Error Decomposition of CRA40-Land and ERA5-Land Reanalysis Precipitation Products over the Yongding River Basin in North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
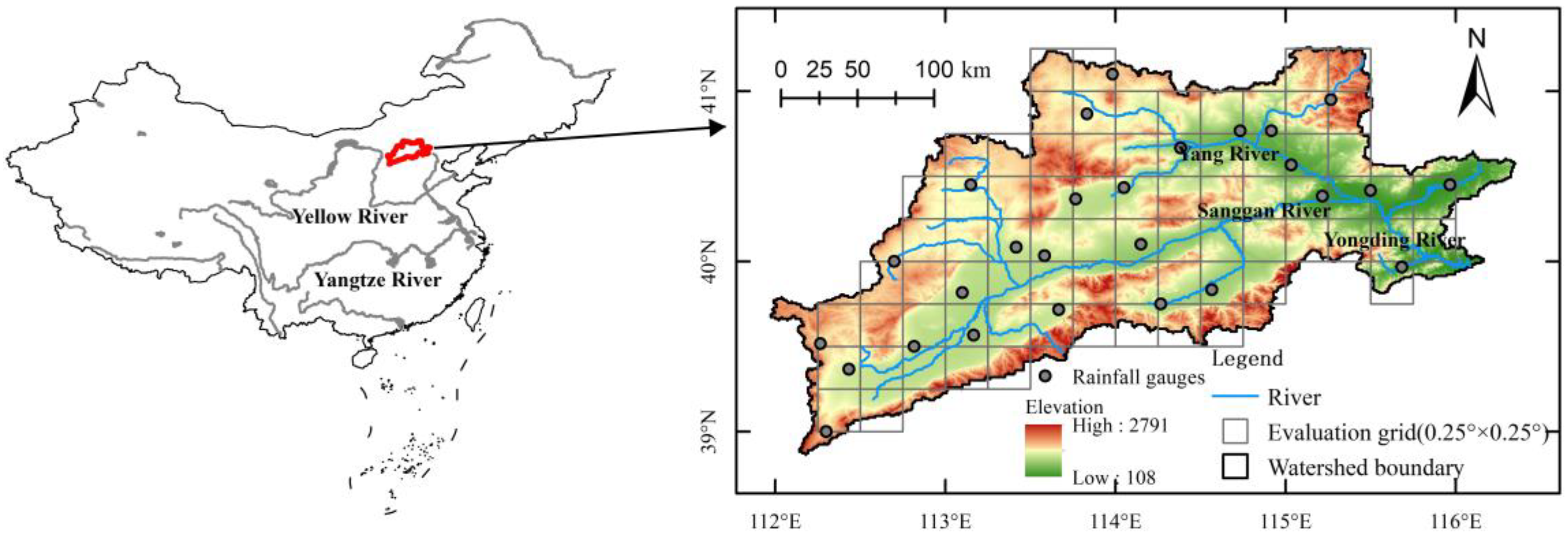
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground Reference Data
2.3. Reanalysis Data
2.3.1. ERA5-Land
2.3.2. CRA40-Land
3. Methods
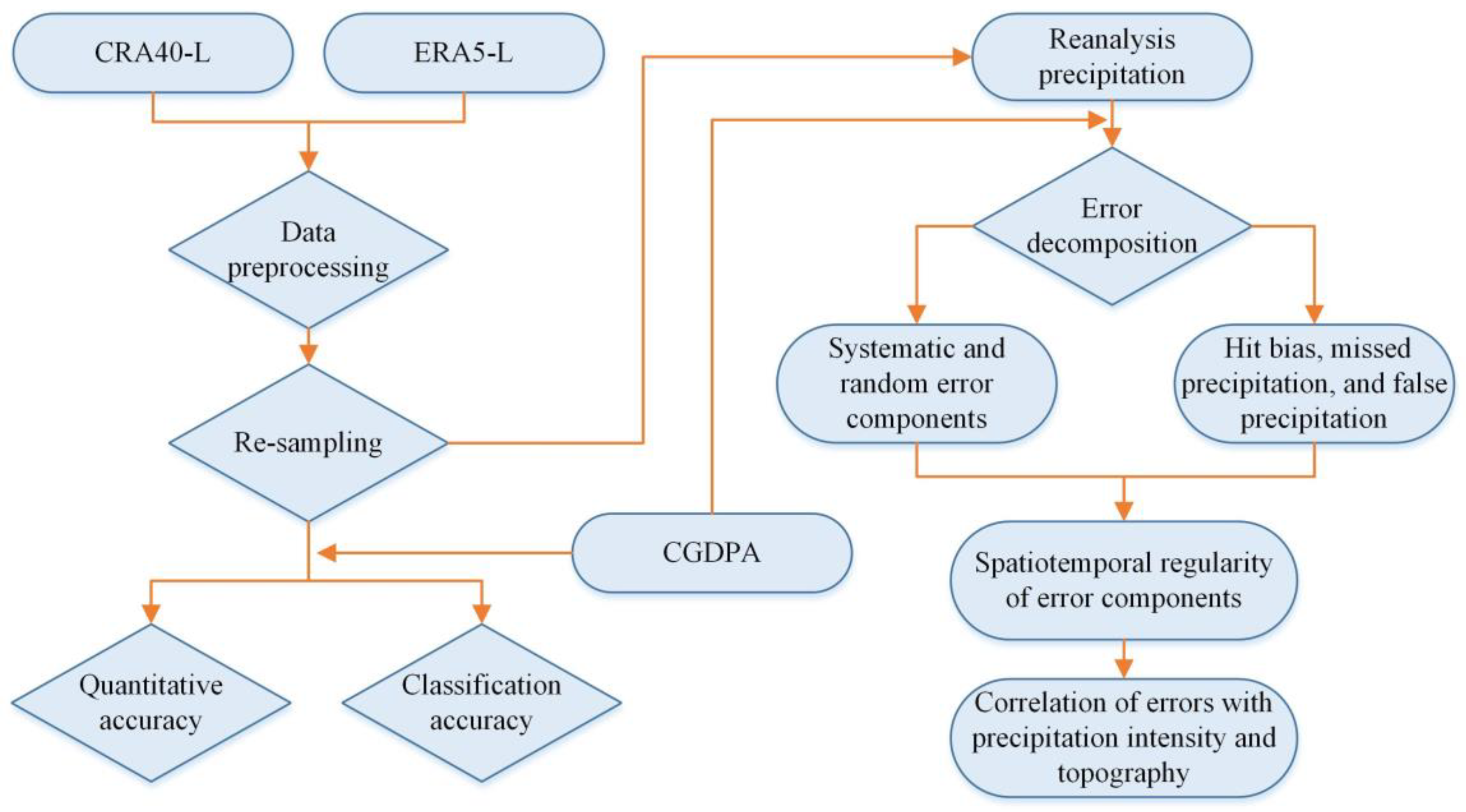
3.1. Technical Scheme
3.2. Systematic and Random Errors Decomposition
3.3. Hit, Missed, and False Errors Decomposition
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Overall Accuracy
4.2. Systematic and Random Errors
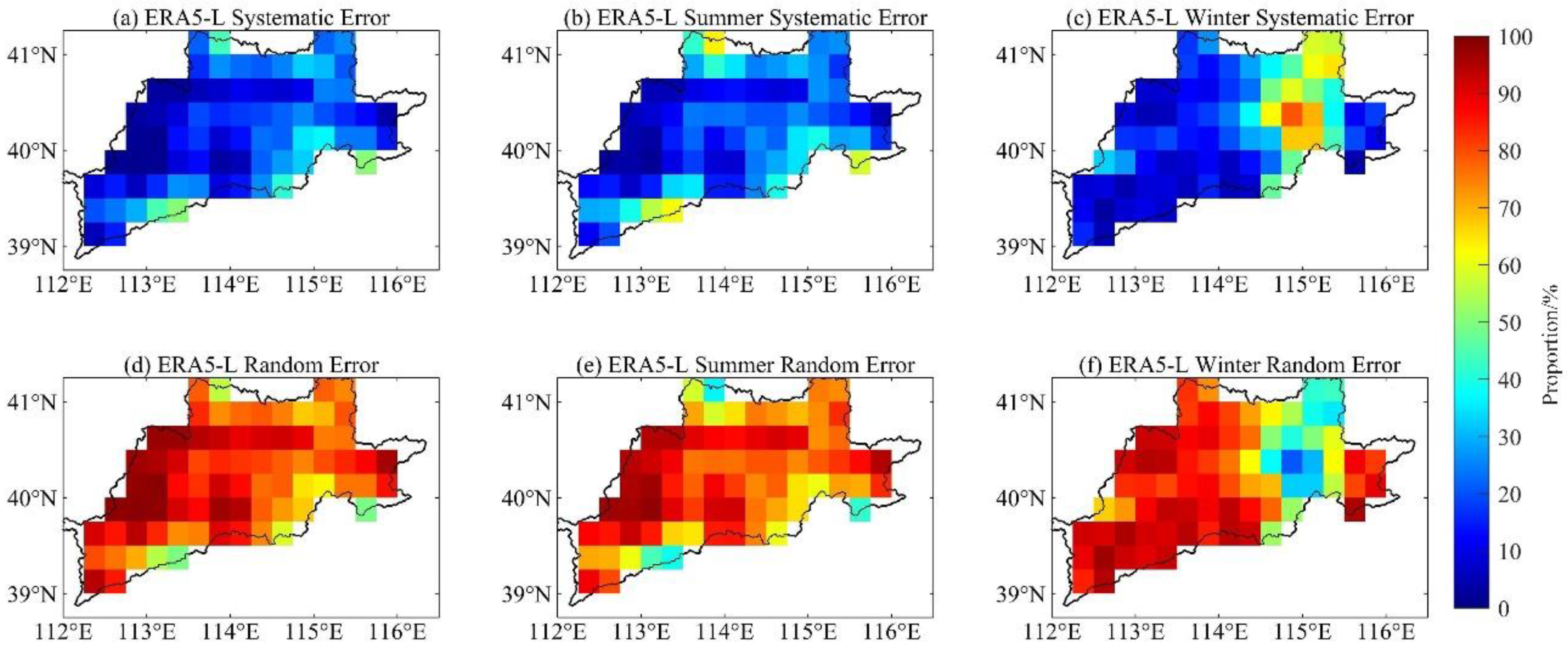
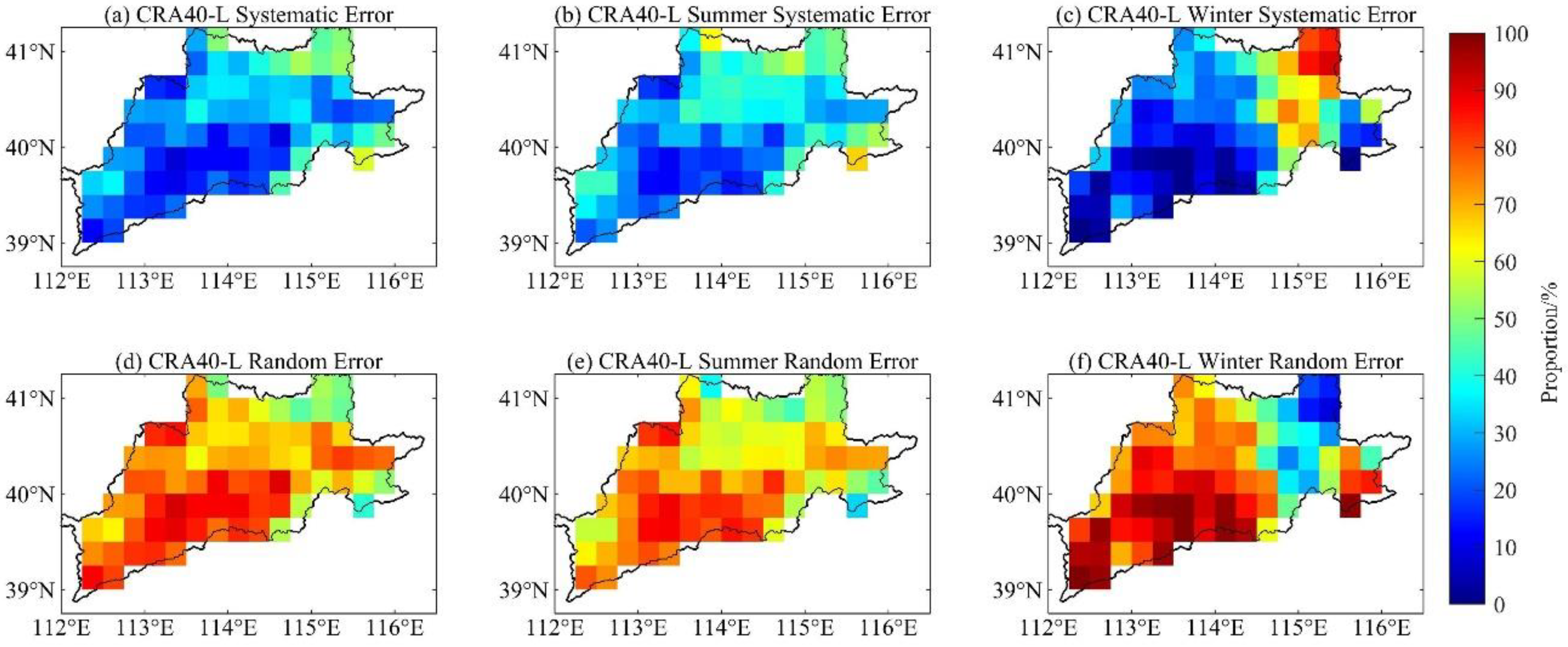
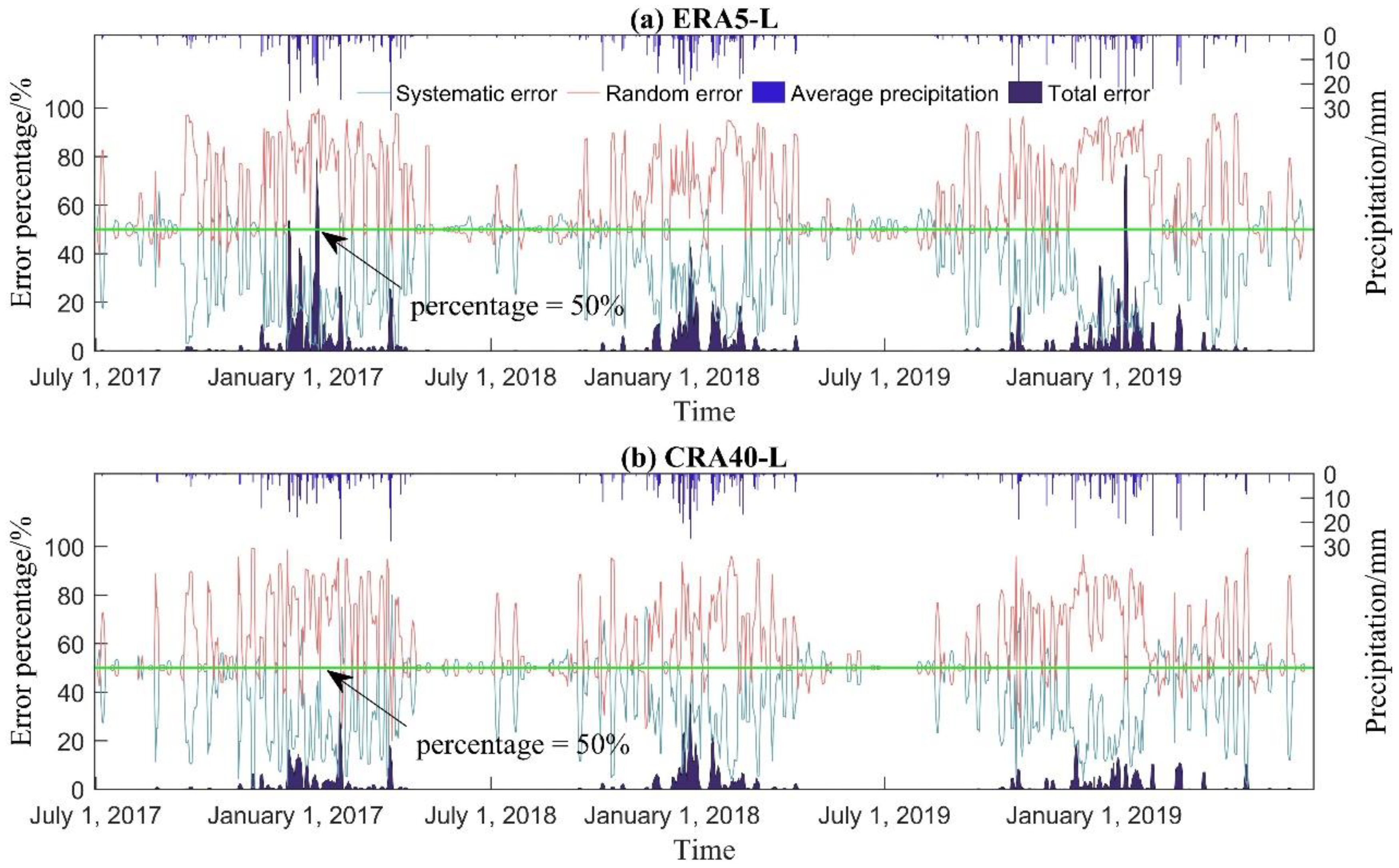
4.2.1. Spatiotemporal Features in Different Seasons
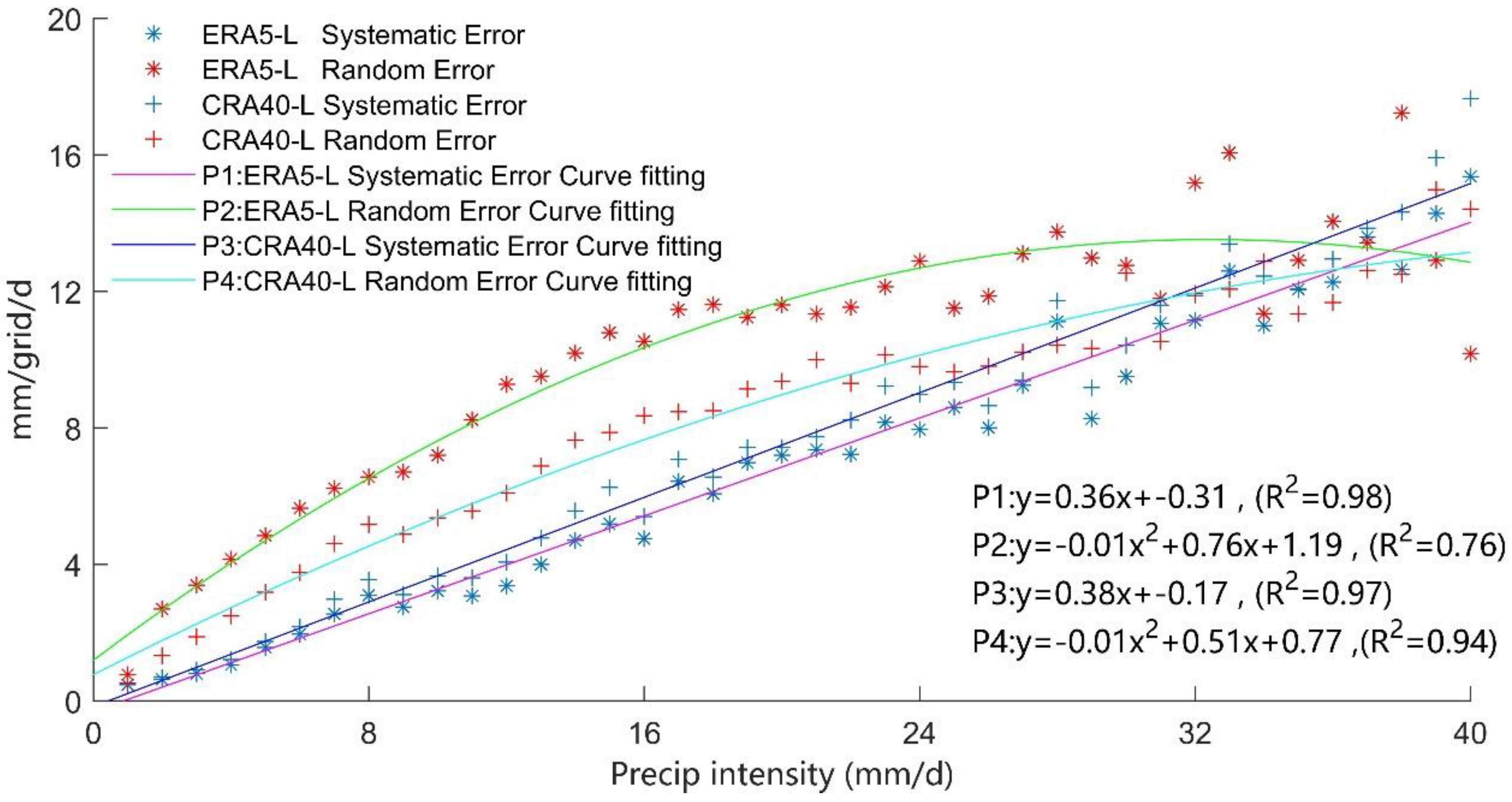
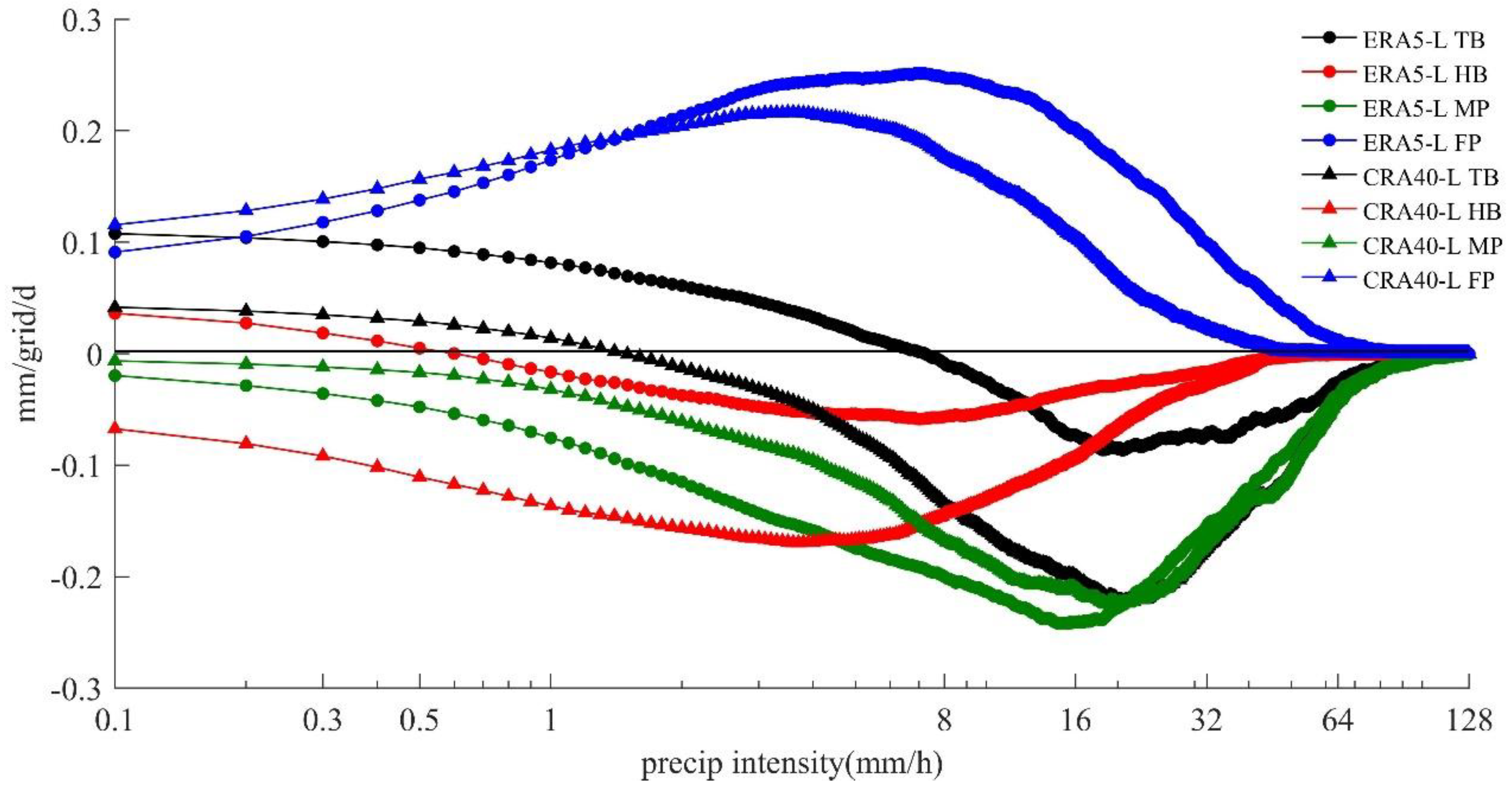
4.2.2. Effect of Precipitation Intensity and Elevation
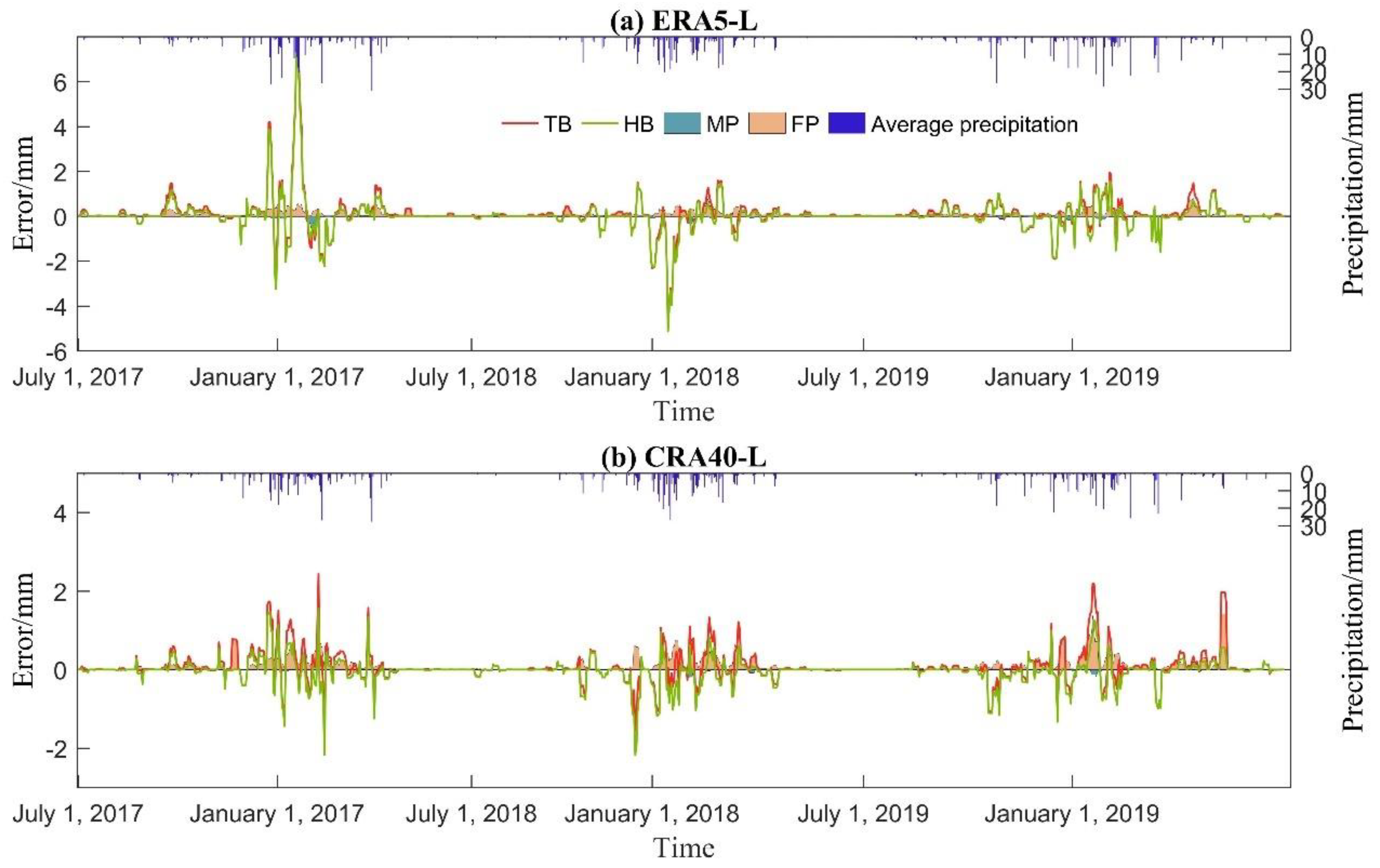
4.3. Hit, Missed, and False Bias
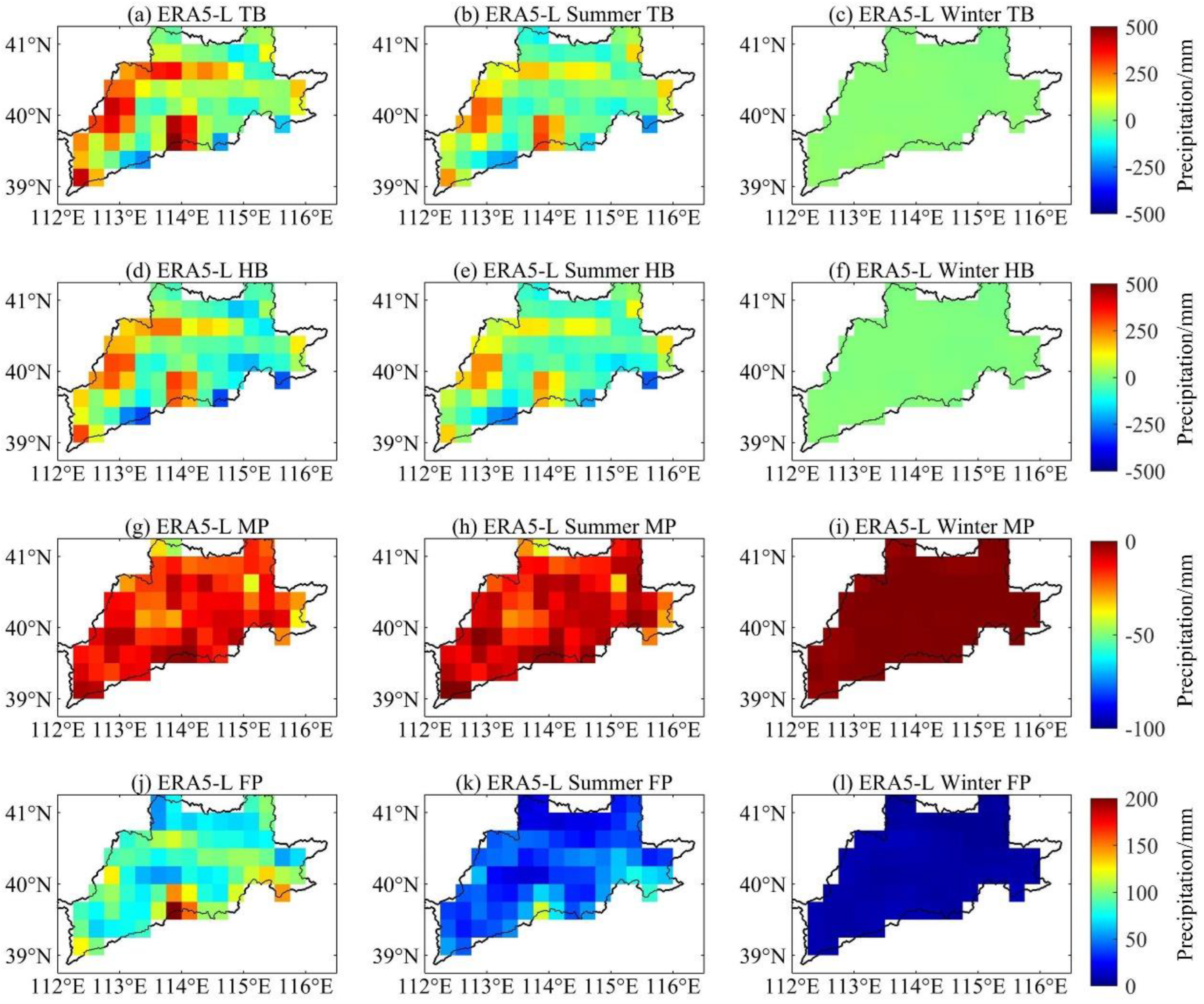
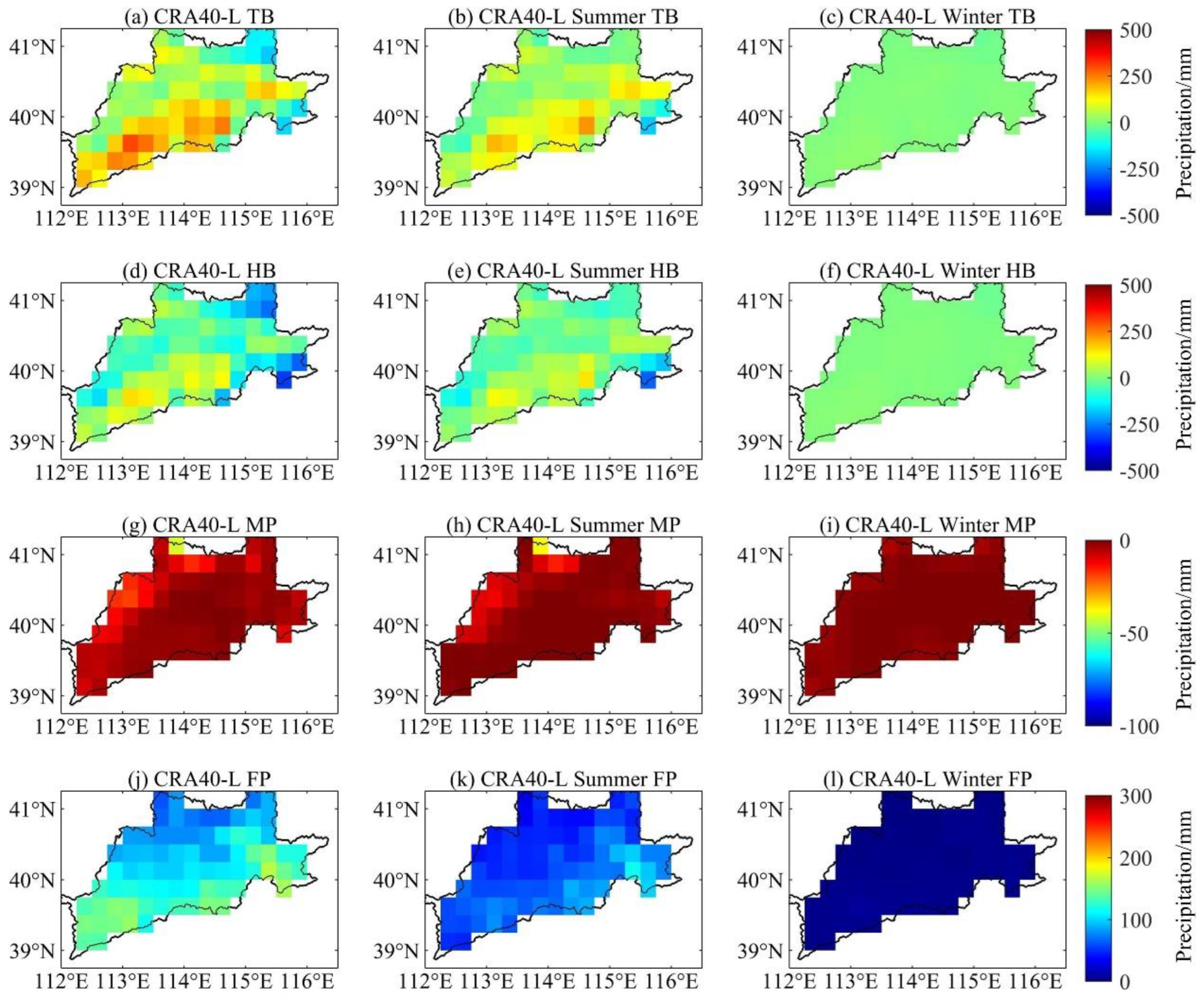
4.3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in Different Seasons
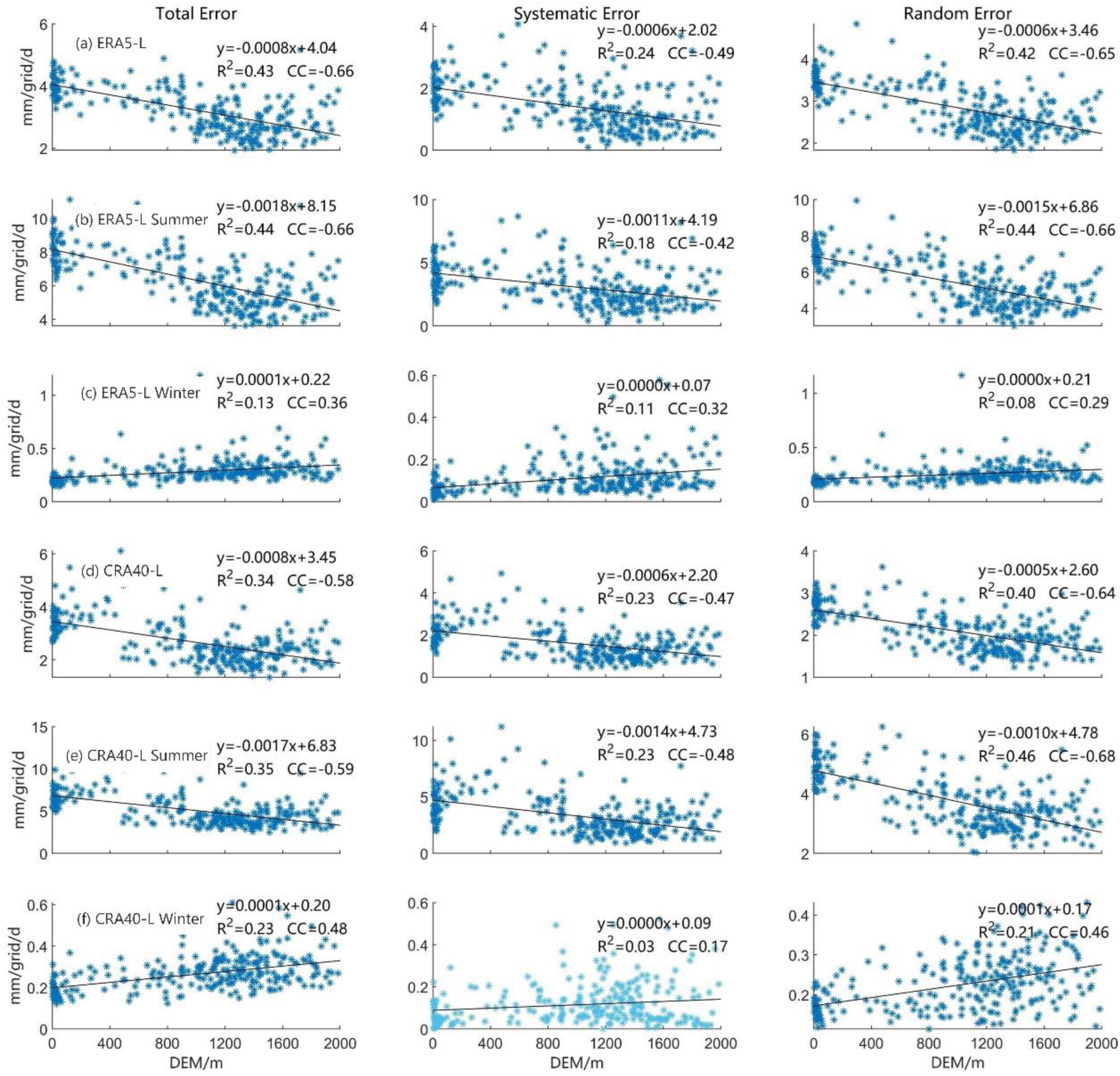
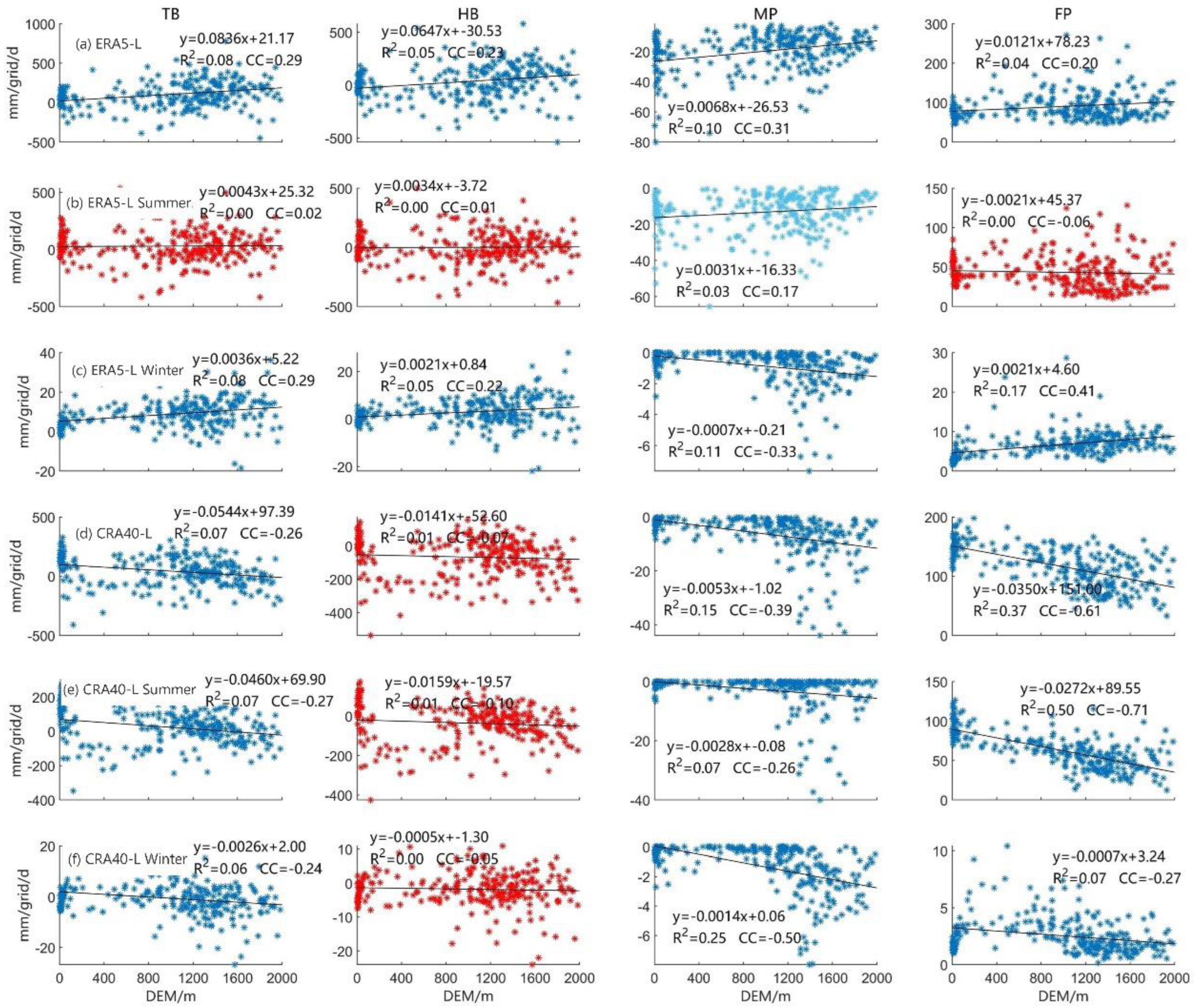
4.3.2. Correlation of Error with Precipitation Intensity and Elevation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The systematic and random error decomposition approach demonstrated that the random error accounted for a large proportion of the total mean square error, and the total error of ERA5-Land was higher than that of CRA40-Land. The spatial distribution of the error components indicated that the annual random error of ERA5-Land accounted for more than 75%, and that of CRA40-Land was between 60 and 70%. The spatial pattern of errors was significantly correlated with the terrain features, and the random errors in mountainous areas were larger. The temporal variation of the error components indicated that they were significantly dependent on the seasons, and the proportion of random errors in summer was larger. Compared with CRA40-Land, ERA5-Land possessed a higher ratio of random errors in summer.
- (2)
- On the basis of the hit, missed, and false errors decomposition approach, the spatial pattern of the errors indicated that the total error of ERA5-Land was strongly related to terrain features. The total bias gradually increased with elevation, and it is consistent with the hit bias. Although, the total error of CRA40-Land presented spatial variability, it had a weak relationship with terrain variation. The magnitudes of the total error and its components for CRA40-Land were significantly lower than those of ERA5-Land. The temporal variations of the error indicated that the summer error was significantly larger than in other seasons, and the total error of ERA5-Land was higher than that of CRA40-Land at high precipitation intensities (p > 20 mm/d).
- (3)
- When the precipitation intensity was lower than 38 mm/d, the random errors of ERA5-Land and CRA40-Land were relatively higher than the systematic errors. This is one of the reasons for the large random error of the solution in the two precipitation reanalysis datasets. In general, the correlation between the elevation and the systematic and random errors was relatively strong, and the error components throughout the year as well as in summer and winter accepted the hypothesis test of significance of the correlation coefficient at α = 0.001. With regard to the hit bias, missed precipitation, and false precipitation, for ERA5-Land, the hit bias was lower than that of CRA40-Land regardless of the precipitation intensity, the missed precipitation was higher than that of CRA40-Land at low rain intensity, and the false precipitation was larger than that of CRA40-Land in the intensity range of 4–40 mm/d. The correlation between hit bias and elevation was weak, and the error associated with the summer precipitation in ERA5-Land generally showed no correlation or weak correlation with elevation. The correlation between the elevation and missed precipitation of CRA40-Land gradually disappeared when elevation exceeded 1000 m.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Pan, M.; Wei, Z.; Wood, E.F.; Sheffield, J. A global drought and flood catalogue from 1950 to 2016. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E508–E535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Becker, A.; Huffman, G.J.; Muller, C.L.; Joe, P.; Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.B. So, how much of the Earth’s surface is covered by rain gauges? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandler, H.; Senftl, T.; Vanselow, K.A. Reanalysis datasets outperform other gridded climate products in vegetation change analysis in peripheral conservation areas of Central Asia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W. Evaluation of satellite and reanalysis precipitable water vapor data sets against radiosonde observations in central Asia. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poccard, I.; Janicot, S.; Camberlin, P. Comparison of rainfall structures between NCEP/NCAR reanalyses and observed data over tropical Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2000, 16, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.; Grimes, D.; Black, E.; O’Neill, A.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E. Evaluation of reanalysis rainfall estimates over Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 29, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.T.; Toniazzo, T.; Shaffrey, L. Ethiopian rainfall in climate models. In African Climate and Climate Change; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado-Ruiz, G.; Cavazos, T. Trends of daily extreme and non-extreme rainfall indices and intercomparison with different gridded data sets over Mexico and the southern United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5406–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z. Assessment of precipitation from the CRA40 dataset and new generation reanalysis datasets in the global domain. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5243–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Fan, Z.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis precipitation dataset over Chinese Mainland. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Lu, N.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L. Performance of ERA5 reanalysis precipitation products in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater Bay Area, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yin, J.; Wang, M.; He, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Xie, Y. Evaluation of five reanalysis products with radiosonde observations over the Central Taklimakan Desert during summer. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Yucel, I.; Yilmaz, K.K. Performance evaluation of satellite-and model-based precipitation products over varying climate and complex topography. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, E.; Eitzinger, J.; Dorigo, W. Performance of the state-of-the-art gridded precipitation products over mountainous terrain: A regional study over Austria. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yong, B.; Yi, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, H. From TRMM to GPM, how do improvements of post/near-real-time satellite precipitation estimates manifest? Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 106029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Wang, L.; Hong, Y. Global component analysis of errors in three satellite-only global precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3087–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, R.; He, J. Modeling and Evaluating Systematic and Random Errors in Multiscale GPM IMERG Summer Precipitation Estimates Over the Sichuan Basin. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4709–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.; Nabi, G.; Babur, M.; Azhar, A.H.; Kaleem Ullah, M. Disintegration of uncertainties associated with real-time multi-satellite precipitation products in diverse topographic and climatic area in Pakistan. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 716–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G. Characterization of the systematic and random errors in satellite precipitation using the multiplicative error model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.l.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Lü, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, G. Component analysis of errors in four GPM-based precipitation estimations over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, W.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J. Impact of the crucial geographic and climatic factors on the input source errors of GPM-based global satellite precipitation estimates. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J. Comparison analysis of six purely satellite-derived global precipitation estimates. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Ndayisaba, F.; Liu, T.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Systematical evaluation of satellite precipitation estimates over central Asia using an improved error-component procedure. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 10906–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takido, K.; VALERIANO, O.C.S.; Ryo, M.; Tanuma, K.; Ushio, T.; Kubota, T. Spatiotemporal evaluation of the gauge-adjusted global satellite mapping of precipitation at the basin scale. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2016, 94, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Peng, T.; Wu, Z.; Guo, J.; Chang, W.; Xu, Z. Performance evaluation, error decomposition and Tree-based Machine Learning error correction of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42 products in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Ao, T.; Li, X. Comprehensive evaluation of satellite and reanalysis precipitation products over the eastern Tibetan plateau characterized by a high diversity of topographies. Atmos. Res. 2021, 259, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Li, C.; Hong, Y.; Long, D. Evaluation of multiple precipitation products across Mainland China using the triple collocation method without ground truth. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 December 2017; p. H21E-1506. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Lai, C.; Chen, X. Evaluation of TMPA 3B42-V7 product on extreme precipitation estimates. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land hourly data from 1981 to present. Copernic. Clim. Change Serv. (C3S) Clim. Data Store (CDS) 2019, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhai, P. Performance of the CRA-40/Land, CMFD, and ERA-Interim datasets in reflecting changes in surface air temperature over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 35, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, L.; Pan, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z. A 10-yr global land surface reanalysis interim dataset (CRA-Interim/Land): Implementation and preliminary evaluation. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Henschke, A.; Adler, R.F. Evaluation of TMPA satellite-based research and real-time rainfall estimates during six tropical-related heavy rainfall events over Louisiana, USA. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hong, Y. Error-component analysis of TRMM-based multi-satellite precipitation estimates over mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ma, Z.; Yan, S.; Peng, J. Do ERA5 and ERA5-land precipitation estimates outperform satellite-based precipitation products? A comprehensive comparison between state-of-the-art model-based and satellite-based precipitation products over mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J. Contributions of local and remote atmospheric moisture fluxes to East China precipitation estimated from CRA-40 reanalysis. J. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 35, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Spatio-temporal accuracy evaluation of MSWEP daily precipitation over the Huaihe River Basin, China: A comparison study with representative satellite-and reanalysis-based products. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 2271–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time | CC | RB (%) | RMSE (mm) | POD | FAR | CSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5-Land | 0.78 | 8.5 | 2.90 | 0.99 | 0.07 | 0.92 |
| CRA40-Land | 0.87 | 6.6 | 2.16 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.91 |
| ERA5-Land summer | 0.70 | 3.7 | 5.63 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 0.93 |
| CRA40-Land summer | 0.84 | 7.3 | 4.00 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.92 |
| ERA5-Land winter | 0.85 | 46.8 | 0.27 | 0.97 | 0.25 | 0.73 |
| CRA40-Land winter | 0.85 | 14.0 | 0.27 | 0.96 | 0.11 | 0.86 |
| Scenario | Type of Precipitation | Index | Annual | Summer (June, July, and August) | Winter (December, January, and February) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error decomposition method considering the precipitation-fitting effect (mm2/grid/d) | ERA5-Land | MSE | 8.64 | 32.81 | 0.08 |
| MSES | 1.72 | 7.63 | 0.02 | ||
| MSER | 6.92 | 25.17 | 0.06 | ||
| CRA40-Land | MSE | 4.86 | 16.78 | 0.08 | |
| MSES | 1.49 | 6.08 | 0.03 | ||
| MSER | 3.37 | 10.70 | 0.05 | ||
| Error decomposition method considering rain/no rain state (mm/grid) | ERA5-Land | TB | 94.13 | 24.65 | 7.28 |
| HB | 18.39 | −5.63 | 0.64 | ||
| MP | −15.55 | −11.22 | −0.62 | ||
| FP | 91.29 | 41.50 | 7.26 | ||
| CRA40-Land | TB | 68.85 | 47.71 | 0.71 | |
| HB | −37.48 | −11.26 | −0.97 | ||
| MP | −5.27 | −2.65 | −0.86 | ||
| FP | 111.61 | 61.62 | 2.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, L. Error Decomposition of CRA40-Land and ERA5-Land Reanalysis Precipitation Products over the Yongding River Basin in North China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111936
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li L, Wang L, Wang Q, Huang Y, Li L. Error Decomposition of CRA40-Land and ERA5-Land Reanalysis Precipitation Products over the Yongding River Basin in North China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111936
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ye, Yintang Wang, Lingjie Li, Leizhi Wang, Qin Wang, Yong Huang, and Liping Li. 2022. "Error Decomposition of CRA40-Land and ERA5-Land Reanalysis Precipitation Products over the Yongding River Basin in North China" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111936
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, L., Wang, L., Wang, Q., Huang, Y., & Li, L. (2022). Error Decomposition of CRA40-Land and ERA5-Land Reanalysis Precipitation Products over the Yongding River Basin in North China. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111936






