Correction to a Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) Simulation of Energy and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes over a Wheat Cropland in East China Using the Random Forest Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
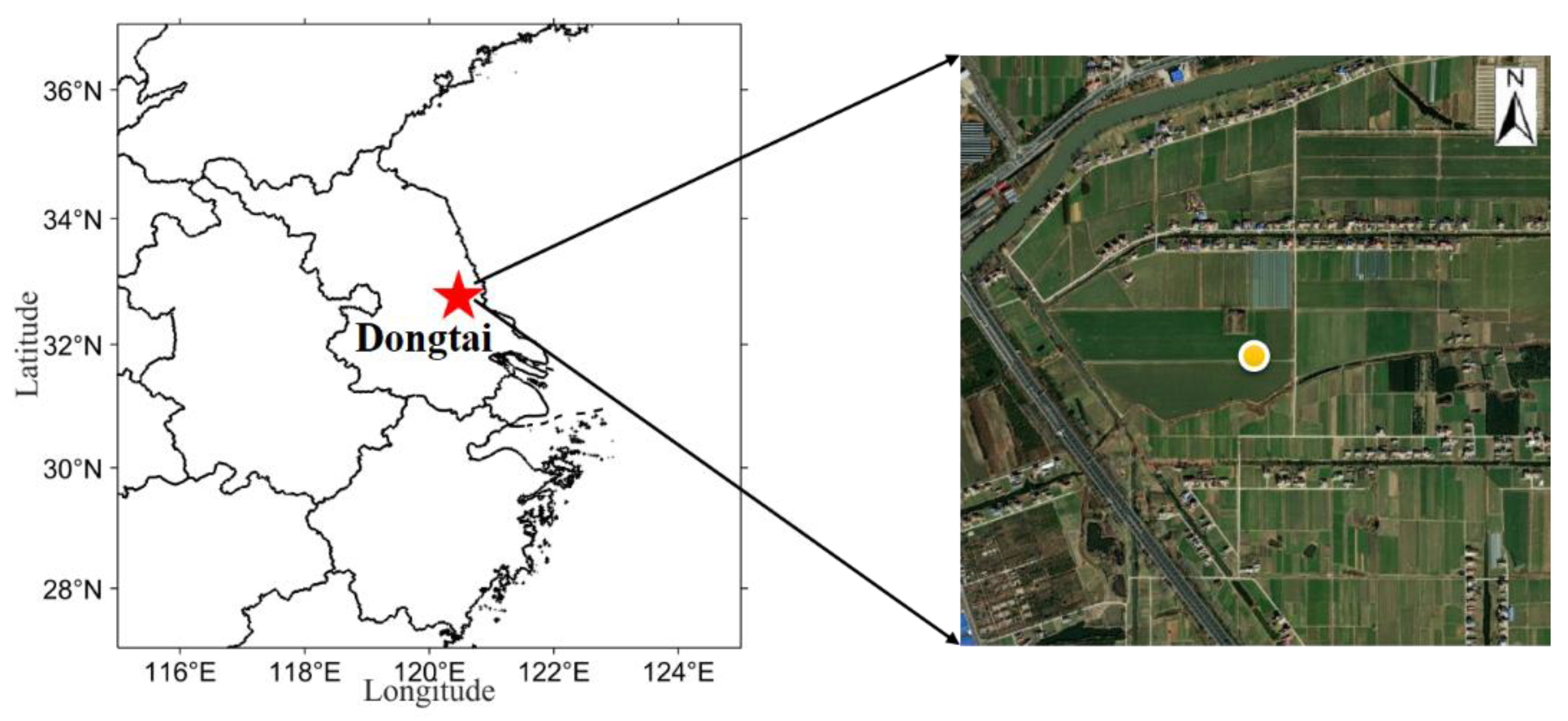
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Instruments and Data Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The SiB2 Model
2.3.2. The RF Model
2.3.3. Radiation and Surface Energy Fluxes
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Radiation, Turbulence, and CO2 Fluxes
3.2. SiB2 Evaluation
3.3. Driving Factors of Turbulence and CO2 Fluxes
3.4. RF Model Evaluation
3.5. Comparison of SiB2 and RF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z2 | Canopy-top height (m) | 0.15, 0.58, 0.86 | S6 | Half-inhibition high temperature, respiration (K) | 328 |
| Z1 | Canopy-base height (m) | 0.1 | Topt | Optimum temperature for vegetation growth (K) | 298 |
| χL | Leaf-angle distribution factor | −0.02 | S3 | Low temperature stress factor, photosynthesis (K−1) | 0.2 |
| Dr | Root depth (m) | 0.1, 0.14, 0.21 | S4 | Half-inhibition low temperature, photosynthesis (K) | 281 |
| ψc | One-half inhibition water potential | −200 | S1 | High temperature stress factor, photosynthesis (K−1) | 0.3 |
| δV,l | Leaf transmittance, visible, live | 0.07 | S2 | Half-inhibition high temperature, photosynthesis (K) | 308 |
| δV,d | Leaf transmittance, visible, dead | 0.25 | DT | Total soil depth (m) | 0.4 |
| δN,l | Leaf transmittance, near IR, live | 0.22 | αsV | Soil reflectance, visible | 0.1 |
| δN,d | Leaf transmittance, near IR, dead | 0.38 | αsN | Soil reflectance, near IR | 0.15 |
| αv,l | Leaf reflectance, visible, live | 0.105 | B | Soil wetness exponent | 8.52 |
| αv,d | Leaf reflectance, visible, dead | 0.58 | ψs | Soil tension at saturation (m) | −0.36 |
| αN,l | Leaf reflectance, near IR, live | 0.36, 0.18 | Ks | Hydraulic conductivity at saturation (m s−1) | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| αN,d | Leaf reflectance, near IR, dead | 0.58, 0.4 | θs | Soil porosity (volume fraction) | 0.48 |
| ε | Intrinsic quantum efficiency (mol mol−1) | 0.08 | ∅s | Mean topographic slope (radians) | 0.176 |
| M | Stomatal slope factor | 13.0 | Vmax0 | Maximum rubisco capacity, top leaf (mol m−2 s−1) | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| b | Minimum stomatal conductance (mol m−2 s−1) | 0.01 | G(μ)/μ | Time-mean leaf projection | 1.0 |
| fd | Leaf respiration factor | 0.015 | G1 | Augmentation factor for momentum transfer coefficient | 1.449 |
| βce | Photosynthesis coupling coefficient | 0.98 | G4 | Transition height factor for momentum transfer coefficient | 11.785 |
| βps | Photosynthesis coupling coefficient | 0.95 | zwind | Wind observation height (m) | 10.0 |
| S5 | High temperature stress factor, respiration (K−1) | 1.3 | zmet | Air temperature and humidity observation height (m) | 10.0 |
| Variable | Unit | Description | Variable | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | – | Normalized difference vegetation index | RH3 | % | Relative humidity at 3 m |
| LAI | – | Leaf area index | P | hPa | Pressure |
| FPAR | – | Fraction of photosynthetically active radiation | q | g g−1 | Specific humidity at 3 m |
| T3 | K | Air temperature observed at 3 m | VPD | hPa | Vapor pressure deficit at 3 m |
| Tg | K | Temperature of land surface | u* | m s−1 | Friction velocity |
| Tm | K | Average temperature of air at 3 m and ground | T* | K | Disturbances in temperature |
| G5 | W m−2 | Soil heat flux at the depth of 5 cm | WS | m s−1 | Wind speed at 3 m |
| dT | K | Bias of temperature for canopy air space and observation height | WDir | degrees from north | Wind direction at 3 m |
| Ts5 | K | Temperature of soil at the depth of 5 cm | Rn | W m−2 | Net radiation |
| Ts10 | K | Temperature of soil at the depth of 10 cm | SiB2H | W m−2 | The H modeled by SiB2 |
| Ts20 | K | Temperature of soil at the depth of 20 cm | SiB2LE | W m−2 | The LE modeled by SiB2 |
| Ts40 | K | Temperature of soil at the depth of 40 cm | SiB2G0 | W m−2 | The G0 modeled by SiB2 |
| Es0 | hPa | Saturated vapor pressure of land surface | SiB2Fc | μmol m−2 s−1 | The Fc modeled by SiB2 |
References
- Chen, C.; Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Tang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Wan, B. Seasonal and Interannual Variations of Carbon Exchange over a Rice-Wheat Rotation System on the North China Plain. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, F.; Qiu, R.; Wido, H. Application of the Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) with Irrigation Module to a Typical Low-Hilly Red Soil Farmland and the Sensitivity Analysis of Modeled Energy Fluxes in Southern China. Water 2019, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, S. Vegetation Physiological Parameter Setting in the Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) for Alpine Meadows in the Upper Reaches of Heihe River. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Chu, Y.; Qi, Y. Characteristics and Simulation of Heat and CO2 Fluxes over a Typical Cropland During the Winter Wheat Growing in the North China Plain. Envrion. Sci. 2010, 31, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, L.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Baker, I. Study of the surface energy flux at the three different sites over China based on SiB2 and SiB3. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 71, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E.; Henderson-Sellers, A.; Rosenzweig, C.; Sellers, P.J. Evapotranspiration Models with Canopy Resistance for Use in Climate Models, a Review. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1991, 54, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chae, N.; Kim, J.; Hong, J.; Choi, T.; Lee, H. Modeling of Surface Energy Partitioning, Surface Temperature, and Soil Wetness in the Tibetan Prairie Using the Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D06102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowntree, P.R. Atmospheric Parameterization Schemes for Evaporation over Land: Basic Concepts and Climate Modeling Aspects. In Land Surface Evaporation; Schmugge, T.J., André, J.-C., Eds.; Springer: New York, USA, 1991; pp. 5–29. ISBN 978-0-387-97359-3. [Google Scholar]
- Baldocchi, D. Assessing the Eddy Covariance Technique for Evaluating Carbon Dioxide Exchange Rates of Ecosystems: Past, Present and Future. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Gao, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z. Seasonal and Interannual Variations in the Surface Energy Fluxes of a Rice–Wheat Rotation in Eastern China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2021, 60, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, L.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Baker, I. Modeling of CO2 Fluxes at Cropland by Using SiB3 Model. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 4000–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Cai, J.; Wang, F. Long-Term Variability of the Carbon Balance in a Large Irrigated Area along the Lower Yellow River from 1984 to 2006. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokupitiya, E.; Denning, S.; Paustian, K.; Baker, I.; Schaefer, K.; Verma, S.; Meyers, T.; Bernacchi, C.; Suyker, A.; Fischer, M. Incorporation of Crop Phenology in Simple Biosphere Model (SiBcrop) to Improve Land-Atmosphere Carbon Exchanges from Croplands. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J. An Application of SiB2 in the Yellow River Irrigation Region. Res. Soil Water Convervation 2011, 18, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, L.; Xing, W.; Zhang, L.; Baker, I.; Zhang, G.; Zuo, J. Evaluating surface energy budgets simulated by SiB3 at three different climate-ecosystem tower sites. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Parameter Estimation of Terrestrial Ecosystem Process Model and Its Application in Carbon and Water Fluxes Simulation—The CEVSA Model as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Manabe, S. Climate and the Ocean Circulation, I, The Atmospheric Circulation and the Hydrology of the Earth’s Surface. Mon. Weather Rev. 1969, 97, 739–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E. Land Surface Processes and Climate—Surface Albedos and Energy Balance. In Advances in Geophysics; Saltzman, B., Ed.; Theory of Climate; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 25, pp. 305–353. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, P.J.; Mintz, Y.; Sud, Y.C.; Dalcher, A. A Simple Biosphere Model (SIB) for Use within General Circulation Models. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Tucker, C.J.; Collatz, G.J.; Los, S.O.; Justice, C.O.; Dazlich, D.A.; Randall, D.A. A Revised Land Surface Parameterization (SiB2) for Atmospheric GCMS. Part II: The Generation of Global Fields of Terrestrial Biophysical Parameters from Satellite Data. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 706–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Randall, D.A.; Collatz, G.J.; Berry, J.A.; Field, C.B.; Dazlich, D.A.; Zhang, C.; Collelo, G.D.; Bounoua, L. A Revised Land Surface Parameterization (SiB2) for Atmospheric GCMS. Part I: Model Formulation. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, A.; Jin, H. The simulation models of the forest carbon cycle on a large scale: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Ren, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Lv, C.; Tao, B. The Dynamic Land Ecosystem Model (DLEM) for Simulating Terrestrial Processes and Interactions in the Context of Multifactor Global Change. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hao, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiao, W.; Pan, M.; Huo, S.; Lyu, T. Enhancing Bioenergy Production from the Raw and Defatted Microalgal Biomass Using Wastewater as the Cultivation Medium. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hu, R.; Wang, N.; Yang, T.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Pan, M.; Lyu, T. Cultivation of Microalgae in Adjusted Wastewater to Enhance Biofuel Production and Reduce Environmental Impact: Pyrolysis Performances and Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, N.P.; Berry, J.A.; Verma, S.B.; Walter-Shea, E.A.; Suyker, A.E.; Burba, G.G.; Denning, A.S. Testing a Model of CO2, Water and Energy Exchange in Great Plains Tallgrass Prairie and Wheat Ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 131, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tao, F.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Bai, H. The contributions of leaf area index and precipitation to surface energy balance in the process of land cover change. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The Observation and Simulation of Turbulence Fluxes Over Rice Paddy and Dry Farming Land. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sha, W. Modeling of Surface Energy Budget in the Tibetan Plateau Using Simple Biosphere Model SiB2. Chin. J. Atmoshperic Sci. 2010, 34, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, H.; Liu, F.; Gao, Z.; Liu, H. Modeling of Surface Flux in Tongyu Using the Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2). J. For. Res. 2010, 21, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Simulation of Evapotranspiration and Carbon Dioxide Flux in the Wheat-Maize Rotation Croplands of the North China Plain Using the Simple Biosphere Model. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3107–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L. Research on air temperature product examination of three numerical forecast and a method of error correction. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2018, 34, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ning, Y.; Tang, R.; Xie, X. Tropical Temperature Correction for Numerical Forecast in Hainan Ba on Spatiotemporal Independence Random Forest Model. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan Univ. 2020, 38, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Jiao, R.; Xia, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z. Adjusting Wind Speed Prediction of Numerical Weather Forecast Model Based on Machine Learning Methods. Meteorol. Mon. 2019, 45, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zhen, Y. Revision of solar radiation product ERA5 based on random forest algorithm. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2022, 34, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J. Temperature Correction Model Based on Machine Learning and Multi-Meteorological Factor Model. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Xing, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, X. Research on correction method of marine environment prediction based on machine learning. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2020, 39, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Brender, P.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.; Mahecha, M.D.; Chevallier, F.; Reichstein, M.; Ottlé, C.; Maignan, F.; Arain, A.; et al. State-Dependent Errors in a Land Surface Model across Biomes Inferred from Eddy Covariance Observations on Multiple Timescales. Ecol. Model. 2012, 246, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, G.; Pitman, A.; Gupta, H.; Kowalczyk, E.; Wang, Y. Systematic Bias in Land Surface Models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; McRoberts, R.; Fernández-Landa, A.; Tomé, J.; Næsset, E. Estimating Forest Volume and Biomass and Their Changes Using Random Forests and Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontana, G.; Jung, M.; Schwalm, C.R.; Ichii, K.; Camps-Valls, G.; Ráduly, B.; Reichstein, M.; Arain, M.A.; Cescatti, A.; Kiely, G.; et al. Predicting Carbon Dioxide and Energy Fluxes across Global FLUXNET Sites with Regression Algorithms. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4291–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Mao, F.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Cui, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Simulation of CO2 Flux and Controlling Factors in Moso Bamboo Forest Using Random Forest Algorithm. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2018, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Gao, Z.; Zong, L.; Fan, S.; Yin, J. Estimating Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) over Rice–Wheat-Rotation Croplands by Using the Random Forest Model and Eddy Covariance Measurements: Upscaling and Comparison with the MODIS Product. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D. Seasonal and Interannual Variations in Carbon Dioxide Exchange over a Cropland in the North China Plain: CARBON DIOXIDE EXCHANGE OVER A CROPLAND. Glob. Chang.Biol. 2009, 16, 2944–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Tian, H.; Zhao, L. Research progress on carbon storage and flux in different terrestrial ecosystem in China under global climate change. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, R.; Ma, Q.; Yang, G. Characteristics Analysis of CO2 and Heat Flux in Winter Wheat Fields. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2012, 41, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Gao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Qin, K.; Yang, Y. A Benchmark Dataset of Diurnal- and Seasonal-Scale Radiation, Heat, and CO2 Fluxes in a Typical East Asian Monsoon Region. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4153–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Gao, Z.; Ning, G.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, M. Modulations of Surface Thermal Environment and Agricultural Activity on Intraseasonal Variations of Summer Diurnal Temperature Range in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 11, 139445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Han, R. Characteristics of Annual Mean Temperature and Precipitation of Jiangsu Dongtai in Recent 65 Years. Water Resour. Power 2017, 35, 6–9+21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Analysis on the trend of rainfall in recent years in the coastal area of Dongtai City. Jiangsu Water Resour. 2019, 9, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Tong, B. Comparison of Sensible Heat Fluxes Measured by a Large Aperture Scintillometer and Eddy Covariance System over a Heterogeneous Farmland in East China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Massman, W.J.; Law, B.E. (Eds.) Handbook of Micrometeorology: A Guide for Surface Flux Measurement and Analysis; Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2004; ISBN 978-1-4020-2264-7. [Google Scholar]
- Moncrieff, J.; Clement, R.; Finnigan, J.; Meyers, T. Averaging, Detrending, and Filtering of Eddy Covariance Time Series. In Handbook of Micrometeorology: A Guide for Surface Flux Measurement and Analysis; Lee, X., Massman, W., Law, B., Eds.; Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 7–31. ISBN 978-1-4020-2265-4. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of Flux Measurements for Density Effects Due to Heat and Water Vapour Transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Bounoua, L.; Thome, K.; Wolfe, R. Modeling Impact of Urbanization in Us Cities Using Simple Biosphere Model SiB2. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 6758–6761. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yunjiang, Z.; Nannan, W.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Two Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Site-Level Net Ecosystem Exchange in Major Biomes. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z. Study of Estimation of Soil Heat Flux at a Wheat Field in Semi-Arid Area Loess Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Regional Turbulent Water and Heat Fluxes from Airborne Eddy Covariance Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Cui, N.; Dong, J. Study on LSTM deep learning model-based prediction of reference crop evapotranspiration in North China. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2019, 50, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. An assessment of summer sensible heat flux on the Tibetan Plateau from eight data sets. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 42, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, X. Surface Energy Budget Observed for Winter Wheat in the North China Plain During a Fog–Haze Event. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2019, 170, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, T.; Yao, B.; Han, P.; Ji, D.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, P. Spatial and Temporal Variations of CO2 Mole Fractions Observed at Beijing, Xianghe, and Xinglong in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11741–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.; Schume, H. Tall Tower Eddy Covariance Measurements of CO2 Fluxes in Vienna, Austria. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 274, 118941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Fan, S.; Chen, C.; Tong, Y.; Lin, X.; Gao, Z. Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Dioxide and Ozone over a Rural-Cropland Area in the Yangtze River Delta of Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Cao, S.; Lin, Z. Simulation of Energy and Carbon Fluxes over a Typical Cropland during the Summer Maize Growing in the Yellow River Irrigation Region by Use of SIB2. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Qingdao, China, 11–14 July 2010; pp. 2309–2312. [Google Scholar]







| Flux | SiB2 | RF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| H | 0.59 | 32.92 | 0.99 | 4.73 |
| LE | 0.75 | 72.87 | 0.85 | 54.92 |
| G0 | 0.60 | 34.33 | 0.78 | 25.53 |
| Fc | 0.62 | 6.82 | 0.71 | 4.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Duan, Z.; Zhou, S.; Gao, Z. Correction to a Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) Simulation of Energy and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes over a Wheat Cropland in East China Using the Random Forest Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13122080
Zhang S, Duan Z, Zhou S, Gao Z. Correction to a Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) Simulation of Energy and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes over a Wheat Cropland in East China Using the Random Forest Model. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(12):2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13122080
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shiqi, Zexia Duan, Shaohui Zhou, and Zhiqiu Gao. 2022. "Correction to a Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) Simulation of Energy and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes over a Wheat Cropland in East China Using the Random Forest Model" Atmosphere 13, no. 12: 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13122080
APA StyleZhang, S., Duan, Z., Zhou, S., & Gao, Z. (2022). Correction to a Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) Simulation of Energy and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes over a Wheat Cropland in East China Using the Random Forest Model. Atmosphere, 13(12), 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13122080







