Intercomparison of Ambient Nitrous Acid Measurements in a Shanghai Urban Site
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle and Experimental Setup
2.1. LOPAP-HONO Setup and Performance Characterization
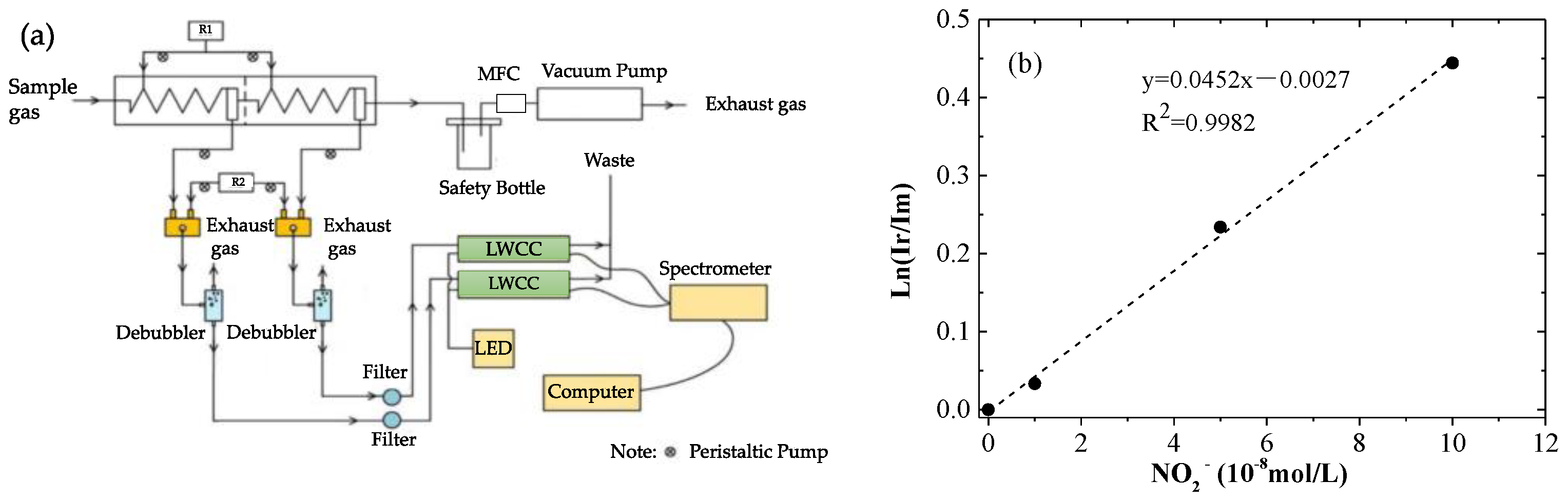
2.1.1. LOPAP-HONO Setup
2.1.2. Calibration of LOPAP-HONO
2.2. IBBCEAS-HONO Setup and Performance Characterization
2.2.1. IBBCEAS-HONO Setup
2.2.2. Reflectivity Calibration of IBBCEAS-HONO
2.2.3. Detection Limits of IBBCEAS-HONO
2.2.4. Sampling Residence Time of IBBCEAS-HONO
2.3. Intercomparison Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Intercomparison of Laboratory Experiments
3.2. Intercomparison of Ambient Air Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elshorbany, Y.F.; Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R.; Lissi, E.; Rubio, M.; Villena, G.; Gramsch, E.; Rickard, A.R.; Pilling, M.J.; Wiesen, P. Seasonal dependence of the oxidation capacity of the city of Santiago de Chile. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5383–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbany, Y.F.; Kleffmann, J.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Kurtenbach, R.; Wiesen, P.; Dorn, H.P.; Schlosser, E.; Brauers, T.; Fuchs, H.; Rohrer, F.; et al. HOx budgets during HOxComp: A case study of HOx chemistry under NOx limited conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alicke, B.; Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Impact of nitrous acid photolysis on the total hydroxyl radical budget during the Limitation of Oxidant Production/Pianura Padana Produzione di Ozono study in Milan. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicke, B. OH formation by HONO photolysis during the BERLIOZ experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8247–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, B.; Vogel, H.; Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R. Measured and simulated vertical profiles of nitrous acid—Part II. Model simulations and indications for a photolytic source. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R.; Lorzer, J.; Wiesen, P.; Kalthoff, N.; Vogel, B.; Vogel, H. Measured and simulated vertical profiles of nitrous acid—Part I: Field measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffmann, J.; Gavriloaiei, T.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Holland, F.; Koppmann, R.; Rupp, L.; Schlosser, E.; Siese, M.; Wahner, A. Daytime formation of nitrous acid: A major source of OH radicals in a forest. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.R.; Harder, H.; Martinez, M.; Lesher, R.L.; Oliger, A.; Simpas, J.B.; Brune, W.H.; Schwab, J.J.; Demerjian, K.L.; He, Y.; et al. OH and HO2 chemistry in the urban atmosphere of New York City. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3639–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N., Jr. Chemistry of the Lower and Upper Atmosphere: Theory, Experiments and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.M.; Peak, J.D.; Collins, G.M. Tropospheric cycle of nitrous acid. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 14429–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T. Nitrous acid in the atmosphere and laboratory experiments on its photolysis. Tellus 1974, 26, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, D.; Platt, U. Detection of nitrous acid in the atmosphere by differential optical absorption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1979, 6, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, J.; Wong, K.W.; Tsai, C. Field Observation of Daytime HONO Chemistry and its Impact on the OH Radical Budget. In Disposal of Dangerous Chemicals in Urban Areas and Mega Cities; Barnes, I., Rudzinski, K.J., Eds.; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtenbach, R.; Becker, K.H.; Gomes, J.A.G.; Kleffmann, J.; Lörzer, J.C.; Spittler, M.; Wiesen, P.; Ackermann, R.; Geyer, A.; Platt, U.; et al. Investigations of emissions and heterogeneous formation of HONO in a road traffic tunnel. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Liu, W.; Xie, P.; Liu, J.; Fang, W.; Zhang, W. Study progress on the source of atmospheric HONO. Environ. Monit. China 2005, 21, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Cheng, Y.; Oswald, R.; Behrendt, T.; Trebs, I.; Meixner, F.X.; Andreae, M.O.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Pöschl, U. Soil nitrite as a source of atmospheric HONO and OH radicals. Science 2011, 333, 1616–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Brauers, T.; Häseler, R.; Bohn, B.; Fuchs, H.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Holland, F.; Lou, S.; Lu, K.D.; Rohrer, F.; et al. Exploring the atmospheric chemistry of nitrous acid (HONO) at a rural site in Southern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Wingen, L.M.; Sumner, A.L.; Syomin, D.; Ramazan, K.A. The heterogeneous hydrolysis of NO2 in laboratory systems and in outdoor and indoor atmospheres: An integrated mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndour, M.; D’Anna, B.; George, C.; Ka, O.; Balkanski, Y.; Kleffmann, J.; Stemmler, K.; Ammann, M. Photoenhanced uptake of NO2 on mineral dust: Laboratory experiments and model simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L05812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.L.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.; Qu, Y. Advances in HONO sources, HONO simulations, and the impacts of the HONO sources on regional or global air quality. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.L.; He, Y.; Huang, G.; Thornberry, T.D.; Carroll, M.A.; Bertman, S.B. Photochemical production of nitrous acid on glass sample manifold surface. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bejan, I.; Abd-el-Aal, Y.; Barnes, I.; Benter, T.; Bohn, B.; Wiesen, P.; Kleffmann, J. The photolysis of ortho-nitrophenols: A new gas phase source of HONO. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spataro, F.; Ianniello, A. Sources of atmospheric nitrous acid: State of the science, current research needs, and future prospects. J. Air Waste Manag. 2014, 64, 1232–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.M.; Kitto, A.M.N. Evidence for a surface source of atmospheric nitrous acid. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, J.; Oh, H.J.; Whitlow, S.I.; Anderson, C.; Dibb, J.E.; Flynn, J.H.; Rappenglück, B.; Lefer, B. Simultaneous DOAS and mist-chamber IC measurements of HONO in Houston, TX. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Detection of Nitrous Acid by Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4221–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, C.L.; Locquiao, S.; Johnson, T.J.; Harris, G.W. Atmospheric Measurements of HONO by Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Atmos. Chem. 2001, 40, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherman, T.; Venables, D.S.; Vaughan, S.; Orphal, J.; Ruth, A.A. Incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy in the near-ultraviolet: Application to HONO and NO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wenger, J.C.; Venables, D.S. Near-ultraviolet absorption cross sections of nitrophenols and their potential influence on tropospheric oxidation capacity. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 12235–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appel, B.R.; Winer, A.M.; Tokiwa, Y.; Biermann, H.W. Comparison of atmospheric nitrous acid measurements by annular denuder and differential optical absorption systems. Atmos. Environ. 1990, 24, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heland, J.; Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R.; Wiesen, P. A new instrument to measure gaseous nitrous acid (HONO) in the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hou, S.Q.; Wang, W.G.; Tong, S.R.; Pei, K.M.; Ge, M.F. Development of a home-made long path absorption photometer for the sensitive detection of nitrous acid. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 30, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger, A.R. Observations of HNO2 in the polluted winter atmosphere: Possible heterogeneous production on aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffmann, J.; Wiesen, P. Technical Note: Quantification of interferences of wet chemical HONO LOPAP measurements under simulated polar conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6813–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleffmann, J. Daytime sources of nitrous acid (HONO) in the atmospheric boundary layer. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2007, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Ye, C.; Ma, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X. Development of stripping coil-ion chromatograph method and intercomparison with CEAS and LOPAP to measure atmospheric HONO. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixneuf, S.; Ruth, A.; Häseler, R.; Brauers, T.; Rohrer, F.; Dorn, H.P. Comparison of nitrous acid detection using open-path incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy and extractive long-path absorption photometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 291, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Cazaunau, M.; Gratien, A.; Michoud, V.; Pangui, E.; Doussin, J.F.; Chen, W. Intercomparison of IBBCEAS, NitroMAC and FTIR analyses for HONO, NO2 and CH2O measurements during the reaction of NO2 with H2O vapour in the simulation chamber CESAM. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 5701–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, B.E. Colorimetric Micro-determination of Nitrogen Dioxide in Atmosphere. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffmann, J.; Lörzer, J.C.; Wiesen, P.; Kern, C.; Trick, S.; Volkamer, R.; Ródenas, M.; Wirtz, K. Intercomparison of the DOAS and LOPAP techniques for the detection of nitrous acid (HONO). Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häseler, R.; Brauers, T.; Holland, F.; Wahner, A. Development and application of a new mobile LOPAP instrument for the measurement of HONO altitude profiles in the planetary boundary layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2009, 2, 2027–2054. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, K.; Dong, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, P.; Zou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. In situ monitoring of atmospheric nitrous acid based on multi-pumping flow system and liquid waveguide capillary cell. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena, G.; Bejan, I.; Kurtenbach, R.; Wiesen, P.; Kleffmann, J. Development of a new Long Path Absorption Photometer (LOPAP) instrument for the sensitive detection of NO2 in the atmosphere. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.; Bejan, I.; Kurtenbach, R.; Liedtke, S.; Villena, G.; Wiesen, P.; Kleffmann, J. Development of a new LOPAP instrument for the detection of O3 in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zha, Q.; Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, T.; He, X. Development and deployment of a cavity enhanced UV-LED spectrometer for measurements of atmospheric HONO and NO2 in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, M.A.; Berke, A.E.; Raff, J.D. Uptake of Gas Phase Nitrous Acid onto Boundary Layer Soil Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharko, N.K.; Berke, A.E.; Raff, J.D. Release of Nitrous Acid and Nitrogen Dioxide from Nitrate Photolysis in Acidic Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11991–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.E.; Washenfelder, R.A.; Dubé, W.P.; Langford, A.O.; Edwards, P.M.; Zarzana, K.J.; Stutz, J.; Lu, K.; Rohrer, F.; Zhang, Y. A broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectrometer for aircraft measurements of glyoxal, methylglyoxal, nitrous acid, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapor. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, Y.; Sadanaga, Y. Validation of in situ Measurements of Atmospheric Nitrous Acid Using Incoherent Broadband Cavity-enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Qin, M.; Ouyang, B.; Fang, W.; Li, X.; Lu, K.; Tang, K.; Liang, S.; Meng, F.; Hu, Z.; et al. Development of an incoherent broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectrometer for in situ measurements of HONO and NO2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4531–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutz, J.; Kim, E.S.; Platt, U.; Bruno, P.; Perrino, C.; Febo, A. UV-visible absorption cross sections of nitrous acid. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 14585–14592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, S.; Orphal, J.; Burrows, J.P. The temperature and pressure dependence of the absorption cross-sections of NO2 in the 250-800 nm region measured by Fourier-transform spectroscopy. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2002, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, K.; George, M.; Orphal, J.; Chandran, S.; Varma, R.; Venables, D.S.; Wang, M.; Chen, J. Open path incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced measurements of NO3 radical and aerosol extinction in the North China Plain. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fullam, D.P.; Yu, S.; Böge, O.; Le, P.H.; Herrmann, H.; Venables, D.S. Improving the accuracy and precision of broadband optical cavity measurements. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 218, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, D.S.; Gherman, T.; Orphal, J.; Wenger, J.C.; Ruth, A.A. High sensitivity in situ monitoring of NO3 in an atmospheric simulation chamber using incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, J.P.; Dibb, J.; Lee, B.H.; Rappengluck, B.; Wood, E.C.; Levy, M.; Zhang, R.; Lefer, B.; Ren, X.; Stutz, J.; et al. Intercomparison of field measurements of Nitrous Acid (HONO) during the SHARP campaign. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 2014, 119, 5583–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.; Ball, S.M.; Bohn, B.; Brauers, T.; Cohen, R.C.; Dorn, H.P.; Dubé, W.P.; Fry, J.L.; Häseler, R.; Heitmann, U. Intercomparison of measurements of NO2 concentrations in the atmosphere simulation chamber SAPHIR during the NO3 Comp campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandran, S.; Puthukkudy, A.; Varma, R. Dual-wavelength dual-cavity spectrometer for NO2 detection in the presence of aerosol interference. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Test No. | Sampling Flow Rate (L/min) | Residence Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.2 | 18.8 |
| 2 | 1.6 | 14.4 |
| 3 | 1.8 | 13.2 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 12.8 |
| 5 | 2.2 | 12.2 |
| 6 | 2.4 | 11.6 |
| 7 | 2.6 | 10.8 |
| 8 | 2.8 | 8.6 |
| 9 | 3.0 | 7.2 |
| 10 | 4.0 | 6.0 |
| 11 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chandran, S.; Varma, R.; Lou, S.; Chen, J. Intercomparison of Ambient Nitrous Acid Measurements in a Shanghai Urban Site. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020329
Yang Z, Wang M, Hou Y, Liu Y, Chandran S, Varma R, Lou S, Chen J. Intercomparison of Ambient Nitrous Acid Measurements in a Shanghai Urban Site. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhenni, Meng Wang, Yanping Hou, Yucun Liu, Satheesh Chandran, Ravi Varma, Shengrong Lou, and Jun Chen. 2022. "Intercomparison of Ambient Nitrous Acid Measurements in a Shanghai Urban Site" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020329
APA StyleYang, Z., Wang, M., Hou, Y., Liu, Y., Chandran, S., Varma, R., Lou, S., & Chen, J. (2022). Intercomparison of Ambient Nitrous Acid Measurements in a Shanghai Urban Site. Atmosphere, 13(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020329







