Abstract
This study proposes a random forest–random pixel ID (RF–RID) method, which could reduce local anomalies in the simulation of NO2 spatial distribution and significantly improve prediction accuracy in rural areas. First, the 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 total and tropospheric vertical column were packed using the two-step method (TWS). Second, using RID, the filled data and auxiliary variables were combined with random forest (RF) to build an RF–RID model to predict the 1 km/d NO2 spatial distribution in southwestern Fujian (SWFJ) in 2018. The results show that the RF–RID achieves enhanced performance in the CV of the observed sample (R = 0.9117, RMSE = 3.895). Meanwhile, RF–RID has a higher correlation with the road length (RL) in remote areas, and the proposed method solves the issue related to strips or patches of NO2 spatial distribution. This model offers insights into the related research on air pollutants in large areas.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is one of the primary pollutants in the atmosphere. Excessive NO2 concentrations can result in a variety of environmental disasters (acid rain, the destruction of vegetation, the main precursors of fine particulate matter and ozone, etc.). It can also have harmful effects on human health (respiratory diseases, skin diseases, mental health, etc.) [1,2,3,4]. The primary emission sources of NOx (NOx = NO + NO2) include natural and anthropogenic sources, such as lightning, motor vehicles, and industrial sources [5,6]. With the development of human society, NOx emissions have increased, and anthropogenic emission sources have also become dominant, drawing widespread attention [7,8,9]. The Chinese government has established a multi-scale air-pollutant-monitoring network. However, the number and distribution of air-pollutant-monitoring stations still cannot cover the complete land area [10,11,12,13], limiting research on NO2 management [14,15,16]. Therefore, the high-precision prediction of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations is of great significance.
With the continuous development of remote sensing technology, satellite inversions to detect NO2 concentrations in the atmosphere have become important technologies [17,18]. The Aqua satellite OMI sensor launched by NASA in 2004 enables the observation of various trace gases worldwide [19]. In addition, the ESA launched the ENVISAT and Sentinel-5P satellites in 2002 and 2017, respectively [20]. The SCIAMACHY and TROPOMI sensors carried by the ENVISAT and Sentinel-5P satellites also provide suitable conditions for capturing the global NO2 distribution. OMI sensor data use the DOAS algorithm to retrieve NO2 tropospheric concentrations as part of NASA’s Making Earth System Data Records for Use in Research Environments (MEaSUREs) program. With advanced data accuracy, large data volume, long storage time (since 2004), and global coverage, the OMI NO2 total and tropospheric vertical column (OMI NO2 column) has contributed critical data to many NO2-related studies [21]. The NO2 column data retrieved by the OMI have some shortcomings, such as the low spatial resolution of the NO2 column. In addition, clouds may interfere with satellite observations, resulting in data gaps [22]. A richer remote sensing spatiotemporal dataset that includes NO2 products, combined with NO2 from the ground air-pollutant-monitoring network, can better simulate and predict the temporal and spatial distribution of near-surface NO2 concentrations [23,24]. Combining machine learning and spatiotemporal interpolation methods can generate satisfactory predictions and recover much missing remote sensing data [25,26,27].
Fossil fuel consumption in urban areas is a major source of anthropogenic NO2 emissions. Therefore, land use and road length data are often used as important indicators of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations. However, land use and road information release is typically delayed by one year. The low temporal resolution makes it difficult to provide sufficient time-dimensional information and reduces the sensitivity to changes in NO2 in local areas. NO2 is crucial in forming nitrate, ozone (O3), and nitro-PAHs. The time needed for NO2 conversion is typically between a few hours and a few days [28]. Meteorological conditions such as a stable atmospheric boundary layer, high temperature, and high humidity are favorable for converting NO2 into nitrate aerosols, which affects aerosol optical depth (AOD). Therefore, many scholars regard AOD as a critical parameter for the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations [29,30]. Compared with the yearly resolution of land use and road length, the daily resolution of AOD is significantly higher, which can effectively improve the reliability of the NO2 concentration spatial distribution prediction [31]. The MODIS sensor combined with the Atmospheric Correction Multi-Angle Implementation (MAIAC) algorithm is used to provide AOD products with a fixed 1 km grid. MAIAC AOD uses time series to detect multi-angle surface features to recover the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF). Compared with traditional DT and DB algorithms, it can better identify AOD information in cloud and snow areas and reduce AOD data gaps [32,33].
There are a variety of models for predicting the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations, including physical and chemical models [34], traditional statistical models [35], and machine-learning methods [36]. The resolution of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in physicochemical models is usually more than 10 km, and it is not easy to apply such models to small-scale regions. Traditional statistical models that predict the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations include spatial interpolation methods [37], land-use-regression models [38], and road-information-regression models [39]. Traditional statistical models are fast, simple, and stable. However, these methods usually have difficulty balancing global information [40]. The machine-learning method is good at exploring the in-depth relationship between NO2 and many auxiliary variables. Numerous studies have applied machine-learning-based approaches to predicting the spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants based on remote sensing [41,42,43]. As a traditional machine-learning model, random forest still has an excellent fitting and generalization ability for multi-parameter data, big data, and nonlinear data distributions. Therefore, applying random forest to predict the spatial distribution of air pollutants has significantly improved reliability [44].
Machine learning predicts air pollutant distributions with excellent cross-validation [45,46,47]. However, the substantial heterogeneity of the spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants in the atmospheric transport process also increases the simulation’s difficulty [48]. In addition to improving the simulation effect of machine-learning models, introducing spatial elements into machine learning as an independent variable is considered a simple and effective way to improve the simulation of air pollutants [49]. Wei et al. [50] and Zhan et al. [51] improved the machine-learning model by introducing spatial elements of different structures. Although the model’s cross-validation was improved, this approach also caused anomalies in the spatial distribution of air pollutants, thus leading to a lack of credibility [52,53]. Therefore, further utilizing spatial elements to improve the effect of the NO2 spatial distribution is key to solving this problem.
This study used a modified random forest model (RF–RID) to improve the effect of simulating the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations. The iterated TWS model was used to restore the gaps of the 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column, and randomly arranged position parameters (RID) were combined in random forest modeling to improve the ability to predict the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration. The no-gap spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in SWFJ in 2018 was predicted using RID with a resolution of 1 km/d. The accuracy and effect of the RF–RID simulation were evaluated based on cross-validation (CV) and the spatial distribution of the effects of the NO2 concentration. Implementing an RF–RID model with good predictive performance and the ability to address missing data will better serve NO2 management. Section 2 describes the dataset and methods, Section 3 shows the model results and analysis, Section 4 discusses the model and application, and Section 5 presents the conclusion.
2. Dataset and Methodology
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
Since 2013, China has established a multi-scale air-pollutant-monitoring network. The network includes the nationwide Atmospheric Monitoring Network and the Fujian ecological environment cloud platform. The number and density of stations constructed in the regional atmospheric-monitoring network are higher than those on the national scale [54]. The study area selected in this paper includes five cities in southwestern Fujian (SWFJ) (115°51′–119°1′ E, 23°31′–27°6′ N). SWFJ includes Xiamen (1700 km2), Quanzhou (11,015 km2), Zhangzhou (12,600 km2), Longyan (19,028 km2), and Sanming (22,965 km2). The total administrative area of SWFJ exceeds 67,000 square kilometers, accounting for 54.3% of the total area of Fujian Province. The total population of SWFJ is 23.17 million, accounting for 59% of the total population of Fujian Province, and the urbanization rate is 67.1%. The topography of SWFJ is inland highland and coastal lowland and covers prosperous cities (industrial areas, road networks, residential areas) and mountainous environments (woodlands, lakes, rivers). Such a complex environment is conducive to testing the stability and universality of the NO2 concentration near-surface distribution model [55]. The location of the study area is shown in Figure 1.
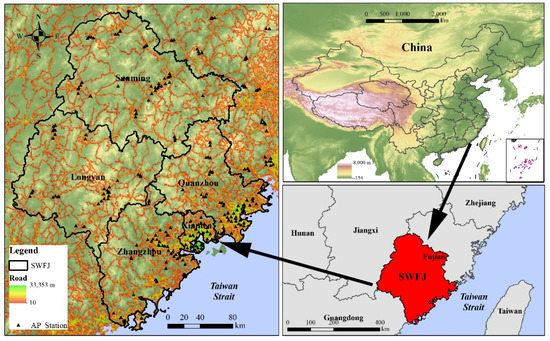
Figure 1.
Study area, including SWFJ. The black dots represent the location of the ground NO2-monitoring station. AP station represents the spatial location of the air-pollutant-monitoring station, and Road represents the total length of the road in independent pixels, ranging from 10 m to 33353 m. Orange pixels represent shorter total road lengths, and green pixels represent longer total road lengths.
2.2. Datasets
This study included ground NO2-monitoring data, remote sensing datasets, and auxiliary data. Data were collected from 1 January 2018 to 31 December 2018.
There were 272 ground NO2-monitoring sites (Figure 1), with 271 provided by the Fujian Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment and one site (Kinmen site) provided by the Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (www.epa.gov.tw, accessed on 27 August 2022). We selected daily averaged NO2-monitoring data. In addition, the ground pollutant-monitoring site data contained four daily meteorological parameters (temperature, air pressure, humidity, and wind speed).
The remote sensing dataset included the (1) AOD dataset, (2) NO2 column, and (3) other datasets. (1) MAIACAOD and Himawari-8 AOD include 470 nm AOD and 550 nm AOD. NO2 has a strong absorption line between near-ultraviolet and visible light [56]. In addition, the differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) algorithm for NO2 inversion uses the 405–465 nm spectrum, closer to the 470 nm AOD [57]. Therefore, 470 nm MAIAC AOD and Himawari-8 AOD were selected. Among them, MAIAC AOD (earthdata.nasa.gov, accessed on 27 August 2022) had a spatial resolution of 1 km and a temporal resolution of 1 day, while the L3 daily product Himawari-8 AOD (ftp.ptree.jaxa.jp, accessed on 27 August 2022) had a spatial resolution of 5 km [58]. (2) The NO2 column used the OMI NO2 L3 data with a time resolution of 1 day and a spatial resolution of 0.25°. (3) Other data included NDVI, terrain, population distribution, road, and land use. The NDVI was calculated from MODIS data (earthdata.nasa.gov, accessed on 27 August 2022), with a time resolution of 16 days and a spatial resolution of 1 km [59]. The terrain data included elevation and slope, extracted from SRTM data (earthdata.nasa.gov, accessed on 27 August 2022), with a spatial resolution of 90 m. The population data were obtained by LandScan (landscan.ornl.gov, accessed on 27 August 2022), with a spatial resolution of approximately 1 km [60]. The road data for 2018 were provided by OpenStreet (www.openstreetmap.org, accessed on 27 August 2022) and consisted of line layers in ESRI .shp format. Land use data were from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) in 2018 and had a spatial resolution of 300 m (cds.climate.copernicus.eu, accessed on 1 November 2022) [61].
Auxiliary data included the day of the year (doy), working days and nonworking days (wdon), the location ID of each pixel, and the 1 km-resolution grid of the UTM coordinate system covering the study area.
2.3. Research Methods
The main processes of the RF–RID for predicting the spatial distribution of near-surface NO2 concentrations included data preprocessing, remote sensing product gap filling (the 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column), random ID (RID) establishment, random forest training, and NO2 spatial distribution. The flow chart is shown in Figure 2.
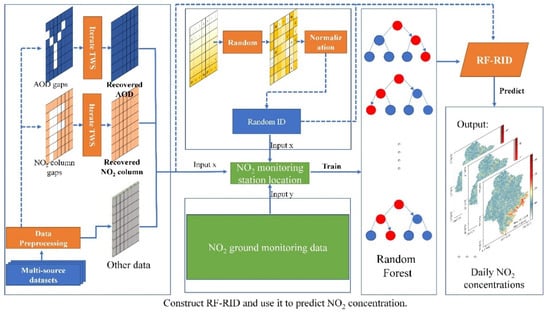
Figure 2.
The flowchart for predicting NO2 concentration using RF–RID. The iterated TWS recovered the AOD and NO2 gaps. Multi-source and NO2-monitoring data are used as the basis for modeling. All the data are used for predicting the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations. Random ID is also used in the modeling and predicting process.
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing
Multi-source data must be transformed to form a consistent temporal and spatial resolution dataset. The time resolution was one day, and the spatial resolution was consistent with the 1 km grid of the UTM coordinate system in the auxiliary data. Elevation (ELE) and slope (SL) were calculated by SRTM. The ELE, SL, land use (LU), road data (RL), 470 nm MAIAC AOD, NDVI (ND), population (POP), 470 nm AHI AOD, and OMI NO2 column data were superimposed on the 1 km UTM grid and reproduced. The reconstruction process was determined according to the weighted average of the pixel value of the data and the coverage area ratio of the UTM 1 km pixel (set the length of road data in the UTM grid as RL). Next, the data were filled in with a time resolution of more than one day (population data, land use, NDVI, etc.). For example, the NDVI fills gaps in the time range with the NDVI value according to a time resolution of 16 days. Finally, the cokriging method [62] was used to interpolate the meteorological parameters (temperature (TEM), pressure (PR), humidity (HUM), and wind speed (WS)), the covariate was ELE, and the output was the UTM 1 km/d resolution. Accuracy verification is provided in Supplementary Figure S5.
The 470 nm MAIAC AOD will undoubtedly and significantly improve the effect and spatial resolution (1 km) of NO2 simulations, but AOD gaps in data are a major challenge. We recovered the gaps in MAIAC AOD using the TWS model developed in previous studies. The method achieved an overall cross-validation R = 0.87 with the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) in a large-scale AOD gap-recovery study in East Asia [63]. This study runs the TWS iteratively and finally obtains the 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column without the gap, where the iterative TWS is in method S1.
2.3.2. Random Forest–Random Pixel Location ID (RF–RID)
Spatial elements assume various expressions, such as latitude, longitude, and continuous pixel location ID. They directly affect the cross-validation and mapping results of machine-learning simulations of the NO2 spatial distribution. However, the above forms will cause banding and patchiness when simulating the spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants [51]. To effectively combat these phenomena, possible solutions are to increase the complexity of the network structure, supplement the data, or modify the data structure of some parameters. However, the cost of increasing the complexity of the network structure and supplementing the data are high. Therefore, to maintain a reasonable cost, this study adjusted and improved the effect of NO2 concentration prediction by changing the arrangement of spatial elements. Parameter randomization, a standard model-optimization method in machine learning, is widely used in many kinds of research. Randomly generated data can combat overfitting in machine-learning training and simulation of extensive data [64]. In addition, more superficial forms of spatial feature generation can reduce the cost of model building. Therefore, we marked the positions of all pixels as independent IDs, shuffled all the IDs with a random algorithm, and introduced random IDs (RIDs) into random forests. The specific steps are as follows:
1. Randomize the position parameter, scramble the value of the position ID with the random algorithm, and assign it to each pixel;
2. Normalize the position parameter and the random position ID by the 0-1 normalization algorithm.
3. The random forest regression method was used to train and predict the spatial distribution of the NO2 concentration.
where the total number of is equal to the total number of pixels in the UTM 1 km grid; and represent the random algorithm and the normalization algorithm, respectively; represents the random forest; represents the NO2 prediction; and represent the NO2 column, 470 nm MAIAC AOD, random ID, meteorological parameters (temperature, air pressure, wind speed, humidity), altitude, slope, NDVI, road length, land use, and day of year, respectively.
2.3.3. Validation
The formal result verification is given by CV. This paper used 10-fold CV to verify the results, randomly selected 90% of the samples for modeling, and reserved the remainder for testing and then repeats this process ten times to test most of the samples. The final verification result used the average of ten verifications, using the correlation coefficient (R) and RMSE for evaluation. The calculation formula of RMSE is shown in Equation (2):
where τ(preNO) and τ(groundNO) represent the predicted NO2 concentration and the ground-observed NO2 concentration, respectively.
In addition, we selected four models (RF, RF–CID, RF–Ps, and RF–RID) to compare the spatial distribution of the predicted NO2 concentrations. Compared with the RF–RID model, RF lacks RID parameters. The RF–CID model replaces the RID parameter with a continuous pixel location ID (CID). The RF–Ps replace the RID parameters in RF–RID with the spatial distance variables in Wei et al. [50].
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Basic Data Description
The average value of NO2-monitoring sites in SWFJ in 2018 was 16.6 μg/m3, the highest concentration month was January (22.2 µg/m3), and the lowest concentration month was September (12.8 µg/m3). For details, see Figure S2 in the supplementary material. The cities with the highest and lowest NO2 concentrations were Xiamen (25.6 µg/m3) and Sanming (11.9 µg/m3), respectively. In addition, we calculated the correlation coefficient (R) between different variables and NO2 observation data, which ranged from 0.02 (OMI-NO2) to 0.32 (NDVI-NO2). The details are shown in Supplementary Figure S3.
3.2. Accuracy Verification
3.2.1. Data Gap Filling Accuracy Verification
After using iterative TWS, we obtained the MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 columns (daily, no data gaps) for the 2018 SWFJ region. There are no publicly available ground-verified data on the AOD and NO2 columns in SWFJ. We achieved acceptable results by randomly setting the gaps and cross-validation with the recovered MAIAC AOD and NO2 columns. The specific results are shown in Table 1 and Figure S9.

Table 1.
Iterative TWS recovery results.
3.2.2. CV of the Spatial Distribution of NO2 Concentration
The effect of the model typically requires multi-angle verification. It includes the cross-validation of training samples and cross-validation of prediction samples. First, we performed 10 CVs to verify the training dataset of the 2018 SWFJ data. The verified models included RF, RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps. The verification results are shown in Figure 3. In Figure 3, RF, RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps performed well in the fitting process, with R and RMSE values of 0.9717, 0.9770, 0.9768, and 0.9776 and 2.417 µg/m3, 2.192 µg/m3, 2.194 µg/m3, and 2.161 µg/m3, respectively. Nonetheless, subtle differences were observed in the four models. Two models (RF–RID and RF–CID) with ID added and RF–Ps with spatial distance were introduced. The slope (0.9122, 0.9129, 0.9138), intercept (1.4895, 1.4784, 1.4629), R, and RMSE values were slightly improved compared to those of RF (slope 0.9077 and intercept 1.6069). The above results show that ID and spatial distance (spatial location information) improve the model-fitting effect. In addition, the R and RMSE of the RF–RID model were better than those of RF–CID, although the slope and intercept were lower than those of RF–CID. These findings show that the overall improvement effect of random fitting in the training process is better than that of continuous fitting (increasing R and reducing RMSE). However, randomness is prone to bias in the simulation of individual data (decrease slope, increase intercept). Moreover, the performance of RF–Ps was better than that of RF, RF–RID, and RF–CID, indicating that the distance variable of the pixel is better than the ID in the model-fitting stage.
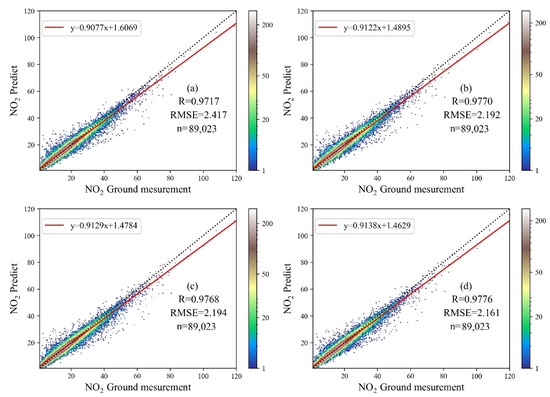
Figure 3.
CV diagram of the training dataset. (a) RF model CV, (b) RF–RID model CV, (c) RF–CID model CV, and (d) RF–Ps CV. The dashed line represents the 1:1 ratio line, the solid red line represents the first-order linear fitting function curve, and the color bar represents the point density.
Then, RF, RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps were applied to verify the test dataset using 10-fold CV (Figure 4). The verification results of the four different models show that introducing new variables in RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps leads to higher R and lower RMSE than RF.
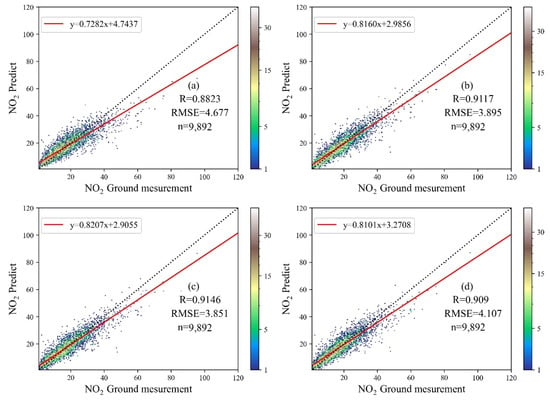
Figure 4.
CV diagram of the verification dataset. CV for (a) RF, (b) RF–RID, (c) RF–CID, and (d) RF–Ps. The dashed line represents the 1:1 ratio line, the solid red line represents the first-order linear fitting function curve, and the colored column represents the point density.
In addition, we tested the RF, RF–Ps, RF–CID and RF–RID models by selecting the data for one month and seven consecutive days (a week) as test samples (Figure 5).
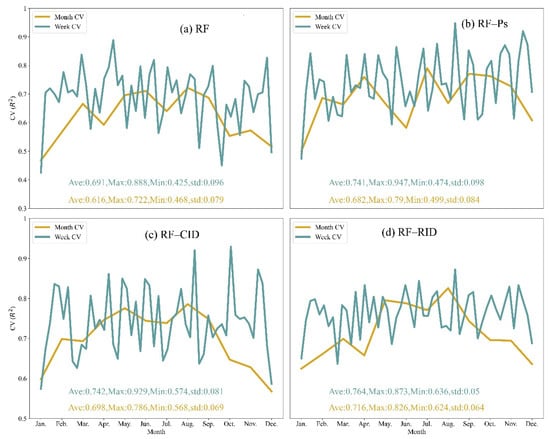
Figure 5.
The CV of RF, RF–Ps, RF–CID and RF–RID for 7 consecutive days and 12 months. Fifty-two groups were validated for 7 consecutive days.
Figure 5 shows that RF, RF–Ps, RF–CID and RF–RID were not as effective at predicting continuous time periods as the method of randomly extracting data. The prediction performance of the end data was consistently the worst, which is not only related to the complex spatiotemporal variability of air pollutants but also to the insufficient performance of the machine-learning model in predicting large amounts of continuous data (Supplement discussion SD1). However, both the weekly CV and monthly CV of RF–RID achieved the best results with the smallest standard deviation. Compared with RF–CID, RF–Ps and RF, the weekly CV increased by 2%, 2.2% and 7.1%, respectively; the monthly CV increased by 3.7%, 5% and 10.5%, respectively. Compared with other methods, RF–RID had better CV in the prediction of continuous time periods. In addition, we display the feature importance of different models in Figure S6.
3.2.3. Evaluation of the Spatial Distribution of NO2 Concentrations
Traditional verification indicators have difficulty in comprehensively evaluating the effect of the model. The cross-validation in Figure 3 and Figure 4 shows that RF–CID and RF–RID outperformed the RF and RF–Ps models. However, Zhan et al. [51] showed that adding location information (such as latitude and longitude) to machine learning caused a striping phenomenon. The predicted striping of air pollutants is highly inconsistent with the aerodynamics of the air pollutants moving in the atmosphere. To this end, we randomly selected 10 January 2018, and compared the results of the NO2 concentrations predicted by the RF, RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps models (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in SWFJ on 10 January 2018. Simulation results for (a) RF–RID, (b) RF, (c) RF–CID, and (d) RF–Ps, where MAX represents the maximum NO2 concentration value of the pixel, MIN represents the minimum NO2 concentration value of the pixel, and the color column on the right represents the NO2 concentration. Circles 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the upper and lower parts of the figure are magnifications of the corresponding circles in the study area.
Figure 6 shows the simulation results of the spatial distribution of NO2 from four models (RF, RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps) in SWFJ on 10 January 2018. The spatial distribution of NO2 predicted by the four models has similar characteristics. The high-value areas of NO2 are concentrated in the coastal zone of the southeast region of SWFJ, and the low-value areas are distributed mainly in the interior of SWFJ. However, the simulation of the spatial distribution of NO2 in the four models is significantly different in detail. 1. The maximum NO2 monitored by the site on 10 January 2018 was 46 µg/m3 (Xiamen). The maximum predictions of the RF and RF–Ps models were 42.64 µg/m3 and 44.04 µg/m3, respectively, which show a significant deviation from the maximum value of the site monitoring. However, the maximum values predicted by the RF–RID model and the RF–CID model were 45.18 µg/m3 and 47.25 µg/m3, respectively, and these results were more reasonable than the predictions of RF and RF–Ps. 2. In the detailed prediction of RF, RF–CID, and RF–Ps, the results deviated significantly from actual empirical findings due to serious overfitting.
In circles 1” and 3” of RF–CID (c), the striping phenomenon leads to obvious geographical boundaries of the spatial distribution of NO2. However, due to the topography, population distribution, weather, and other factors, it is difficult for the spatial distribution of NO2 to show regular deviations on a straight line. In contrast, the striping phenomenon does not appear in circles 1 and 3 in RF–RID (a). In addition to the striping phenomenon, there is a patchy phenomenon of the spatial distribution of NO2 in circle 2” of RF–CID (c). This phenomenon also appears in the RF–Ps Model (d) circle 2’’’ and circle 4’’’. Similarly, this phenomenon does not frequently occur in the spatial distribution of NO2 in the natural world. Compared with circle 2 of RF–RID (a), there is no patchy NO2 distribution. In circle 2’ of RF (b), although a striping or patchy phenomenon is not observed for the NO2 distribution, a rapid change (boundary) in NO2 concentration is still found. This geographical boundary phenomenon of NO2 concentration appears regularly and on a large scale in the results of RF (b) (10 January 2018). Comparing the land use types in Figure 1 shows that circle 2’ is not a critical junction between urban and mountainous areas. Thus, RF models that do not contain key geographic elements are likely to be insufficiently fitted in the process of simulating the spatial distribution of NO2. Similarly, this phenomenon does not appear in RF–RID (a) circle 2.
NOx emissions are closely related to motor vehicles, and statistics on RL pixels and NO2 concentrations effectively reveal the model’s reliability. The RL was divided into three categories according to the length of the road in the pixel, namely, high, medium, and low, and the correlation coefficient between the ground monitoring data of NO2 concentration, the results of this method, the RF model, the RF–Ps model and the RF–CID model and the RL data was calculated. The results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of the correlation between different methods and RL.
From Table 2, the correlation of NO2 concentration predicted by RF–RID with RL was the highest among the three categories. Among them, in areas with sparse roads (low classification), the correlation coefficient between RF–RID and RL is significantly better than in other models. This result shows that RF–RID has the best simulation effect on the spatial distribution of NO2 in the SWFJ area.
In addition, we further verified the model stability. We collected 365-day observation data from Kinmen Station in the Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration in 2018 (annual average NO2 at Kinmen Station = 9.75 µg/m3) and compared them with the results of RF–RID (predicted annual average NO2 at Kinmen Station = 10.51 µg/m3); R = 0.944 and RMSE = 2.88 µg/m3. This result further proves that the RF–RID model has good stability.
3.2.4. Comparison with Related Research
With the advancement of data and algorithms, the accuracy and resolution of NO2 concentration spatial distribution predictions have been improved. However, few studies reported the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in SWFJ in 2018. Accordingly, we selected the R2, RMSE, and resolution in five studies that were relatively close in recent years to compare with the results of this study (details are shown in Table 3). Young et al. [65] had a higher R than RF–RID but a lower NO2 spatial resolution. In addition, in the comparison of RMSE, the RF–RID model was better than GWR, LUR, and RF–STK. We used the TWS model to fill the gaps in the MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column products. These two parameters play a critical role in simulating NO2 with a resolution of 1 km near the ground. In addition, RID improves model CV and avoids local overfitting of simulations. Due to the significant differences between the comparative study and this study area, the study time and resolution were considered. The direct comparison of the indicators of these models is biased, and some indicators that are difficult to quantify need to be considered in the actual comparison process (such as the spatial distribution of predicted NO2). Nevertheless, the RF–RID model has significant advantages in comparing R, RMSE, and resolution. This finding further shows the stability and excellent performance of the RF–RID model.

Table 3.
Comparison of the effects of the spatial distribution of the NO2 concentration model.
3.2.5. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of NO2 in SWFJ
Optimizing the NO2 distribution prediction model is important because it can quickly and cost-effectively obtain the high-precision spatial distribution of air pollutants and compensate for errors caused by the insufficient and uneven distribution of sites [36]. Figure 7 and Figure 8 show that the average concentration of NO2 in each city of SWFJ is higher during spring (Jan. to Mar.) and winter (Oct. to Dec.) and lower in summer and autumn (Apr. to Sep.). High concentration areas are located in the coastal cities of Quanzhou, Zhangzhou, and Xiamen. At the same time, low values are distributed in the inland cities of Sanming and Longyan (Figure S4 in the supplementary material). The NO2 concentrations from high to low were as follows: Xiamen (17.2 µg/m3, 1/2 std = 2.8 µg/m3), Zhangzhou (13.6 µg/m3, 1/2 std = 2.4 µg/m3), Quanzhou (12.6 µg/m3, 1/2 std = 2.5 µg/m3), Longyan (10.6 µg/m3, 1/2 std = 1.4 µg/m3), and Sanming (10.2 µg/m3, 1/2 std = 1.3 µg/m3). Compared with statistical data from the air-pollutant-monitoring site in Figure S1 in the supplementary material, we found that the average concentration and standard deviation of the five cities in the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration were much smaller than the site statistics. In addition, the city rankings of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration were different from the site statistics (the prediction result of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration shows that Zhangzhou is second and Quanzhou is third; according to site statistics, Quanzhou is second, and Zhangzhou is third). The site monitoring of air pollutants was not statistically consistent with the RF–RID predictions, further confirming the importance of RF–RID. Furthermore, we counted the monthly average of Figure 7 and the monthly average of the OMI data in Figures S7 and S8, which can further determine the reliability of the near-surface NO2 simulation results.
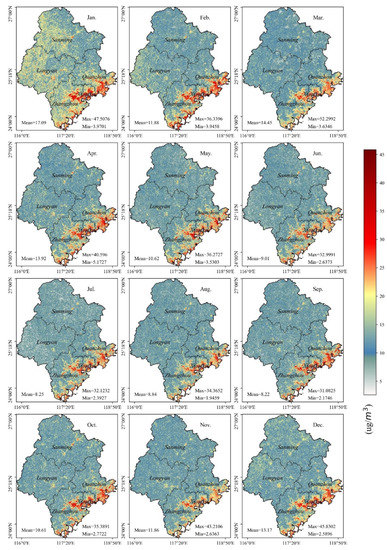
Figure 7.
Monthly NO2 spatial distribution in SWFJ in 2018. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May Jun. Jul. Aug. Sep. Oct. Nov. Dec. represents the average of the daily NO2 concentration distribution in 2018 each month. Mean, Max and Min represent the average, maximum, and minimum of monthly average pixels, respectively. The red highlighted region represents the high NO2 concentration value, and the blue part represents the low NO2 concentration value. The color bar on the right represents the NO2 concentration.
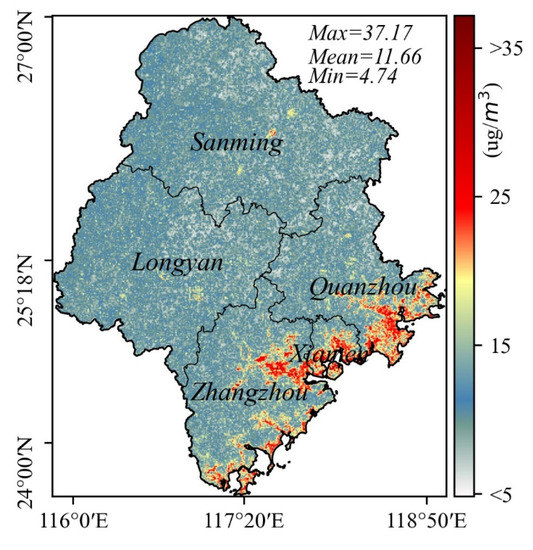
Figure 8.
Annual average distribution of NO2 concentrations in SWFJ in 2018. Mean, Max and Min represent the average, maximum, and minimum of monthly average pixels, respectively. The red highlighted region represents the NO2 concentration high value, and the blue part represents the NO2 concentration low value. The color bar on the right represents the NO2 concentration.
4. Discussion
Exploring methods for predicting the spatial distribution of near-surface NO2 concentrations with higher accuracy can facilitate NO2 management. Machine-learning models effectively stimulate the spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants, but there are also problems such as banding and patching. In this study, randomly distributed pixel IDs (RID) were established as spatial elements and were combined with the iterative TWS to restore gaps such as the 470 nm MAIAC AOD, OMI NO2 column, and other independent variables. We used RID, a simple and effective parameter, to optimize the random forest model and predict the spatial distribution of NO2 at a 1 km resolution without gaps. The model optimizes the local spatial anomaly of the NO2 spatial distribution and improves the application prospect.
This study used iterative TWS to fill data gaps for the 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column. The RF–RID was then combined with the reduced 470 nm MAIAC AOD, reduced NO2 column, interpolated meteorological parameters, ND, LU, RL, ELE, SL, POP, RID, and other variables to predict the spatial distribution of near-surface NO2 concentrations. The simulation results of RF, RF–RID, RF–Ps, and RF–CID were compared with NO2-monitoring data (training, validation, and other samples). RF–RID achieved cutting-edge performance in training (R = 0.9770, RMSE = 2.192 µg/m3), validation (R = 0.9117, RMSE = 3.895 µg/m3), and additional samples (R = 0.9440, RMSE = 2.88 µg/m3). This result was close to RF–CID and better than RF–Ps and RF. Meanwhile, the comparison results of RF–RID and RL were better than those of RF, RF–CID, RF–Ps and RL. In addition, the R2, RMSE, and resolution indicators of RF–RID were also better than or equal to those of related studies in recent years [36,38,41,65,66]. Combining the results of cross-validation with different parameters in Figure S2 also reflects the solid fitting ability of random forest to complex data. The new variables (random ID, continuous ID, and spatial distance) significantly affected the NO2 simulation. Meanwhile, ID (location information) had better verification accuracy than distance variables, which shows that ID (unique) can better represent the location of each pixel than the distance variable (not unique).
Furthermore, in SWFJ, the distribution of NO2 concentration is high in coastal areas, low in inland areas, high in the southeast, and low in the northwest. It has a specific correlation with a continuous ID and a better fitting effect than RID in the cross-validation. Compared with Figure 3, the R of the RF model showed the most significant decrease, and the RMSE showed the largest increase, which further shows that the new variables (random ID, continuous ID, and spatial distance) result in improved model stability. The RF–Ps model showed the second-largest decrease in R and the second-largest increase in RMSE, which shows that the CV of the RF–Ps model in the test dataset is more evident than that of the RF–RID RF–CID models. In addition, RF–CID is more stable than RF–RID during the prediction process. Specific performance: the R value of the RF–CID model decreased by 6.22%, the RMSE increased by 1.659 µg/m3, while for the RF–RID model, R decreased by 6.53%, and the RMSE increased by 1.703 µg/m3. These findings show that the continuous ID is more stable than RID in the CV of the prediction process. In addition, RF–RID solves the stripe and patch phenomenon of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration predicted by RF–CID and RF–Ps and solves the geographical boundary phenomenon of the irregular spatial distribution of NO2 concentration predicted by RF. In addition, in the comparison of NO2 spatial distribution results and road information, it was found that RF–RID results were better than other models. These findings suggest that the RF–RID model estimated using 470 nm MAIAC AOD data and NO2 column data recovered by iterative TWS, RID, and other parameters can provide highly accurate and stable near-surface NO2 concentration spatial distribution results.
The 470 nm MAIAC AOD is not highly correlated with NO2 site observation data, and it still plays a significant role in predicting the spatial distribution of NO2 (Figure S6). The possible reason is that the conversion time of NO2 to nitrate is usually not long, and nitrate is also an important component of SWFJ, especially in coastal regions [67,68]. Therefore, AOD, a key aerosol parameter, still positively influences the prediction of the near-surface NO2 spatial distribution. Similarly, the NO2 column is the vertical integral of tropospheric NO2, representing the NO2 concentration near the ground to a certain extent [69]. The restored 470 nm MAIAC AOD and OMI NO2 column can provide more training samples (by iterative TWS), enable the model to be sufficiently trained, and improve the CV (increase R and reduce RMSE). In addition, AOD and NO2 columns with fewer gaps can obtain a complete spatial distribution of NO2. First, NO2 predictions develop from a site to a regional scale, and the number of gaps determines the size of the NO2 prediction area. Fewer gaps between the AOD and NO2 columns increase the value of NO2 spatial distribution predictions. Then, by recovering the gaps in the critical variables (AOD and NO2 column), it is easy to obtain simulations of the spatial distribution of the NO2 concentration without gaps. Therefore, RF–RID improved the accuracy of model training and the spatial visualization effect of the NO2 spatial distribution.
The CV of RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps was better than that of RF (Figure 3 and Figure 4), indicating that the input parameters (RID, CID, and Ps) of RF–RID, RF–CID, and RF–Ps improve the RF model training performance. Among them, we used randomly distributed pixel ID (RID) as the input variable of RF–RID, which does not reduce the CV. Compared with RF–CID, RF, and RF–Ps, RF–RID solves the abnormal situation of the spatial distribution prediction of NO2 concentration and the natural world (banding, patchy, and apparent geographic boundary phenomena). Particularly, when the selected features have large differences in temporal and spatial resolution (such as the coarse resolution of the OMI), it is likely to cause the aforementioned phenomena, which we attribute to local overfitting [70,71,72]. The spatial distribution of air pollutants is nonstationary. The regular ID (CID) and Ps parameters become the noise in the data in the prediction stage. The excellent performance on the training dataset reflects that the regular ID distribution is consistent with the trend of low NO2 inland and high coastal areas. Therefore, the CV (R and RMSE) of the training dataset was better than that of RID in training the dataset. However, compared with RID and CID, the Ps parameter overfitted the data, showing that the regular Ps parameter was noisier than the spatial distribution of NO2 concentration. Similarly, in predicting the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations, the CID and Ps parameters were noisier than RID. Consequently, overfitting of local strips and patches appears. Moreover, the distribution of air-pollutant-monitoring stations is clustered (more cities, fewer mountainous areas), leading to a severe bias between the training dataset and the prediction dataset and increasing regular data noise. Randomness is widely used in model construction (random forest) and in model control overfitting (random dropout suppresses overfitting). One of the advantages of random sampling is to control overfitting and maintain model stability. Therefore, the introduced RID balances the bias between the training and prediction data (inhibiting noise) concerning the regular distribution, controlling overfitting, and solving the banding and spotting of RF–CID, RF, and RF–Ps. Apparent geographic boundary phenomena, such as massive boundaries, ensure the stability of the spatial distribution of the NO2 concentration predicted by RF–RID.
According to the information published in the 2018 Ecological and Environmental Bulletin (https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/tpxw/201905/t20190529_704841.shtml, accessed on 2 August 2022), the high-value areas of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in China are mainly in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (43 µg/m3) and the Yangtze River Delta (35 µg/m3). In contrast, the NO2 concentration in SWFJ is relatively low (the observed value is 16.57 µg/m3, and the predicted value is 11.66 µg/m3). However, acid rain is severe in parts of Sanming and Xiamen [73]. Although the factors affecting acid rain are very complicated, two of the essential factors are the concentration and spatial distribution of NO2. In addition, the results of air-pollutant-monitoring sites differ significantly from the predicted results of the spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations, especially in Zhangzhou and Quanzhou. The main reason for this difference is that the representativeness of the geographical distribution of air-pollutant-monitoring sites needs improvement. Hence, the predicted average concentration of NO2 was significantly different from the monitored concentration. In addition, the monitoring site’s average concentration of NO2 in Quanzhou is higher than that in Zhangzhou; the simulation average of the spatial distribution of NO2 in Quanzhou is also lower than that in Zhangzhou. Combined with Figure 1 and Table 2, the distribution of air pollution points is concentrated mainly in urban population clusters and is lacking in areas with sparse roads. Although this distribution method can improve the monitoring level of air pollutants in critical urban areas, it ignores the distribution of air pollutants in small counties and the overall situation. Advanced air pollutant concentration spatial distribution prediction methods can compensate for this deficiency, shifting the temporal and spatial distributions of air pollutants in different cities closer to the correct level. Therefore, a more accurate estimation of the spatial and temporal distribution of regional NO2 concentrations will provide a basis for policy formulation for environmental management.
The nearest distance between Kinmen and Xiamen is only 2 km; however, the difference in NO2-monitoring concentration between Kinmen and Xiamen is significant. The convective movement of the land-sea breeze circulations in the local area may have blocked regional NO2 transmission. Meanwhile, differences in the urbanization process between Xiamen and Kinmen have enhanced the accumulation of air pollutants caused by the land-sea breeze circulation [74,75]. Therefore, the variables related to the transmission distance of NO2 (such as gridded atmospheric convection products) should be increased, and the volume of NO2-monitoring station data (based on atmospheric pollutant observation station data in China) should be increased. In addition, adding new parameters, including TROPOMI, has excellent potential to improve the feasibility of accuracy and the spatial resolution of NO2 simulations [76,77]. In the future, we will provide optimized high-resolution (1 km) products for the near-surface temporal and spatial distribution of NO2 concentrations in China. In addition, most current research on predicting the spatial distribution of air pollutants near the ground, whether applying a traditional model or a machine-learning model, still requires accurate ground observation data of air pollutants as the basis for modeling. However, significant errors in ground-based observations can affect prediction models, interfering with local or global predictions of atmospheric pollutants. Therefore, we will also research feasible solutions to eliminate or correct abnormal air-pollutant-monitoring data values.
5. Conclusions
The introduction of geocoding information to improve the performance and stability of NO2 concentration prediction is of great help for NO2 environmental management and ecological applications. This study predicted the NO2 concentration spatial distribution (without gaps) in SWFJ in 2018 at a 1 km/d resolution by constructing an RF–RID. The results show that RF–RID has improved accuracy (R = 0.9110, RMSE = 3.89 µg/m3) and enhanced generalization ability (Kinmen Station R = 0.9440 and RMSE = 2.88 µg/m3) compared with existing studies. In addition, in contrast to the RF, RF–CID, and RF–Ps models, RF–RID has better prediction results for NO2 concentrations in remote areas and solves the local overfitting problem of NO2 concentration spatial distribution prediction. Among them, the random distribution feature of RID reduces the input noise of location information, improves the reliability of simulating NO2 spatial distribution in remote areas with sparse roads, and reduces streaks and patches. Finally, the RF–RID model enhances model stability by optimizing the data structure without requiring higher-performance hardware and data volume and provides an essential reference for optimizing the air pollutant prediction model. In follow-up research, continuous improvements in NO2 concentration prediction accuracy, temporal resolution, and spatial resolution will be the priority research direction. The primary way to achieve this advancement is to continuously optimize the model and introduce a deep learning model to further explore the critical impact of multiple heterogeneous data on NO2 concentration prediction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13111832/s1, Method S1 (Iterate TWS), Figure S1. Iterate TWS technology roadmap. Figure S2. Monthly average of NO2 monitoring data in SWFJ in 2018. Figure S3. Correlation coefficient between NO2 monitoring data and remote sensing products in SWFJ in 2018. Figure S4. Monthly and annual averages of NO2 in different cities in SWFJ. (A) Monthly average trend chart of NO2 in different cities; (b) annual average and 1/2 standard deviation of different cities. The value and the value in parentheses represent the annual average and 0.5 times the standard deviation, respectively. Figure S5. (a), (b), (c), and (d) represent the cross−validation of the spatial interpolation of air pressure, humidity, air temperature, and wind speed, respectively. The horizontal axis represents the observation results, and the vertical axis represents the interpolation results. R represents the correlation coefficient, and n represents the number of samples. The black line represents the 1:1 ratio line, the solid red line represents the first−order linear fitting function curve, and the color bar represents the point density. Figure S6. RF, RF−Ps, RF−CID and RF−RID feature importance. The x−axis represents the factors used to build the different models. The y−axis represents importance values. Figure S7. 2018 RF−RID monthly Average. The x−axis represents the different months of 2018. The y−axis represents the mean NO2 concentration. Figure S8. 2018 OMI monthly Average. The x−axis represents the different months of 2018. The y−axis represents the mean OMI value. Figure S9. The CV scatterplot of TWS recovery OMI and AOD. (a) represents the cross−validation of the first step of TWS to restore AOD. (b) represents the cross−validation of the AOD recovery in the second step of TWS. (c) represents the cross−validation of TWS second−step recovery OMI. References [78,79].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C. and Y.Z.; methodology, Y.C. and Y.Z.; validation, Y.C. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, Y.C. and Y.Z.; resources, Y.C. and Y.Z.; data curation, Y.C. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.C. and Y.Z.; visualization, Y.C.; supervision, Y.C. and Y.Z.; project administration, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the introduction of high-level talent at Sanming University (111-RD21006P).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be provided after request to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Fujian Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment for providing air-pollutant-monitoring data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brimblecombe, P.; Stedman, D.H. Historical evidence for a dramatic increase in the nitrate component of acid rain. Nature 1982, 298, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.E.; Driscoll, C.T.; Buso, D.C. Long-Term Effects of Acid Rain: Response and Recovery of a Forest Ecosystem. Science 1996, 272, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worton, D.R. Future Adoption of Direct Measurement Techniques for Regulatory Measurements of Nitrogen Dioxide: Drivers and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14785–14786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H. Acid rain may hit coastal waters hard. Nature 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz, M.; Bai, E.; Wang, C.; Trousdell, J.; Conley, S.; Faloona, I.; Houlton Benjamin, Z. Agriculture is a major source of NOx pollution in California. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, K.; Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Cai, K. Spatiotemporal evolution analysis of NO2 column density before and after COVID-19 pandemic in Henan province based on SI-APSTE model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpus-Mendoza, A.N.; Ruiz-Segoviano, H.S.; Rodríguez-Contreras, S.F.; Yañez-Dávila, D.; Hernández-Granados, A. Decrease of mobility, electricity demand, and NO2 emissions on COVID-19 times and their feedback on prevention measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Geng, G.N.; He, K.B. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over three megalopolises in China using satellite-derived aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.-e.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C. Air quality forecasting with artificial intelligence techniques: A scientometric and content analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 149, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, M.; O’Neill, J.; Bien, B.; Hood, C.; Jackson, M.; Jackson, R.; Johnson, K.; Oades, M.; Stidworthy, A.; Stocker, J.; et al. A Multi-model Air Quality System for Health Research: Road model development and evaluation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 155, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Synergy of AERONET and MODIS AOD products in the estimation of PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Ku, T.; Sang, N. Inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in the hearts of mice co-exposed to SO2, NO2, and PM2.5. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Guo, Y.; Abramson, M.J.; Williams, G.; Li, S. Exposure to low concentrations of air pollutants and adverse birth outcomes in Brisbane, Australia, 2003–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainio, M.; Jovanovic Andersen, Z.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Hu, L.; de Nazelle, A.; An, R.; Garcia, L.M.T.; Goenka, S.; Zapata-Diomedi, B.; Bull, F.; et al. Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Karppinen, A.; Kurppa, M.; Kousa, A.; Niemi, J.V.; Kukkonen, J. An operational urban air quality model ENFUSER, based on dispersion modelling and data assimilation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, G.H.; Rusch, D.W.; Noxon, J.F.; Zawodny, J.M.; Barth, C.A. Measurements of stratospheric NO2 from the Solar Mesosphere Explorer satellite: 1. An overview of the results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984, 89, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianhui, X.; Huaming, X.; Kai, W.; Jing, W.; Zishang, X. Analyzing the spatial and temporal variations in tropospheric NO2 column concentrations over China using multisource satellite remote sensing. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 014519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Virta, H.; Eskes, H.; Hovila, J.; Douros, J. Comparison of TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor NO2 observations with ground-based measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.C.; Eskes, H.J.; Eichmann, K.U.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Granville, J.; Niemeijer, S.; Cede, A.; et al. Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. Overview of NASA’s MODIS and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) snow-cover Earth System Data Records. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.-M.; Chai, T.; Ngan, F.; Pan, L.; Lee, P. A Conservative Downscaling of Satellite-Detected Chemical Compositions: NO2 Column Densities of OMI, GOME-2, and CMAQ. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Zeng, Y.-T.; Candice Lung, S.-C.; Su, H.-J.; Chao, H.J.; Wu, C.-D. A hybrid kriging/land-use regression model with Asian culture-specific sources to assess NO2 spatial-temporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Amini, H.; Shi, L.; Kloog, I.; Silvern, R.; Kelly, J.; Sabath, M.B.; Choirat, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Assessing NO2 Concentration and Model Uncertainty with High Spatiotemporal Resolution across the Contiguous United States Using Ensemble Model Averaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addesso, P.; Longo, M.; Montone, R.; Restaino, R.; Vivone, G. Interpolation and combination rules for the temporal and spatial enhancement of SEVIRI and MODIS thermal image sequences. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2017, 38, 1889–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Broday, D.M.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, S.N. Evaluation of MODIS Collection 6 aerosol retrieval algorithms over Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of aerosols types and mass loading. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. Long-term trends in NO2 columns related to economic developments and air quality policies from 1997 to 2016 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.D.; Heaps, W.; Philen, D.; McGee, T. Boundary layer measurements of the OH radical in the vicinity of an isolated power plant plume: SO2 and NO2 chemical conversion times. Atmos. Environ. 1979, 13, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-A.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-T.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Chou, C.C.K. Satellite-Derived Correlation of SO2, NO2, and Aerosol Optical Depth with Meteorological Conditions over East Asia from 2005 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hu, B.; Liu, H.; Du, C.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y. The influence of aerosols on the NO2 photolysis rate in a suburban site in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul-Haq, Z.; Rana, A.D.; Tariq, S.; Mahmood, K.; Ali, M.; Bashir, I. Modeling of tropospheric NO2 column over different climatic zones and land use/land cover types in South Asia. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2018, 168, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Lyapustin, A.; Liu, Y. Full-coverage high-resolution daily PM2.5 estimation using MAIAC AOD in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghude, S.D.; Pfister, G.G.; Jena, C.K.; van der A, R.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Kumar, R. Satellite constraints of Nitrogen Oxide (NOX) emissions from India based on OMI observations and WRF-Chem simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 40, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zoest, V.; Osei, F.B.; Hoek, G.; Stein, A. Spatio-temporal regression kriging for modelling urban NO2 concentrations. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Di, B. Satellite-Based Estimates of Daily NO2 Exposure in China Using Hybrid Random Forest and Spatiotemporal Kriging Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.O.; Mazloum, R.; Abou-Ali, H. Spatiotemporal interpolation of air pollutants in the Greater Cairo and the Delta, Egypt. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Cai, J.; Zou, B.; Wu, C.F.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kan, H. A land use regression model for estimating the NO2 concentration in Shanghai, China. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Presto, A.A.; Zimmerman, N. Spatial Modeling of Daily PM2.5, NO2, and CO Concentrations Measured by a Low-Cost Sensor Network: Comparison of Linear, Machine Learning, and Hybrid Land Use Models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8631–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Subramanian, R. A machine learning calibration model using random forests to improve sensor performance for lower-cost air quality monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Shima, M.; Yamamoto, K. Spatiotemporal land use random forest model for estimating metropolitan NO2 exposure in Japan. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 634, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q. Remote Sensing Estimation of Regional NO2 via Space-Time Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chang, L.C.; Kang, C.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Huang, A. Explore spatio-temporal PM2.5 features in northern Taiwan using machine learning techniques. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 736, 139656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bi, J.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based assessment of the long-term efficacy of PM2.5 pollution control policies across the Taiwan Strait. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, M.; Barceló, M.A. Spatial prediction of air pollution levels using a hierarchical Bayesian spatiotemporal model in Catalonia, Spain. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 151, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Choi, H.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Shin, M.; Song, C.-K.; Kim, S. Estimation of surface-level NO2 and O3 concentrations using TROPOMI data and machine learning over East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; He, H. Significant concurrent decrease in PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations in China during COVID-19 epidemic. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ye, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, D.; Nie, D.; Shen, F.; Huang, X.; et al. Fast sulfate formation from oxidation of SO2 by NO2 and HONO observed in Beijing haze. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space–time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Shen, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal prediction of continuous daily PM2.5 concentrations across China using a spatially explicit machine learning algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 155, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Khorsandi, E.; Liu, S.; Baier, F.; Valks, P. Estimation of Surface NO2 Concentrations over Germany from TROPOMI Satellite Observations Using a Machine Learning Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. FusionCNN: A remote sensing image fusion algorithm based on deep convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 14683–14703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Luo, X.S.; Pan, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Tang, A.H.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.H.; Wu, Q.H.; Yang, D.W.; et al. Quantifying atmospheric nitrogen deposition through a nationwide monitoring network across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12345–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal estimation of satellite-borne and ground-level NO2 using full residual deep networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 254, 112257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, C.C.; Manfred, K.M.; Wagner, N.L.; Adler, G.; Franchin, A.; Lamb, K.D.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schwarz, J.P.; Brock, C.A.; Brown, S.S.; et al. Complex refractive indices in the ultraviolet and visible spectral region for highly absorbing non-spherical biomass burning aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7235–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Brinksma, E.J.; van der A, R.J.; Sneep, M.; van den Oord, G.H.J.; Levelt, P.F.; Stammes, P.; Gleason, J.F.; et al. Near-real time retrieval of tropospheric NO2 from OMI. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2103–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Min, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, F.; Yang, C.; Sun, Z. Assimilating Himawari-8 AHI aerosol observations with a rapid-update data assimilation system. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Mbow, C. Evaluation of earth observation based long term vegetation trends—Intercomparing NDVI time series trend analysis consistency of Sahel from AVHRR GIMMS, Terra MODIS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1886–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, K.W.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Bright, E.A.; Cheriyadat, A.; Karnowski, T.P.; Palathingal, P.J.; Potok, T.E.; Price, J.R. Automated Feature Generation in Large-Scale Geospatial Libraries for Content-Based Indexing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2006, 72, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, R.B.; Buontempo, C.; Mysiak, J.; Karali, E.; Pulquério, M.; Murray, V.; Swart, R. How could climate services support disaster risk reduction in the 21st century. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 34, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilibarda, M.; Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gräler, B.; Pebesma, E.; Perčec Tadić, M.; Bajat, B. Spatio-temporal interpolation of daily temperatures for global land areas at 1 km resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2294–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liao, K.; Ren, Y. Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravuri, S.; Lenc, K.; Willson, M.; Kangin, D.; Lam, R.; Mirowski, P.; Fitzsimons, M.; Athanassiadou, M.; Kashem, S.; Madge, S.; et al. Skilful precipitation nowcasting using deep generative models of radar. Nature 2021, 597, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.T.; Bechle, M.J.; Sampson, P.D.; Szpiro, A.A.; Marshall, J.D.; Sheppard, L.; Kaufman, J.D. Satellite-Based NO2 and Model Validation in a National Prediction Model Based on Universal Kriging and Land-Use Regression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3686–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.P.; Lloyd, C.D.; McKinley, J.M. Increasing the accuracy of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution mapping using geographically weighted regression (GWR) and geostatistics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Represa, N.S.; Della Ceca, L.S.; Abril, G.; García Ferreyra, M.F.; Scavuzzo, C.M. Atmospheric Pollutants Assessment during the COVID-19 Lockdown Using Remote Sensing and Ground-based Measurements in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, J. Optical properties of PM2.5 and the impacts of chemical compositions in the coastal city Xiamen in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; Fischer, P.; Brunekreef, B.; Boersma, K.F.; Veefkind, P. Satellite NO2 data improve national land use regression models for ambient NO2 in a small densely populated country. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, J.; Mantas, C.J.; Castellano, J.G. A Random Forest approach using imprecise probabilities. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 134, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, S. Feature selection in machine learning: A new perspective. Neurocomputing 2018, 300, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, J.X.; Wu, D.H.; Lian, D.Y.; Chen, B.B. A Meteorological Potential Forecast Model for Acid Rain in Fujian Province, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.F.; Lau, A.K.H.; Fung, J.C.H.; Chen, F. Investigation of enhanced cross-city transport and trapping of air pollutants by coastal and urban land-sea breeze circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, K. Diurnal Variations of the Land–Sea Breeze and Its Related Precipitation over South China. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 4793–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Brunner, D.; Kuhlmann, G. Importance of satellite observations for high-resolution mapping of near-surface NO2 by machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 4793–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremanloo, M.; Lops, Y.; Choi, Y.; Yeganeh, B. Deep Learning Estimation of Daily Ground-Level NO2 Concentrations from Remote Sensing Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, J. Spatial interpolation techniques: Their applications in regionalizing climate-change series and associated accuracy evaluation in Northeast China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, B.; Harris, D.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Scale issues in verification of precipitation forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 11775–11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).