Accurately Quantifying Clear-Sky Radiative Cooling Potentials: A Temperature Correction to the Transmittance-Based Approximation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Atmospheric Irradiance and the Transmittance-Based Cosine Approximation
3. Issues with the Transmittance-Based Cosine Approximation
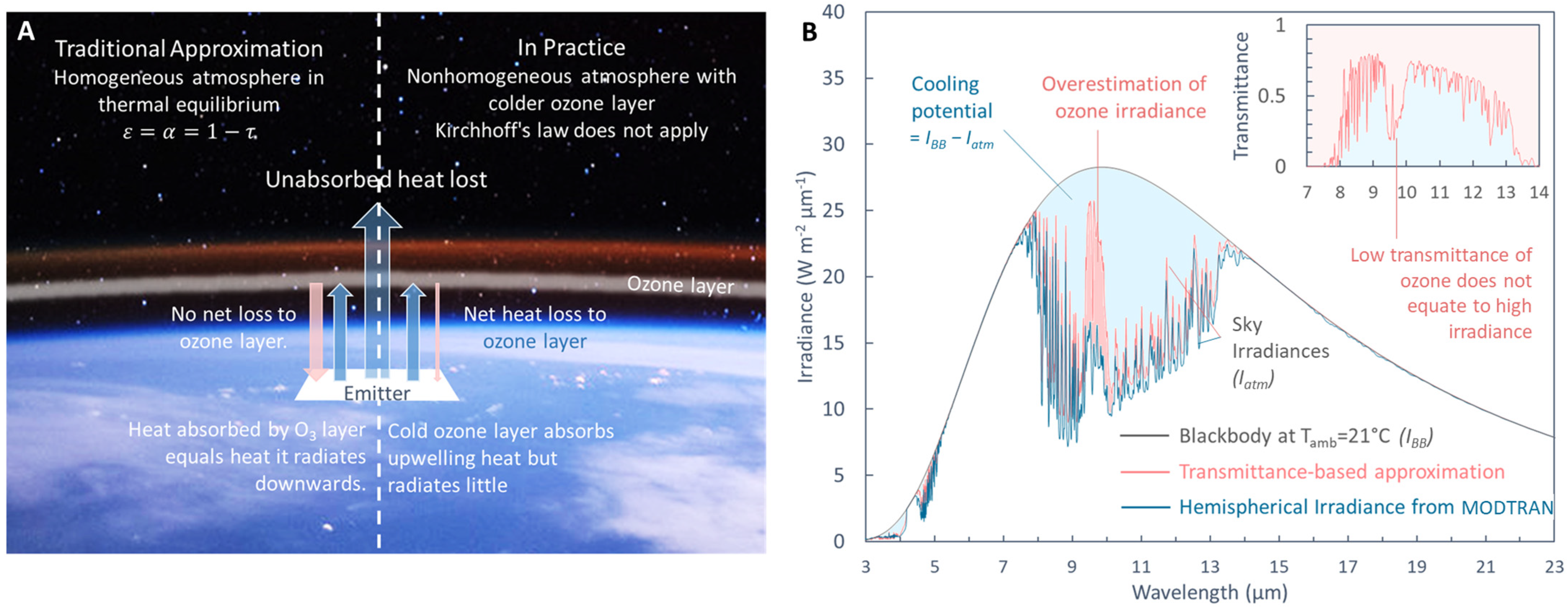
4. Temperature-Corrections of the Transmittance-Based Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granqvist, C.G.; Hjortsberg, A. Radiative Cooling to Low Temperatures: General Considerations and Application to Selectively Emitting SiO Films. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 4205–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, N.; Raman, A.P. Paints as a Scalable and Effective Radiative Cooling Technology for Buildings. Joule 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.; Akbari, H. Potential Benefits of Cool Roofs on Commercial Buildings: Conserving Energy, Saving Money, and Reducing Emission of Greenhouse Gases and Air Pollutants. Energy Effic. 2010, 3, 53–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munday, J.N. Tackling Climate Change through Radiative Cooling. Joule 2019, 3, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, T.S.; Granqvist, C.G. Radiative Cooling Computed for Model Atmospheres. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 4381–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Berdahl, P. Characteristics of Infrared Sky Radiation in the United States. Sol. Energy 1984, 33, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berdahl, P.; Fromberg, R. The Thermal Radiance of Clear Skies. Sol. Energy 1982, 29, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peterson, H.B.; Coimbra, C.F.M. Radiative Cooling Resource Maps for the Contiguous United States. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, X.; Buriot, D.; Garnier, F. About the Equivalent Radiative Temperature for Clear Skies. Sol. Energy 1984, 32, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M. New Formulae for the Equivalent Night Sky Emissivity. Sol. Energy 1982, 28, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.M.; Duchon, C.E. An Improved Parameterization for Estimating Effective Atmospheric Emissivity for Use in Calculating Daytime Downwelling Longwave Radiation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1999, 38, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iziomon, M.G.; Mayer, H.; Matzarakis, A. Downward Atmospheric Longwave Irradiance under Clear and Cloudy Skies: Measurement and Parameterization. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2003, 65, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.P.; Anoma, M.A.; Zhu, L.; Rephaeli, E.; Fan, S. Passive Radiative Cooling below Ambient Air Temperature under Direct Sunlight. Nature 2014, 515, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rephaeli, E.; Raman, A.; Fan, S. Ultrabroadband Photonic Structures to Achieve High-Performance Daytime Radiative Cooling. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentle, A.R.; Smith, G.B. A Subambient Open Roof Surface under the Mid-Summer Sun. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Jia, B.; Gu, M. A Metamaterial Emitter for Highly Efficient Radiative Cooling. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Gu, M. Radiative Cooling: Principles, Progress, and Potentials. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Aili, A.; Zhai, Y.; Xu, S.; Tan, G.; Yin, X.; Yang, R. Radiative Sky Cooling: Fundamental Principles, Materials, and Applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 021306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Zhao, D.; Lu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Yin, X.; Tan, G.; Yang, R. A KW-Scale, 24-Hour Continuously Operational, Radiative Sky Cooling System: Experimental Demonstration and Predictive Modeling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 186, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Liu, Y.; Chae, D.; Lee, H. Cross-Linked Porous Polymeric Coating without a Metal-Reflective Layer for Sub-Ambient Radiative Cooling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57832–57839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Bao, H. Effect of Atmospheric Water Vapor on Radiative Cooling Performance of Different Surfaces. Sol. Energy 2019, 183, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qian, H.; Yang, R.; Zhao, D. Radiative Sky Cooling Potential Maps of China Based on Atmospheric Spectral Emissivity. Sol. Energy 2021, 218, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Mandal, J.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Tsai, C.-C.; Shan, Z.; Yu, N.; Yang, Y. Scalable Aqueous Processing-Based Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling Coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yi, Z.; Tao, S.; Wang, S.; Fang, Z.; Lu, C.; Xu, Z. A Pragmatic Device Based on a Double-Sided Functional Structure for Efficient Water Harvesting. Glob. Challenges 2020, 4, 1900094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Lee, D.; Son, S.; Yang, Y.; Lee, H.; Rho, J. Visibly Transparent Radiative Cooler under Direct Sunlight. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2002226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Ma, C. Design of Selectively Multilayered Periodic Gratings by PSO Algorithm for Radiative Cooling. Opt. Commun. 2021, 500, 127323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Min, H.; Tang, S.; Meng, X. 3D Porous Polymer Film with Designed Pore Architecture and Auto-Deposited SiO2 for Highly Efficient Passive Radiative Cooling. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Li, W.; Patel, B.B.; Tao, R.; Chang, Y.; Fan, S.; Diao, Y.; Cai, L. Three-Dimensional Printable Nanoporous Polymer Matrix Composites for Daytime Radiative Cooling. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Gu, Y. Plasmon-Enhanced Infrared Emission Approaching the Theoretical Limit of Radiative Cooling Ability. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6974–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spectral Sciences Incorporated MODTRAN®. Available online: http://modtran.spectral.com/modtran_home (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Johnson, N. The Atmospheric Glow and the Milky Way’s Stars; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- University of Chicago MODTRAN Infrared Light in the Atmosphere. Available online: http://climatemodels.uchicago.edu/modtran/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Mandal, J.; Fu, Y.; Overvig, A.C.; Jia, M.; Sun, K.; Shi, N.N.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, X.; Yu, N.; Yang, Y. Hierarchically Porous Polymer Coatings for Highly Efficient Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling. Science 2018, 362, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gentle, A.R.; Smith, G.B. Radiative Heat Pumping from the Earth Using Surface Phonon Resonant Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Raman, A.; Fan, S. Radiative Cooling to Deep Sub-Freezing Temperatures through a 24-h Day–Night Cycle. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E. Evaluation of Effective Atmospheric Emissivity and Parameterization of Cloud at Local Scale. Atmospheric Res. 1997, 45, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M. Longwave Sky Radiation Parametrizations. Sol. Energy 1994, 53, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Saco, P.M.; Kumari, N.; Yetemen, O. Global Analysis of Atmospheric Transmissivity Using Cloud Cover, Aridity and Flux Network Datasets. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, E.; Agassi, E.; Koren, I. A Novel Technique for Extracting Clouds Base Height Using Ground Based Imaging. Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, J.A.; Nugent, P.W. Physics Principles in Radiometric Infrared Imaging of Clouds in the Atmosphere. Eur. J. Phys. 2013, 34, S111–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J. A Survey of Radiative Coolers in the Literature. Available online: https://engrxiv.org/nup6c/ (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Mandal, J. Resources for Radiative Cooling Research. Available online: https://jyotirmoymandal.com/radiative-cooling-resources/ (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Raman, A.P. Raman Lab @ UCLA. Available online: https://github.com/Raman-Lab-UCLA (accessed on 31 July 2021).
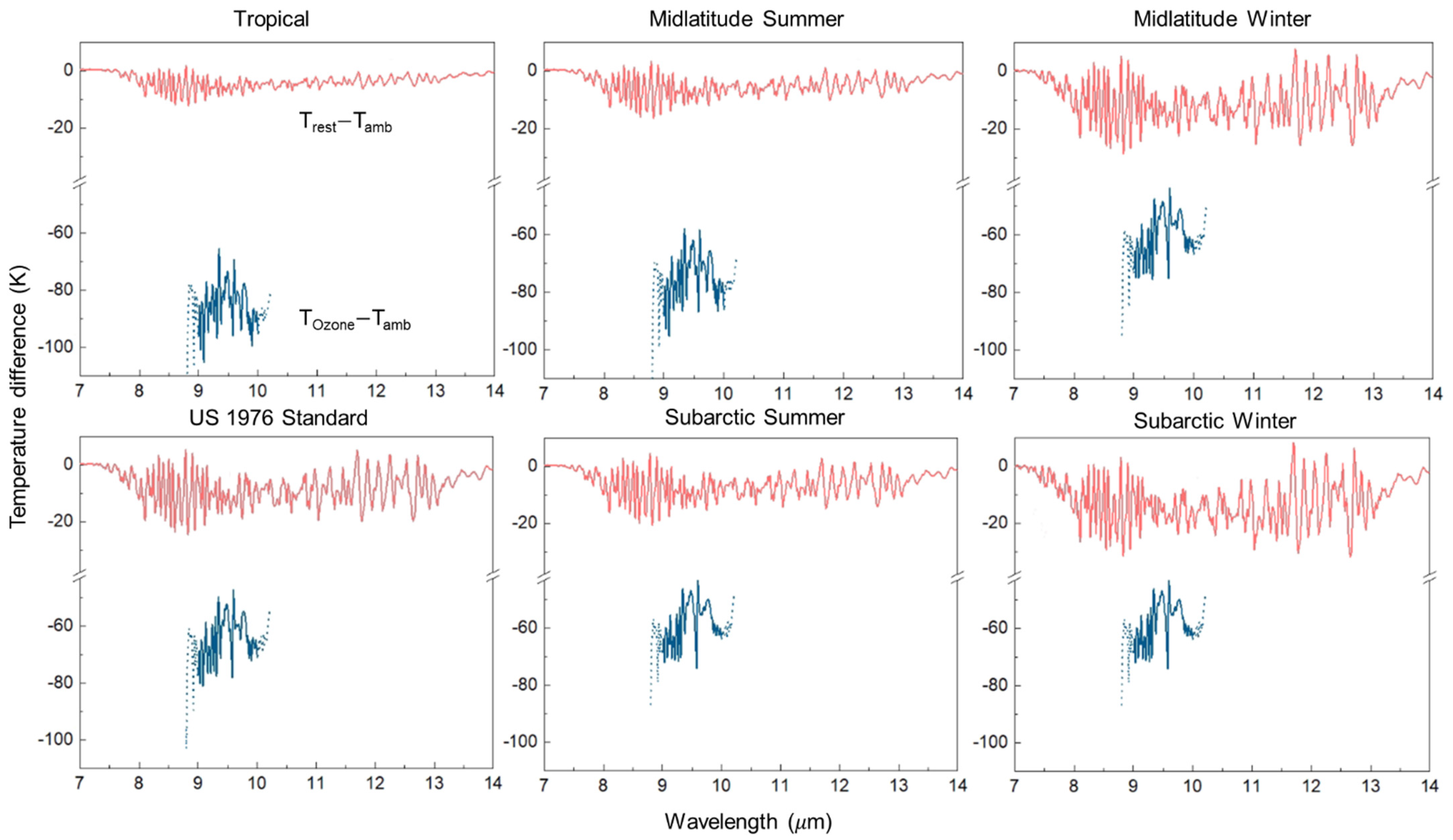


| Tropical | Midlatitude Summer | Midlatitude Winter | US 1976 Standard | Subarctic Summer | Subarctic Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMODTRAN-PCorrected | 0.0011T2 − 0.57T + 72.7 | 0.0012T2 − 0.6T + 72.6 | −0.002T2 + 0.15T − 32.7 | −0.0005T2 + 0.32T − 53.32 | 0.0008T2 − 0.385T + 45 | −0.0007T2 + 0.49T − 82.2 |
| PMODTRAN-PTraditional | 0.001T2 − 0.4T + 41.9 | 0.0009T2 − 0.31T + 26.1 | −0.001T2 + 0.767T − 127.2 | −0.0001T2 + 0.29T − 59.8 | 0.0005T2 − 0.071T − 7.9 | −0.002T2 + 1.39T − 214.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandal, J.; Huang, X.; Raman, A.P. Accurately Quantifying Clear-Sky Radiative Cooling Potentials: A Temperature Correction to the Transmittance-Based Approximation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091195
Mandal J, Huang X, Raman AP. Accurately Quantifying Clear-Sky Radiative Cooling Potentials: A Temperature Correction to the Transmittance-Based Approximation. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091195
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandal, Jyotirmoy, Xin Huang, and Aaswath P. Raman. 2021. "Accurately Quantifying Clear-Sky Radiative Cooling Potentials: A Temperature Correction to the Transmittance-Based Approximation" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091195
APA StyleMandal, J., Huang, X., & Raman, A. P. (2021). Accurately Quantifying Clear-Sky Radiative Cooling Potentials: A Temperature Correction to the Transmittance-Based Approximation. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091195






