Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
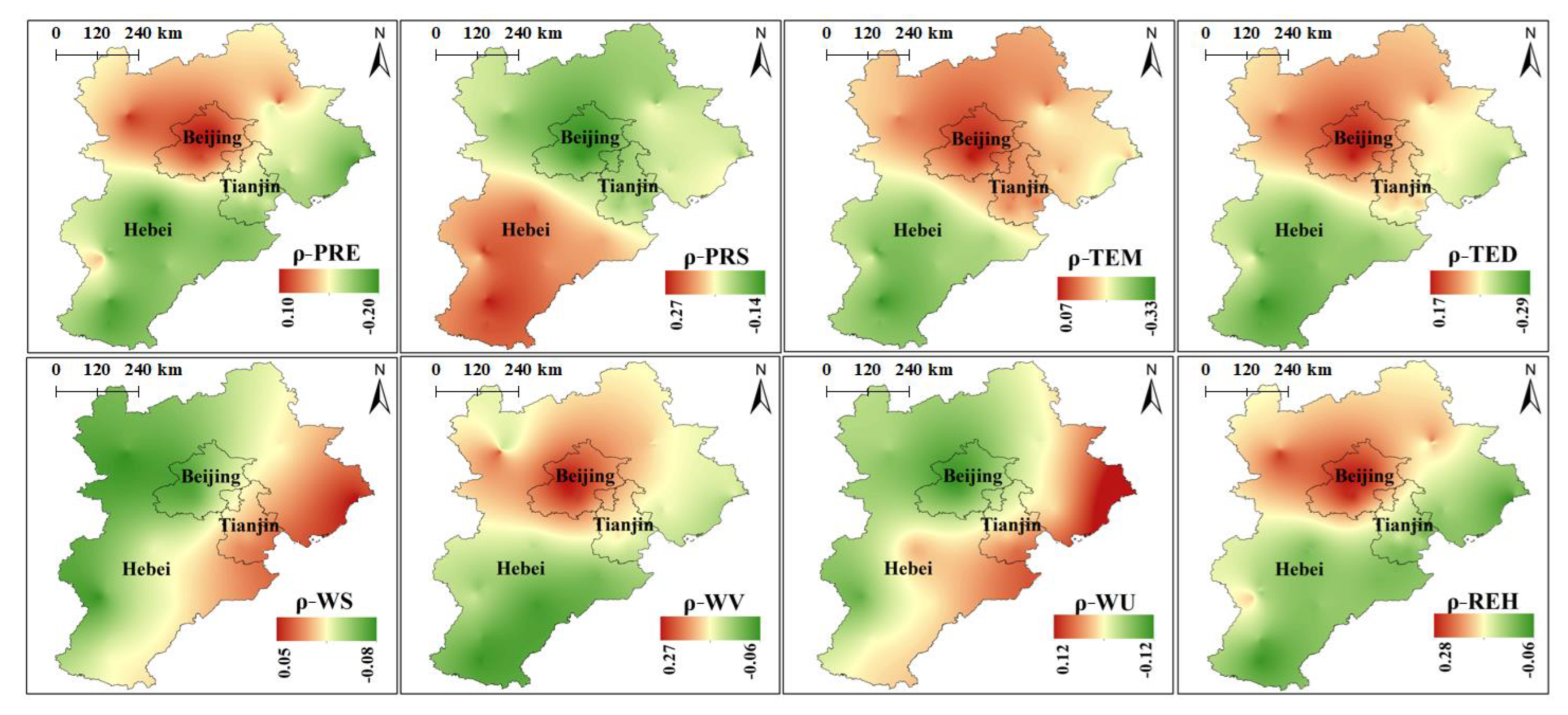
2.3.1. Kriging Interpolation & Spatial Spearman
2.3.2. Wavelet Transform & Wavelet Transform Coherence
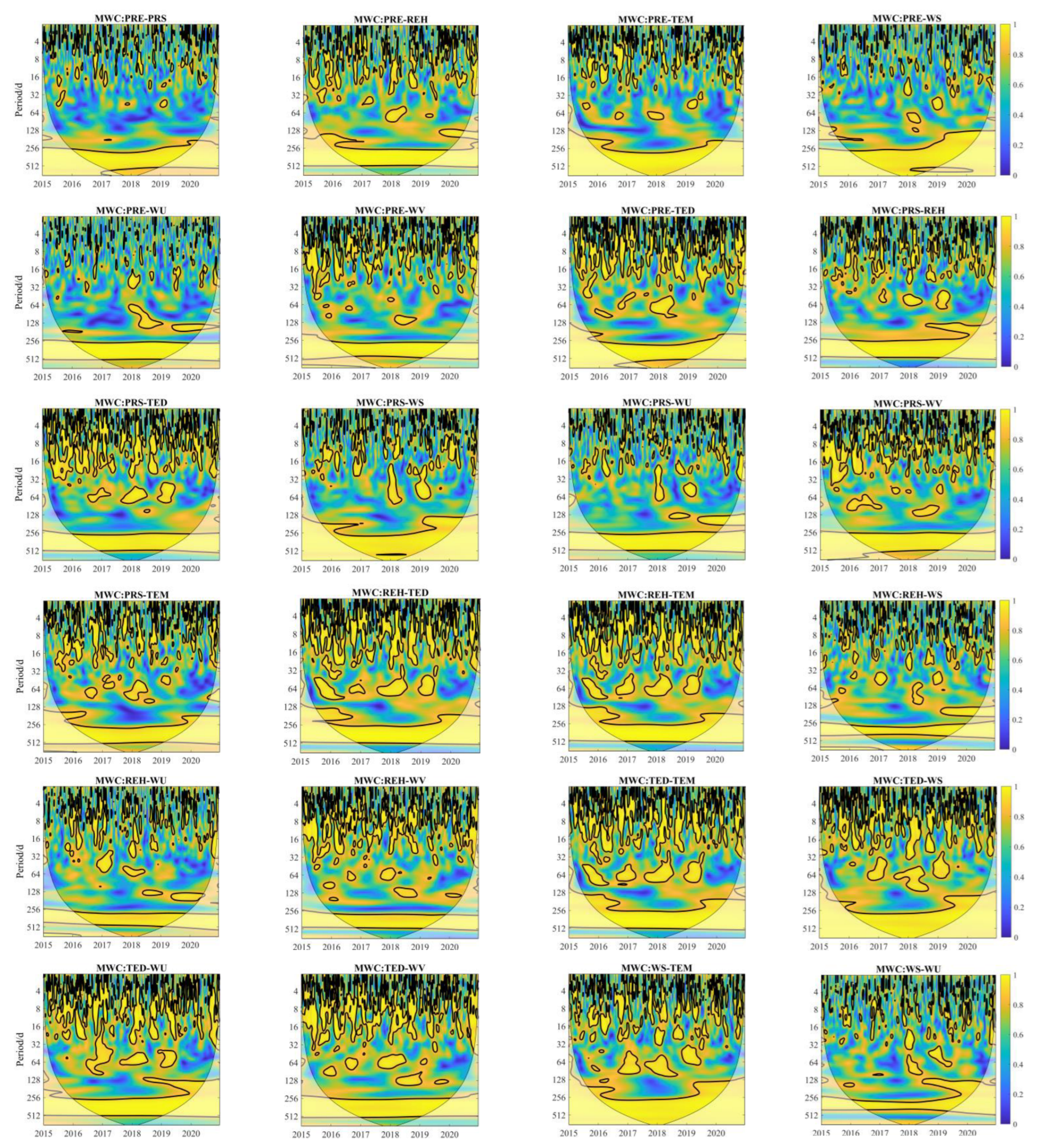
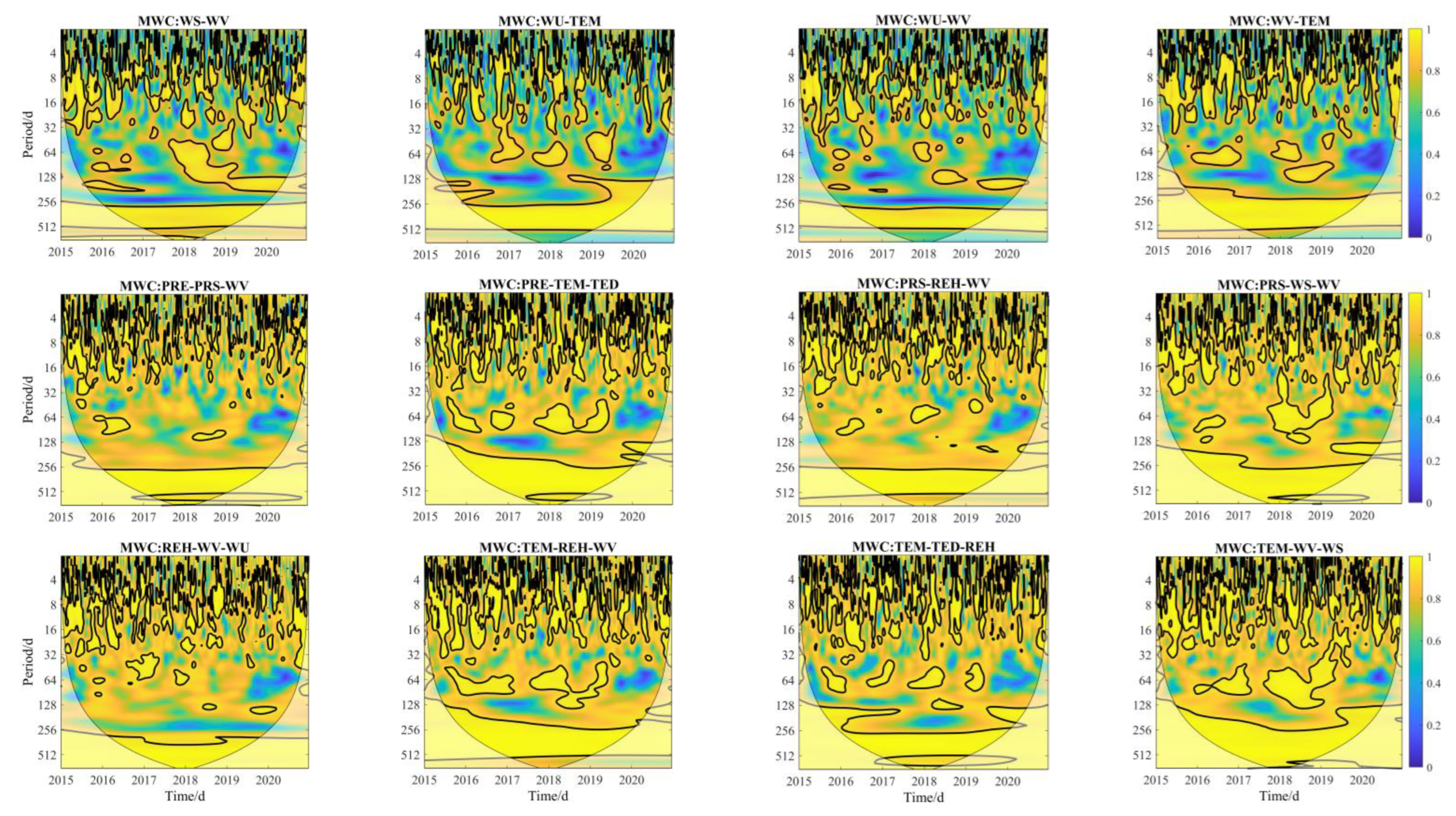
2.3.3. Multiple Wavelet Coherence
3. Results
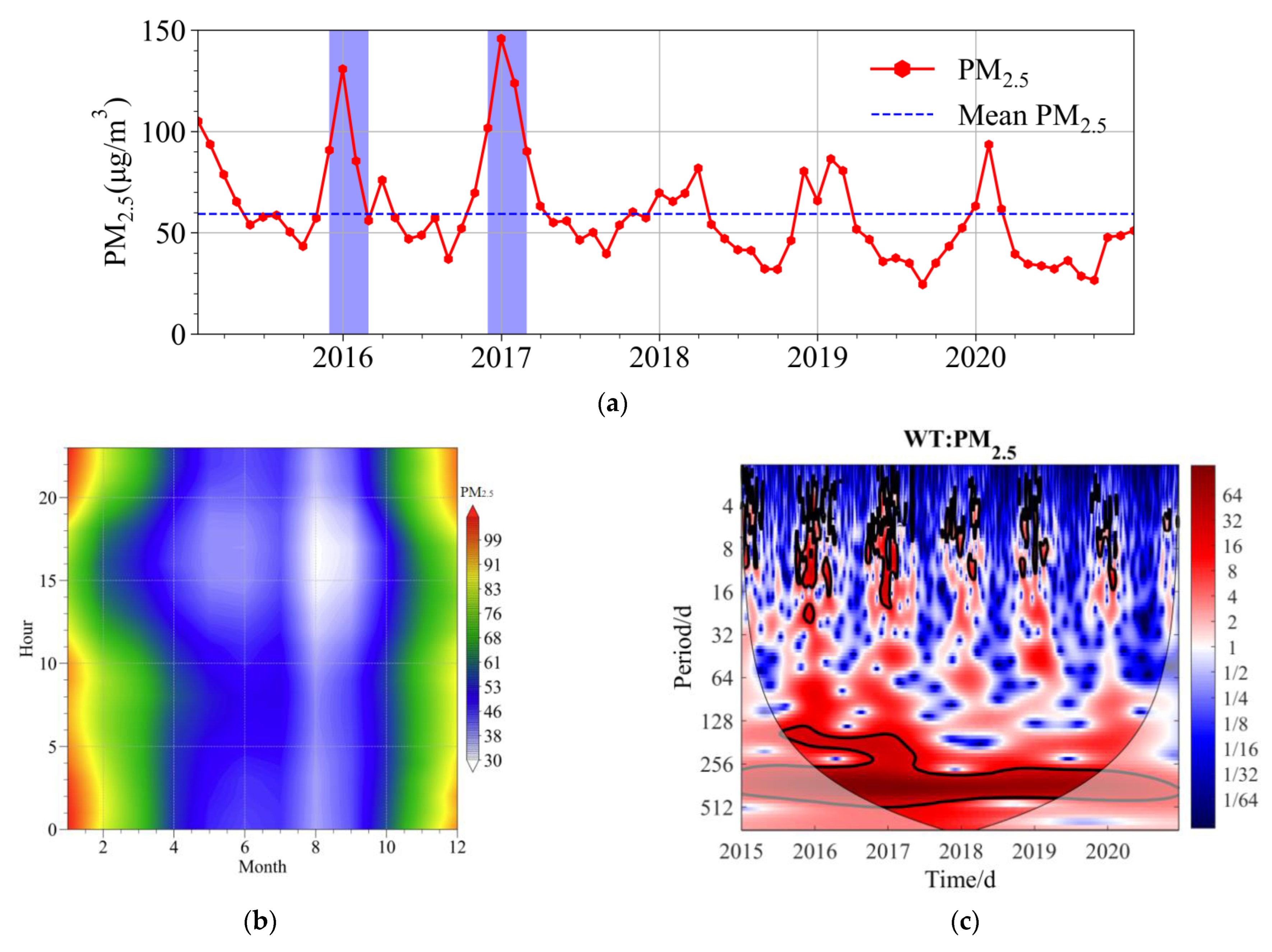
3.1. Temporal Evolution of PM2.5 in the BTH from 2015 to 2020
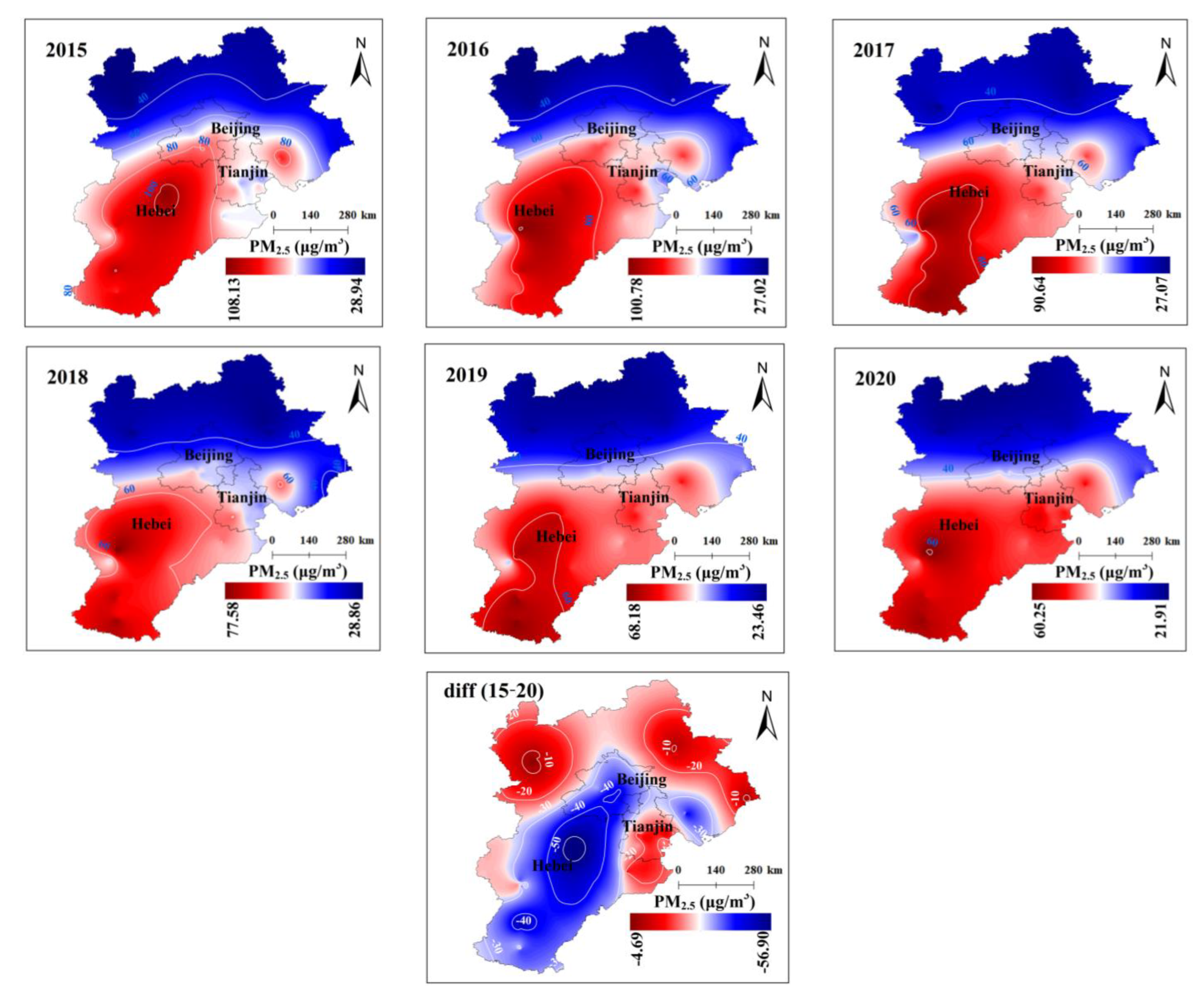
3.2. Annual Spatial Variation of PM2.5 in the BTH from 2015–2020
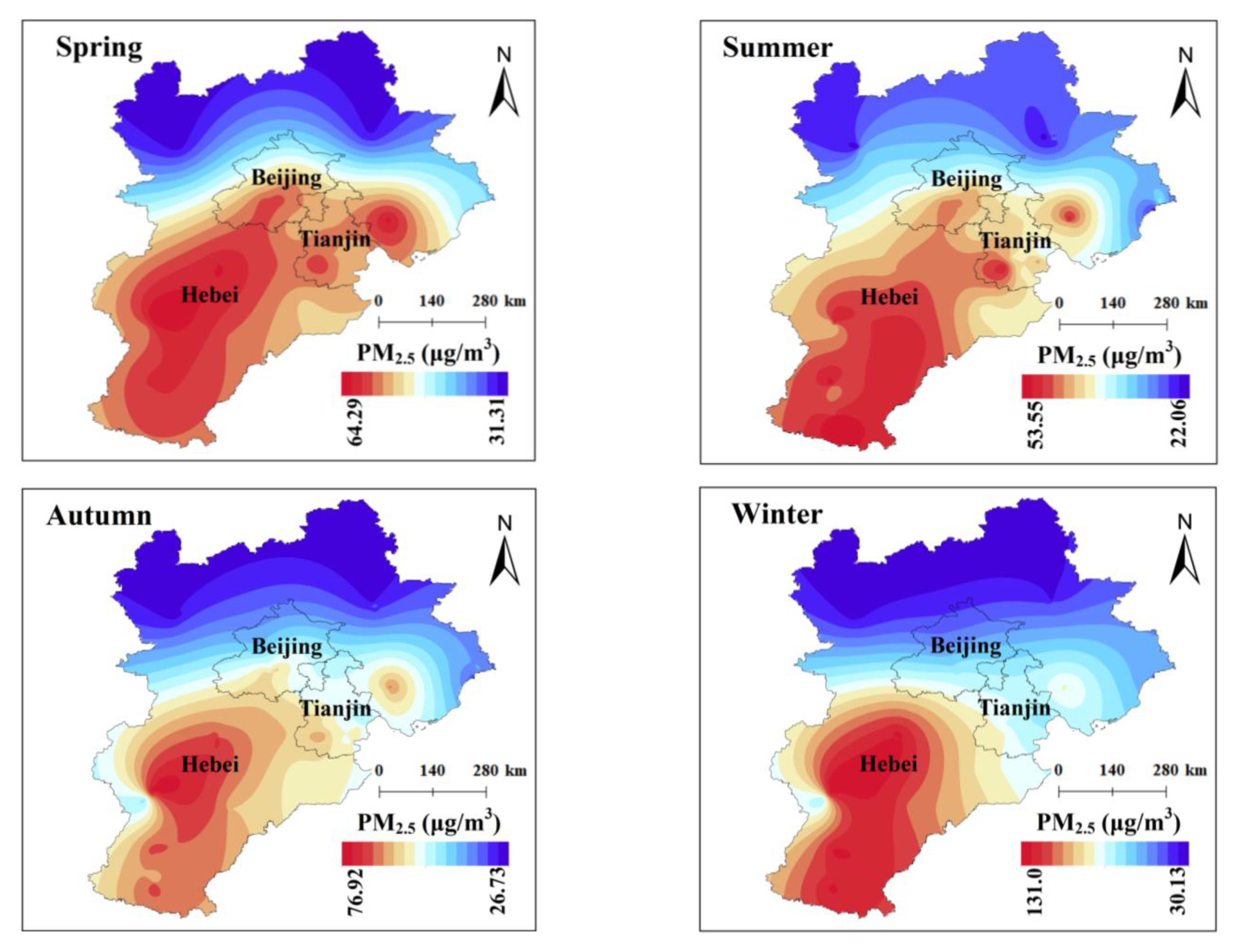
3.3. Seasonal Spatial Change of PM2.5 in the BTH Region
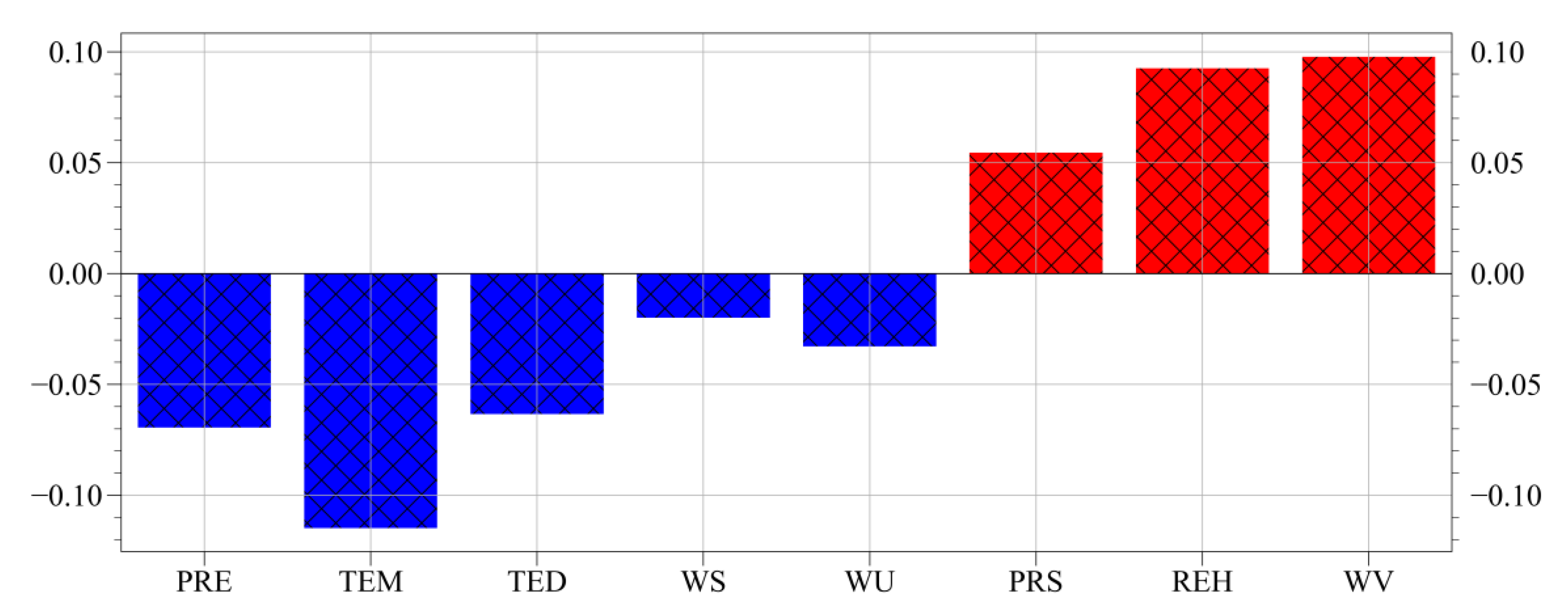
3.4. Overall Correlation between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors
3.5. Wavelet Transform Coherence between PM2.5 and Single Factor
3.6. Multiple Wavelet Coherence between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etchie, T.O.; Sivanesan, S.; Adewuyi, G.O.; Krishnamurthi, K.; Rao, P.S.; Etchie, A.T.; Pillarisetti, A.; Arora, N.K.; Smith, K.R. The health burden and economic costs averted by ambient PM2.5 pollution reductions in Nagpur, India. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Chirkov, V.; Dentener, F.; Van Dingenen, R.; Pachauri, S.; Purohit, P.; Amann, M.; Heyes, C.; Kinney, P.; Kolp, P.; et al. Environmental Modeling and Methods for Estimation of the Global Health Impacts of Air Pollution. Environ. Model. Assess. 2012, 17, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.F.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.Z. Estimation of the PM2.5 health effects in China during 2000–2011. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10695–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.J.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, W.H.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.M. Progress of Air Pollution Control in China and Its Challenges and Opportunities in the Ecological Civilization Era. Engineering 2020, 6, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wong, T.W.; Law, C.K.; Dong, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Impacts of sectoral emissions in China and the implications: Air quality, public health, crop production, and economic costs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69–E74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, H.Y. Air Pollution and Central Nervous System Disease: A Review of the Impact of Fine Particulate Matter on Neurological Disorders. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 575330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tan, Z.B.; Yu, X.H.; Zhang, R.T.; Wei, Y.M.; Zhang, M.J.; Sun, H.X.; Meng, J.; Mi, Z.F. The health benefits and economic effects of cooperative PM2.5 control: A cost-effectiveness game model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Hu, J.; Qi, Y.X.; Li, C.L.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, X.M.; He, J.W.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Emission characterization, environmental impact, and control measure of PM2.5 emitted from agricultural crop residue burning in China. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 149, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Song, G.J.; Gong, X.Q. The unidirectional causality influence of factors on PM2.5 in Shenyang city of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zang, L.; Du, W.; Xu, D.; Shen, G.F.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, Q.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhao, M.R.; Yao, D.F. Ambient air pollution of particles and gas pollutants, and the predicted health risks from long-term exposure to PM2.5 in Zhejiang province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23833–23844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.X.; Tao, L.X.; Gao, Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, S.P.; et al. PM2.5 Spatiotemporal Variations and the Relationship with Meteorological Factors during 2013–2014 in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Yuan, Q.Q.; Li, T.W.; Shen, H.F.; Zhang, L.P. The Relationships between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors in China: Seasonal and Regional Variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Ma, L. Expansion of Industrial Parks in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration: A Spatial Analysis. Land 2021, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.C.; Zhou, J.B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.M. Industrial agglomeration and air pollution: A new perspective from enterprises in Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel Cities (APTCC) of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and its surrounding areas, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.L.; Liu, F.Y.; Song, Y.J.; Geng, J.B. Impact of Air Pollution Regulation and Technological Investment on Sustainable Development of Green Economy in Eastern China: Empirical Analysis with Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Gao, J.B.; Guo, L.H.; Nie, X.J.; Xiao, X.M. Meteorological Influences on Spatiotemporal Variation of PM2.5 Concentrations in Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel Cities of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Li, X.C.; Li, H.T. Factors Influencing PM2.5 Concentrations in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using a Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, C.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z. The spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 73, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, D.L.; Zhao, C.F.; Kwan, M.P.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Influence of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A review of methodology and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.O.; Liu, X.H.; Yu, J.Y.; Jiao, Y.L. Impact of synoptic weather patterns on 24 h-average PM2.5 concentrations in the North China Plain during 2013–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Jin, H.B.; Mao, H.C.; Geng, D.; Hou, S.G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.F. Characteristic and Spatiotemporal Variation of Air Pollution in Northern China Based on Correlation Analysis and Clustering Analysis of Five Air Pollutants. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Xu, H.D.; Liang, D. Spatiotemporal variations and connections of single and multiple meteorological factors on PM2.5 concentrations in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 275, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.Q. Investigating the aerosol mass and chemical components characteristics and feedback effects on the meteorological factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.H.; Wang, X.S.; Zhang, S.Q. Risk-based air pollutants management at regional levels. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 25, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Lei, Y.L.; Shi, Y.K.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Evolution of the spatiotemporal pattern of PM2.5 concentrations in China—A case study from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.N. The flexibility pathways for integrating renewable energy into China’s coal dominated power system: The case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Xiao, D.P.; Bai, H.Z.; Tang, J.Z.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal Distributions of PM2.5 Concentrations in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region from 2013 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 842237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.L.; Hu, Y.T.; Chang, H.H.; Russell, A.G.; Cai, J.; Xu, B.; Bai, Y.Q. Daily estimation of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations at 4 km resolution over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei by fusing MODIS AOD and ground observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huo, H.; Lin, J.T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.K.; Guan, D.B.; He, K.B. Environment-economy tradeoff for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei’s exports. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.F.; Lin, R.S.; Tang, W.; Zhou, Y. Forecasting Model of Short-Term PM2.5 Concentration Based on Deep Learning. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. 2019, 42, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agusti-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J S. Afr Inst. Min. Metall. 1951, 52, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Matheron, G. Principles of geostatistics. Econ. Geol. 1963, 58, 1246–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Sajjad, M.; Kanwal, S.; Xiao, T.Y.; Khalid, S.; Shoaib, F.; Gul, H.N. Spatial-temporal characterization of rainfall in Pakistan during the past half-century (1961–2020). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lu, X.M.; Yan, Y.T.; Zhou, L.G.; Ma, W.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 concentration in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China on the application of big data and wavelet analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Luo, Y.Q.; Wan, N.; Zheng, Z.; Sternberg, T.; Liao, Y.L. Performance comparison of LUR and OK in PM2.5 concentration mapping: A multidimensional perspective. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy Functions into Square Integrable Wavelets of Constant Shape. Siam J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process Geophys 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlet, J.; Arens, G.; Fourgeau, E.; Glard, D. Wave propagation and sampling theory—Part I: Complex signal and scattering in multilayered media. Geophysics 1982, 47, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusasananan, P. Wavelet spectrum analysis of PM10 data in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1380, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihanovic, H.; Orlic, M.; Pasaric, Z. Diurnal thermocline oscillations driven by tidal flow around an island in the Middle Adriatic. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S157–S168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Webster, P.J. Interdecadal changes in the ENSO–monsoon system. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Si, B.C. Technical note: Multiple wavelet coherence for untangling scale-specific and localized multivariate relationships in geosciences. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Si, B.C.; Biswas, A.; Chau, H.W. Temporally stable patterns but seasonal dependent controls of soil water content: Evidence from wavelet analyses. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.K.W.; Chan, J.C.L. Geophysical Applications of Partial Wavelet Coherence and Multiple Wavelet Coherence. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, L.H. The Spectral Analysis of Time Series; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 119–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Wang, W.X.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, S.J.; Xu, J.; He, Y.J.; Meng, F. The contribution of residential coal combustion to PM2.5 pollution over China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in winter. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.Z.; Chai, P.F.; Lin, H.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ye, Z.H.; Gu, M.J.; Lu, H.C.; Shen, P.; Jin, M.J.; Wang, J.B.; et al. Association of PM2.5 pollution with the pattern of human activity: A case study of a developed city in eastern China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Xie, X.M.; Cai, J.; Chen, D.L.; Gao, B.B.; He, B.; Cheng, N.L.; Xu, B. Understanding meteorological influences on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A temporal and spatial perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5343–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.B.; Li, H.S. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Air Quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas (‘2 + 26’ Cities). Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

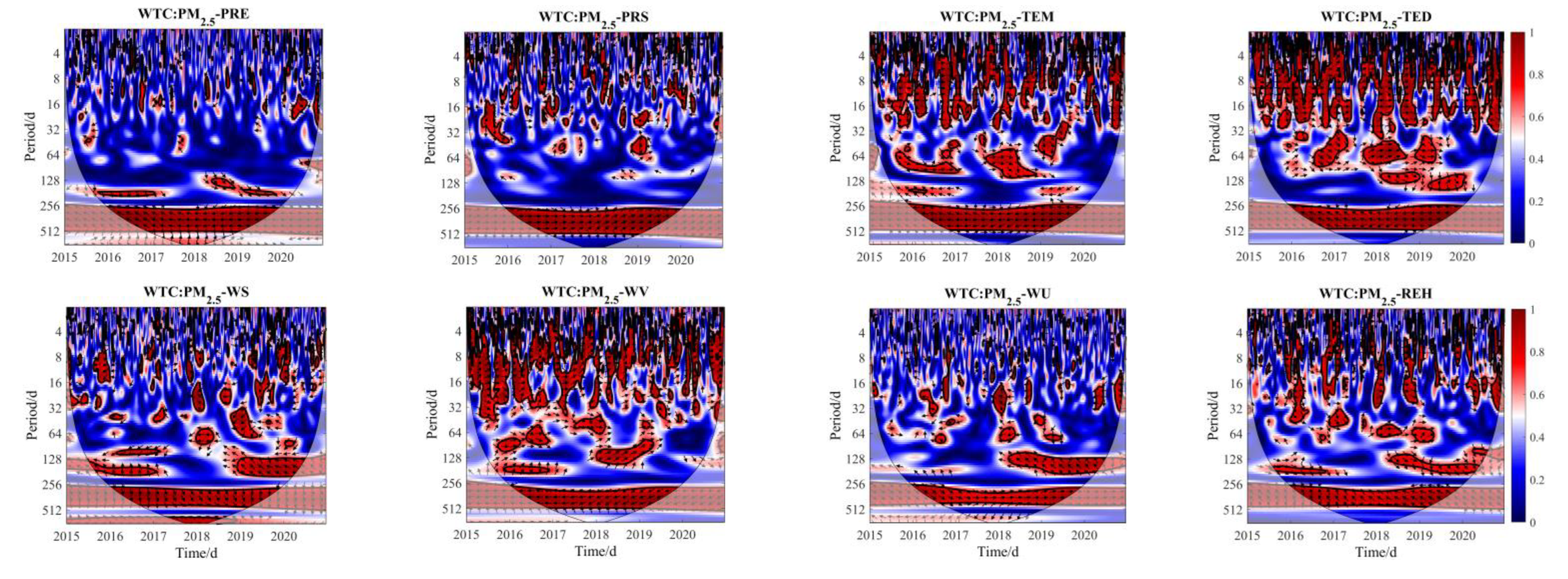
| Meteor-Factor | AWC | PASC (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5-PRE | 0.39 | 0.16 |
| PM2.5-PRS | 0.42 | 0.20 |
| PM2.5-TEM | 0.51 | 0.29 |
| PM2.5-TED | 0.54 | 0.34 |
| PM2.5-REH | 0.47 | 0.22 |
| PM2.5-WU | 0.40 | 0.15 |
| PM2.5-WV | 0.55 | 0.32 |
| PM2.5-WS | 0.47 | 0.23 |
| Meteor-Factors | AWC | PASC | Meteor-Factors | AWC | PASC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE-WU | 0.63 | 0.18 | TED-WS | 0.77 | 0.41 |
| PRE-PRS | 0.65 | 0.22 | TED-WU | 0.75 | 0.34 |
| PRE-REH | 0.72 | 0.27 | TED-WV | 0.75 | 0.34 |
| PRE-TED | 0.74 | 0.34 | TED-TEM | 0.75 | 0.38 |
| PRE-WS | 0.69 | 0.28 | WS-WU | 0.68 | 0.20 |
| PRE-WV | 0.71 | 0.26 | WS-WV | 0.76 | 0.36 |
| PRE-TEM | 0.70 | 0.31 | WS-TEM | 0.76 | 0.40 |
| PRS-REH | 0.70 | 0.27 | WU-WV | 0.72 | 0.28 |
| PRS-TED | 0.72 | 0.30 | WU-TEM | 0.74 | 0.33 |
| PRS-WS | 0.71 | 0.34 | WV-TEM | 0.76 | 0.37 |
| PRS-WU | 0.68 | 0.23 | PRE-TEM-TED | 0.86 | 0.41 |
| PRS-WV | 0.74 | 0.30 | TEM-TED-REH | 0.86 | 0.39 |
| PRS-TEM | 0.71 | 0.28 | PRS-REH-WV | 0.86 | 0.29 |
| REH-TED | 0.75 | 0.36 | TEM-REH-WV | 0.87 | 0.40 |
| REH-WS | 0.69 | 0.21 | TEM-WV-WS | 0.89 | 0.45 |
| REH-WU | 0.68 | 0.21 | REH-WV-WU | 0.85 | 0.31 |
| REH-WV | 0.72 | 0.27 | PRE-PRS-WV | 0.84 | 0.29 |
| REH-TEM | 0.75 | 0.37 | PRS-WS-WV | 0.88 | 0.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, F. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121993
Liu N, Li S, Zhang F. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(12):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121993
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nanjian, Song Li, and Fengtai Zhang. 2022. "Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020" Atmosphere 13, no. 12: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121993
APA StyleLiu, N., Li, S., & Zhang, F. (2022). Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020. Atmosphere, 13(12), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121993







