were identified which are important to understand the influence of the MCS on the fires.
After 16:30, as the system was transitioning into a dissipating stage over a region to the east–southeast of the fire areas, the onset of a relatively large-scale overturning flow formed by two main limbs was captured on radar: a front-to-rear deep layer inflow ascending over the more prominent convective region of the MCS and a rear-to-front mid-level inflow descending below the anvil structure of the MCS, the rear inflow jet (RIJ, Figure 3). A front-to-rear flow (FRJ) was also identified beneath the RIJ (Figure 3) as a part of the circulation of this second limb. Rear inflow notches (RIN) were identified on reflectivity fields and found to be upwind of the areas where the stronger rear-to-front low-level winds were observed. The maximum winds of the RIJ were, in general, increasing during this period as well as the maximum winds that were concurrently observed at the lower levels. The FRJ was identifiable beneath the RIJ nearly at all times.
Three windmill parks were used as ground truth data since no surface weather stations were located close to the fire areas. These were the Alvelos (PE AL) and Rendeiros (PE RN) parks, located 15 km to the east and east–southeast of the fires, respectively, and the Pampilhosa-da-Serra (PE PS) Park, located 30 km to the northeast of the fires (e.g., Figure 11 (middle panel)). The wind sensors in the windmill towers are installed at a height of 60–80 m a.g.l., instead of the standard 10 m.
The observations from 16:26 and 16:36 (Figure 11 (top panel), Figure 11 (middle panel)) showed that the RIJ axis was still relatively far from the fires. At those times the PE RN Park was still under the influence of a north–north–westerly flow that had been affecting the area for the previous few hours, corresponding to the environmental wind (Figure 15). The orientation of the fire plume was from the north. A continuous monitoring revealed that this orientation had shifted some minutes earlier (not shown), from northwest to north, in accordance with the PE RN Park observations (Figure 15). This means that the first low-level reflectivity maximum of the plume (observed at 16:15), occurred as the fires were still under the influence of the environmental flow. However, the PE AL Park observations showed that this location was influenced by north–westerly environmental winds only until 15:50 (Figure 15) and that by 16:26, 16:36 it was already consistently under the influence of an easterly flow, although still relatively weak (wind gusts below 12 m/s, Figure 15). At the same time the PE PS Park, that was located further north (e.g., Figure 11 (middle panel)) was still showing a north–westerly flow, driven by the larger scales.
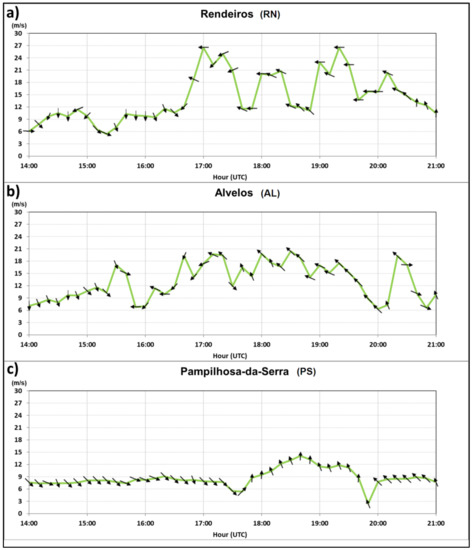
Figure 15.
Wind gusts magnitude (green line), average wind direction (arrows) at (a) Rendeiros (PE RN) windmill Park, (b) Alvelos (PE AL) Windmill Park and (c) Pampilhosa da Serra (PE PS) Windmill Park. Observations at 60–80 m a.g.l., 14:00–21:00 UTC, 17 June 2017.
At 16:56, as the MCS approached the fire areas (Figure 11 (bottom panel)), a linear pattern of maximum inbound winds oriented southeast–northwest was identified, roughly over the PE RN Park and the PN AWS (Figure 11 (bottom panel)). This signature was located slightly downwind (southwest) of the MARC signatures and its relative maximum winds were seen as a surge of the developing RIJ (Figure 11 (bottom panel)). By that time, the PE RN Park started to be influenced by a north–easterly–easterly flow, which was relatively light initially (12 m/s gusts at 16:40) but strengthening soon after (18.9 m/s gusts, at 16:50) and peaking by 17:00 (26.5 m/s gusts) (Figure 15). Moreover, by that time the PN station started to record a stronger north–easterly–easterly flow (13 m/s gusts) that peaked by 17:10 (23 m/s gusts) (Figure S6). On both locations, these strong gusts were seen as the result of the referred RIJ surge over a large area (PE RN and PN locations are more than 20 km apart). As noted, the video images of the fire showed that the orientation of the fire plume changed suddenly from north to the north–northeast in the period 16:40–16:50 although at the time no increase was observed in the low-level reflectivity close to the updraft source. This change in the plume orientation was verified only 10 min later than the wind shift observed at the PE RN Park, which denoted a more backed wind from the east at low levels. This was considered to be the result of a first major direct influence of the RIJ over the fire areas. At the PE AL Park, located outside the radar Doppler range, a strong north–easterly flow was also recorded with gusty winds in the range 14–20 m/s, by 16:40–17:00 (Figure 15). This was also seen as the result of the onset of the RIJ surge over the location. At the same time the PE PS Park, located farther northeast, was still dominated by a light north–westerly flow, thus remaining unaffected by the MCS.
By 17:00 the anvil of the MCS was already overhead the fires (Figure S21). The 17:06 and 17:16 observations continued to show MARC signatures in the higher tilt and strong inbound winds at the lower tilt, to the east–southeast of the fires (Figures S10 and S11). The PE RN and PE AL parks continued to record strong gusts from 20–25 m/s from the east–northeast and 20 m/s from the east–southeast, respectively, whereas the PE PS Park remained influenced by environmental winds (Figure 15). During this period the orientation of the plume was kept around the northeast (Figure 14), showing that the flow at 400 m a.g.l. was persistently established from that direction, as driven by the MCS, slightly veered relative to the windmill observations. This continuous flow of strong gusty winds has probably played an important role in the 20 min steady increase of the low-level reflectivity close to the updraft source. This increase has materialised as the second intensification of the pyroconvective plume, exactly at 17:15 (Figure 14).
During the following period, 17:26–17:46, the RIJ was closer to the fire areas and also better resolved on radar (Figure S12, Figure 12 (top panel), Figure 12 (middle panel)). As the RIJ surged, the maximum inbound winds at the lowest tilt suddenly increased between 17:26 and 17:36 (Figure 13) suggesting an intensification of the low-level flow. The analysis of the SRV pattern in the lowest tilt at 17:26, 17:36 and 17:46 confirmed that the magnitude growth of these low-level winds occurred over an extensive area. The pattern of enhanced winds was oriented southeast–northwest and collocated with the frontal (western) area of the MCS, downwind (west–southwest) of the PE RN Park and of the PN station (Figure 12 (top panel)). The wind observations at these locations showed that by 17:40 and 17:50 wind gusts were at a relative minimum. That was probably due to the fact that the transition zone between the RIJ and FRJ (Figure 3; Figure 12 (top panel)) was crossing the area around that time. However, it can also be seen that the northern sector of the observed area of increasing low level winds that was detected at 17:36, approached the fire areas and that by 17:46 it was very close (less than 5 km) and to its east (Figure 12 (top panel), Figure 12 (middle panel)). This surge of the RIJ was concurrent with a displacement, to the southwest, of the maximum inbound winds in the period 17:36–17:46 (Figure 12 (top panel), Figure 12 (middle panel)) and, by 17:40–17:50, with a shift in the plume orientation from the north–northeast to the northeast (Figure 14). The observations at the PE AL and PE RN parks showed the onset of stronger winds right after 17:50 that lasted for at least 30 min and had gusts from the east and east–southeast at or exceeding 20 m/s (Figure 15). These stronger winds were observed nearly simultaneously at these parks and arrived at the active fire area slightly later. Again, backed when compared to the orientation of the plume, they were considered as an important causal factor in the fire intensification process. This plume shift was driven by the incoming winds and considered as a second major direct influence of the RIJ over the fire areas.
A close monitoring of the plume orientation at the lowest level (400 m a.g.l.) in the period 17:40–18:30 (Figure S22) shows that as the shift occurred, at 17:50, the pattern revealed it in a small segment downstream of the active fire area (Figure S22b) but only very close to it, as the rest of the plume kept its more northerly orientation. However, as time passed, this shift occurred gradually farther away from the fire areas, so that by 18:30 a 40 km long pattern on reflectivity was entirely oriented along the prevailing winds, which were from the northeast at that level (Figure S22f) and convectively driven by the MCS.
In the period between 17:56–18:36, as the MCS continued to slowly propagate over the fire areas and as the RIJ was surging (2500–2800 m a.m.s.l.), low-level winds were concurrently increasing (i the layer 400–700 m a.m.s.l.). An absolute maximum was observed at 18:26, exceeding 30 m/s (Figures S13–S16). A slight decrease in SRV winds of the RIJ was observed only by 18:36 along with a slight decrease in the maximum inbound winds observed at low levels (−28.4 m/s, Figure 12 (bottom panel)). The increase in the magnitude of maximum low-level winds observed by radar during this period was even more meaningful as the patterns were progressively detected at less favourable angles by the radar beam, thus retrieving comparatively lower velocity components. Ground observations from the PE RN Park showed that even after 18:30, wind gusts at or in excess of 20 m/s were affecting the location, whereas observations from the PE AL Park showed roughly the same orientation of the average wind but with lighter gusts, in the range 15–20 m/s.
The evolution of the plume orientation and of its low-level reflectivity between 18:00 and 18:30 was followed by the largest rate of vertical expansion of the fire plume observed by radar (Figure 14). Indeed, it took only 10 min (18:30–18:40) for the fire plume to raise from 3700 m to 8600 m altitude. This outstanding vertical growth occurred a few minutes after the merging of the two independent fires (Escalos Fundeiros, EF, and Regadas, RE) that occurred by 18:30–18:40 as described below, according to ground reports [14]. A close inspection of the average wind direction observed at the PE RN and at the PE AL parks showed that during 17:40–18:30, on both sites, these winds veered so that they became more east–south–easterly oriented than before (blowing from 82–113° in PE RN and from 130–158° in PE AL), while maintaining their strength. The two fires had ignited 2 km from each other and by 18:00 the ground survey determined they were still a few hundred meters apart (Figure 16). At that time the more active part of the EF fire was evolving to the southeast of the RE fire. It is hypothesised that the slight veering of the low-levels winds to the southeast may have been important, as it may have directed the EF fire to the west–northwest, ultimately favouring the merging of the two fires by 18:32. This merge was followed by an extremely violent and widespread firestorm that covered a large area of terrain. The sequence of phenomena was considered to be largely driven by the influence that the convectively induced flows of the MCS played initially over the fires.
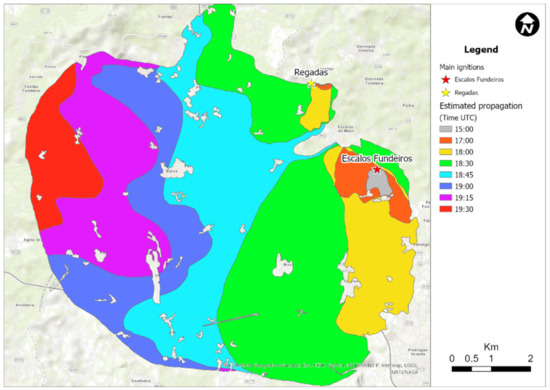
Figure 16.
Approximate evolution of the fires between 19:30 and 20:30 UTC, as per ground survey. RE and EF represent Regadas and Escalos fire ignition, respectively.
6.2. Evolution of the Fire
As referred above, the two ignitions that contributed to the fire of Pedrógão Grande on the 17 June 2017 were located at Escalos Fundeiros (EF) and at Regadas (RE), separated 2.6 km from each other, as it is shown in the map of Figure 16. The fire contours shown in this map were derived from an extensive field survey based on interviews with many fire fighters and residents in the area, who witnessed the evolution of the fire, as well as on documents like photos, video and satellite images that were provided to the authors. More details can be found in [14]. The fire of EF developed initially in the bottom of a valley under the influence of changing winds mainly from northwest direction. Although it was attacked few minutes after it started, due to the changing winds, the occurrence of spotting and the presence of houses and settlements, the limited firefighting resources were not able to suppress the fire. When the ignition of RE was perceived by the command post, there were no sufficient resources to allocate to this second fire and it was left spreading almost freely towards east until 17:00.
As was mentioned above, after 16:30 the MCS induced wind gusts from northeast, turning to east, over the areas of the fire, affecting strongly both EF and RE fires. Video images from the cameras located in Pedrógão Grande show that between 17:00 and 17:15 the plume of EF fire dropped to the ground and became completely out of control. Until 18:00, both fires started to spread with great intensity towards south, as shown in Figure 16. With the turning of the wind to east and southeast the western flanks of the fires of EF and RE spread like a fire front increasing largely their areas until 18:30.
Around this time, the two fires were now sufficiently large and close to each other, so they began to interact and merge with each other. There is photographic evidence that around 18:30 the two flanks of these fires are almost parallel to each other and separated less than 0.5 km. This situation is similar to the one described in [65,66], of the junction of two linear fires making a relatively small angle between them. Laboratory and field experiments show that in the case of merging fire fronts, a very quick fire spread is produced between the two fires, with very strong convective effects, like fire whirls and tornados. There is ample evidence in the area in which these fires merged that tornado-type winds exceeding 200 km/h broke tree trunks with more than 20 cm of diameter, lifted sheep and heavy roof structures causing great destruction. A similar situation was reported in the fires of Canberra in 2003, as reported in Reference [67], in which the merging of two very large fires with the same configuration also produced destructive tornados.
The very fast spread of the fire between 18:30 and 19:00 in a vast area between the two fires corresponded to a great release of energy and smoke into the atmosphere and contributed to the rapid increase of the height of the plume from 4 to 9 km between 18:30 and 18:45, as shown in Figure 14. The height of the plume remained between 9 and 12 km for more than one hour as a very large amount of fuel was burning in that period of time in the area affected by the fire, as can be seen in Figure 14 from the extreme reflectivity values.
It should be noticed that between 19:00 and 19:30, the fire impacted the road N236-1 between Figueiró dos Vinhos and Castanheira de Pera, killing 30 persons who were trying to escape from the fire, in a stretch of 200 m of this road.
The interaction between the MCS and the two fires of EF and RE had a decisive importance in increasing their intensity and spread, between 17:00 and 19:00. If this did not happen the two fires would have merged anyway, as they were spreading almost out of control. However due to the MCS interaction at around 17:30, both fires reached a size and configuration that made their merging with the pattern of extreme violence that was described.
6.3. Radar Observation
Radar observations revealed that from 16:26 onwards, a front-to-rear flow (FRJ) located beneath the RIJ was observed concurrently with it. Ground observations were coherent with such flow. By 17:50, the PE PS Park started to reveal a southerly flow (Figure 15) and at the same time, the PA AWS (Figure S6), located very close to the PE PS Park, also showed a wind shift to the southern quadrant. Even considering that wind observations at 10 m (AWS) and 60–80 m a.g.l. (windmill parks) may reflect some difference at the same location, their general agreement strengthens the conclusion that only then this location became influenced by the MCS convectively driven flows.
This southerly flow was observed at several locations (PA, CB) for a couple of hours and is coherent with the onset of the FRJ depicted on radar. In the current event this flow was nearly as strong as the one associated with the RIJ itself according to ground truth data (Figure S6). Therefore, it is likely that both diverging mesoscale flows that emanated from the MCS (RIJ and FRJ) had the potential to influence the course of the fires, and it is important to recognise that this potential was restricted to the RIJ during the current episode, only due to the relative location of the fires downwind of the MCS.
After the merging of the two fires and the consequent firestorm, a period of more than 1.5 h followed during which the plume top was always observed on radar above 8000 m a.m.s.l. and even above 12,000 m (19:30), probably above the tropopause (Figure 14). During this period the magnitude of the low-level reflectivity close to the updraft source was always high in the context of a wildfire [67] reaching a maximum of 29 dBZ by 20:00 (Figure 14). For the vast majority of the time, the plume was of a convective type, nearly vertically stacked (Figure 14).
As extensively remarked along this study, stronger convergence was observed on radar in atmospheric volumes located downwind of weak reflectivity cores (e.g., 45 dBZ) when compared to the more common observations in the USA (e.g., 50–60 dBZ) [57,61]. The short-term forecasts of the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre (BSC) BSC-DREAM8b model for 12:00 and 18:00 of the 17 June 2017 showed that the airmass where the MCS was embedded in was characterised by a non-negligible mineral dust load that was being transported from the Sahara Desert (Figure S23). This extra supply of cloud condensation nuclei suggests the presence of a larger concentration of small droplets in the MCS which is coherent with lower reflectivity values. It has been recognised that atmospheric aerosols impact the microphysical structure in convective systems [68] and, more specifically, that in systems with high freezing level and in dry atmospheres (as in the current case) the increased concentration of aerosols tends to generate stronger evaporative cooling effects at low levels, as compared with systems propagating in higher humidity environments [69]. These effects could explain the generation of strong downdrafts in an environment characterised by modest reflectivity cores.
7. Conclusions
The current study analysed the influence of an MCS in the evolution of two wildfires that started during the afternoon of 17 June 2017 in Pedrógão Grande, central mainland Portugal. These wildfires developed in a complex terrain, including versants and canyons with steep slopes. The region was in severe drought situation and a heatwave was ongoing. The value of fuel moisture content was very low, indicating that spot fires, if any, were likely to rapidly intensify. The weather conditions were those of a hot and dry environment, namely in the low troposphere, that presented an inverted V shape profile typical from dry downburst environments [48]. Moreover, an MCS evolved in the region during the afternoon.
The MCS developed as a chaotic system, escaping the linear archetypes more commonly observed. In its more initial stages, still relatively far from the fires, this system supported deep convection. Radar observations showed that the leading sector of the MCS was initially a prolific discrete downburst producer. Moreover, ground truth data confirmed that airmass changes and gusty winds were felt, accordingly, at ground levels in a number of locations to the east–southeast of the fires. However, during these initial stages the fires were not significantly influenced by the downburst activity of the MCS.
As the system continued to propagate towards the fire areas, it started to dissipate, as less convective cores of lower reflectivity were being observed and a more stratiform structure was apparent. At this stage radar data showed that the system, now slightly upwind of the fire areas, was producing strong winds at low levels but, unlike the earlier stages of its lifecycle, those winds were now spawned over a much wider area and not consistent with discrete downburst activity. An extensive radar data analysis demonstrated that, by then, the MCS was exhibiting a relatively large-scale overturning flow, formed by (i) a front-to-rear deep layer inflow ascending through the more convective region of the MCS and (ii) a rear-to-front mid-level inflow descending below the anvil structure of the system. A front-to-rear flow beneath this rear-to-front descending flow was also persistently identified. The same analysis showed that evaporative signatures were systematically detected upwind of the stronger areas of a coherent rear-to-front flow that was descending and accelerating towards the lower levels, materialising a rear-inflow-jet. The inclination of this jet compared well with an estimation made by other authors on a study of a MCS over the USA [22]. A storm-relative wind profile was also derived, and it showed that, in a layer between the zero-degree isotherm and lower levels, a north–easterly–easterly inflow would be expected, just below the anvil of the MCS. Further, it was verified that the airmass in which this weather system was embedded had a substantial dust load transported from the Sahara Desert. It is hypothesised that this extra supply of cloud condensation nuclei favoured a large concentration of small droplets in the MCS, which is coherent with the relatively lower observed reflectivity values as compared with other authors [57] and with stronger evaporative cooling effects at low levels, as compared with systems propagating in higher humidity environments [69].
The evolution of the fire behaviour and fire plume was monitored by a radar-based method blended with ground survey data and weather observations at and close to ground levels. As a result, it was found that strong, gusty winds associated with convectively driven flows originated in the MCS, had persistently affected the fire areas and the fire behaviour. Several major influences of the convective system over the fires were identified. In each of those instances, a substantial shift in the orientation of the plume at low-levels was observed initially and, also, that the plume maintained a steady orientation afterwards. This suggested that the shift was driven by the onset of a relatively strong and coherent airflow. Then, slightly after each shift, the intensity of the fire started to increase steadily, as observed by radar. This delay was considered as a result of the time required for the incoming and stronger low-level winds that increased the combustion process in the fire spot and, subsequently, increased fire intensity. Simultaneously, or shortly after, the fire’s intensification reached a maximum, the vertical expansion of the pyroconvective plume was observed, as a result of the brutal increase in local instability that, in turn, resulted from the increased release of heat in the fire area.
The largest rate of vertical expansion of the fire plume, from 3700 m to 8600 m a.m.s.l. was observed a few minutes after the merging of the two independent fires had occurred, as confirmed by ground survey [14]. These fires ignited 2 km apart from each other more than 3 h before they merged. Even 30 min before the merged, they were still a few hundred meters apart. As radar detected stronger wind signatures associated to the MCS, close to the fires and about 40 min before their merging, two windmill parks showed the onset of stronger winds that endured for at least 30 min and had exceeded 20 m/s. These stronger, long lasting gusty winds were considered to have favoured the merging of the two fires. After the merging, the junction fire became very intense and impossible to control, as an extremely violent and widespread firestorm started.
In the studied case the overturning flow of an MCS, by its relatively long-lasting nature, proves to be extremely hazardous regarding the influence it may have in fire behaviour. The strong and gusty winds that it generates can be maintained for a much longer time span than the one associated to discrete downburst events, even when their outflows merge and produce strong low-level winds.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13030414/s1, Figures S1–S23.PNG.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, P.P., D.X.V., Á.P.S., M.A., J.R. and L.M.R.; methodology, P.P. and Á.P.S.; resources, P.P., D.X.V., Á.P.S., M.A., J.R. and L.M.R.; writing—original draft: P.P., D.X.V. and Á.P.S. and writing—review and editing: P.P., D.X.V., Á.P.S., M.A. and L.M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research projects supported by the Portuguese Science and Technology Foundation—FCT: “FireStorm: Meteorology and fire storm behavior” under the reference PCIF/GFC/0109/2017 and “SmokeStorm: Forecasting and communicating wildland fire smoke effects” under the reference PCIF/MPG/0147/2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank to the anonymous reviewers whose comments contributed to the improvement of this manuscript. A special thanks to João Paulo Martins and Millo Magnocavallo for the extensive English review. Additionally, we acknowledge the use of data and support from IPMA (Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
a.g.l.—above ground level; A/PG—Arouca/Pico do Gralheiro; AL—Alvega; AWS-Automatic Weather Station; BE—Benavila; C/CL—Coruche/Cruz do Leão; CB—Castelo Branco; DP—Dual Polarization; dBZ—decibel of reflectivity; ECMWF—European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts; EF—Escalos Fundeiros; ENE—east-northeast; FRJ—Front-to-Rear flow beneath the rear inflow jet; FTR—Front-to-Rear; GO—Góis; IPMA—Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera; LCL—lifted condensation level; LFC—level of free convection; MARC—Mid Altitude Radial Convergence; MAXZ—Maximum Returns of reflectivity; MCS—mesoscale convective system; N—north; NE—northeast; NNE—north-northeast; NW—northwest; PA—Pampilhosa-da-Serra; PE AL—windmill park of Alvelos; PE PS—windmill park of Pampilhosa-da-Serra; PE RN—windmill park of Rendeiros; PG—Pedrógão Grande; PN—Proença-a-Nova; PPI—plane position indicator; PPV—plane position indicator of velocity; PPZ—plane position indicator of reflectivity; RE—Regadas ρhv-correlation coefficient; RIJ—Rear Inflow Jet; RIN—Rear Inflow Notch; RTF—Rear-to-Front; S—south; SRM—storm relative motion; SRV—storm-relative velocity; TO—Tomar; TOPS—Echo tops; TPW—total precipitable water; USA—United States of America; UTC—Coordinated Universal Time; V—velocity.
References
- Countryman, C.M. Mass Fires and Fire Behavior; Research paper, PSW; U.S. Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, G.F.; Fendell, F.E.; Feldman, P.S. Firestorms. J. Heat Transf. 1985, 107, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.A.; Clark, T.; Coen, J. Coupling Atmospheric and Fire Models. In Forest Fires; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, M.A.; McAllister, S.S. A review of fire interactions and mass fires. J. Combust. 2011, 2011, 548328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, J.L.; Riggan, P.J. Simulation and thermal imaging of the 2006 Esperanza Wildfire in southern California: Application of a coupled weather-wildland fire model. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2014, 23, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, P.A.; Potter, B.E.; Alexander, M.E.; Clements, C.B.; Cruz, M.G.; Finney, M.A.; Forthofer, J.M.; Goodrick, S.L.; Hoffman, C.; Jolly, W.M.; et al. Synthesis of knowledge of extreme fire behavior: Volume 2 for Fire Behavior Specialists, Researchers, and Meteorologists. In General Technical Report PNW-GTR-891; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Portland, OR, USA, 2016; Volume 2, p. 258. [Google Scholar]
- Viegas, D.X. A Mathematical Model for Forest Fires Blowup. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2005, 177, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X. Parametric study of an eruptive fire behaviour model. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2006, 15, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.H.; Schumacher, R.S.; Ruppert, J.H.; Lindsey, D.T.; Ruthford, J.E.; Kriederman, L. The Role of Convective Outflow in the Waldo Canyon Fire. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 3061–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A. Mesoscale convective systems. Rev. Geophys. 2004, 42, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.T. Tornadoes and downbursts in the context of generalized planetary scales. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.T. The downburst: Microburst and macroburst. In Satellite and Mesometeorology Research Project; Research Pap. No. 210; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, N.; McGowan, H.; Guyot, A.; Dowdy, A. Mobile X-pol radar: A new tool for investigating pyroconvection and associated wildfire meteorology. Bull. Am. Met. Soc. 2018, 99, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X.; Almeida, M.; Ribeiro, L.; Raposo, J.; Viegas, M.T.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, D.; Pinto, C.; Humberto, J.; Rodrigues, A.; et al. O Complexo de Incêndios de Pedrógão Grande e Concelhos Limítrofes, Iniciado a 17 de Junho de 2017. ADAI-CEIF, Coimbra. 2017 (In Portuguese). Available online: http://www.portugal.gov.pt/donwload-ficheiros/ficheiro.aspx?v=3bb97773b-59fb-4099-9de5-a22fdcad1e3b (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- IPMA. Boletim Climatológico Maio 2017; IPMA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2017. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagner, C.E. Development and structure of the Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index System. Can. For. Serv. For. Tech. Rep. 1987, 35, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Rotunno, R.; Klemp, J.B.; Weisman, L.M. A theory for strong, long-lived squall lines. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, M.L. The genesis of severe long-lived bow echoes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 1826–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, M.L.; Rotunno, R. “A theory for strong long-lived squall lines” revisited. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, J.A.; Rauber, R.M.; McFarquhar, G.M.; Jewett, B.F. Development and forcing of the Rear Inflow Jet in a Rapidly Developing and Decaying Squall Line during BAMEX. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 1206–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, D.D.; Houze, R.A. Development and structure of winter monsoon cloud clusters on 10 December 1978. J. Atmos. Sci. 1984, 41, 933–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A. 100 years of research on mesoscale convective systems. Meteorol. Monogr. 2018, 59, 17.1–17.54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smull, B.F.; Houze, R.A. Rear inflow in squall lines with trailing stratiform precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 2869–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsmill, D.; Houze, R. Kinematic characteristics of air flowing into and out of precipitating convection over the west Pacific warm pool: An airborne Doppler radar survey. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 1999, 125, 1165–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M. Mesoscale unsaturated downdrafts driven by rainfall evaporation: A numerical study. J. Atmos. Sci. 1979, 36, 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.A.; Houze, R.A. The evolution of the 10–11 June 1985 PRE-STORM squall line: Initiation, development of rear inflow and dissipation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 478–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Atkins, N.; Bartels, D.; Bosart, L.; Coniglio, M.; Bryan, G.; Cotton, W.; Dowell, D.; Jewett, R.; Johns, R.; et al. The Bow Echo and MCV Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 85, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisala. User Guide, Utilities, IRIS and RDA; Vaisala Oyj: Vantaa, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, N.; Guyot, A.; Dowdy, A.; McGowan, H. Wildfire and Weather Radar: A Review. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Christopher, S.A. Satellite and radar observations of the 9 April 2009 Texas and Oklahoma grassfires. Bull. Am. Met. Soc. 2010, 91, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, G.P.; Christopher, M.G.; Lindley, T.; Mahale, V. Identifying Plume Mode via WSR-88D Observations of Wildland Fire Convective Plumes and Proposed Tactical Decision Support Applications. J. Oper. Metereol. 2019, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Zrnic, D.S. Use of Polarization to Characterize Precipitation and Discriminate Large Hail. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.J.; Rutledge, S.A.; Dolan, B.; Krehbiel, P.; Rison, W.; Lindsey, D.T. Lightning in Wildfire Smoke Plumes Observed in Colorado during Summer 2012. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRoche, K.T.; Lang, T.J. Observations of Ash, Ice, and Lightning within Pyrocumulus Clouds Using Polarimetric NEXRAD Radars and the National Lightning Detection Network. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 4899–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, M.T.; Lin, Y.L.; Charney, J.J. A study of two-dimensional dry convective plume modes with variable critical level height. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 448–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, M.T.; Parker, M.D. Regimes of dry convection above wildfires: Idealized numerical simulations and dimensional analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 806–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothermel, R. Predicting Behavior and Size of Crown Fires in the Northern Rocky Mountains; Research Paper INT-RP-438; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 1991; p. 46.
- Mphale, K.; Heron, M.; Verma, T. Effect of wildfire-induced thermal bubble on radio communication. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2007, 68, 197–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Olivier, L.D.; Holloway, E.T.; Kropfli, R.A.; Bartram, B.W.; Cupp, R.E.; Post, M.J. Smoke-column observations from two forest fires using Doppler lidar and Doppler radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 1328–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareau, N.P.; Clements, C.B. The mean and turbulent properties of a wildfire convective plume. J. Appl. Metorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiden, T.; Janousek, M.; Bidlot, J.; Ferranti, L.; Prates, F.; Vitart, F.; Bauer, P.; Richardson, D. Evaluation of ECMWF Forecasts, Including 2016–2017 Upgrades. ECMWF Technical Memorandum (Forecast Department). 2017. Available online: http://www.ecmwf.int/publications/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Viegas, D.X.; Simeoni, A. Eruptive Behaviour of Forest Fires. Fire Technol. 2011, 47, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Viegas, D.; Raposo, J. Analysis of firebrand release on the spot fire mechanism. In Advances in Forest Fire Research; Imprensa da Universidade de Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2014; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPMA. Condições Meteorológicas Associadas ao Incêndio de Pedrógão Grande de 17 de Junho 2017; IPMA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2017. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. Analysis of Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) data for drought assessment. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X.; Rossa, C.; Ribeiro, L.M. Incêndios Florestais, 1st ed.; Verlag Dashöfer Edições Profissionais Unipessoal Lda.: Lisbon, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Weisman, M.L.; Klemp, J.B. Characteristics of Isolated Convective Storms. In Mesoscale Meteorology and Forecasting; Ray, P., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, H.B.; Jain, M.H. Formation of mesoscale lines of precipitation: Severe squall lines in Oklahoma during the spring. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 42, 1711–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.O. Mesoscale Convective Patterns of the Southern High Plains. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1990, 71, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parker, M.D.; Johnson, R.H. Organizational modes of midlatitude mesoscale convective systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 3413–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, R.A. Mesoscale convective complexes. Bull. Am. Met. Soc. 1980, 61, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A.; Betts, A.K. Convection in GATE. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1981, 19, 541–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingle, D.L.; Smith, D.R.; Wolfson, M.M. Gust Front Characteristics as Detected by Doppler Radar. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R. A model of intense downdrafts driven by the melting and evaporation of precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 1752–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmocker, G.; Przybylinski, R. Mid-Altitude Radial Convergence (MARC) Velocity Signature. NWS. 2009. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/lsx/marc_signature (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Eilts, M.D.; Johnson, J.T.; Mitchell, E.D.; Lynn, R.J.; Spencer, P.; Cobb, S.; Smith, T.M. Damaging Downburst Prediction and Detection Algorithm for the WSR-88D. In Preprints, 18th Conf. on Severe Local Storms; American Meteorological Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.C.; Houze, R.A. The precipitating cloud population of the Madden-Julian Oscillation over the Indian and west Pacific Oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6996–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smull, B.F.; Houze, R.A. A midlatitude squall line with a trailing region of stratiform rain: Radar and satellite observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1985, 113, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylinski, R.W. The Bow Echo: Observations, Numerical Simulations, and Severe Weather Detection Methods. Weather Forecast 1995, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A.; Rutdledge, S.A.; Biggerstaff, M.I.; Smull, B.F. Interpretation of Doppler weather radar displays of mid-latitude mesoscale convective systems. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1989, 70, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Weisman, M.L.; Klemp, J.B. Three-dimensional evolution of simulated long-lived squall lines. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 2563–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.W.; Roberts, R.D.; Kessinger, C.; McCarthy, J. Microburst wind structure and evaluation of Doppler radar for airport wind shear detection. J. Clim. Appl. Meteor. 1984, 23, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnic, D.; Zhang, P.; Melnikov, V.; Mirkovic, D. Of fire and Smoke Plumes, Polarimetric Radar Characteristics. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Pokrovsky, A. Aerosol impact on the dynamics and microphysics of convective clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2639–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X.; Raposo, J.; Davim, D.; Rossa, C. Study of the jump fire produced by the interaction of two oblique fire fronts. Part 1. Analytical model and validation with no-slope laboratory experiments. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, J.R.; Viegas, D.X.; Xie, X.; Almeida, M.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Porto, L.; Sharples, J. Analysis of the physical processes associated with junction fires at laboratory and field scales. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2018, 27, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doogan, M. The Canberra Fire Storm. Inquests and Inquiry into Four Deaths and Four Fires Between 8 and 18 January 2003; ACT Coroners Court: Canberra, Australia, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khain, A.; Leung, L.; Lynn, B.; Ghan, S. Effects of aerosols on the dynamics and microphysics of squall lines simulated by spectral bin and bulk parameterization schemes. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D22203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).