Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth from Sun Photometer at Shouxian, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Site and Data
2.1. Site Introduction
2.2. Instrument Introduction
2.3. Other Data
3. Data Processing and Method
3.1. Data Screening
3.2. Retrieval Method
3.3. Cloud Screening Methods
3.3.1. The Multiplet Method
- (1)
- Data quality checks
- (2)
- Triplet stability criterion
- (3)
- Diurnal stability check
- (4)
- Smoothness criteria
- (5)
- Three standard deviation criteria
3.3.2. The Clustering Method
- (1)
- Data quality checks
- (2)
- Triplet stability criterion
- (3)
- K-nearest-neighbor algorithm
3.4. Comparison Method
4. Results and Discussion
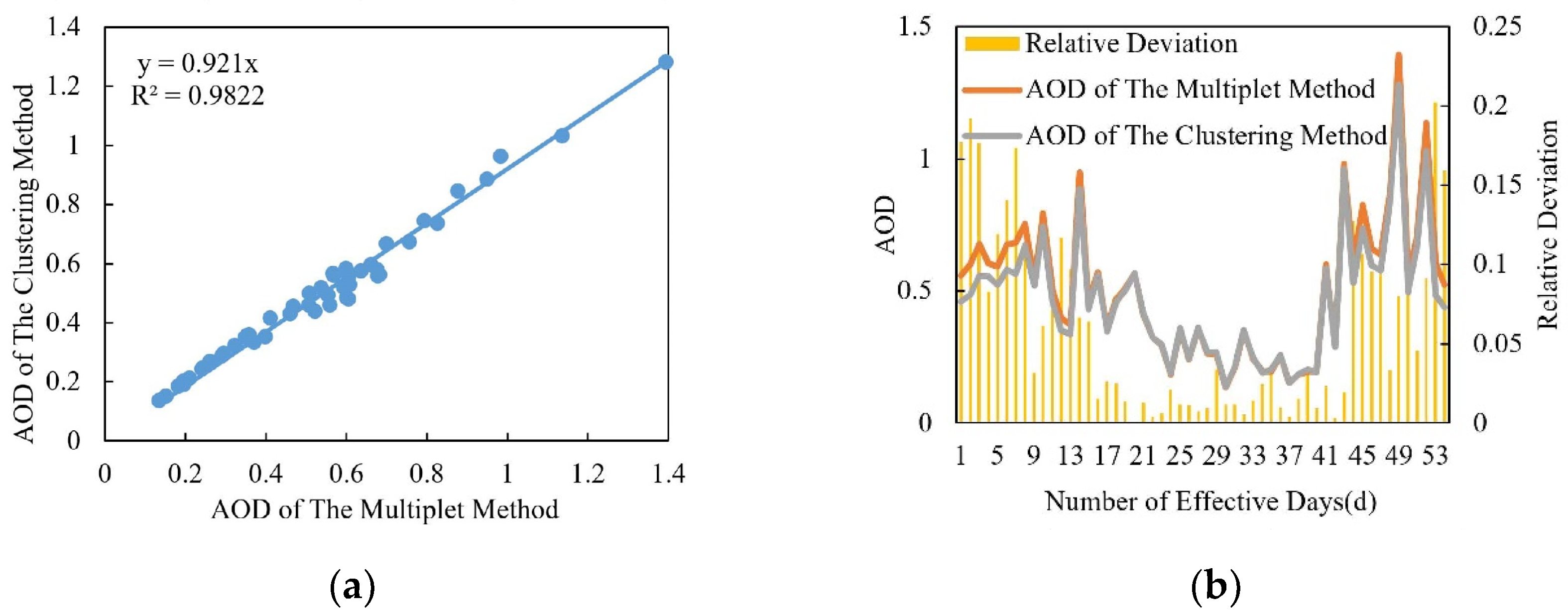
4.1. Analysis of Retrieval Results of Different Cloud Screening Methods
4.2. Analysis of Diurnal Variation of AOD
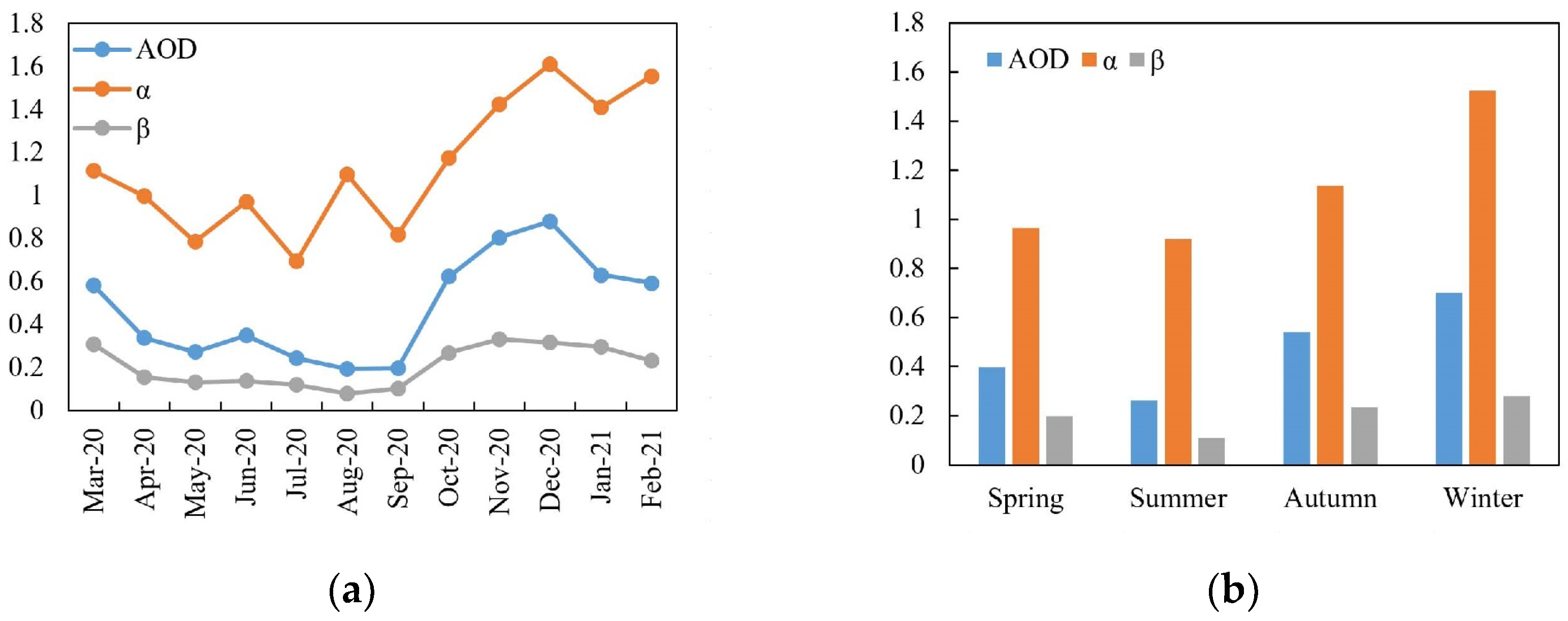
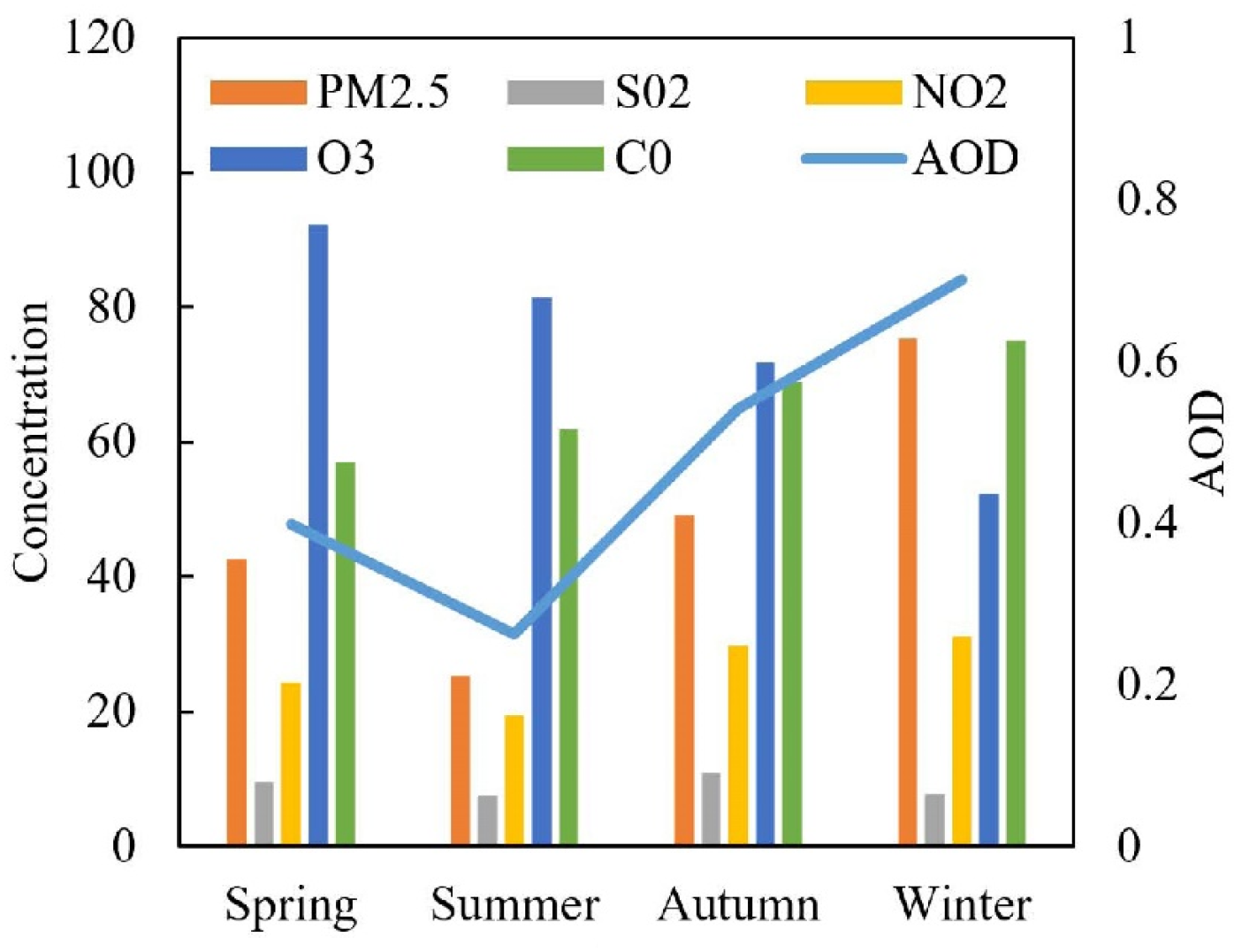
4.3. Variation Characteristics of AOD, α, and β
4.4. Single Scattering Albedo
5. Conclusions
- The variation trend of the retrieval results of the clustering method and the multiplet method is consistent, while the fitting coefficient is 0.921. The clustering method can flag thin clouds better, and some effective data points may be mistaken, with less effective points and the number of days than the multiplet method at the same time.
- The diurnal variation of AOD in Shouxian can be divided into three types: Flat type, convex type, and concave type. The flat type has the lowest frequency and occasionally appears in April and September. In contrast, the convex type mainly appears from April to September, and the concave type mainly occurs from October to next March—the main variation types.
- During the observation, the overall average value of AOD in Shouxian was 0.48, which is at a higher level. Owing to the influence of climate, precipitation, and other factors, August had the lowest monthly average value, and the highest was in December. The average AOD was the highest in winter of the study, and in summer was the smallest. The variation trend of AOD and β was highly consistent, and the monthly mean value of α was between 0.69 and 1.61, involving mainly continental and urban aerosols.
- Compared with other regions, the single scattering albedo in the Shouxian was high, reflecting the strong scattering and weak aerosol absorption in Shouxian. Biomass combustion emitted organic carbon and black carbon aerosols, resulting in lower SSA in winter during the observation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mou, F.S.; Li, A.; Xie, P.H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.C. Retrieval of aerosol optical properties at Hefei by sun-photometer CE318 data. Infrared Laser Eng. 2016, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.; Palacios-Peña, L.; Gutiérrez, C.; Jiménez-Guerrero, P.; López-Romero, J.M.; Sarabia, E.P.; Montávez, J.P. Sensitivity of surface solar radiation to aerosol–radiation and aerosol–cloud interactions over Europe in WRFv3.6.1 climatic runs with fully interactive aerosols. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 1533–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, B.H. Estimation of Net Surface Shortwave Radiation From Remotely Sensed Data Under Dust Aerosol Conditions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 52718–52727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Sci-ence Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Q.G.; Hao, Z.Z.; Yan, Y.W.; Tao, B.Y.; Chung, C.; Kim, S. Aerosol Optical Properties around the East China Seas Based on AERONET Measurements. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Cheng, Y.F.; Poschl, U. New Multiphase Chemical Processes Influencing Atmospheric Aerosols, Air Quality, and Climate in the Anthropocene. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Jeong, J.I.; Park, R.J.; Kim, M.J. Impact of Meteorological Changes on Particulate Matter and Aerosol Optical Depth in Seoul during the Months of June over Recent Decades. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, K.; Bodor, Z.; Szép, R. Spatial distribution of trace elements (As, Cd, Ni, Pb) from PM10 aerosols and human health impact assessment in an Eastern European country, Romania. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahan, M.; Alahmadi, S. Numerical Dust Storm Simulation Using Modified Geographical Domain and Data Assimilation: 3DVAR and 4DVAR (WRF-Chem/WRFDA). IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128980–128989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.H. Researches on Aerosol Optical Properties of Kunming Using CE318 Sunphotometer and MODIS Measurements. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J. Study on Characteristics of Aerosol Optical Property and Spatio-Temporal Distribution Based on Multi-Source Datasets. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Pan, Y.P.; Larssen, T.; Tang, J.; Mulder, J. Acid deposition in Asia: Emissions, deposition, and ecosystem effects. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.F.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhan, X.; Kong, X.N. Advances in Research of Impacts of Aerosol Pollution on Crop in China. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.W.; de Leeuw, G.; Mei, L.L.; Che, Y.H.; Rippin, W.; Guang, J.; Hu, Y.C. Long-time series aerosol optical depth retrieval from AVHRR data over land in North China and Central Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.H.; Chen, H.B.; Xia, X.A. Progress in observation studies of atmospheric aerosol radiative properties in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 37, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Zhu, J.; Che, H.Z.; Xia, X.G.; Zhang, R.J. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on sun photometer measurements at a semi-arid rural site in Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Xin, J.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Z.R.; Chen, C.L. Comparison of atmospheric particulate matter and aerosol optical depth in Beijing City. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, P.S. Variations of Aerosol Optical Depth in Bhaktapur, Nepal. J. Inst. Eng. 2018, 13, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ningombam, S.S.; Larson, E.J.L.; Dumka, U.C.; Estelles, V.; Campanelli, M.; Steve, C. Long-term (1995–2018) aerosol optical depth derived using ground based AERONET and SKYNET measurements from aerosol aged-background sites. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.K.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, W.; Dubovik, O.; Liu, B.M.; Shi, Y.F.; Yang, C.L. Retrieval of 500 m Aerosol Optical Depths from MODIS Measurements over Urban Surfaces under Heavy Aerosol Loading Conditions in Winter. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.W.; Zhou, R.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhu, J. The spatiotemporal variations of aerosol types in representative sites of China basing on the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET). China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Wang, G.Y.; Xu, Z.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Q.; Hua, D.X. Study on calibration method of sky radiometer and aerosol optical properties in Xi’an region. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.T. Optical Characteristics of Aerosol in China Based on MERRA-2 Reanalysis and AERONET Ground-Based Remote sensing. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.Q. Validation and Spatiotemporal Analysis of MODIS Multi-angle Atmospheric Calibration Aerosol Products in China from 2008 to 2016. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2021, 36, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.R. Study of Aerosol Optical Properties in Shouxian, Anhui Based on ARM Mobile Facility. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.H.; Chen, H.B.; Xia, X.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Cribb, M. Aerosol optical properties from the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Mobile Facility at Shouxian, China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.J.; Dong, X.Q.; Xi, B.K.; Wang, Z.H. Effects of Clouds and Aerosols on Surface Radiation Budget Inferred from DOE AMF at Shouxian, China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2013, 6, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.P.; Wang, P.C.; Duan, M.Z.; Chen, H.B.; Xia, X.A.; Liao, H. An Evidence of Aerosol Indirect Effect on Stratus Clouds from the Integrated Ground-Based Measurements at the ARM Shouxian Site. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2011, 4, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Deng, X.L.; Zhai, J.; Yang, G.Y.; Yu, C.X. Study on Aerosol Optical Properties in Shouxian Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 40, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chen, K.; Ling, X.F.; Xun, S.P.; Yu, C.X. Atmospheric Optical Characteristics of National Climate Observation in Shouxian County in Winter. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2019, 56, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.O. Omi/Aura Near Uv Aerosol Optical Depth and Single Scattering Albedo L3 1 Day 1.0 Degree X 1.0 Degree V3. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). 2008. Available online: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/OMAERUV_003/summary (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/ (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- Duffie, J.A.; Beckman, W.A. Solar Radiation. In Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes, 4th ed.; Duffie, J.A., Beckman, W.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, F. A new table and approximation formula for the relative optial air mass. Arch. Für Meteorol. Geophys. Und Bioklimatol. Ser. B 1965, 14, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, B. Improvement in solar declination computation. Sol. Energy 1985, 35, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angström, A. On the Atmospheric Transmission of Sun Radiation and on Dust in the Air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-Screening and Quality Control Algorithms for the AERONET Database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenzinger, V.; Kreuter, A. Reducing cloud contamination in aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.B.; Shen, Z.B.; Wang, W.F. Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Thickness and Dusty Weather in Northern China in Spring of 2001. Plateau Meteorol. 2003, 22, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrli, C. GAWPFR: A Network of Aerosol Optical Depth Observatioins with Precision Filter Radiometers. In WMO/GAW Experts Workshop on a Global Surface-Based Network for Long Term Observations of Column Aerosol Optical Properties; Balten-sperger, U., Barrie, L., Wehrli, C., Eds.; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, H.Q. The trend of persistent regional haze in Anhui Province and corresponding characteristics of aerosol pollution. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J.; Zhou, D.; Wu, X.X.; Tie, H.B.; Tan, F.; Li, X.Y.B.; Deng, T.; Jiang, D.H. Effect of atmospheric aerosol on surface ozone variation over the Pearl River Delta region. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Han, S.Q.; Tie, X.X.; Sun, M.L.; Liu, A.X. Evidence of impact of aerosols on surface ozone concentration in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4672–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Wang, T.J.; Xie, M.; Han, Y. Impacts of atmospheric particles on surface ozone in Nanjing. Environ. Res. 2013, 18, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.Z.; Che, H.Z.; Qi, B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dong, Y.S.; Xia, X.G.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H.J.; et al. Zhang. Aerosol optical characteristics and their vertical distributions under enhanced haze pollution events: Effect of the regional transport of different aerosol types over eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2949–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.H.; Chantara, S.; Wang, S.H.; Khamkaew, C.; Prapamontol, T.; Janjai, S. Radiative response of biomass-burning aerosols over an urban atmosphere in northern peninsular Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Env. 2018, 633, 892–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Pham, H.V.; Lasko, K.; Bui, M.T.; Laffly, D.; Jourdan, A.; Bui, H.Q. Spatiotemporal analysis of ground and satellite-based aerosol for air quality assessment in the Southeast Asia region. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Study on the Impacts of Aerosols on Surface Ozone in Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.L.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Lu, C.; Chen, X.D.; Liu, A.M. The Measurement of Aerosol Optical Properties Over Shenzhen. Acta Photonica Sin. 2012, 41, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y. Research on Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Characteristics in Xuzhou. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Li, J.; Chu, Y.Q.; Dong, Y.M.; Tan, W.S.; Xu, X.J.; Ren, J.J.; Tian, X.Q.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Variability of surface aerosol properties at an urban site in Beijing based on two years of in-situ measurements. Atmos. Res. 2021, 256, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.K.; Che, H.Z.; Xia, X.G.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.Z.; Li, X.P.; et al. Aerosol Optical Properties over an Urban Site in Central China Determined Using Ground-based Sun Photometer Measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Index Items | Technical Indicators |
|---|---|
| Number of bands | 9 |
| Central wavelength | 340 nm, 380 nm, 440 nm, 500 nm, 670 nm, 870 nm, 940 nm, 1020 nm, 1640 nm (replaceable) |
| Bandwidth | 2–340 nm, 4–380 nm, 10–440 nm, 500 nm, 670 nm, 870 nm, 940 nm, 1020 nm, 1640 nm |
| Field of view | ≤1.3° |
| Sun tracking accuracy | 0.1° |
| Temperature control range and accuracy | 25 ± 0.1 °C |
| Rotation angle of sun tracker | horizontal 0 ~ 360°, vertical 0 ~ 180° |
| Operating temperature range | −30 °C~ +60 °C |
| Relative humidity | 0~100% RH |
| Communication mode | serial port/CAN bus/BeiDou Satellite/4G (optional) |
| Power supply mode | lightning protection/220 V AC/lithium battery/solar battery (optional) |
| Environmental perception | temperature, humidity, rain, air pressure |
| AOD and PM2.5 | AOD and SO2 | AOD and NO2 | AOD and O3 | AOD and CO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial correlation coefficient | 0.7902 | −0.0524 | −0.2363 | −0.5323 | −0.0356 |
| Location | Observation Time | λ (nm) | SSA | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shouxian | 2020/03–2021/02 | σsp = 500,σap = 500 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | This study |
| Shouxian | 2014/09–2015/08 | σsp = 525,σap = 520 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | [29] |
| Shouxian | 2008/05–2008/12 | σsp = 550,σap = 550 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | [26] |
| Pudong, Shanghai | 2008–2010 | σsp = 525,σap = 532 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | [48] |
| Shenzhen | 2010/12–2011/08 | σsp = 525,σap = 532 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | [49] |
| Xuzhou | 2014–2017 | σsp = 525,σap = 532 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | [50] |
| Beijing | 2017/09–2019/08 | σsp = 525,σap = 525 | 0.88 ± 0.07 | [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xun, L.; Lu, H.; Qian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, S.; Li, X. Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth from Sun Photometer at Shouxian, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091226
Xun L, Lu H, Qian C, Zhang Y, Lyu S, Li X. Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth from Sun Photometer at Shouxian, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091226
Chicago/Turabian StyleXun, Lina, Hui Lu, Congcong Qian, Yong Zhang, Shanshan Lyu, and Xin Li. 2021. "Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth from Sun Photometer at Shouxian, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091226
APA StyleXun, L., Lu, H., Qian, C., Zhang, Y., Lyu, S., & Li, X. (2021). Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth from Sun Photometer at Shouxian, China. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091226







