Spatial Variation and Relation of Aerosol Optical Depth with LULC and Spectral Indices
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To study the spatial variation of AOD in the current study area.
- (2)
- To analyze the change in LULC from 2010 to 2019.
- (3)
- To examine the correlation between AOD and LULC-derived indices.
2. Study Area
3. Data Used and Methodology
| Data Description | Site | Duration | Sites to Download Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| AERONET (Version 3 Level 2 Aerosol Optical Depth at 500 nm) | Amity University | 2010, 2016, 2017, and 2018 | http://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/ [68] |
| Gual Pahari | 2017, 2018, 2019 | ||
| MCD19_A2 (AOD at 1 km) | Gautam Buddha Nagar, Faridabad, Gurugram, Ghaziabad | 2010–2019 | https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ [66] |
| MOD13A2 (16 days Terra composite of NDVI, EVI, Red, NIR, MIR reflectance at 1 km) | 2019 | ||
| MYD13A2 (16 days Aqua composite of NDVI, EVI, Red, NIR, MIR reflectance at 1 km) | 2019 | ||
| MCD12Q1 (Land Cover type 1 at 500 m) | 2010–2019 |
4. Results
4.1. Validation of AODMAIAC Using AODAERONET
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Variations of AOD
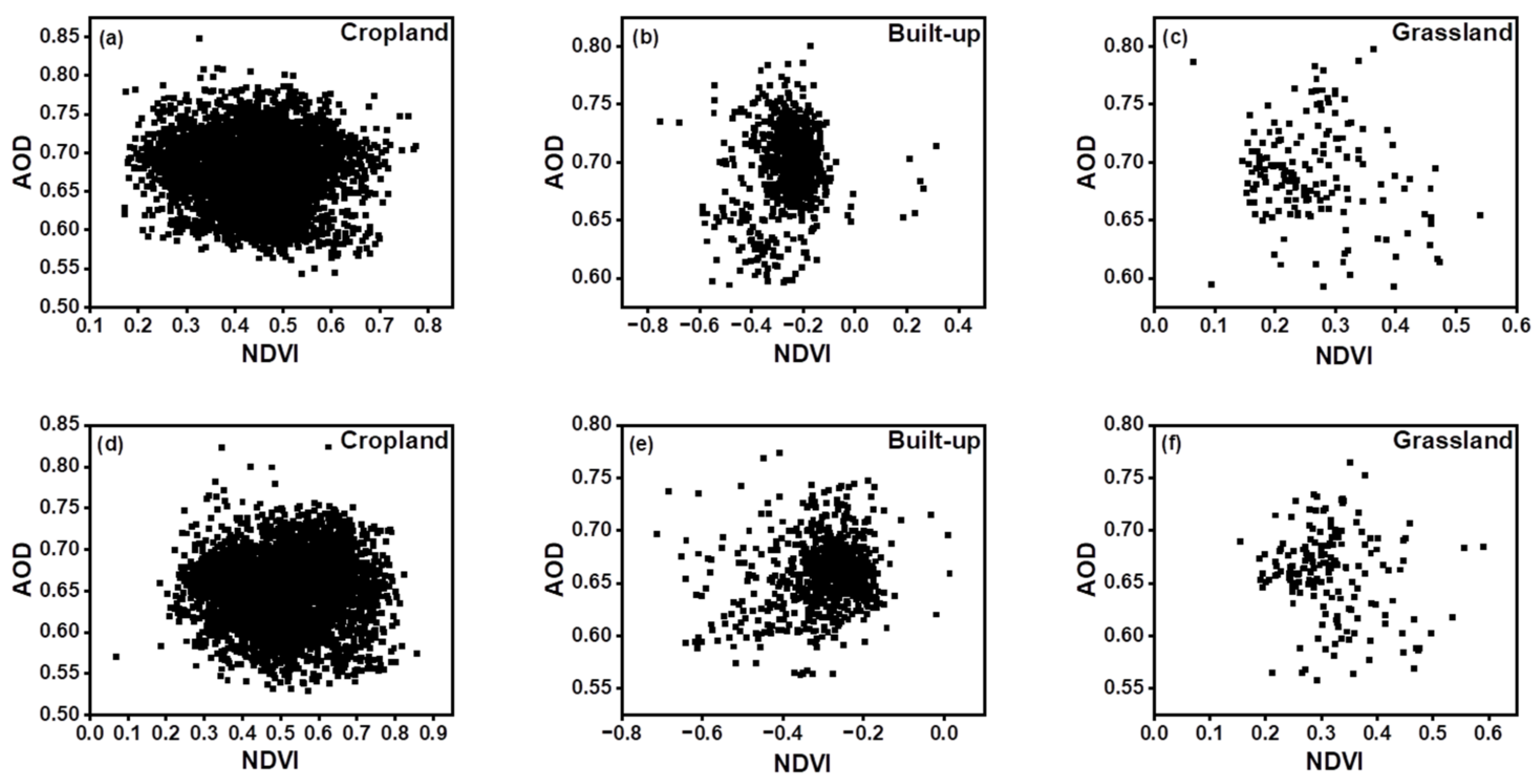
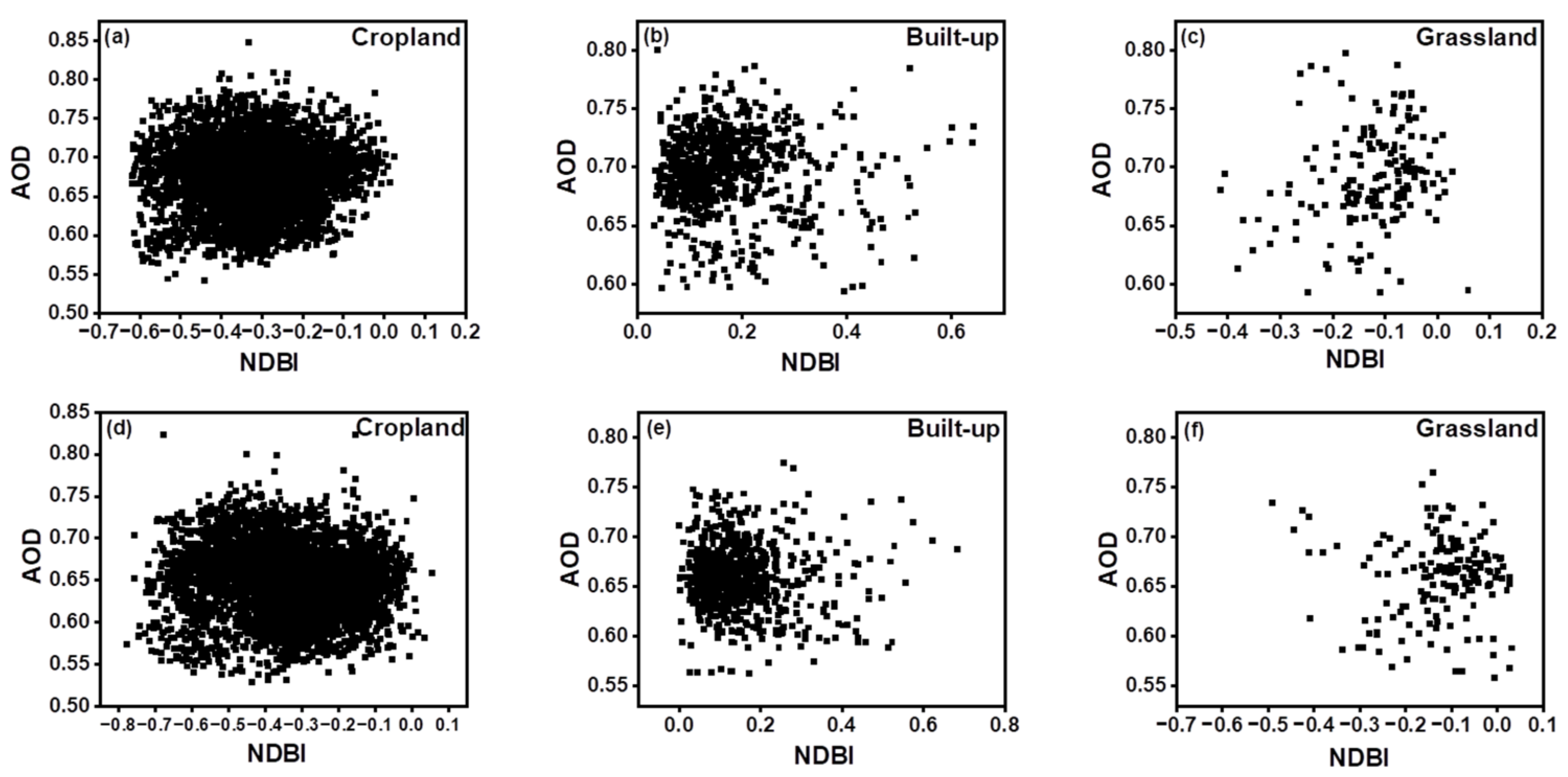
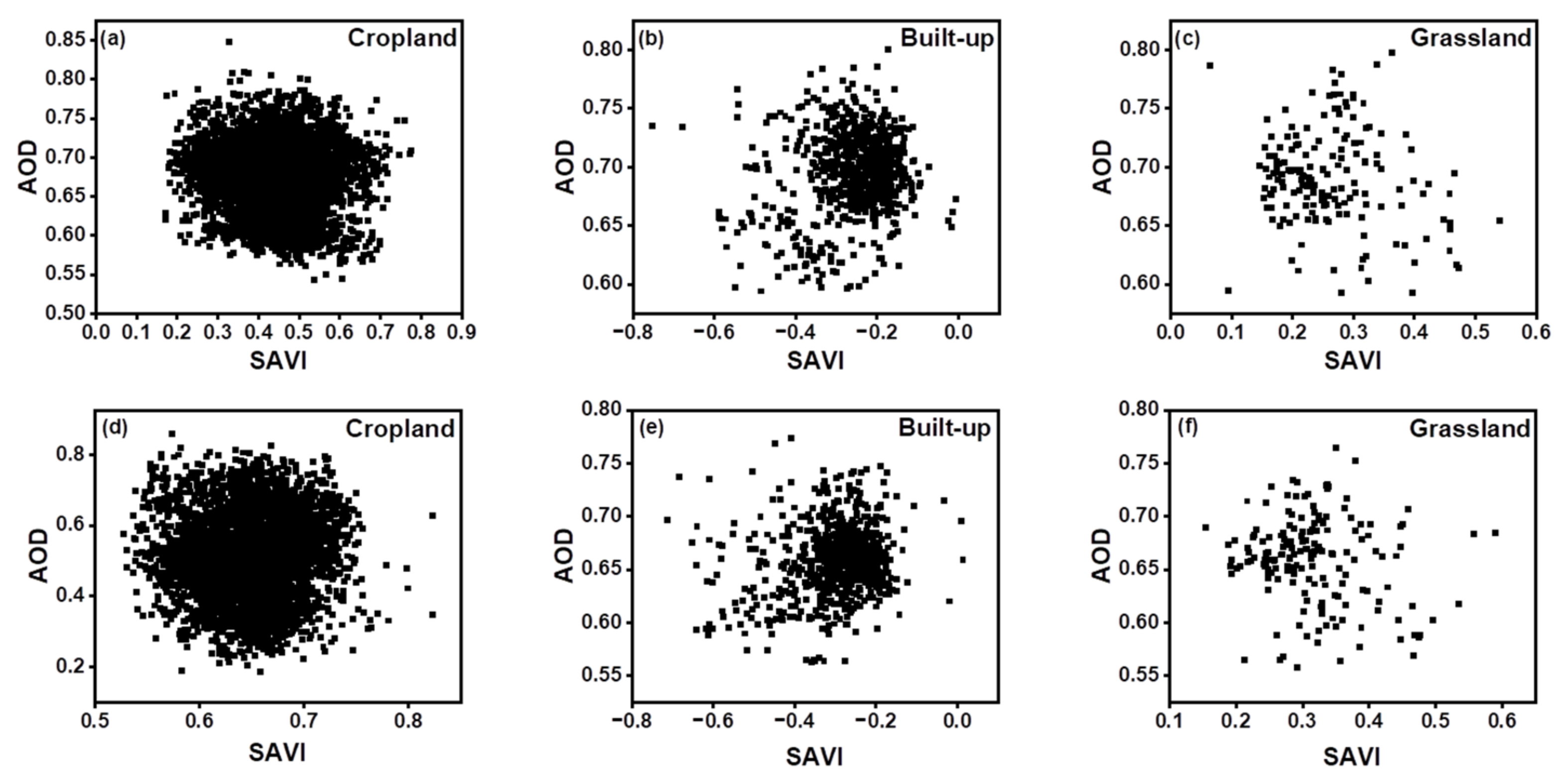
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Variations of LULC and Its Impact on AOD
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AERONET | Aerosol Robotic Network |
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| EE | Expected Error |
| EVI | Enhanced Vegetation Index |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| IGBP | International Geosphere and Biosphere Program |
| IGP | Indo-Gangetic Palin |
| IHDP | International Human Dimensions Program |
| LULC | Land Use Land Cover |
| MAIAC | Multiangle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| NCR | National Capital Region |
| NDBI | Normalized Difference Built-up Index |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| SAVI | Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEZ | Special Economic Zone |
References
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Bretherton, C.; Carslaw, K.S.; Coe, H.; DeMott, P.J.; Dunlea, E.J.; Feingold, G.; Ghan, S.; Guenther, A.B.; Kahn, R.; et al. Improving Our Fundamental Understanding of the Role of Aerosol-Cloud Interactions in the Climate System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Atmosphere: Aerosols, Climate, and the Hydrological Cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Raju, M.P.; Singh, R.S.; Banerjee, T. Impact of Drought and Normal Monsoon Scenarios on Aerosol Induced Radiative Forcing and Atmospheric Heating in Varanasi over Middle Indo-Gangetic Plain. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 113, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, K.M. Observational Relationships between Aerosol and Asian Monsoon Rainfall, and Circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, J.; Ramanathan, V. Recent Climate and Air Pollution Impacts on Indian Agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16319–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; Kumar, M.; Singh, N. Aerosol, Climate, and Sustainability; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1–5, ISBN 9780128096659. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R. Radiative Forcing and Climate Rrsponse. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 6831–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Burnett, R.; Rainham, D.G.; Birkett, N.J.; Krewski, D. Estimates of Global Mortality Attributable to Particulate Air Pollution Using Satellite Imagery. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, R.S.; Banerjee, T. Associating Airborne Particulates and Human Health: Exploring Possibilities: Comment on: Kim, Ki-Hyun, Kabir, E. and Kabir, S. 2015. A Review on the Human Health Impact of Airborne Particulate Matter. Environment International 74 (2015) 136–143. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Kumar, M.; Mall, R.K.; Singh, R.S. Airing ‘Clean Air’ in Clean India Mission. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6399–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tie, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Q. Effect of Aerosols on Visibility and Radiation in Spring 2009 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.-A. Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Relationship between Air Quality and Urban Land-Use Patterns Based on an Integrated Method. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.W.; Rihan, M.; Ishtiaque, M.; Shahfahad. Analyses of Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Change and Built-up Expansion in the Suburb of a Metropolitan City: Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Delhi NCR Using Landsat Datasets. J. Urban Manag. 2020, 9, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Sun, D.; Miao, Z. Estimating the Impact of Urbanization on Air Quality in China Using Spatial Regression Models. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15570–15592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.A.; Neumayer, E. Examining the Impact of Demographic Factors on Air Pollution. Popul. Environ. 2004, 26, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Zhou, X.; Singh, R.P.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Venkatramanan, V.; Deshmukh, B. Monitoring of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics and Prediction of Urban Growth Using Land Change Modeler in Delhi and Its Environs, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71534–71554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Lyapustin, A.; De Carvalho, L.A.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Validation of High-Resolution MAIAC Aerosol Product over South America. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 7537–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 Km Aerosol Product: Algorithm and Global Perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS Aerosol Products over Land and Ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of MODIS Aerosol Retrieval Algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region during Low to Very High Pollution Events. Nature 2015, 175, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Broday, D.M.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, S.N. Evaluation of MODIS Collection 6 Aerosol Retrieval Algorithms over Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of Aerosols Types and Mass Loading. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Zhu, W. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Variations of Aerosol Optical Depth over Yellow and Bohai Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7969–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote Sensing of Particulate Pollution from Space: Have We Reached the Promised Land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7823–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, A.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Banerjee, T. Remote Sensing of Aerosols From Space: Retrieval of Properties and Applications. In Remote Sensing of Aerosols, Clouds, and Precipitation; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 45–83. ISBN 9780128104385. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm: The Second Generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexei, L.; John, M.; Yujie, W.; Istvan, L.; Sergey, K. Multiangle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC):1. Radiative Transfer Basis and Look-up Tables. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC):2. Aerosol Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D03211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol Properties over Bright-Reflecting Source Regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Broday, D.M.; Chatfield, R. Comparison and Evaluation of MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) Aerosol Product over South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S. Validation of MODIS 3km Land Aerosol Optical Depth from NASA’s EOS Terra and Aqua Missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3145–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S.; Bilal, M.; Dey, S.; Singh, S. Performance of MODIS C6.1 Dark Target and Deep Blue Aerosol Products in Delhi National Capital Region, India: Application for Aerosol Studies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, R.; Zuo, H. Validation and Comparison of High-Resolution MAIAC Aerosol Products over Central Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 251, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabash, M.; Balcik, F.B.; Glantz, P. Validation of MODIS C6.1 and MERRA-2 AOD Using AERONET Observations: A Comparative Study over Turkey. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 905. [Google Scholar]
- Economic & Statistics Division State Planning Institute Planning Department. Statistical Diary Uttar Pradesh; Economic & Statistics Division State Planning Institute Planning Department: Lucknow, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IQAir. WAQR World Air Quality Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/world-most-polluted-cities/world-air-quality-report-2019-en.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- IQAir. 2018 World Air Quality Report PM2.5 Ranking; IQAir: Goldach, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, L.; Dev, R.; Zaidi, K.; Sunder Raman, R.; Habib, G.; Ghosh, B. Assessment of PM10 and PM2.5 over Ghaziabad, an Industrial City in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Spatio-Temporal Variability and Associated Health Effects. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, S.S.; Kumari, M. Comparative Analysis of Different Vegetation Indices with Respect to Atmospheric Particulate Pollution Using Sentinel Data. Appl. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 7, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Impact Factors Analysis of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Sun, Q. Monitoring the Spatial Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth and Its Correlation with Land Use/Land Cover in Wuhan, China: A Perspective of Urban Planning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lili, L.; Yunpeng, W. What Drives the Aerosol Distribution in Guangdong—The Most Developed Province in Southern China? Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hong, S.; Feng, N.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatial Distributions and Temporal Variations of Atmospheric Aerosols and the Affecting Factors: A Case Study for a Region in Central China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3672–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, S.; Ge, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Characteristics of Aerosol Optical Depth over Land Types in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhu, A.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chan, A. Modeling the Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Meteorology and Air Quality during 2000–2018 in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Purohit, B.; Balyan, P.; Dixit, K.; Bali, K. A Satellite-Based High-Resolution (1-Km) Ambient PM 2. 5 Database for India over Two Decades Quality Management. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Dey, S.; Di Girolamo, L.; Smith, K.R.; Pillarisetti, A.; Lyapustin, A. Tracking Ambient PM 2.5 Build-up in Delhi National Capital Region during the Dry Season over 15 Years Using a High-Resolution (1 km) Satellite Aerosol Dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 204, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Census of India. Cities Having Population 1 Lakh and Above. 2011. Available online: http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/India2/Table_2_PR_Cities_1Lakh_and_Above.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Ghosh, S.; Vidhata, N.K.G.; Kumar, S.; Midya, K. Seasonal Contrast of Land Surface Temperature in Faridabad: An Urbanized District of Haryana, India. In Methods and Applications of Geospatial Technology in Sustainable Urbanism; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 217–250. ISBN 9781799822493. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Singh, S. Polycentric Urban Growth and Identification of Urban Hot Spots in Faridabad, the Million-plus Metropolitan City of Haryana, India: A Zonal Assessment Using Spatial Metrics and GIS. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 8246–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Midya, K.; Ghosh, S.; Singh, S. Pixel-Based vs. Object-Based Anthropogenic Impervious Surface Detection: Driver for Urban-Rural Thermal Disparity in Faridabad, Haryana, India. Geocarto Int. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horo, J.P.; Punia, M. Urban Dynamics Assessment of Ghaziabad as a Suburb of National Capital Region, India. GeoJournal 2018, 84, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Joshi, P.K. Mapping Environmental Impacts of Rapid Urbanization in the National Capital Region of India Using Remote Sensing Inputs. Urban Clim. 2016, 15, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Myllyvirta, L.; Sivalingam, N.; Airpocalyse-Assessment of Air Pollution in Indian Cities. Greenpeace, India. Available online: https://secured-static.greenpeace.org/india/Global/india/Airpoclypse--Not-just-Delhi--Air-in-most-Indian-cities-hazardous--Greenpeace-report.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Gogikar, P.; Tyagi, B. Assessment of Particulate Matter Variation during 2011–2015 over a Tropical Station Agra, India. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC Algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.; Campbell, J.R.; Spak, S.N.; Shen, X.; Nazeer, M. A New MODIS C6 Dark Target and Deep Blue Merged Aerosol Product on a 3 Km Spatial Grid. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesnulyte, V.; Lindfors, A.V.; Pitkänen, M.R.A.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Morcrette, J.J.; Arola, A. Comparing ECMWF AOD with AERONET Observations at Visible and UV Wavelengths. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.R.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.; Fekete, B.M.; et al. Sixteen Years of Change in the Global Terrestrial Human Footprint and Implications for Biodiversity Conservation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.; Villar, S.C.; Klepeis, P.; Mendoza, P.M.A.; Ogneva-Himmelberger, Y.; Chowdhury, R.R.; Turner, B.L.; Vance, C. Modeling Tropical Deforestation in the Southern Yucatán Peninsular Region: Comparing Survey and Satellite Data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, E.G.; Geoghegan, J. Theory, Data, Methods: Developing Spatially Explicit Economic Models of Land Use Change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, L.R.; Brovkin, V.; Arora, V.K.; Cadule, P.; De Noblet-Ducoudré, N.; Kato, E.; Pongratz, J.; Gayler, V. Global and Regional Effects of Land-Use Change on Climate in 21st Century Simulations with Interactive Carbon Cycle. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2014, 5, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change {(LUCC)} Implementation Strategy. Int. Geosph. -Biosph. Program. A Study Glob. Chang. 1999, 125. [Google Scholar]
- LAADS DAAC. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/search/ (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Han, C. Bi-Temporal Characterization of Land Surface Temperature in Relation to Impervious Surface Area, NDVI and NDBI, Using a Sub-Pixel Image Analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AERONET (AEROSOL ROBOTIC NETWORK). Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Qu, J.J.; Che, H. Validation of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Product over China Using CARSNET Measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5970–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.K.; Rao, S.V.B. Seasonal variations of aerosol optical depth over indian subcontinent. IJCRR 2012, 04, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Nivit, Y.K. Makeover: Conversion of Brick Kilns in Delhi-NCR to a Cleaner Technology—A Status Report; Centre for Science and Environment: New Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG. Urbanisation in the National Capital Region. Available online: https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/in/pdf/2017/03/Urbanisation-in-the-National-Capital-Region.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Campbell, B.M.; Beare, D.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Ingram, J.S.I.; Jaramillo, F.; Ortiz, R.; Ramankutty, N.; Sayer, J.A.; Shindell, D. Agriculture Production as a Major Driver of the Earth System Exceeding Planetary Boundaries. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttippurath, J.; Singh, A.; Dash, S.P.; Mallick, N.; Clerbaux, C.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Coheur, P.F.; Raj, S.; Abbhishek, K.; et al. Record High Levels of Atmospheric Ammonia over India: Spatial and Temporal Analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Hooda, R.S.; Singh, S. Monitoring and Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Changes and Its Impact on Land Surface Temperature in the Central Part of Hisar District, Haryana under Semi-Arid Zone of India. J. Landsc. Ecol. Repub. 2019, 12, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, K.; Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S. Assessment of Urban Growth and Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Faridabad District, Haryana, India. Pollution 2022, 8, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Fang, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Zhang, M.; Su, X.; Bilal, M.; Liang, X. MODIS High-Resolution MAIAC Aerosol Product: Global Validation and Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 264, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, I.; Shahid, M.Z.; Chen, Z.; Asif, Z. Long-Term Variability of Aerosol Concentrations and Optical Properties over the Indo-Gangetic Plain in South Asia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, C. The Greening of Northwest Indian Subcontinent and Reduction of Dust Abundance Resulting from Indian Summer Monsoon Revival. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Capital Region Planning Board. Economic Profile of NCR 2015 Final Report; National Capital Region Planning Board: Delhi, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cermak, J.; Yang, K.; Pauli, E.; Chen, Y. Land Use and Land Cover Influence on Sentinel-2 Aerosol Optical Depth below City Scales over Beijing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zeng, J.; Namaiti, A. Research on the Spatial Heterogeneity and Influencing Factors of Air Pollution: A Case Study in Shijiazhuang, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleed, M.; Mubeen, M.; Ahmad, A.; Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Amin, A.; Farid, H.U.; Hussain, S.; Ali, M.; Qaisrani, S.A.; Nasim, W.; et al. Evaluating the Efficiency of Coarser to Finer Resolution Multispectral Satellites in Mapping Paddy Rice Fields Using GEE Implementation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Lu, L.; Mubeen, M.; Nasim, W.; Karuppannan, S.; Fahad, S.; Tariq, A.; Mousa, B.G.; Mumtaz, F.; Aslam, M. Spatiotemporal Variation in Land Use Land Cover in the Response to Local Climate Change Using Multispectral Remote Sensing Data. Land 2022, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


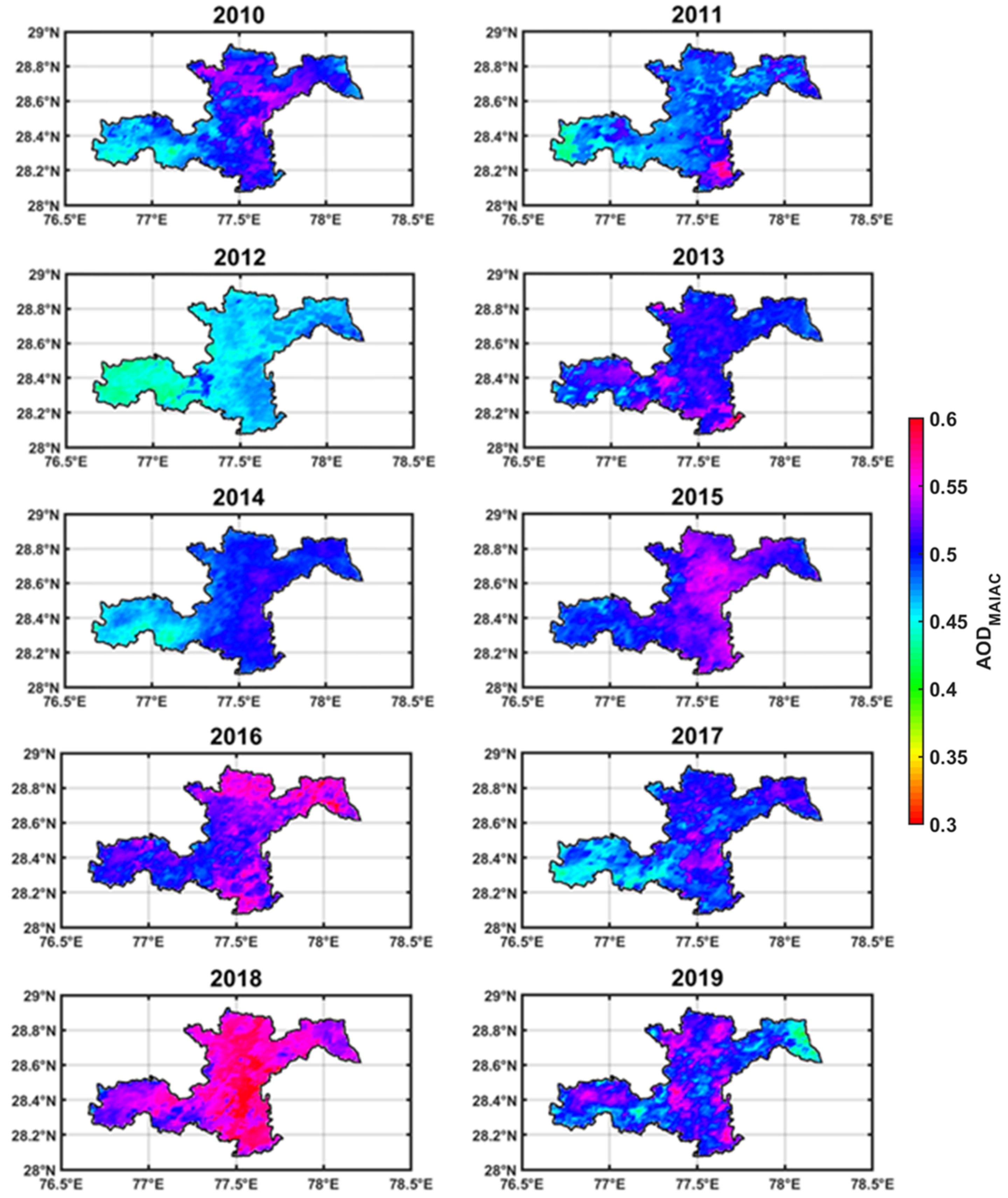
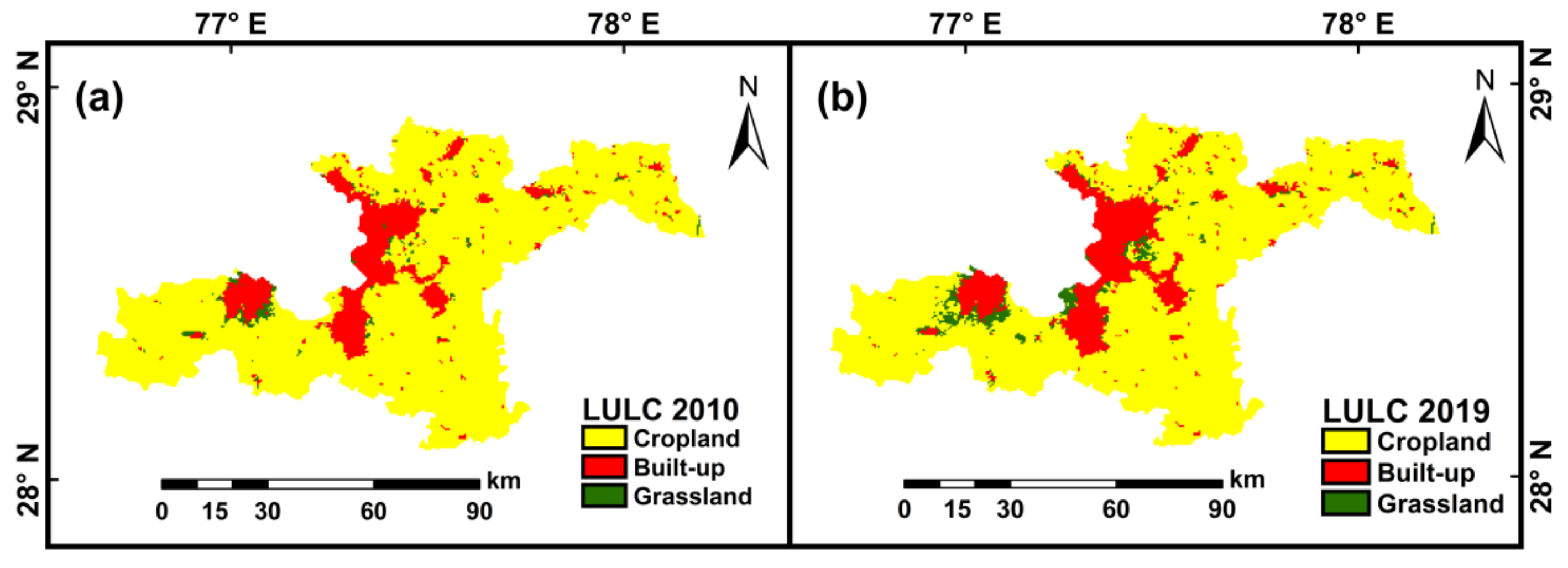
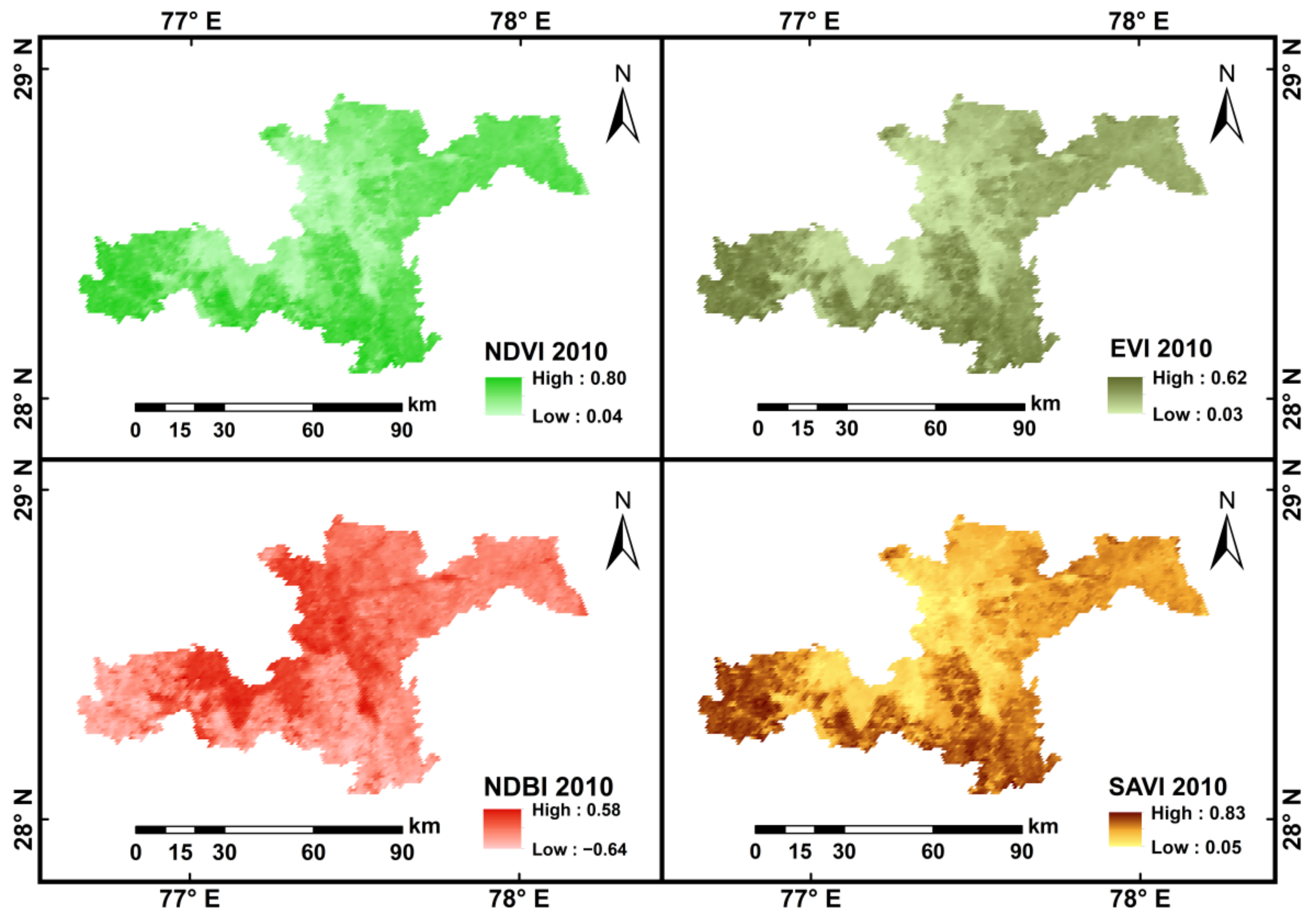
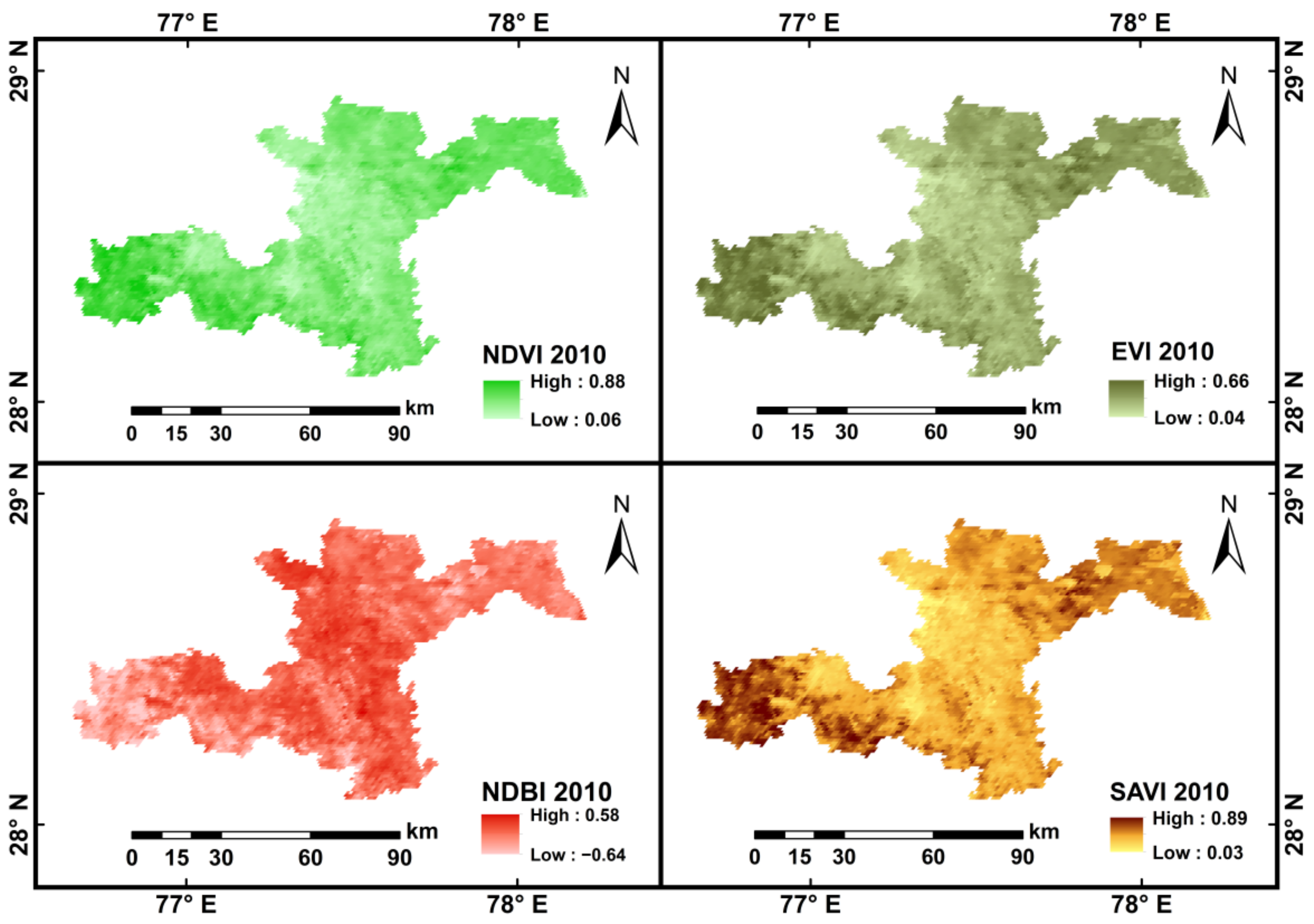

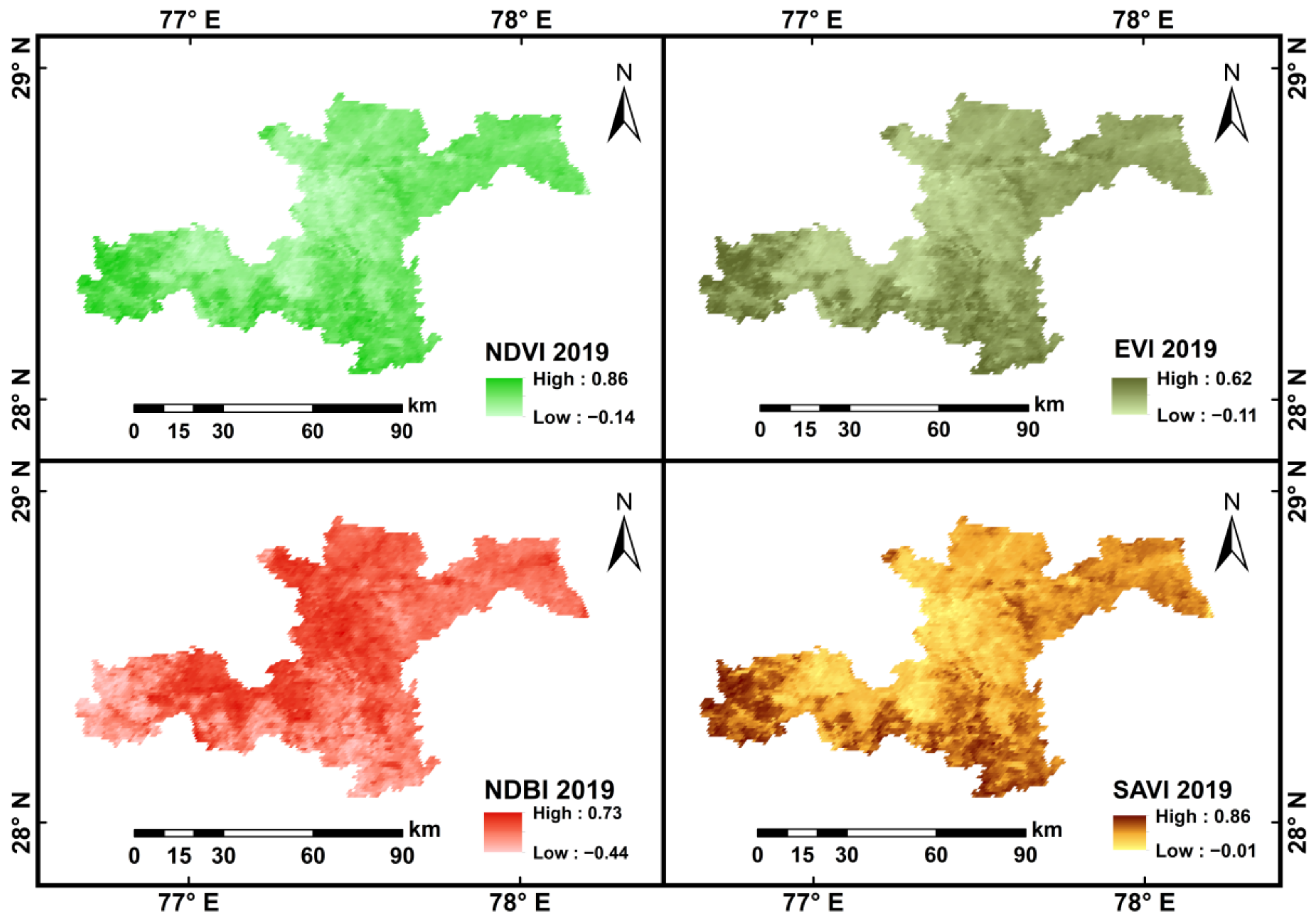

| EE | <0.5 | 0.5–1.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amity University | % within | 70 | 92.86 | N = 105 R = 0.81 RMSE = 0.16 |
| % below | 25 | 7.14 | ||
| Gual Pahari | % within | 65 | 78.79 | |
| % below | 35 | 21.21 |
| LULC Class | Percentage Change (%) | Percentage Change in a Decade (2010–2019) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| Cropland | −0.69 | −0.42 | −0.55 | −0.88 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.15 | −0.05 | −2.35 | −4.46 |
| Built-up | 1.91 | 1.10 | 1.58 | 1.42 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 4.68 | 12.05 |
| Grassland | 15.79 | 8.88 | 9.77 | 17.57 | −5.87 | −11.90 | −7.94 | −1.88 | 34.27 | 51.13 |
| Cropland | Built-Up | Grassland | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqua | Terra | Aqua | Terra | Aqua | Terra | |
| Mean | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.66 |
| S.D. | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Min | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
| Max | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.76 |
| NDVI | NDBI | SAVI | EVI | |
| R | −0.24 | 0.35 | 0.27 | −0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S.; Singh, S.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Al-Ansari, N.; Tiwari, R.K.; Kuriqi, A. Spatial Variation and Relation of Aerosol Optical Depth with LULC and Spectral Indices. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121992
Sharma V, Ghosh S, Singh S, Vishwakarma DK, Al-Ansari N, Tiwari RK, Kuriqi A. Spatial Variation and Relation of Aerosol Optical Depth with LULC and Spectral Indices. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(12):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121992
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Vipasha, Swagata Ghosh, Sultan Singh, Dinesh Kumar Vishwakarma, Nadhir Al-Ansari, Ravindra Kumar Tiwari, and Alban Kuriqi. 2022. "Spatial Variation and Relation of Aerosol Optical Depth with LULC and Spectral Indices" Atmosphere 13, no. 12: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121992
APA StyleSharma, V., Ghosh, S., Singh, S., Vishwakarma, D. K., Al-Ansari, N., Tiwari, R. K., & Kuriqi, A. (2022). Spatial Variation and Relation of Aerosol Optical Depth with LULC and Spectral Indices. Atmosphere, 13(12), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121992








